Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors: Biology Study Terms & Definitions
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
name the types of odontogenic tumors that have an odontogenic epithelial origin:
1. ameloblastoma
2. adenomatoid odontogenic tumor
3. calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor
4. squamous odontogenic tumor
5. clear cell odontogenic carcinoma
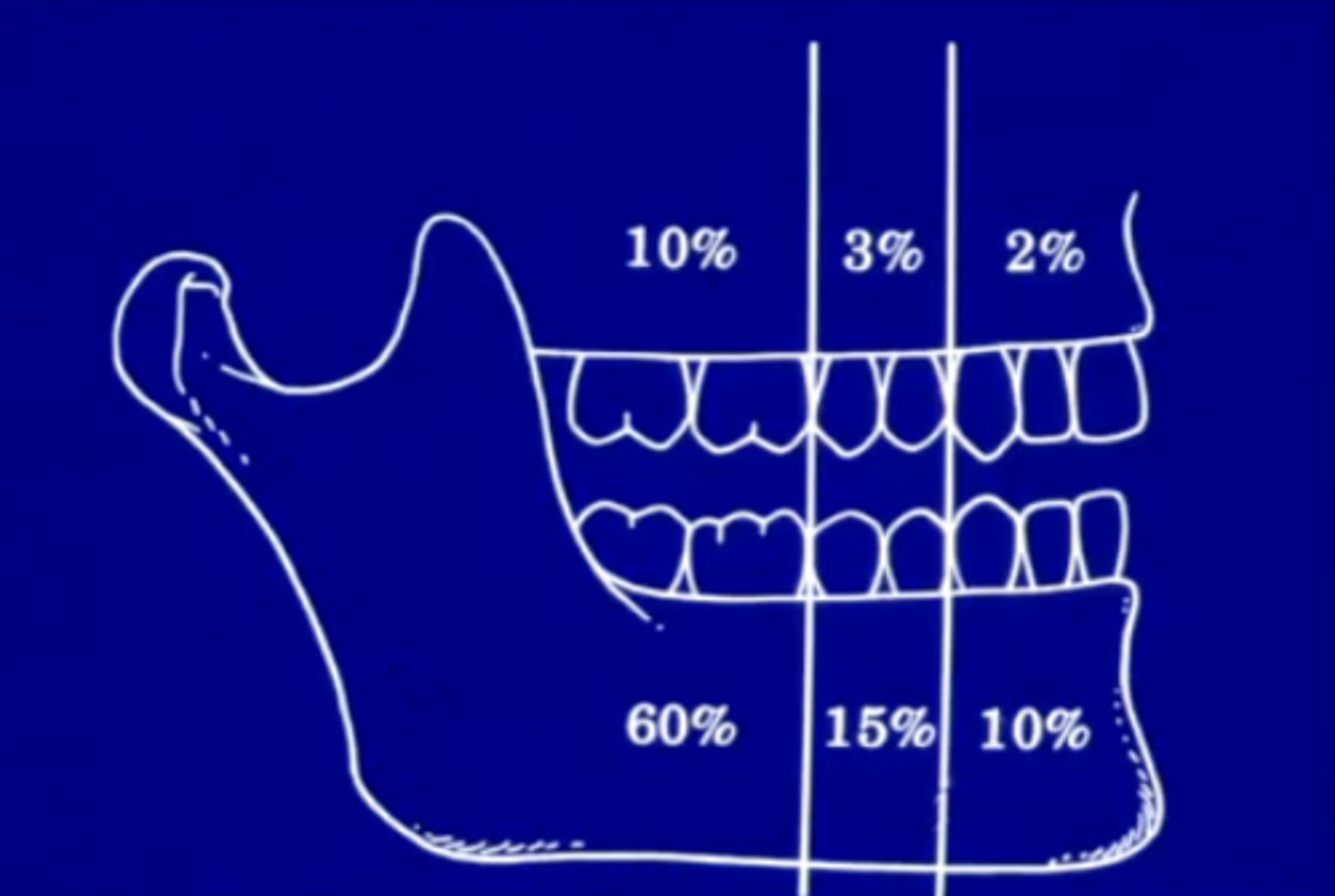
where do most conventional solid ameloblastoma's form?
posterior mandible
~85 occur in the mandible in general
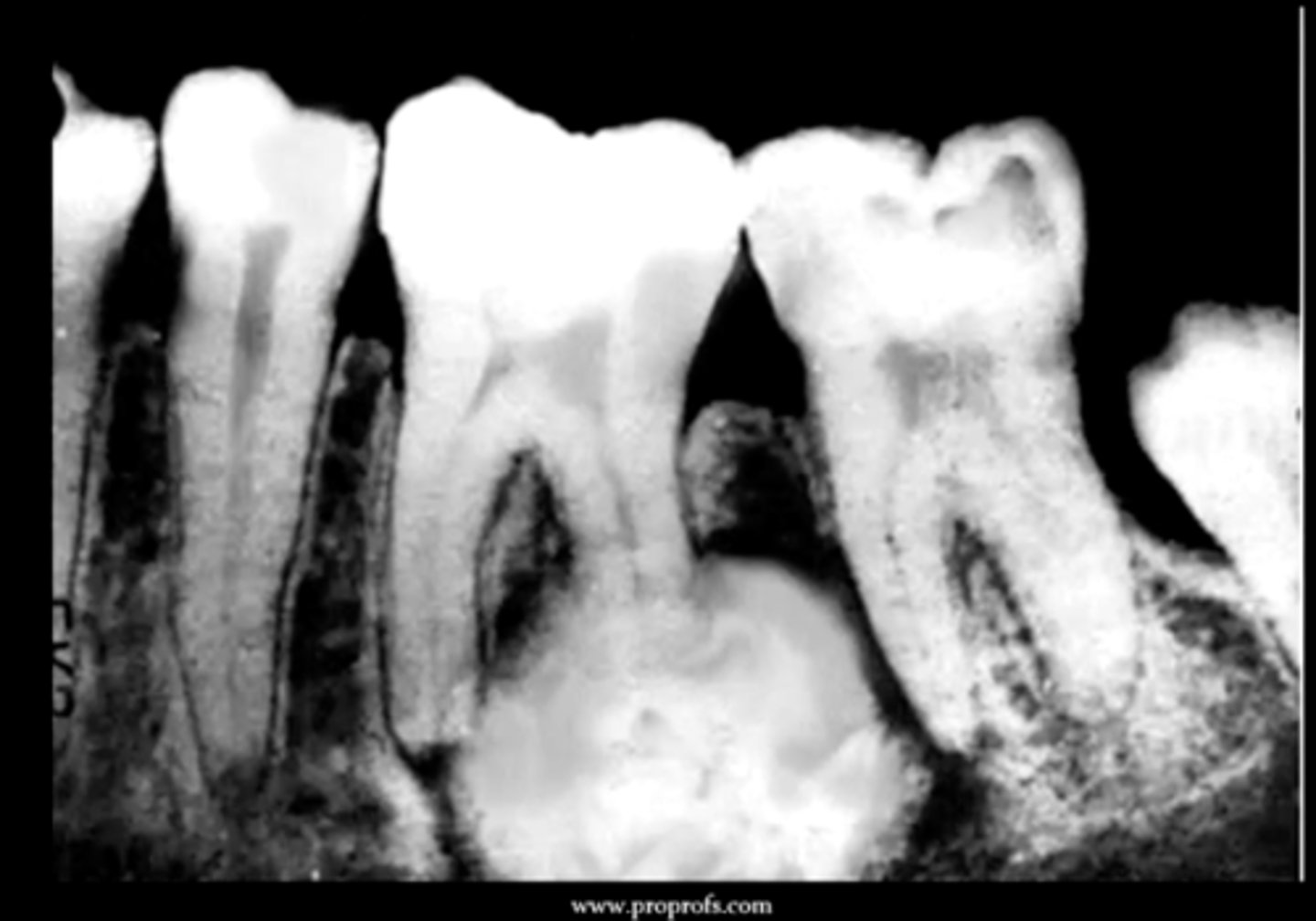
how does conventional solid ameloblastoma present symptomatically?
