Lec 10: Oxygen therapy
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
what is the order of a resp assessment
inspection
auscultation
palpation
percussion
wheezing def
high pitched musical note
from air traveling through narrow passage on inspiration
common in asthma
Cough def/purpose
to clear bronchi of irritant
productive, non productive
ask pt about quality of cough
dyspnea def
subjective
difficulty breathing
due to underlying pulmonary or heart disease
sign of hypoxia
Risk factors for potential oxygenation issues include
smoking
substance exposure and/or abuse=causes malnutrition=anemia
pain
fatigue
Risk factors for oxygenation issues in the older adult
atherosclerotic plaques
osteoporosis
Oxygen therapy def/purpose/characteristics
used to relieve or prevent tissue hypoxemia
is often used in conjunction with other interventions
requires a prescribers order
treated like a medication- so all rights and checks apply
once initiated, pt needs to be continuously assessed
complications can arise and safety measures followed
what are the diff ways oxygen can be administered
nasal cannula
simple face mask
mask with reservoir bag
face tent=if mask not tolerable
oxygen hood=usually for children
oxygen tent=children, ten must be filled 1st
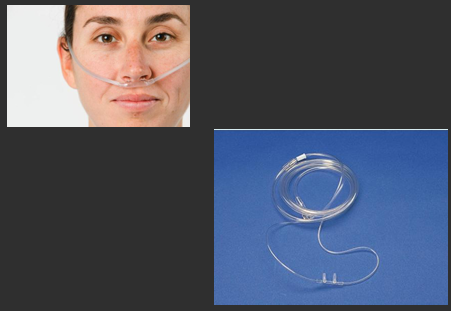
nasal cannula
most common
the easiest tolerated
easily dislodged, can cause dryness, can cause blockage if deviated septum
can talk/eat with it
best for low flow oxygenation, 1-6 LPM (high flow 6-15) or 24-44% Fio2
nasal cannula oxygen concentrations
1L/min=24% fio2
2L/min=28% fio2
3L/min=32%
4L/min=36%
etc
administration guidelines for nasal cannula
check patency of nostrils with penlight, put prongs in nostrils
position canula tubing behind ears and under chin, secure under chin with clip
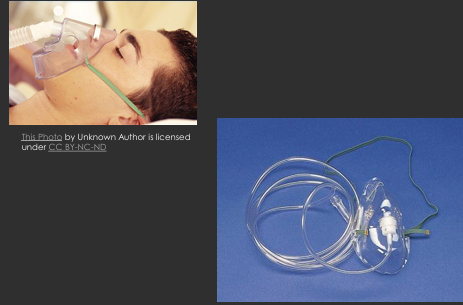
Simple face mask
medium to high flow oxygen
6-10L/min or 40-60% fio2, never less
not for long term use, uncomfy
must remove for eating
best used post surgery/recovery
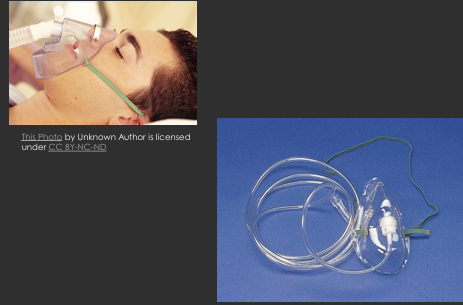
administration guidelines for simple mask
ensure mask is tight fitting
place mask over pts nose, mouth, and chin, then mold metal to bridge of nose
minimum flow rate is 5L or co2 will build up
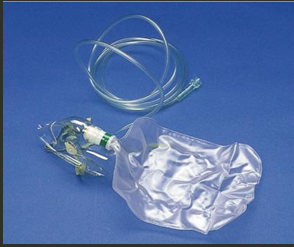
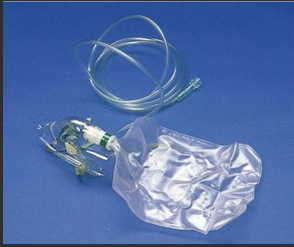
Mask with reservoir bag
higher flow oxygen flow, 10-15LPM
bag must be inflated 2/3rds during inspiration
best for emergencies
Do you always need an order for oxygen?
