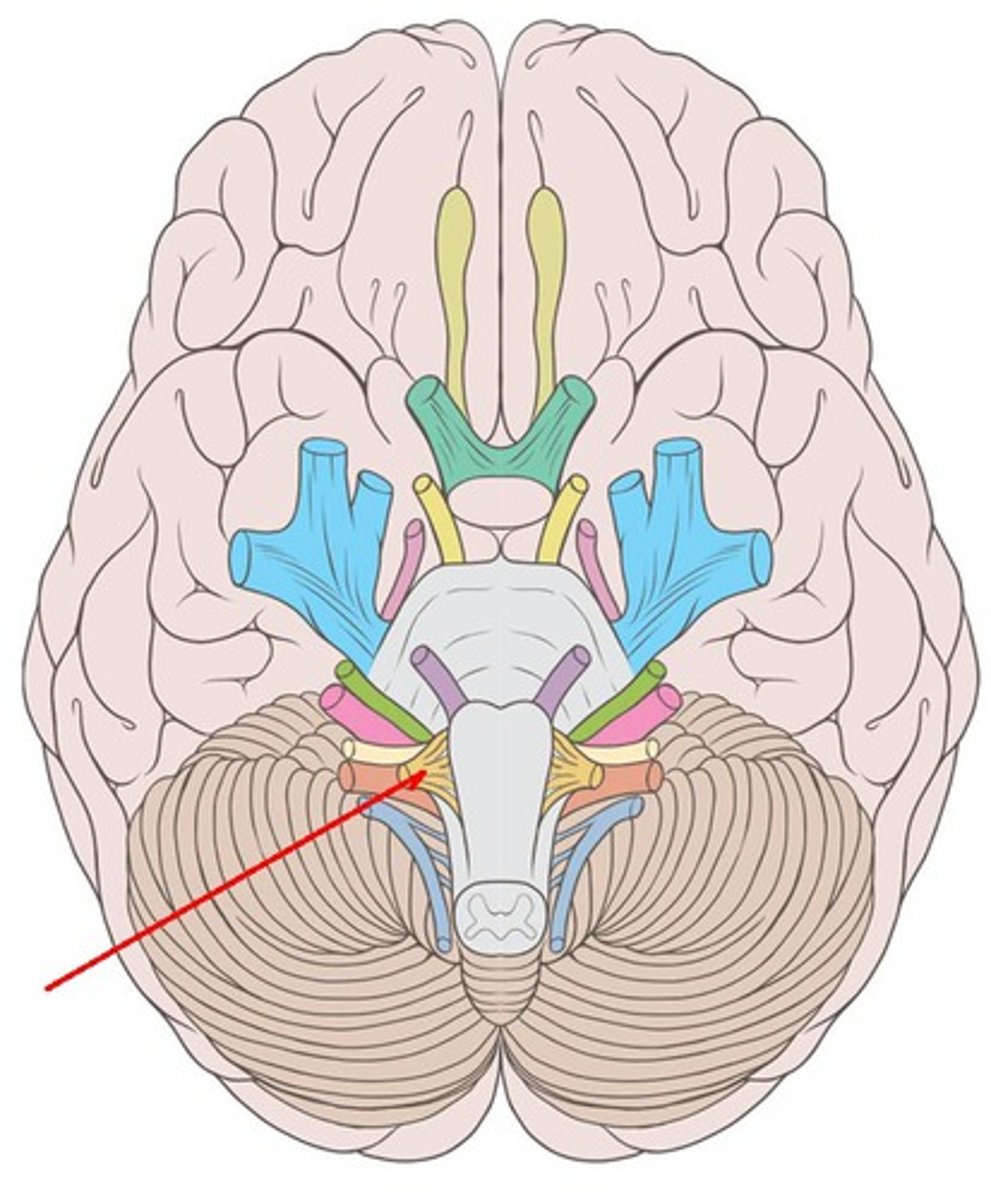
Brain and cranial nerves
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Cell Body
Largest part of a typical neuron; contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm
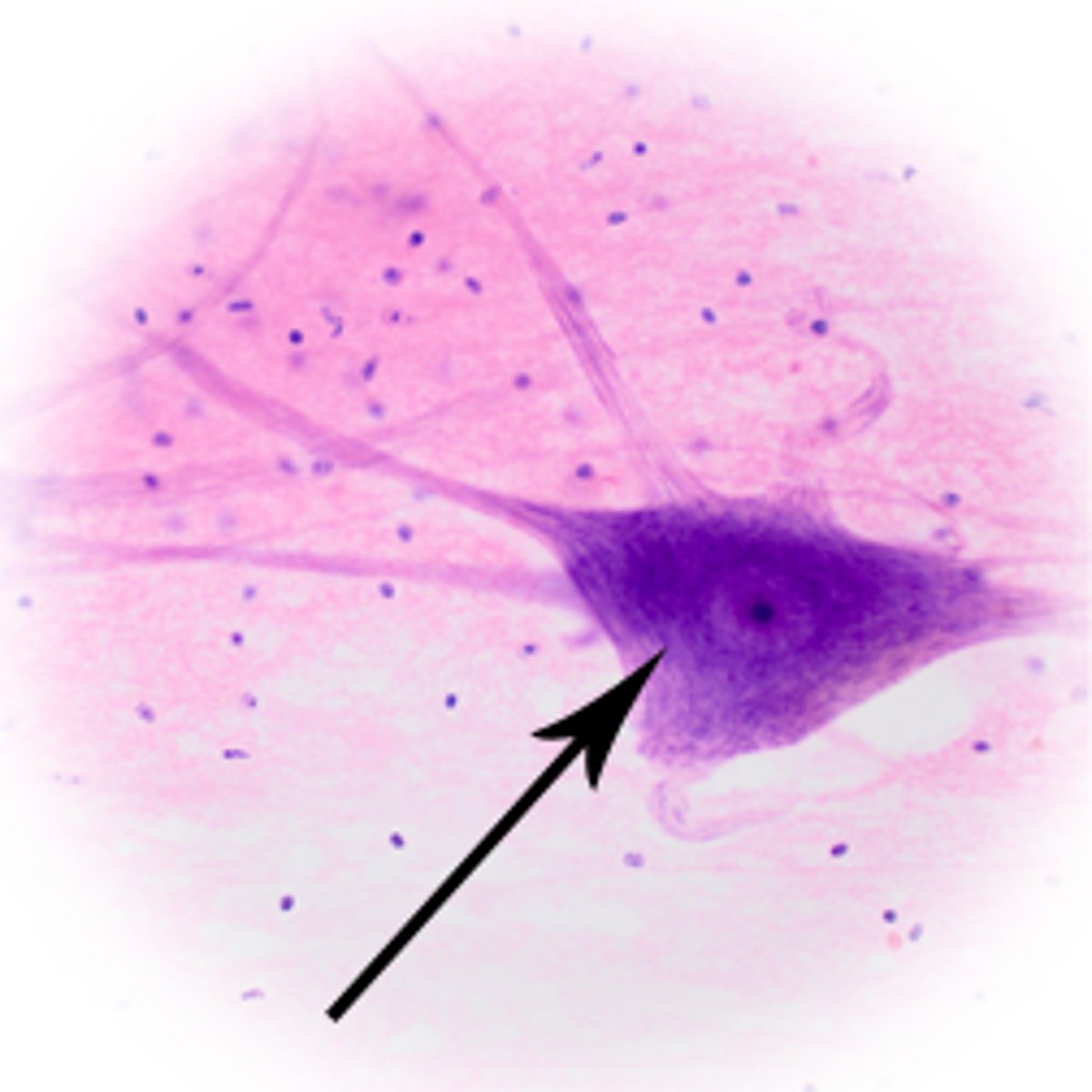
Nucleus
Contains the neuron's DNA; controls cell activities.
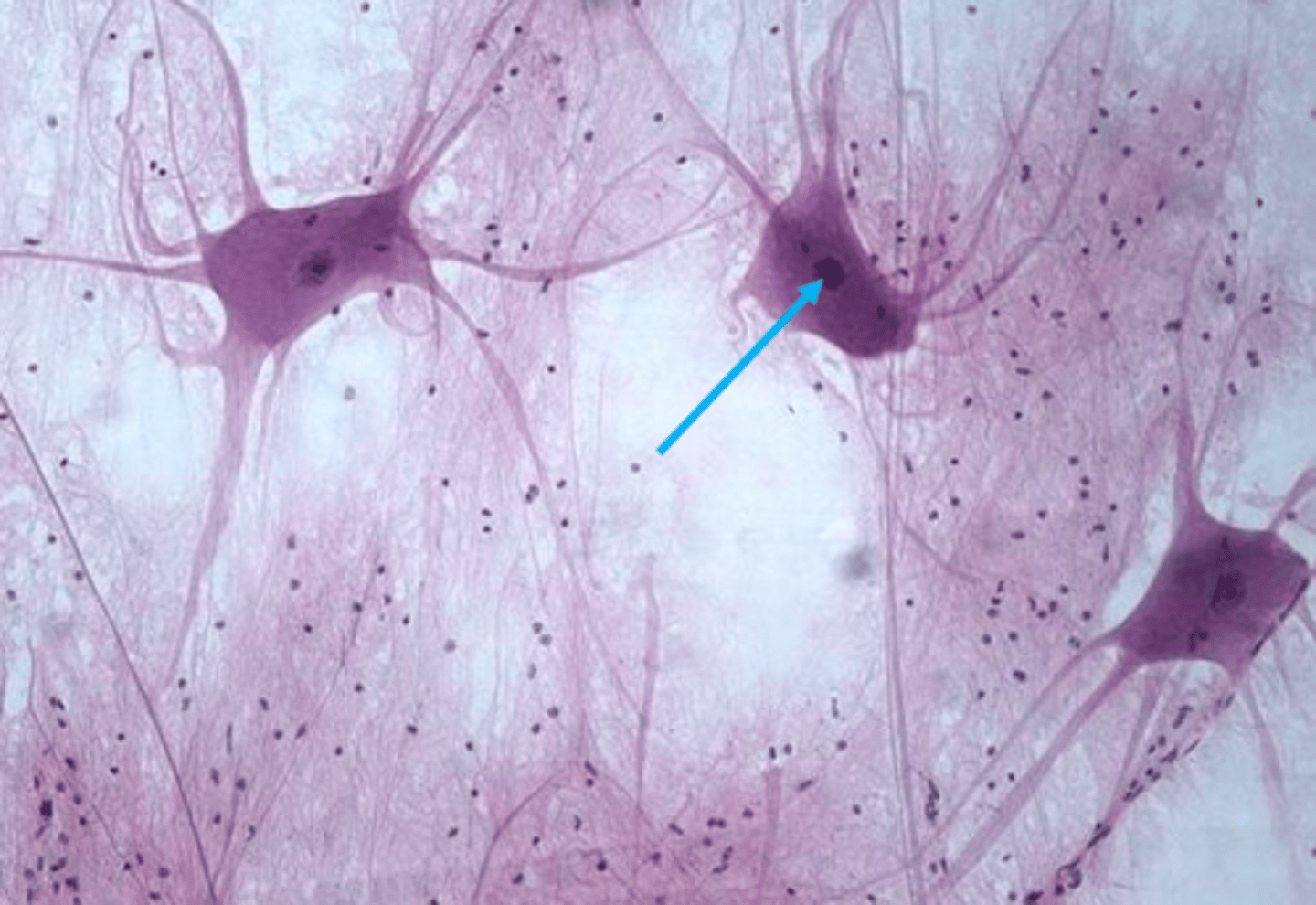
Dendrites
Branch-like extensions that receive signals from other neurons.
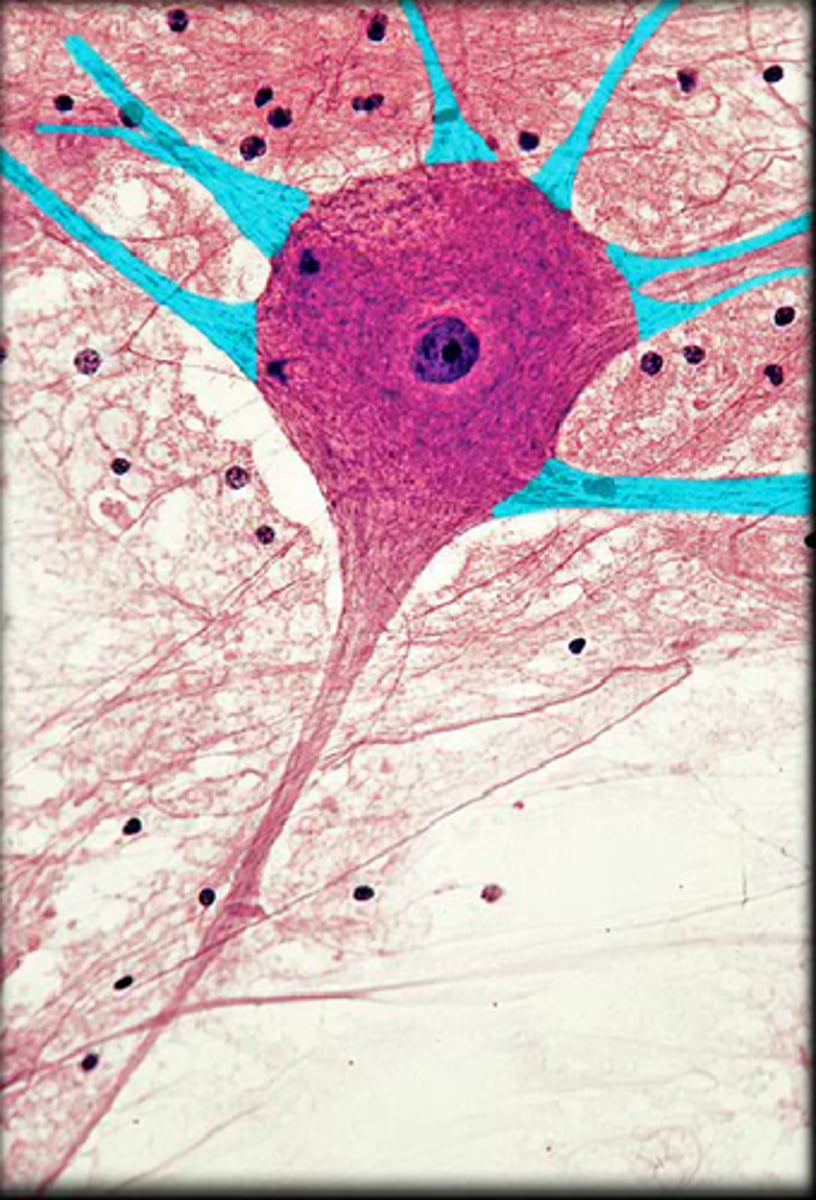
Axon
Long fiber that transmits signals away from the cell body.
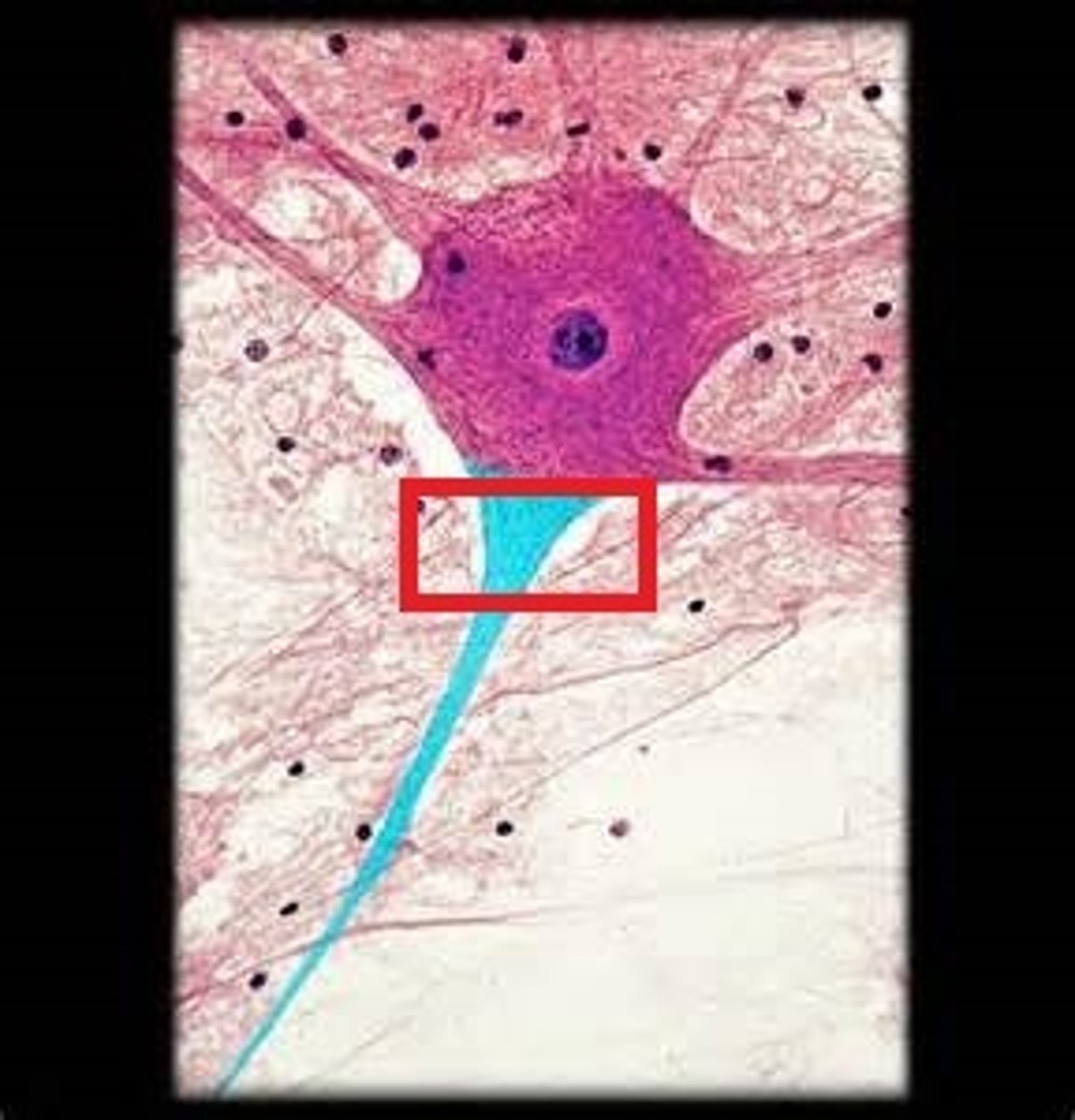
Axon Terminal
Ends of the axon where neurotransmitters are released.
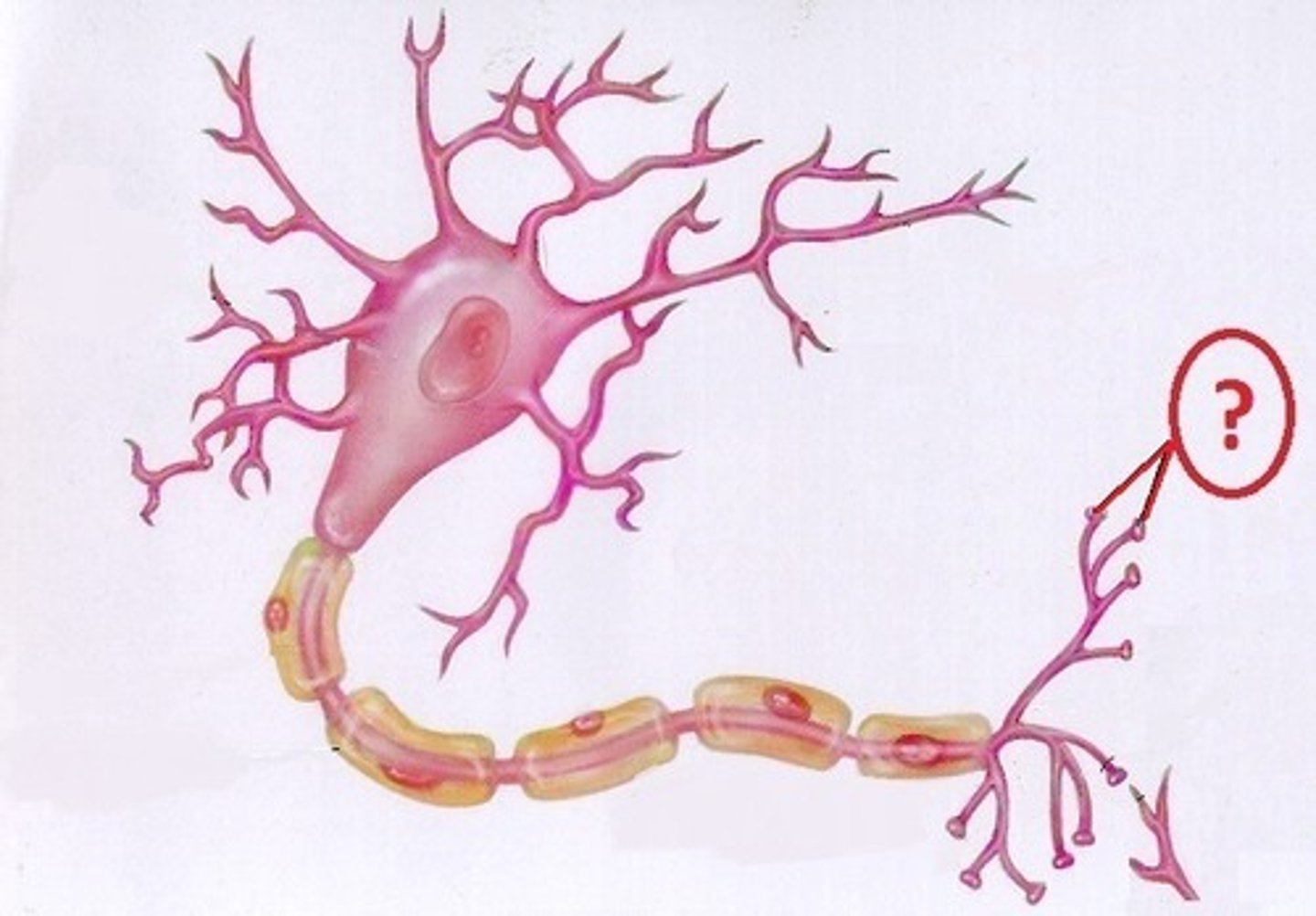
Schwann Cell
Produces myelin in the peripheral nervous system.
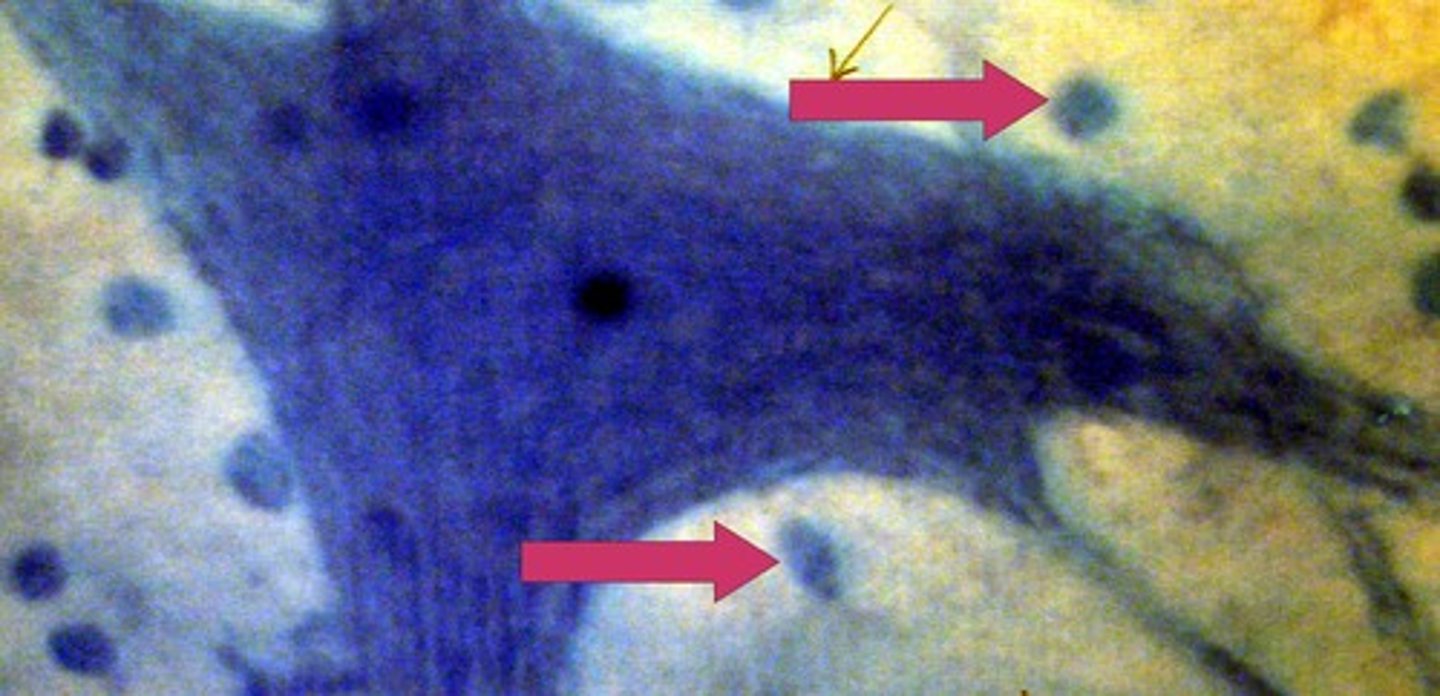
Neuroglia
Supporting cells that protect and nourish neurons.
