Animal Nutrition: Digestion, Modes, and Essential Nutrients
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
155 Terms
What do all organisms require for metabolism, homeostasis, growth, and reproduction?
Sources of matter and energy.
What is the process of feeding in animals?
The uptake of food from the surroundings.
What does animal nutrition include?
Processes by which food is ingested, digested, and absorbed into body cells and fluids.
What is ingestion?
The feeding method used to take food into the digestive cavity.
What is digestion?
The splitting of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids in foods into chemical subunits for absorption.
What is absorption in the context of animal nutrition?
The process of food being brought into cells of the organism via subunits.
What are herbivores?
Animals that obtain organic molecules primarily by eating plants.
What are carnivores?
Animals that primarily eat other animals.
What are omnivores?
Animals that may consume any source of organic matter with appropriate digestive enzymes.
What is a calorie?
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 g of pure water by 1°C.
What is a kilocalorie?
1,000 calories or one Calorie (capital C).
How many kilocalories do carbohydrates provide per gram?
About 4.2 kcal
How many kilocalories do fats provide per gram?
About 9.5 kcal
How many kilocalories do proteins provide per gram?
About 4.1 kcal
What is undernutrition?
A condition resulting from inadequate intake or abnormal assimilation of organic fuels. Is a form of malnutrition.
What is overnutrition?
A condition caused by excessive intake of specific nutrients. Is another type of malnutrition.
What is malnutrition?
A condition resulting from an improper diet.
What are essential nutrients?
Molecules that cannot be synthesized by the organism and must be obtained in the diet.
Name 4 essential nutrients
Amino acids, vitamins, essential minerals, and essential fatty acids.

How many essential amino acids are there for humans?
Nine essential amino acids.
What is a mnemonic to help memorize the essential amino acids?
HILL Makes Perfectly Tall Trees Very (tidy)
H - histidine
I - isoleucine
L - leucine
L - lysine
M - methionine
P - phenylalanine
T - threonine
T - tryptophan
V - valine
List the essential amino acids.
histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, valine.
What are some sources of the essential amino acids?
Meat, eggs, fish, cheese and milk.
What is a consequence of amino acid deficiency?
Ineffective protein synthesis.
How many known vitamins do humans require?
13 vitamins.
What do many vitamins act as in biochemical reactions?
Co-enzymes.
How do people get enough vitamins?
Through a normal and varied diet. (Eat foods that are all the colors of the rainbow in a week).
What are the two classes of vitamins?
Water-soluble and fat-soluble.
Which class of vitamins are stored in the body?
Fat-soluble vitamins, the excess is stored in adipose tissue.
Which class of vitamins are NOT stored in the body?
Water-soluble vitamins, the excess is secreted in the urine.
Which vitamin can humans synthesize in the skin?
Vitamin D, when exposed to UV light.
How do humans get vitamin K?
The gut bacteria, humans cannot make vitamin K.
What is a mnemonic to help remember the water-soluble vitamins and the fat-soluble vitamins.
Wash BeCause! (you wash/ pee out B and C) and A DEck of cards has a fat King (you store A, D, E and K in fat).
List the water-soluble vitamins and the fat-soluble vitamins.
B complex & C vitamins.
List the fat-soluble vitamins.
A, D, E and K.
Define macrominerals.
Minerals required in large amounts (50 mg to more than 1 gram per day).
List the macrominerals
Na, Ca and K.
Define trace minerals.
Minerals required in small amounts (some less than 1 mg per day).
List the trace minerals.
Fe and Zn.
Why do we need minerals?
Because the body needs these inorganic elements for critical physiological functions, such as calcium, iron and magnesium.
Define essential fatty acids.
Fatty acids that must be obtained through the diet.
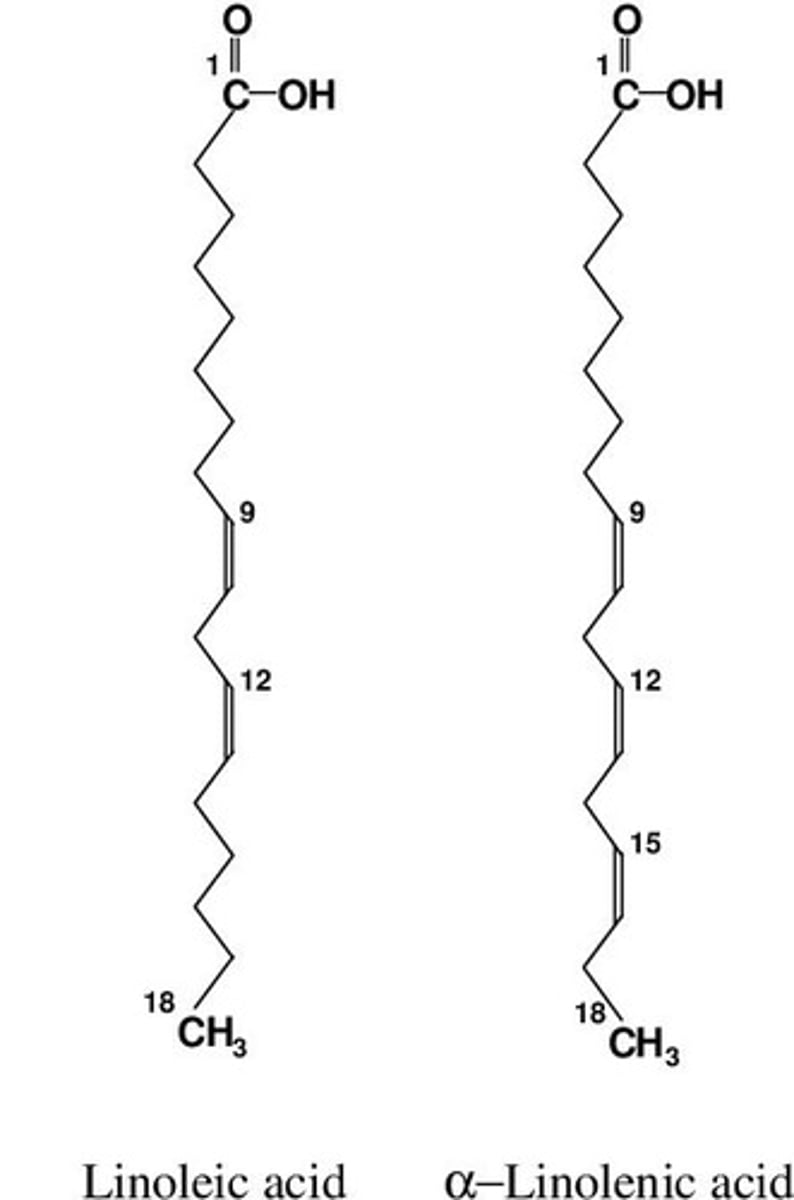
List the essential fatty acids.
linoleic acid and linolenic acid.
Essential fatty acids are needed to make what?
Phospholipids that make up biological membranes and certain hormones.
Why are essential fatty acids important for humans diet?
People on low-fat diets are at serious risk for developing coronary heart disease.
What are the types of feeding methods?
1. Fluid feeders
2. Suspension feeders
3. Deposit feeders
4. Bulk feeders
What are fluid feeders?
Organisms that ingest liquids that contain organic molecules in solution.
