Genetics exam 3
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
microRNAs (miRNAs)
Eukaryotic gene regulaiton
Naturally occurring regulatory RNA’s encoded in the genome, regulate the expression of other genes (abt 300 target on average)
Function to regulate target genes by reducing translation of their mRNAs → down regulate by degradation
Preliminary miRNA transcripts are self-complementary (double stranded)
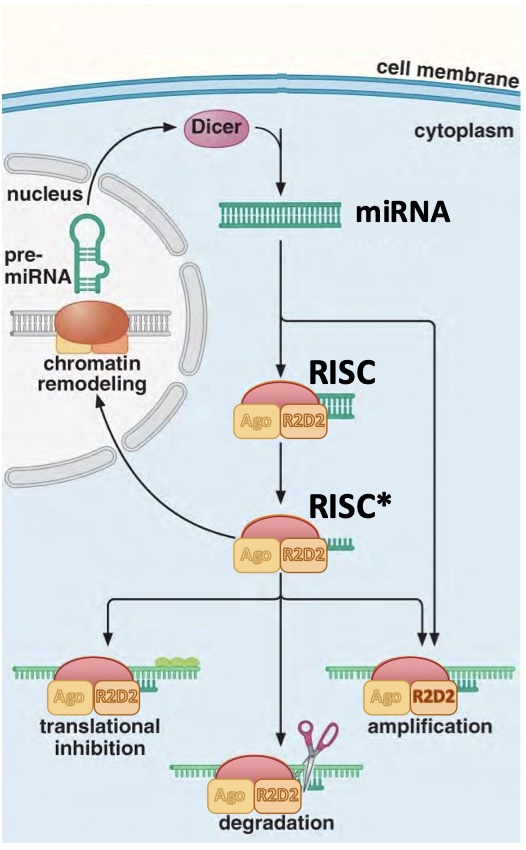
dsRNAs (double stranded)
Complementary RNA strands, including miRNAs and double stranded RNA used experimentally in RNA interference (RNAi)
Dicer
An enzyme that cuts double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) to produce single-stranded guide RNAs
usually 22 nucleotides long
will bind to argonaut to form complex RISC
Argonaute (Ago) proteins
Proteins that bind to the single-stranded guide RNAs produced by dicer to form the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC)
RISC (RNA induced silencing complex)
Complex formed when guide RNAs bind to argonaut proteins, will bind to mRNAs with complimentary to the guide RNA
mRNA silenced by:
digestion of mRNA
blocking translation of mRNA
RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP)
Enzyme that creates a new complementary RNA using RISC-bound mRNA as a template
Results in more dsRNA to amplify gene silencing effect
RdRP pathway part of of miRNA mechanism and RNAi
RNAi (RNA interference)
Experimental use of double stranded RNA to regulate gene expression
To silence a target gene
Used in experiments or therapeutics
Homologous chromosomes
Copies of a chromosome present in a diploid cell (one from each parent)
similar but not identical
may differ in alleles or may have structural variants
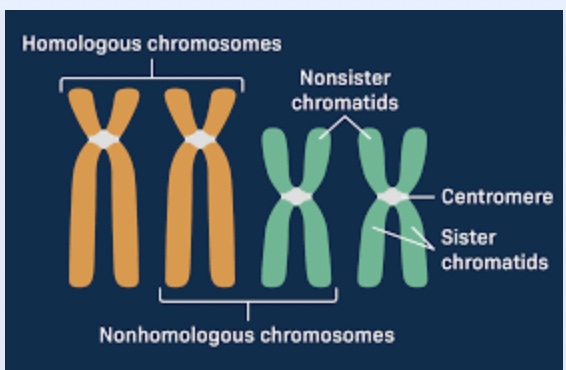
Synapsis
The pairing up of homologous chromosomes that occurs during prophase I of meiosis
Bivalent
The structure to describe a pair of homologous chromosomes during meiosis, come together during synapsis
Tetrad
The structure composed of 2 pairs of sister chromosomes
Homologous pairs within the tetrad separate during anaphase I
same as bivalent but emphasis on the chromatids (4)
Crossing over
Process that occurs during synapsis, where non sister chromatids exchange genetic material → recombination between linked loci
Chiasma (pl. chiasmata)
Observable regions on non-sister (homologous) chromatids where crossing over occurs
Polar bodies
Cells produced during gamete maturation in females (ovum maturation)
Ploidy (n)
Indicates number of chromosomes in a single, haploid copy of the genome
used with a multiplier
Haploid (1n)
Cells that have only a single copy of each chromosome
gametes, after meiosis II and cytokinesis
Diploid (2n)
Organisms or cells that have two copies of the genome
somatic cells after mitosis, gametes after replication but before meiosis
Gene
A segment of DNA that is responsible for one or more phenotypes, a unit of inheritance
Allelic segregation (Mendel’s first law)
The principle that the two alleles for a trait segregate with equal probability into gametes during meiosis
Independent assortment (Mendel’s second law)
Two or more traits are inherited independently of each other (ex: dihybrid cross)
Test cross
Cross typically used to identify the genotype of an individual expressing a dominant trait by mating it with a homozygous recessive individual
How to generate variation in meiosis
