CS 161
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
How to find O(?) between two functions
How to Solve
Take limit to infinity of g(n)/f(n) <= C, for some C > 0
If true, then g(n) is O(f(n))
Rule, put the one inside the big O in the denominator, and the other in the numerator.
How to find Ω(?) between two functions
Take limit to infinity of g(n)/f(n) >= C, for some C > 0
If true, then g(n) is omega(f(n))
How to find θ(?) between two functions
True if both functions are O(?) and Ω(?)
How to find o(?) between two functions
Take limit to infinity of g(n)/f(n) = 0
If true, then g(n) is o(f(n))
L’hopital’s Rule

⅀(from 1 to n) of c
c*n
⅀(from 1 to n) of i
(n*(n+1))/2
⅀(from 1 to n) of i²
(n*(n+1)*(2n+1))/6
⅀(from 1 to n) of i³
(n² * (n+1)²)/4
Summation to theta rule
For ⅀(from 1 to n) ik, it is θ(k+1)
⅀(from 1 to n) of ai
(1-an+1)/(1-a), as long as a != 1
⅀(from 1 to ∞) of ai assuming a| < 1
1/(1-a)
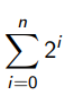
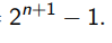
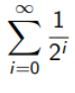
2
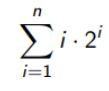
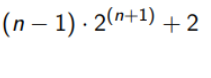
logb(a*c) = ?
logb(a) + logb(c)
logb(a/c) = ?
logb(a) - logb(c)
logb(ac)
c*logb(a)
logb(a) = ? (3 things)
logc(a) / logc(b)
logc(a) * logb(c)
1/loga(b)
blogc(a) = ?
alogc(b)
(ba)c = ?
ba*c
ba*bc = ?
ba+c
ba/bc = ?
ba-c
logb1 = ?
= 0
logb(ba)
= a
(n k) = ? (combination)
n! /(k! * (n-k)!)
Harmonic Number, what is it, whats is the limit of it, what is it’s θ(?)
Theta(logn)
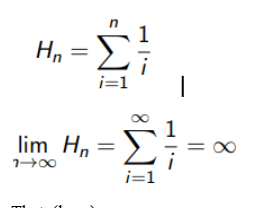
How to solve x = b^n for n
Basically do n = logb(x)
How to solve probability problems like x has y chance to appear in n size array, using sequential search, what is probability
probability that x appears at z position in the array of size n is 1/n, if x is 100% in the array, or 1/(y*n) if it has y chance
Then you need to do i+1 operations to find it
So probability is sum from 0 to n-1 of (i+1)/(y*n), which u can simplify down.
How to do an inductive proof
Prove that base case is true f(0) or f(1) usually.
Assume that f(k) is true
Prove that f(k+1) is true using f(k)
Post Order Traversal of a tree
Left, Right, RootP
Pre Order Traversal of a Tree
Root, Left, Right
In Order Traversal of a tree
Left, Root, Right
When is a binary tree considered to be proper
If every internal node has two children
What is the depth of a tree
Distance from root node to x node, where depth of the root is 0
Height
Distance from root node to furthest leaf.
Whats max amount of nodes of tree at level x
2x nodesM
Max amount of nodes and max amount of leaves of tree with height h
Max amount of nodes: 2h+1-1
Max amount of leaves: 2h
A binary tree with n nodes has atleast a depth of
>= floor(logn)
A binary tree with n leaves has atleast a depth of
>= ceiling(logn)
How to do binary search steps, what is the bigO of binary search
Set low to lowest index in array, high to highest index in array
Check Base Case that high>low, make sure thats true
Calculate mid by doing floor((high+low)/2)
If x==A[mid], return mid
If x<A[mid], set high to mid+1, recalculate starting at step #2
If x>A[mid], set low to mid+1, recalculate starting at step #2
Binary Search is O(logn)
What is the O of insertion sort, is it stable, What about the memory notation, and what are the steps of insertion sort, assuming ascending order,
O(n2)
It is stable
Memory: In place)
Start with 2nd element in the array, lets say x
Compare the with the element to the left of it, say y
If x<y, swap x and y, and repeat step 2
If x>y, leave it, set x to next position to sort in array, and go again at step 2
Repeat until end of array
What is the O-notation of selection sort, is it stable, and what are the steps of selection sort, assuming ascending order
O(n2)
It is not stable
Two Ways:
Search array for min, swap it to front, keep doing this
Search array for max, swap it to back, keep doing this
What is the O-notation of quick sort, is it stable, what is the average case, What is the memory requirement, what are the steps,
WOrst Case: O(n2)
It is not stable
Memory: O(logn) for extra stack
Average Case: O(nlogn)
1. This one is hard to explain in steps, you just really need to go over example #6 in HW2, or #1 in HW3
What is the O-notation of Merge Sort, is it stable, what is the memroy requirement, what are the steps
Worst Case: O(nlogn)
It is stable
Memory: O(n) extra for merge
Basically, keep splitting array in half, recursively, until its just two elements, then merge together, starting with left, then right, make sure to do example.
What is the O-notation of HeapSort, is it stable, what is the memroy requirement, what are the steps, how do you find parent of leaf, how do you find left child of parent, right child of parent
Worst Case: O(nlogn)
It is NOT stable
Memory: In Place
Steps:
1. Heapify the array (basically make it into heap, easiest way is draw a tree
2. RemoveMin or Max (depending on tpye of heap)
3. Replace with last leaf in heap, siftdown.
Right Child of i = 2i+2
Left child of i = 2i+1
Parent of i = floor((i-1)/2)
Rank the following: logn, ny. (for y >1 and y<=1 , 1/n, 1, (logn)y, an nn, n!, nn, n!, ab^n, (logn)n
O(1/n)
O(1)
O(logn)
O(logn)y
O(ny) for 0 < y <= 1
O(nlogn)
O(ny) for y > 1
O(an)
O((logn)n)
O(n!)
O(ab^n)
O(nn)
In average qucijk sort case, how do you sort the keys of permutations, how do you find the probability that two keys are compared.
Sort array in ascending order, then list keys based on index
The probability that the keys sj and si are compared (assuming j>i) is: 2/(j-i+1)
Inversion
Pair of items in a sequence such that the larger one precedes the smaller one
Steps To solving line intersections
Assign labels for left side top to bottom (6 at top, 1 at bottom for example)
Assign labels to right side, for where the lines meet on the left side (line labels should be the same)
The list created is bottom to top of right side
Count permutations in list = intersections