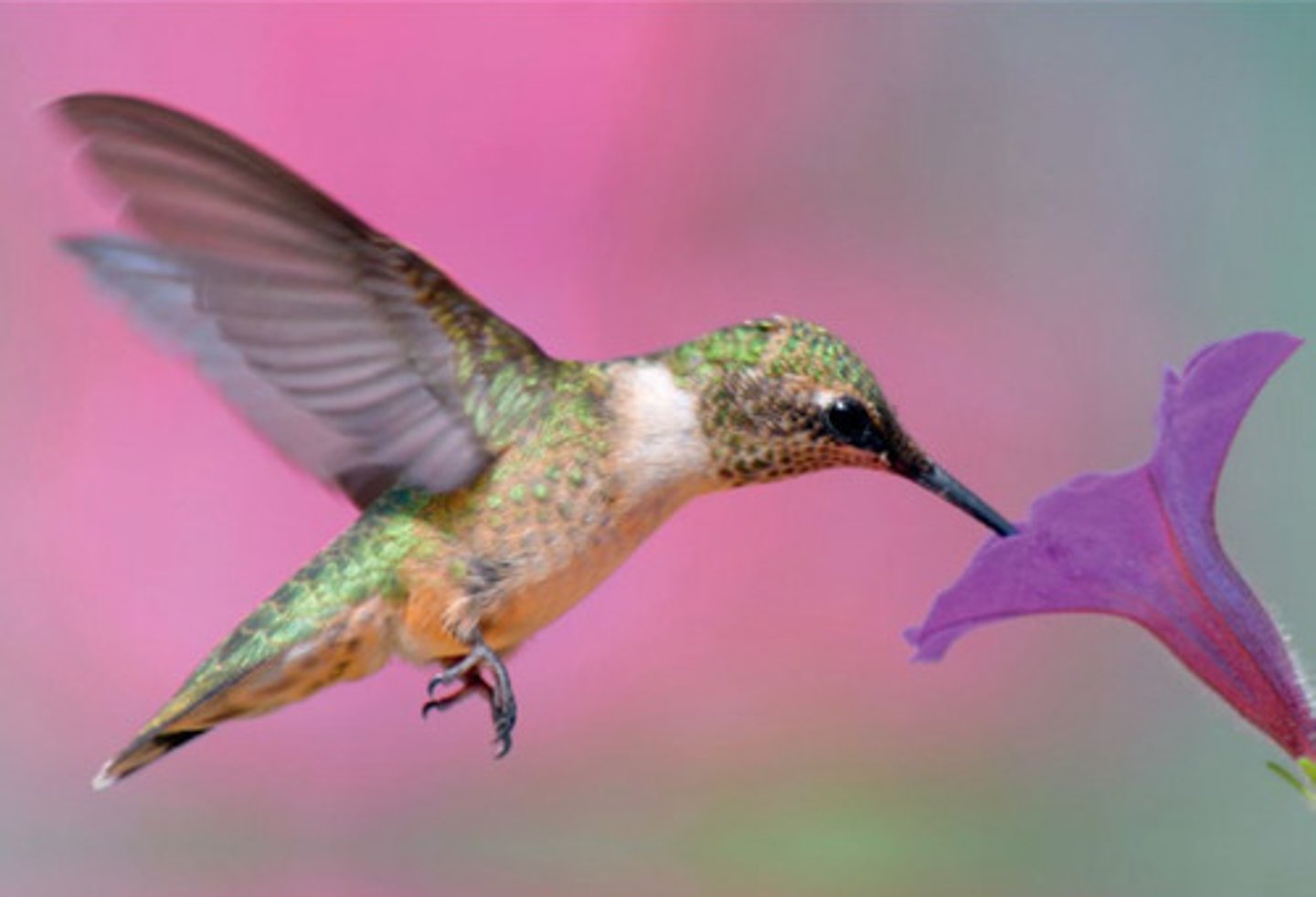

What are suspension feeders?
Organisms that ingest small organisms that are suspended in water.
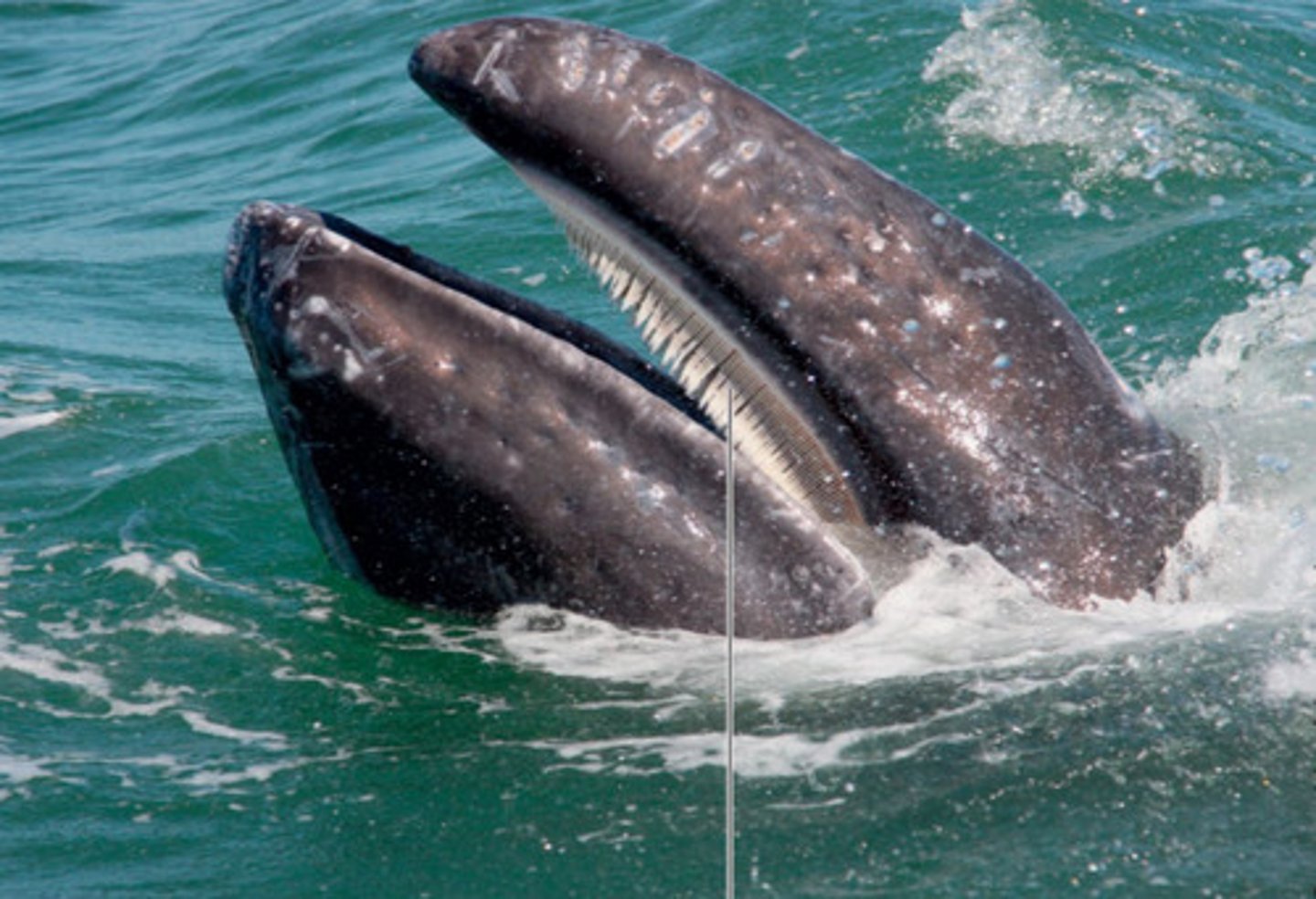

What are deposit feeders?