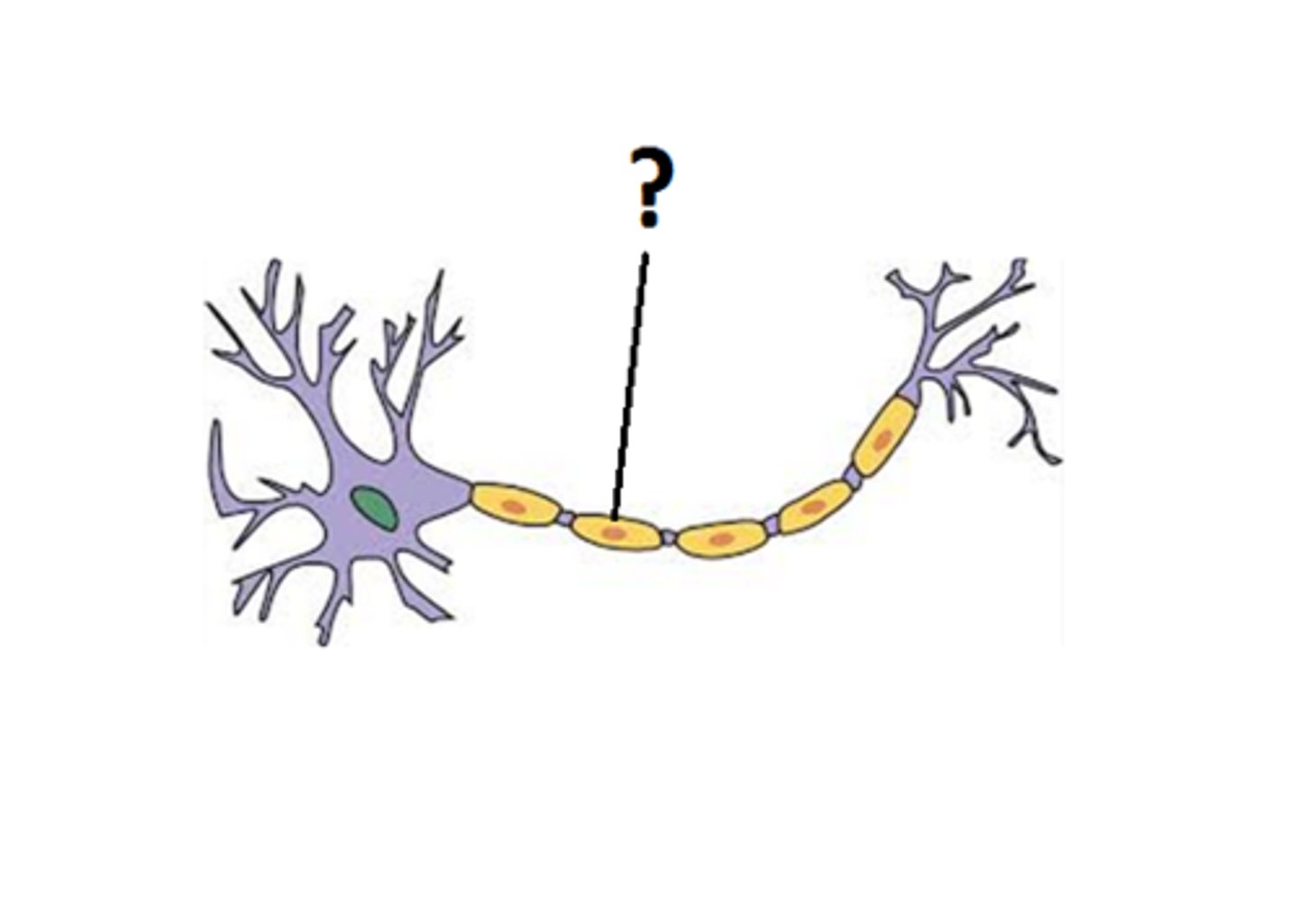
node of ranvier
a gap in the myelin sheath of a nerve, between adjacent Schwann cells.
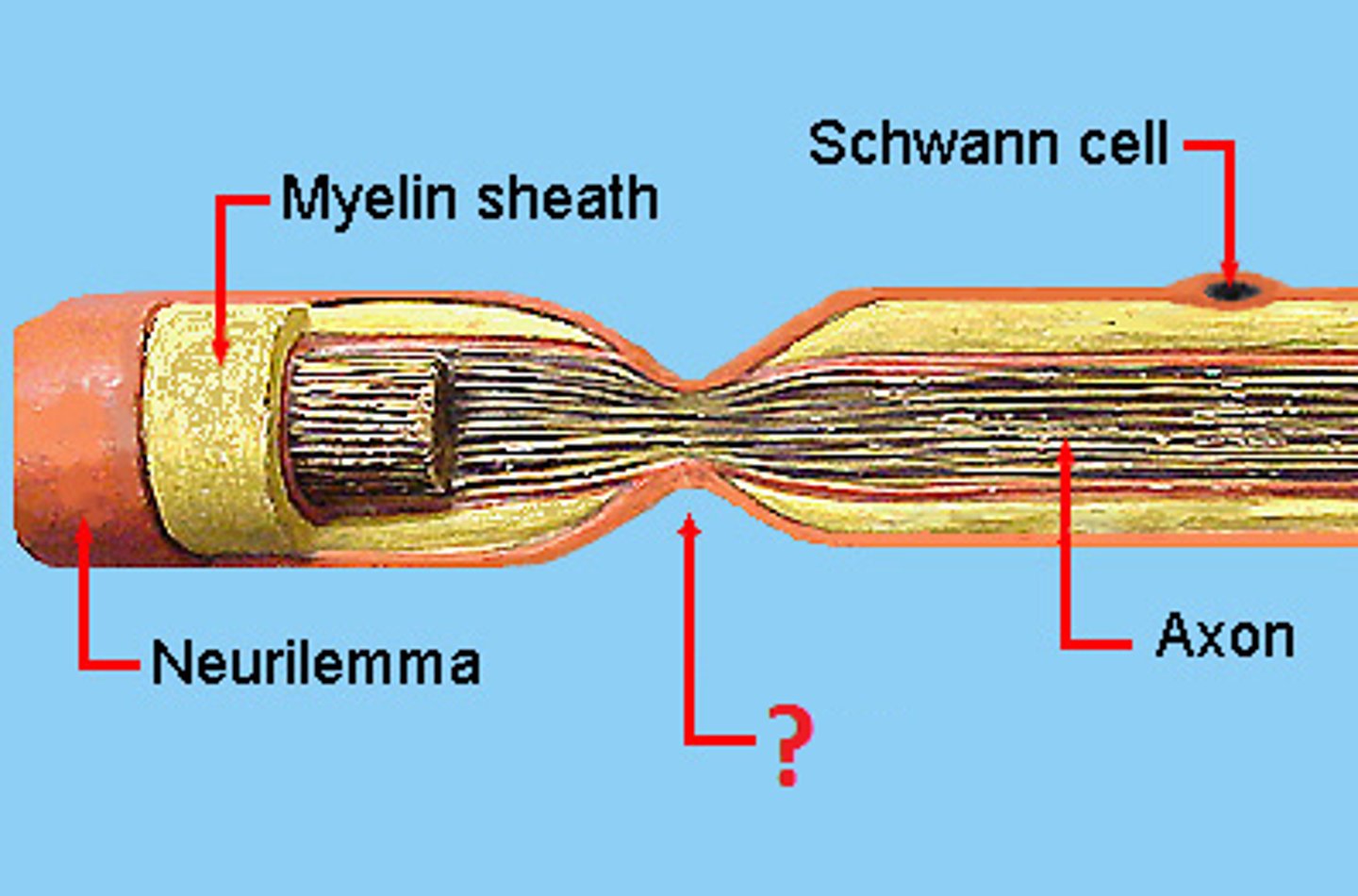
Axon hillock
Cone shaped region of an axon where it joins the cell body.
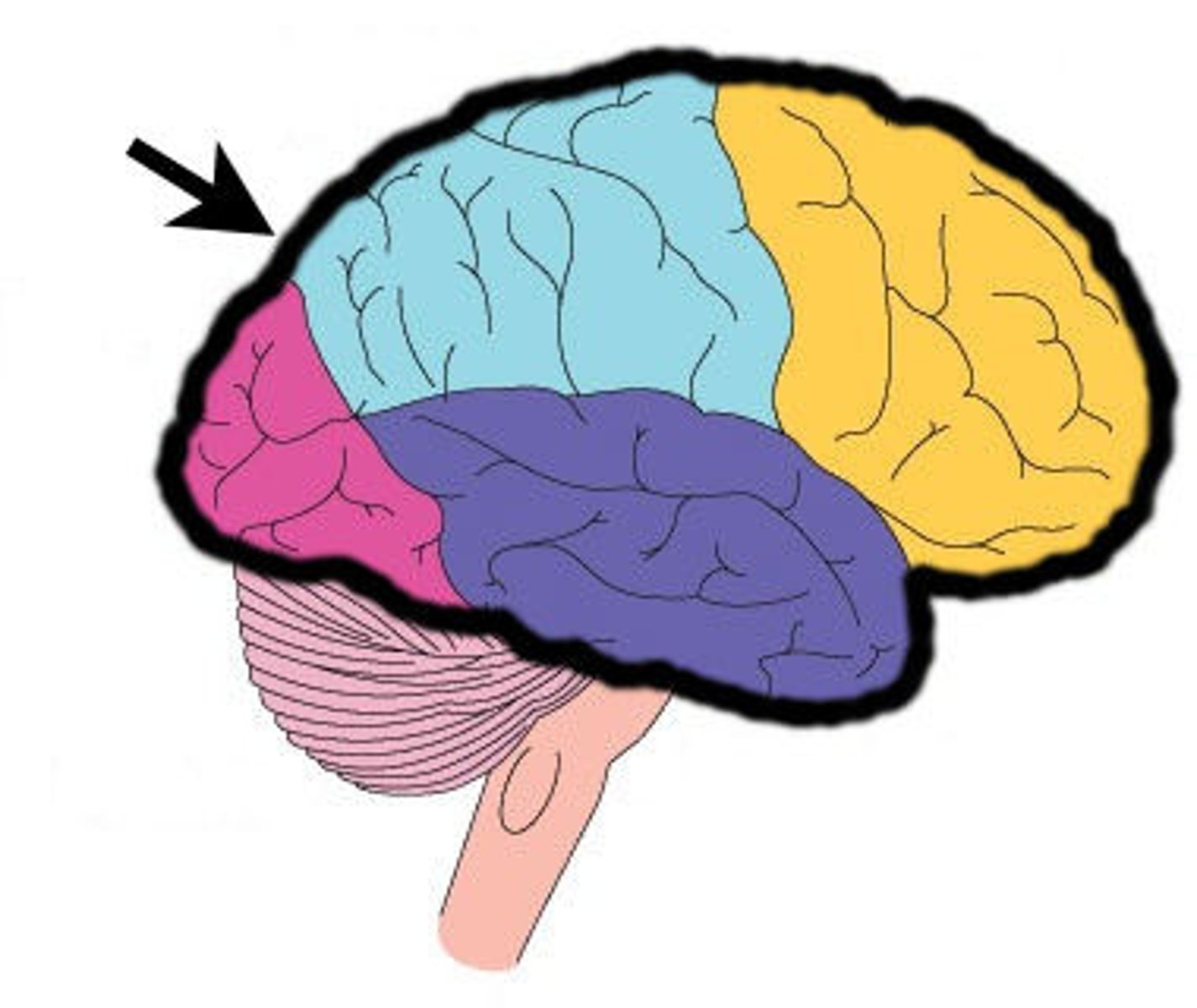
Cerebrum
Largest brain region, responsible for conscious thought, learning, memory, and voluntary movement.
Cerebral Hemispheres
Left and right halves of the cerebrum, separated by the longitudinal fissure.
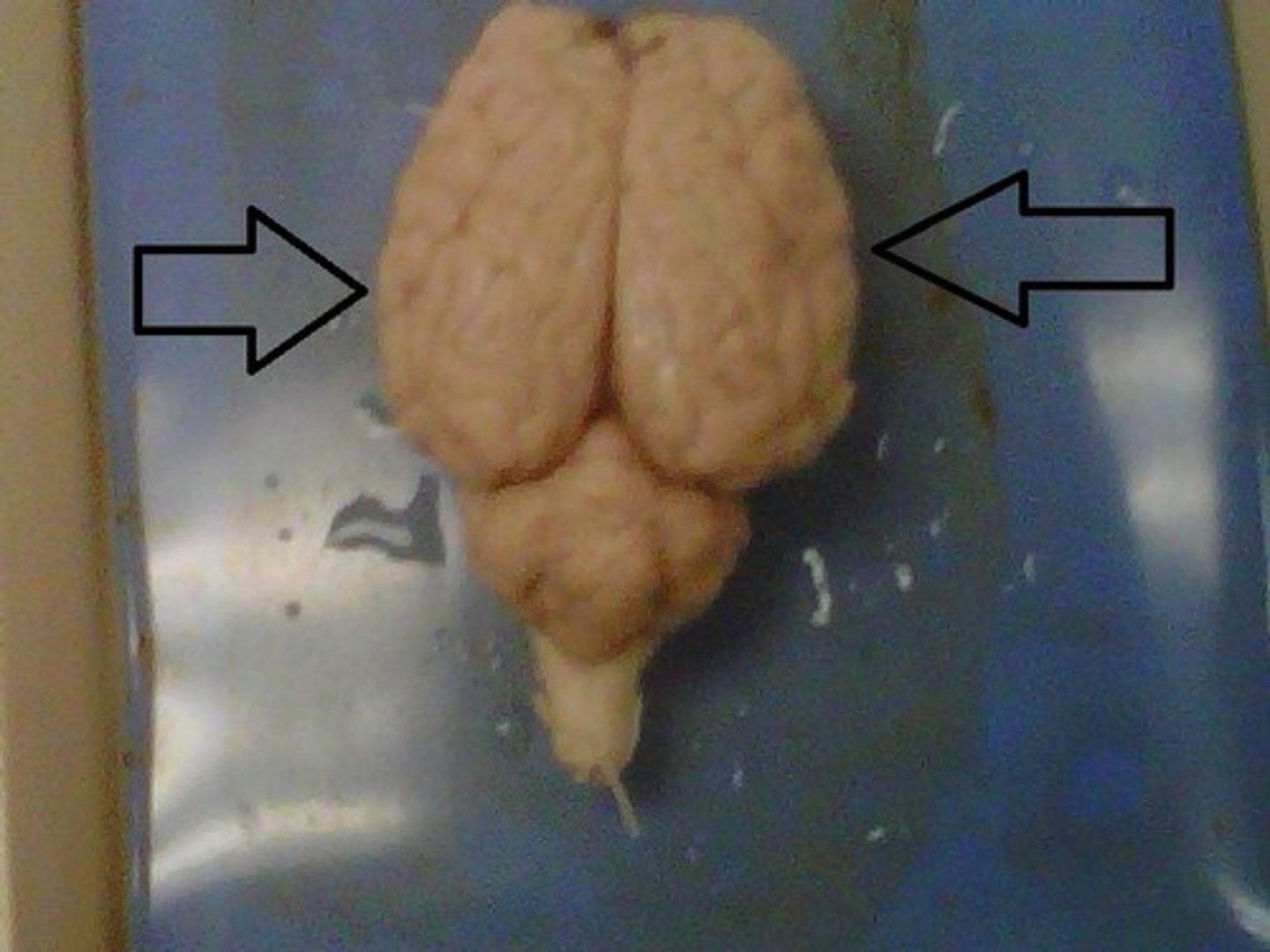
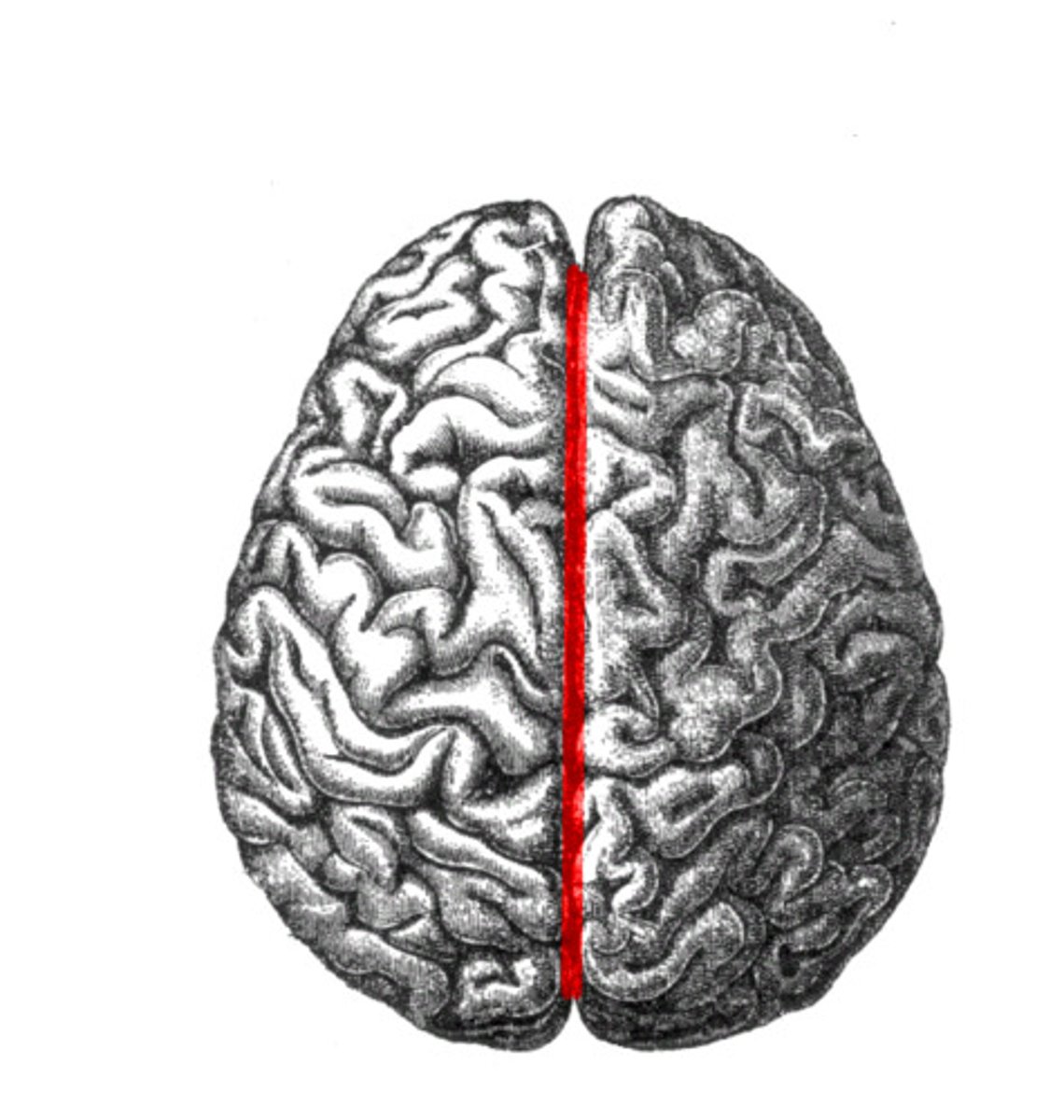
Longitudinal Fissure
Deep groove dividing the two cerebral hemispheres.
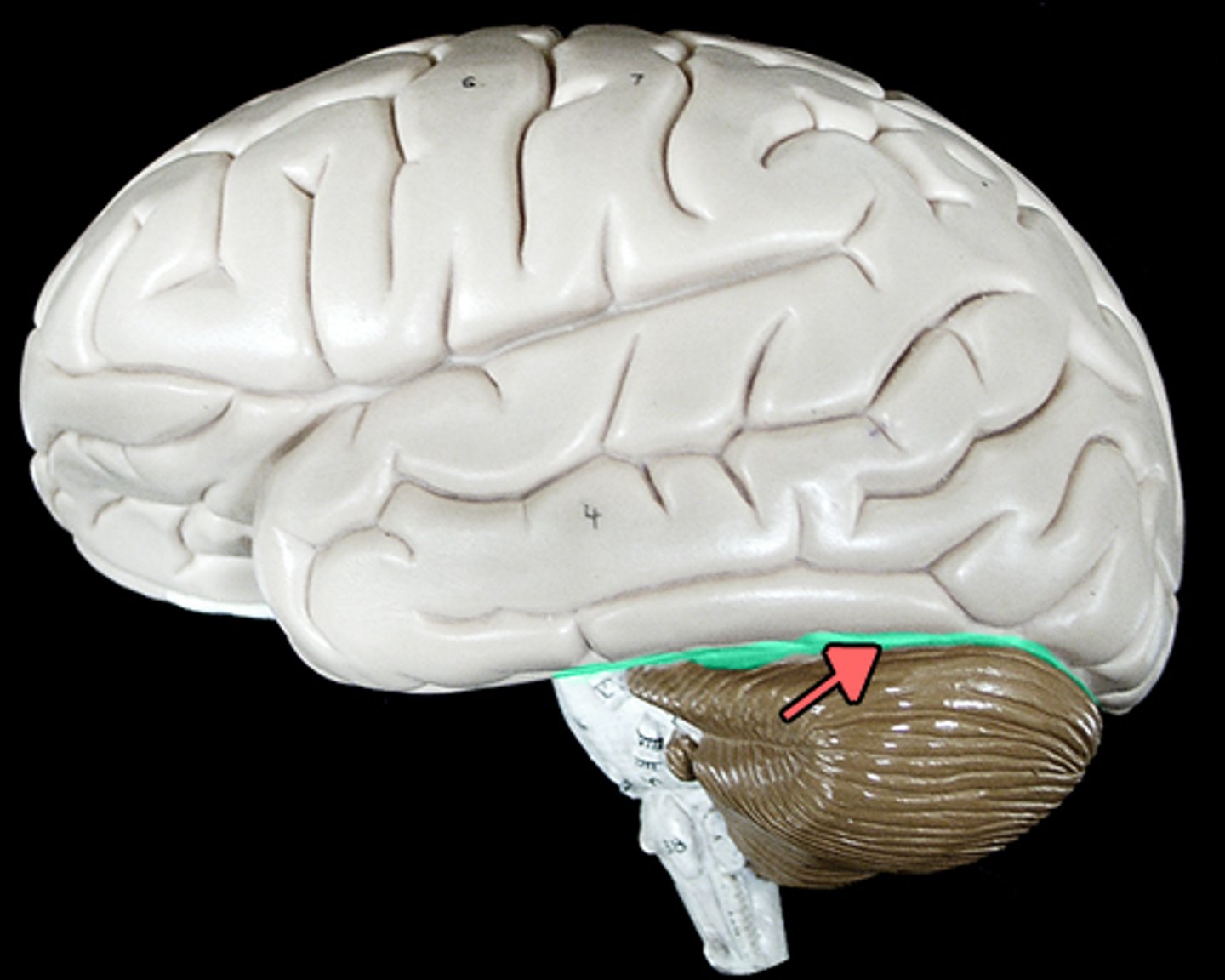
Transverse Fissure
Separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum.
