nervous system part 2
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
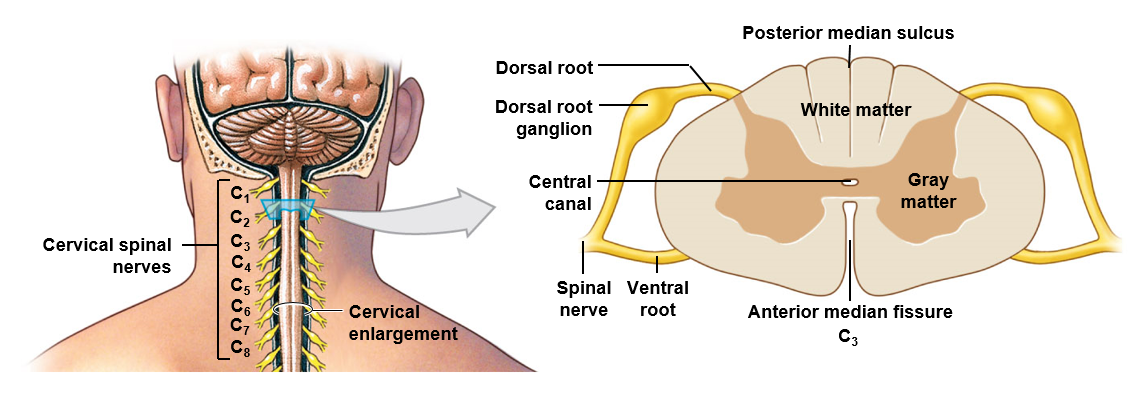
Spinal cord consists of two types of matter…
white matter
Gray matter
White matter
Typically broken down anatomically into posterior, lateral, and anterior horns and columns respectively
Superficial (in the spinal cord); contains myelinated and unmyelinated axons
Associated with the tracts that either project ascending information towards the brain or descending information towards the body
Gray matter
Typically broken down anatomically into posterior, lateral, and anterior horns and columns respectively
Surrounds the central canal; contains cell bodies, Neuroglia, and unmyelinated axons
Associated with sensory and motor nuclei; these nuclei are associated with the areas of the body they lie in close proximity to
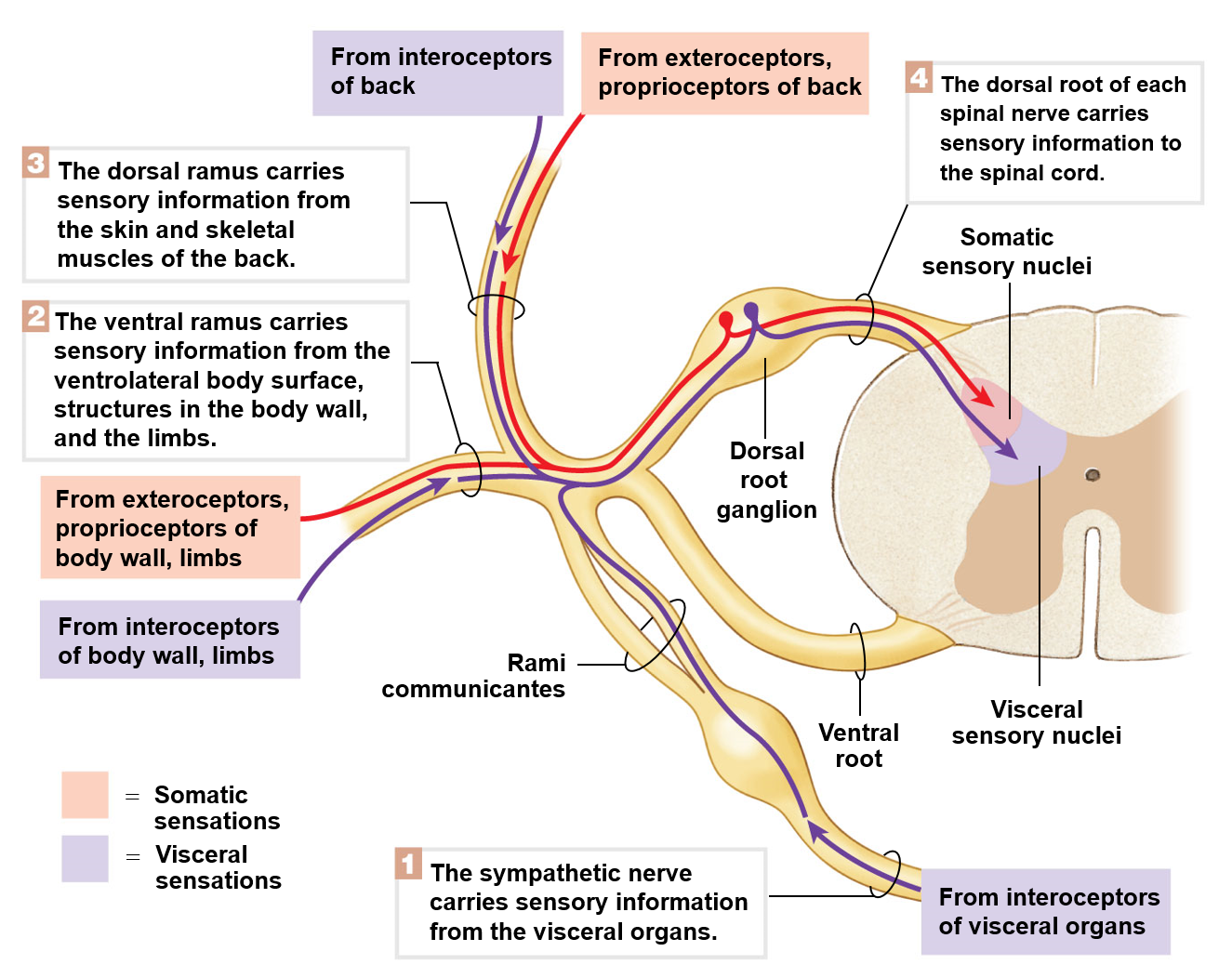
Somatic afferent neurons
Sensory neurons that conduct impulses initiated in receptors in the skin, skeletal muscles, tendons, and joints
Visceral afferent neurons
Sensory neurons that conduct impulses initiated in receptors in smooth and cardiac muscle