Organisms that ingest particles of organic matter from solid material they live in or on.

What are bulk feeders?
Organisms that consume sizable food items whole or in large chunks.

What do amylases hydrolyze?
Starches (complex carbohydrates) into simple sugars.
What do proteases hydrolyze?
Proteins into amino acids.
What is the purpose of digestive process?
To break food molecules into smaller molecular subunits that can be absorbed into body fluids and cells.
What do lipases hydrolyze?
Fats and other lipids.
What type of reaction breaks down food molecules during digestion?
Enzymatic hydrolysis.
What is hydrolysis?
A chemical reaction in which water (H⁺ and OH⁻) is added to break chemical bonds in molecules.
What is intracellular digestion?
Digestion that occurs within cells, primarily used by sponges and some cnidarians.
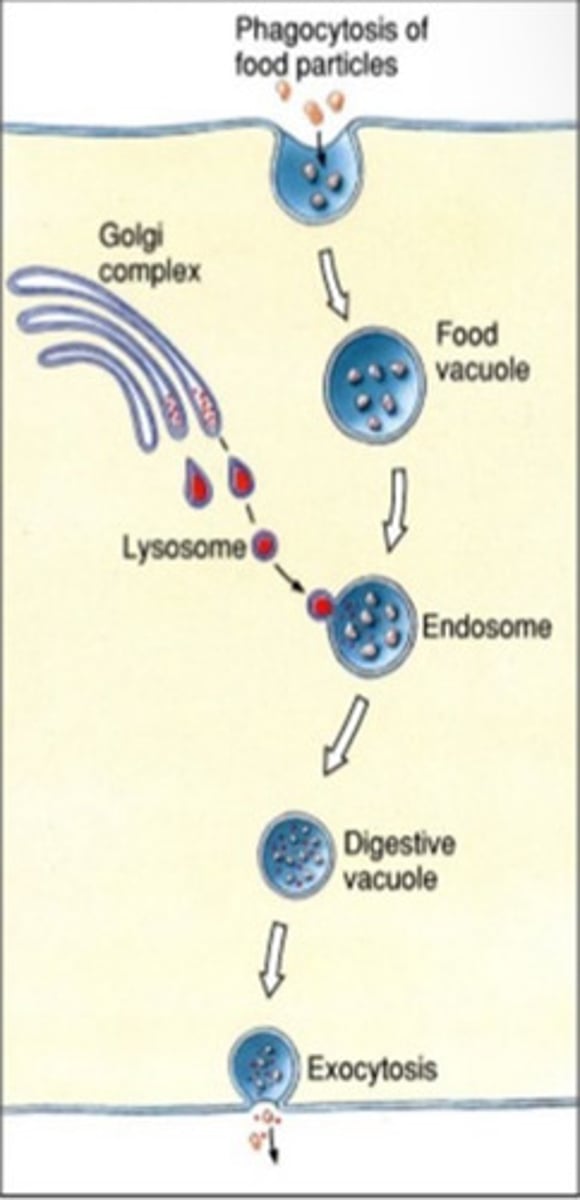
What do nucleases hydrolyze?
Nucleic acids (DNA & RNA) into nucleotides. (A nucleoside is a molecule made up of a nitrogenous base, a sugar and a phosphate group).
What is extracellular digestion?
Digestion that occurs outside body cells, in a pouch or tube enclosed within the body.
Why is enzymatic digestion necessary?
Because large biomolecules must be broken into absorbable units before entering the bloodstream or cells.
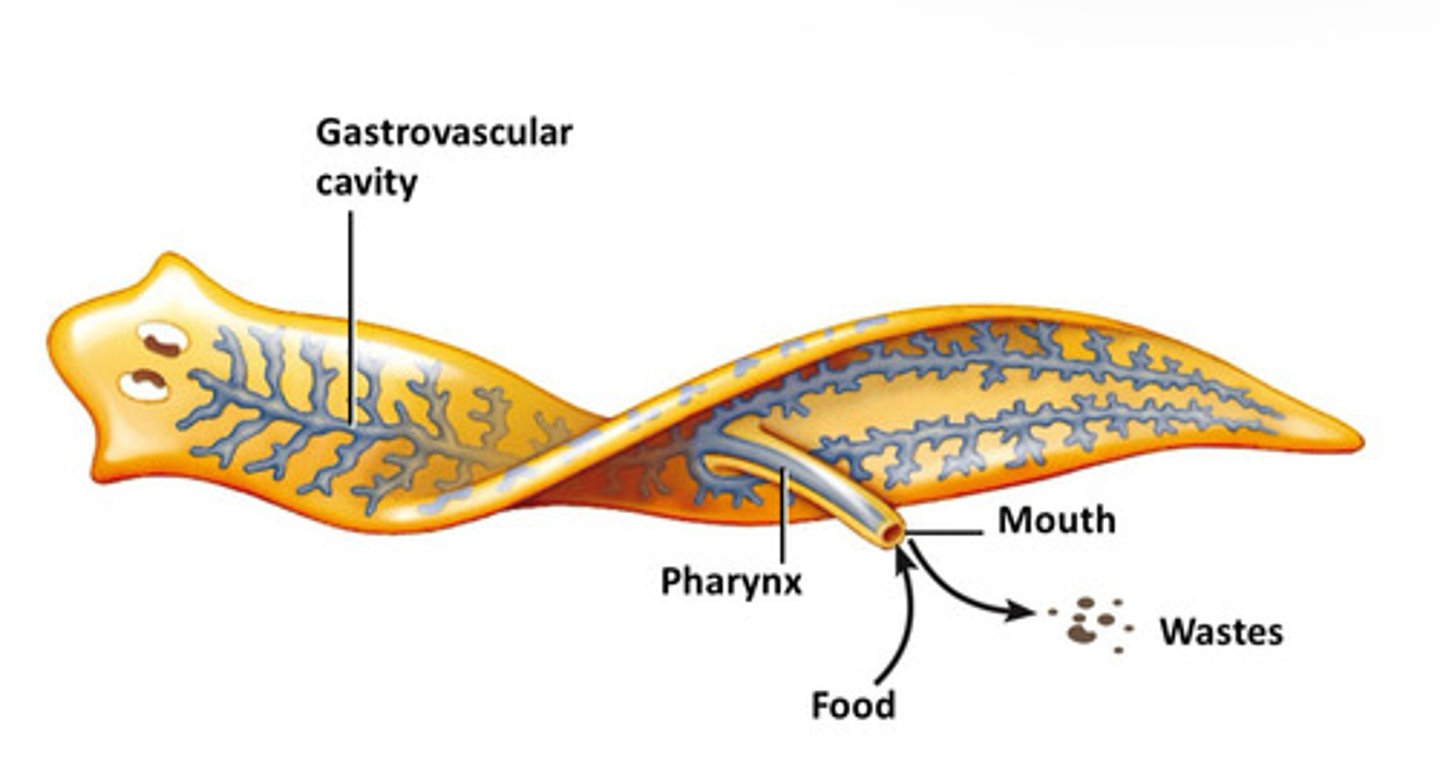
What are saclike digestive systems?