Independent assortment (2n, n = haploid number)
Recombination, crossing over
Mendel
Addressed question of why offspring resemble their parents and how transmission of traits occurs….
To answer:
Blending inheritance
Inheritance of acquired characteristics
Used pea plants as model organism
Could control matings
Traits easily recognizable
Mendel’s Postulates
Alleles (unit factors) exist in pairs
For a pair of unit factors one is dominant and the other recessive
The paired unit factors (of the same gene) segregate independently during gamete formation
Law of independent assortment
Complete dominance
Phenotype of hetero is identical to phenotype of dominant homozygote (normal)
Partial (incomplete) dominance
Heterozygote exhibits a phenotype that is intermediate (blend) of two homozygotes
Codominance
Both alleles are simultaneously and fully expressed in the phenotype of the heterozygote
ex: AB blood type
ABO blood group
Example of multiple alleles where three alleles exist at a single locus, ex of com dominance and complete dominance
Haploinsufficient
Describes a gene where a single functional copy of the allele is insufficient to produce the wild-type phenotype
often results in a dominant mutant phenotype
Loss of function mutation
A mutation that reduces or eliminates the normal function of a gene product due to two alleles encoding non-functional proteins
often recessive
Gain of function mutation
A mutation that causes a gene to do something extra/new, causes the protein to be active when it should be inactive
These mutations often dominant
Hemizygous
A genotype in which only one copy of a gene is present
Ex: genes located on the single X chromosome in human males
Compound heterozygotes
Individuals who have two different mutant alleles (different base pair changes) at a given locus
Autosomal dominant
Mode of inheritance where the trait is controlled by a gene on an autosome, only 1 copy of allele is required for the phenotype to be expressed
Autosomal recessive
Mode of inheritance where trait is controlled by a gene on an autosome, two copies of allele are required for the phenotype to be expressed
Incomplete penetrance
When an individual has the genotype for a trait but does not express the corresponding phenotype
Variable expressivity
When individuals with same genotype exhibit a range in the severity or expression of a phenotype
Chi-square test
Stat test used to compare observed genetic data (offspring ratios) to expected results from hypothetical model
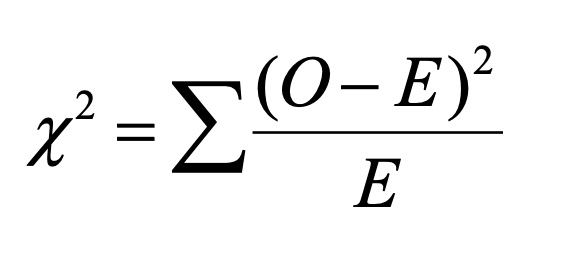
Product rule
Used to calculate probability of two or more independent events occurring together
ex: segregation of alleles at two diff loci
AND rule
Sum rule
Used to calculate probability of any one of two or more mutually exclusive events occurring
OR rule
p < 0.05
Reject the null hypothesis, difference between observed and expected results is substantial
0.05 bc value is at least two standard deviations from the expected mean
Recessive lethal alleles
Mutations where lethality requires two (homozygous) copies of the allele
can still have a dominant phenotype in heterozygotes
Dominant lethal alleles
Alleles that cause death even in heterozygotes
Only maintained in a population if they impact survival after reproductive maturity
ex: Huntington’s disease
Pleiotropy
Influence of one gene on multiple traits
ex: frizzle mutation in chickens effects feather shape, body temp, blood flow, etc.