Visceral efferent neurons
Motor neurons that conduct impulses to smooth and cardiac muscle, as well as glands
Somatic efferent neurons
Motor neurons that conduct impulses from the spinal cord to skeletal muscles
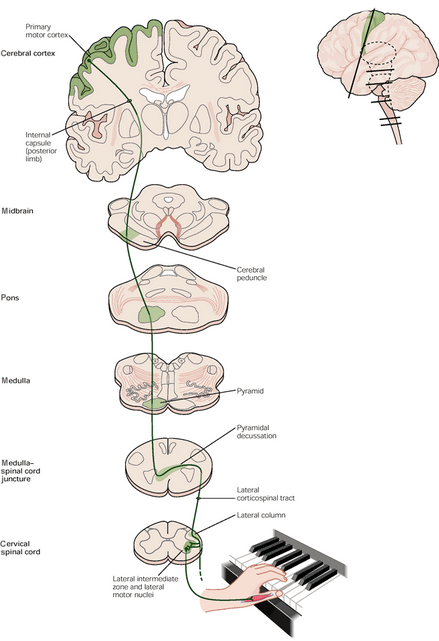
Corticospinal tract is…
responsible for sending motor information from the brain towards the muscles of the body
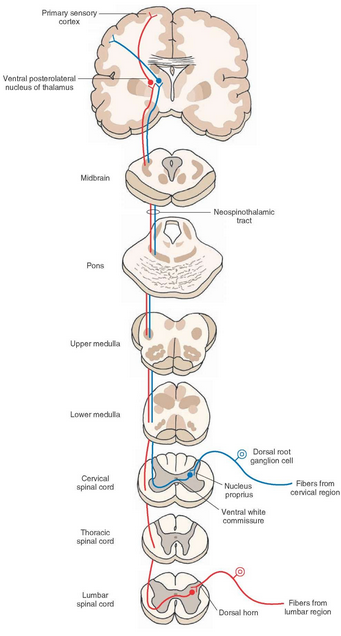
Neospinothalamic tract is responsible for…
Transmitting sensory information up towards the brain
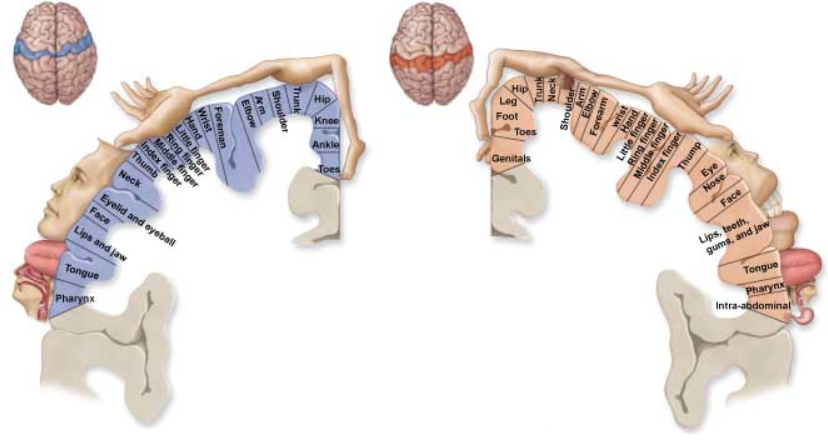
Humunculi
The concept of the body within the brain
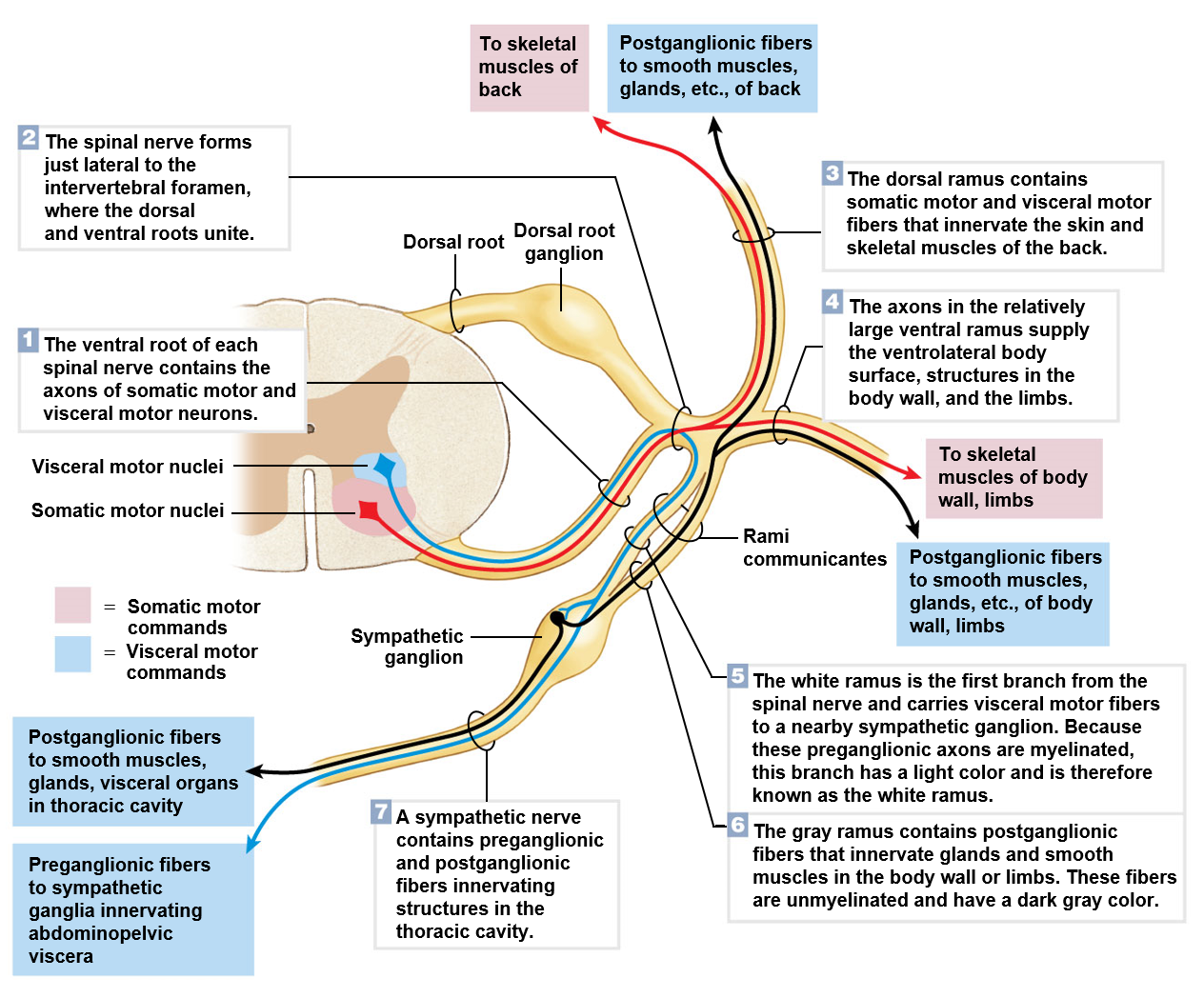
Spinal nerve
Formed by the union of ventral roots and dorsal roots
Ventral root
Contains axons of the motor neurons
Dorsal root
Contains axons of the sensory neurons
Is also associated with a ganglion
Ganglion
Cluster of cell bodies located in the peripheral nervous system
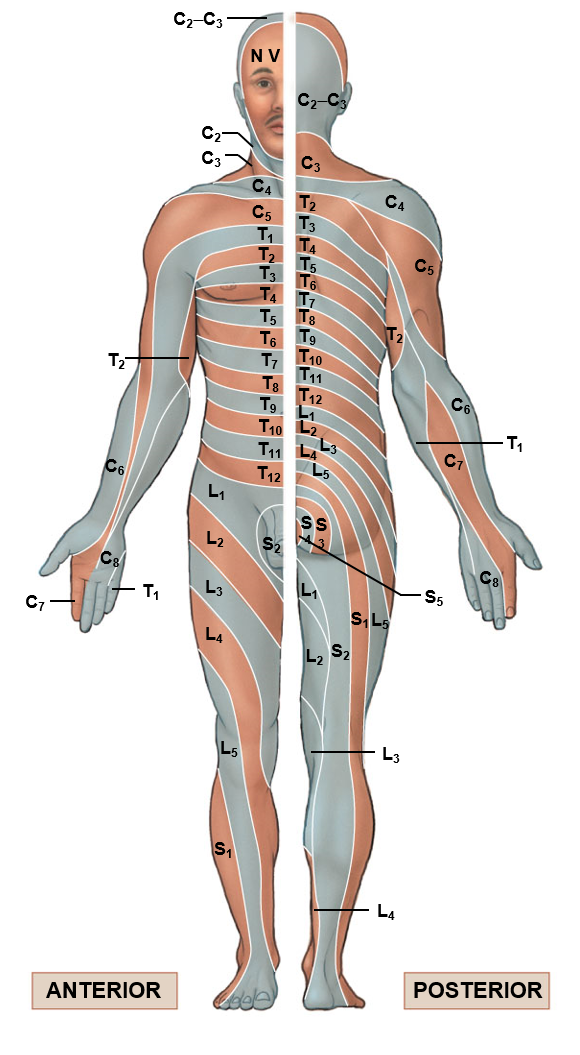
Spinal nerve distribution 1
Spinal nerve distribution 2
Spinal cord
Sends off to the following branches
8 vertical spinal nerve pairs