Digestive systems with a single opening, such as those found in flatworms and cnidarians.
What is the key role of enzymes in digestion?
Speeding up hydrolysis reactions that break down food molecules.
Where does digestion begin in saclike digestive systems?
In the gastrovascular cavity (extracellular digestion).
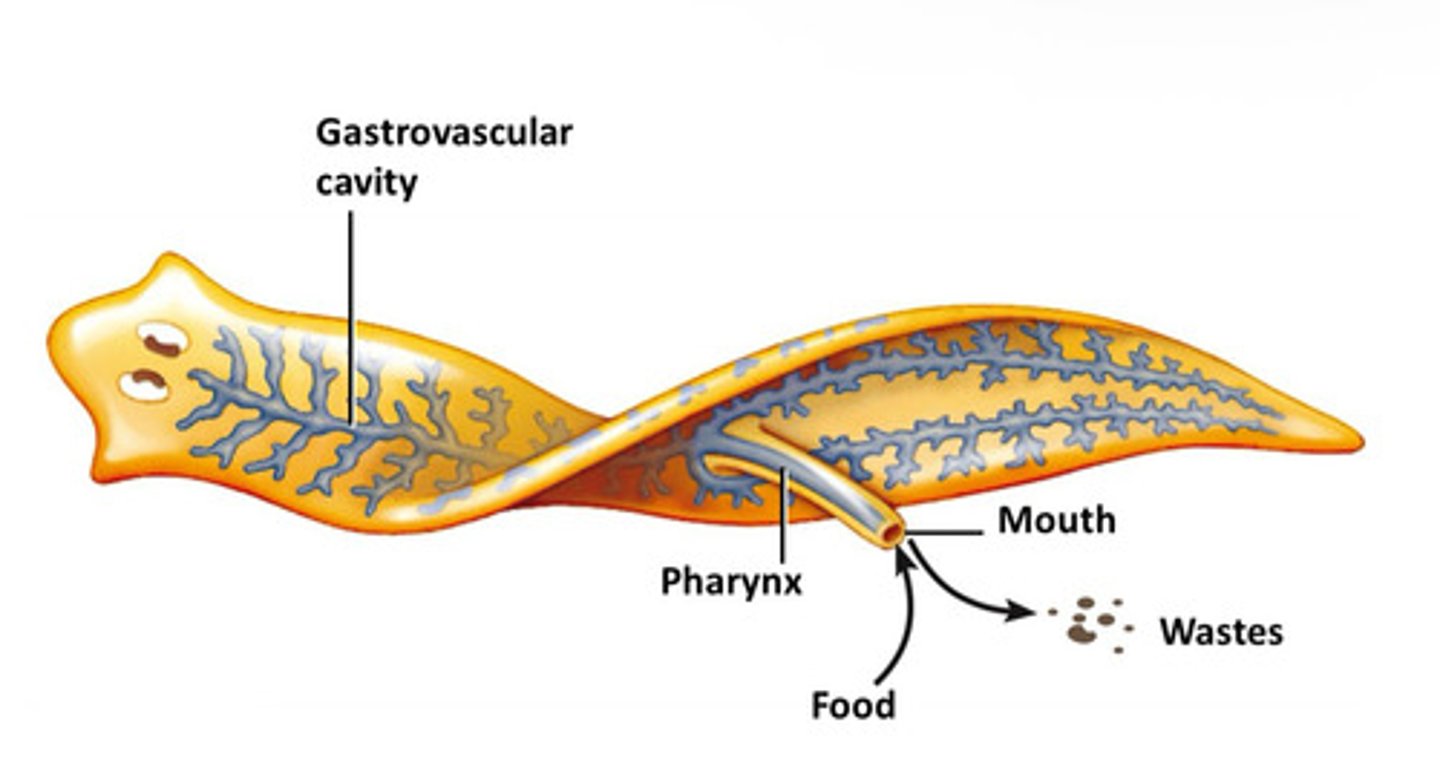
Where is digestion completed in saclike digestive systems?
Intracellularly (inside cells).
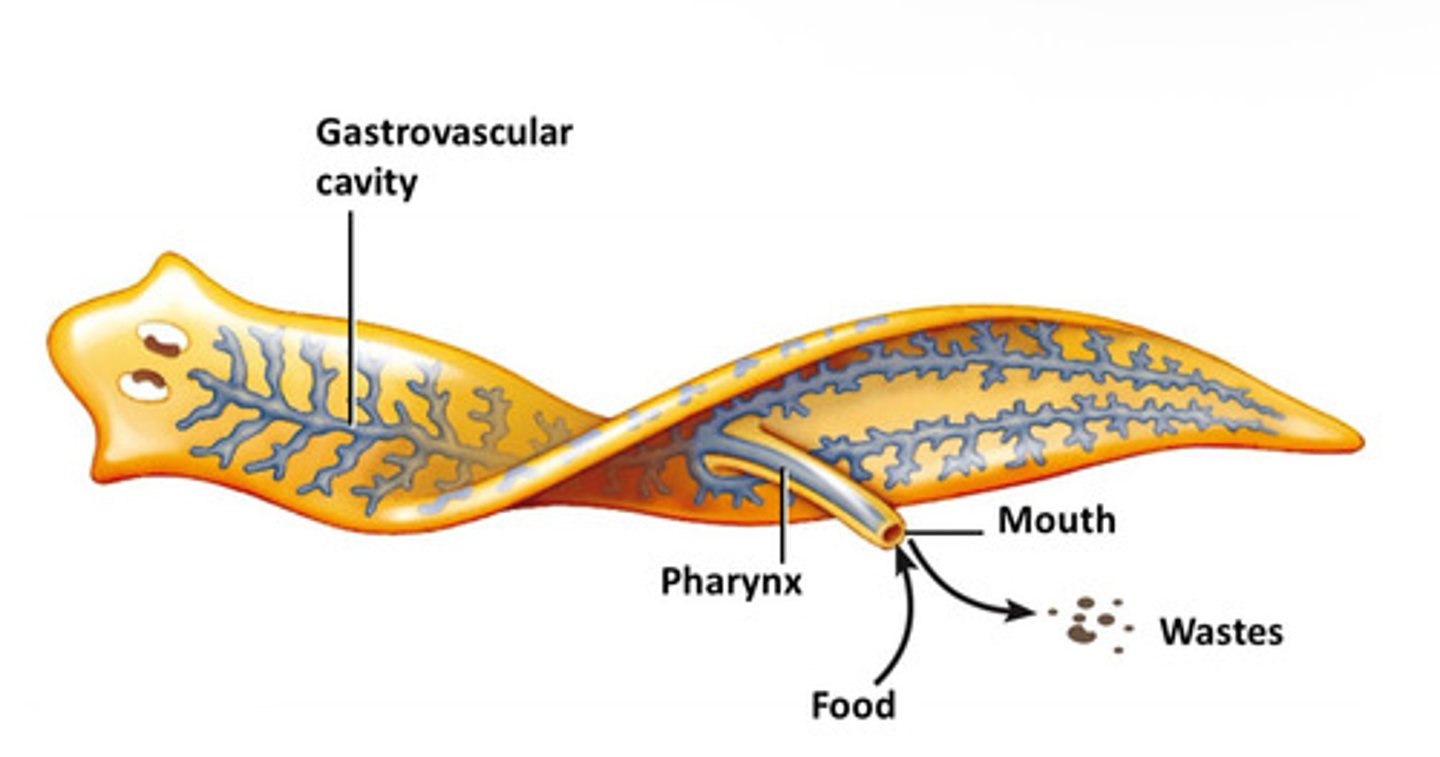
What is the lumen of the digestive tube?
