M6S1: Aromatic Compounds and Carbonyls
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Benzene
C6H6
Cyclic structure
Delocalised Model
P-orbitals of all six carbons overlap to crate a π-system made of a clouds of electrons above and below
Evidence of delocalisation
Enthalpy of hydration of benzene is less exothermic than expected
Indicating it is more stable due to delocalised electrons being spread over more atoms
Naming aromatic compunds
If benzene ring is main functional group,
prefix = other group
suffix = benzene
If benzene is not main functional group
prefix = phenyl
suffix = from functional group of other group
Why doesn’t benzene react with bromine water
Due to benzene’s π-system, it is very stable and negative charge is spread out which is unfavourable for this reaction
Prefers reacting with electrophiles
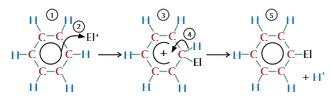
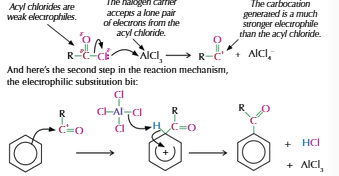
Benzene electrophilic substituion
Electron dense region attracts electrophile
Electrophile take pair of electrons from centre and form bond
Partially breaking delocalised ring = positive charge
Lose hydrogen to regain stability
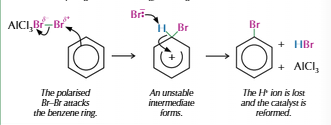
Halogenation of benzene
Uses halogen carrier to allow electrophilic substitution
Halogen carrier polarises the halogen allowing it to react
Eg. AlCl3, FeCl3
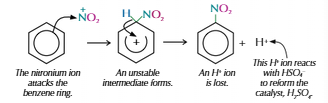
Nitration of benzene
Warm benzene to 55°C
Concentrated nitric acid
Concentrated sulfuric acid (catalyst), makes NO2+
HNO3 + H2SO4 → HSO4- + NO2+ = H2O
Increase temp = more substitutions
Acyl group
-C(=O)-R
Acylation
Used to add acyl group to benzene
Need to use halogen carrier to make acyl group positive
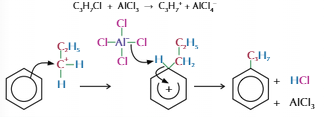
Alkylkation
Used to add alkyl group to benzene ring
Haloalkane and halogen carrier used
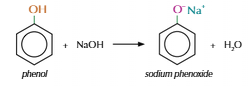
Phenol
C6H5OH
Suffix: -phenol
Phenol neutralisation
Phenol weakly acidic
Reacts with base to make salt and water
Phenol electrophilic substitution
Undergoes electrophilic substitution in bromine water
OH group has electron donating effect = more reactive
Electron donating groups
-OH, -NH2
Have electrons in orbitals that overlap with π-system
Increasing electron density at carbons 2,4, 6
Electron withdrawing groups
-NO2
Doesn’t have orbitals that overlap with delocalised ring
So withdraws electron density from ring at carbons 2, 4, 6
Directs electrophilic substitution to 3 & 5 position
Reduction of carbonyls
Can reduce carbonyl groups to alcohol using reducing agent
Usually NaBH4
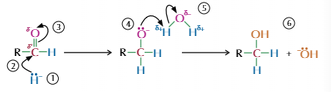
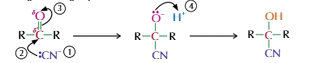
Carbonyls and Hydrogen Cyanide
React to produce hydroxy nitrile
Nucleophilic addition
Brady’s Reagent - test for carbonyl
Formed from 2,4-DNPH dissolved in methanol & conc H2SO4
Forms bright orange precipitate if carbonyl group present
Each carbonyl group forms different crystalline derivative with different melting points - can be used to identify
Tollens’ Reagent
Used to distinguish aldehyde & ketone
AgNO3 dissolved in (aq) ammonia
Heated in test tube with aldehyde = silver mirror
Ag+ + e- → Ag(s)
Carboxylic acid
-COOH
-oic acid
Always on 1st carbon when naming
Polar = small carboxylic group very soluble
Weak acid
Carboxylic acid reactions
Undergoes same reaction with metals, carbonates and bases as a weak acid
Acyl chlorides
COCl-
CnH2n-1OCl
Suffix: -oyl chloride
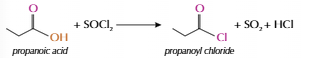
Formation of acyl chlorides
React carboxylic acid and SOCl2
-OH group replaced with -Cl
Nucleophilic substitution
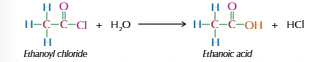
Acyl chloride with water
-Cl group replaced by -OH
Produces carboxylic acid & HCl
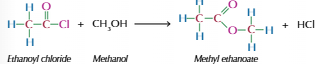
Acyl chloride with alcohols
Produces ester
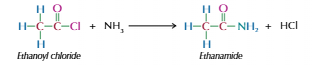
Acyl chloride with ammonia
Produces primary amide
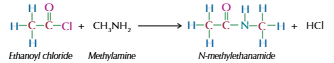
Acyl chloride with amines
Produces secondary amide
Acyl chloride with phenol
Produces ester
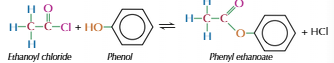
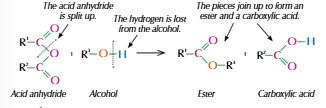
Esters
Formed form carboxylic acid and alcohols
Naming ester
First part form alcohol
Second part from carboxylic acid & replace ‘-oic acid’ with ‘oate’
Eg. Ethyl methanoate
Ways of producing ester
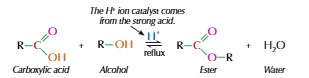
Alcohol & carboxylic acid
Alcohol & acid anhydride (dehydration)
Alcohol & Carboxylic acid
Heat carboxylic acid with alcohol in presence of strong catalyst
Usually conc H2SO4 used
Esterification
Dehydration
Alcohol and acid anhydride
Acid anhydride made from two identical carboxylic acid molecules, joined via oxygen
Acid anhydride also called dimers
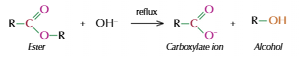
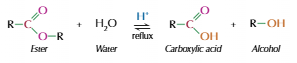
Hydrolysis of esters
Splits ester
Acid/Alkali used to speed up
Both produce alcohol but second product is different
Acid hydrolysis
Ester split into alcohol and carboxylic acid
As it is reversable, needs water to push reaction forwards
Base hydrolysis
Reflux ester with dilute alkali, such as NaOH
Forms alcohol and carboxylate salt