12 thoracic spinal nerve pairs
5 lumbar nerve pairs
5 sacral nerve pairs
1 coccygeal nerve pair
In the cervical region, the nerve comes out above the corresponding vertebrae
From the thoracic region to the coccygeal region, the nerve comes out below the corresponding vertebrae
Along the four areas of the spinal cord…
The ventral rami join into a plexus
Plexus
Branching network of nerves
Cervical plexus
Brachial plexus
Lumbar plexus
Sacral plexus
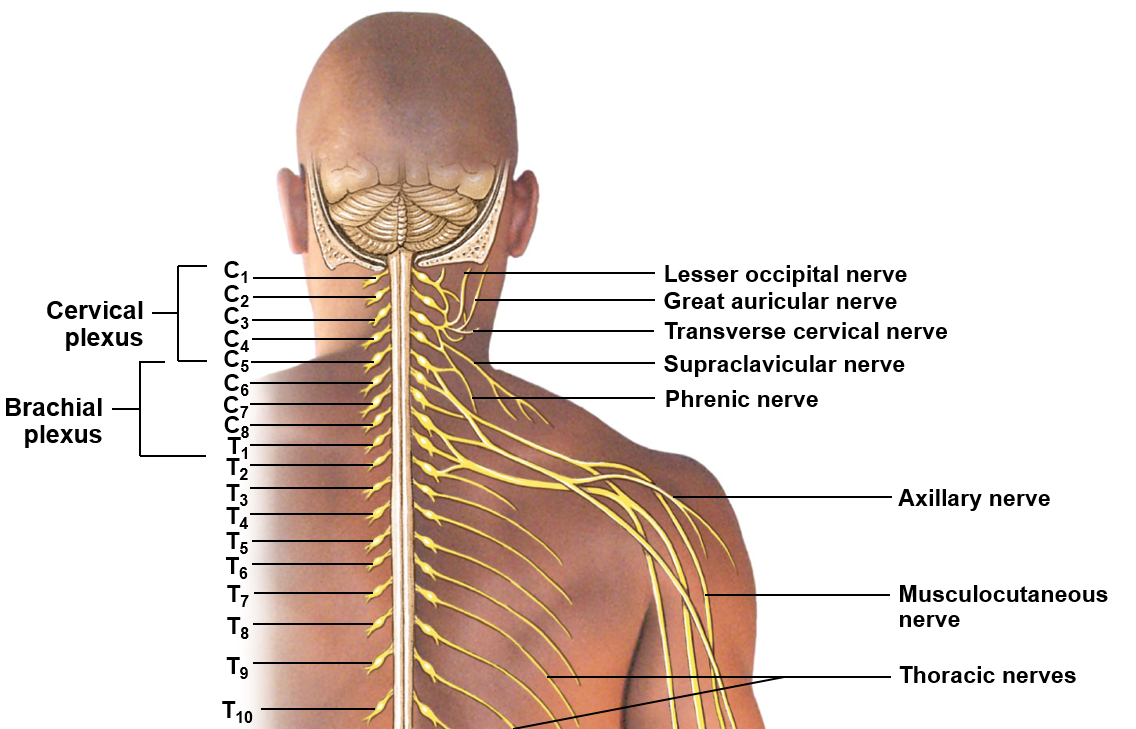
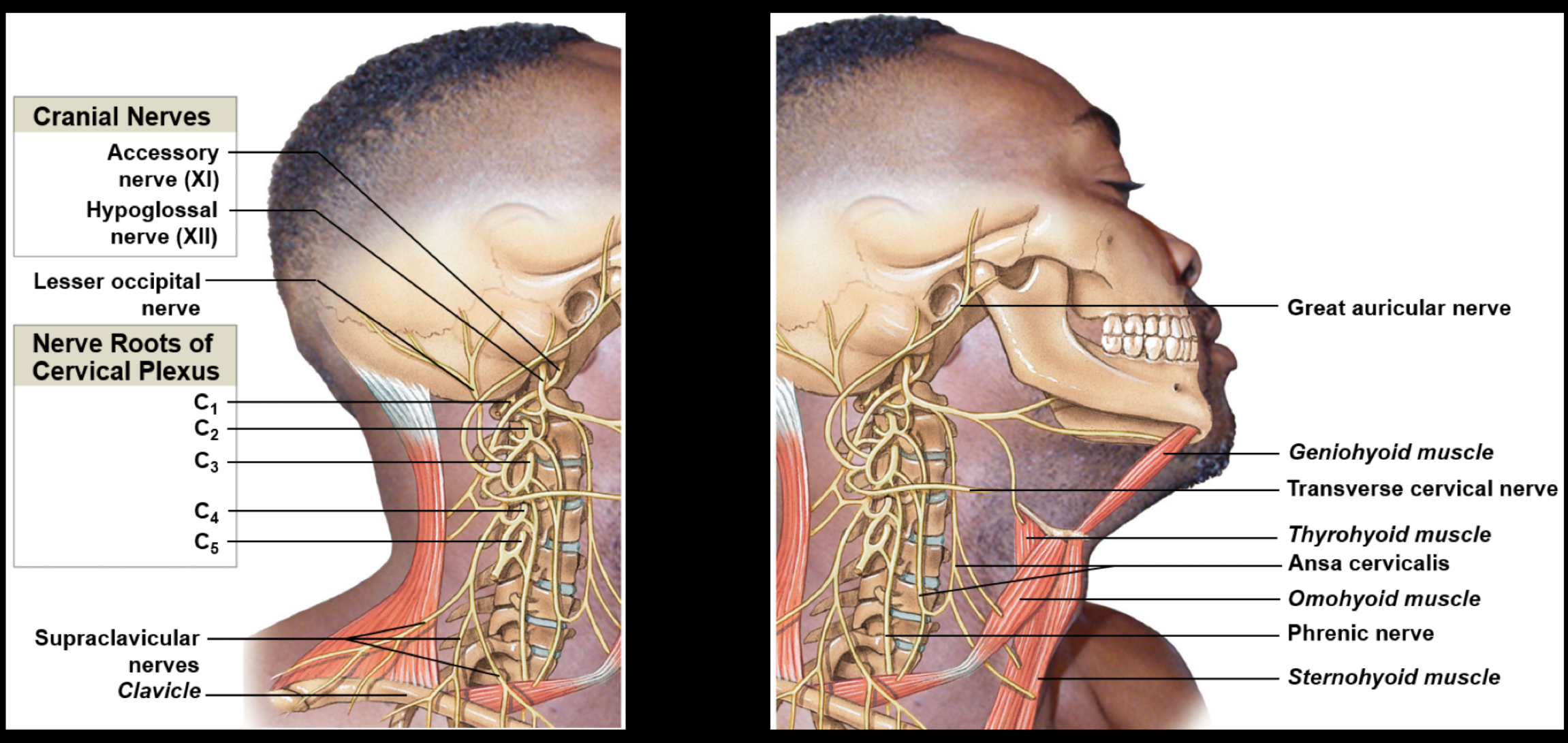
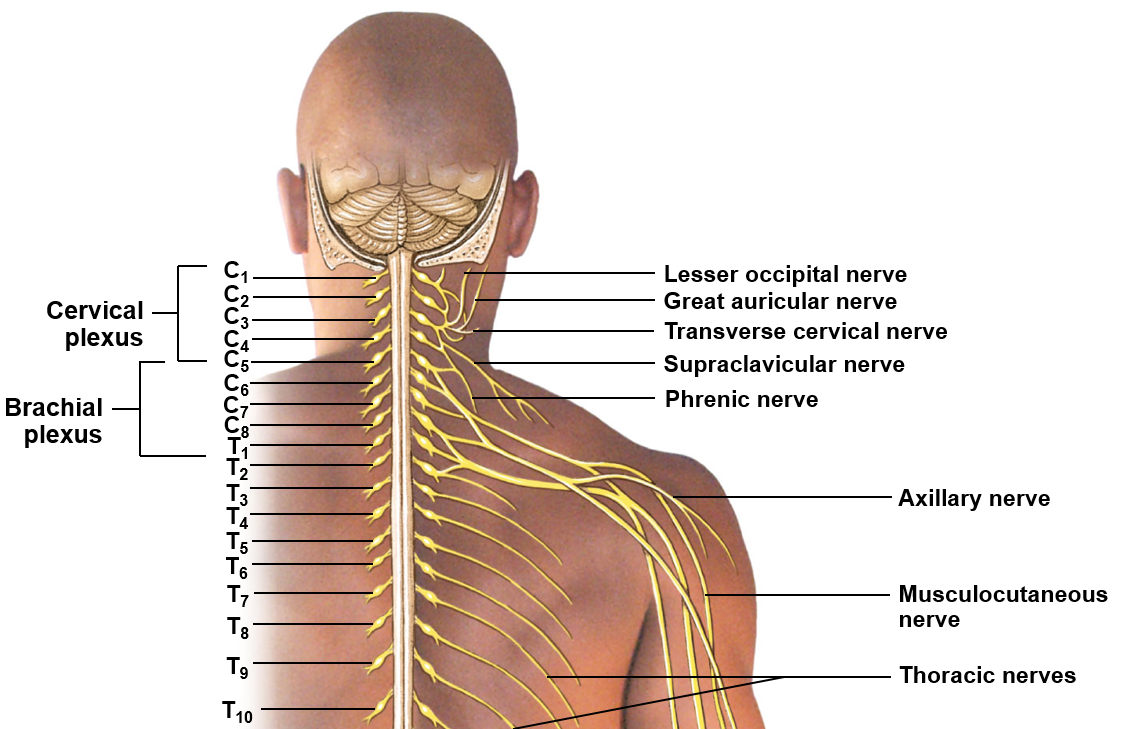
Cervical plexus
Includes ventral rami of C1-C5; innervates the neck, thoracic cavity, and diaphragm
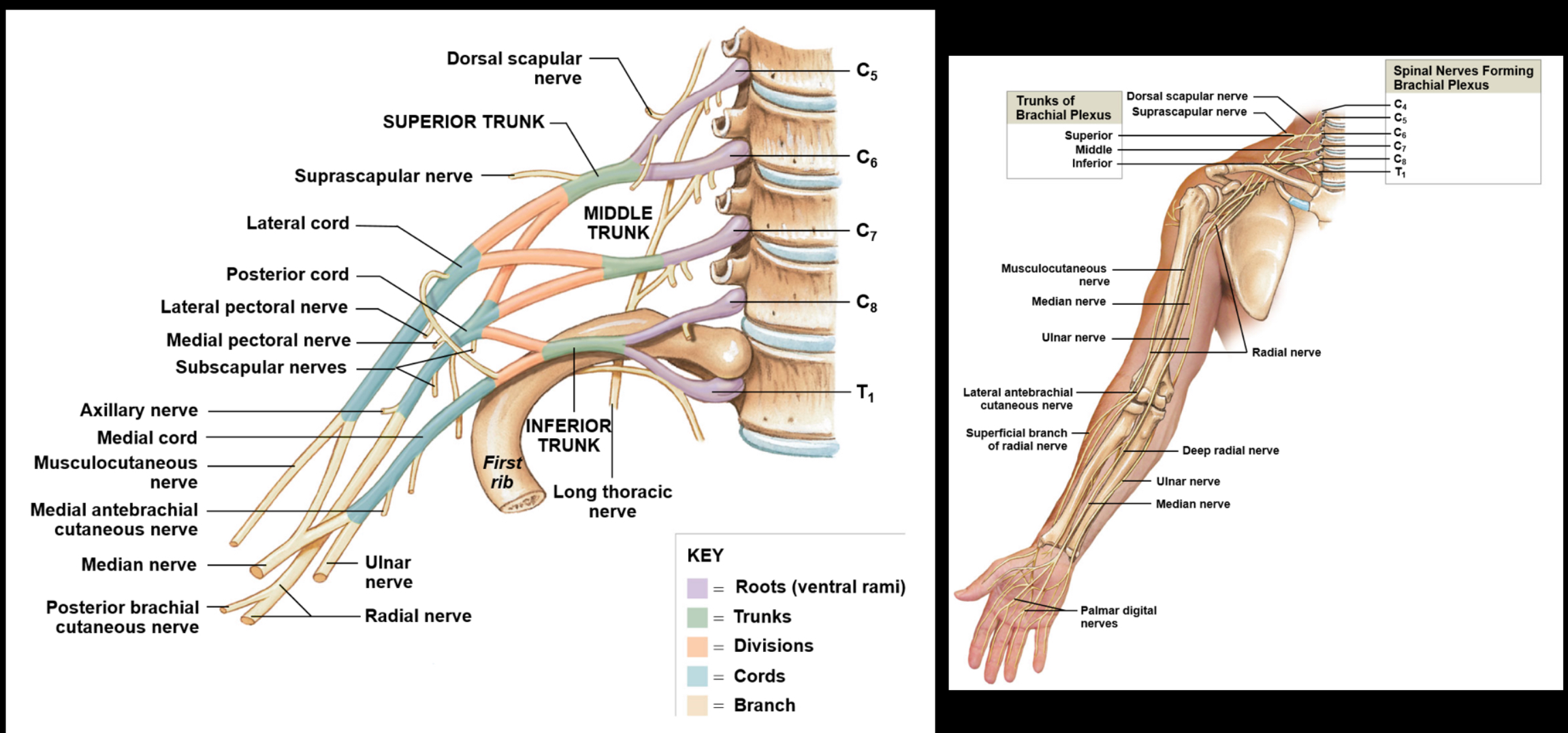
Brachial plexus
Includes the ventral rami of C5-T1; serves to innervate the arm
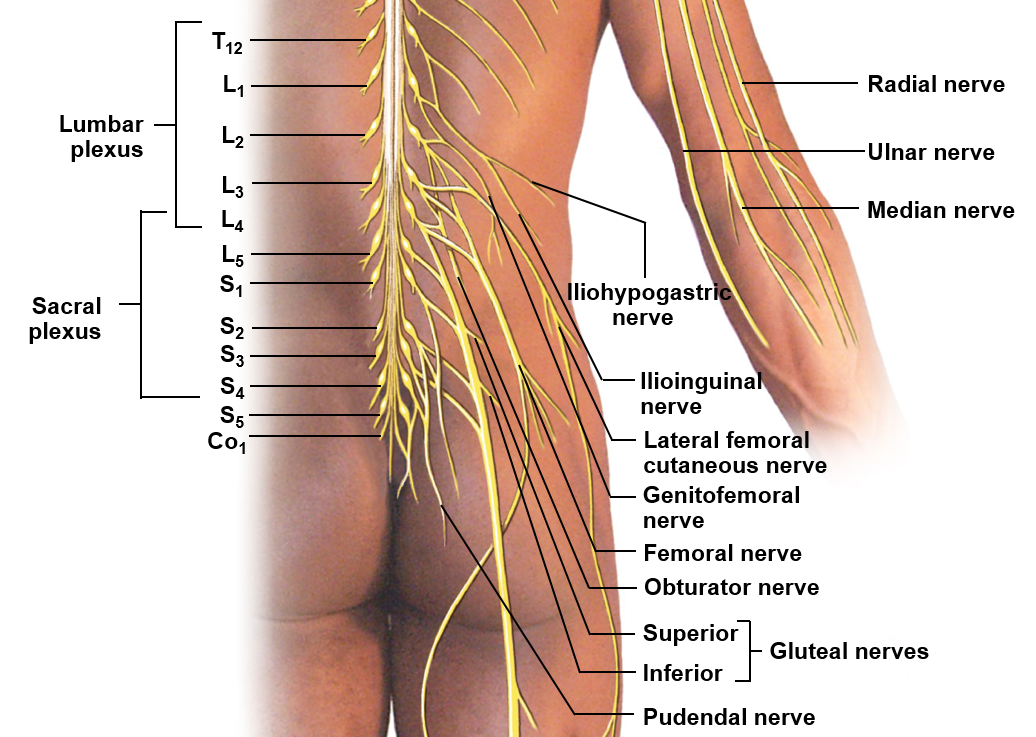
Lumbar plexus
Includes ventral rami of T12-L4; helps innervate the thigh and leg
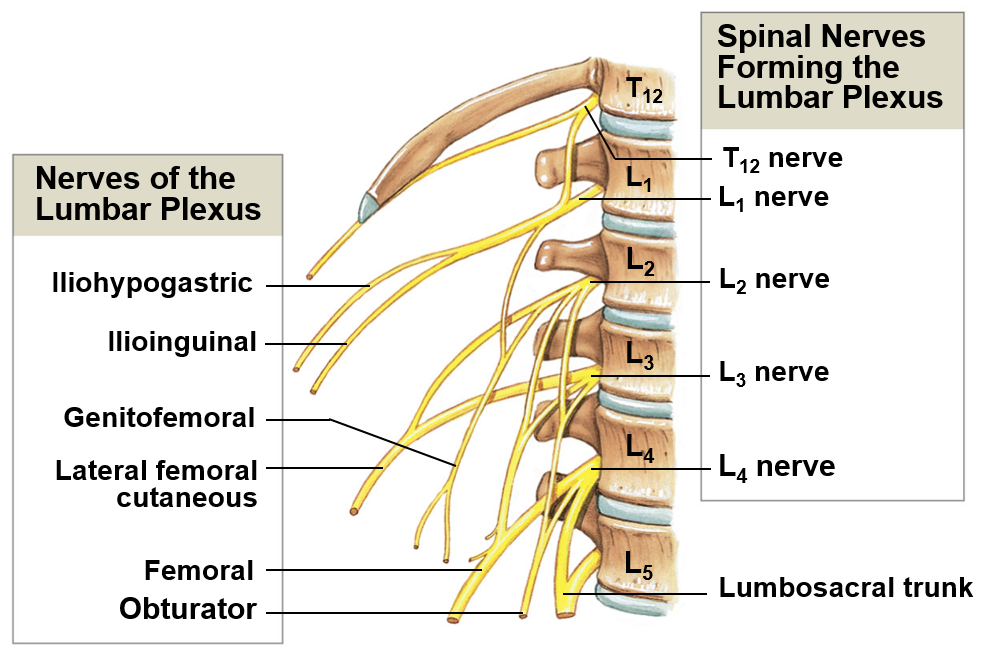
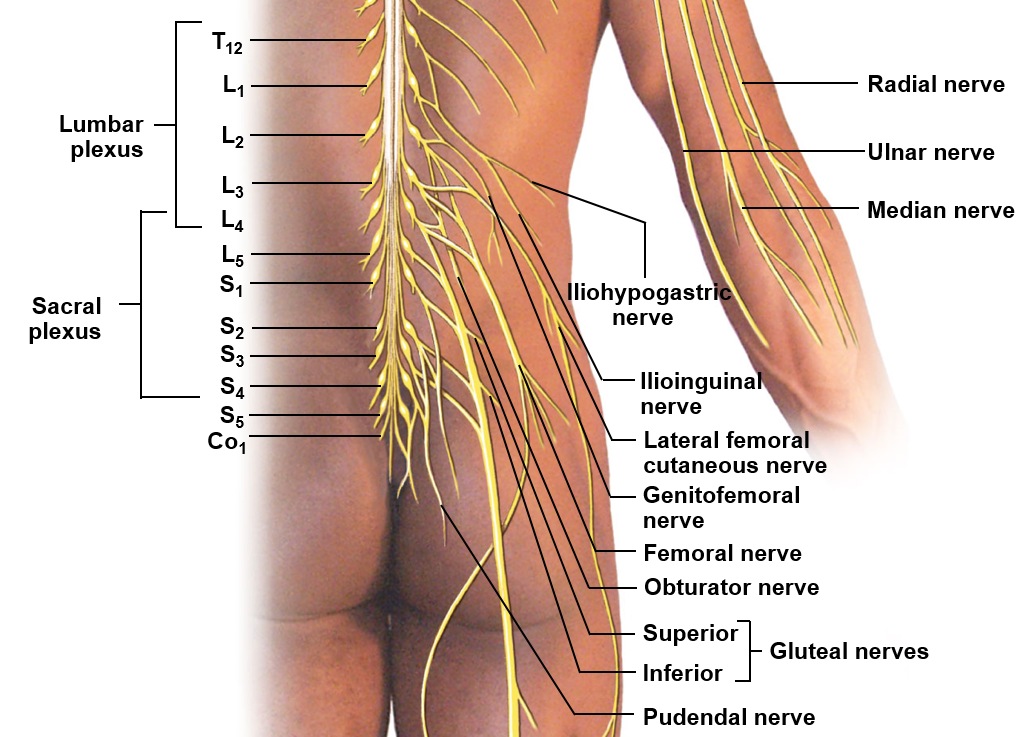
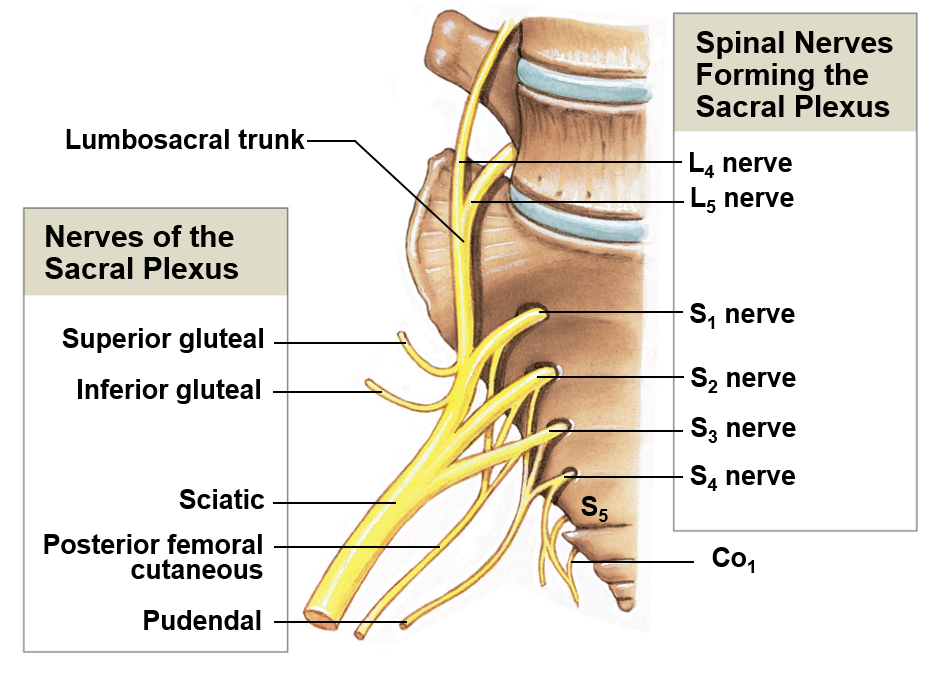
Sacral plexus
Includes the ventral rami of L4-S4; helps innervate the leg
