12 - intro to mood disorders
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
A childhood condition of extreme irritability, anger, and frequent temper outbursts.
What is Disruptive Mood Dysregulation (DMDD)?
▶ Begins before age 10
▶ not diagnosed in children under 6 or adolescents over 18.
At what age does Disruptive Mood Dysregulation (DMDD) begin and when is it not diagnosed?
Child should be irritable and angry daily for 12 months
must not meet criteria for manic/hypomanic or oppositional deviant disorder.
What are the criteria for diagnosing Disruptive Mood Dysregulation DMDD (Duration + differential diagnosis)?
Also called clinical depression
it is a mental health condition that significantly affects daily functioning, including work, school, and social relationships.
What is Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)?
Clinical judgment
Patient history
Cultural norms
What factors are considered when diagnosing MDD?
a mood disorder
that causes a persistent feeling of sadness
and loss of interest in normal activities.
What is depression?
Symptoms occur most of the day, nearly every day
How often do depression symptoms occur during episodes?
Feelings of sadness
angry outbursts, irritability or frustration
loss of interest or pleasure in normal activities like sex, hobbies, or sports.
Sleep disturbances, including insomnia or sleeping too much
Tiredness and lack of energy, so even small tasks take extra effort
Reduced appetite and weight loss or increased cravings for food
and weight gain
Anxiety, agitation or restlessness
Slowed thinking, speaking or body movement
Feelings of worthlessness or guilt, fixating on past failures or self-
blame
Trouble thinking, concentrating, making decisions and
remembering things
Frequent or recurrent thoughts of death, suicidal thoughts
What are common symptoms of depression?
A mood disorder characterized by a depressed mood
lasting ≥2 years
(≥1 year in youth).
What is Persistent Depressive Disorder (PDD / Dysthymia)?
Yes, MDD may occur during these 2 years; previously this was not allowed.
Can Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) occur during PDD?
At least 5 symptoms must appear before menses.
At least one (≥1 of 4) symptom must be one of the four core emotional symptoms
mood lability
irritability
depression
anxiety
How many symptoms are required to diagnose premenstrual dysmorphic disorder PMDD?
Fatigue
sleep or appetite changes
poor concentration
physical symptoms (bloating, breast tenderness, headache).
What additional symptoms may occur in premenstrual dysmorphic disorder PMDD?
They must cause significant distress or impairment
What level of impact must premenstrual dysmorphic disorder PMDD symptoms cause to be considered a disorder?
after menses beginS
When do premenstrual dysmorphic disorder PMDD symptoms resolve?
substance/medication induced depression disorder (S/MIDD): هو اكتئاب ناتج بسبب مواد او مخدر زي مثلا ادوية الاكتئاب
Depressive Disorder Due to Another Medical Condition: اكتئاب ناتج مباشرة عن حالة طبية أخرى (مثل حالات عصبية أو غددية)
What is the difference between substance/medication induced depression disorder (S/MIDD) & Depressive Disorder Due to Another Medical Condition ?
elevated, expansive, or irritable mood was removed.
What was removed from the criteria of Substance/Medication-Induced Depressive Disorder?
other specified depressive disorder: A depressive presentation that does not meet full criteria but the clinician specifies the reason.
unspecified depressive disorder: When there is insufficient information to make a specific diagnosis.
What is the difference between other specified depressive disorder and unspecified depressive disorder?
▶ 5-7%
▶ 2:1
What is the prevalence rate of depression? + What is the female-to-male ratio in depression?
53
How much does depression cost per year in the US?
most costly disorders
How is depression ranked in cost globally in developed countries?

What are the groups of differential diagnosis of depression?
Psychodynamic model
Not strongly supported by research
Behavioral model
Modestly supported by research
Cognitive model
Has considerable research support
What are models of depres?
Depression results from changes in rewards and punishments.
▶ People who retire from work.
According to the behavioral view, what causes depression? Mention an example?
As life changes, we experience a change (loss) of rewards.
How does life changes affect rewards according to the behavioral view?
Negative thinking theory
Learned helplessness theory
What are the two main cognitive theories of depression?
Upsetting situations later in life.
What can trigger further rounds of negative thinking later in life?