Antagonistic pleiotropy
When some phenotypic effects increase fitness, while others decrease it
Gene interaction
When genes at multiple loci collectively determine a single phenotype
ex: A- and B- blood antigens are produced from substance H, made by enzyme FUT1
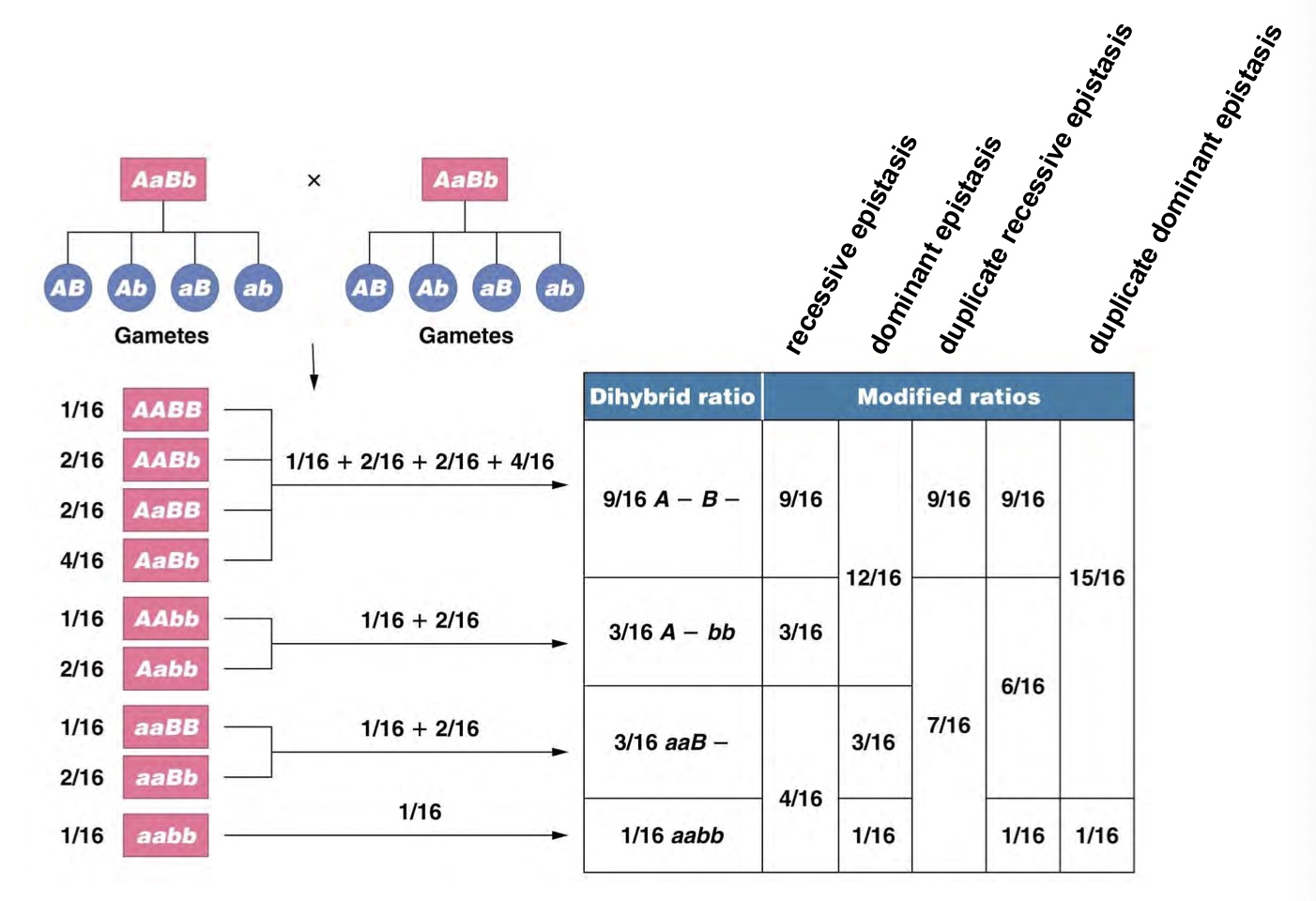
Epistasis
Phenotype of one locus (earlier) masks/prevents the phenotypic expression of a second locus (acting later)
How to recognize:
Focused one trait with 2 to 4 character states
F2 phenotypic ratios are fractions of 16

Epistasis in squash example
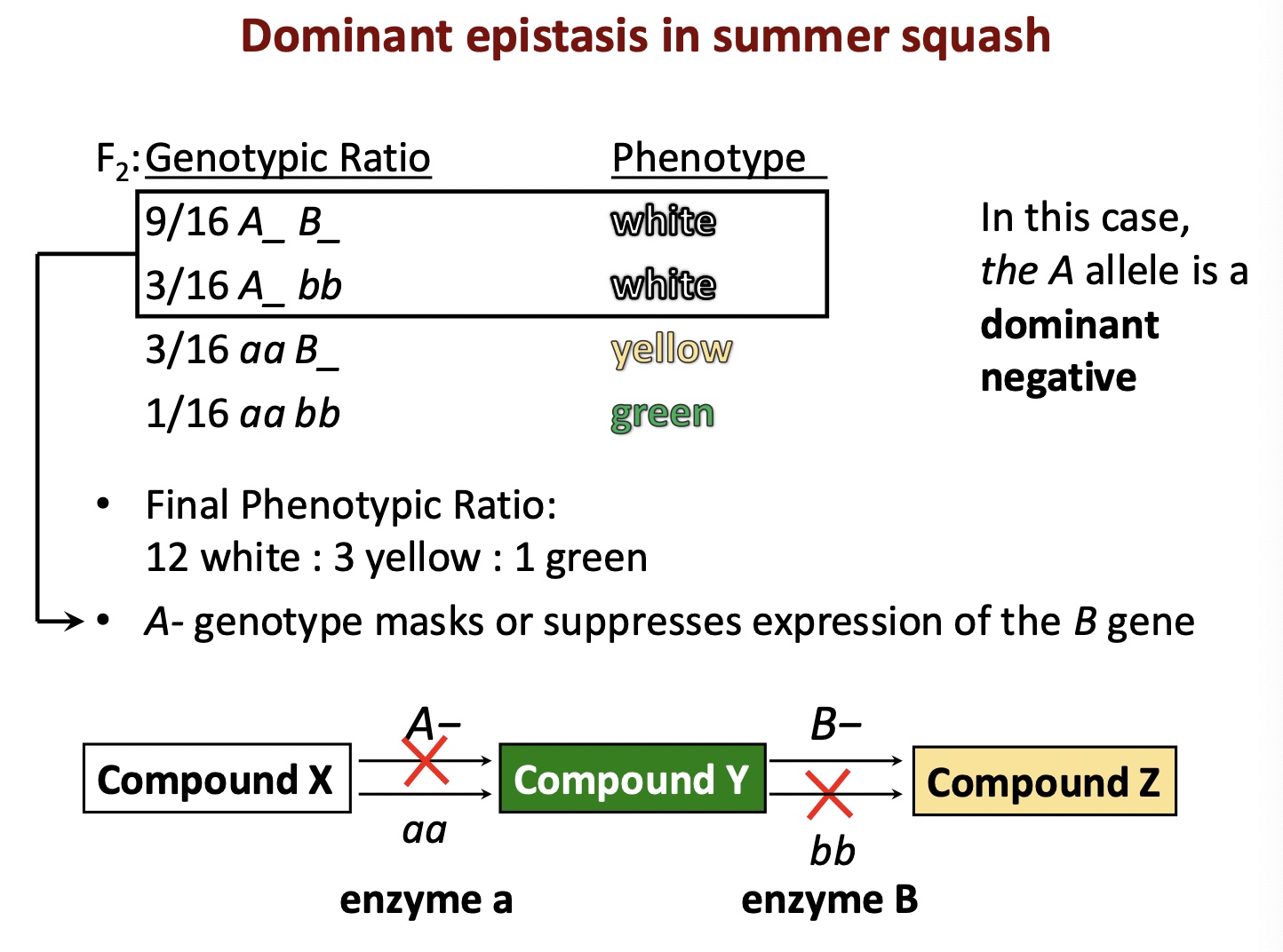
Duplicate recessive epistasis
Homozygous condition of either recessive allele masks the expression of the dominant allele at the other locus
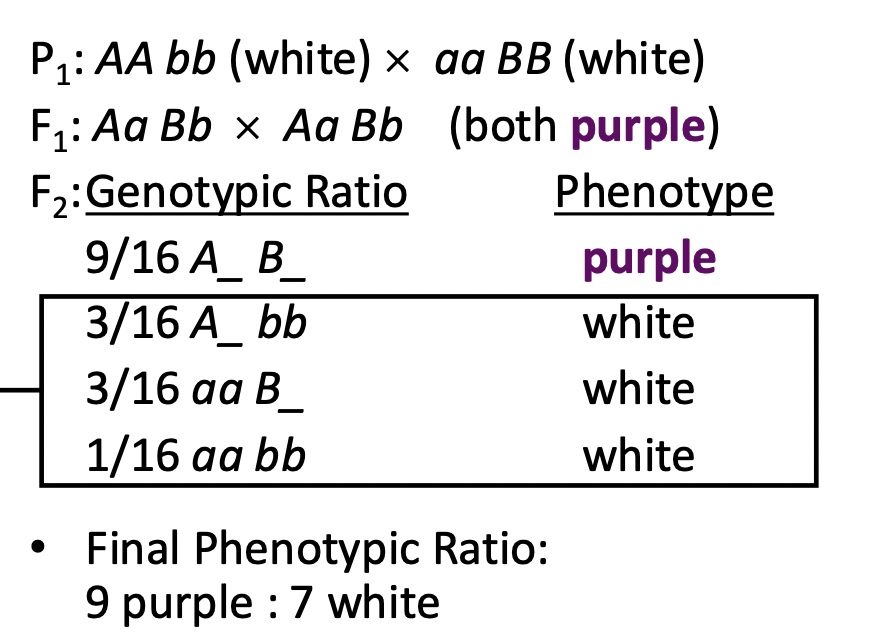
Epistasis combines categories from the og 9:3:3:1 ratio