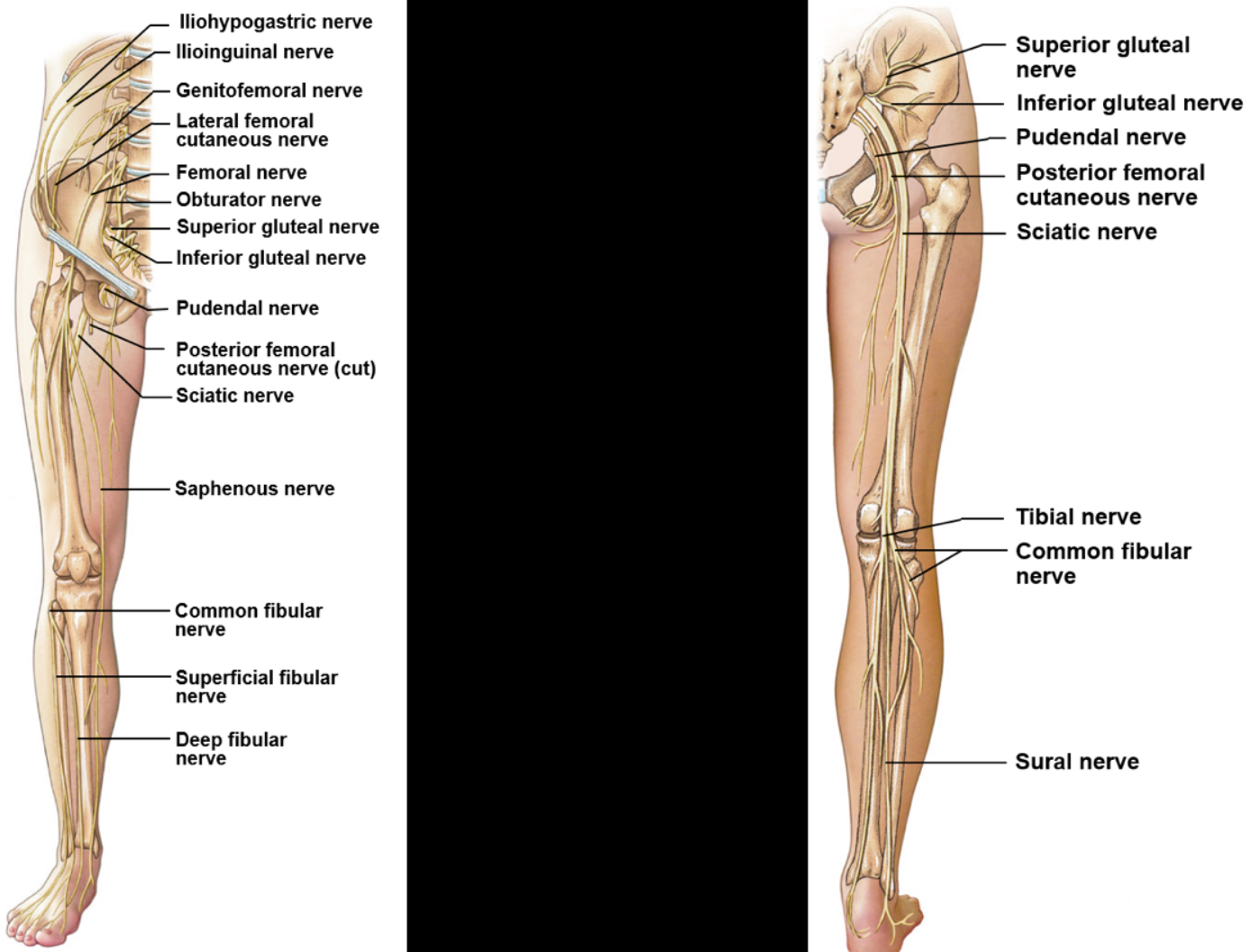
Nerves of the leg
Dermatologist
Area of skin supplied by a single spinal nerve
supplied b peripheral nerves
Are stacked like discs in the thoracic and abdominal regions, yet run more longitudinally in the upper and lower extremities
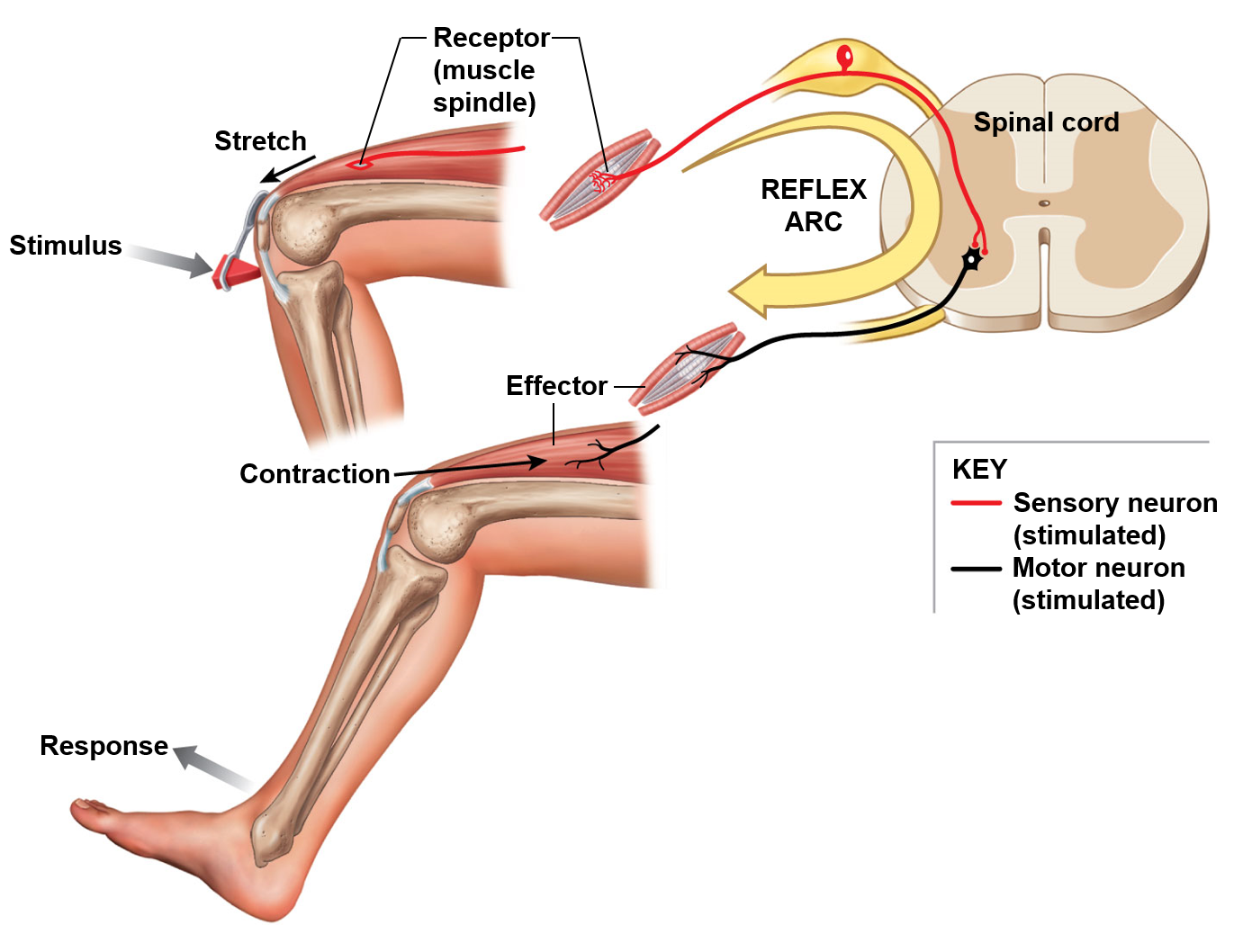
Reflex
Involuntary and nearly instantaneous movement in response to a stimulus
They help test the integrity of the peripheral nervous system and/or central nervous system
Primitive reflexes are a special category of reflexes that are only found in human infants (babinski reflex)
Stretch reflex
Patellar reflex (hit the knee)
called monosynaptic
Checks integrity of dorsal root, spinal cord, and ventral root
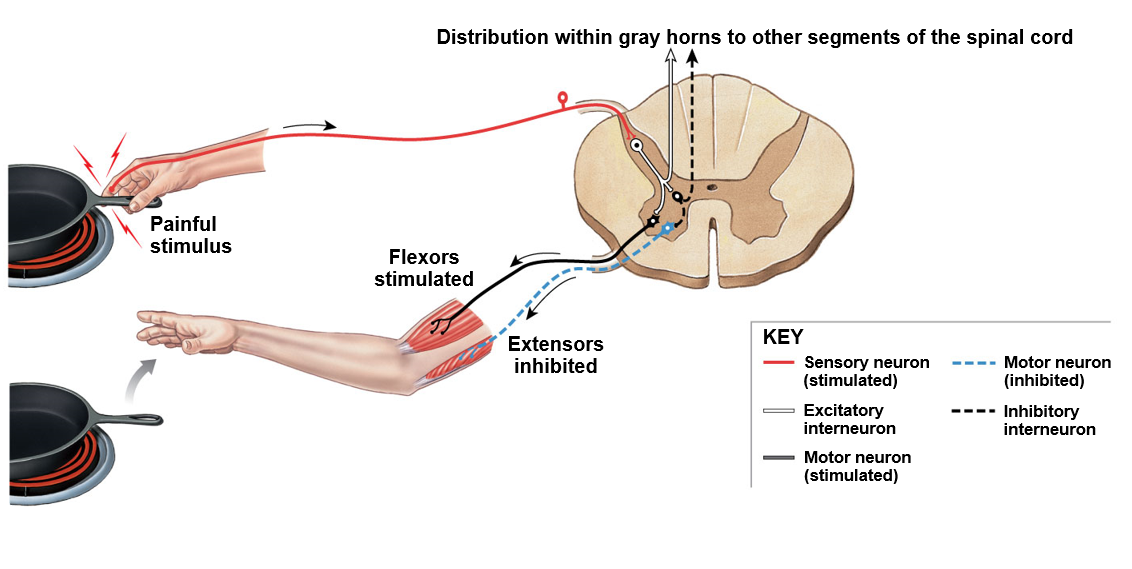
Withdrawal reflex
Polysynaptic reflex
have to do something to “excite” the inhibitors in order to create movement
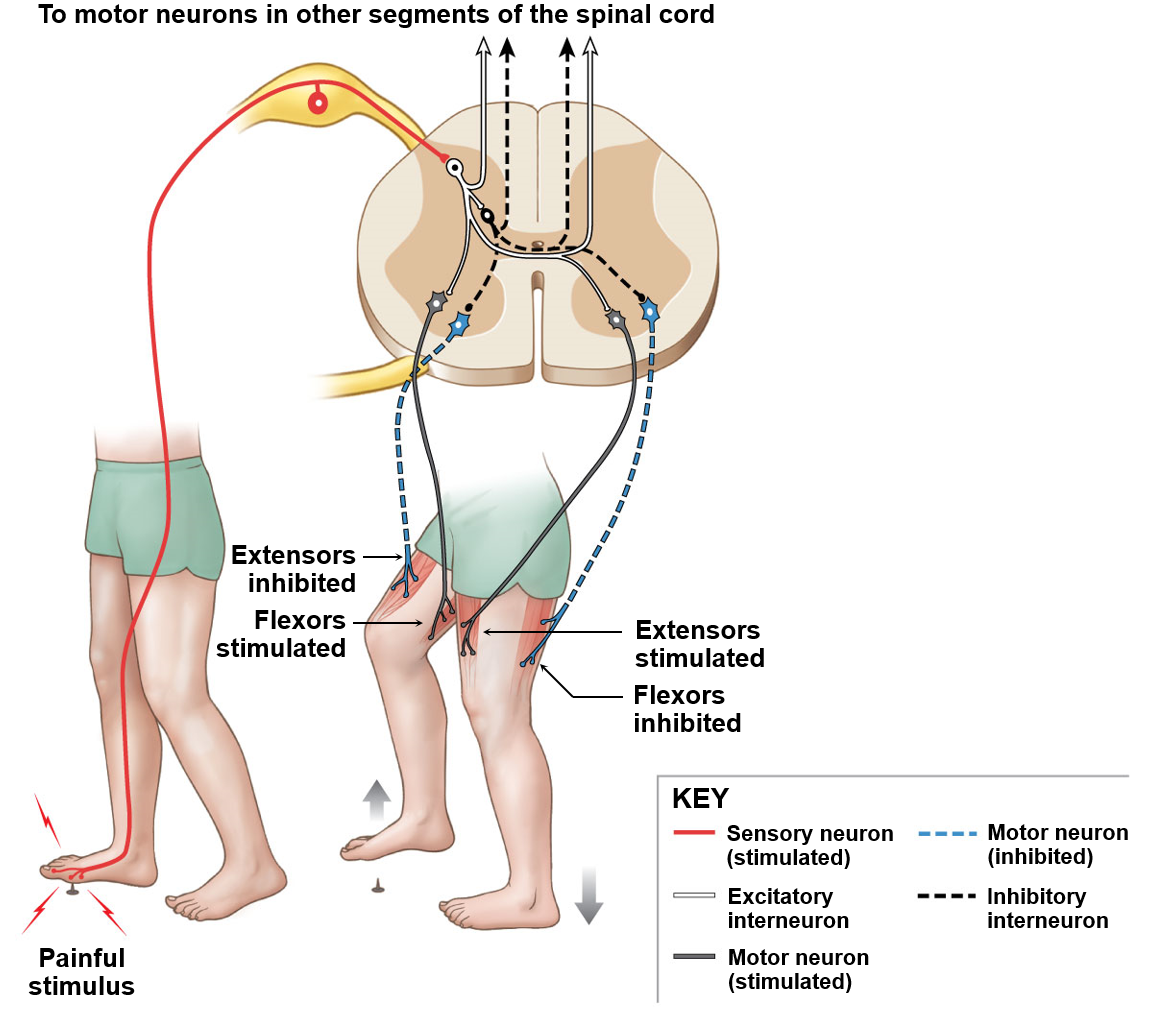
Crossed extensor reflex
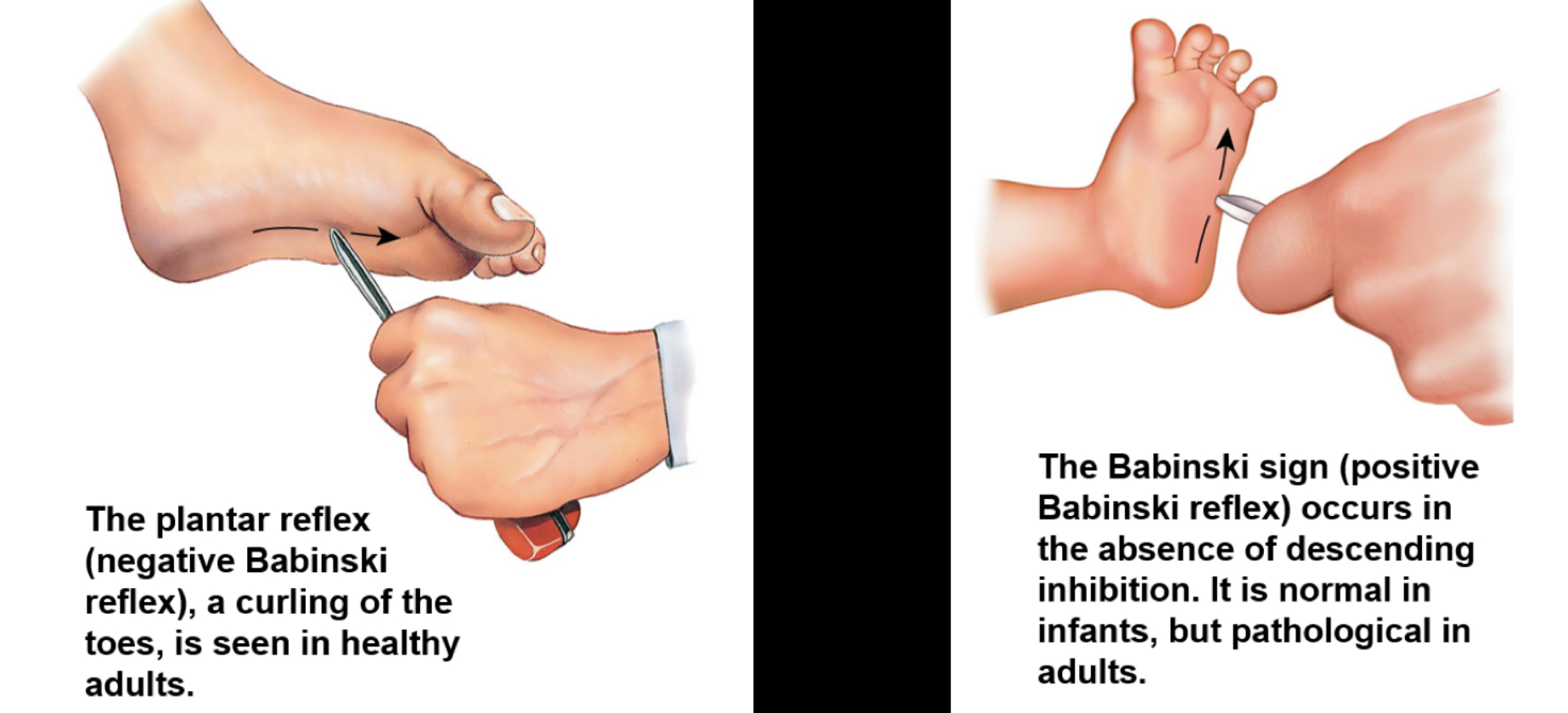
Babinski reflex and sign
(Pathological test)
the curling of toes is healthy (flexor response)