may be asymptomatic or present as a painless swelling
this is why people often do not go get it checked because there is no pain
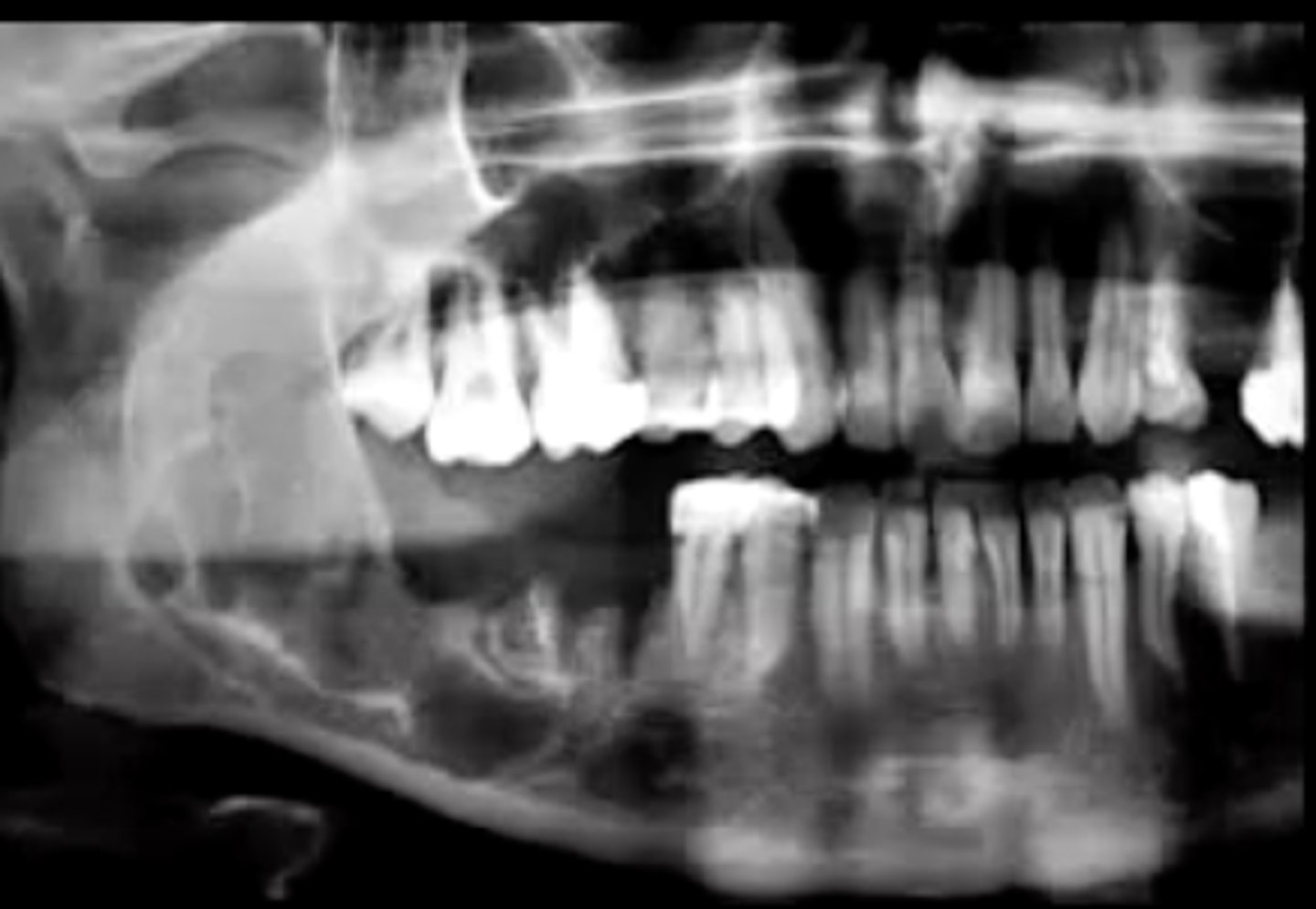
how does conventional solid ameloblastoma present radiographically?
multilocular radiolucent lesion
"soap bubble" or "honey combed"
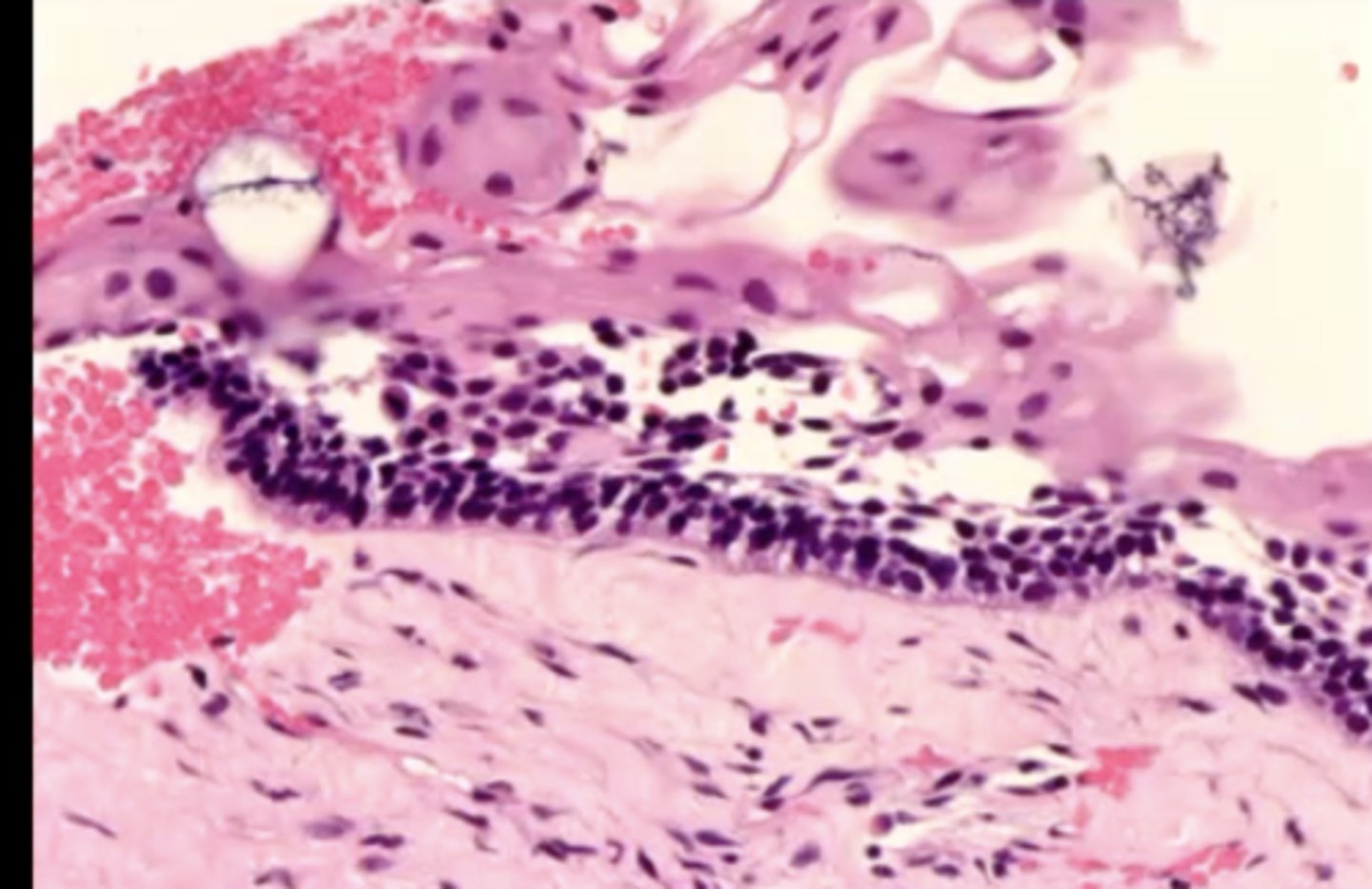
what are the 3 histological criteria for diagnosis of conventional solid ameloblastoma?
