Lec 3 Lipids as Signals
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
general definition of a hormone
hormones travels in bloodstream to tissues or organs —> endocrine signalling
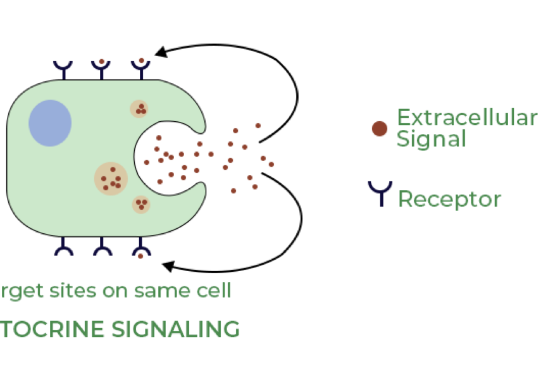
general definition of autocrine
= the production and secretion of extracellular mediate by cell followed by BINDING of that mediator to receptors on SAME cell to initiate signal transduction
paracrine vs juxtacrine signalling
PARACRINE=cell produces a signal to indice changes in nearby cells which alters behaviour of those nearby cells
JUXTACRINE= requires CLOSE contact, cell-to-cell or cell-to-extracellular matrix
what is a pheromone?
= chemical that animal produces which changes behaviour of another animal of same species
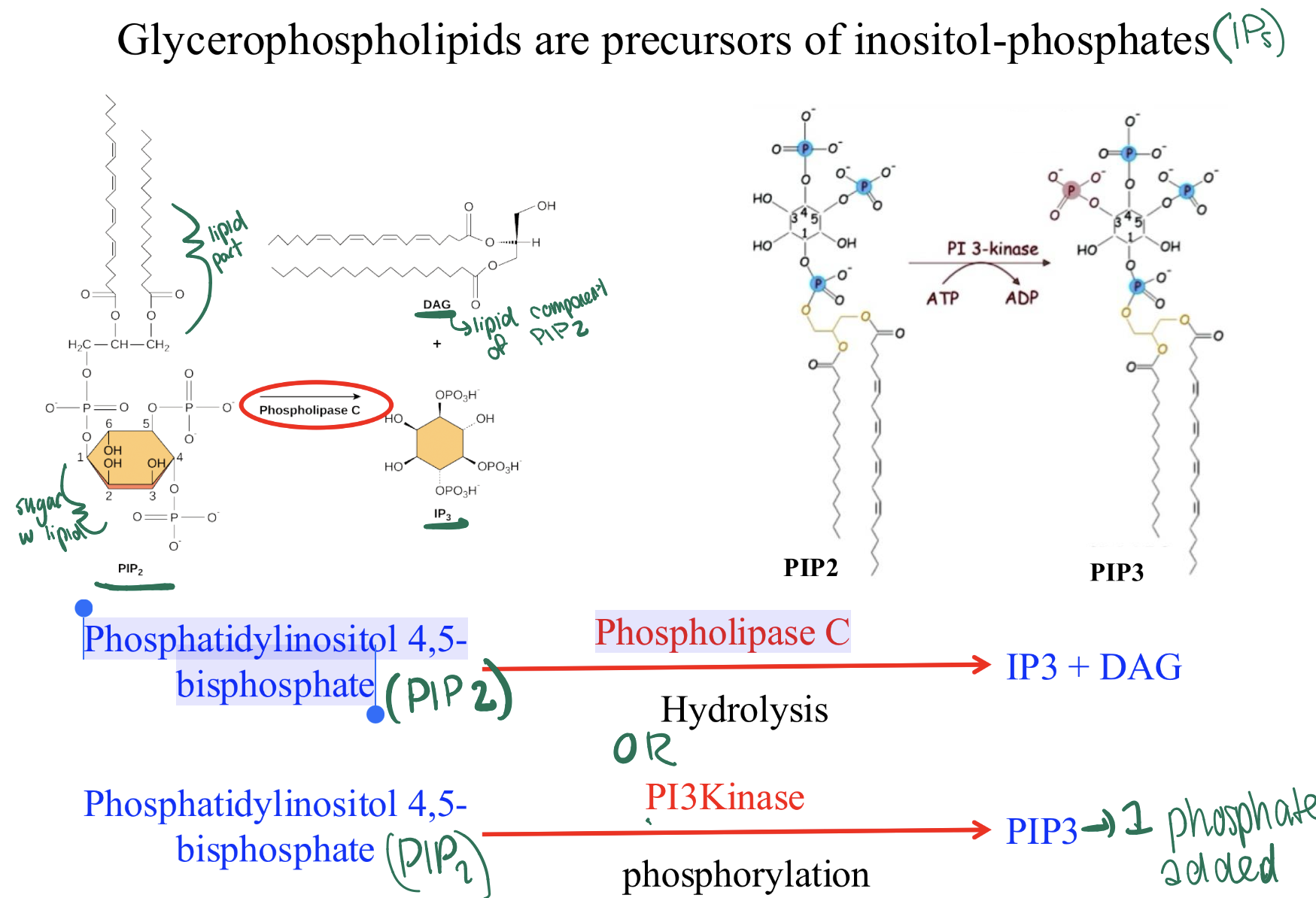
how do glycerophospholipids act as intracellular signals?
they are precursors of inositol phosphates (IPs) second messengers!
EX: Phosphatidylinositol 4,5- bisphosphate (PIP2) can convert to IP3 2nd messenger
what are eicosanoidds? what are they involved with in body? what are they derived from? how do they signal?
= paracrine hormones involved in inflammation (fever and pain associated with and injury or disease); reproductive function; formation of blood clots, regulation of blood pressure; and in gastric acid secretion among other functions.
