Serum Electrophoresis
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
Electrophoresis
the Margination of charged solutes or particles in an electric field
Migration with electricity
Separates proteins on the basis of their electric charge densities, determined by the pH of their surrounding buffer
Arne Wilhelm Kaurin Tiselius
Swedish biochemist
Won Nobel Price in chemistry
He separated proteins dissolved in an electrolyte solution by application of an electric current through a U-shaped quartz tube that held the protein solution.
Moving Boundary or Frontal Electrophoresis
What was the term of the technique of protein separation by Arne Wilhelm Kaurin Tiselius ?
It separates proteins on the basis of their electric charged densities
How does Electrophoresis work?
Cathode
Negative Pole
Anode
Positive Pole
Their charge density, which is influenced by the pH of the surrounding buffer.
What determines the movement of proteins in an electric current?
Positively charged protein
What is a cation in protein electrophoresis?
Negatively charged protein
What is an anion in protein electrophoresis?
Negative pole
Toward which pole do cations migrate?
Positive pole
Toward which pole do anions migrate?
Oppositely charged electrodes
What are charged particles attracted to in electrophoresis?
Net charge of the particle
Size of the particle
Shape of the particle
Strength of the electric field
Chemical and physical properties of the supporting
electrophoretic medium
List the factors that control the rate of protein migration in electrophoresis.
Net charge of the particle
The rate of migration is directly proportional to what?
Size of the particle
Viscosity of the buffer
The rate of migration is inversely proportional to what two factors?
Net charge of the particle
What is the most important factor affecting protein migration?
Iontophoresis
Refers to the migration of small ions
A transdermal delivery system that uses electrophoresis to the skin by a low electrical current
Hyperhidrosis
What condition is commonly treated using iontophoresis?
Zone Electrophoresis
Usually used in clinical laboratories
Is the migration of charged macromolecules in a porous support medium.
paper
Cellulose acetate (commonly used)
Agarose gel film (DNA analysis)
What are the porous support medium for Zone Electrophoresis?
Electrophoretogram
is the result of zone electrophoresis
A visualization of the migration of proteins
Consists of sharply separated zones of a macromolecule
Smaller molecules
It terms of size , these molecules will migrate faster because they are lighter
Globular proteins
In terms of shape, these proteins migrate faster than fibrous proteins.
they have a more compact spherical shape leading to greater mobility.
Fibrous proteins
These proteins have long, rod-like structure that hinders movement
Support medium
Is a porous matrix that serves as the stationary phase for separating molecules like DNA, RNA, or proteins
Agarose gel
Polyacrylamide gel
Cellulose acetate
Give the different kinds/types of support medium
Agarose gel
A support medium that has neutral charge
Polyacrylamide gel
A support medium that is porous.
Electrical charge
Basis of separation and Migration of Agarose gel
Molecular weight or Size of molecules
Basis of separation and Migration of Cellulose acetate and Polyacrylamide gel
cluster around a migrating particle
What is the action of the ions during electrophoresis?
The higher the size of the ionic cloud
Lower the mobility of the particle
Complete the sentence:
Ionic Strength
The higher the ionic concentration , ______________________and the __________________.
It produces sharper protein-band separation
What effect does greater ionic strength have on protein-band separation?
It causes increased heat production
What is a disadvantage of increased ionic strength in electrophoresis?
denature heat-labile proteins
What is the consequence of excessive heat during electrophoresis?
Bands become broader instead of sharp
What happens to protein bands when heat denaturation occurs?
False.
Although it may sharpen bands, it also increases heat, which can damage proteins.
True or False:
Increasing ionic strength always improves electrophoresis results.
Why?
Ampholyte binds with H+ , becomes positively charged , and migrates toward the cathode
What happens if the buffer is more than the isoelectric point (pl) of the ampholyte?
Ampholyte loses H+ , becomes negatively charged, migrate towards the anode
What happens if the buffer is more basic than the isoelectric point (pl)?
5 minutes
How long is the sample soaked in hydrated support ?
Buffer
What is added to the chamber to maintain contact with the support?
50 V - 200 V
Electrophoresis is carried out by applying a constant voltage of ?
Driving force
Support medium
Buffer
Sample
Detecting system
Components of Electrophoresis
pH
Ionic strength
Two buffer properties that affect the charge of Ampholytes
8.6
pH of Cellulose Acetate gel
Ampholyte
Is a molecule , such as protein, whose net charge can be either positive or negative
Paper electrophoresis
Has been replaced by cellulose acetate or agarose gel in clinical laboratories
Acetic anhydride
Cellulose is acetylated to form cellulose acetate by treating it with ?
Cellulose acetate
A dry, brittle film composed of about 80% air space, is produced commercially
Can be made Transparent
Advantage of cellulose acetate
Agarose gel
Used as a purified fraction of agar, it is neutral and, therefore,does not produce electroendosmosis.
2mL
How many mL of sample does Agarose gel require?
Seaweeds
Where does Agarose gel come from?
Polyacrylamide gel
separates serum proteins into 20 or more fractions
Widely used to study individual proteins
Going Down
Direction of migration for Polyacrylamide gel
Starch Gel
Not widely used because of technical difficulty in preparing the gel
Used for research and never in clinical laboratory
Surface charge and molecular size
Starch gel basis of separation ?