Genetic background
Influence of numerous weak epistatic interactions (between multiple genes) that affect a single phenotype
Genetic suppression
mutation that makes the phenotype look more wild-type (less mutant) by overriding another mutation
Genetic enhancement
Mutation that makes the phenotype more mutant by increasing the severity of another mutation, complementation
Complementation analysis (test)
Crosses used to determine if two independent mutations causing a similar phenotype are alleles of the same gene
only works for recessive alleles
inbred (homozygous) stocks of each mutation are crossed
Complementation
Occurs when crossing two homozygous mutants yields a wild-type phenotype in the F1 descendants, indicating mutations are in different genes
Complementation group
A group of mutant strains that fail to complement one another, all members of the groups are understood to have mutations in the same gene
Allelic mutations
Two mutations that cause a similar phenotype and reside in the same gene
Maternal effect inheritance
An inheritance pattern where the offspring’s phenotype is determined by the genotype of the mother, regardless of the offspring’s own genotype
Sex-influenced trait
Trait where the phenotype is modulated/influenced by the sex of the individual
loci responsible may be linked to autosomes or sex chromosomes
Reciprocal cross
Pair of crosses used to test the influence of parental sex on offspring phenotypes, often shows different outcomes for sex-linked genes
Isogametic
Gametes with multiple mating types that are biochemically compatible or not
similar in size and form, can’t be distinguished as male (smaller) or female (larger)