22 - Electric fields
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is a field in physics?
a region in which an object will experience a force at a distance
what creates an electric field?
A charged object
define the term electric field
a region of space in which a charged particles are subject to an electric force
define electric field strength
what is the formula?
The force experienced per unit positive charge at that point
E = F/Q
electric field is a vector quantity
what direction does it act?
the direction of electric field at a point is the direction in which a positive test charge would move when placed at that point
What is Coulomb's Law?
what is the formula?
any two point charges exert an electrostatic force on each other that is proportional to the product of their charges & inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them
F=Qq/4πε0r²
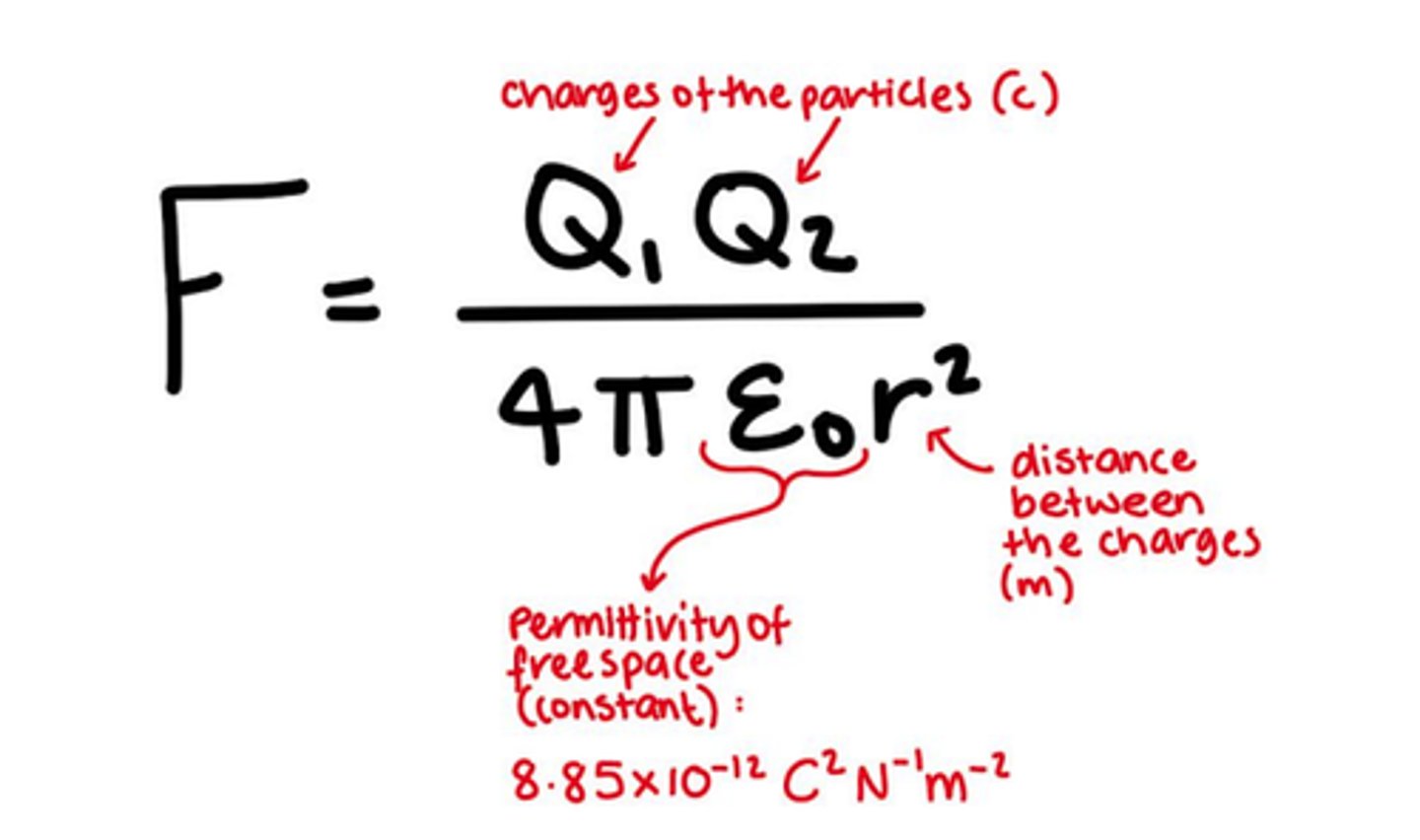
what is the formula for electric field strength E at a distance r from the centre of a sphere in a radial field
E = Q/4πε0r²
graph of E against 1/r²
Straight line through the origin, with gradient Q / 4πε₀

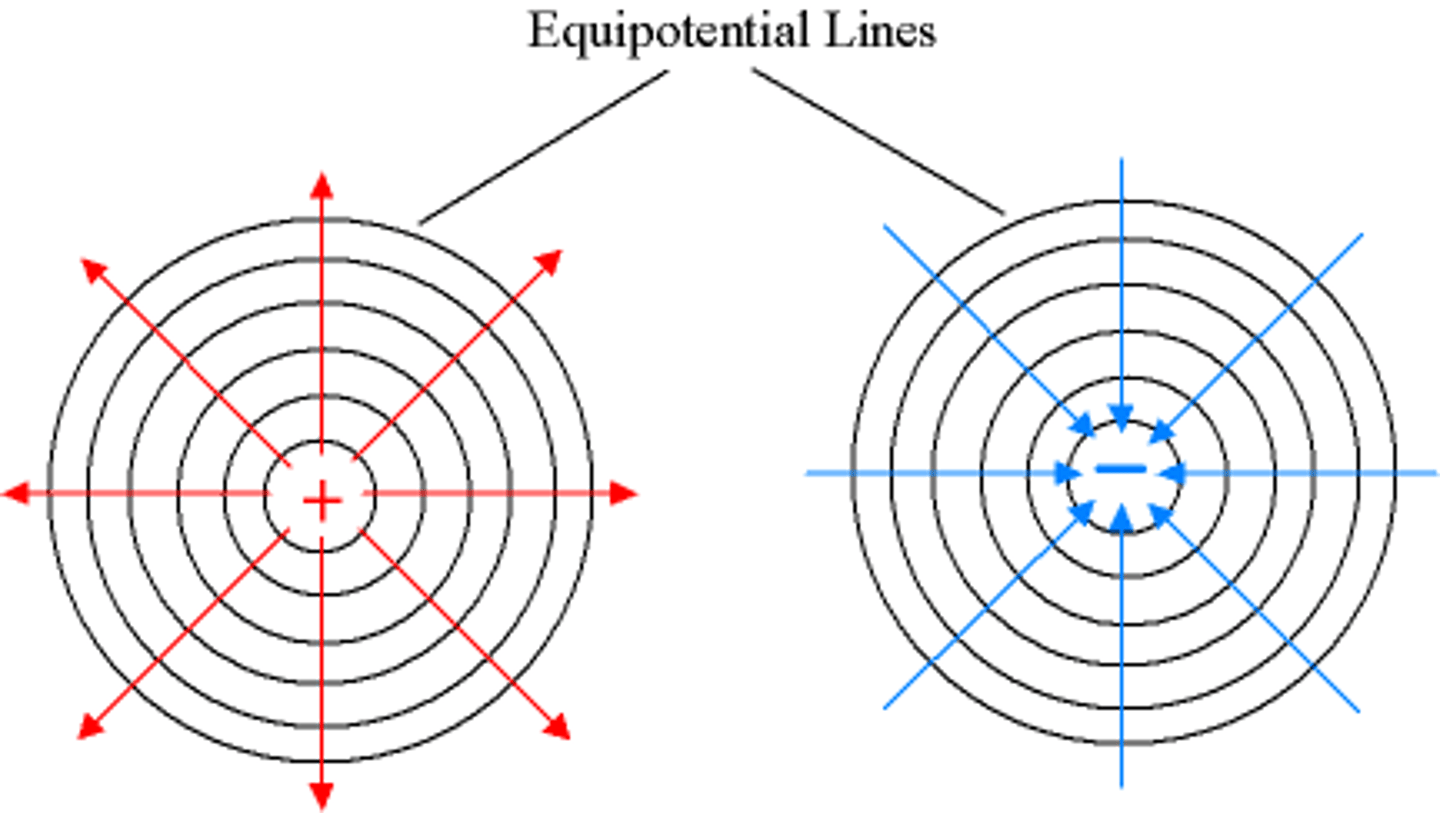
What are equipotential lines?