A baby doesn’t curl their toes due to them not walking yet (up to age 1)
Also called extensor response
if an adult extends toes, something is not right with upper motor neuron
Very few ppl have paradoxical extensor response or no response at all
Automatic nervous system
Functions as a control system over the body’s internal organs and glands; influences heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, salivation, perspiration, pupillary dilation, urination, sexual arousal, breathing and swallowing
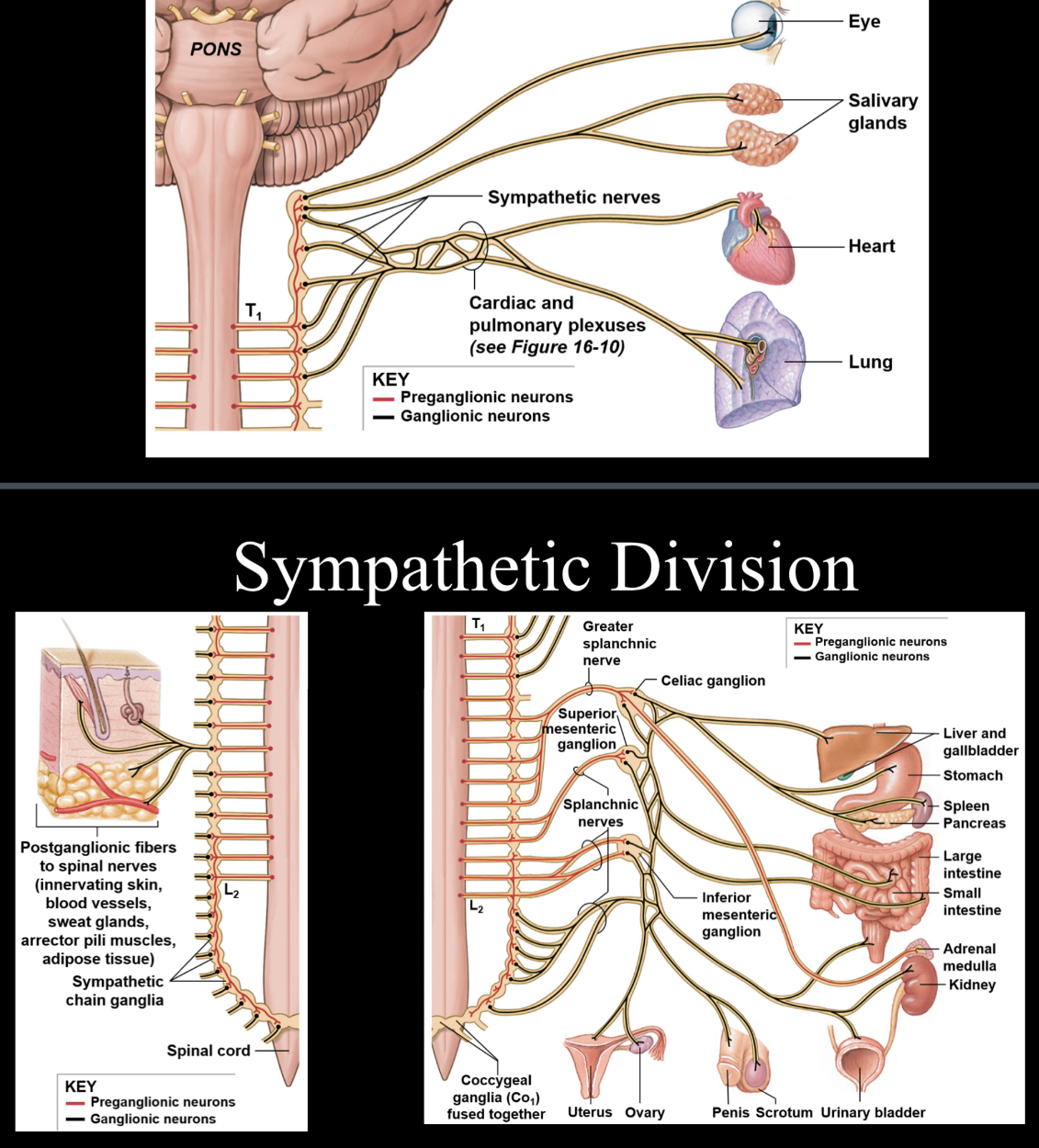
Sympathetic nervous system
Involved with the “fight or flight” aspect of the ANS; sympathetic nerves originate inside of the vertebral column and extend from the first thoracic vertebral level down to second or third vertebral level; extensively involved with close proximity ganglia, which are cell bodies that reside in the peripheral nervous system
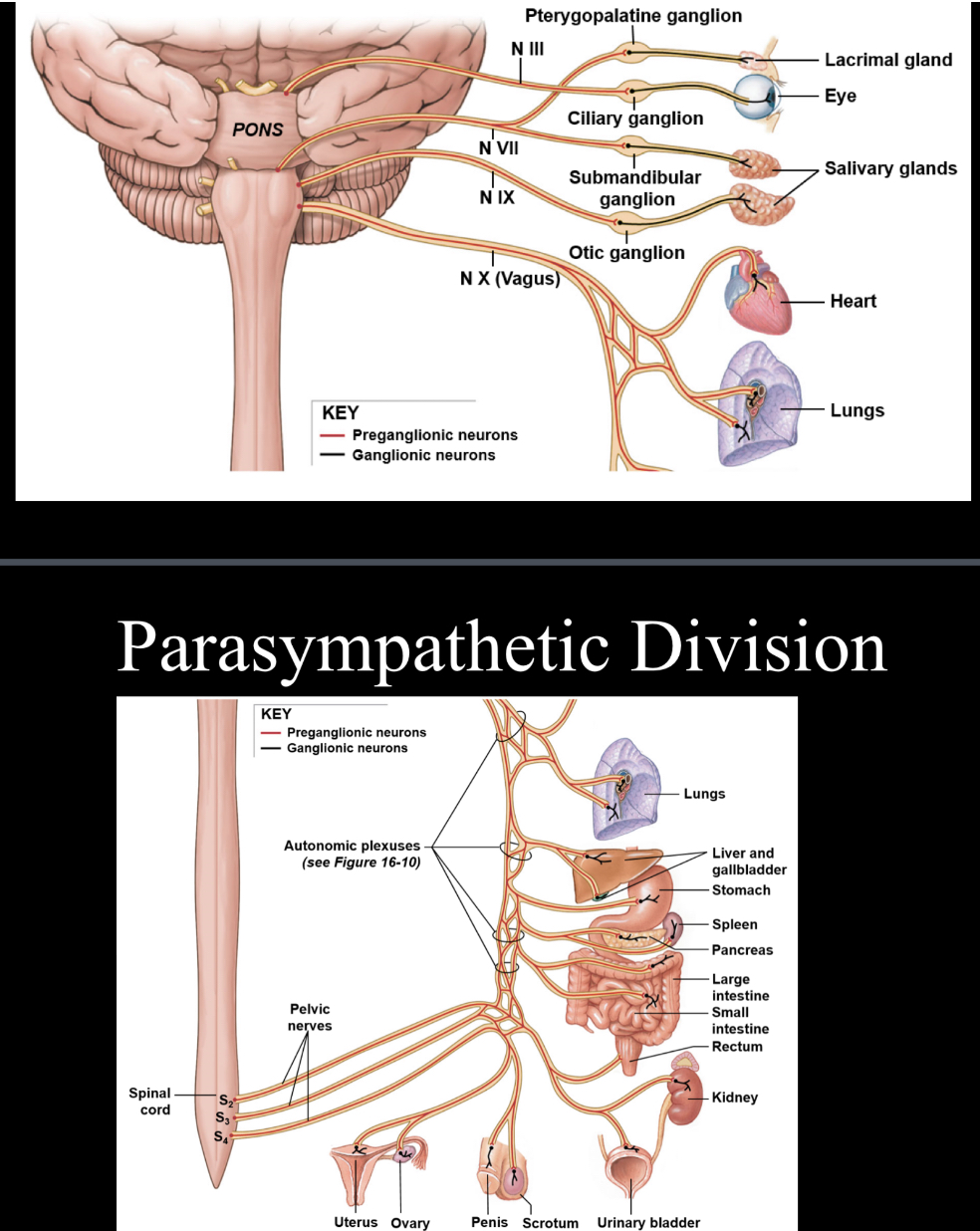
Parasympathetic nervous system
Involved with the “rest and digest” aspect on the ANS; parasympathetic nerves are either cranial nerves or are associated with sacral spinal nerves