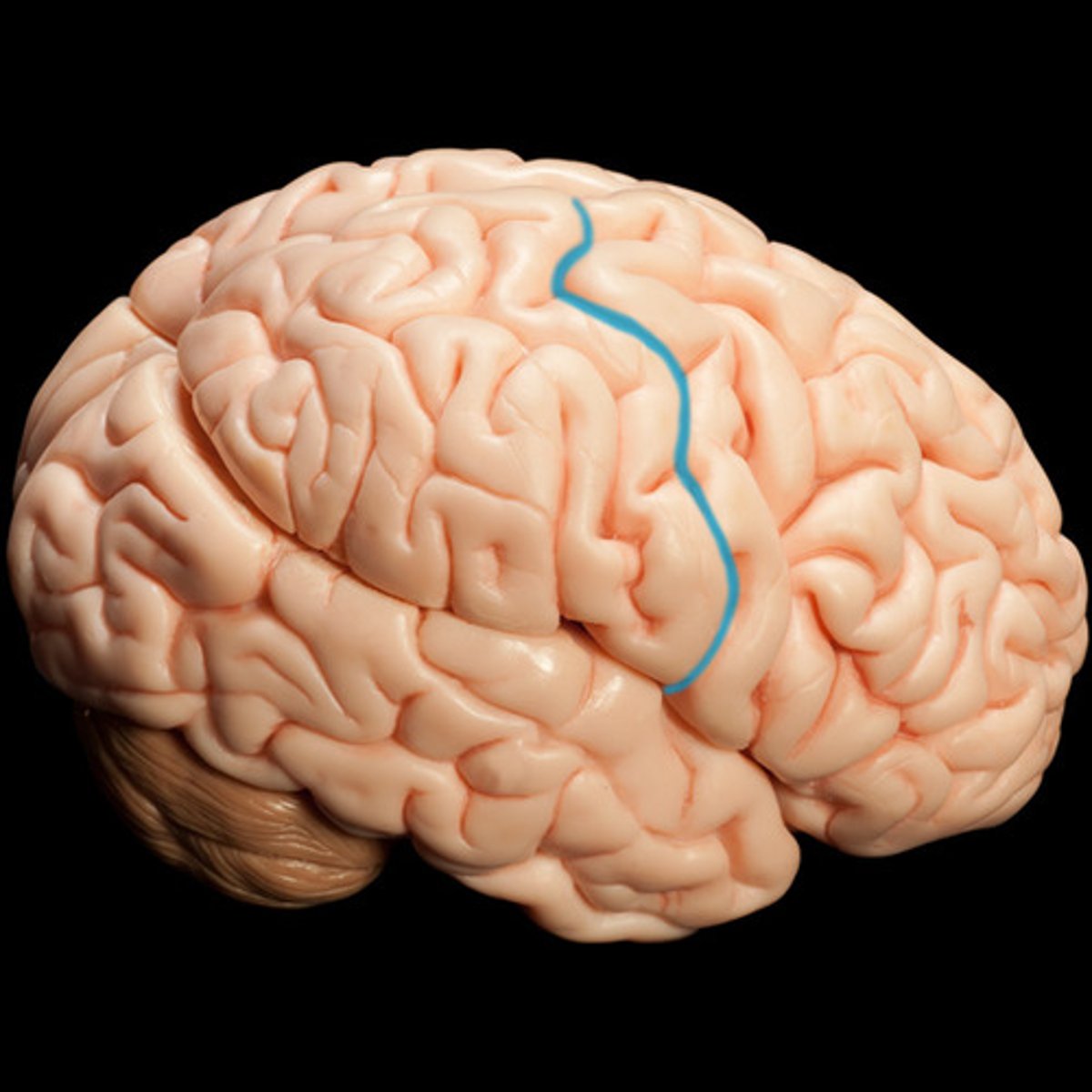
Central Sulcus
Separates frontal and parietal lobes.
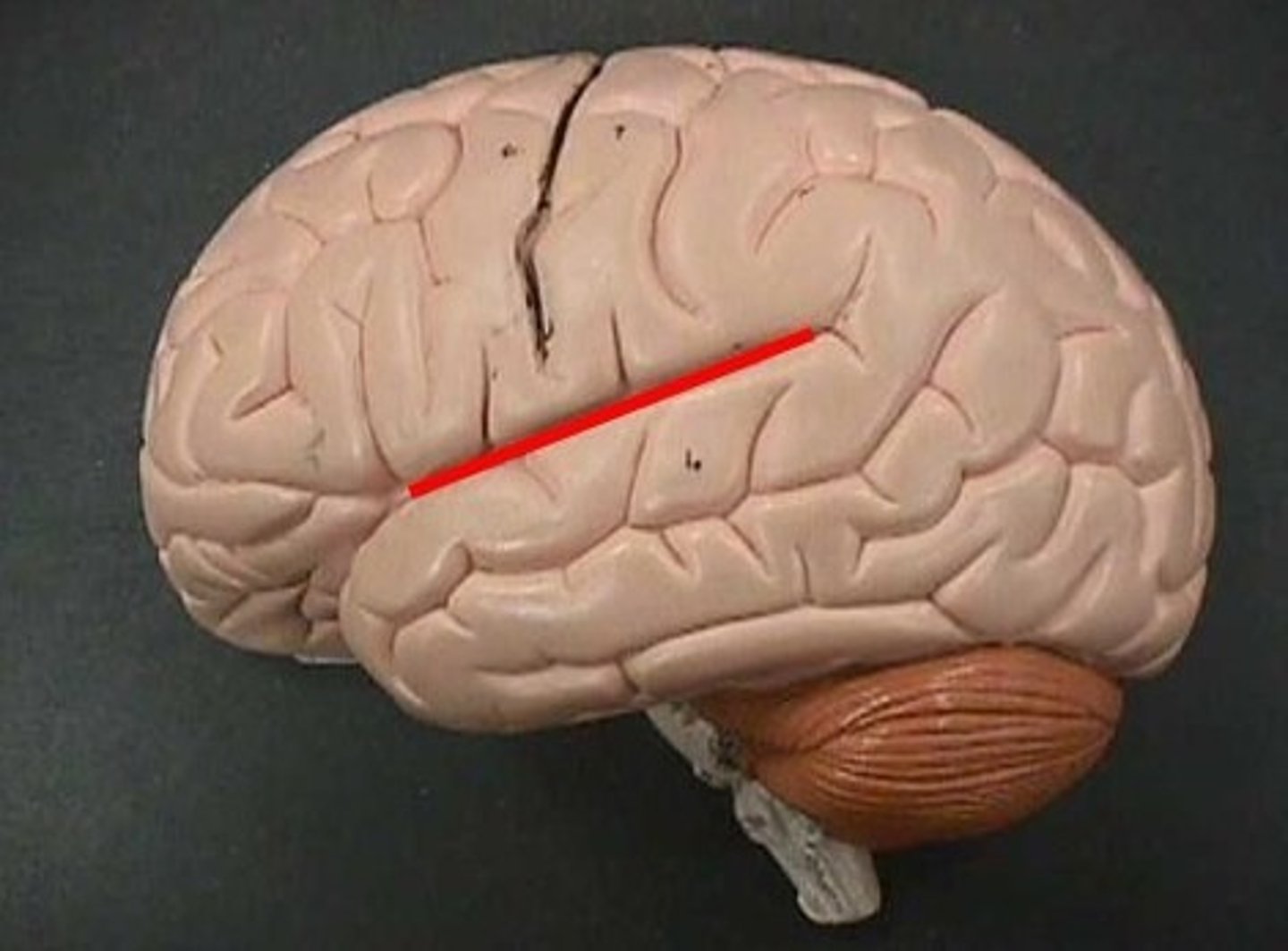
Lateral Sulcus
Separates temporal lobe from frontal and parietal lobes.
Precentral Gyrus
Primary motor cortex; controls voluntary muscle movement.
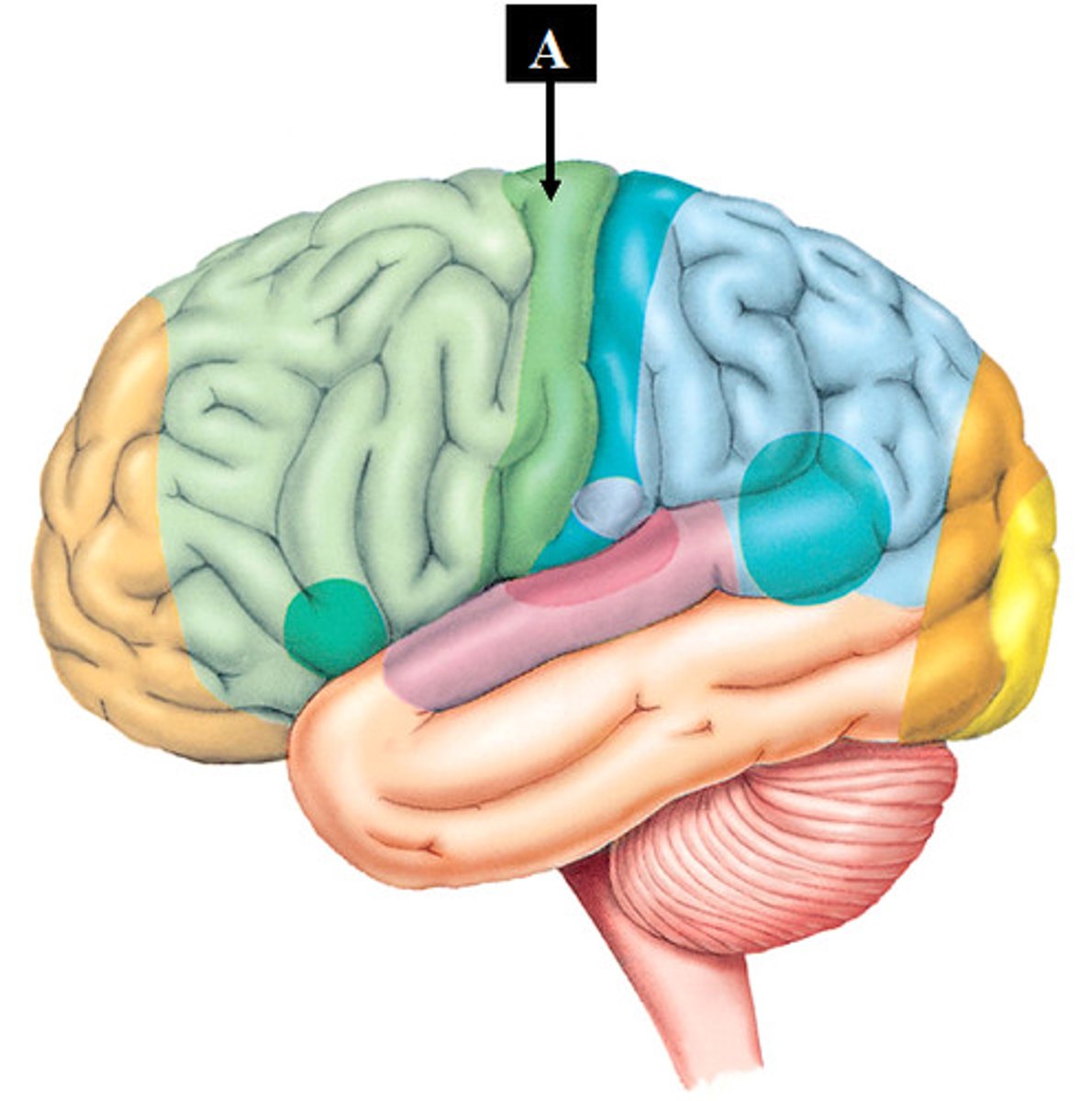
Postcentral Gyrus
Primary somatosensory cortex; processes body sensations.
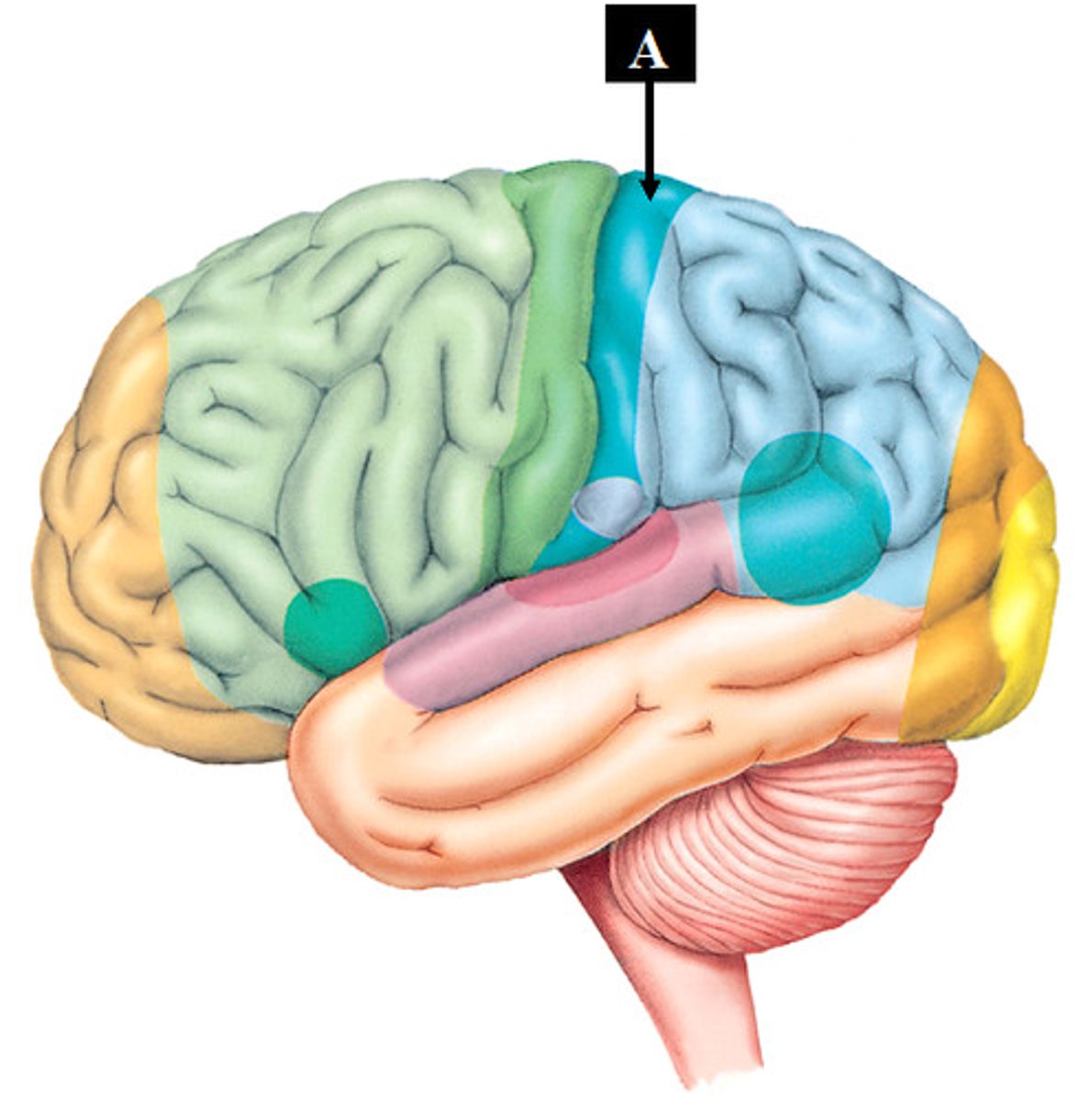
Frontal Lobe
Responsible for planning, decision-making, voluntary movement, and speech (Broca's area).
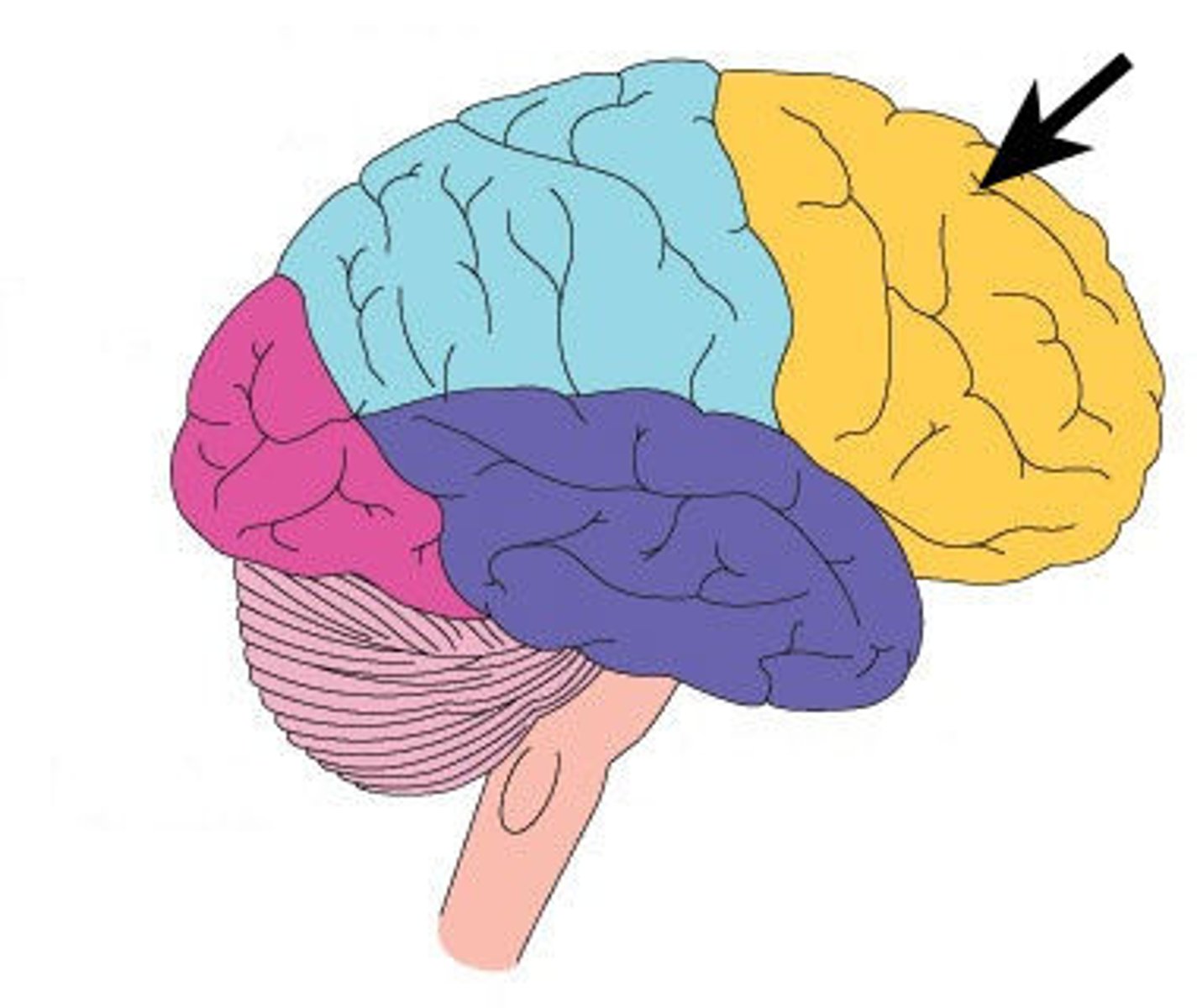
Parietal Lobe
Processes touch, pressure, temperature, and pain.
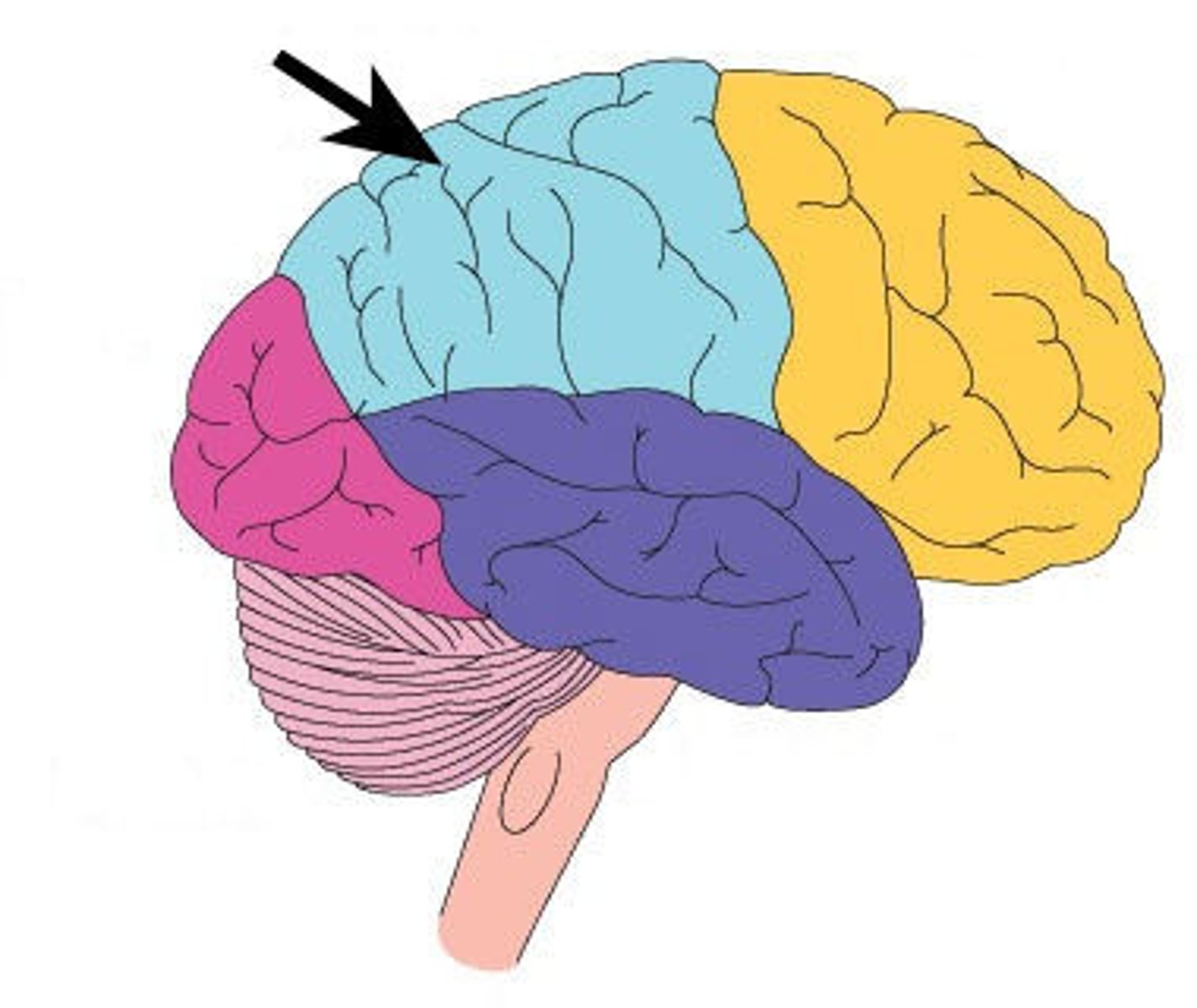
Temporal Lobe
Involved in hearing, memory, and Wernicke's area (language comprehension).
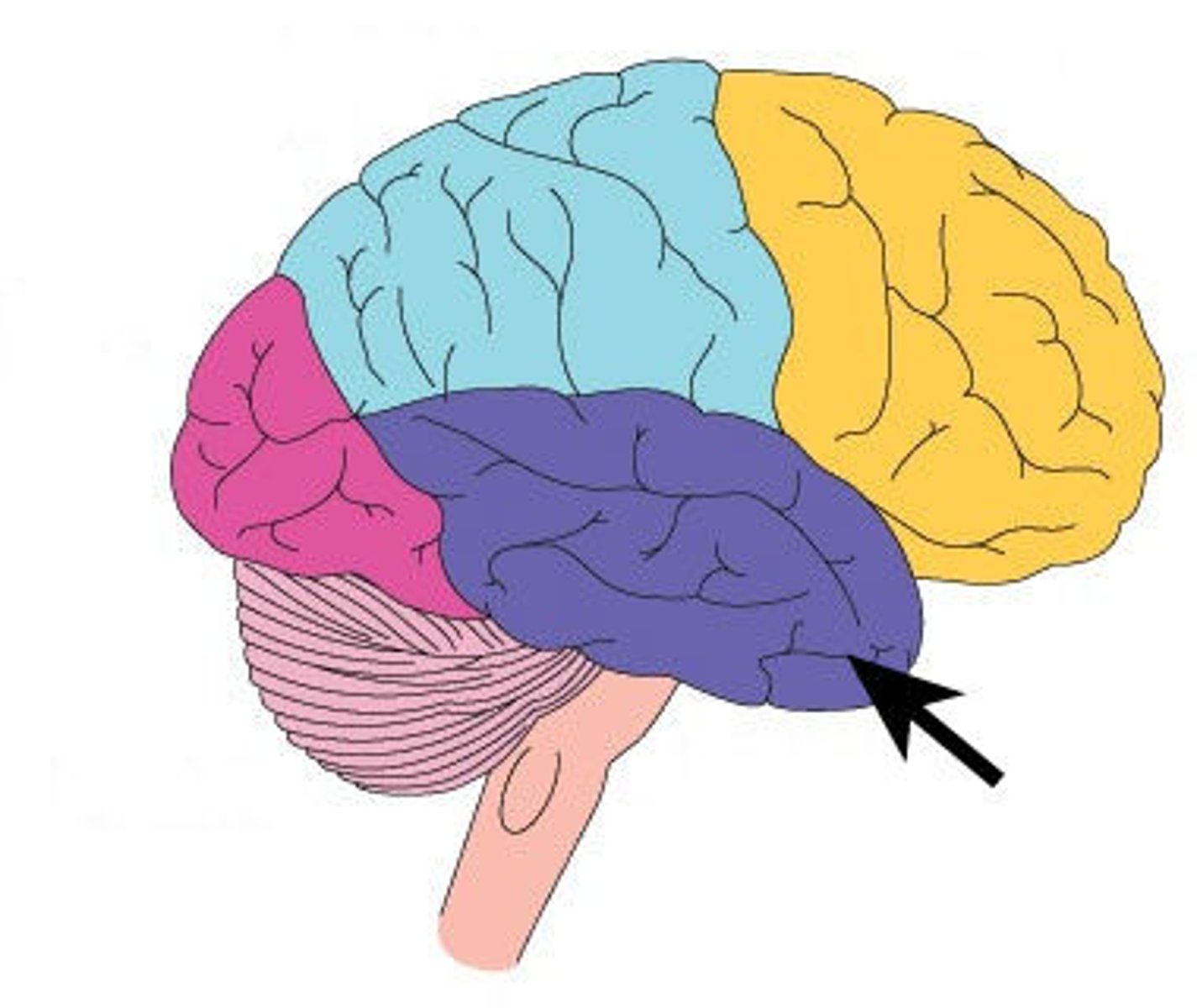
Occipital Lobe
Processes visual information.
