Corso PP 1-2
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Which of the following parts is incorrectly matched to it’s definition?
a. dendrites- receive information
b. cell body- white matter
c. synapses- junctions between neurons
d. terminal arborization- branches
b
Name the biogenic NTs:
Dopamine (DA)
Norepinephrine (NE)
Epinephrine (Epi)
Serotonin (5-HT)
Acetyl Choline (ACh)
Histamine
Melatonin
Name the AA NTs:
glutamate (glu)
glycine (gly)
GABA
Name the purigenic NTs:
Adenosine
ATP
Name the peptide NTs:
Encephalins (met-enkephalin, leu-enkephalin)
Endorphins (beta-endorphin)
Name the retrograde NTs:
NO
endocannabinoids
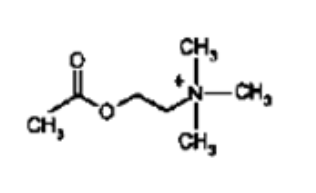
What NT is this?
ACh
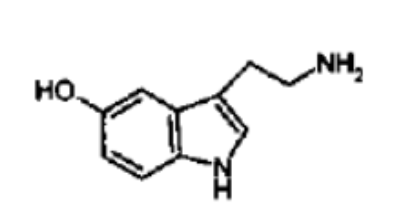
What NT is this?
Serotonin
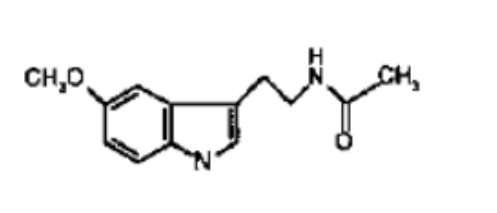
What NT is this?
Melatonin
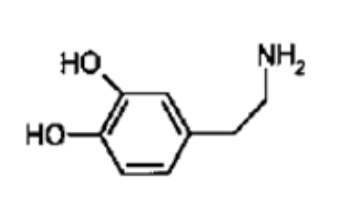
What NT is this?
Dopamine
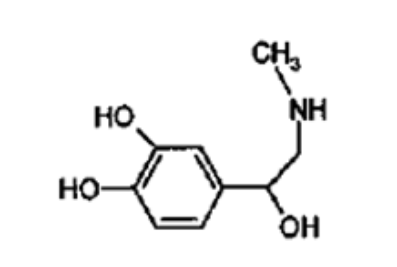
What NT is this?
Epi
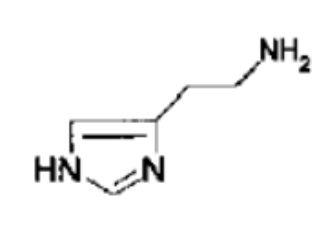
What NT is this?
Histamine
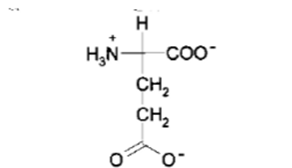
What NT is this?
Glutamate
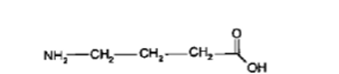
What NT is this?
GABA
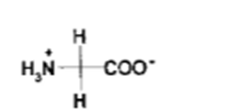
What NT is this?
Glycine
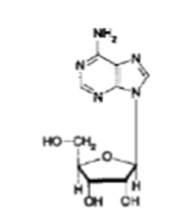
What NT is this?
Adenosine
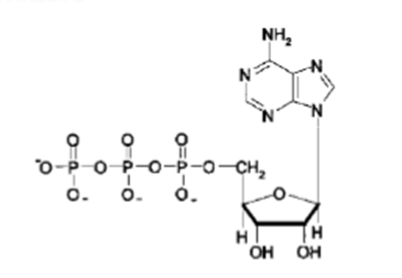
What NT is this?
ATP
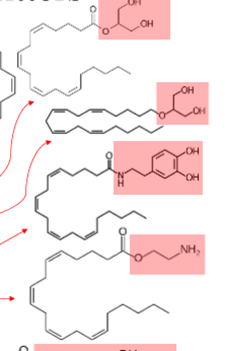
What CLASS of NTs is this?
endocannabinoids
Where is dopamine found?
Substantia nigra or Nigrostriatal Pathway
Where is serotonin found?
raphe
Where is melatonin found?
pineal gland
Where is histamine found?
hypothalamus
Where is ACh found?
Basal Ganglia or nucleus basalis
Where is NE found?
Locus coeruleus
Where is Epi found?
Adrenal gland
Low dopamine causes what disease? High dopamine causes what disease?
low DA= Parkinsons
high DA= Schizophrenia
What disease is caused by cell death to the substantia nigra?
Parkinsons
What disease is caused by overactivation of the mesolimbic section of the brain?
Schizophrenia
What’s a side effect of Haloperidol?
What’s a side effect of L-dopa?
Haloperidol—> was used for schizophrenia—> side effect of Parkinson’s symptoms
L-dopa—> used for Parkinson’s—> side effect of hallucinations
Spinal motor neurons use ________ as their primary neurotransmitter?
a. NE
b. Epi
c. DA
d. ACh
d
In the parasympathetic nervous system, __________ serves as the primary neurotransmitter at both the preganglionic and postganglionic neuron.
a. NE
b. Epi
c. DA
d. ACh
d.
In the sympathetic nervous system, what is the primary NT at the pre and post ganglionic neuron?
pre—> ACh
post—> NE
What 3 types of cells are found in the nervous system? function?