The inside space of the digestive tract, is functionally external to all body tissues (outside the body).
What are the five steps in digestion?
1. Mechanical processing
2. Secretion of enzymes
3. Enzymatic hydrolysis
4. Absorption
5. Elimination
What is mechanical processing in digestion?
Physical breakdown of food (chewing, grinding, tearing) that increases surface area and mobility for enzyme action.
What happens during secretion in digestion?
Enzymes and substances such as acids, emulsifiers, and mucus are released into the digestive tube to aid digestion.
What are digestive tubes?
Tubular digestive tracts with two openings, allowing for a one-way movement of food, digestion occurs in specialized regions.
What is enzymatic hydrolysis?
Enzyme-catalyzed reactions that chemically break food molecules into absorbable molecular subunits.
What is absorption in digestion?
Movement of molecular subunits from digestive contents into body fluids and cells.
What is elimination in digestion?
Expulsion of undigested material from the body through the anus.
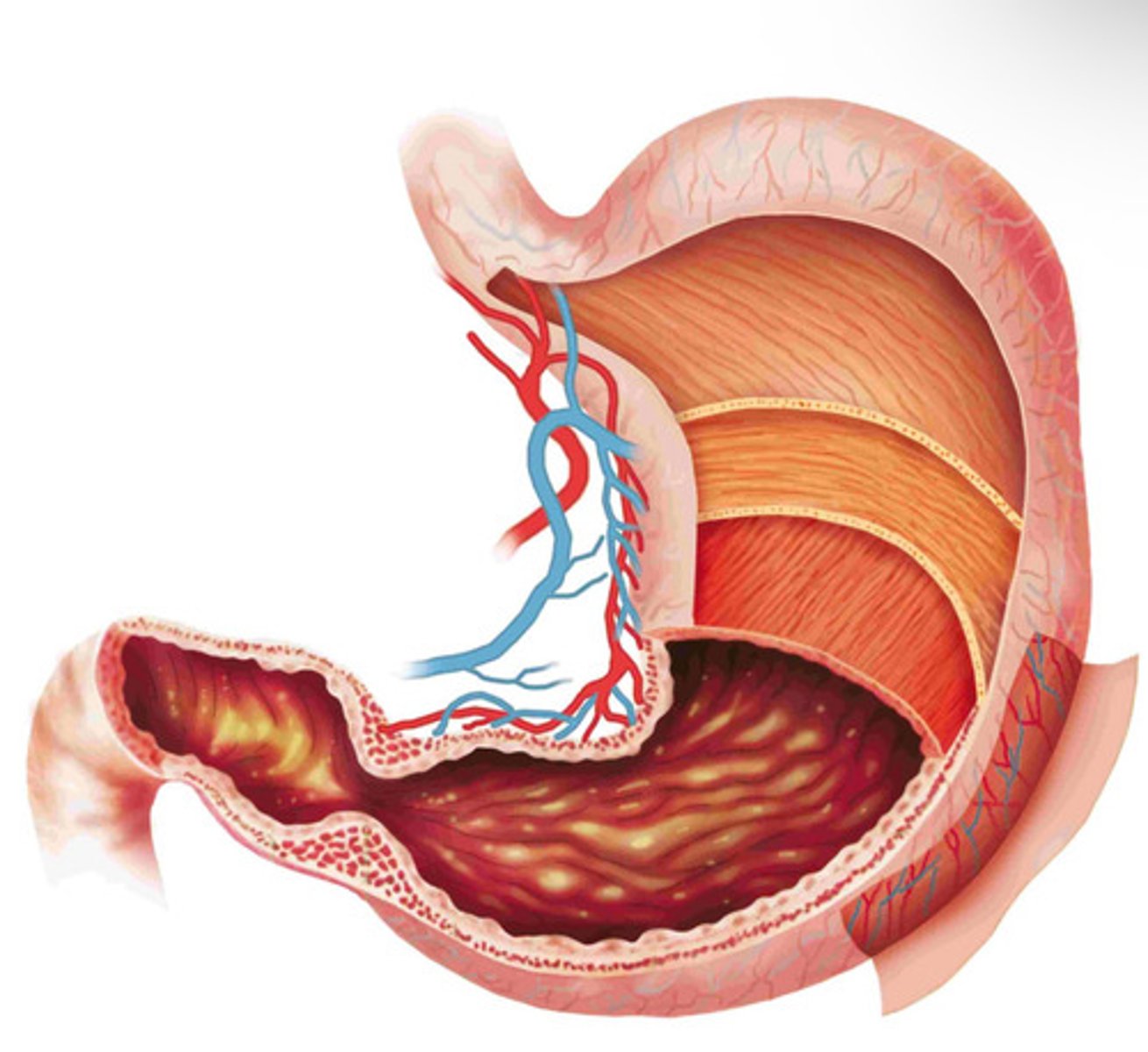
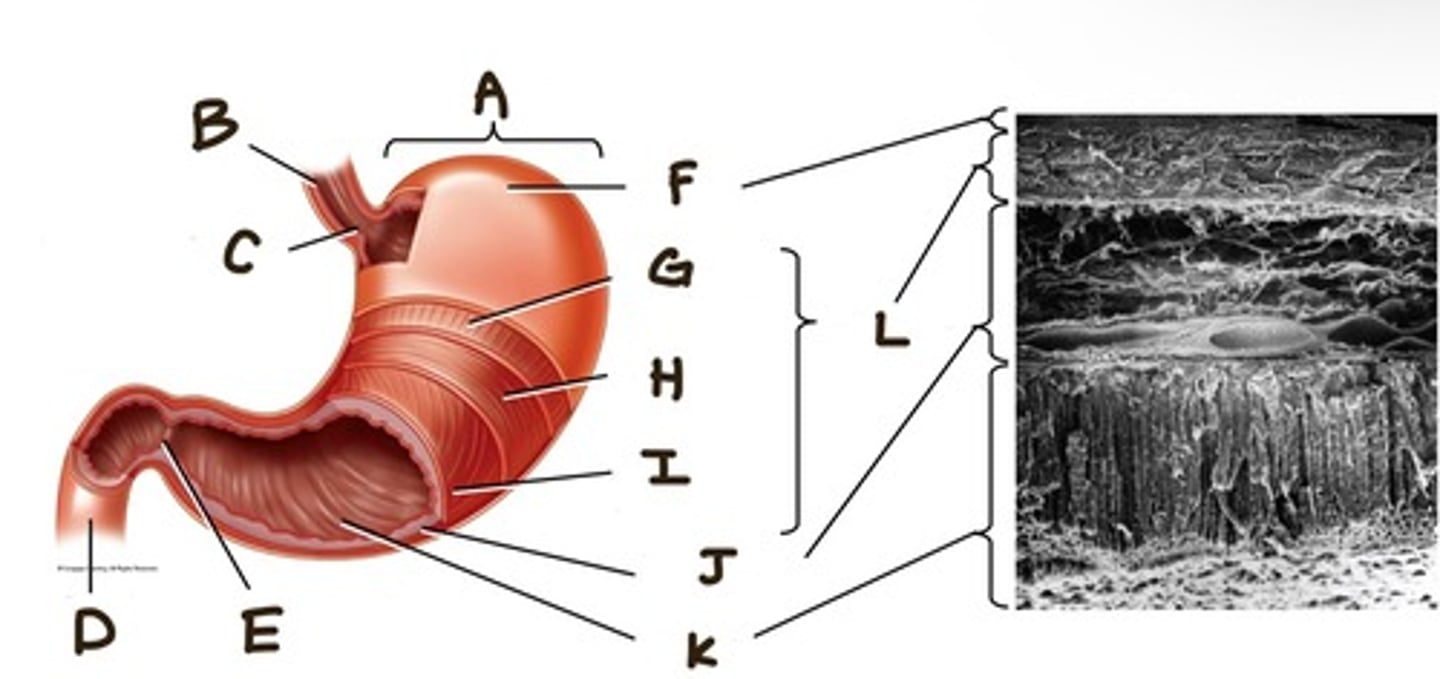
What structures are labeled in diagram 1? https://share.icloud.com/photos/089aUuf-Bet7wAF4rIY32Oo0w
A -> Stomach
B -> Esophagus
C -> Gastroesophageal
sphincter
D -> Duodenum
E -> Pyloric sphincter
F -> Serosa
G -> Longitudinal muscle
H -> Circular muscle
I -> Oblique muscle
J -> Submucosa
K -> Mucosa
L -> Muscularis
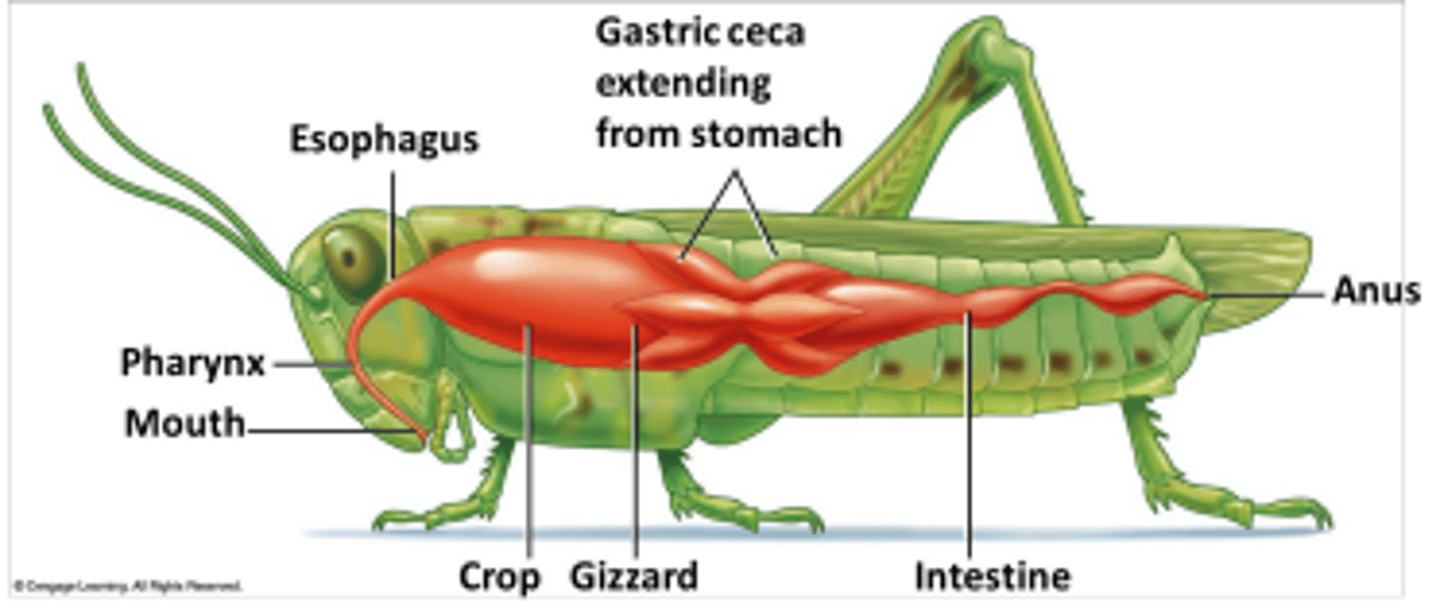
Where does most enzymatic digestion occur in insects?
In the stomach via enzymes secreted by the gastric ceca.
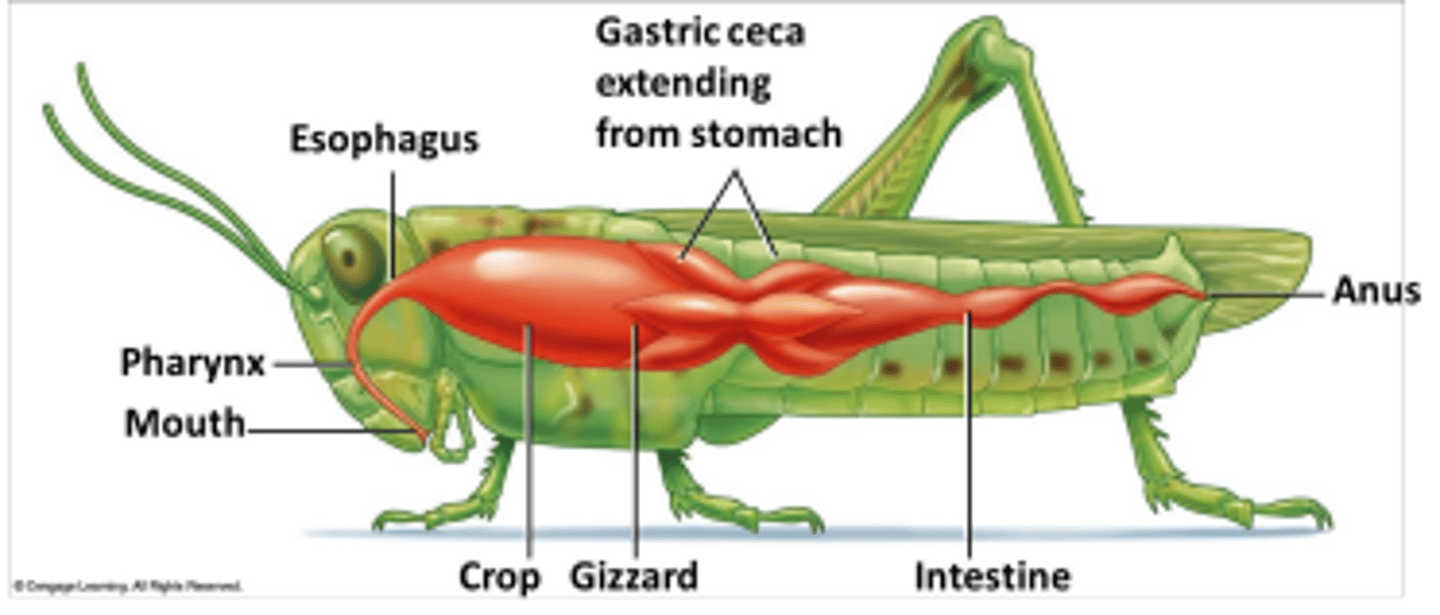
What are gastric ceca and what is their function?