yes but if o2 sat is less than or equal to 90% or if no pulse oximeter available and pt has signs of hypoxia, you are allowed but must require to contact provider for an order
Oxygen orders examples
Darth Vader
ULI# 123456789
DOB: 01/01/50
November 17, 2025
Administer oxygen at 2L/min via nasal canula continuously
Dr. Athena Grant
DarthVader
ULI# 123456789
DOB: 01/01/50
November 17, 2025
Administer oxygen to maintain a saturation above 90% via nasal canula continuously
Dr. Athena Grant
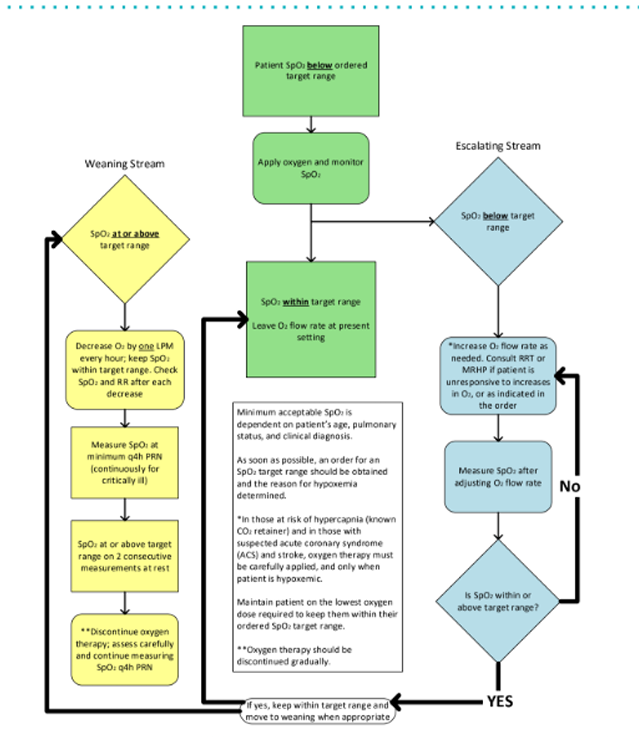
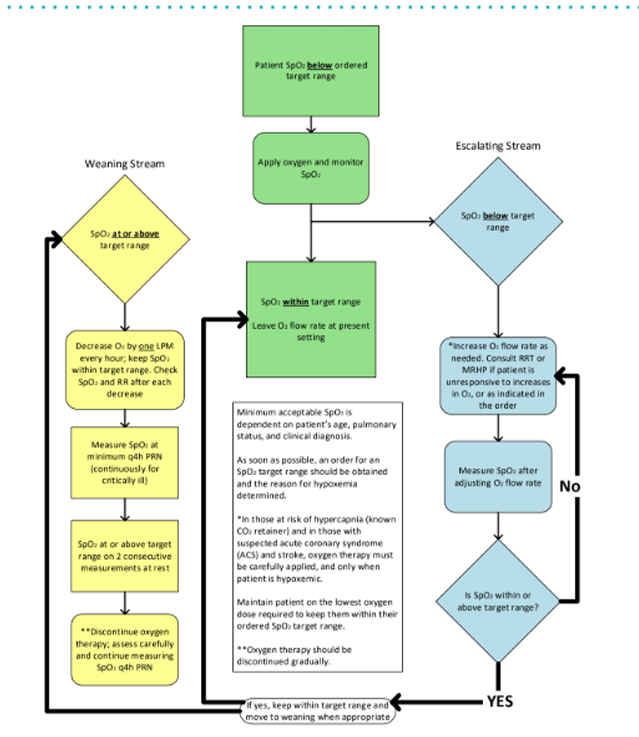
AHS oxygen therapy titration tool pic

diff oxygen devices and flow rates pic

do medication checks/rights apply to oxygen
yes, its a medication
Conditions that can lead to alterations in oxygenation
hypoxia (normal sat is ≥92%)=can occur with others on list
pneumonia
airway obstruction (complete or partial)
COPD
asthma
Oxygen Toxicity def/cause
when too high a concentration of oxygen (> 50-60%) is administered for an extended period (longer than 24 hours)
causes an overproduction of free radicals, if not tx, free radicals can damage/kill cells
s&s of oxygen toxicity
substernal pain
paresthesia
dyspnea
restlessness
fatigue
malaise
progressive respiratory difficulty
refractory hypoxia
atelectasis
infiltrates
strategies for Prevention of Oxygen Toxicity
lowest amount of oxygen is used to obtain the necessary PaO2 level
if possible decrease or monitor the amount of time on higher oxygen levels
tx the underlying cause or why the o2 is needed
monitor often for s&s and report immediately
Safety reminders in Oxygen Therapy
oxygen is highly combustible
inform everyone that oxygen is in the area ex verbal reminder, put signage in room, no smoking
remove items that cause spark
o2 tank should be stored upright and secured with a chain or in a holder
ensure all electrical equipment is functioning or correctly grounded
ensure you are up to date on fire safety and procedures
pt/family education on o2 safety
ensure adequate portable oxygen supply should pt leave the unit
comfort and hygiene measures related to oxygen therapy
assess for areas of redness, dryness and skin breakdown (where equipment is in contact with skin) every 4 hrs
use water based nasal ointment
cleanse the skin that is contact with any oxygen equipment
good care of the nares, lips and oral mucosa
list Interventions to promote airway clearance
positioning=pt upright, semi/high fowler
deep breathing & coughing=opens up alveoli, increased gas exchange
incentive spirometer
hydration
chest physio
postural drainage
diff types of Deep Breathing & Coughing
diaphragmatic breathing=strengthens diaphragm
pursed lip breathing=prolongs exhalation stage, prevents airway collapse, increases airway pressure during expiration=reduces amount of air trapped