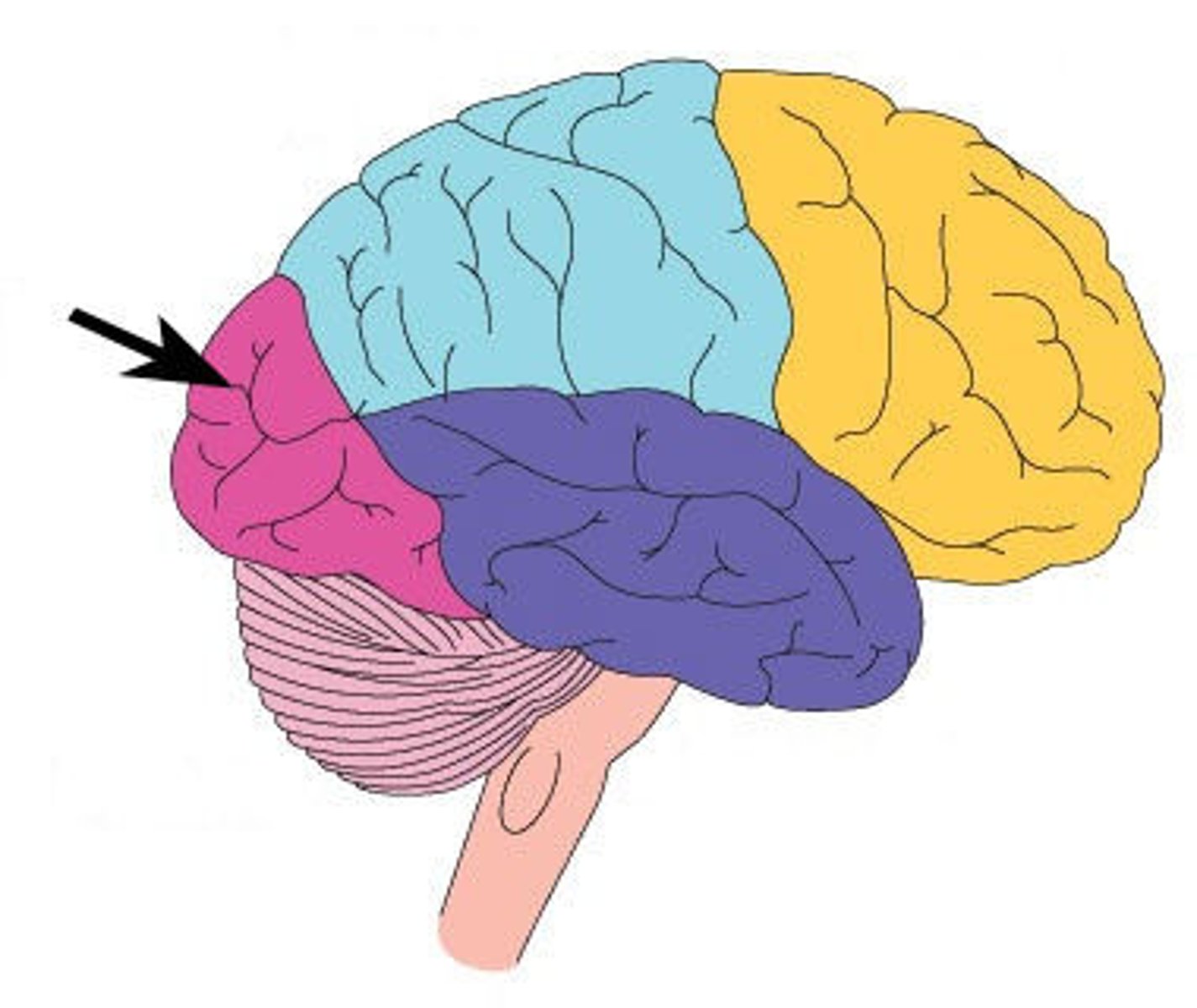
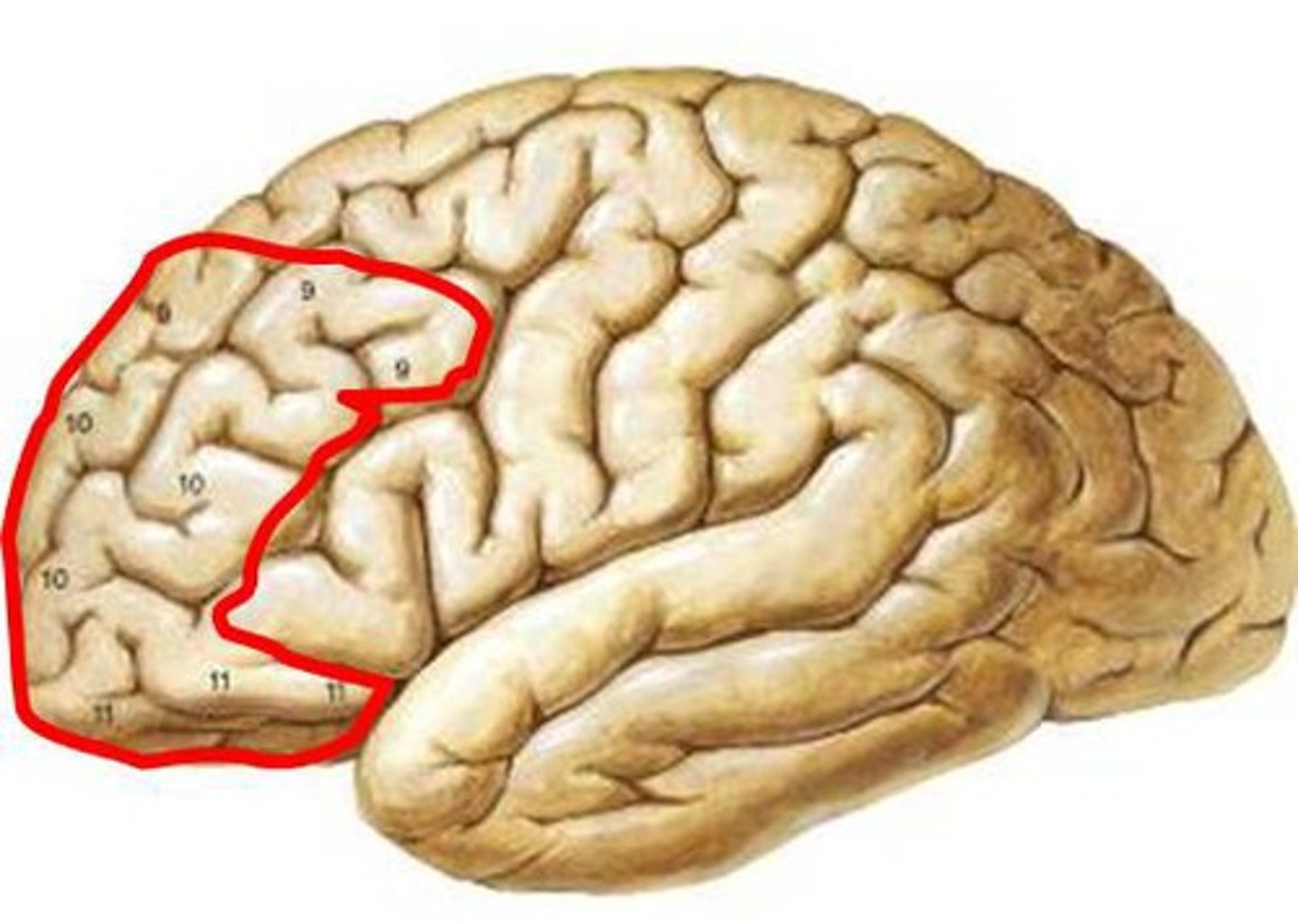
Prefrontal Cortex
Involved in complex thinking, planning, and personality.
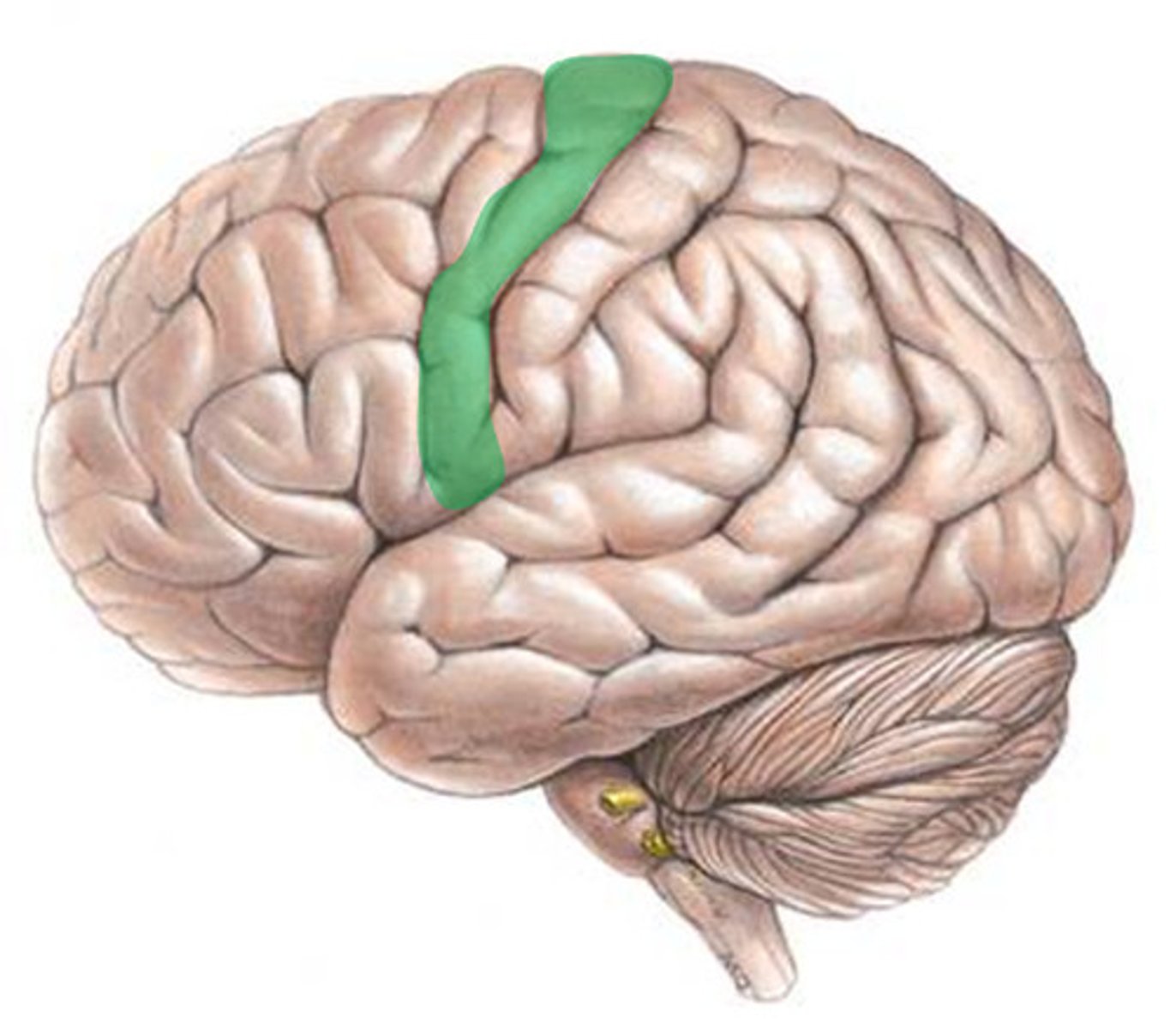
Primary Motor Area
Located in the precentral gyrus; initiates movement.
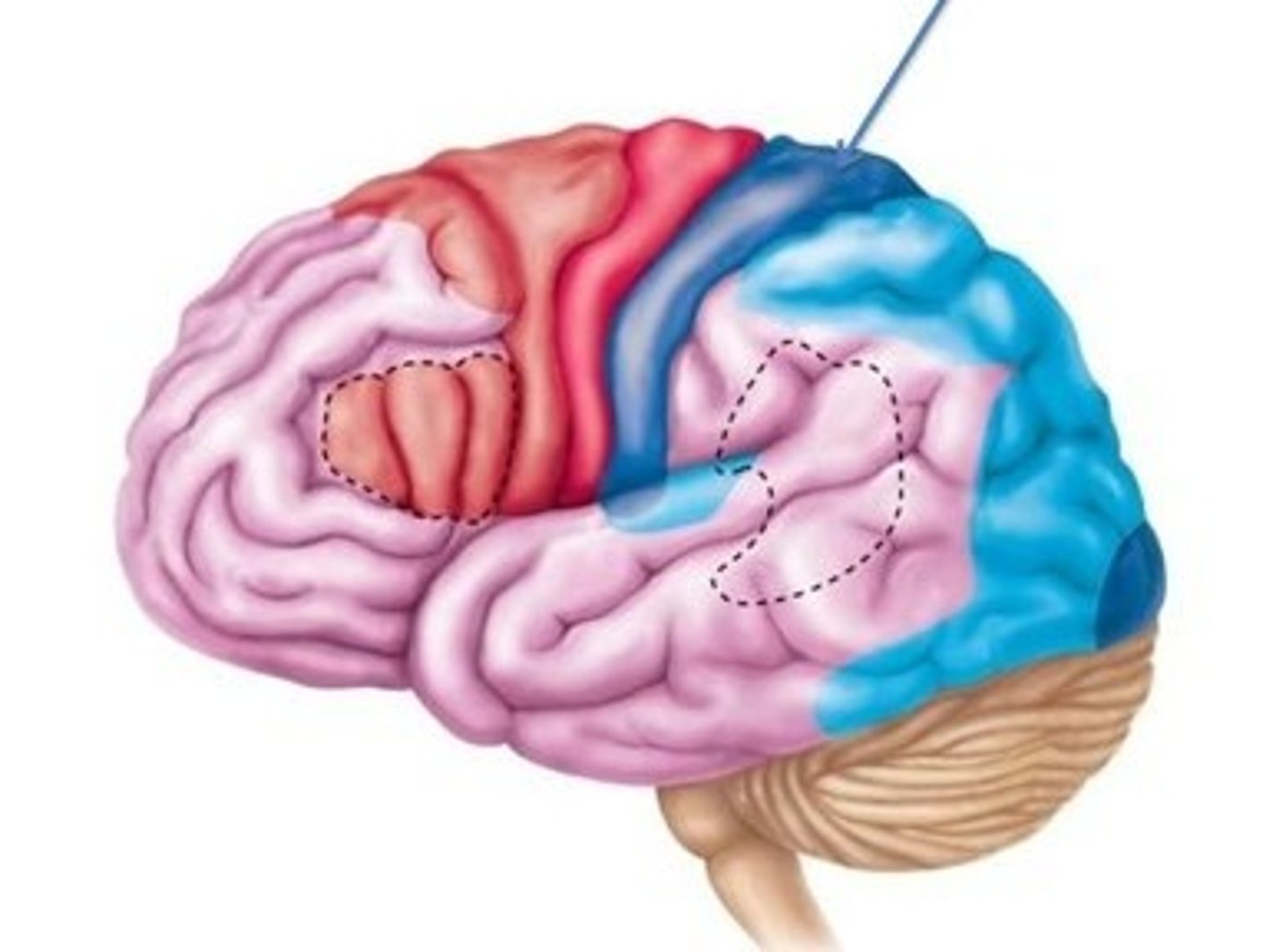
Broca's Area
Controls speech production (usually in the left frontal lobe).💡 Mnemonic Tip: "Broca = Broken Speech"
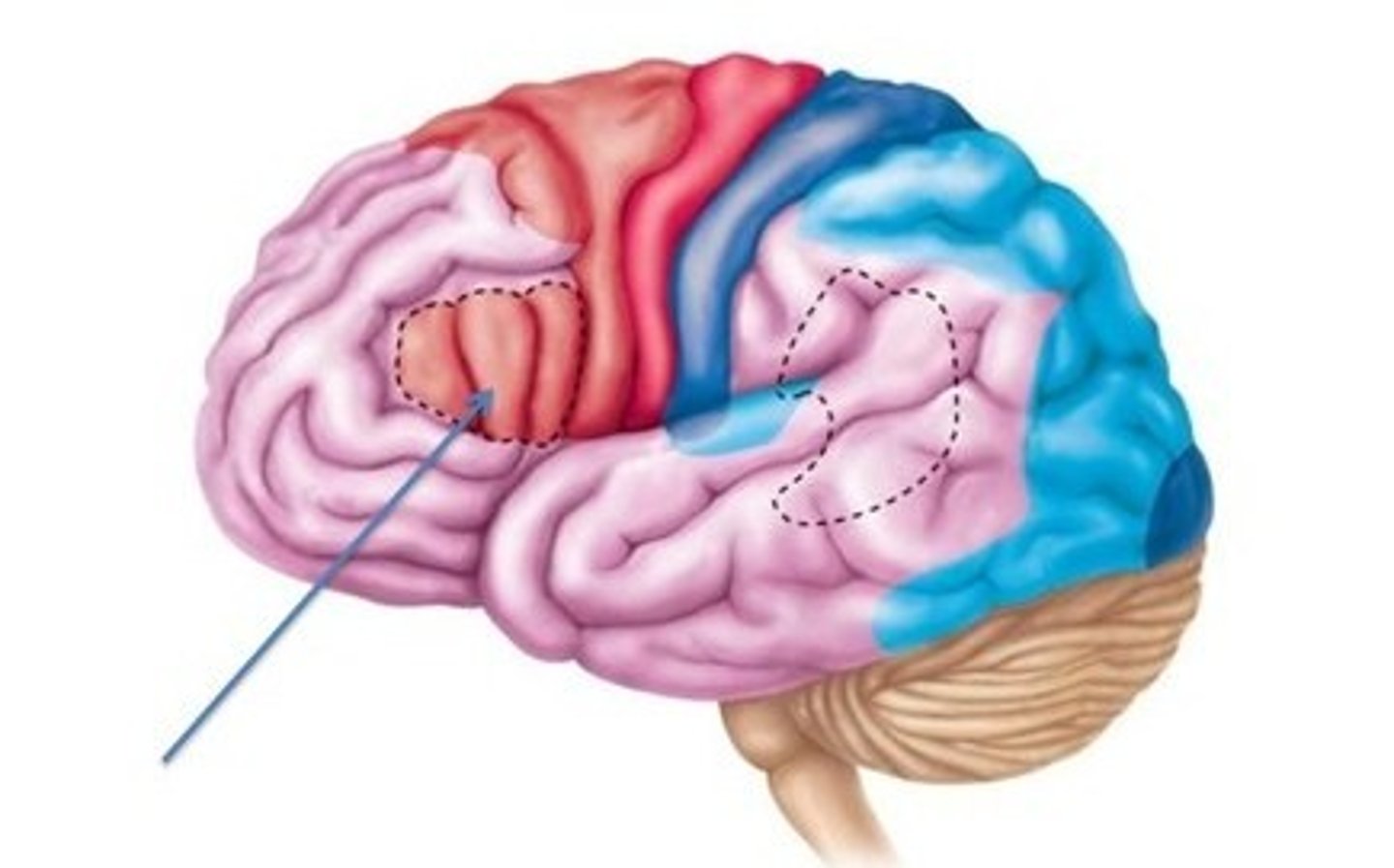
Wernicke's Area
Controls speech comprehension (temporal lobe).💡 Mnemonic Tip: "Wernicke = Word Salad when damaged"
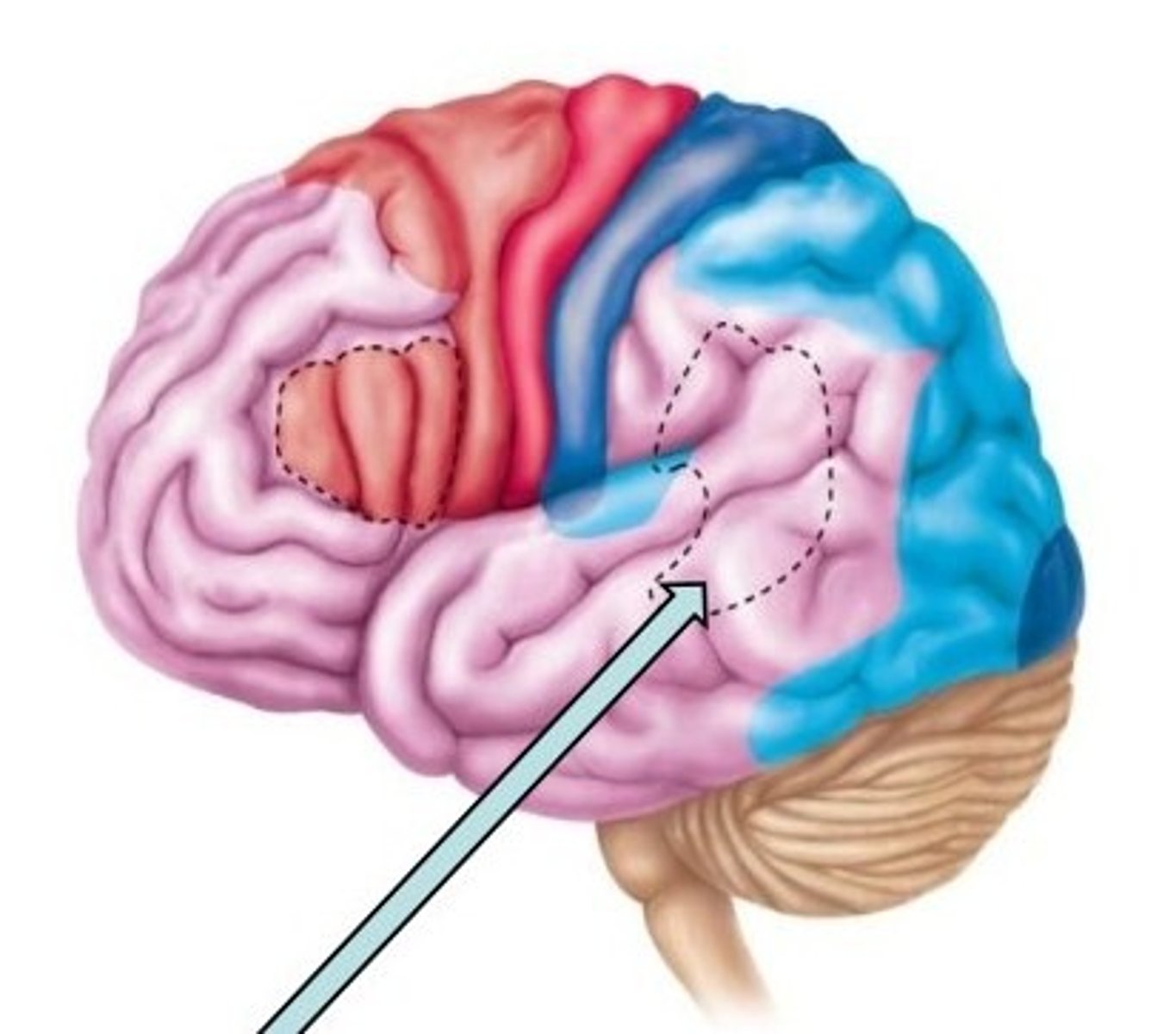
Primary Somatosensory Area
Receives and interprets sensory input.