Finger-like extensions from the stomach that secrete digestive enzymes and absorb digested nutrients.
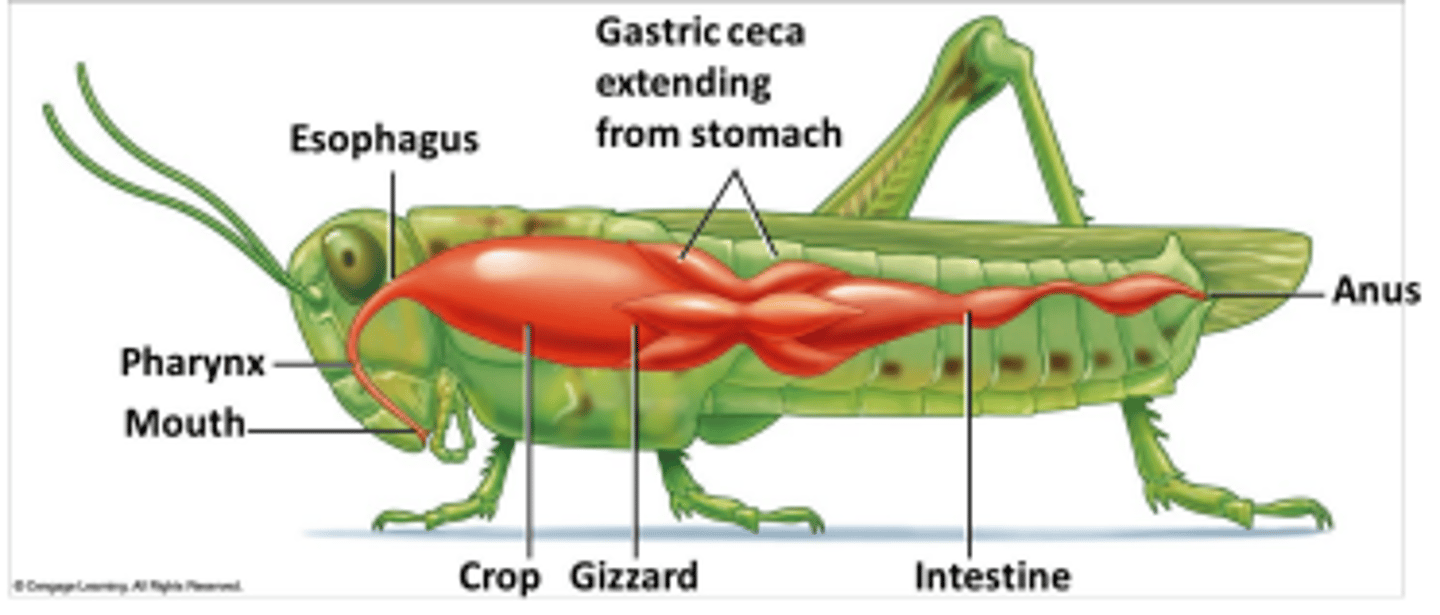
Where are digested nutrients absorbed in insects?
Through the walls of the gastric ceca and intestine.
What is the mammalian digestive system?
A series of specialized digestive regions controlled by the nervous and endocrine systems.
Which systems regulate the mammalian digestive system?
The nervous system and the endocrine system.
What structures make up the mammalian digestive tract?
Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus.
Which organs are considered accessory digestive organs in mammals?
Salivary glands, exocrine pancreas, liver, and gallbladder.
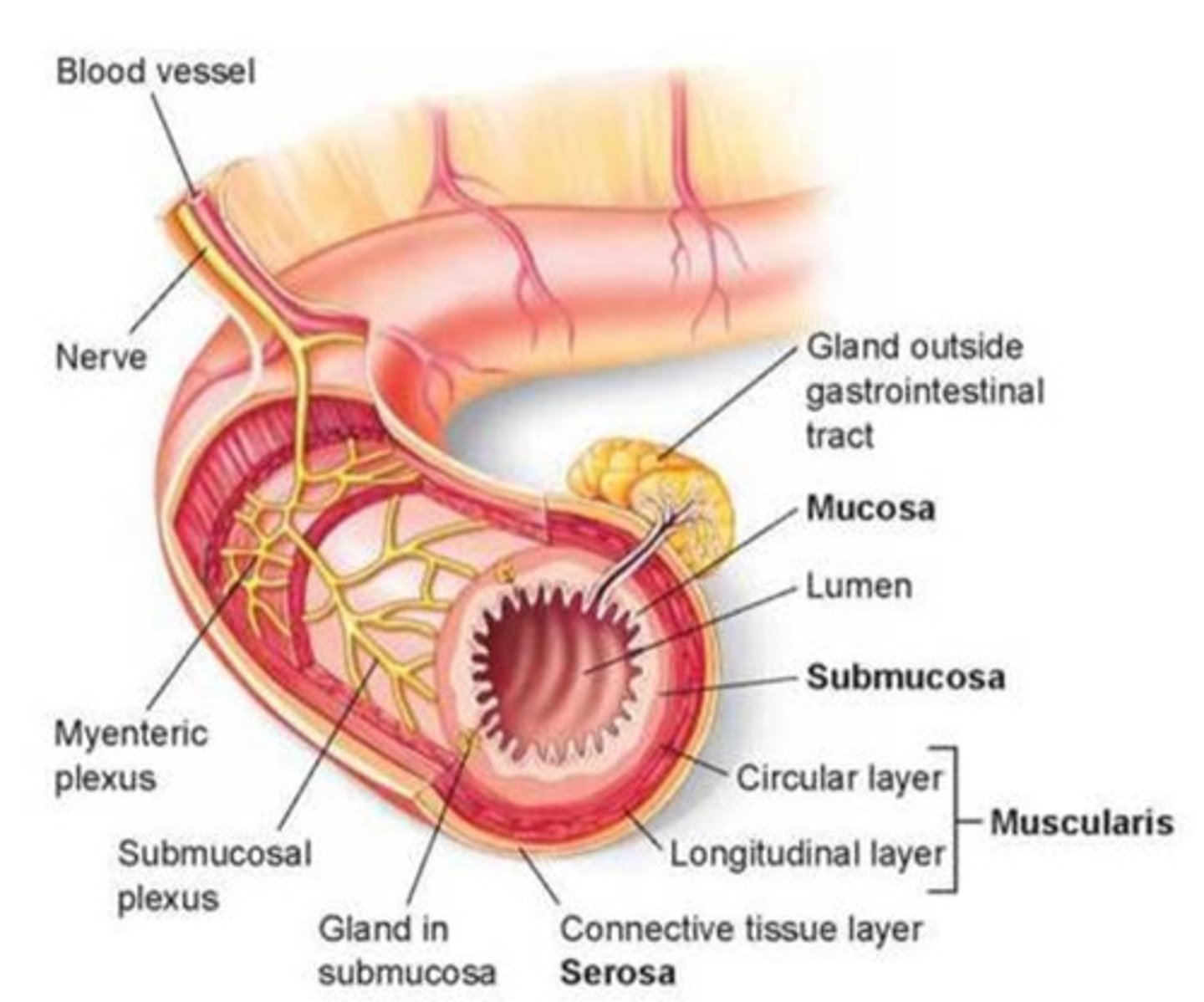
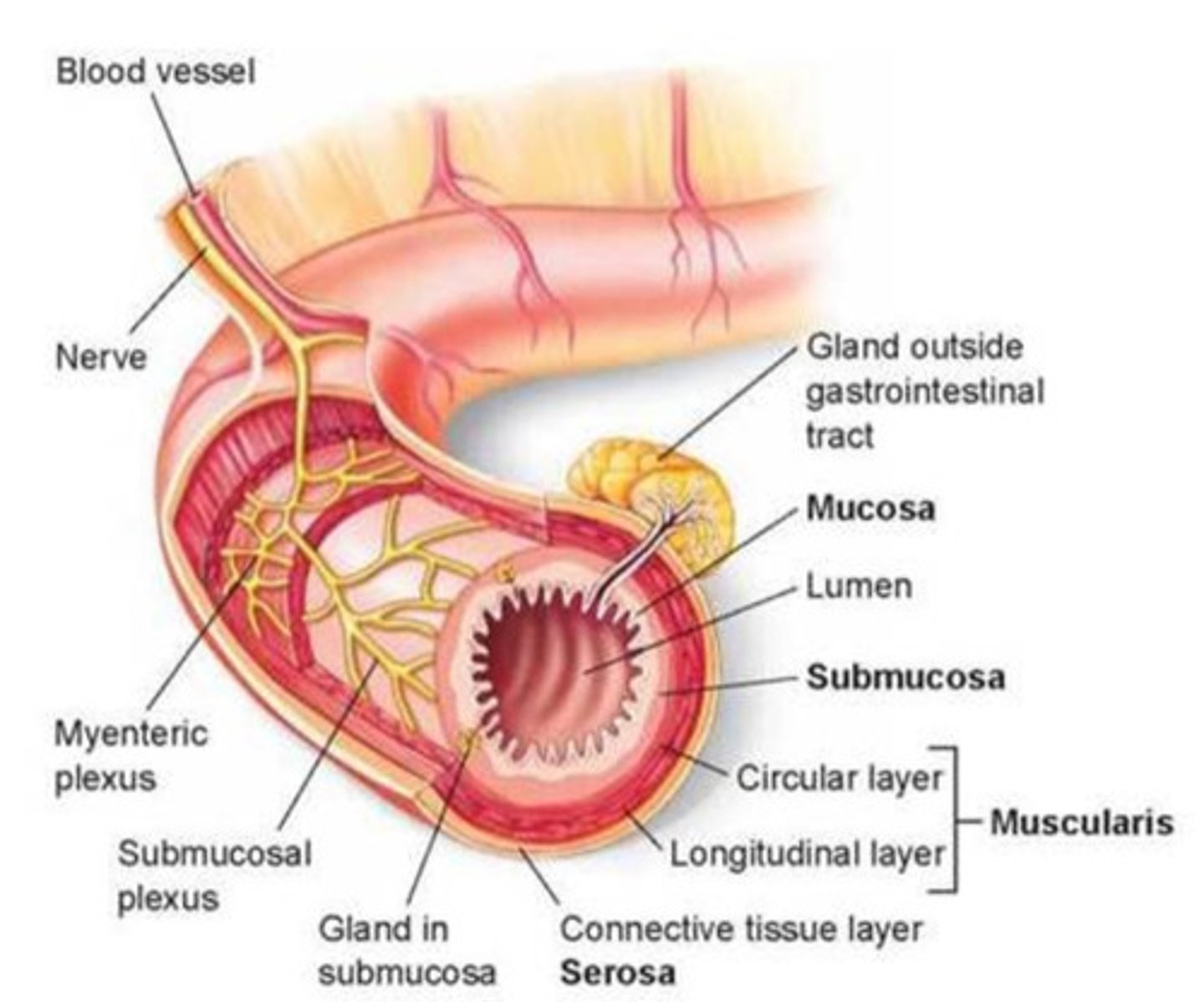
What are the four major layers of the mammalian gut (from inner to outer)?
Mucosa → Submucosa → Muscularis → Serosa
What is the function of the mucosa?
Lines the inside of the gut; contain epithelial cells and glandular cells.
What is the function of epithelial cells?
absorb nutrients and seal digestive contents from body fluids.
What is the function of glandular cells?
secrete enzymes, mucus, and pH-regulating substances.
What is the function of the submucosa?
A connective tissue layer containing neuron networks, blood vessels, and lymph vessels that provide local digestive control, communicate with the CNS, and transport absorbed lipids.
What is the function of the muscularis?
Two smooth muscle layers (circular and longitudinal) coordinate contractions to produce peristalsis and move digestive contents through the gut.
What is the function of the serosa?
Outermost layer that secretes lubricating fluid and connects to the mesentery, which suspends the digestive system in the abdominal cavity.