Lines at which all of the test charges have the same voltage
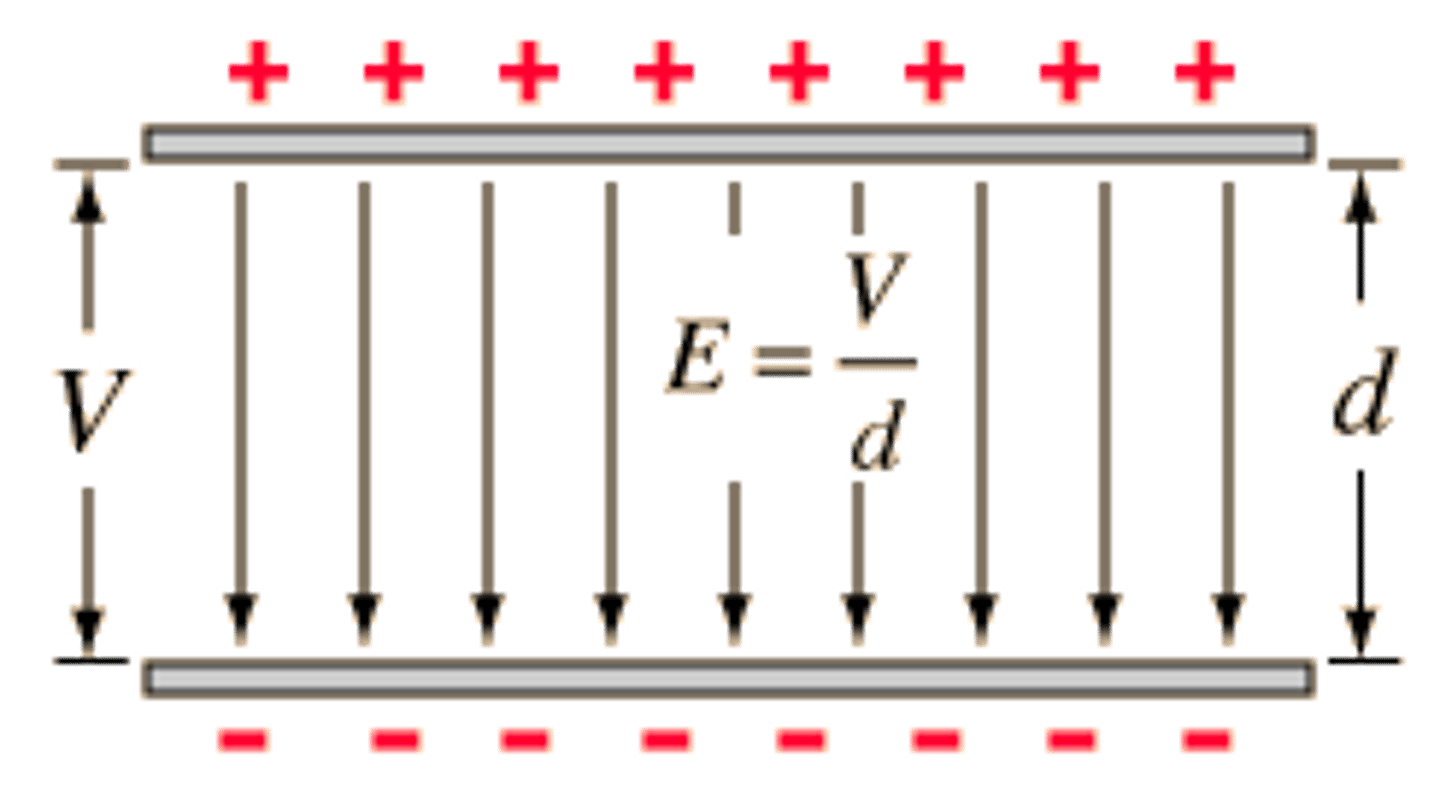
what is the formula for the electric field strength E between two parallel plates
E = V/d
V = potential difference between the plates
d = separation
E = electric field strength
what physical characteristics does the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor depend on? what are the proportionalities?
so what is the formula, using this idea?
when can you only use this constant of proportionality?
how does the constant of proportionality differ in different capacitors?
the area A of the insulator between the two plates (C∝A)
the separation d between the plates (C∝1/d)
C = ε0A/d
- ε0 can only be used when the dielectric is a vacuum
- if the dielectric is another material, you need to use the permittivity of that material itself, ε
- multiply the permittivity of free space, ε0, by the relative permittivity of the insulator to give the overall permittivity of the insulating substance
how do you calculate the force exerted on a charged particle in a uniform electric field, where the particle is moving parallel to the direction of the field?(you know p.d. and seperation between two plates)
if an electron is travelling in the direction of the electric field, is it accelerating or decelerating?