Special senses
Intimately involved with the nervous system are as follows
Olfaction
Gustation
Vision
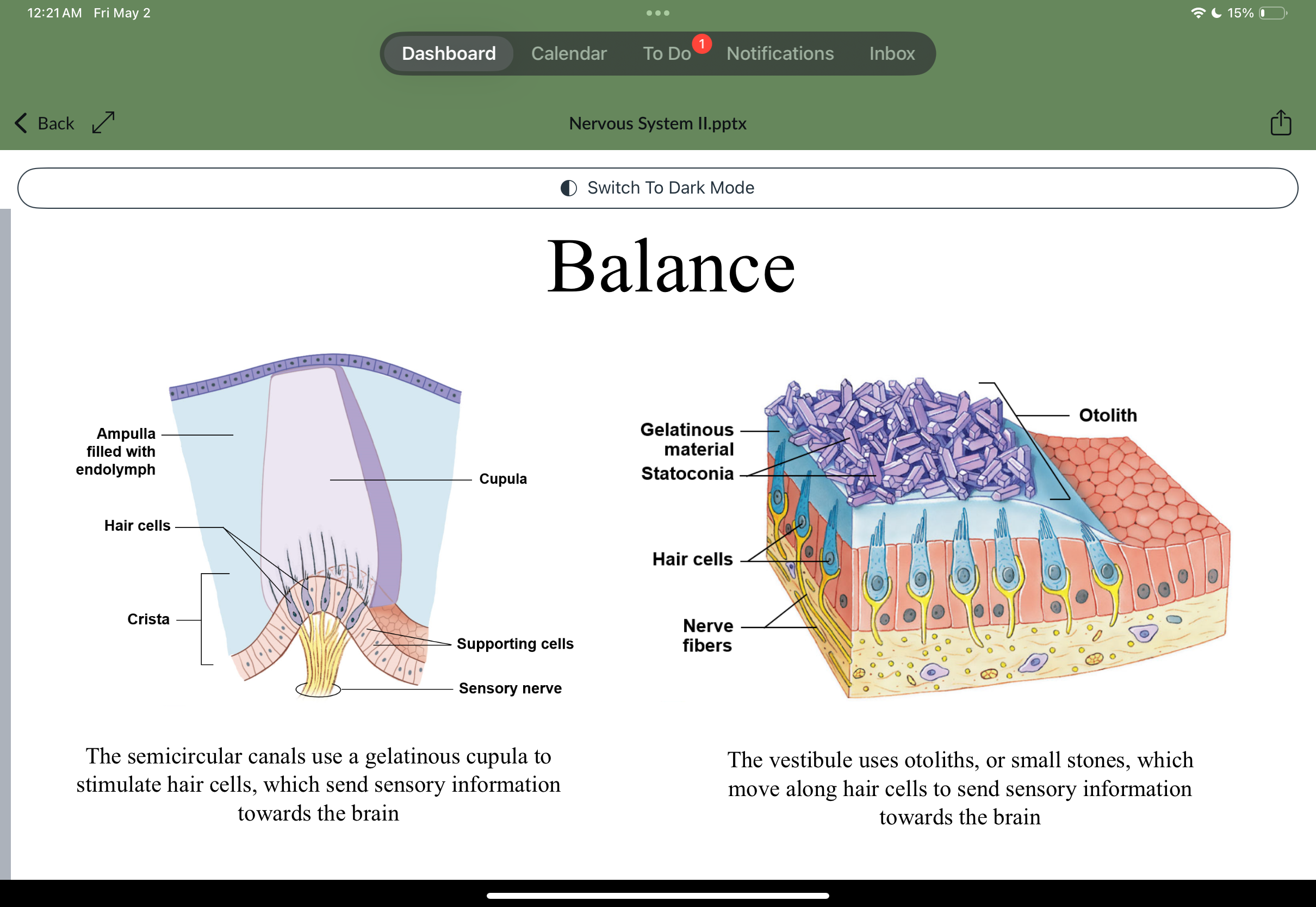
Balance
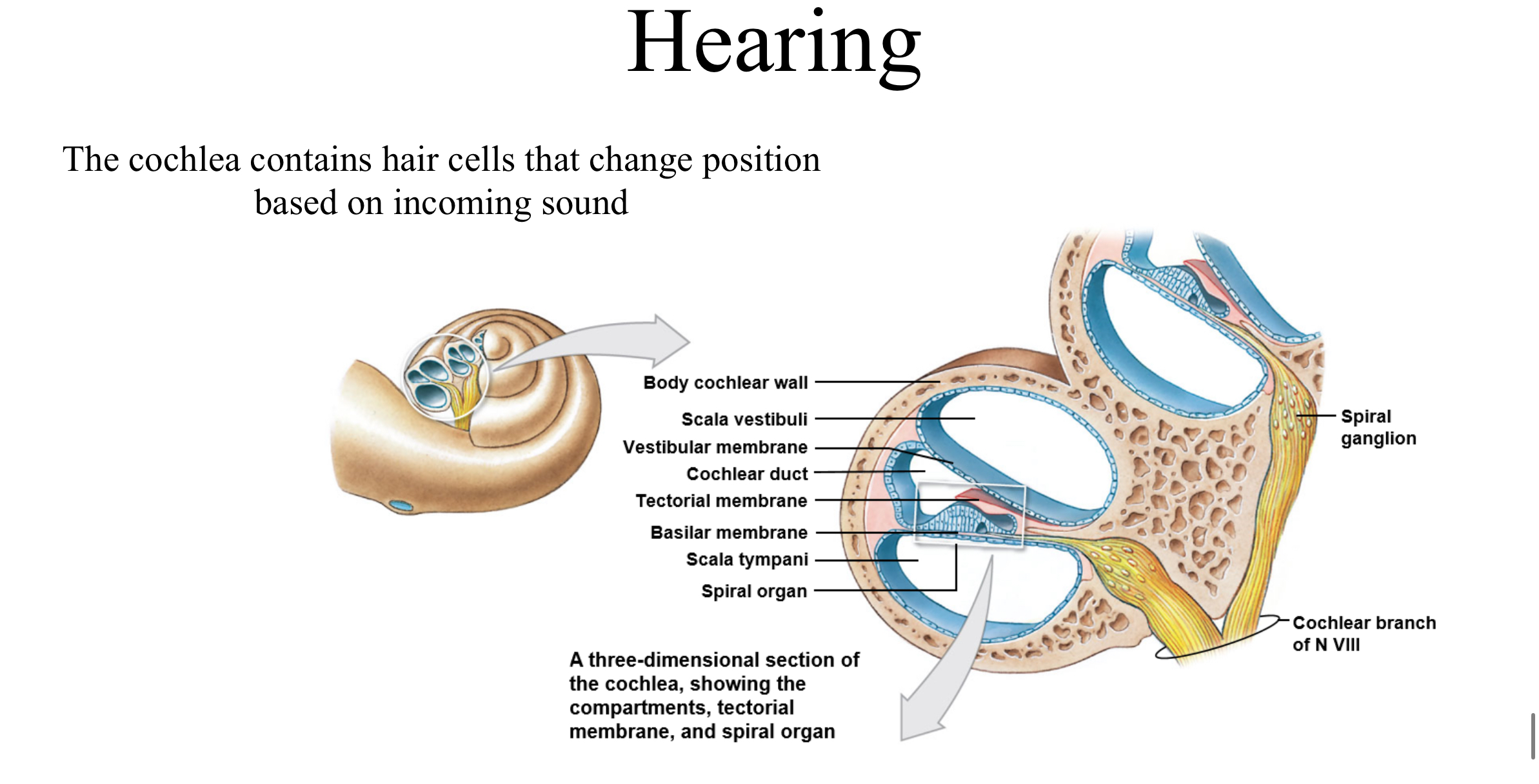
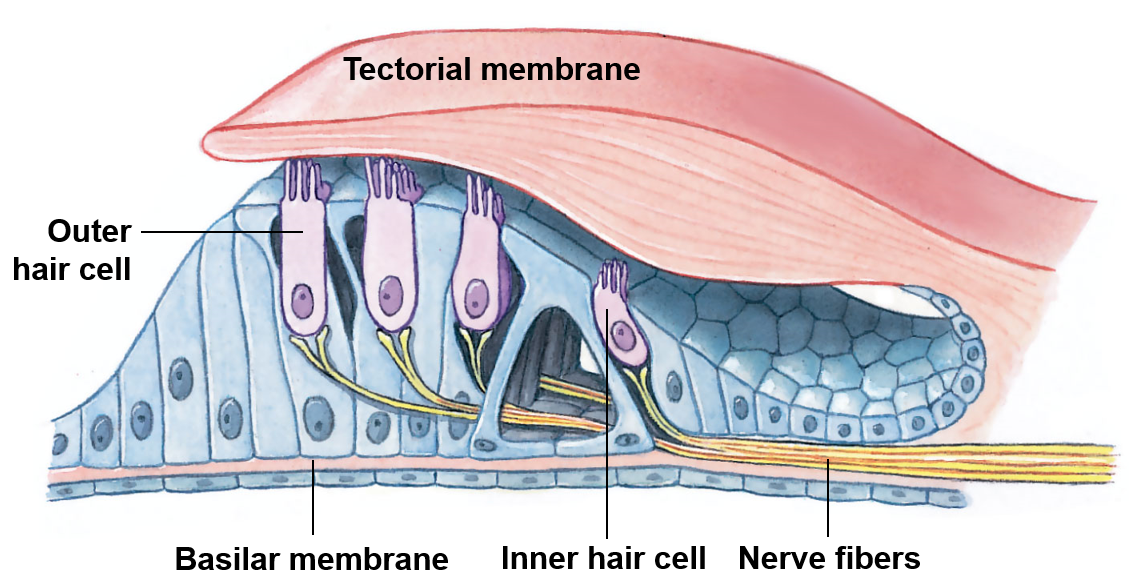
Hearing
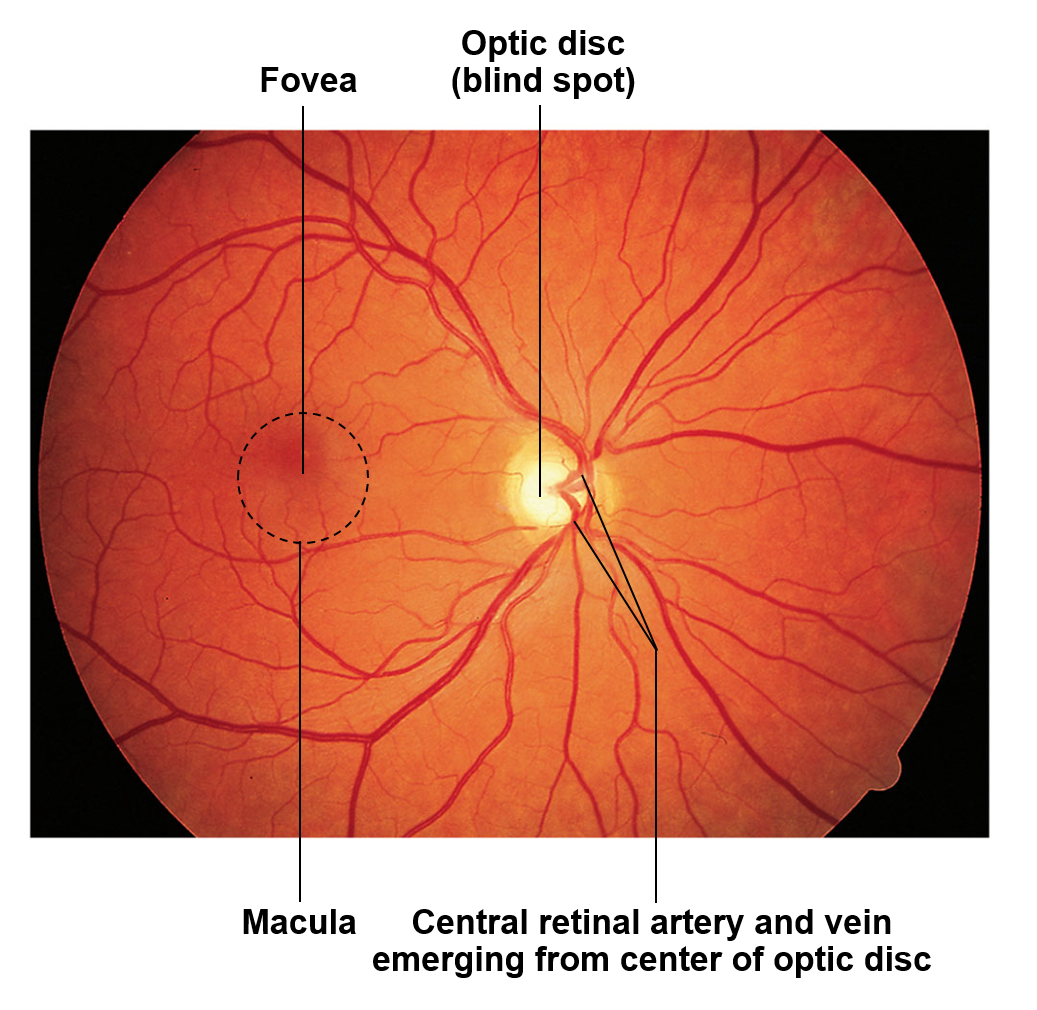
pictured is the retina
Olfaction
Allows sense of smell, and begins the olfactory epithelium
Olfactory glands secret a mixture which coats the olfactory epithelium; the functions of this coat are unclear
Receptor cells
Highly modified neurons which can detect dissolved chemicals as they interact with odorant-binding proteins
Basal cells
Divide within the olfactory epithelium to replace worn out receptor cells
Gestation
Allows what is generally considered taste
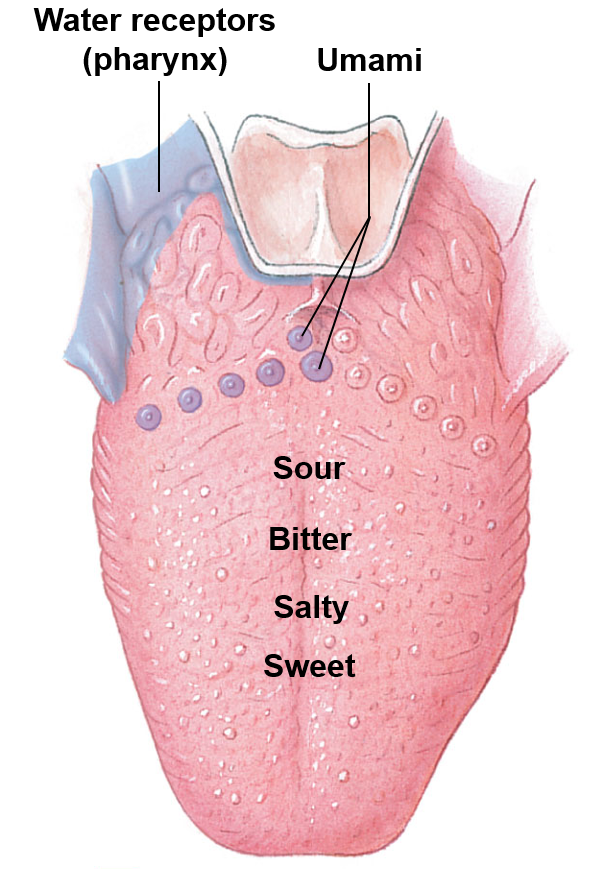
The taste receptors, which are clustered into taste buds, are found on the tongue and pharynx
Taste sensations
Sweet
Salty
Bitter
Sour
Umami
Quenched thirst is also detected by water receptors
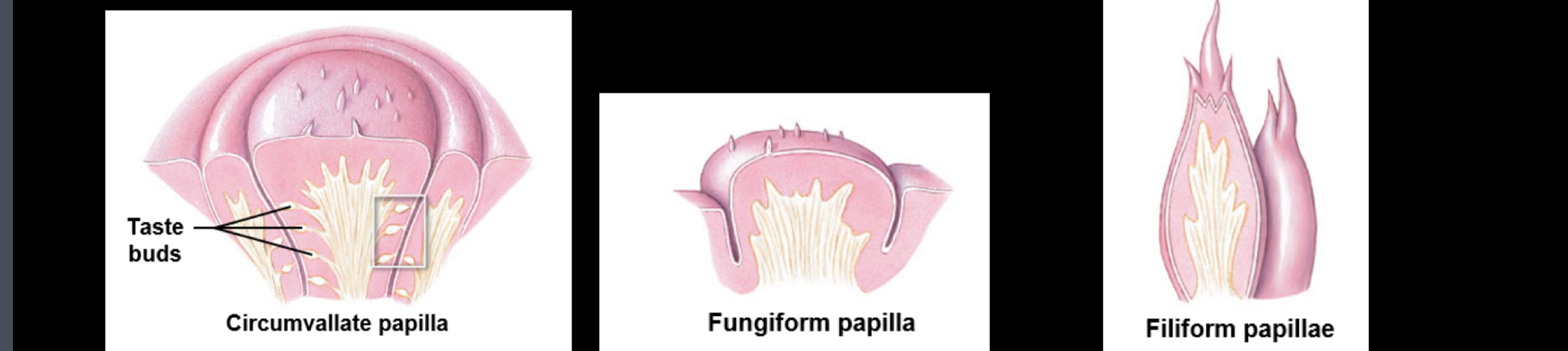
Three cases of lingual papillae
Circumvallate papilla
Fungi form papilla
Filiform papillae