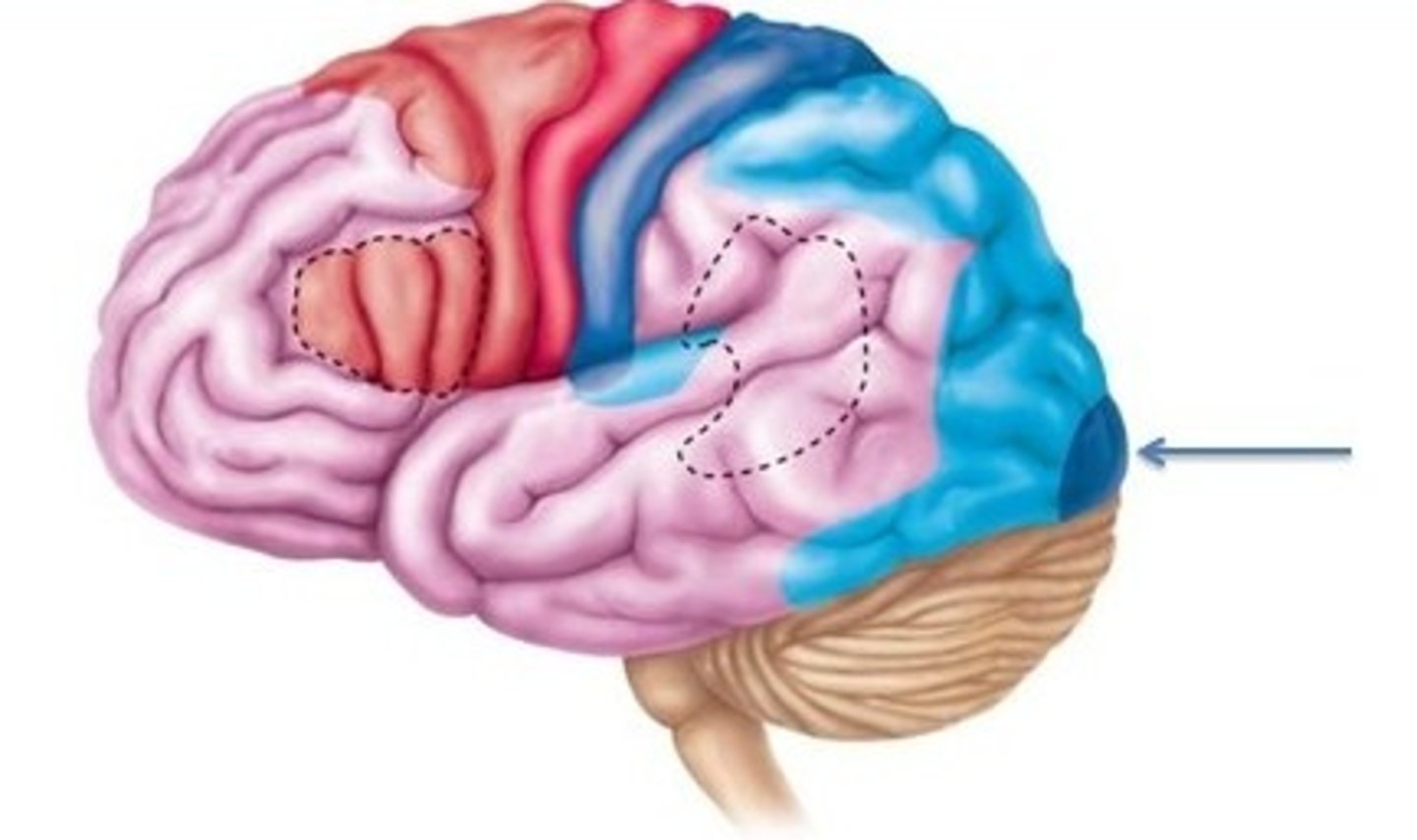
Primary Visual Cortex
Interprets visual stimuli (occipital lobe).
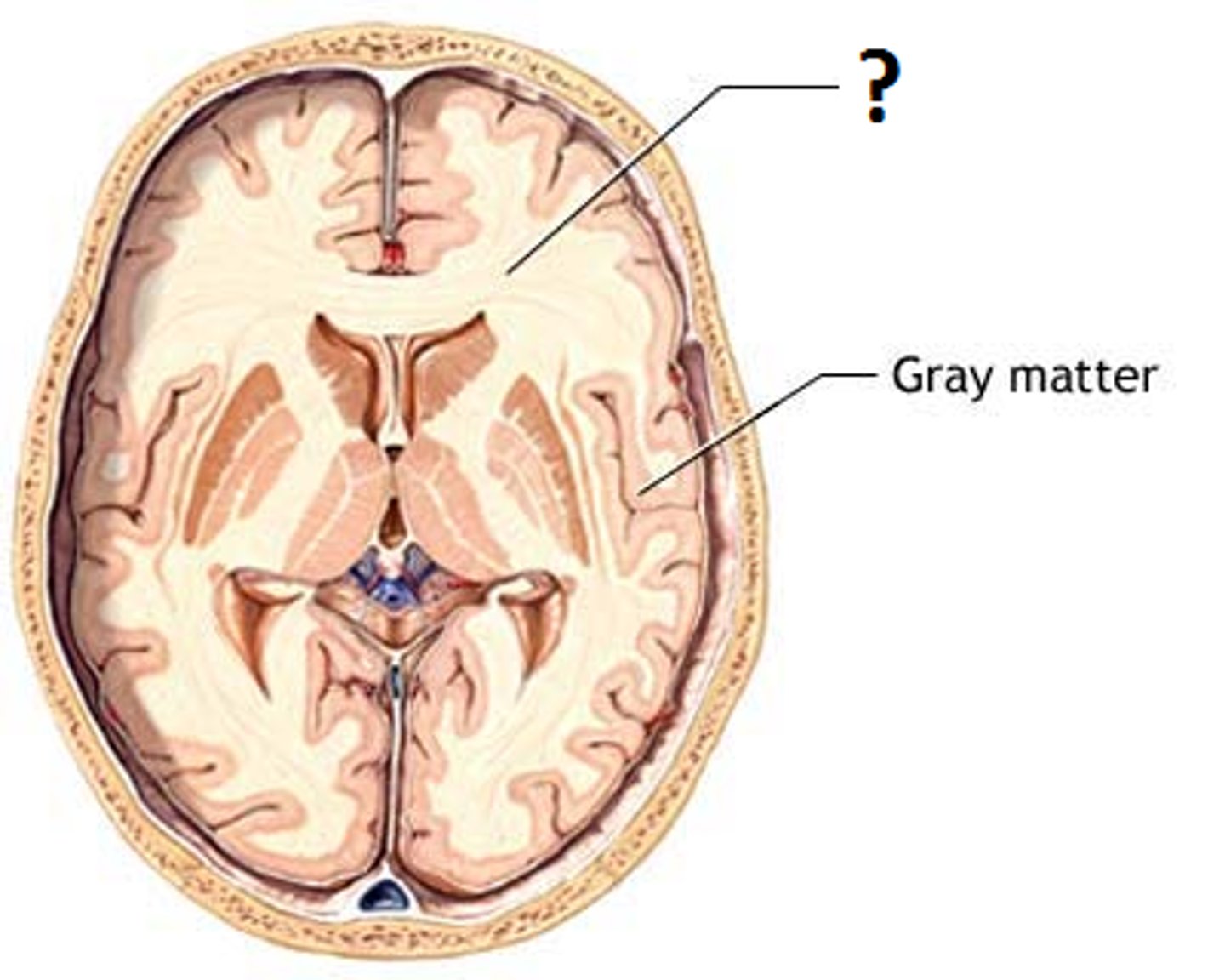
Gray Matter
Contains neuron cell bodies; found on brain surface and inside spinal cord.(opposite of spinal cord)
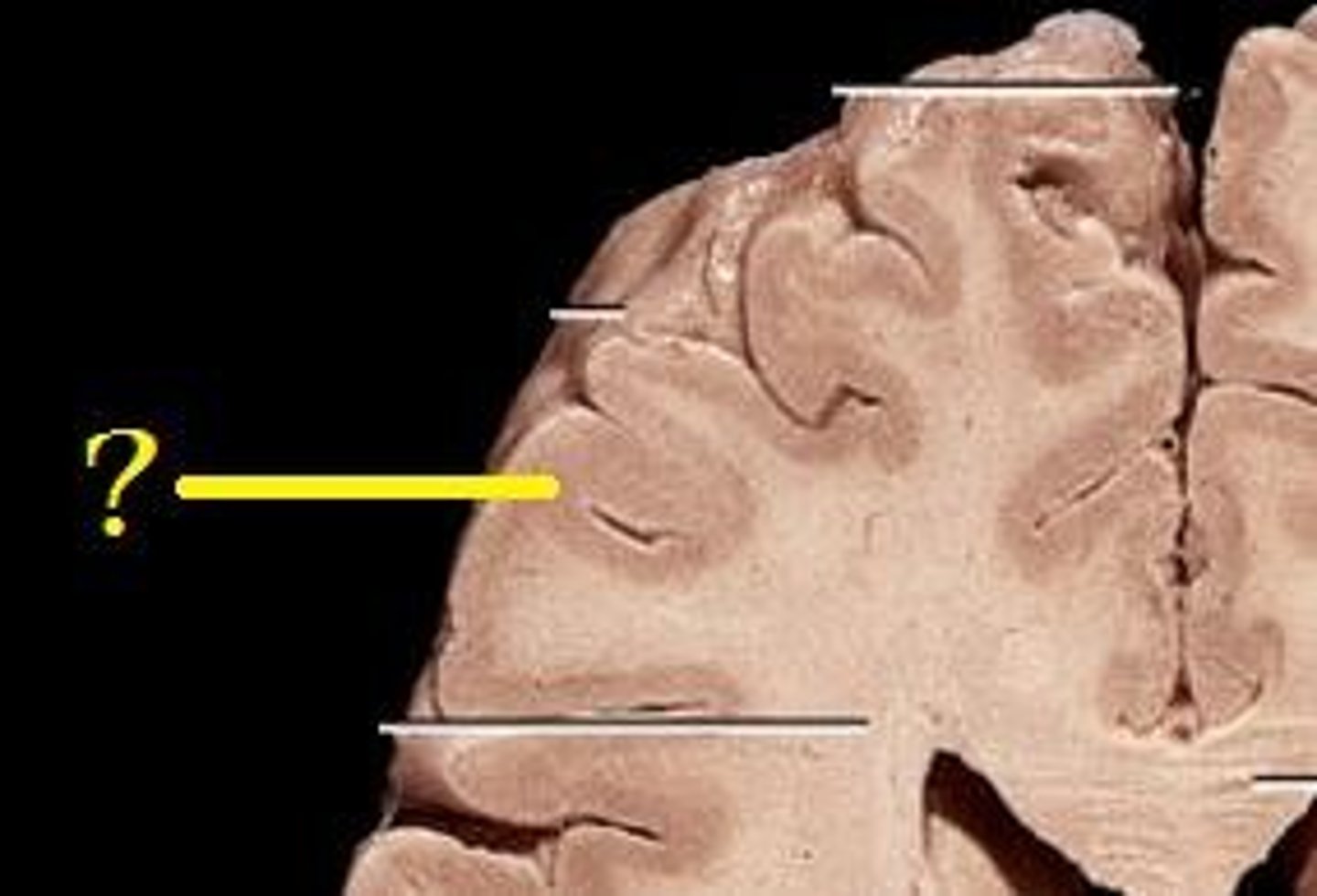
White Matter
Myelinated axons; transmits signals between brain regions.
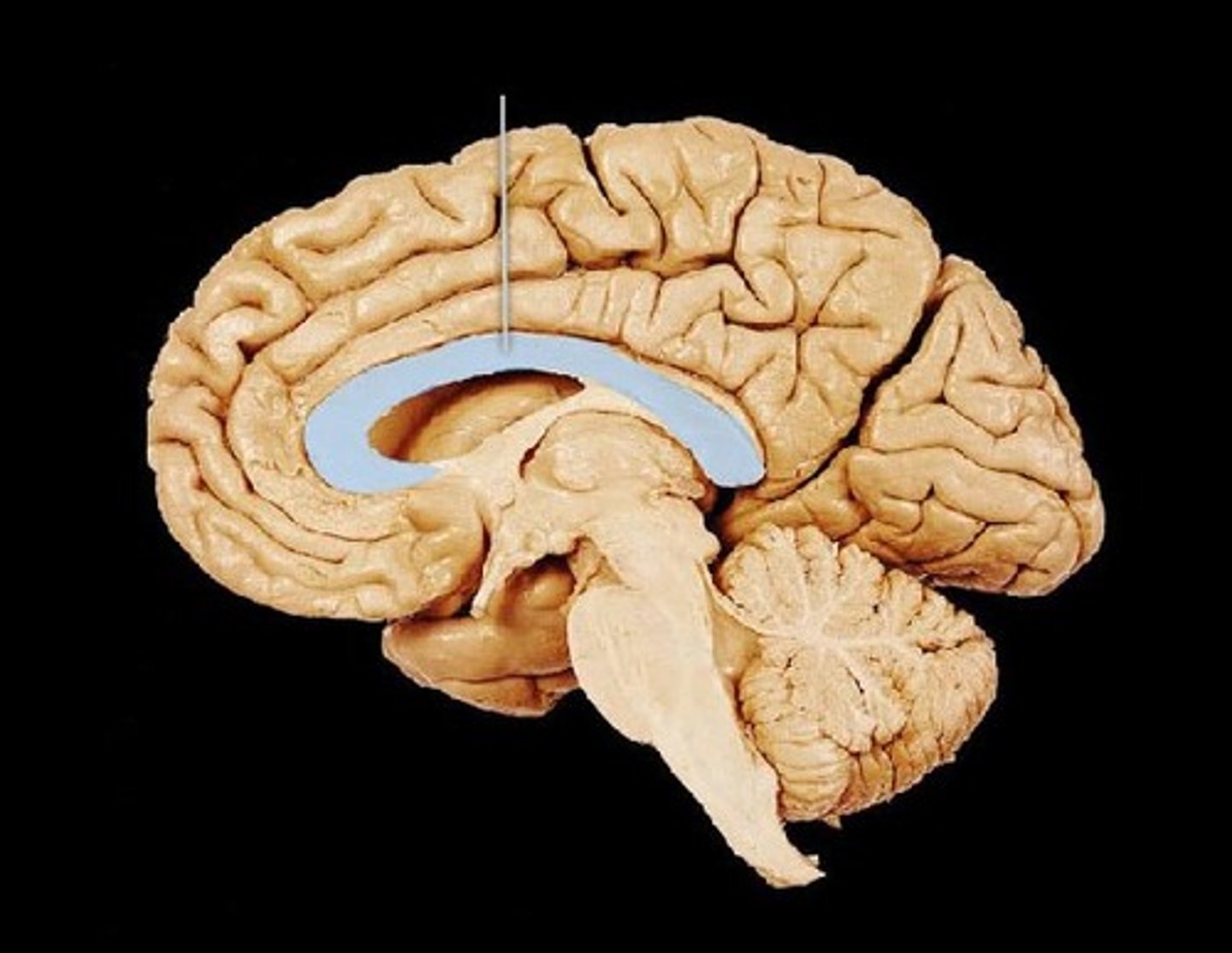
Corpus Callosum
Thick band of white matter connecting the two cerebral hemispheres.
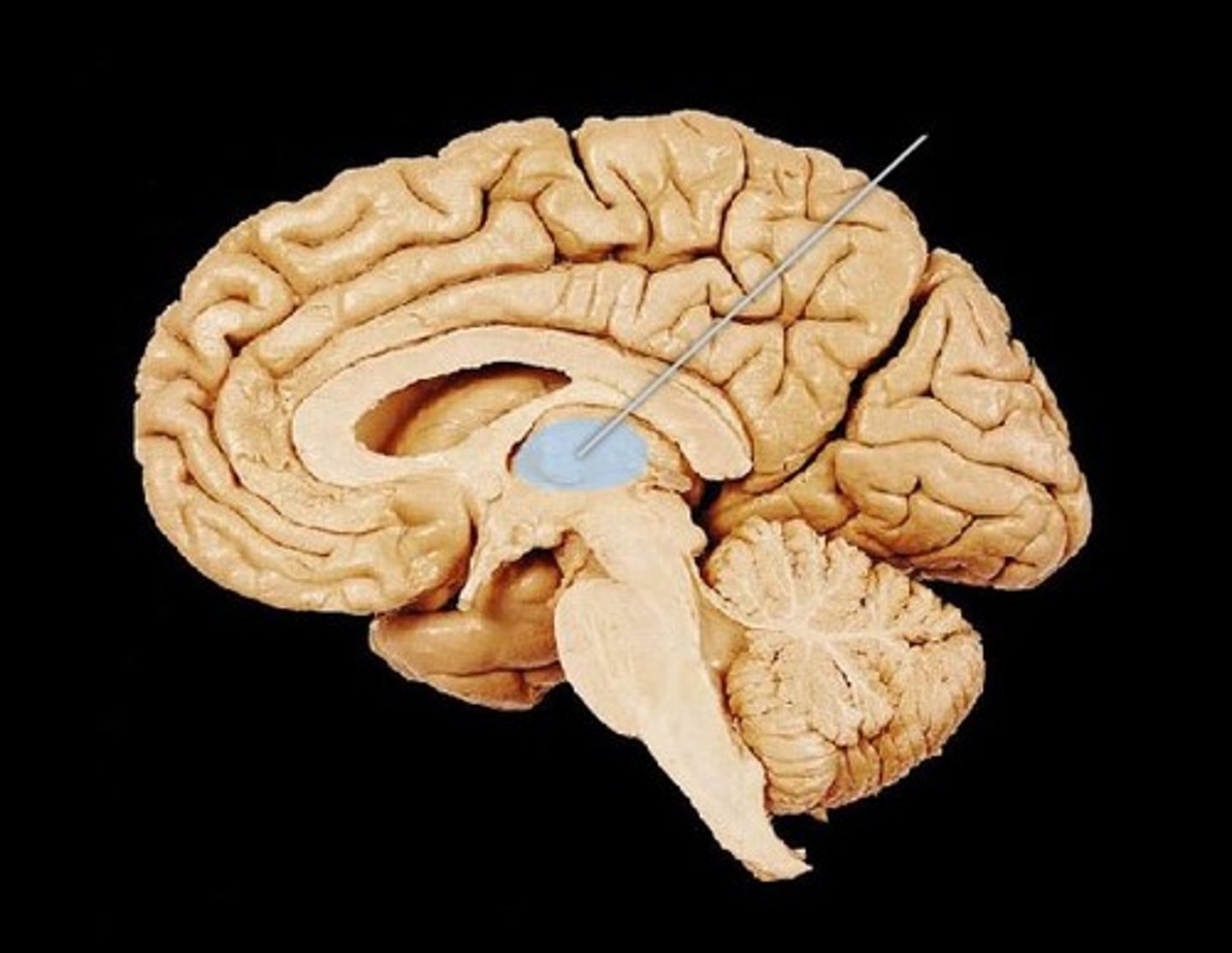
Thalamus
Relay station for sensory information.( Diencephalon)
Hypothalamus
Regulates temperature, hunger, thirst, hormones.( Diencephalon)
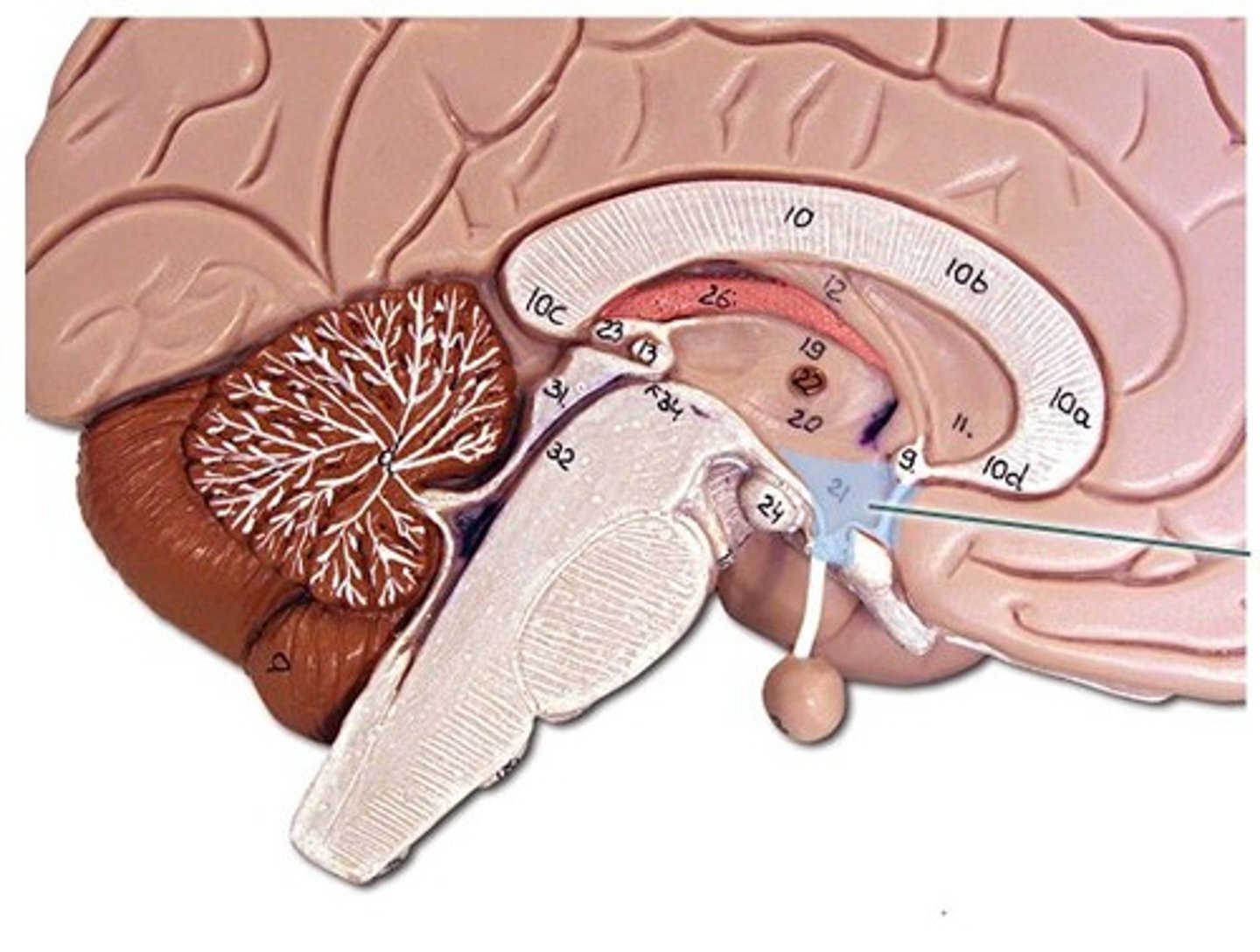
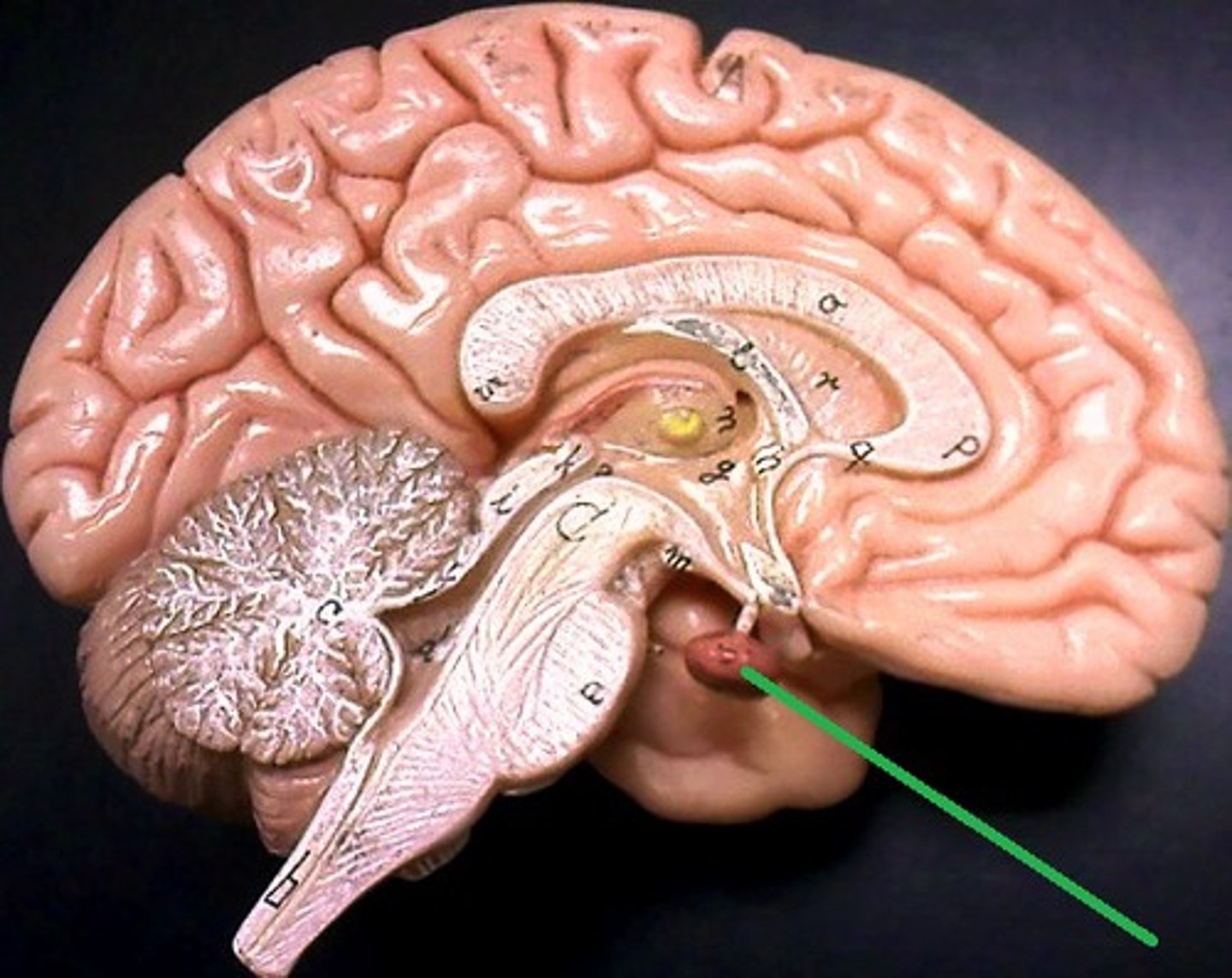
Pituitary Gland
Master gland; releases hormones under hypothalamus control. ( Diencephalon)