1. stellate reticulum
2. columnar ameloblasts with polarized nuclei toward stellate reticulum
3. apical clearing of cytoplasm
what is tx and prognosis for conventional solid ameloblastoma?
wide excision (1 cm margins) with a fair to good prognosis
how does unicystic ameloblastoma present radiographically?
unilocular radiolucency that often appears around 3rd molars
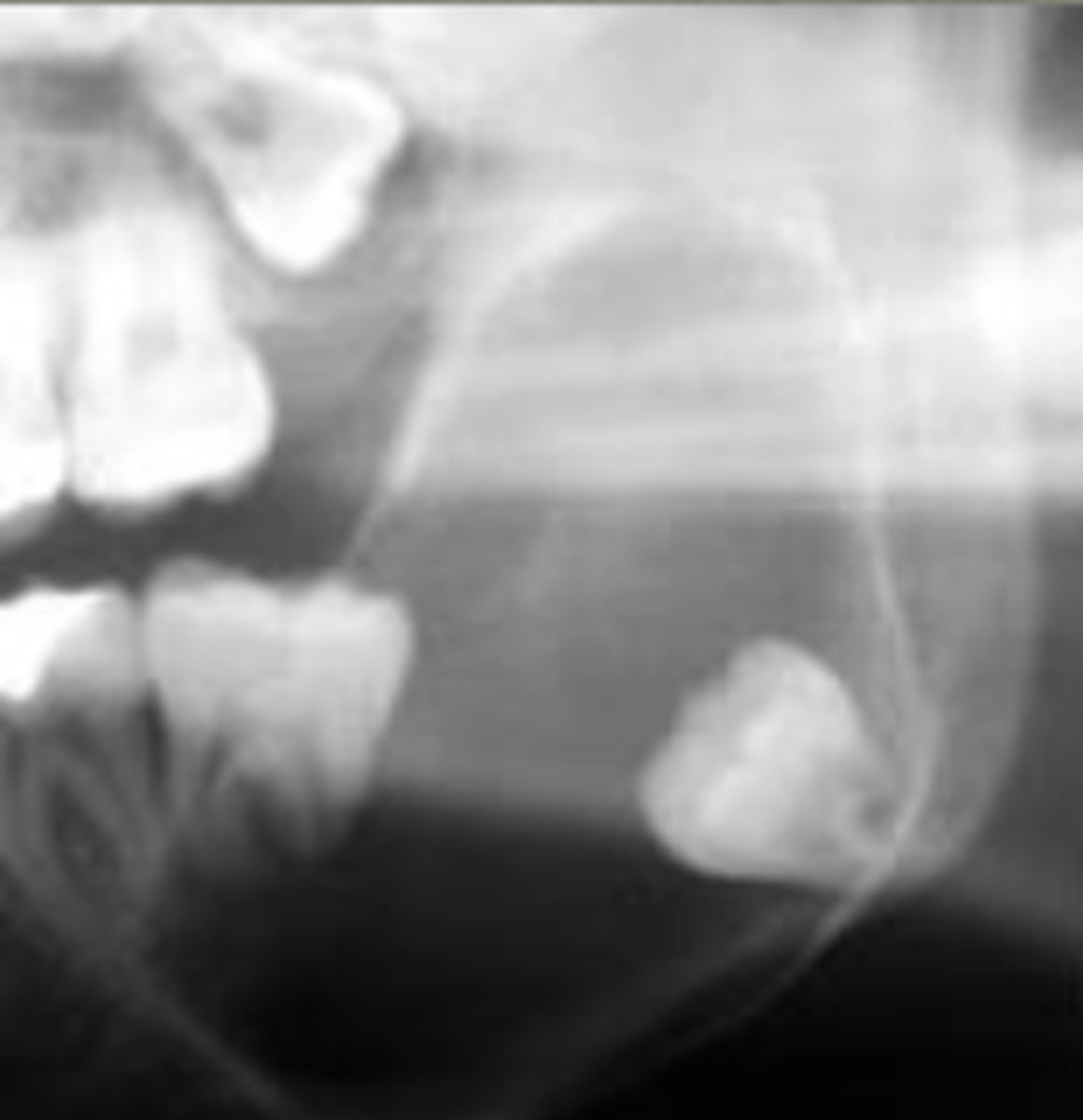
are ameloblastomas more commonly benign or malignant?
benign
the 2 malignant types are malignant ameloblastoma or ameloblastic carcinoma
how does an adenomatoid odontogenic tumor present symptomatically?
asymptomatic or painless
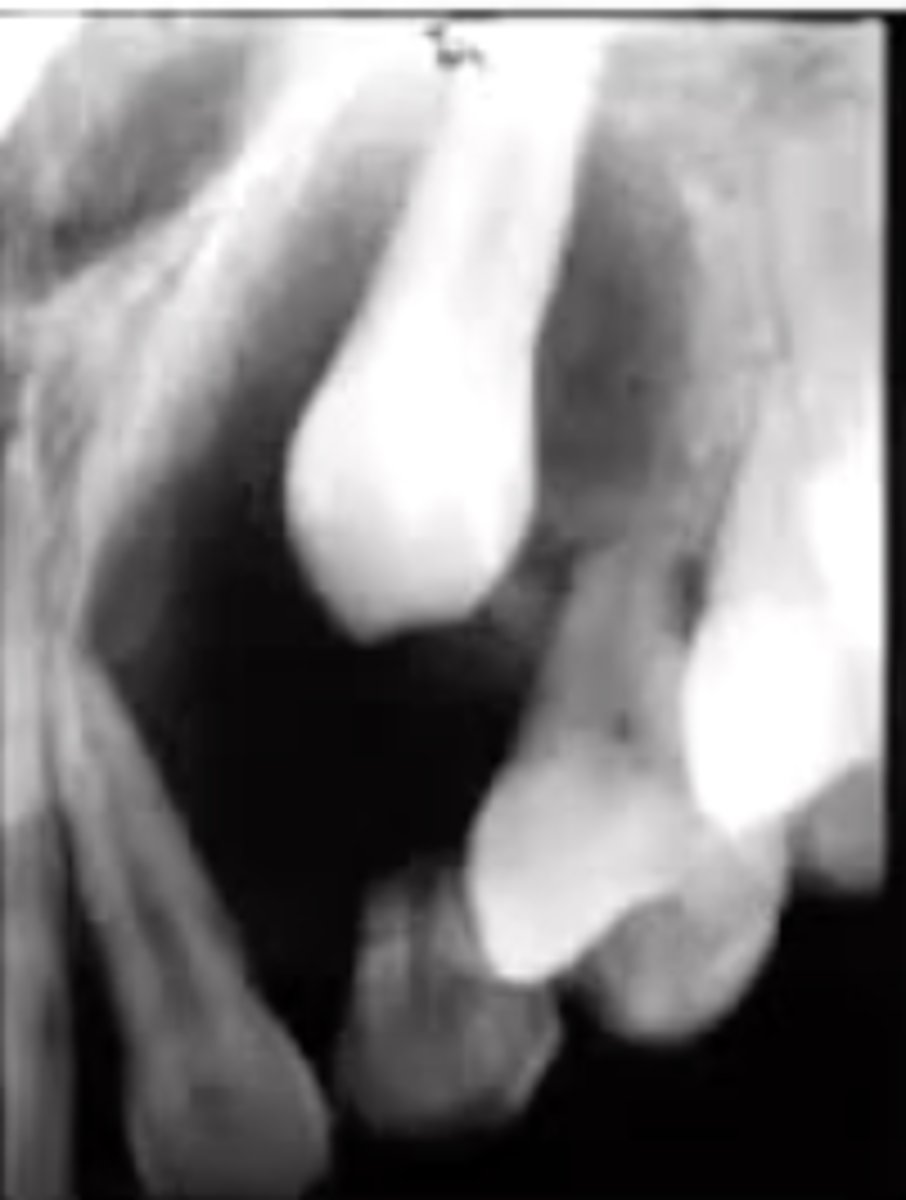
how does an adenomatoid odontogenic tumor present radiographically?
