Biochemistry Review
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards on Biochemistry and the properties of water.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Biochemistry
Explains life in terms of atomic structures of biological molecules and the chemical changes they undergo when they interact with other biological and non-biological molecules.
Non-polar molecules
Molecules with predominantly C-H and C-C bonds (e.g. Saturated hydrocarbons) that tend to be non-reactive.
Polar functional groups
Give biological molecules their structural and functional properties.
includes: carboxyl, carbonyl, alcohol, amino, thiol/sulfhydryl, phosphate/phosphoryl
Electronegativity
A measure of the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself.
Biomolecule reactivity
Found in functional groups that have polar bonds.
Water properties
Explained by its structure and the ability of the O to form additional bonds with H2O and other molecules.
Hydrogen bond
An electrostatic attraction between polarized molecules containing O-H, N-H, or F-H.
Hydrogen-bonded matrix in water
Gives rise to its high melting and boiling points relative to its low molecular weight.
Water exists as
A Hydrogen-bonded network with an average of 4 H-bonds per molecule in ice and 3.4 in liquid.
H-bonds strength
Strongest when linear i.e. the two heavy atoms and the shared H are in a line.
Weak Interaction
H-bonding (free energy = 8-21 kJ/mol) as compared to covalent bonding.
These are stable, but since they’re weak, they’re able to move
Breaking H-bonds
Requires the addition of enthalpy.
Gibbs free energy equation
G = H - T S
Hydrophilic molecules
Water will dissolve polar and charged molecules.
Electrostatic Interactions