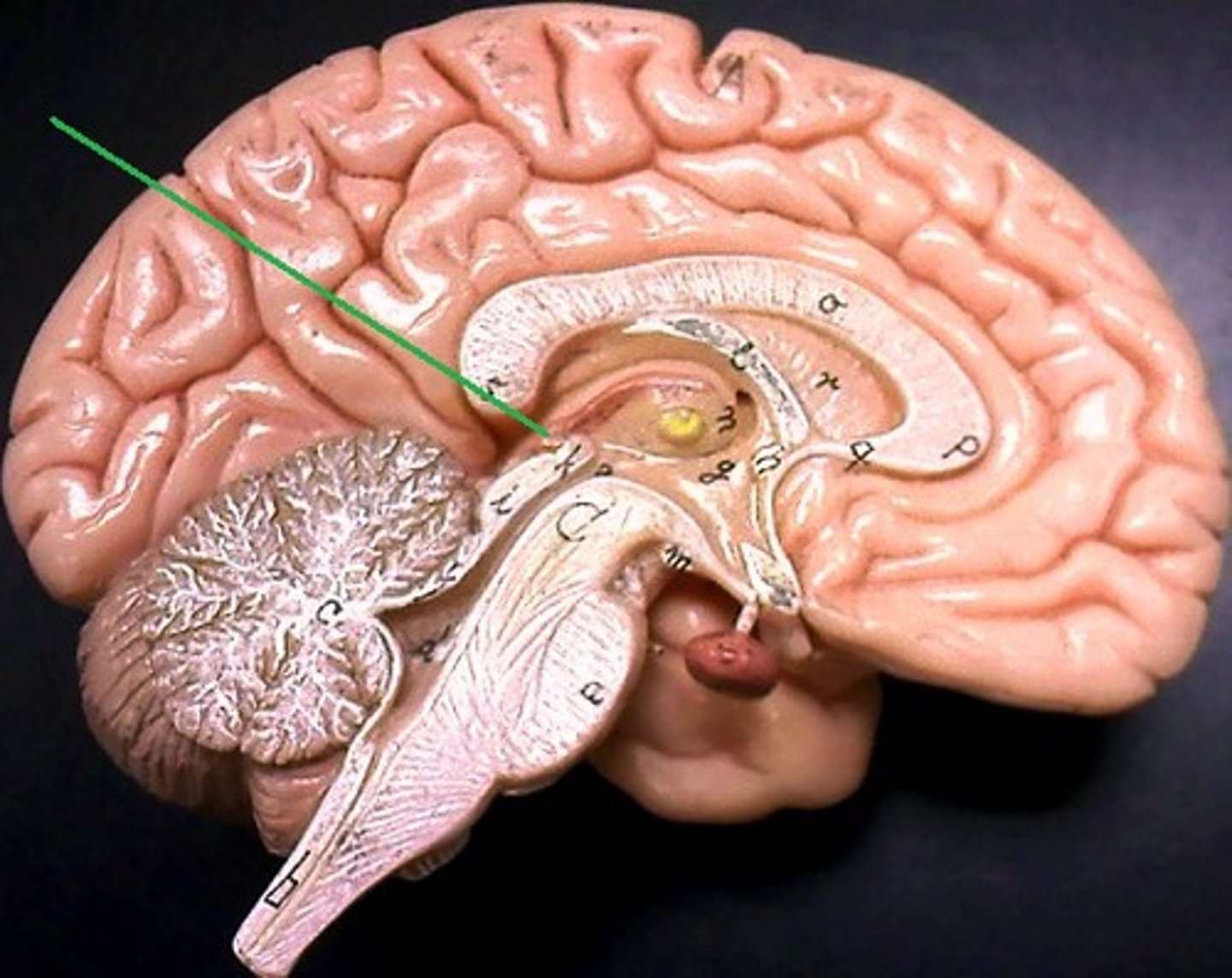
Pineal Gland
Secretes melatonin; controls sleep-wake cycle. .*part of the epithalamus ( Diencephalon)
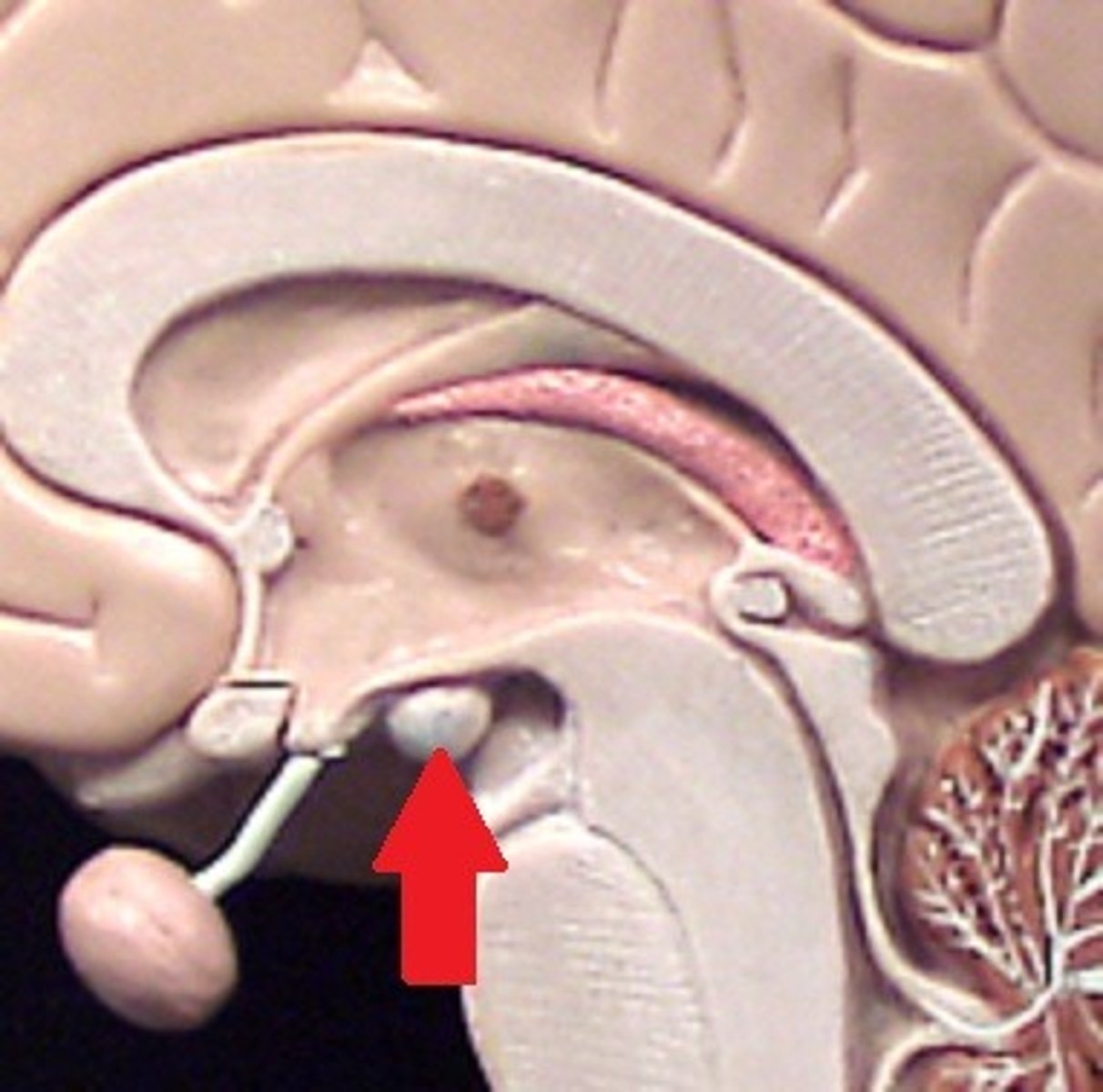
Mammillary Bodies
Involved in memory processing.( Diencephalon)
Midbrain
Coordinates visual and auditory reflexes.( Brain Stem)
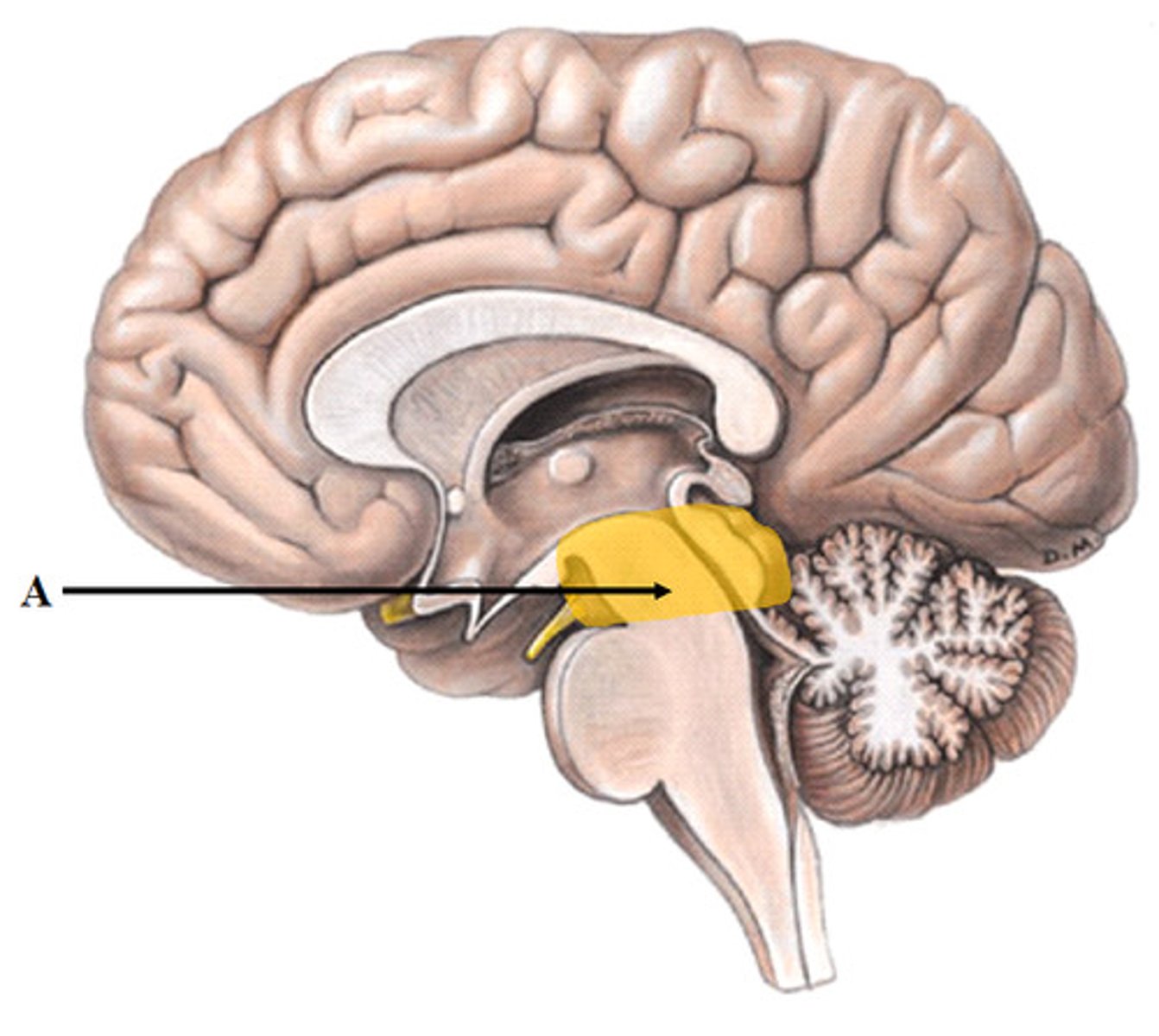
Corpora Quadrigemina
Four bumps on the midbrain:( Brain Stem) Superior Colliculi = visual reflexes Inferior Colliculi = auditory reflexes
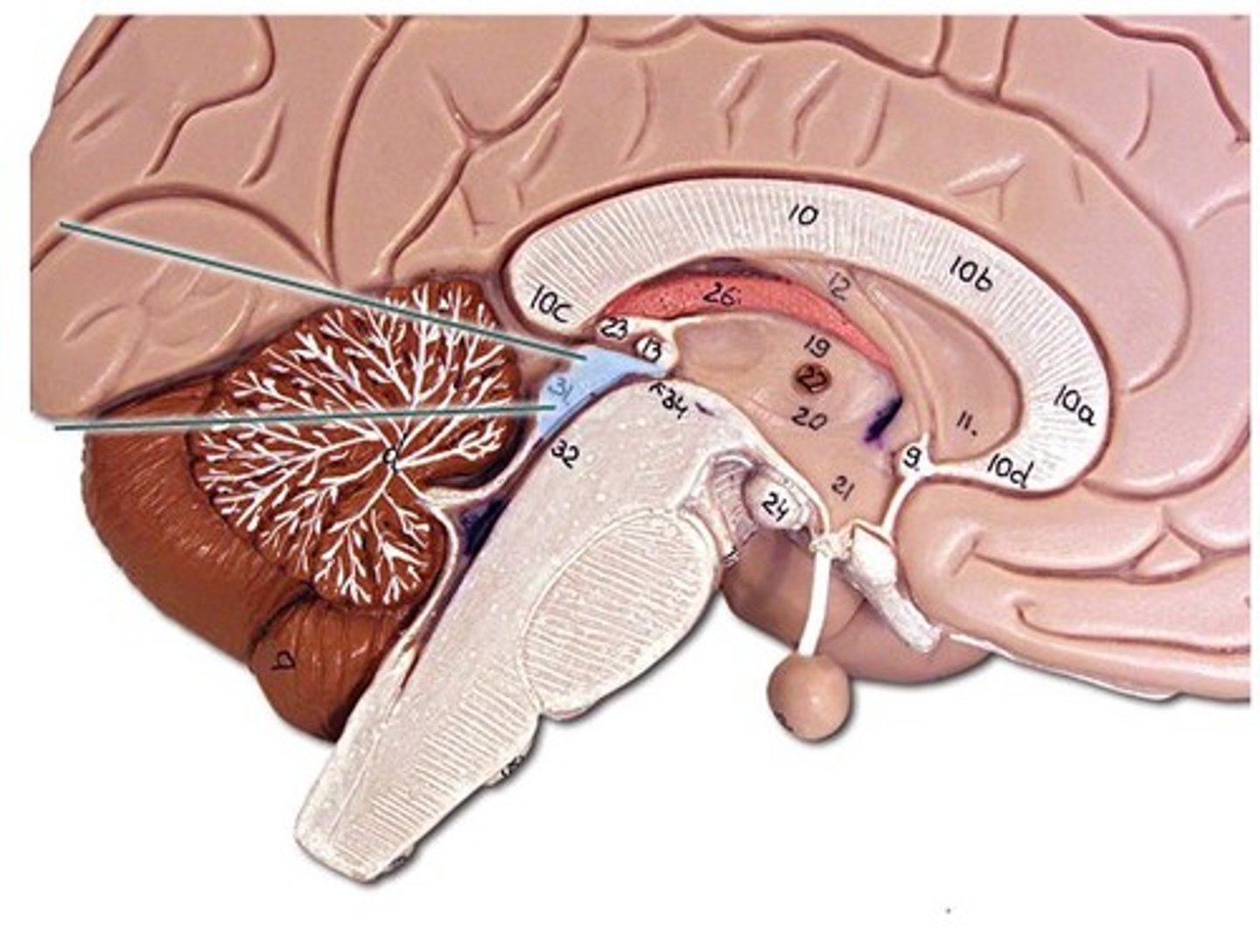
Pons
Relays information between the cerebrum and the cerebellum; assists in breathing. ( Brain Stem)
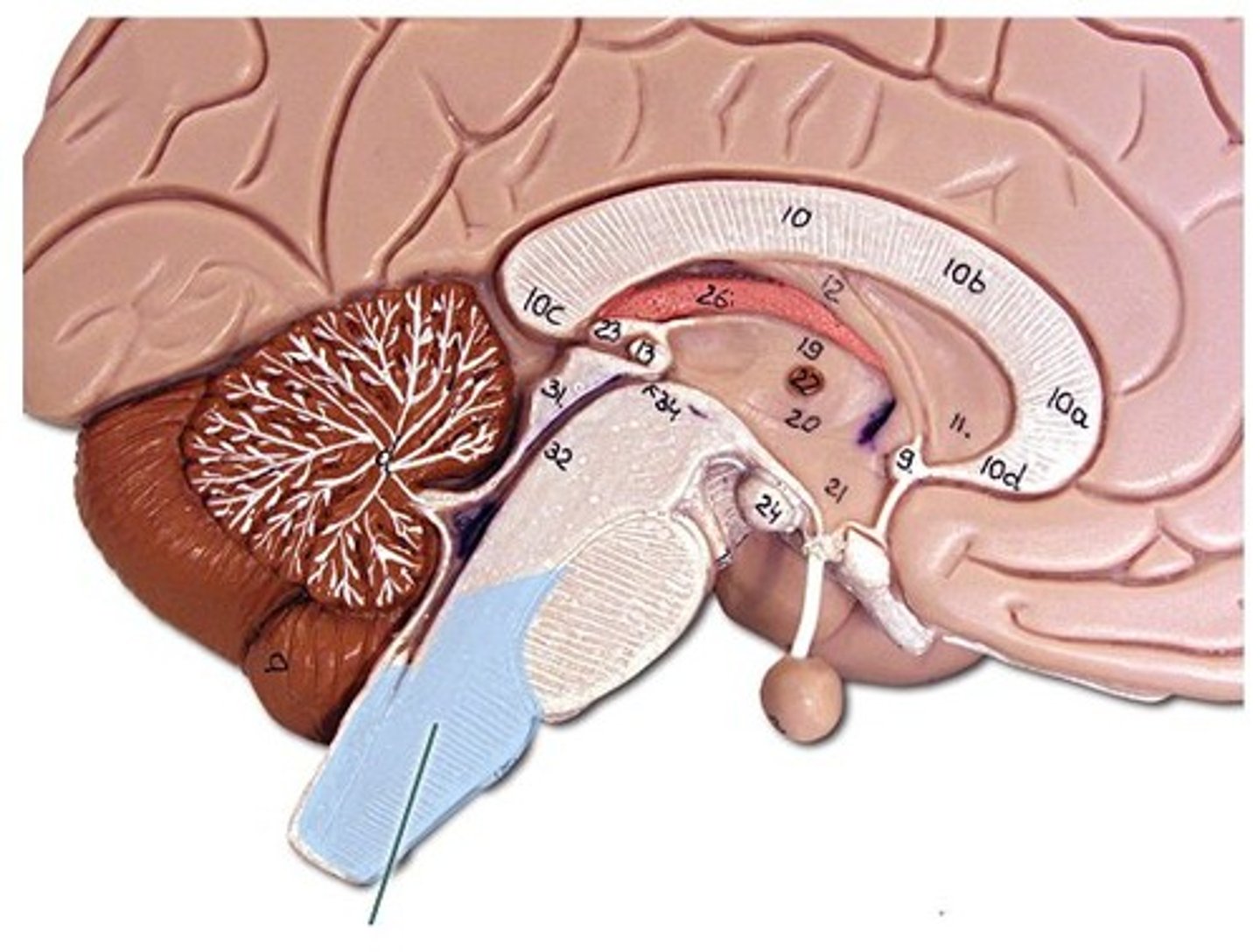
Medulla Oblongata
Controls vital functions—heart rate, breathing, blood pressure.( Brain Stem)
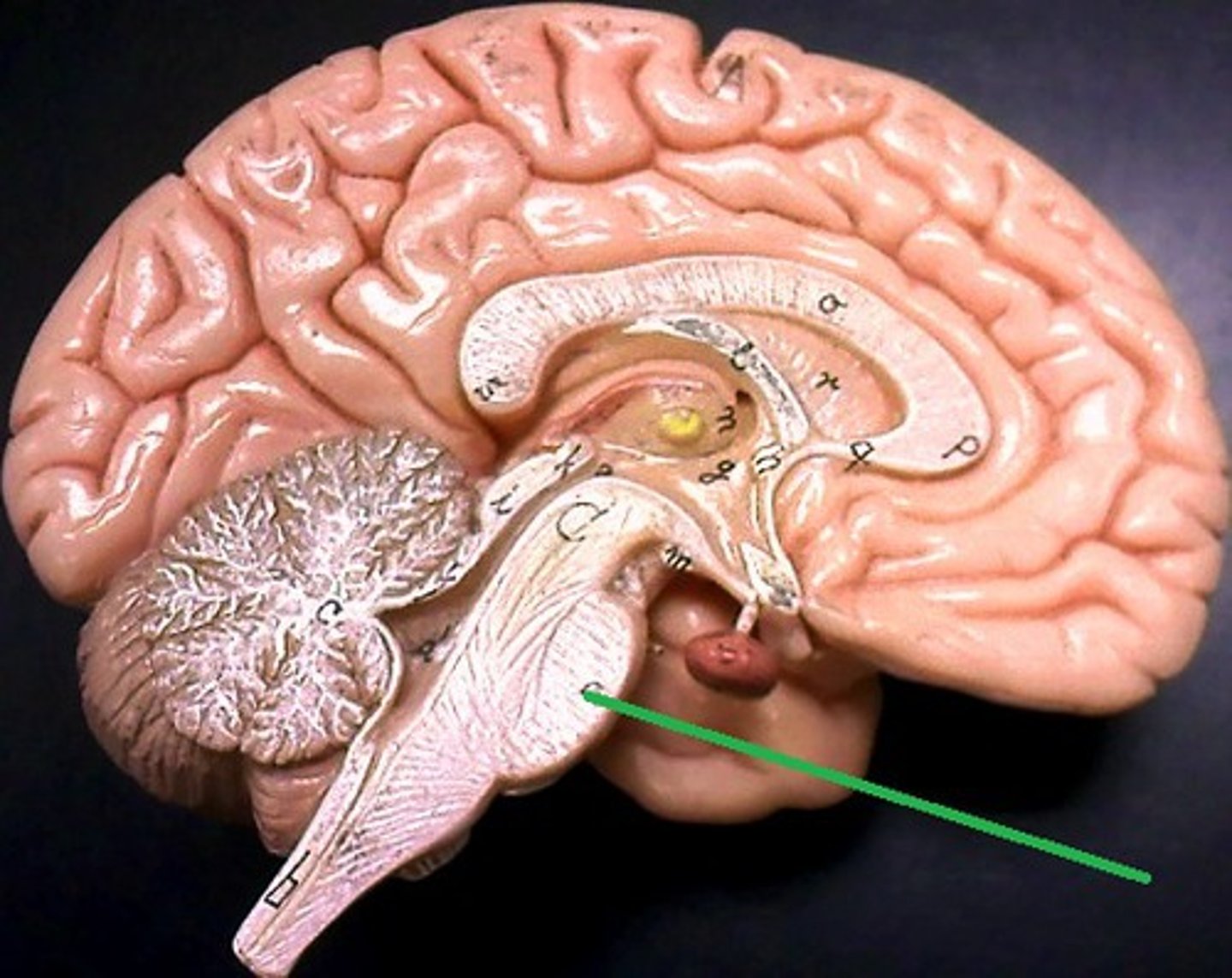
Cerebellum
Coordinates balance, posture, and fine motor movements.