radiolucency around the crown of an unerupted tooth that may contain calcifications
this is usually in the anterior maxilla (canines)
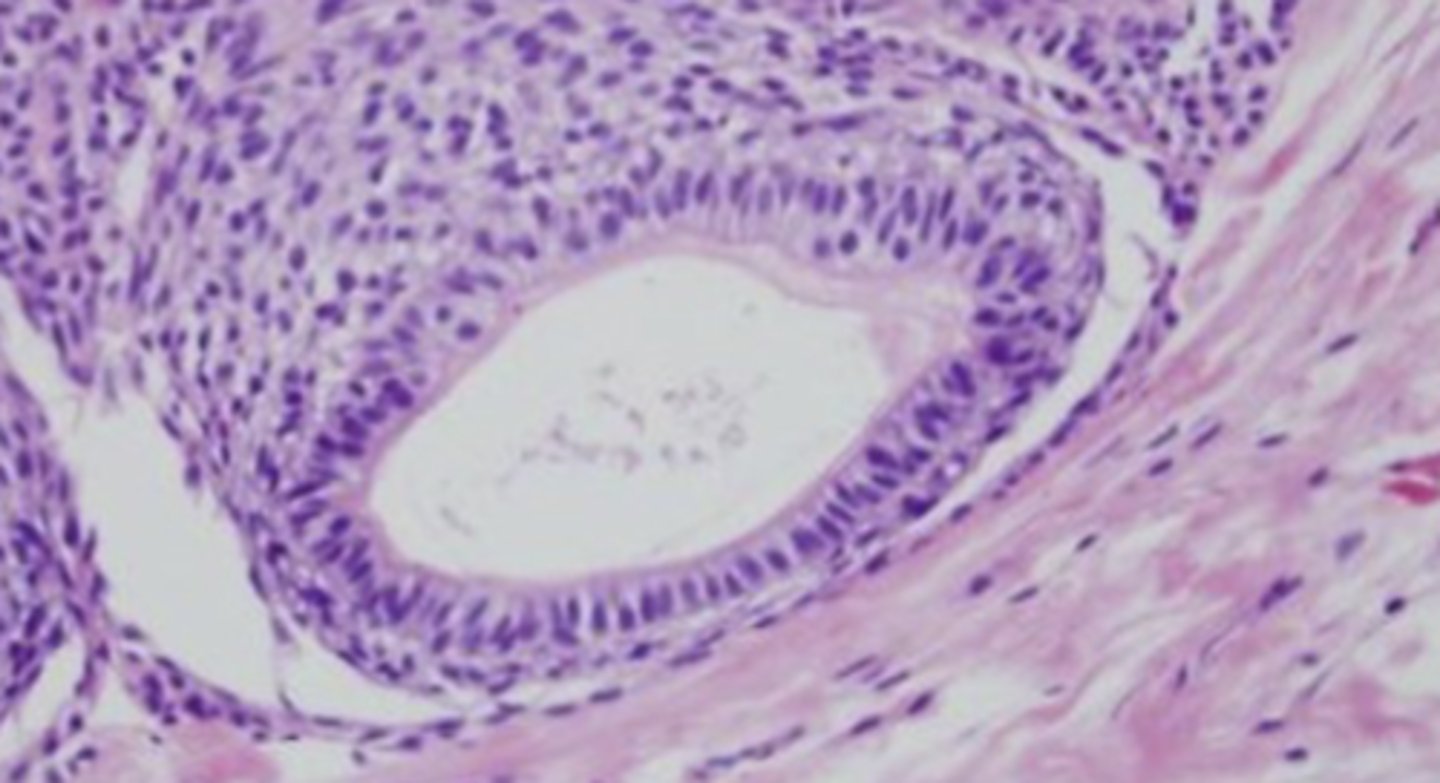
describe the histology of adenomatoid odontogenic tumor:
duct-like structures with nuclei polarized away from lumen
filled with amyloid and may have calcifications
where are most odontogenic tumors found?
posterior mandible
the only exception to this is AOT (adenomatoid odontogenic tumor), which is anterior maxilla
how does a calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor present radiographically?
variable presentation, but is associated with a "driven-snow" appearance
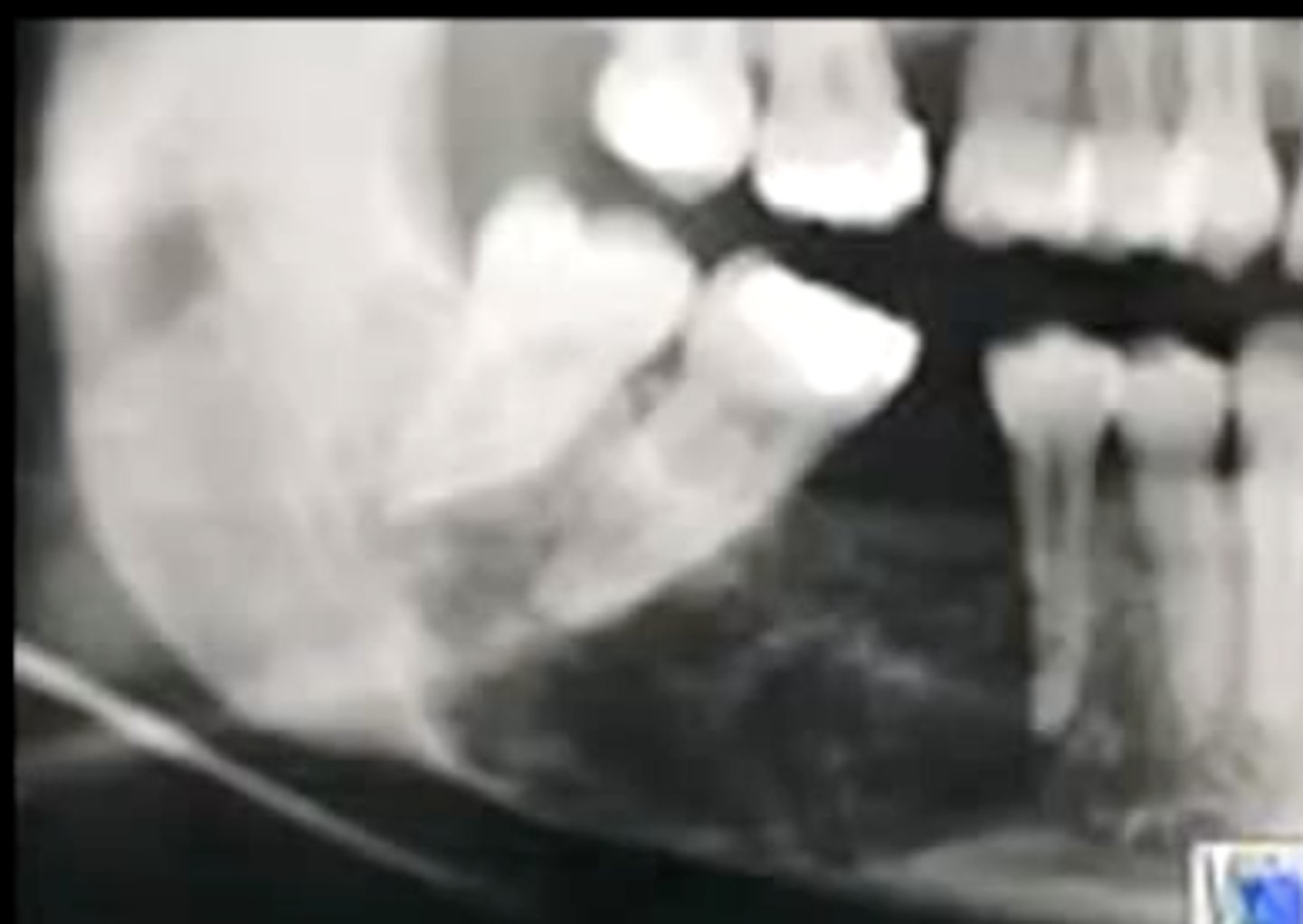
what is another name for a calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor?
