2 Geothermal
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Earth Science Unit 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

14 Terms
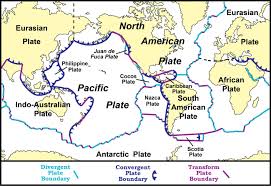
Plate Tectonics
The theory that Earth’s surface is broken into large pieces (plates) that move around slowly over time.
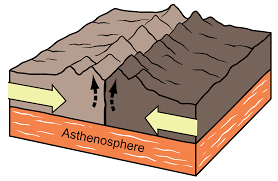
Convergent Boundary
A place where two tectonic plates are moving toward each other, often causing mountains or volcanoes.

Divergent Boundary
A place where two tectonic plates slide past each other sideways, usually causing earthquakes.

Transform Boundary
A place where two tectonic plates slide past each other sideways, usually causing earthquakes.
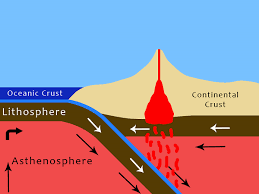
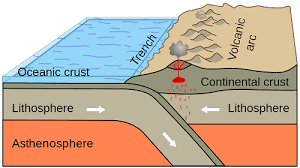
Subduction Zone
A place where one tectonic plate is pushed under another, usually creating deep trenches and volcanoes.
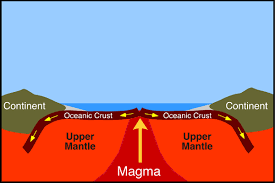
Mid- Ocean Ridge
A long chain of mountains under the ocean, where new crust is formed as plates pull apart.
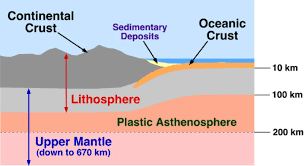
Oceanic Crust
The thinner, denser part of Earth’s crust that makes up the continents.
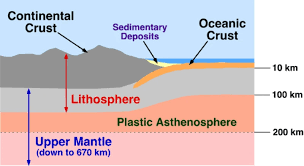
Continental Crust
The thicker, less dense part of Earth’s crust that makes up the continents.
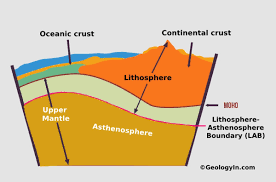
Lithosphere
The rigid outer layer of Earth that includes the crust and the uppermost mantle. This layer forms the tectonic plates.
Asthenosphere
The softer, flowing layer of the mantle that allows the tectonic plates to move on top of it.
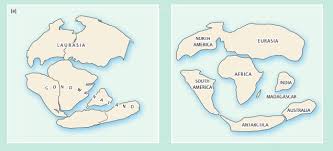
Continental Drift
The idea that Earth’s continents have slowly moved across the planet over time due to plate tectonics.
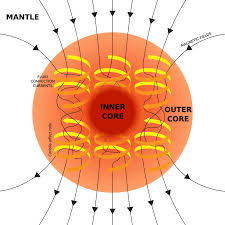
Earth’s Magnetic Field
The invisible field made by Earth’s spinning molten iron core, recorded in rocks and occasionally reversing direction.
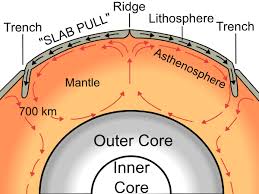
Convection
The movement of heat through a fluid (like the mantle) where hot material rises and cooler material sinks, creating a flow that pushes tectonic plates.
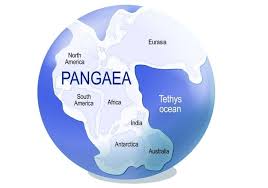
Supercontinent
A giant landmass made up of most or all of Earth’s continents joined together in the past.