What is the role of the pharynx in digestion?
Directs food from the mouth to the esophagus during swallowing.
What is the function of the esophagus?
Transports food to the stomach via peristalsis.
What structures are labeled in diagram 2? https://share.icloud.com/photos/0ddRCZGOYPE2Iuwmsvf56r9tQ
A - Salivary duct
B - Tooth
C - Tongue
D - Sublingual gland
E - Submandibular gland
F - Parotid gland
What initiates movement of food from the mouth into the pharynx?
The swallowing reflex moves the bolus into the pharynx.
What is the function of the epiglottis during swallowing?
It prevents food from entering the trachea.
How does food move through the esophagus?
Peristalsis moves the bolus downward and through the gastroesophageal sphincter.
What is the function of the gastroesophageal sphincter?
It prevents acidic stomach contents from reentering the esophagus.
What structures are labeled in diagram 3? https://share.icloud.com/photos/0f9LabtJ4iQ7BVQIWCiPDbbfA
A - nasal cavity
B - hard palate
C - tongue
D - nasopharynx
E - oropharynx
F - laryngopharynx
G - soft palate
H - epiglottis
I - larynx
J - esophagus
K - trachea
What triggers the swallowing reflex?
When the bolus reaches the pharynx.
What happens to the soft palate during swallowing?
It elevates to prevent food from entering the nasal passages.
What is the role of the epiglottis during swallowing?
It moves downward to block the airway and prevent food from entering the trachea.
What happens to the larynx during swallowing?
It moves upward, helping the epiglottis block the airway.
What is the function of the pharyngoesophageal sphincter?
It relaxes to allow the bolus to enter the esophagus.
How does peristalsis move food through the esophagus?
Circular muscles contract behind the bolus while longitudinal muscles contract ahead of it, pushing food downward.