Pindborg tumor
describe the histology of a calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor:
variable presentation, but there are Liesegang ring calcifications and amyloid
prob will be on exam
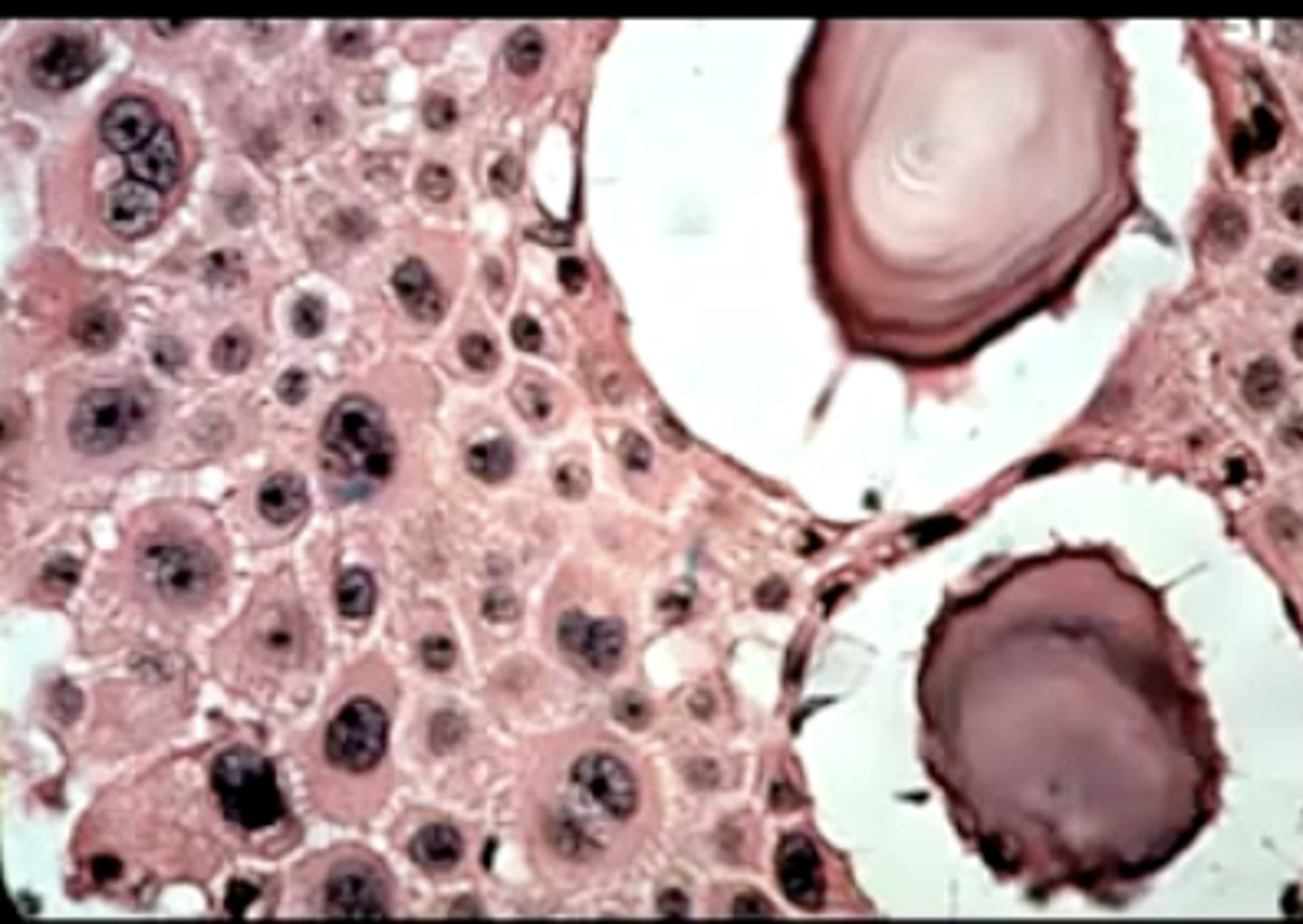
what type of stain is used to identify a Pindborg tumor (calcifying epithelial odontogenic tumor)?
Congo red stain
where does a squamous odontogenic tumor originate?
within the PDL (epithelial rests of Malassez)
the patient often presents with mobility of the tooth
how does a squamous odontogenic tumor present radiographically?
triangular/semicircular radiolucency on lateral and cervical portion of the root
may resemble vertical bone loss
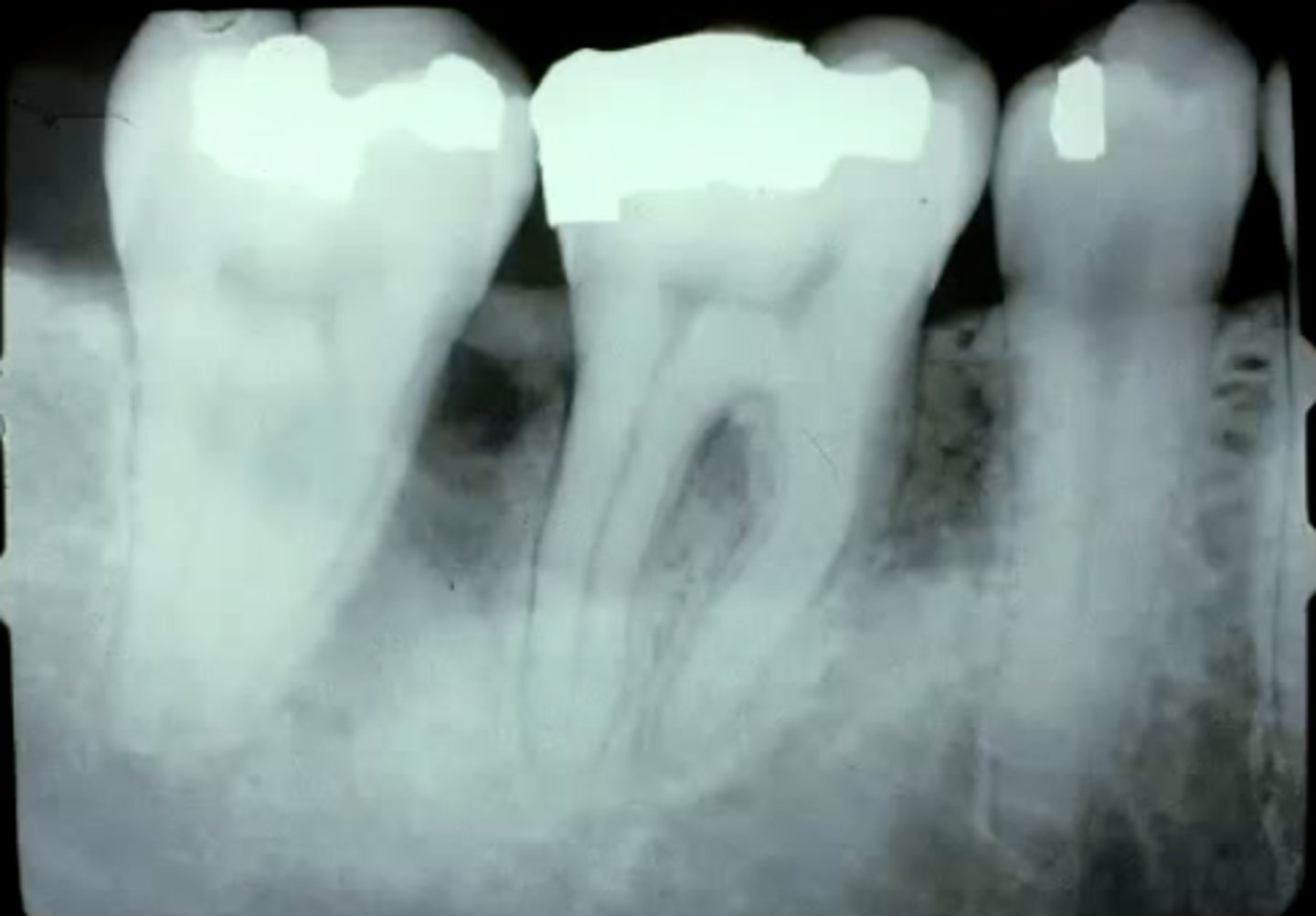
describe the histology of a squamous odontogenic tumor:
islands of bland squamous epithelium, no amyloid, no polarized nuclei
think of this one as being boring
why in the past has an adenomatoid odontogenic tumor been called adenoameloblastoma?