Derived from: arachidonic acid (arachidonate)
and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA);
❖ Arachidonate (ionized form of arachidonic acid) is released from glycerophopholipids
by Phopholipase A2;
ALL SIGNAL VIA GPCR!
what are 4 classes of eicosanoidds and what are they involved w?
Prostaglandins: Muscle contraction during menses and labour. Blood flow to organs, wake- sleep cycle, responsiveness of certain tissues to hormones such as epinephrine and glucagon.,
Tromboxanes:- BLOOD clot formation and reduction of blood flow to clot sites, produced by platelets
Leukotrienes: induces contraction of smooth muscle lining the airways to the lung, overproduction causes asthma
Lipoxins: anti-inflammatory agents. Individuals with cardiovascular disease are prescribed a low dose of aspirin which stimulates synthesis.
what are steroid hormones ? how do they move around in body? how do they signal? what re some major important examples?
= oxidized derivatives of sterol—> mostly cholesterol
move through blood via carrier proteins from production site to target tissues, enter cells, bind and SIGNAL to nuclear receptors, trigger changes in gene expression.
major groups= M&F sex hormones, cortisol, aldosterone
why are are A and D important?
they are hormone precursors!
VIT. D—> formed in skin upon UV light component, converted by enzymes in liver and kidney to calcitriol, which regulates calcium uptake in intestine and calcium levels in kidney and bone,
VIT A1—> its metabolites retinoic acid and retinal -development, cell growth and differentiation and vision.
❖ B carotene is the precursor
❖ Retinal bound to opsin (group of proteins that absorb light) forms rhodopsin= photoreceptor that helps to see in low light situation
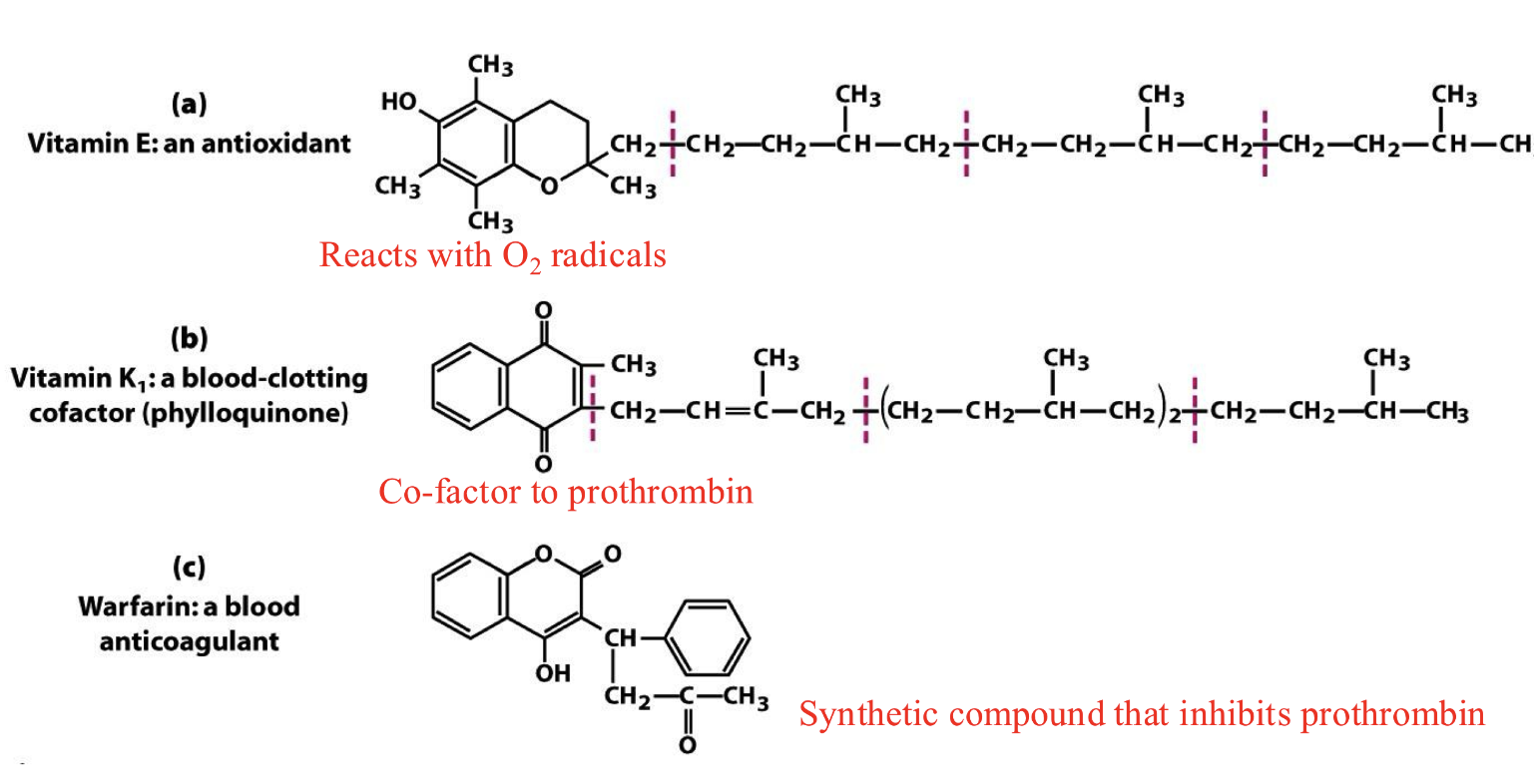
what are tocopherols and why are they important??
= Vitamin E, all antioxidants
ex: vit E itself, Vit. K1 blood clotting cofactor, Warfarin blood anticoagulant
how do NSAIDs work?
inhibit the enzyme cyclooxygenase that is key for prostaglandin an thromboxane formation from aranchidinoate