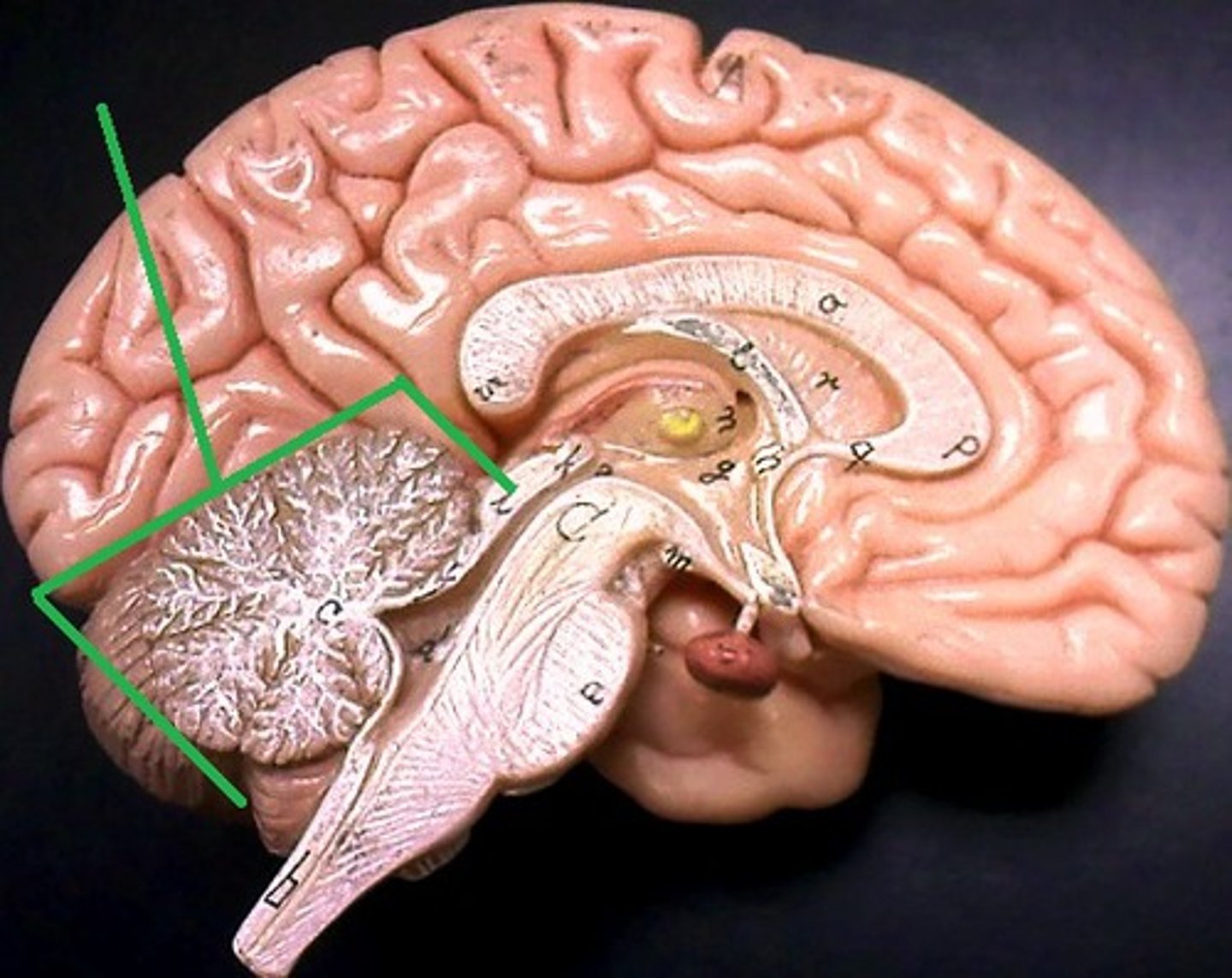
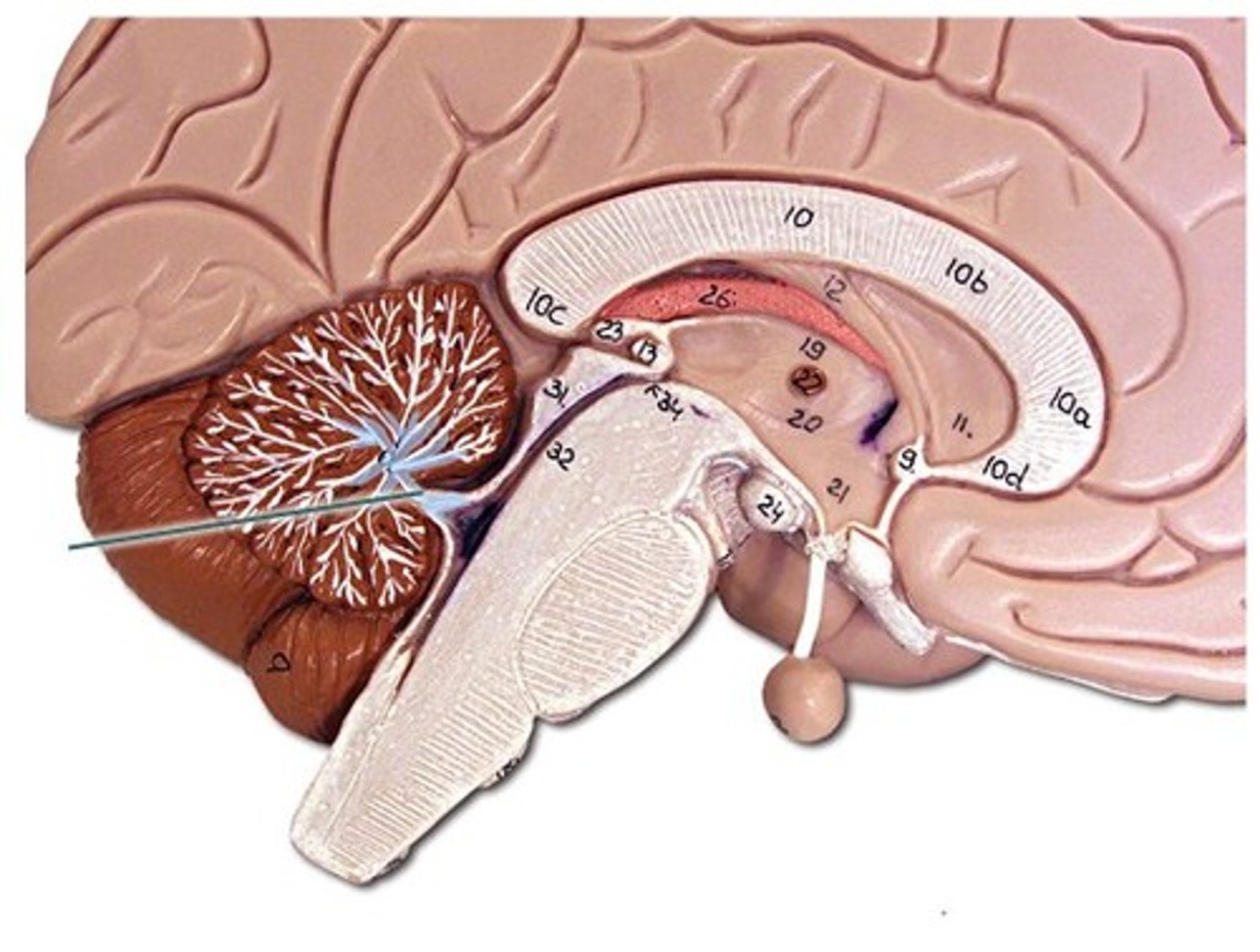
Arbor Vitae
Tree-like white matter inside cerebellum/( Cerebellum)
“Some Say Marry Money But My Brother Says Big Brains Matter More”
Mnemonic for Function (S = Sensory, M = Motor, B = Both)
“Oh, once one takes the anatomy final, very good vacations are heavenly.”
Mnemonic for Cranial Nerves I-X
Olfactory Nerve (Sensory)
Cranial Nerve I - Responsible for sense of smell.
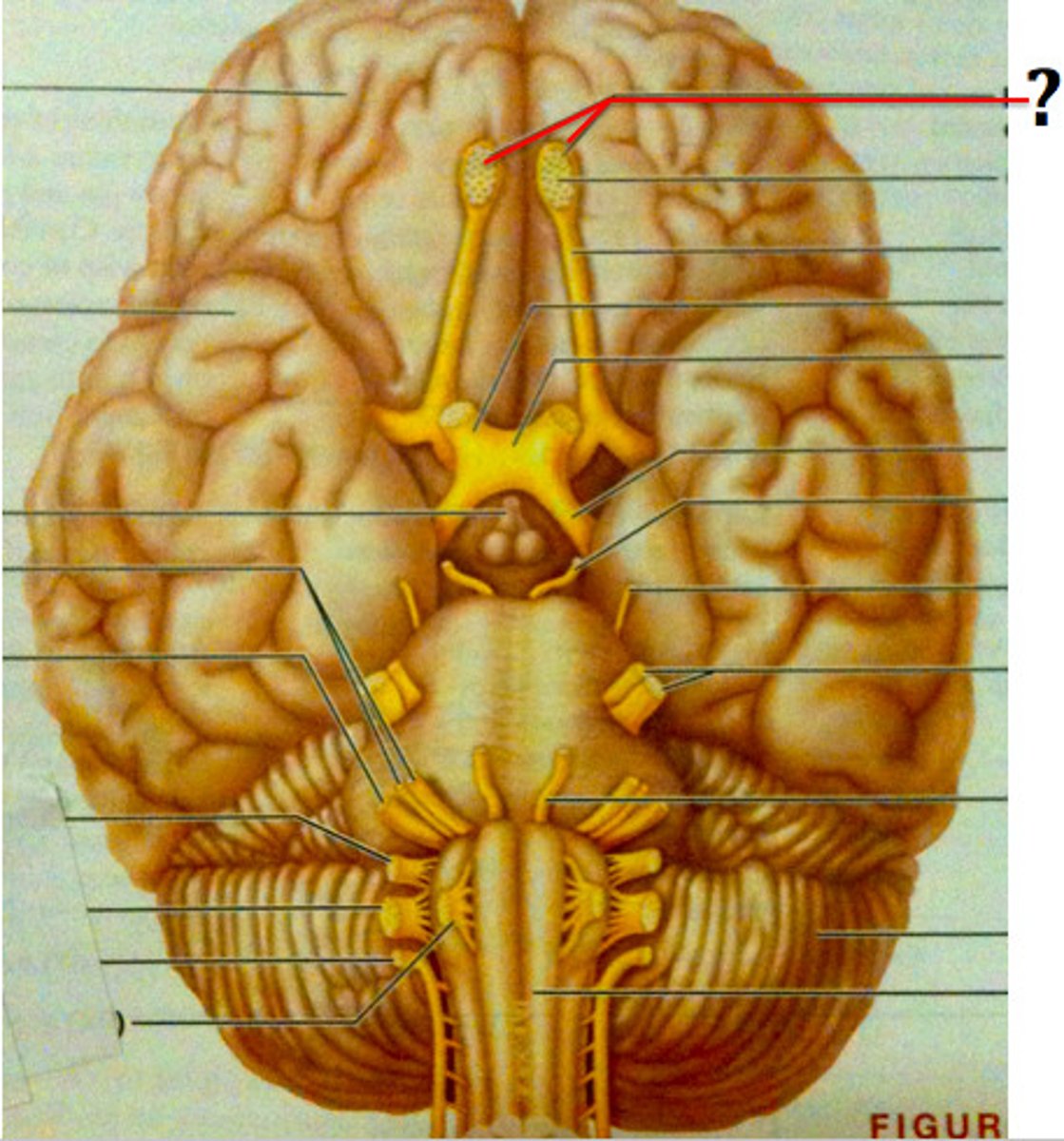
Optic Nerve (Sensory)
Cranial Nerve II - Responsible for vision.
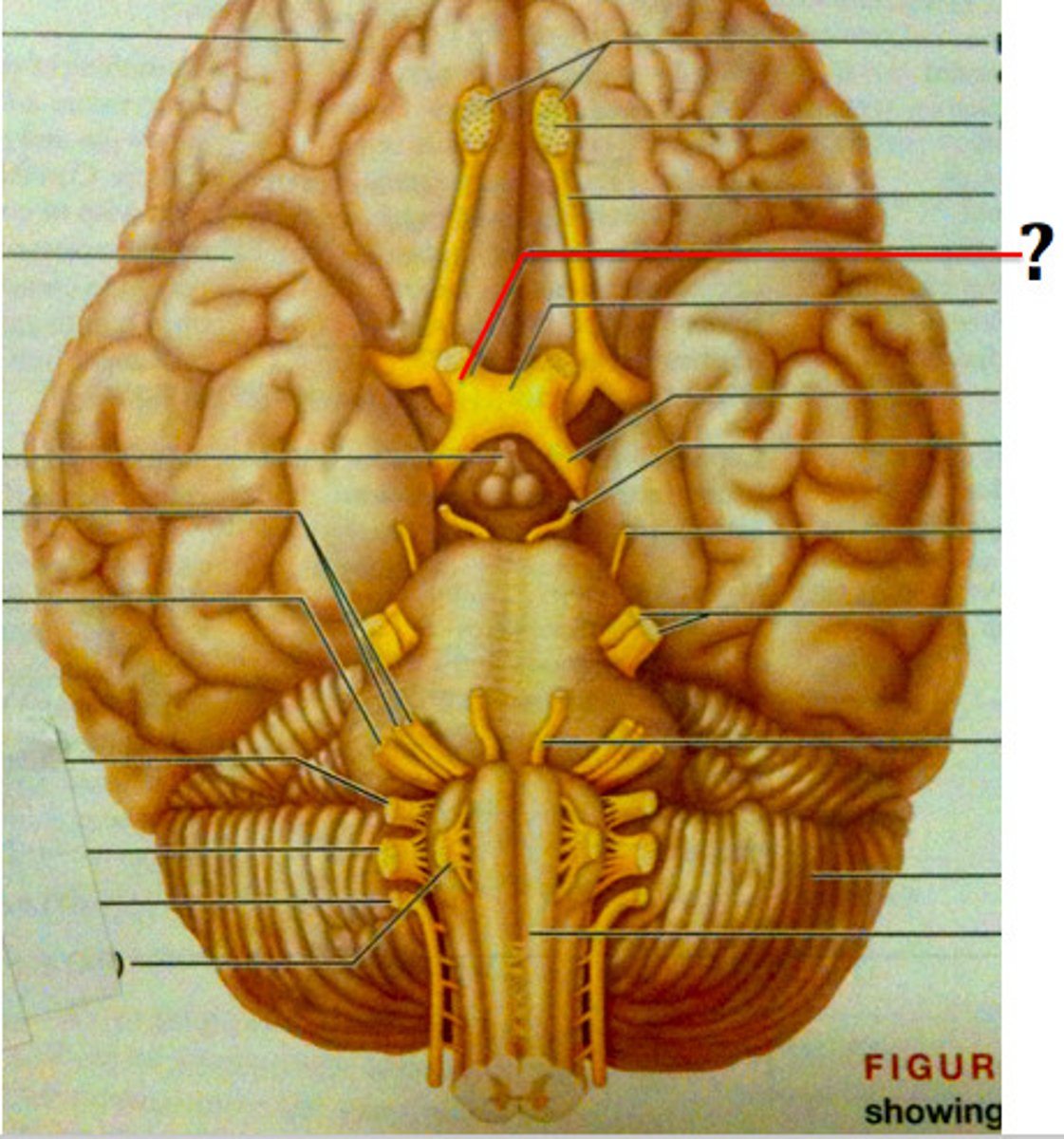
Oculomotor Nerve (Motor)
Cranial Nerve III - Controls most eye movements, pupil constriction, and eyelid movement.
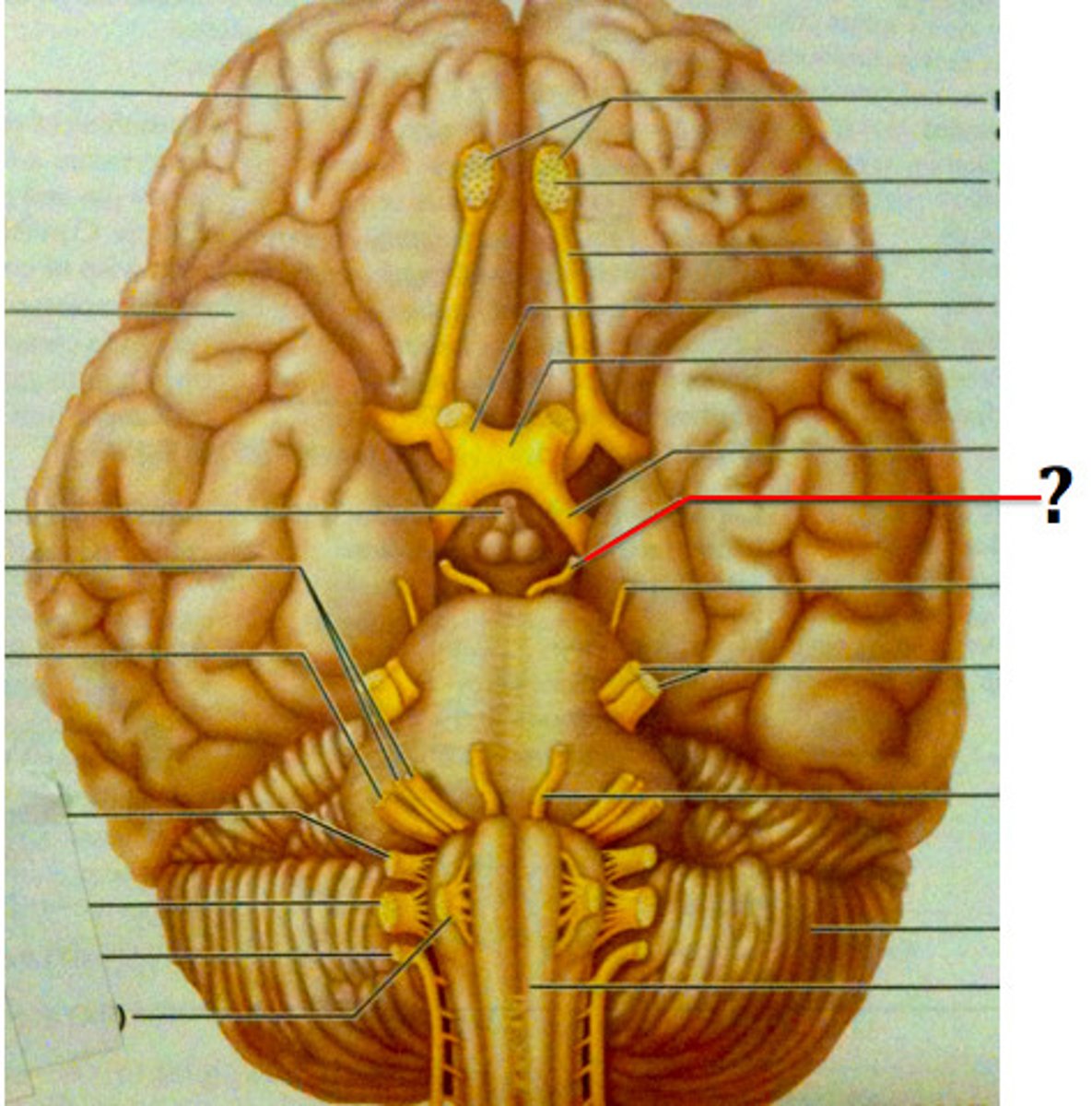
Trochlear Nerve (Motor)
Cranial Nerve IV - Moves the eye downward and laterally via the superior oblique muscle.
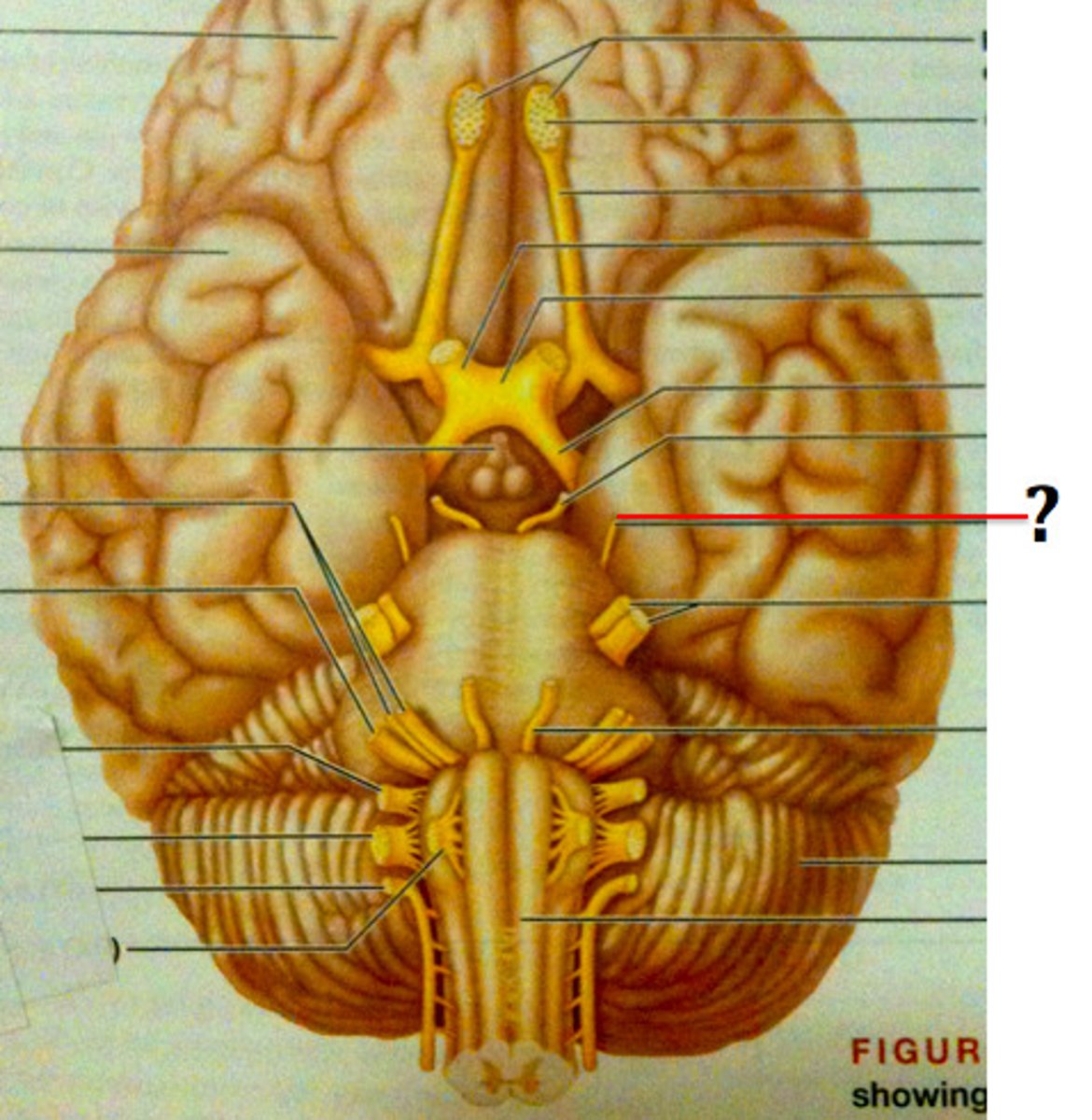
Trigeminal Nerve (Both)
Cranial Nerve V - Controls facial sensation, chewing muscles (mastication).
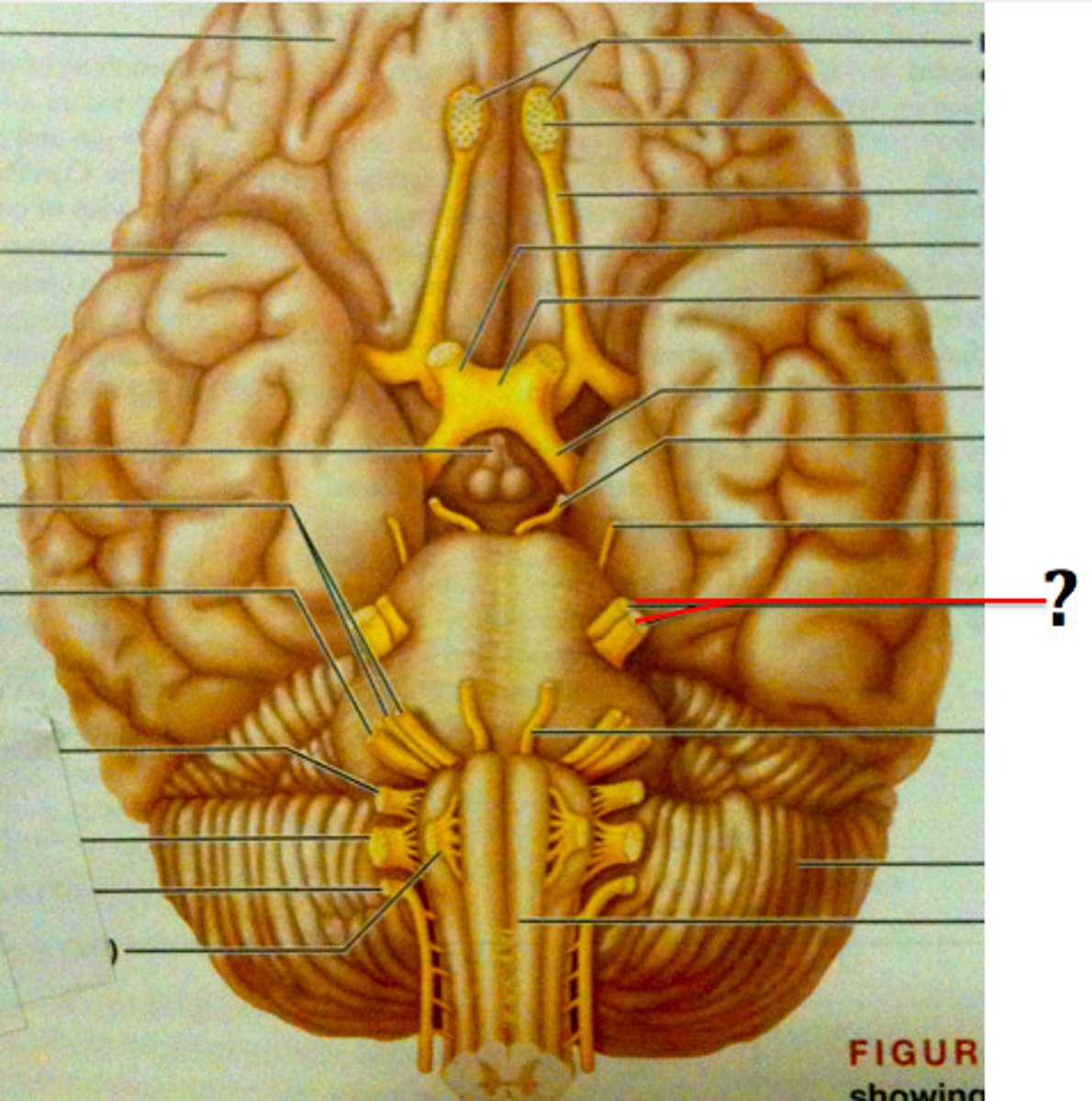
Abducens Nerve (Motor)
Cranial Nerve VI - Moves the eye laterally via the lateral rectus muscle.