it looks glandular/duct like with a polarized epithelium
remember they are polarized away from the center
name the types of odontogenic tumors that have an mixed epithelial and ectomesenchymal origin:
1. odontoma
2. ameloblastic fibroma
3. ameloblastic fibro-odontoma
4. ameloblastic fibrosarcoma
5. odontoameloblastoma
what is the most common odontogenic tumor?
odontoma
this usually happens in a younger population
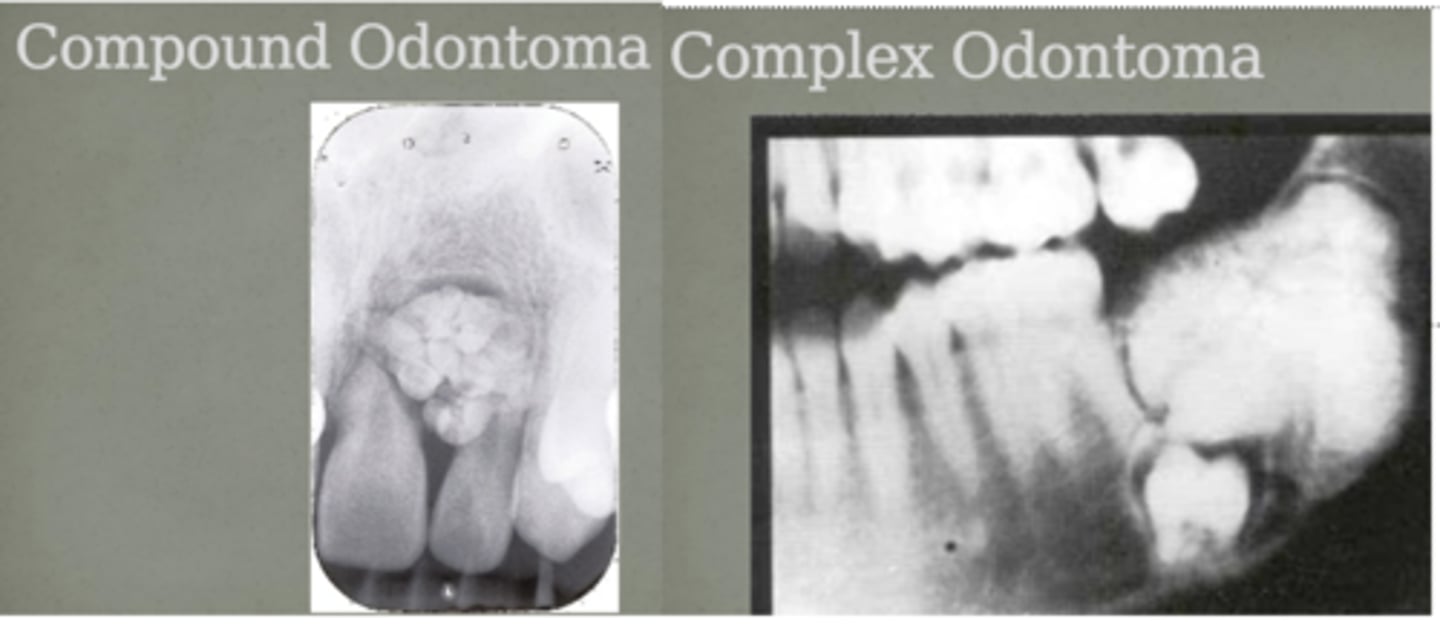
list the main differences between a compound and complex odontoma:
compound: appear as multiple little "toothlets" that often occur in the anterior maxilla
complex: appear as haphazard deposition of enamel and dentin that often occur in the posterior mandible
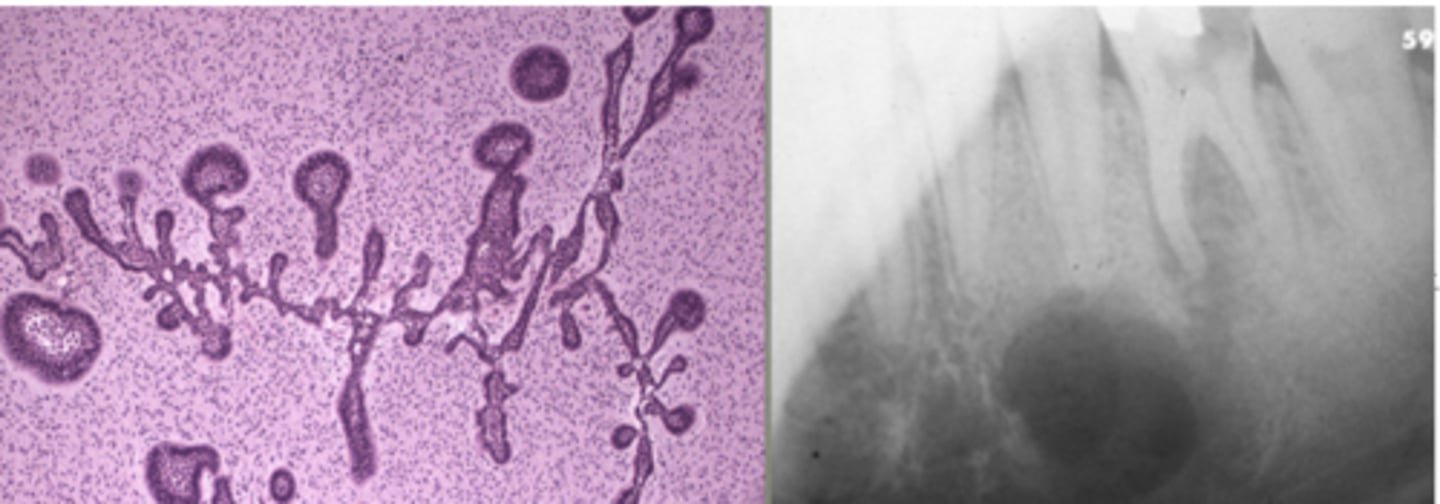
describe how an ameloblastic fibroma presents:
painless swelling, circumscribed radiolucency, and a pulp-like stroma with islands of ameloblastic epithelium