huff coughing=lean forward cough twice, huff on exhale, forces air out and increases airway expansion
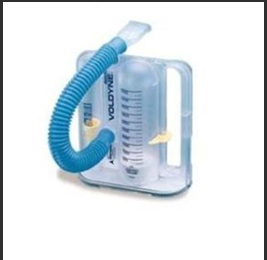
Incentive spirometer
for post op pts
increases pt intake of air, needs pt teaching
suck in mouthpiece
flow oriented has >1 ball, keep balls up long as possible
helps gas exchange, loosens excretions
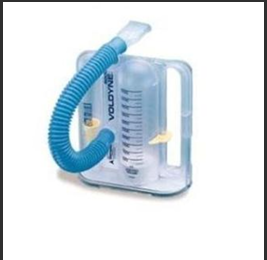
how often should a pt use an incentive spirometer
4 times every hr, taking 10 breaths each time
practice coughing after
why is hydration important
as a person becomes dehydrated, their airway secretions become thicker
thicker=harder to breathe
use a humidifier in room
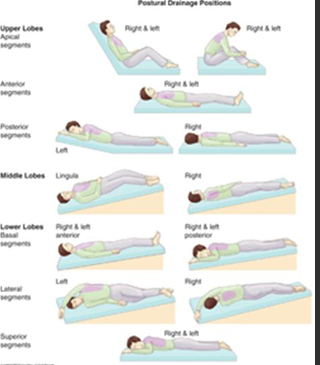
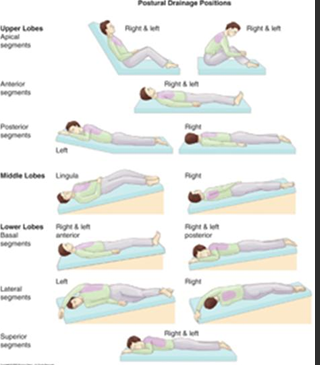
Chest Physiotherapy (changing of positions) & Postural Drainage techniques
helps clear secretions
percussion=pt must breath slow/deeply, uses fists
vibration=done when pt exhales through pursed lips, used instead of percussion if in pain
Oropharyngeal & Nasopharyngeal Suctioning
clears the oral airway of secretions
prevents pooling of secretions
never longer than 10-15s
uses negative pressure
for when yankauer device ineffective
apply pulse oximeter throughout
Discharge education for pts
be aware of hydration status and diet
use of water soluble nasal sprays, balms and moisturizers
cautious if smoking or around those who are smoking
potential complications such as pneumonia
If Mr. Vader is breathing room air, the Fi02 (% of inspired air) that he is breathing is which of the following?
21%
what if a pt has pneumonia with thick secretions and coughing
humidification of oxygen is recommended to loosen secretions
what factors determine if pt needs oxygen therapy
need
o2 sat levels
doctor/resp therapist recommendations
hypoxemia
emphysema def
condition where alveoli become abnormally enlarged and destroyed over time
condition of COPD with chronic bronchitis
how should we administer o2 to pt with COPD
titrate o2 to lowest effective dose according to o2 sat levels
continually assess pt
what positions are best during postural drainage for specific lobes
secretions=upright
lower/middle lob bronchi=head down position
upper lobe bronchi=head up position
does suctioning require gloves
yes
how often do we check the nasal cannlua/oxygen device
every 8 hrs, keep the humidification container filled at all times
what do we do before administering any oxygen
check dosing etc and resp assessment on pt
if at oxygen flow rate at 4L/min or longer/higher, what do you do
add humidification
do we check the oxygen level in the portable cylinder before you ambulate or transport a patient
yes
what diff techniques can you use to collect a sputum sample
expectoration or by suctioning (in nose, suction valve off, 2-10ml)
do not use mouthwash or toothpaste before
take deep breaths before coughing into cup (5-10ml)