▶ Maladaptive attitudes
▶ Cognitive triad
▶ Thinking errors
▶ Automatic thoughts
According to Beck, how many interrelated cognitive components of depression are there? And what are they?
Self-defeating attitudes developed during childhood.
What are maladaptive attitudes?
“My general worth is tied to every task I perform.
Give an example of a maladaptive attitude.
Individuals repeatedly interpret
(1) their experiences/world
(2) themselves
(3) their futures
▶ in negative ways leading to depression.
What is the cognitive triad?
Arbitrary inferences
minimization of the positive and magnification of the negative
overgeneralization.
What thinking errors are common in depressed people?
A steady train of unpleasant thoughts that suggest inadequacy and hopelessness.
What are automatic thoughts in depression?
When they think they no longer have control over the reinforcements in their lives and are responsible for this helpless state.
According to the learned helplessness theory, when do people become depressed?
Seligman’s work with laboratory dogs
On whose work is the learned helplessness theory based?
Even when presented with an opportunity to escape, they made no attempt to do so.
What happened to dogs subjected to uncontrollable shocks in Seligman’s experiments?
The dogs had “learned” to be “helpless,”
drawing parallels to human depression.
What did Seligman theorize about the dogs’ behavior?
▶ Human subjects undergoing helplessness training
score higher on depression scales
demonstrate passivity in laboratory trials سلوكيات سلبية
▶ animal subjects lose interest in sex and social activities
▶ uncontrollable negative events ↓ serotonin and norepinephrine levels in rats.
What research support exists for the learned helplessness model?
Pharmacological treatment
Psychotherapy (CBT) cognitive behavioral therapy
What are the main types of treatment for depression?
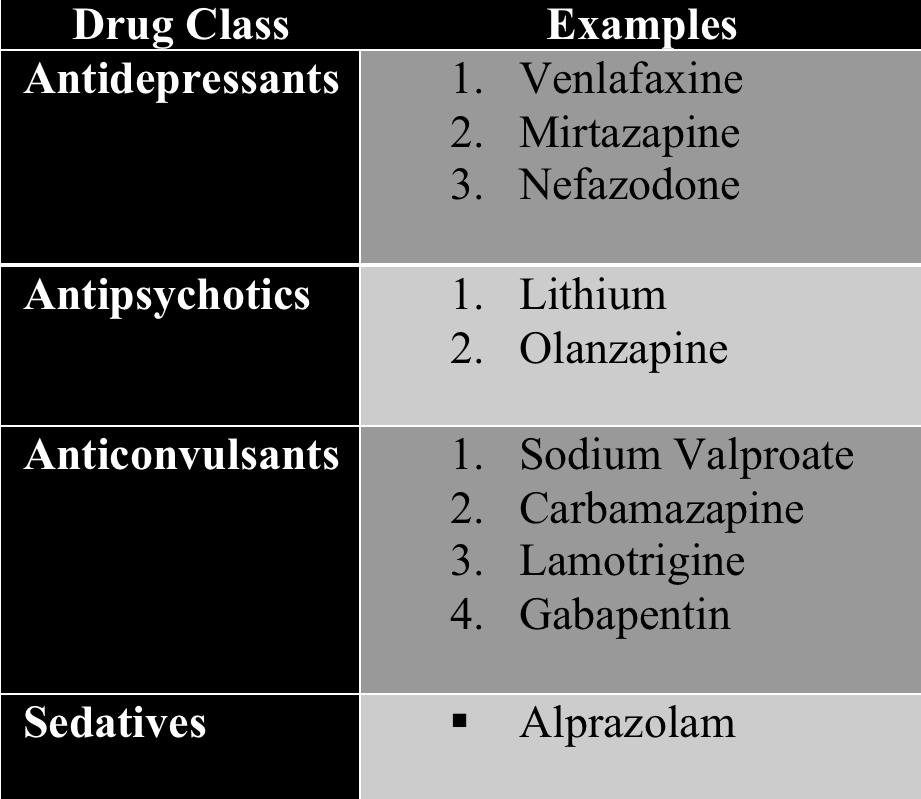
What are the main drugs therapy for depression?