45% of them are recurrent, so important to excise well
describe how an ameloblastic fibro-odontoma presents:
combination of ameloblastic fibroma and odontoma, presents as a circumscribed radiolucency that contains "spiky" radiopacities
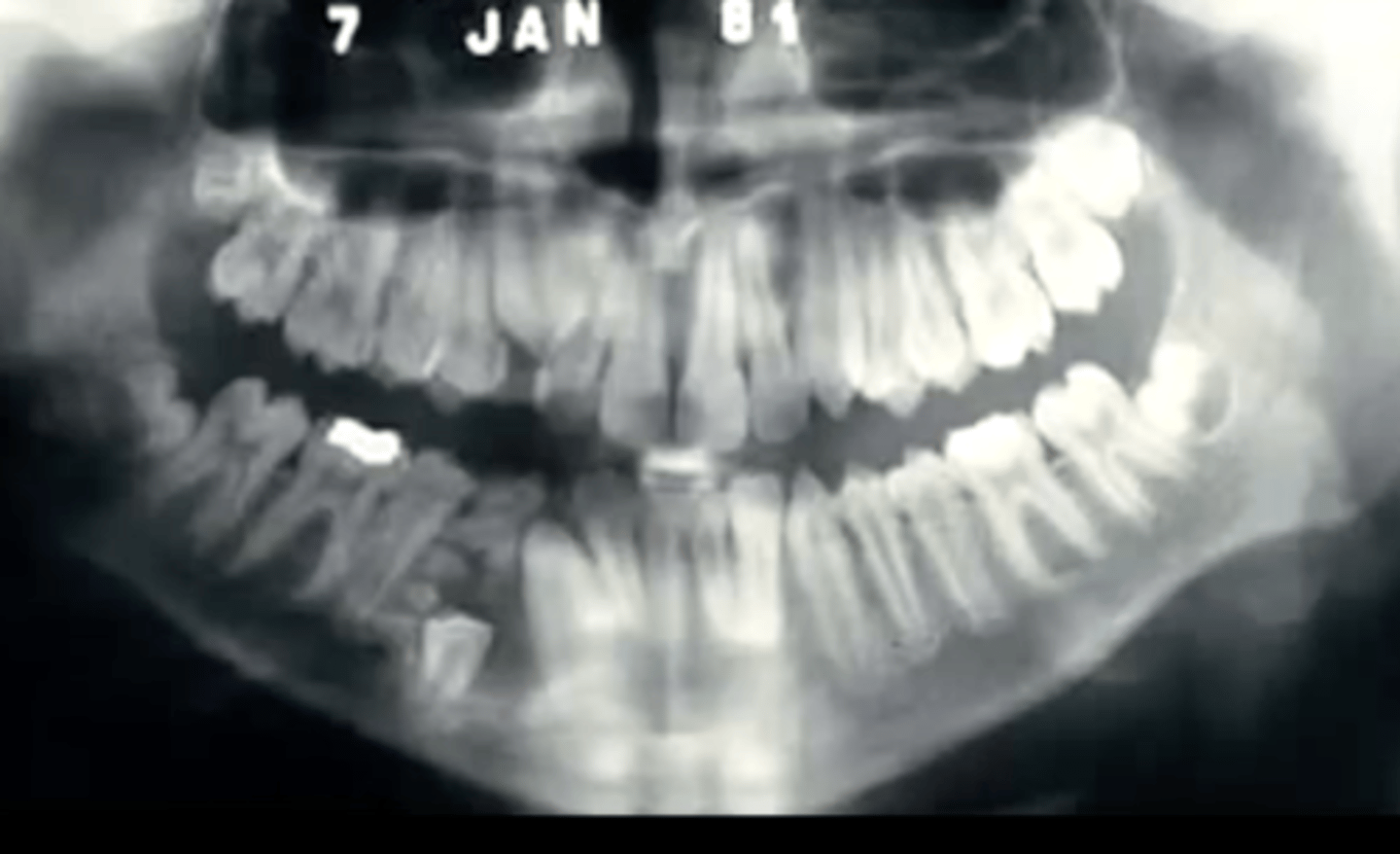
can ameloblastic fibromas transform into a malignancy?
yes, they can transform into ameloblastic fibrosarcoma
name the types of odontogenic tumors that have an ectomesenchymal origin:
1. central odontogenic fibroma
2. peripheral odontogenic fibroma
3. granular cell odontogenic tumor
4. odontogenic myxoma
5. cementoblastoma
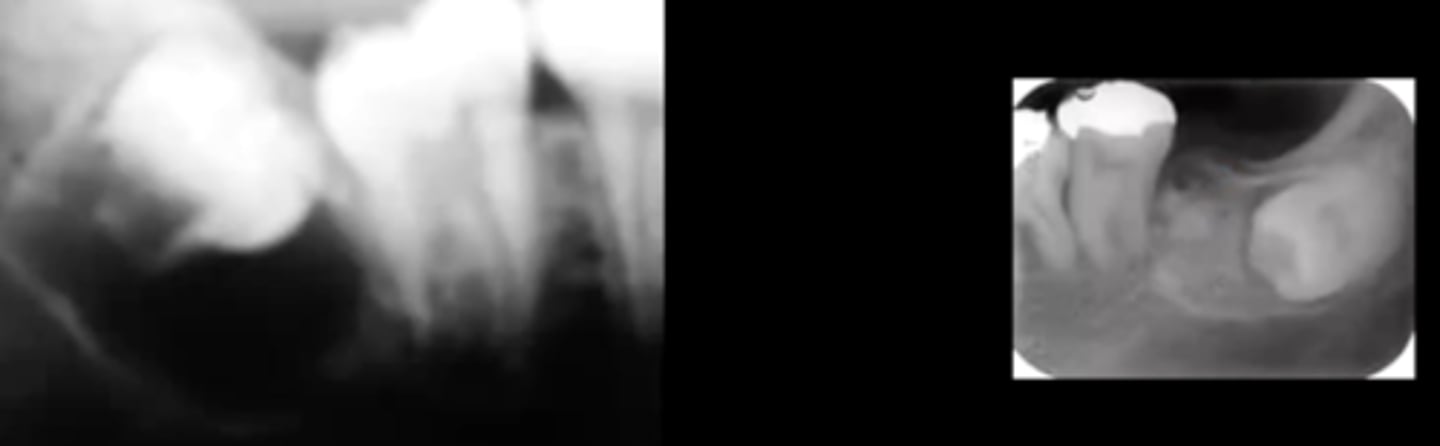
how do central odontogenic fibromas present?
they are fibrous tumors with benign bone in it
radiographically present as either a RL or RO circumscribed lesion
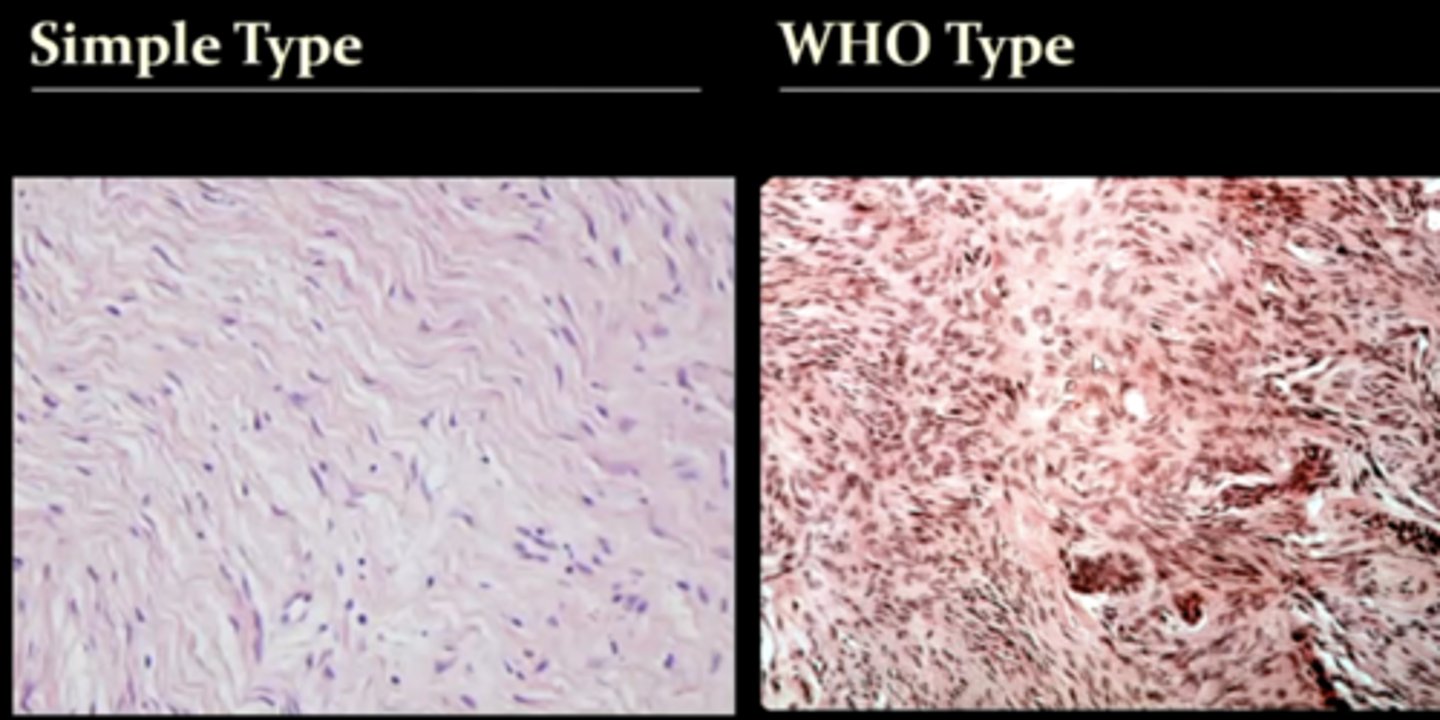
what are the 2 types of odontogenic fibromas?