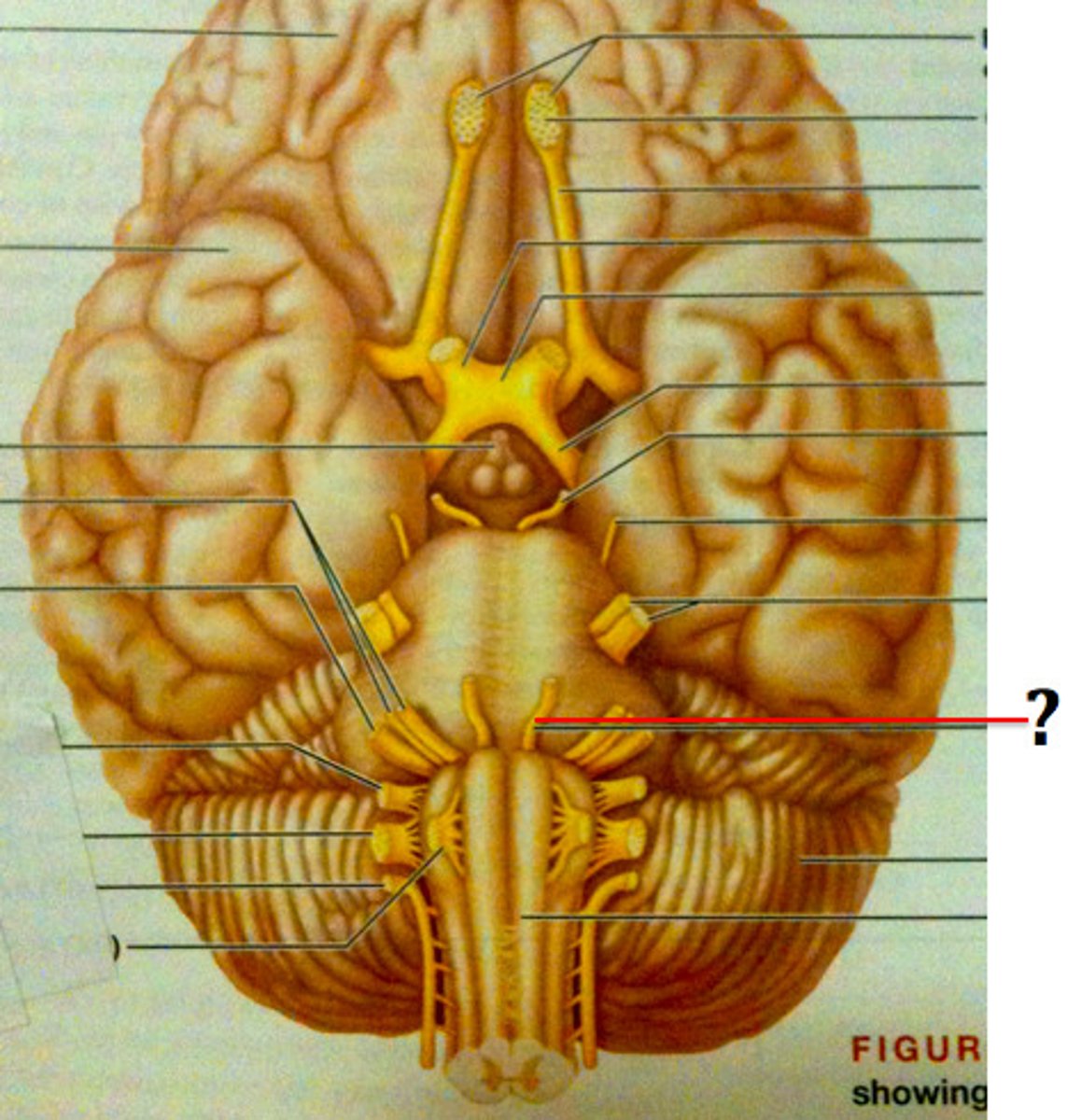
Facial Nerve (Both)
Cranial Nerve VII - Controls facial expressions, taste on front 2/3 of tongue, and tears/saliva.
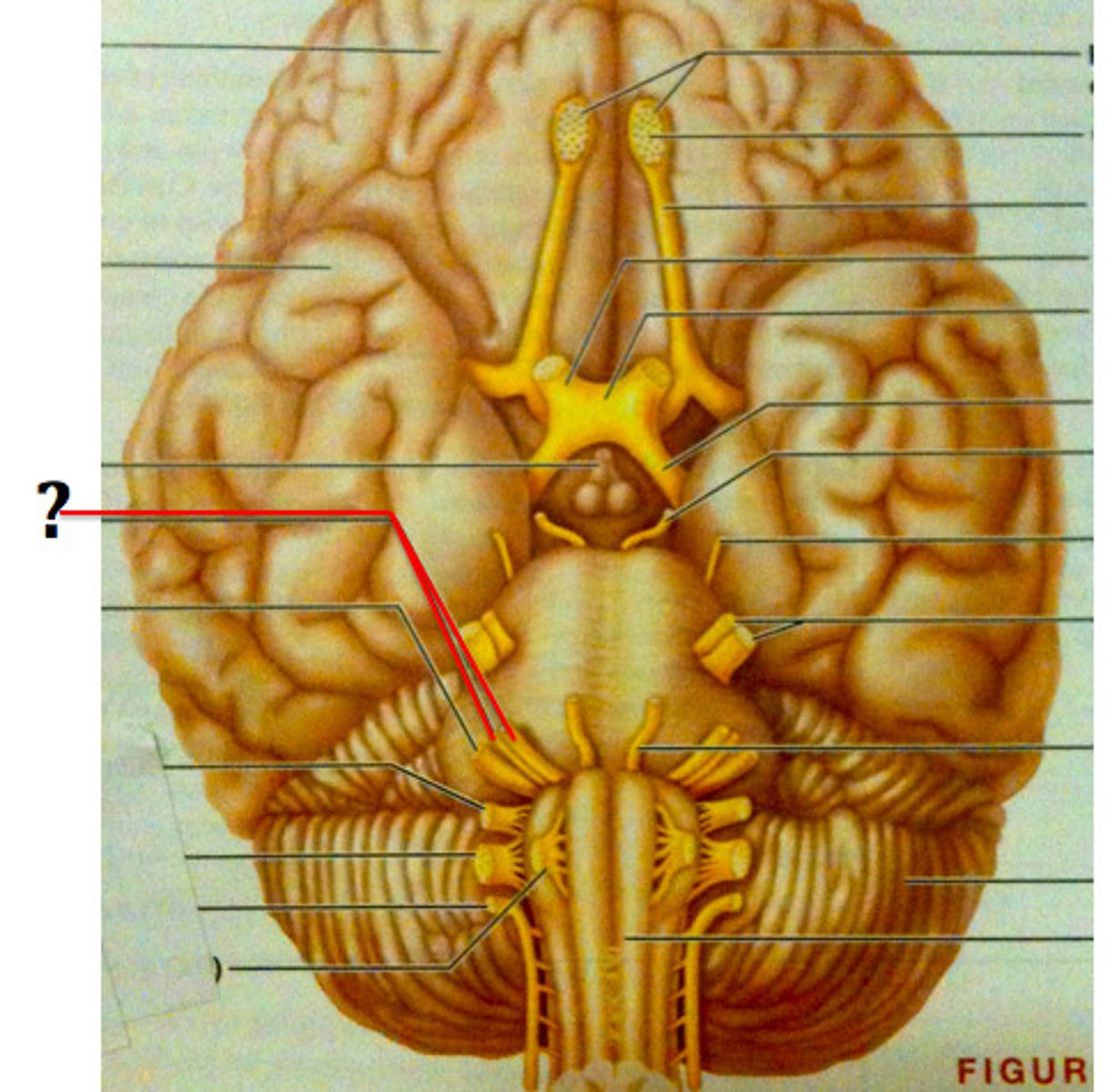
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (Sensory)
Cranial Nerve VIII - Responsible for hearing and balance.
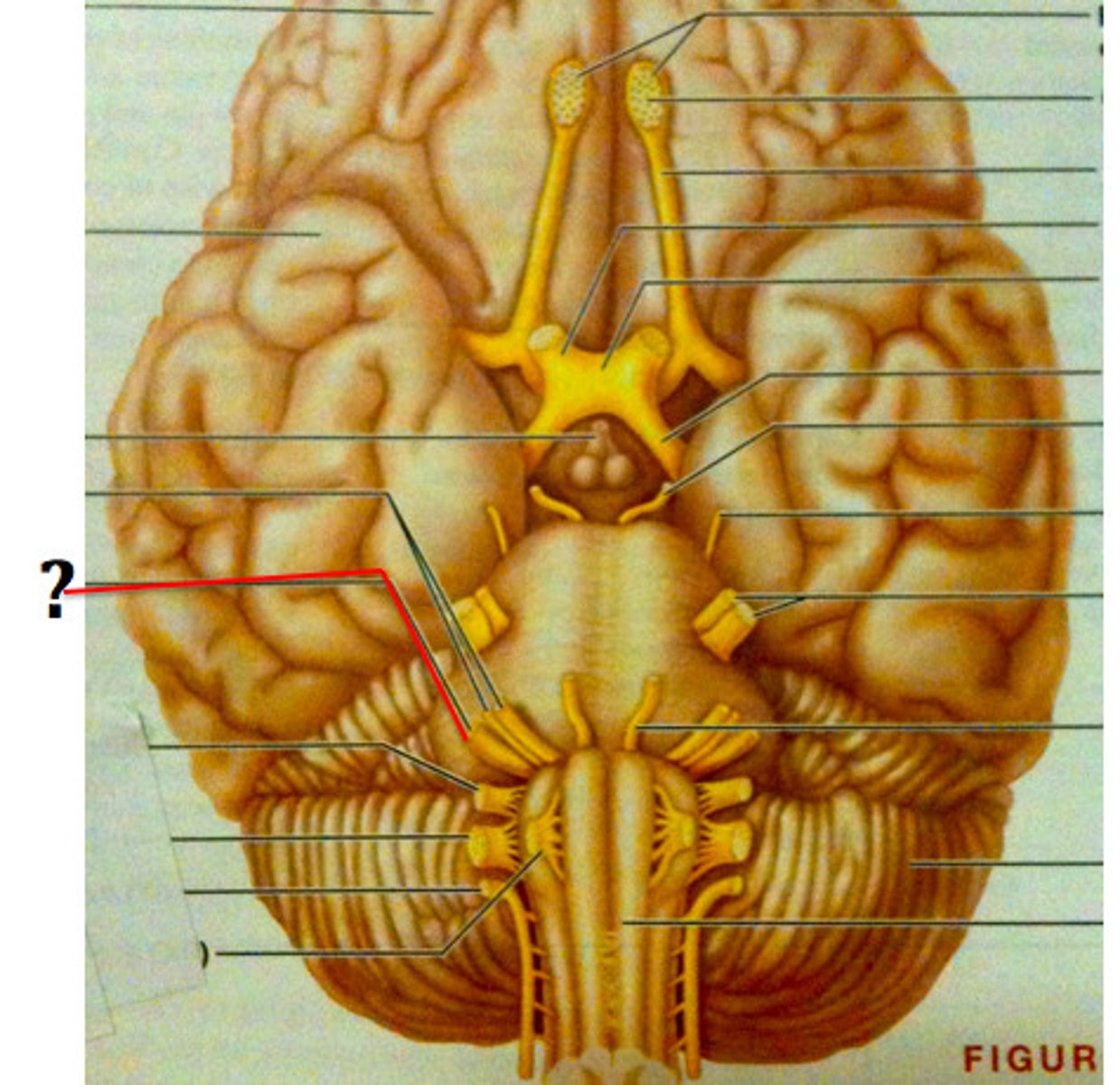
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (Both)
Cranial Nerve IX - Controls taste on back 1/3 of tongue, swallowing, salivation.
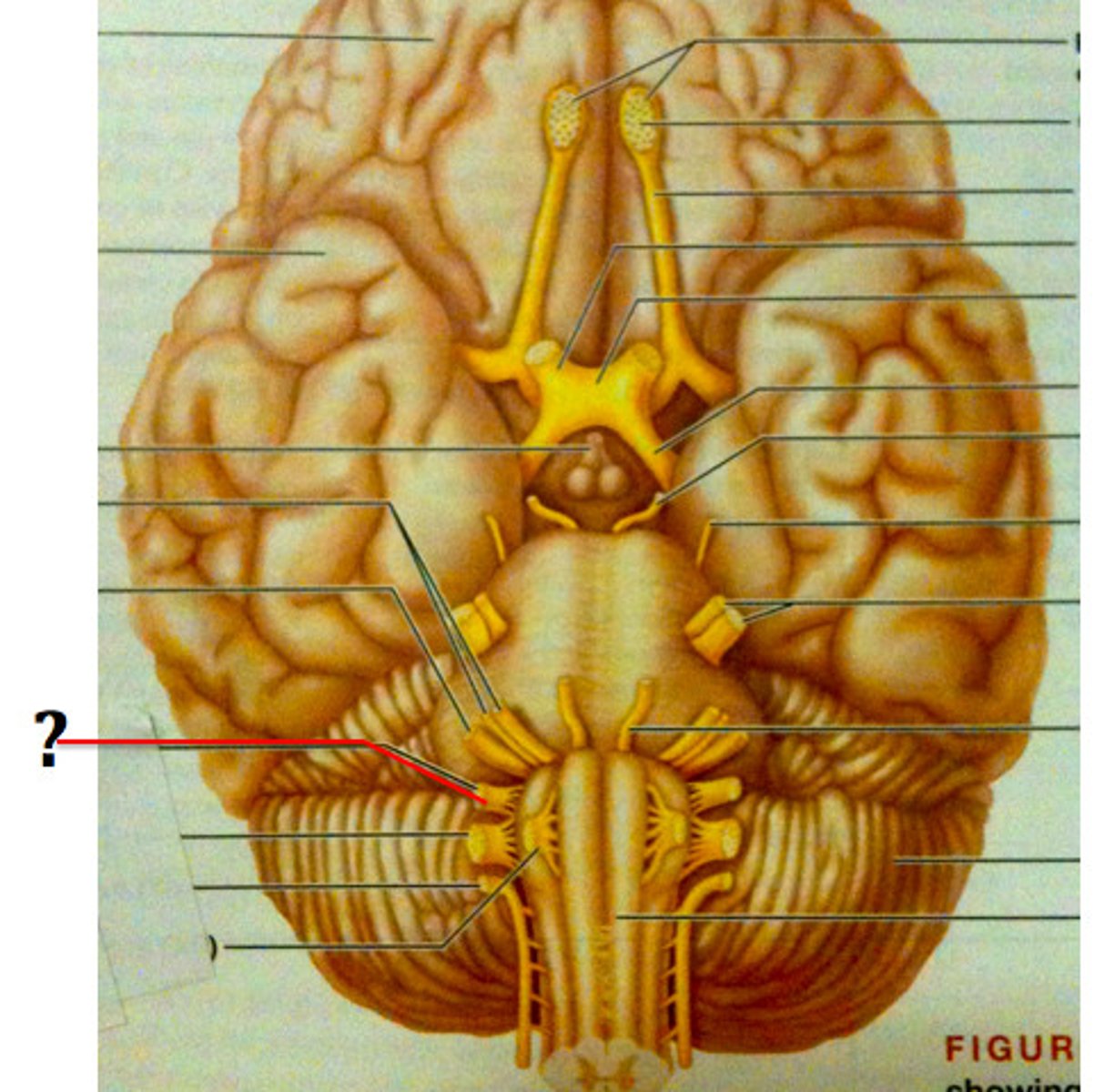
Vagus Nerve (Both)
Cranial Nerve X - Regulates heart rate, digestion, and parasympathetic control of organs.
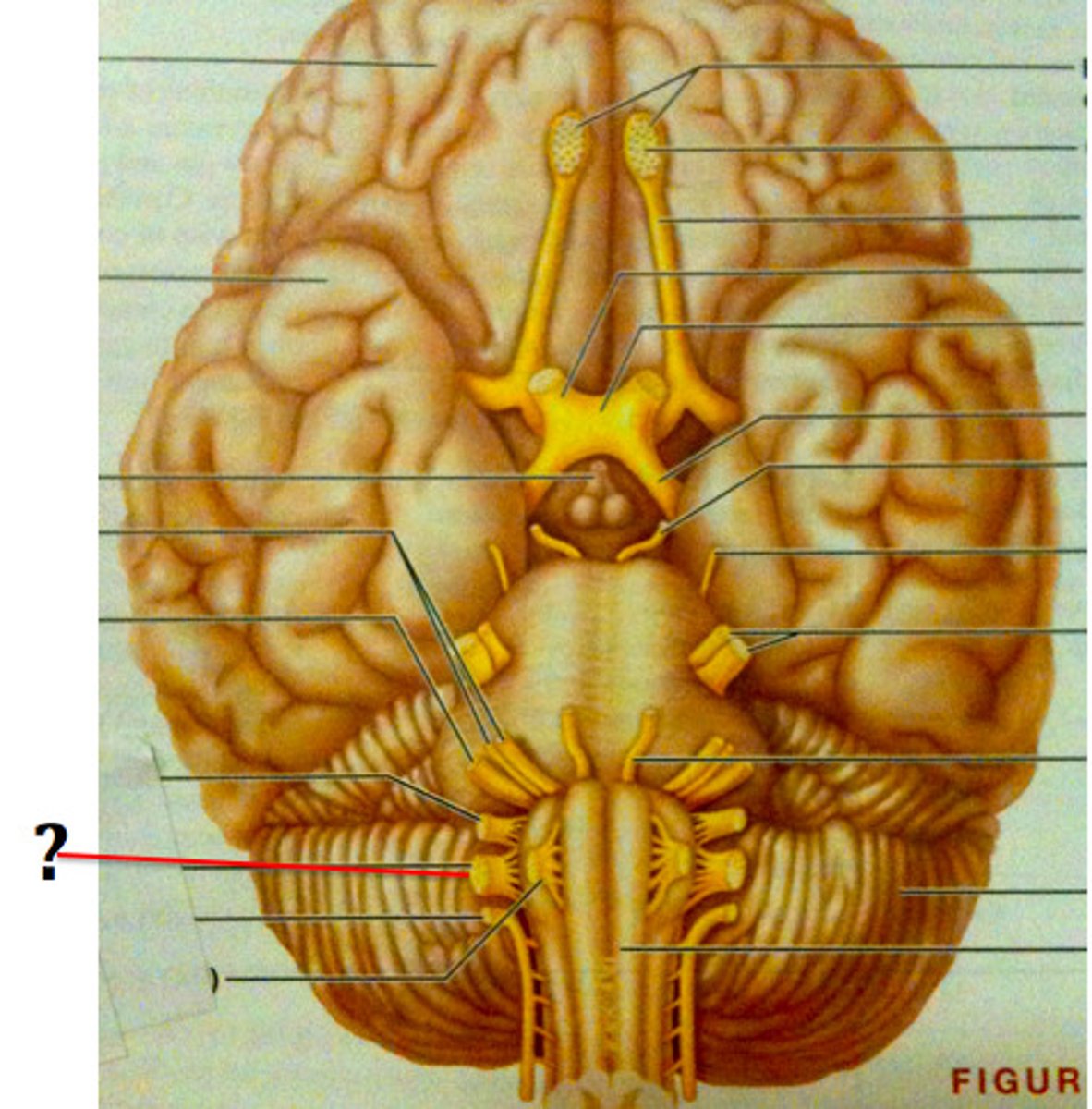
Accessory Nerve (Motor)
Cranial Nerve XI - Controls head, neck, and shoulder movement.
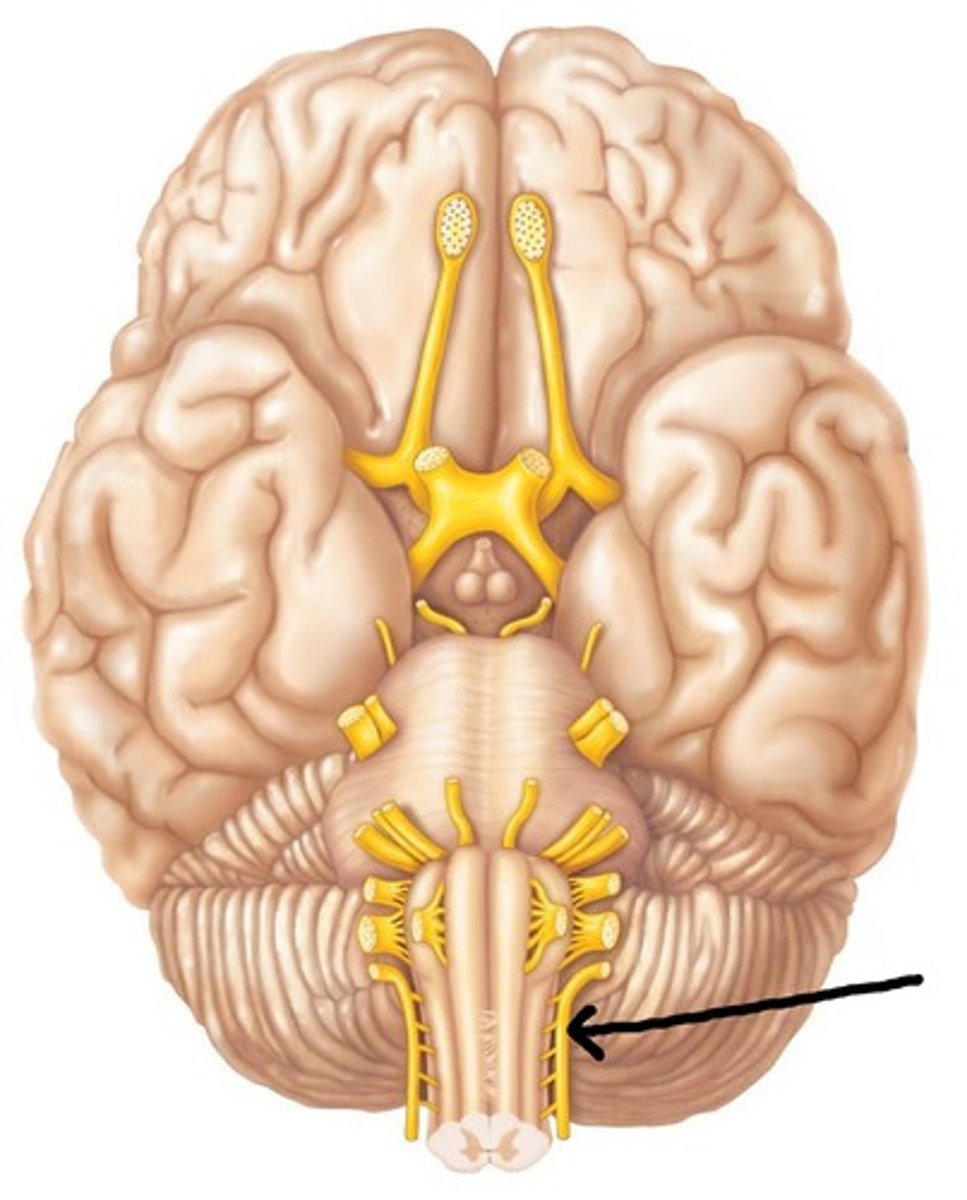
Hypoglossal Nerve (Motor)
Cranial Nerve XII - Controls tongue movements for speech and swallowing.