Greater uniformity
Advantage of Starch gel
Electroendosmosis
The movement of buffer ions and solvent relative to the fixed support
Negative charge
Hydroxyl ions
In Electroendosmosis, Support media (paper, cellulose acetate, and agar gel) take on a _________ charge from absorption of ___________.
hydroxyl ions
Free positive ions
When current is applied to the electrophoresis system, the _________ remained fixed, while the ___________ move toward the cathode.
They are swept toward the cathode with the solvent
What happens to molecules that are nearly neutral?
True
True or False:
Support media such as agarose and acrylamide gel are essentially neutral, eliminating electroendosmosis.
The support medium should have electric neutrality
How to achieve optimum separation of proteins?
Serum
What is the preferred specimen?
Plasma
This specimen should be avoided because fibrinogen will appear as a distinct narrow band between the beta and gamma fractions.
M spike
Using Plasma specimen can be mistaken as ?
Monoclonal gammopathy
Appearance of fibrinogen is important because it is used to detect?
Cerebrospinal fluid
This specimen can be used if concentrated up to 300 times, depending on the original protein concentration.
Hemoglobin hemolysate
Is used without further concentration
2-5 mL
Cellulose acetate and Agarose gel electrophoresis require approximately volume range of sample?
Twin-wire applicator
Designed to transfer a small amount of sample
Densitometry
Most common and reliable way for quantitation
measurement of the density of light passing through the fraction
Stained
Separated protein fractions are ______ to reveal their locations?
Amido black
Ponceau S
Coomassie blue
What are the stains used in Detection and quantitation?
Comassie blue
stain used for Urine and CSF
Silver staining
This stain is used in cases where the protein concentrations are low
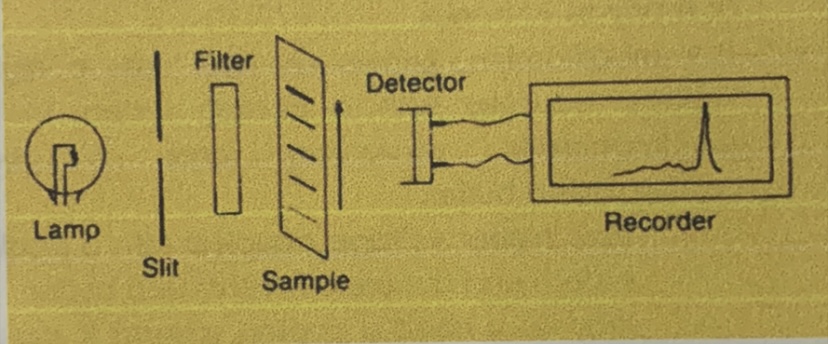
Identify the parts of the densitometer

Filters
This part of the densitometer permit only a certain wavelength range to spike the strip.
Isoelectric Focusing
High-Resolution Protein Electrophoresis
Types of Electrophoresis
Isoelectric Focusing
A modification of electrophoresis
Charged proteins migrate through a support medium that has a continuous pH gradient.
Isoelectric point
Isoelectric focusing exploits a different parameter associated with protein charges. What parameter is this?
Isoelectric point
For each protein molecule, there is a pH where the net charge on the molecule is zero.
High-Resolution Protein Electrophoresis
Uses a higher voltage coupled with a cooling system in the electrophoretic apparatus and a more concentrated buffer.
Agarose buffer
Most commonly used medium for High-Resolution Protein Electrophoresis
Prealbumin
What protein is present in zone 1?
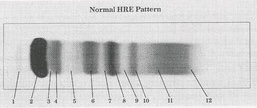
Albumin
What protein is present in zone 2?

a-Lipoprotein (a-Fetoprotein)
What protein is present in zone 3?
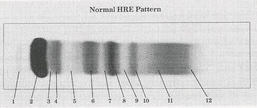
a1 - Antitrypsin , a1 - Acid glycoprotein
What protein is present in zone 4 ?
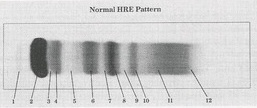
Gc - globulin , inter-a-trypsin inhibitor, a1 - antichymotrypsin
What protein is present in zone 5 ?
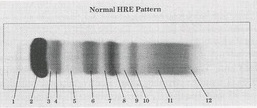
a2 - Macroglobulin , Haptoglobin
What protein is present in zone 6 ?
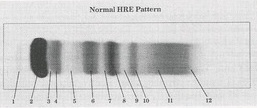
Cold insoluble globulin, (Hemoglobin)
What protein is present in zone 7 ?
Transferrin
What protein is present in zone 8 ?
B - Lipoprotein
What protein is present in zone 9 ?
C3
What protein is present in zone 10 ?
IgA (Fibrinogen) ,
IgM (Monoclonal Igs, light chain)
What protein is present in zone 11 ?
IgC (C- reactive protein)
What protein is present in zone 12 ?
Serum Electrophoresis
Serum samples are applied close to the cathode end of a support medium that is saturated with an alkaline buffer . (ph 8.6)
Cathodes and Anodes
Electrode that will be used to separate the protein
True
True or False:
All major proteins carry a net negative charge at pH 8.6 and migrate toward the anode