1. simple type
2. WHO type
know that the WHO type has more calcifications in it
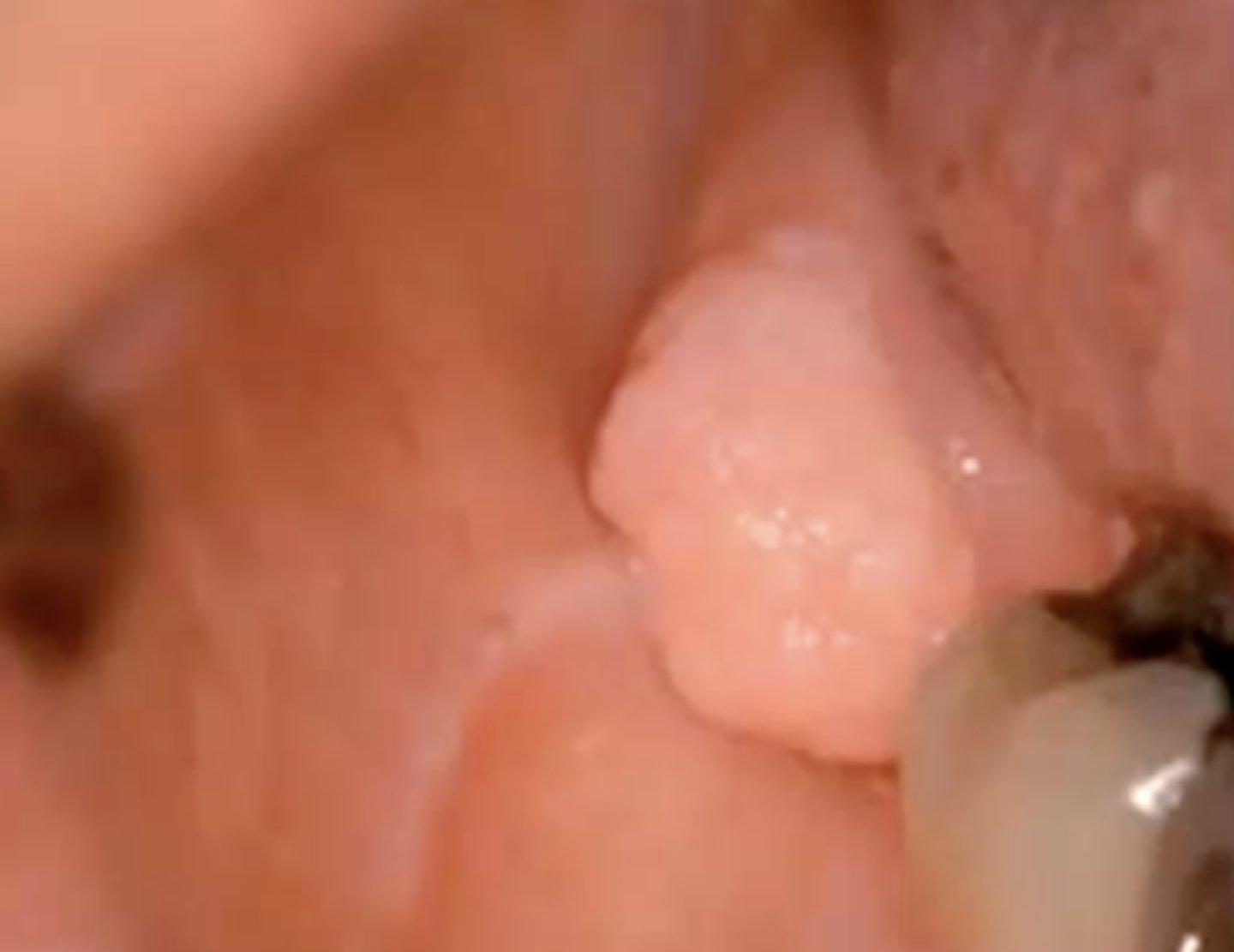
how does a peripheral odontogenic fibroma present?
a soft tissue counterpart of a central odontogenic fibroma
describe the histology of a granular cell odontogenic tumor:
islands of odontogenic epithelium that are scattered among granular cells
these are rare
how does an odontogenic myxoma present radiographically?
appears as a shadow in a radiograph due to slimy substance, but has a "stepladder" pattern
this means that it contains wispy trabeculae at right angles to each other
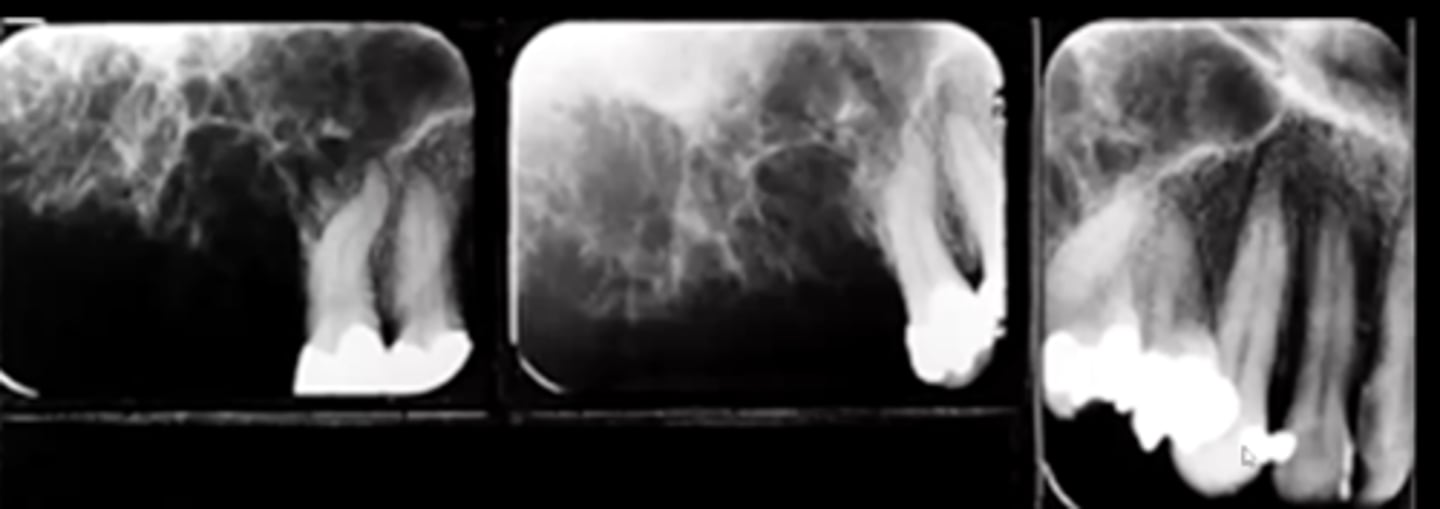
how does a cementoblastoma present radiographically and histologically?
a large ball of cementum at the end of the root that presents as a round radiopacity with a RL border/rim
histologically, it basically presents as cementum