Nerve cells (neurons)—> conducting cells
Support cells (neuroglia)—> nonconducting cells
Blood vessel cells—> separated from the brain via the BBB
What classes of neurons are sensory?
pseudounipolar
bipolar
What classes of neurons are motor?
multipolar
Which cells wrap myelin around axons and dendrites? What’s the difference between the 2 cells?
oligodendrocytes—> myelin in CNS
Schwann cells—> myelin in PNS
Which glial cells form the blood brain barrier?
astrocytes
What cells does Guillain-Barre syndrome effect?
Schwann cells
What is the difference between anterograde transport and retrograde transport?
Anterograde
Going away
Moves materials from cell body to the terminal
Can be fast/slow
Retrograde
Coming back
Moves materials from the terminals back to the cell body
Only occurs at fast rate
Describe each type of synapse:
axodendritic
axosomatic
axoaxonic
dendrodendritic
Axodendritic—> classical synapse
Axosomatic —> axon to cell body
Axoaxonic—> axon to axon
Dendrodendritic—> dendrite to dendrite
What is the most abundant NT in the CNS?
glutamate
What is GABA made from? What 1 step reaction occurs?
made from glutamate
made form 1 step carboxylation
How is GABA degraded?
GABA is converted back to glutamate
Answer the following about Glycine:
What AA is the precursor to glycine?
How is it created?
serine
Serine (3C) donates its carbon to folate (TH4) to create Glycine (2C)
How is ACh made? How is it degraded?
made:
1 step—> AcCoA + Choline= ACh using the enzyme choline acetyltransferase
degrade:
degraded in the SYNPASE
1 step—> Ach degraded to acetic acid and choline using acetylcholinesterase
Explain how acetylcholinesterase inhibitors increase synaptic ACh levels for treatment of MG and Alzheimer’s.
Inhibit the enzyme that degrades ACh and causes ACh to hang out longer in the synapse.
What are the precursor molecules to dopamine?
Phenylalanine—> L-Tyrosine —> L-Dopa —> Dopamine
What are the precursor molecules of EPI and NE?
Dopamine—> NE—> Epi
What are the precursor molecules of serotonin and melatonin?
Tryptophan—> 5-hydroxytrptophan—> serotonin —> N-acetyl serotonin —> melatonin
What is the tx for Parkinsons?
L-dopa + Carbidopa
Why is L-DOPA given to Parkinson’s patients?
Dopamine cannot cross the BBB
L-dopa can cross the BBB
Why is carbidopa also give to patients taking L-Dopa?
Does not cross the BBB
Prevents L-dopa —> dopamine conversion in the peripheral tissues/ outside the brain
Why are some Parkinson’s pts. also given MAO-I’s or COMT-I’s?
Prevents degradation of dopamine
Increases concentration of dopamine
Name the enzymes involved in the catabolism of each of the following:
NT | Enzymes for catabolism |
Dopamine | |
NE and Epi | |
Serotonin | |
Histamine |
NT | Enzymes for catabolism |
Dopamine |
|
NE and Epi |
|
Serotonin |
|
Histamine |
|
(I would just pay attention to whether its MAO-A or B)
How do small molecule NTs get into vesicles?
secondary active transport using a proton (H+)/ NT antiporter
How and where are peptide NTs made?
how?—> how normal proteins are made (transcription, translation, etc.)
where?—> rough ER
What NT’s do VMAT1 and VMAT2 transport?
VMAT1—> neuroendocrine
VMAT2—> DA, NE, 5HT, H
WHAT DRUG inhibits VMAT2?
Reserpine
For a cell to polarize there are ___ Na+ out and ___K+ in to create a - charge inside the cell.
3 Na+ out and 2 K+ in
What’s the clinical correlation to depolarization and AP in the synapse?
pufferfish toxin blocks V-gated Na+ channels
What’s the clinical correlation to NT release?
Botulinum toxin blocks ACh release
Describe how NTs are released into the synapse:
____ reaches terminal
_________________ channels open
__________ binds to __________
release of NTs
AP reaches terminal
V-gated Ca++ channels open
Calcium binds to proteins on vesicles
Release of NTs
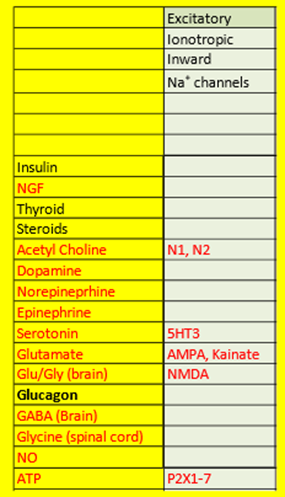
List the NT that use excitatory, inotropic, inward, Na+ channels:
(just memorize the table)
Ach, Serotonin, Glutamate, Glu/Gly in the brain, and ATP
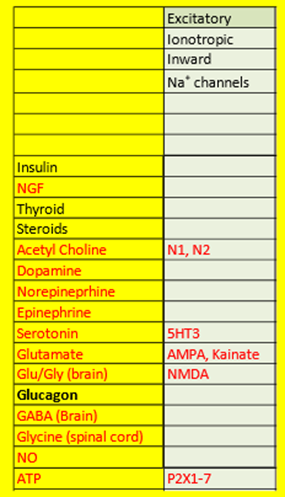
List the receptor for each of the following that are excitatory, ionotropic inward Na+ channels:
ACh
Serotonin
Glutamate
Glu/Gly in the brain
ATP
(just memorize the table)
ACh- N1, N2
Serotonin- 5HT3
Glutamate- AMPA, Kainate
Glu/Gly in the brain- NMDA
ATP- P2X1-7