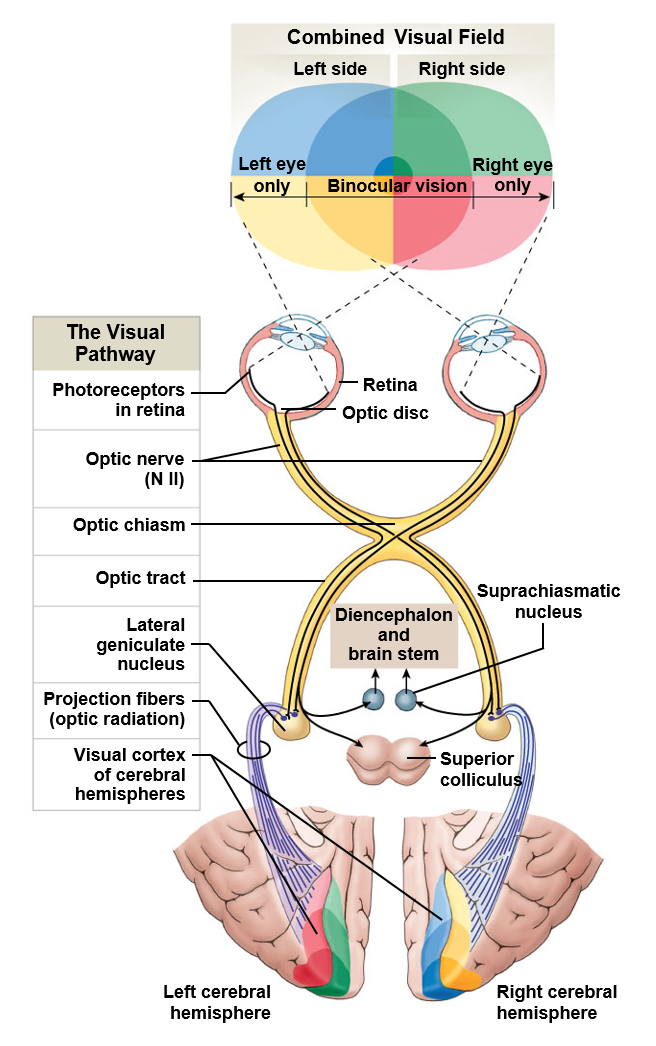
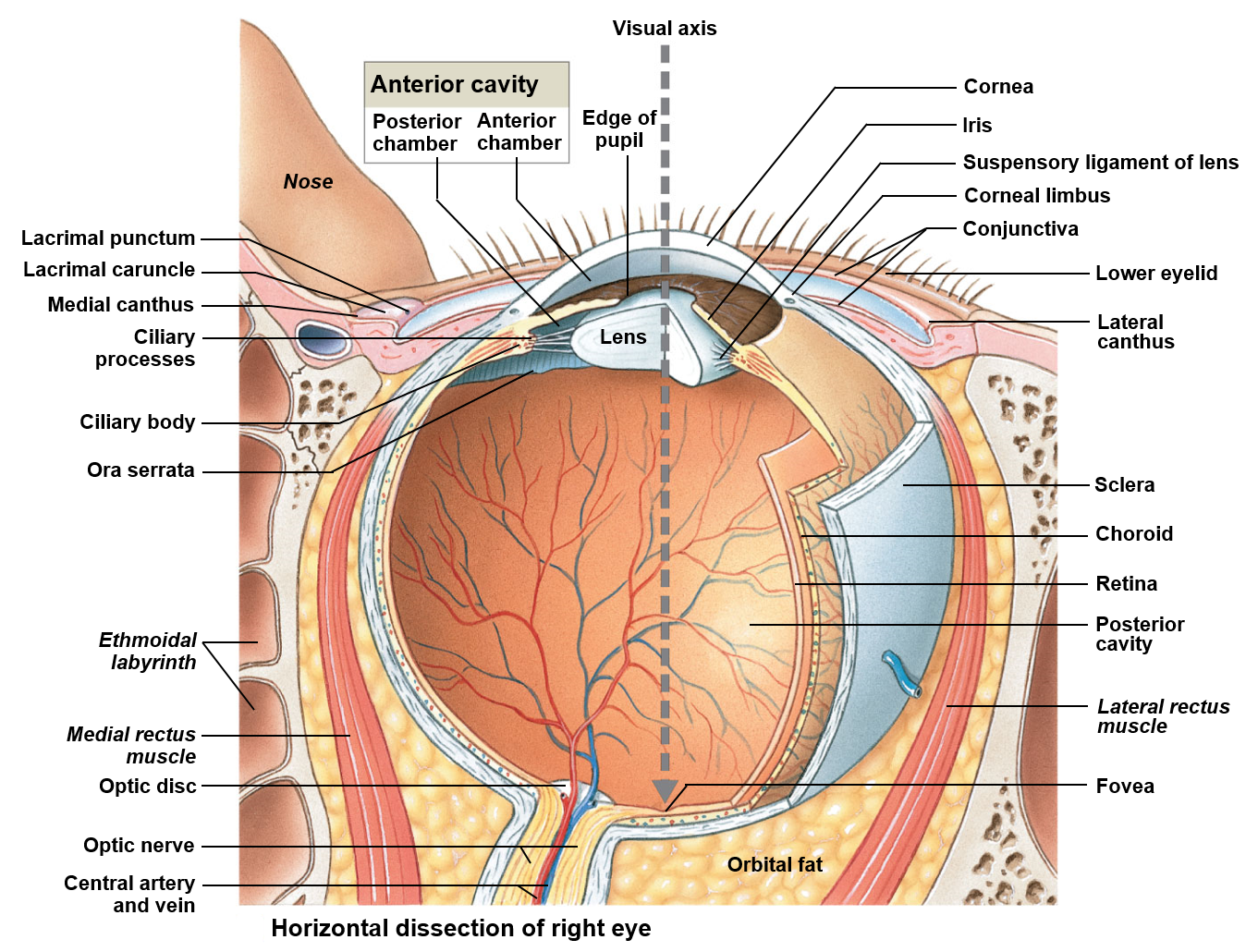
Vision
Allows for what is commonly called sight
Light passes through a protective cornea, an anterior chamber, the lens of the eye, and a posterior cavity on its way to the retina
Retina cells react in response to light, sending nerve impulses towards the brain via the optic nerves (CN II)
Visions anterior chamber
Is filled with a fluid like substance called aqueous humor
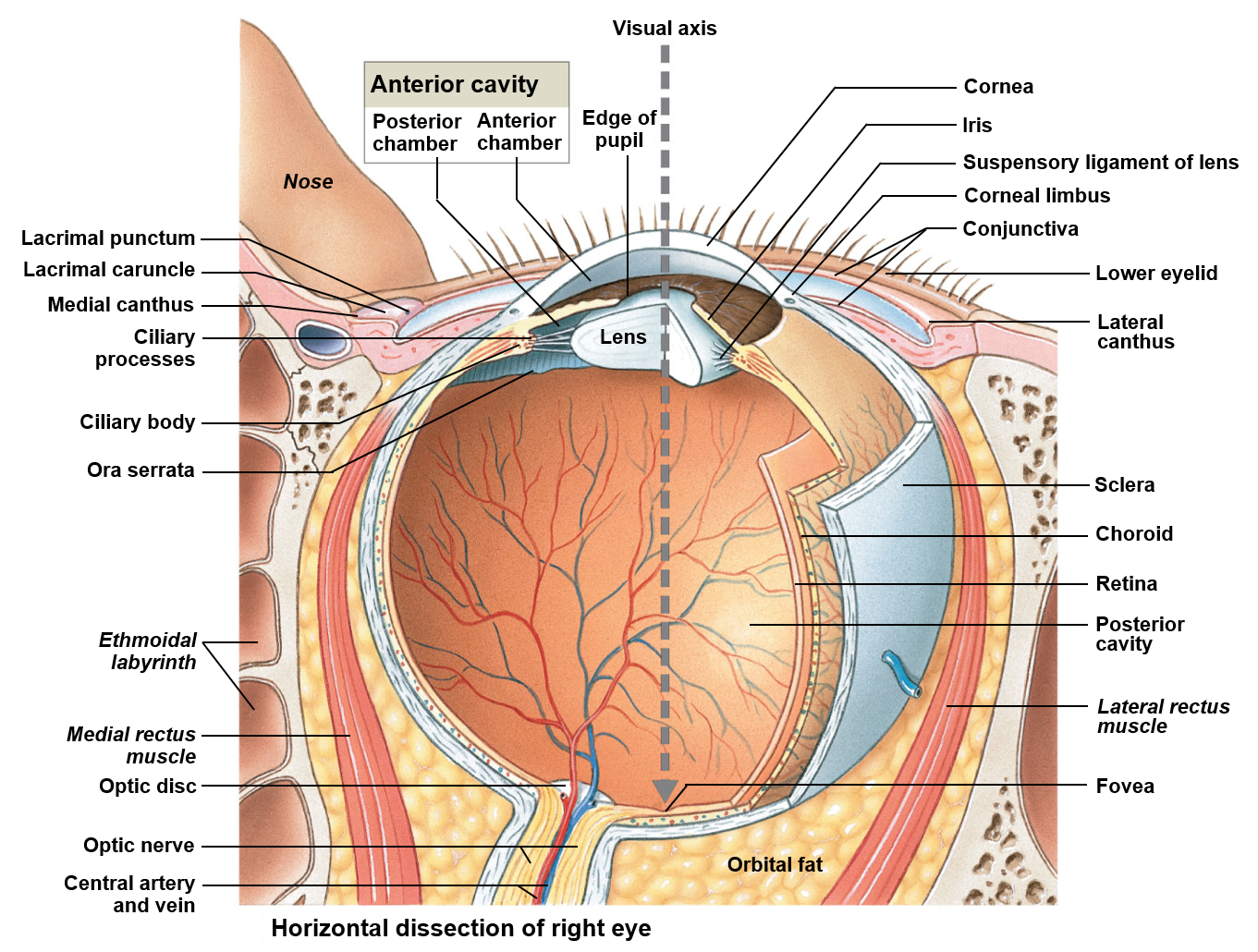
Visions posterior chamber
Is filled with a clear, transparent, gelatinous mass called the vitreous humor
Rods
More numerous; have a high sensitivity to light; do not discriminate colors
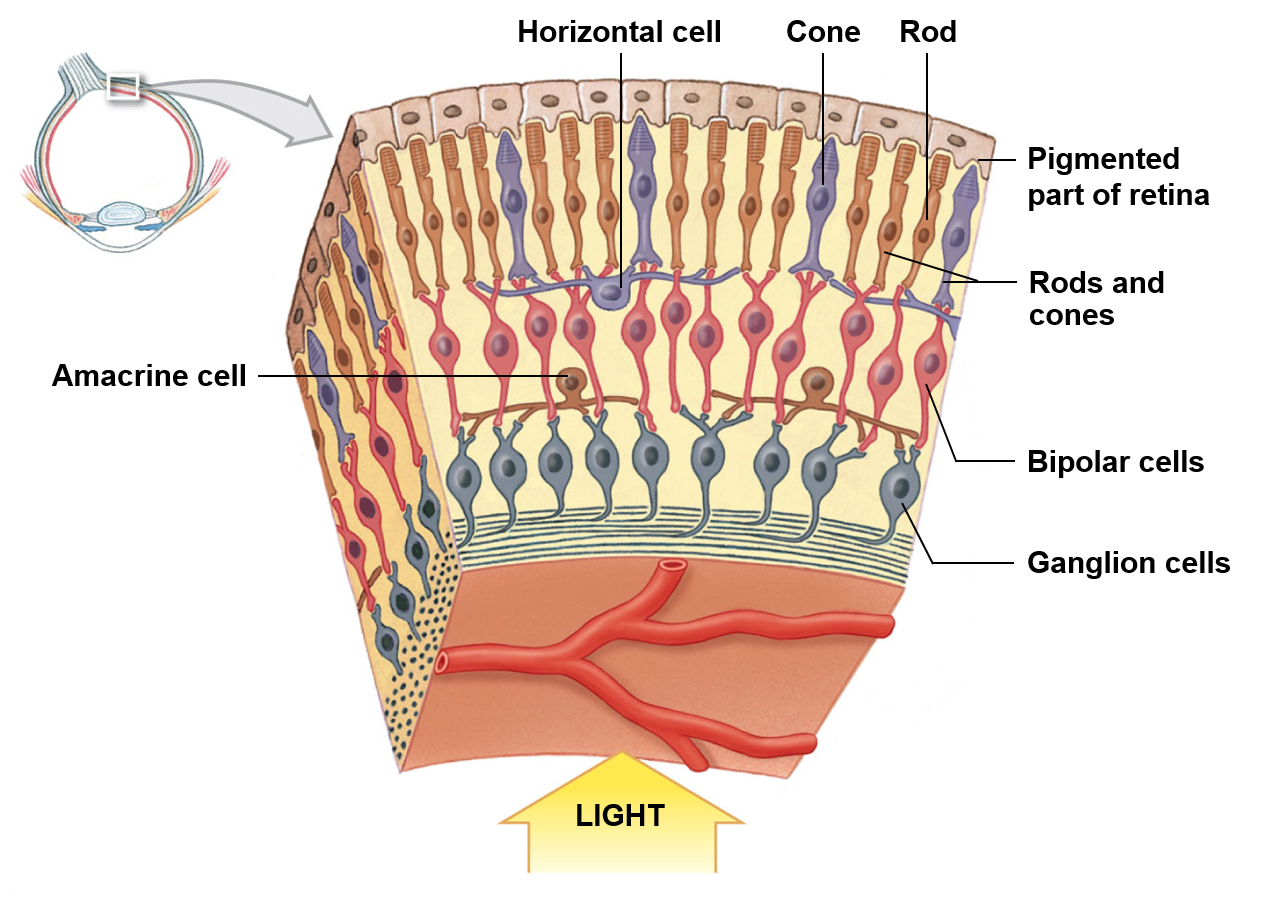
Cones
Less numerous; most individuals possess three distinct types; make up the entirety of the fovea centralis
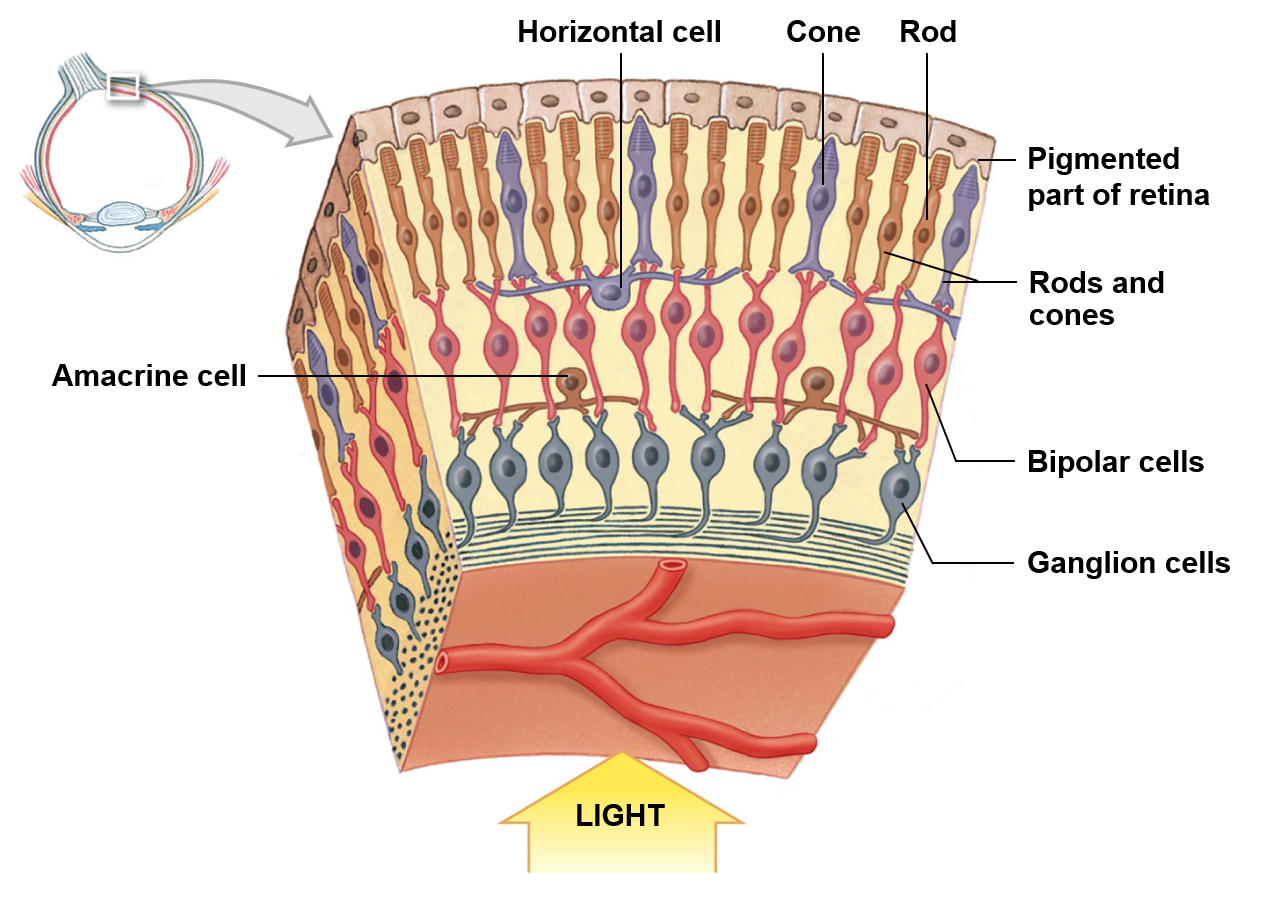
Macula lutes
Area near the center of the retina that contains closely packed photoreceptors for high acuity vision
Fovea centralis
Small indentation or put found in the central macula lutes; photoreceptors in this region are strictly cones