Attraction between oppositely charged ions: free energy up to 50 kJ /mol
Salts such as sodium chloride (NaCl)
Easily solubilized because water hydrates and stabilizes Na+ and Cl+ ions via Electrostatic interactions.
van der Waals Interaction
A short range, very weak attraction, free energy ~ 4 kJ / mol.
Hydrophobic Effect
The entropy of water is reduced, disfavouring dissolution of hydrocarbons in water.
Amphipathic molecules
Contain both polar and non-polar groups. E.g. detergents, lipids, proteins.
Detergent micelle
Hydrocarbons interact with each other via vdW forces to form a hydrophobic core, while the hydrophilic groups associate with water.
Micelles of fatty acids
Form with a hydrophobic core and hydrophilic exterior.
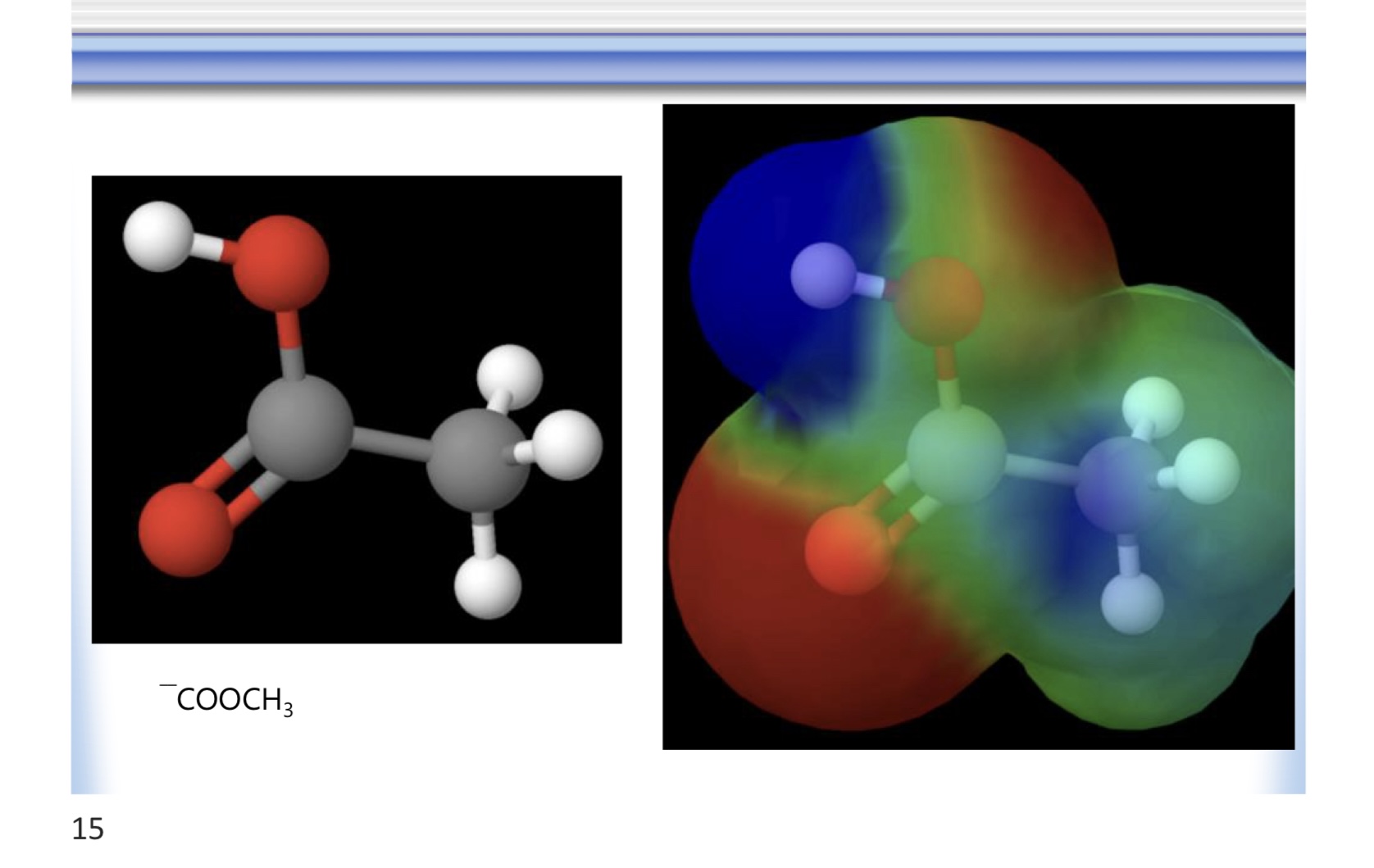
carboxyl
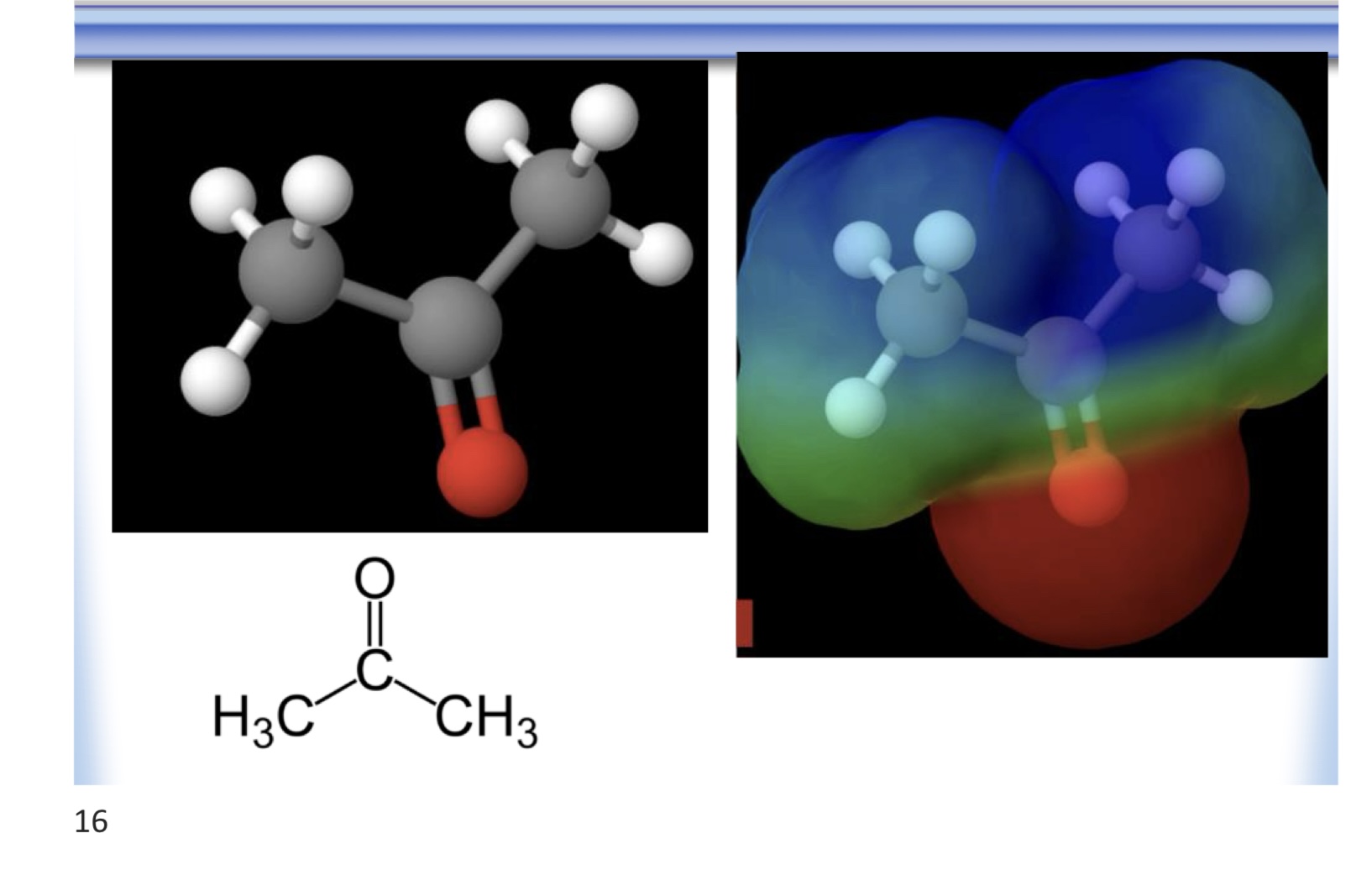
carbonyl
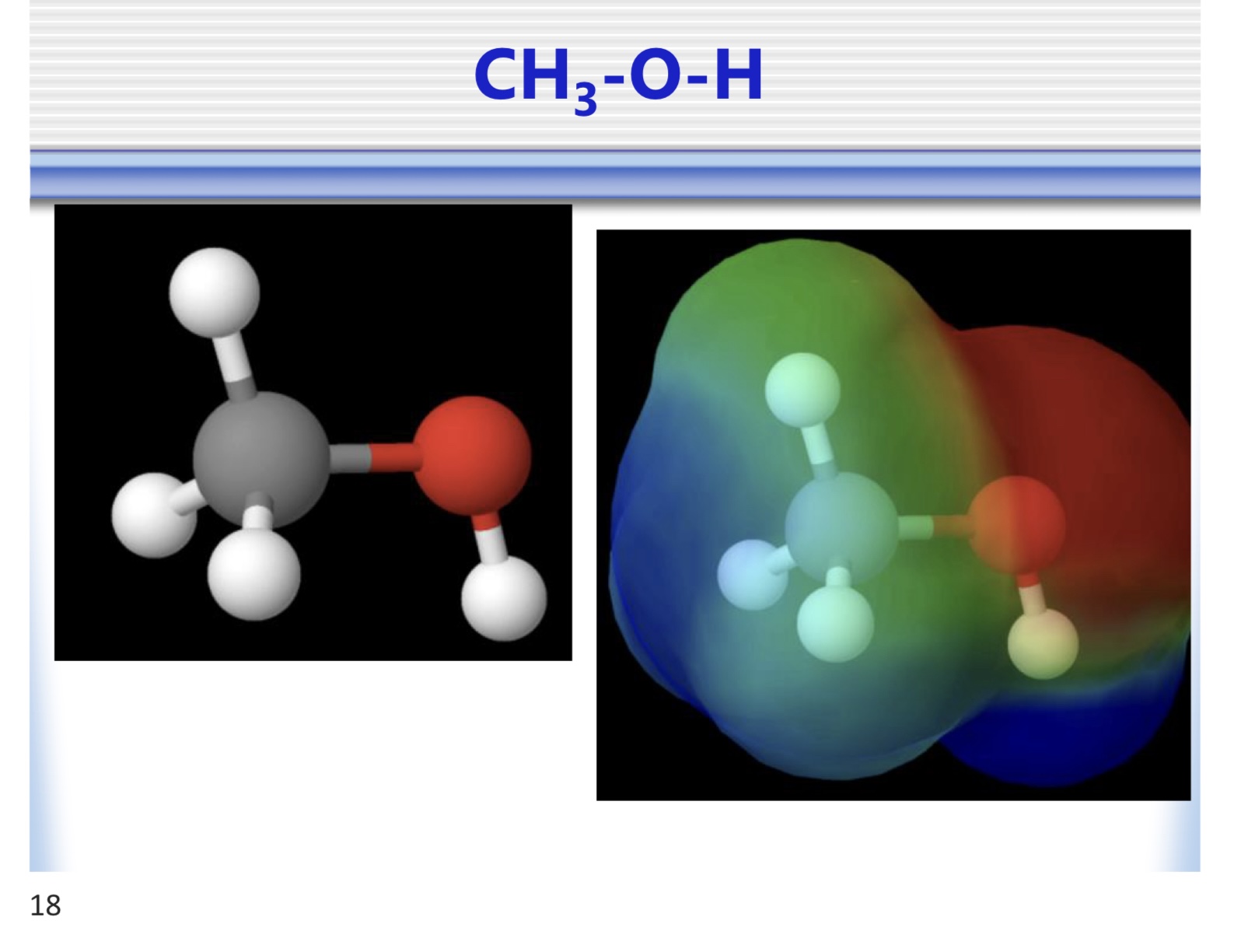
alcohol