Optic disc
Allows ganglion cells to exit from the optic nerve; provides a passageway for the major blood vessels of the retina; due to the fact it is not associated with any rods or cones, each corresponds to a physiological blind spot
Focal point
Changes in the ciliary muscle help direct light onto the focal point of the retina for close distant vision
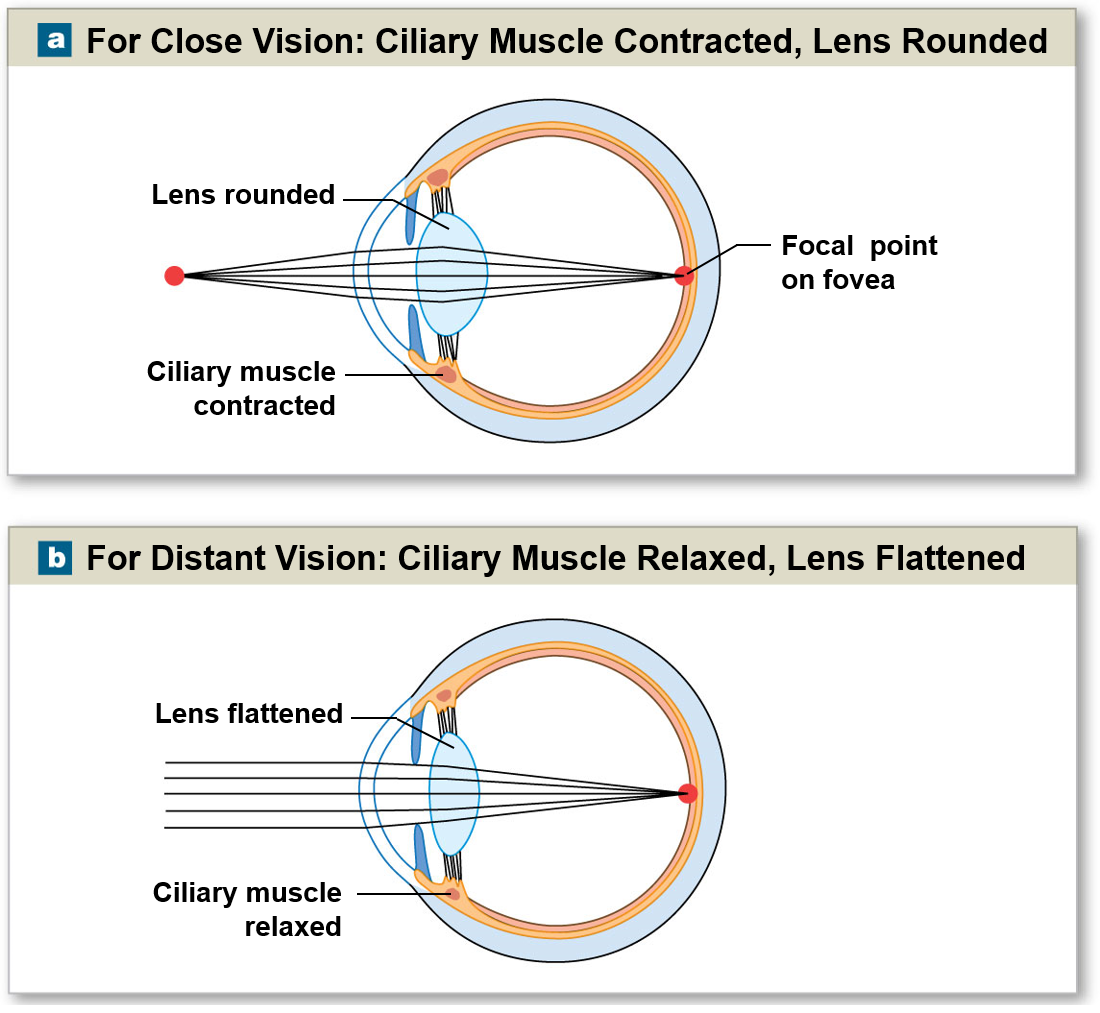
Myopia and hyperopia
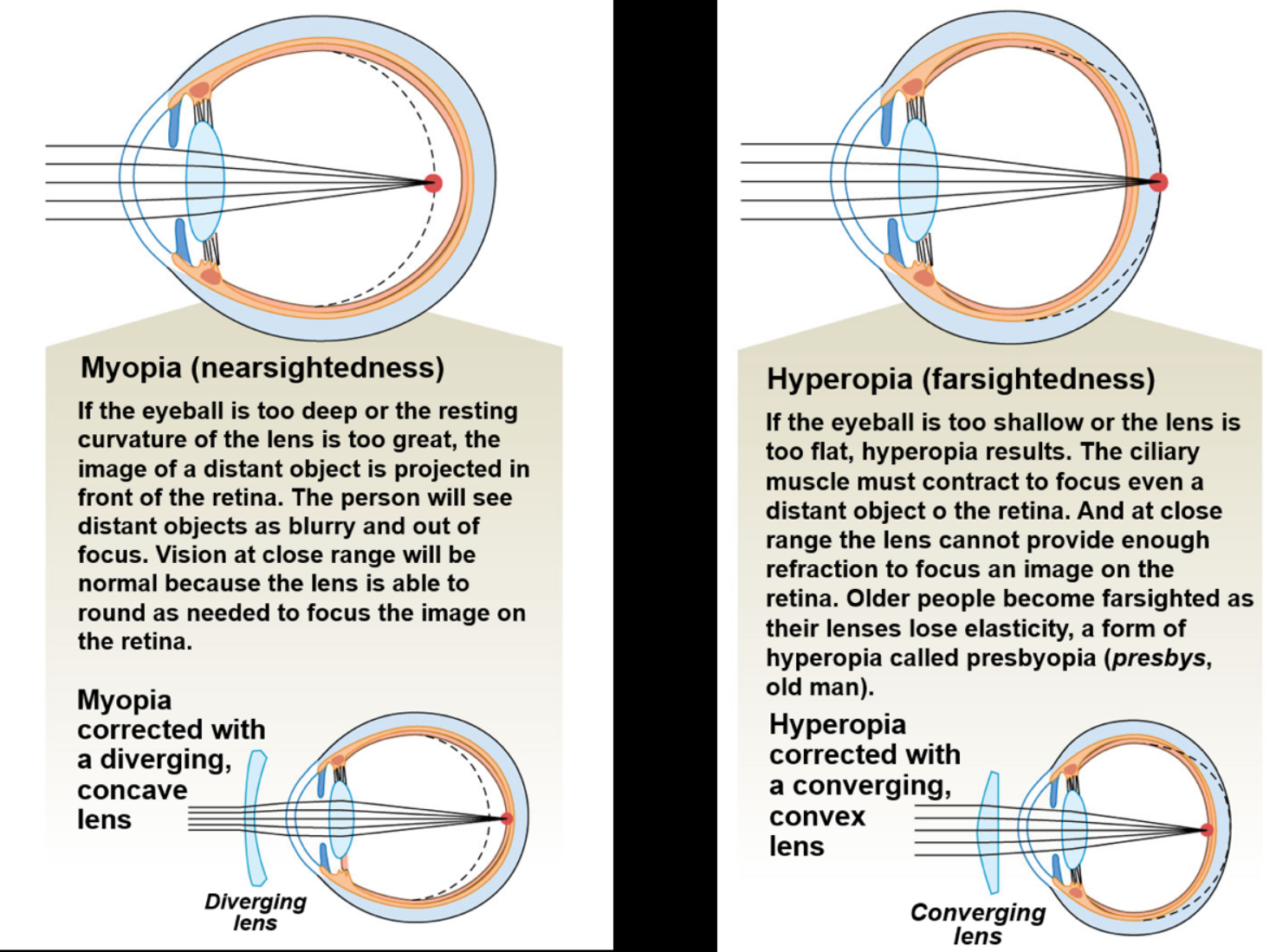
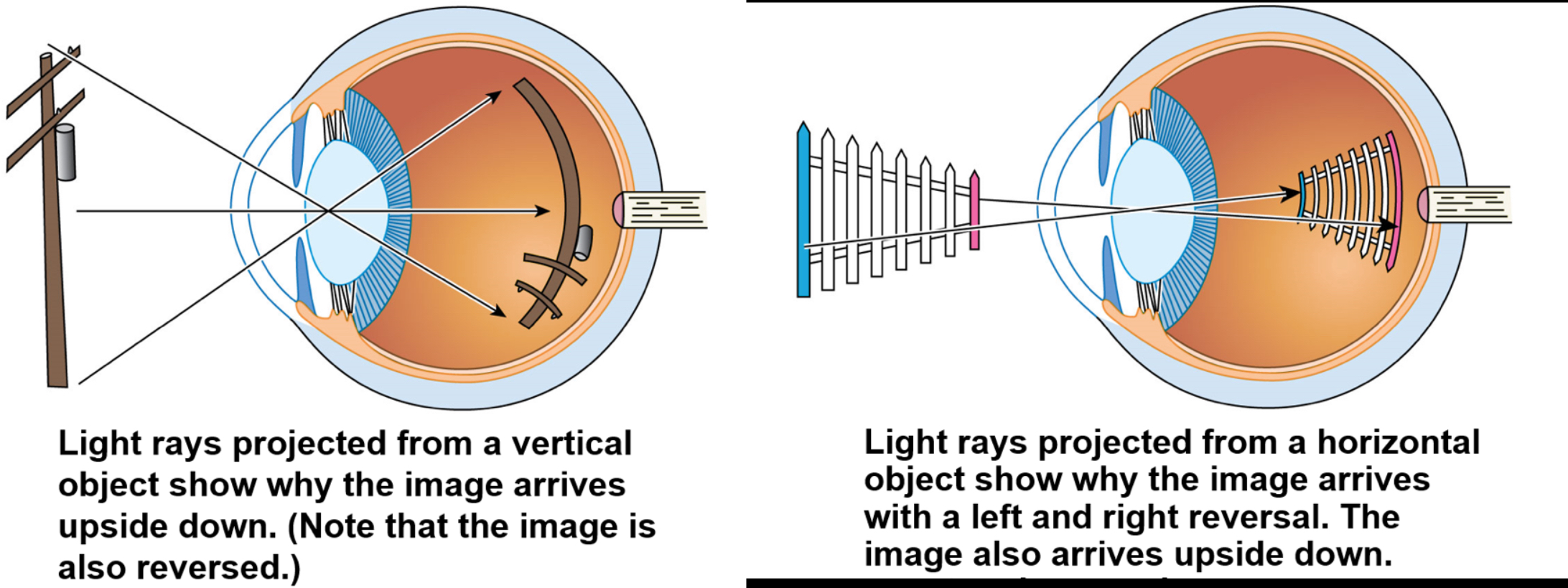
Image formation
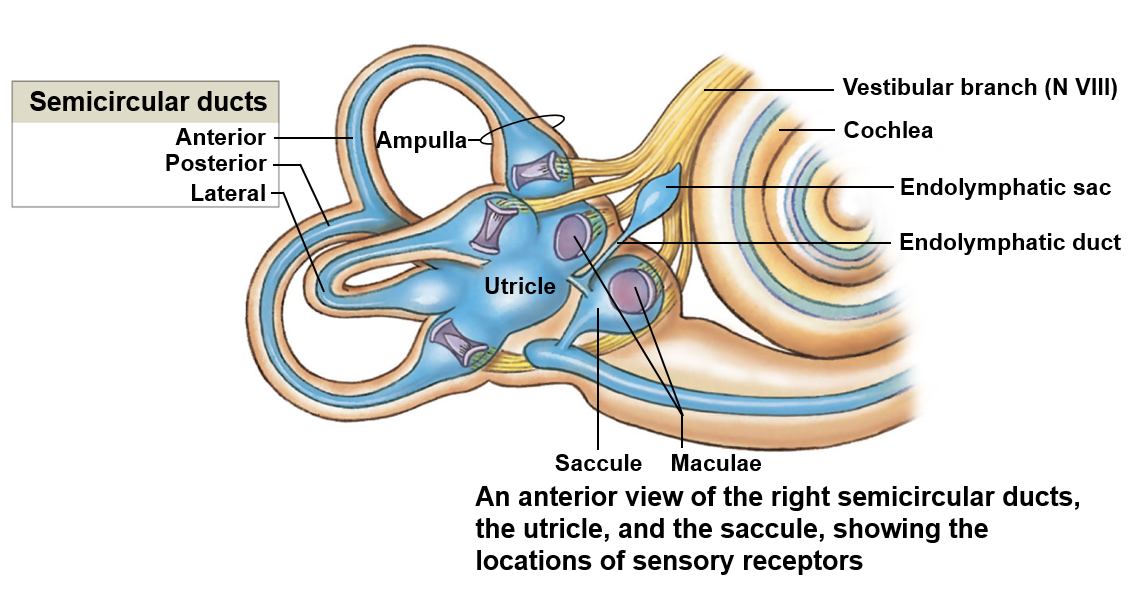
Balance and hearing
The cochlea associated with hearing
Balance is associated with the vestibule and semicircular canals
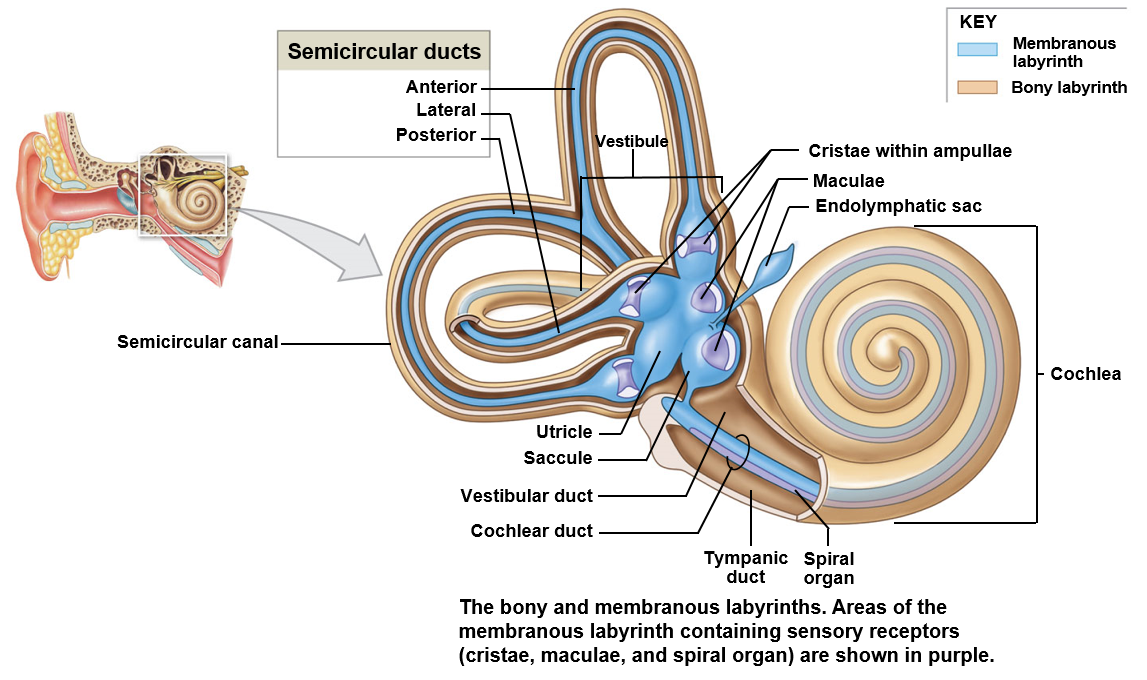
Vestibule
Encloses the saccule and utricle; responsible for detecting gravity and linear acceleration
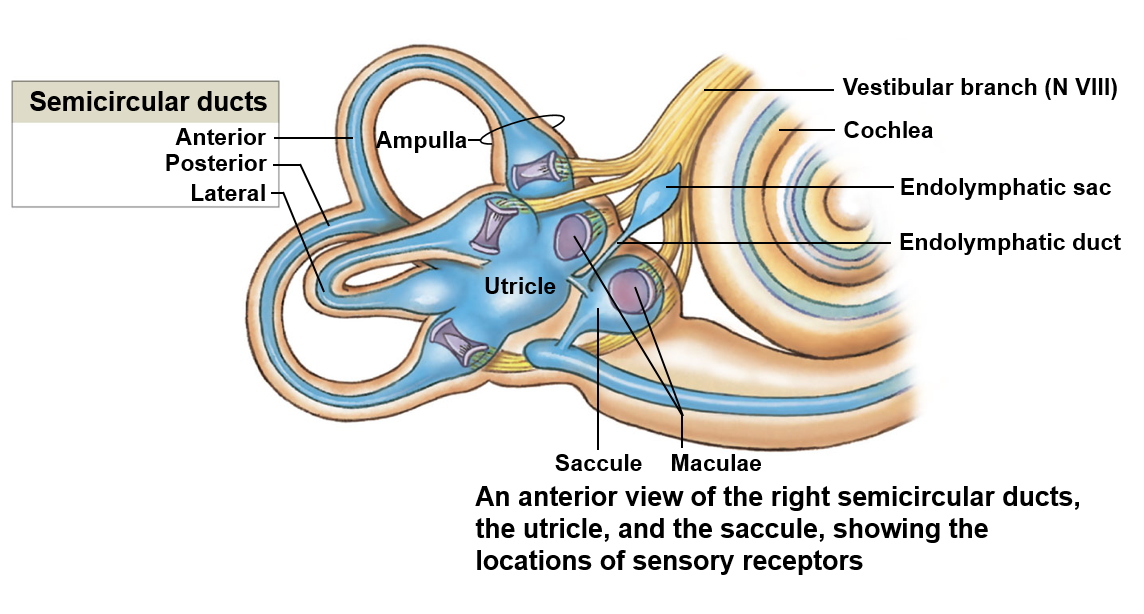
Saccule
Detects movement in the vertical plane
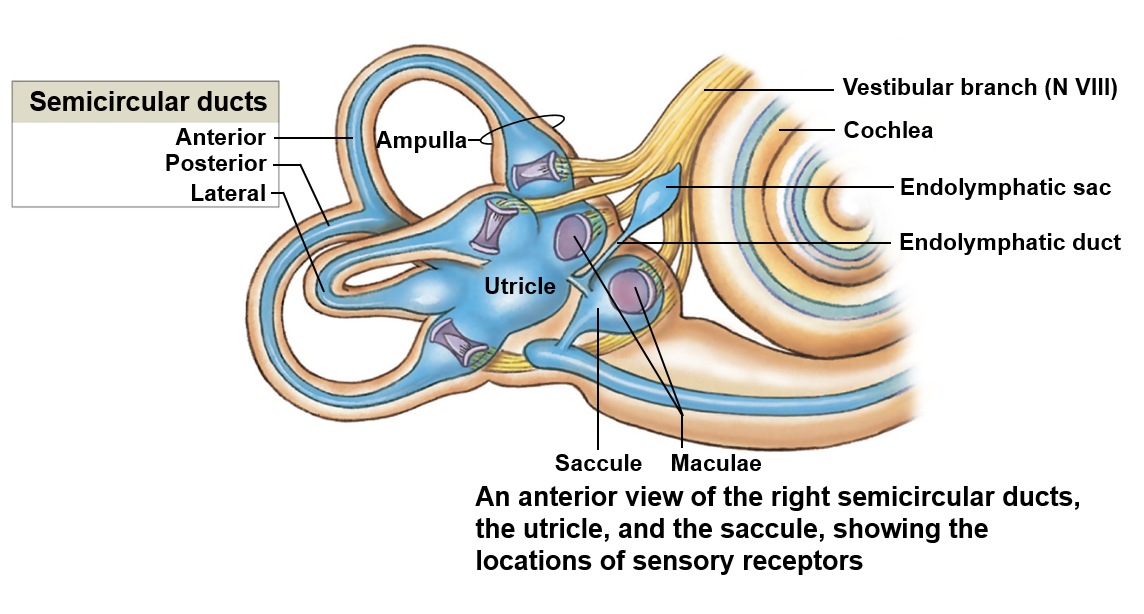
Utricle
Detects movement in the horizontal plane
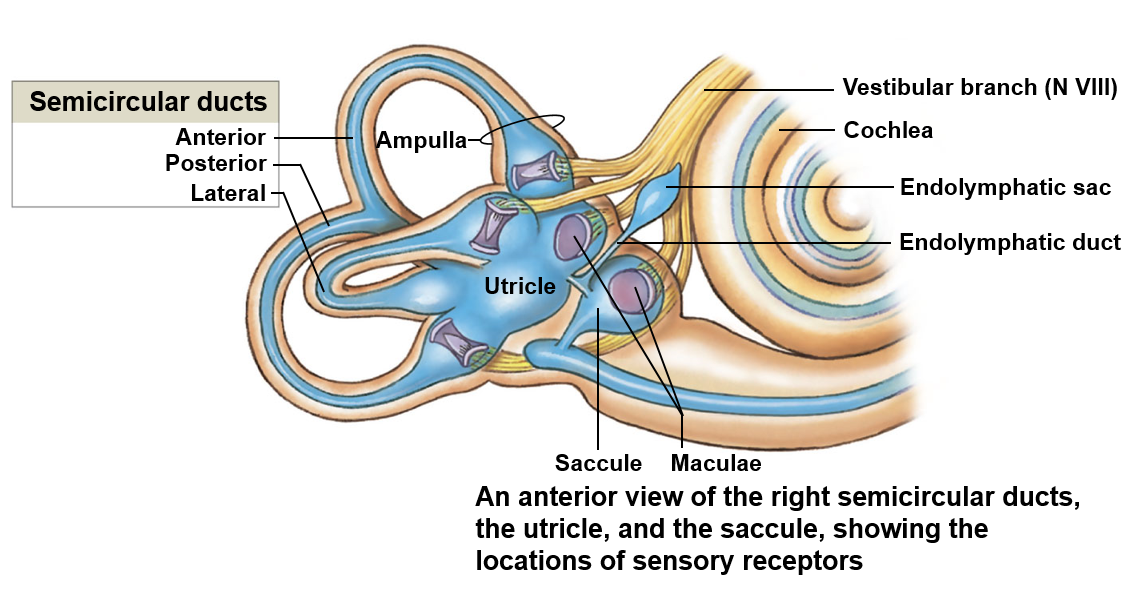
Semicircular ducts
Detects the rotation of the head