- E=F/Q → F = EQ
- Q = charge of the particle, if electron, Q = e
- E (electric field strength in a uniform electric field) = V/d where V = p.d. between the plates and d is the separation between the plates
- electron is decelerating
How do we analyse the motion of a charged particle moving at right angles to the direction of the electric field?
- analyse horizontal and vertical motion separately
- horizontally, there is no acceleration so use speed = distance/time
- vertically, analyse using SUVAT equations
what is the difference between the eletric potential energy for like charges, and opposite charges
- for like charges, force is required to decrease their separation
- for opposite charges, a negative force is required to increase their separation
- The energy will also be negative as it will take energy to separate
- the energy will now represent the total work done to move a charged particle from a distance 'r' away from a point charge, Q, to infinity
define electric potential difference
The work done per unit charge between two points around a particle of charge Q.
what is formula for capacitance of a sphere
C = 4πε0R
where R = radius of sphere
area under force distance graph for a point and spherical charge
- total work done to bring the point charge from infinity to a separation r
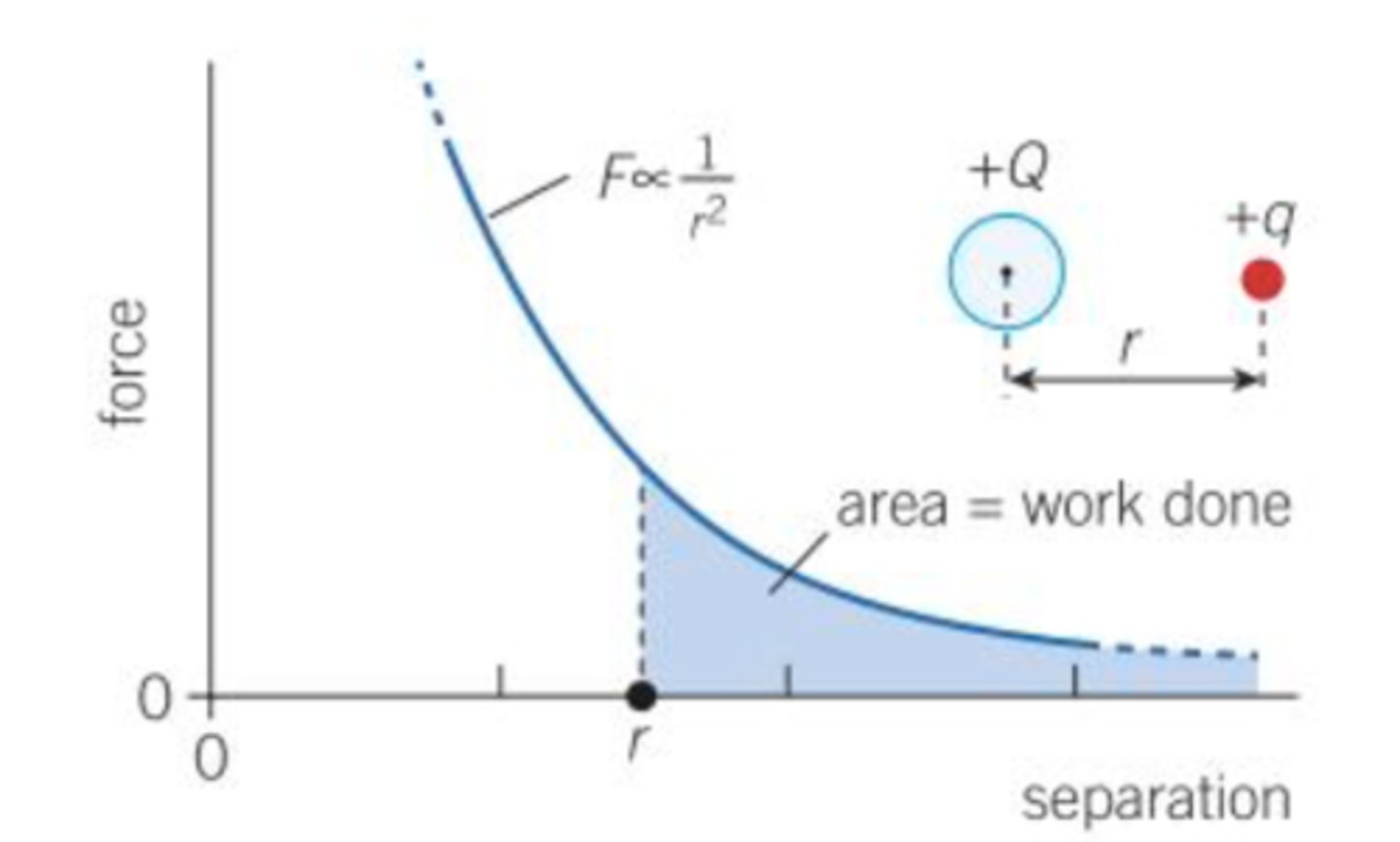
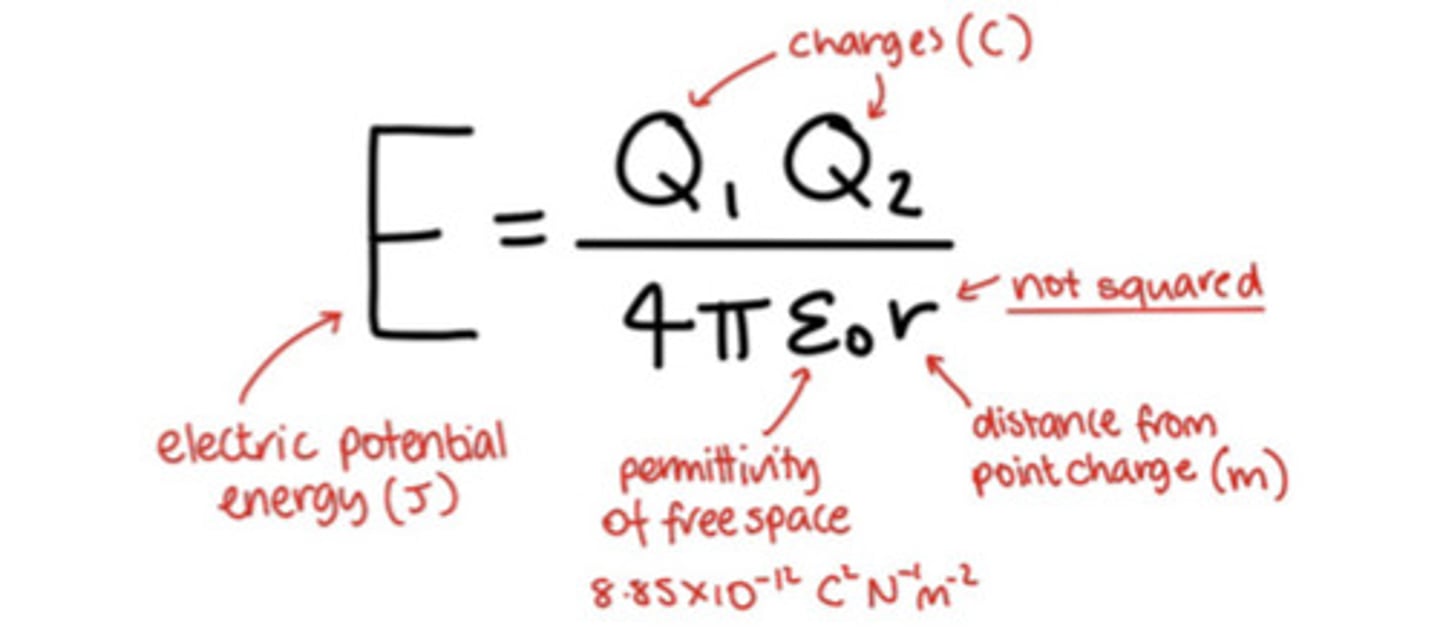
what is electric potential energy?
what is the formula
the work done needed to move a point charge q from infinity to a radius r
- energy = Qq/4πε0r
What is electric potential?
what is the formula?
the work done per unit charge in bringing a positive charge from infinity to that point
- V = Q/4πε0r
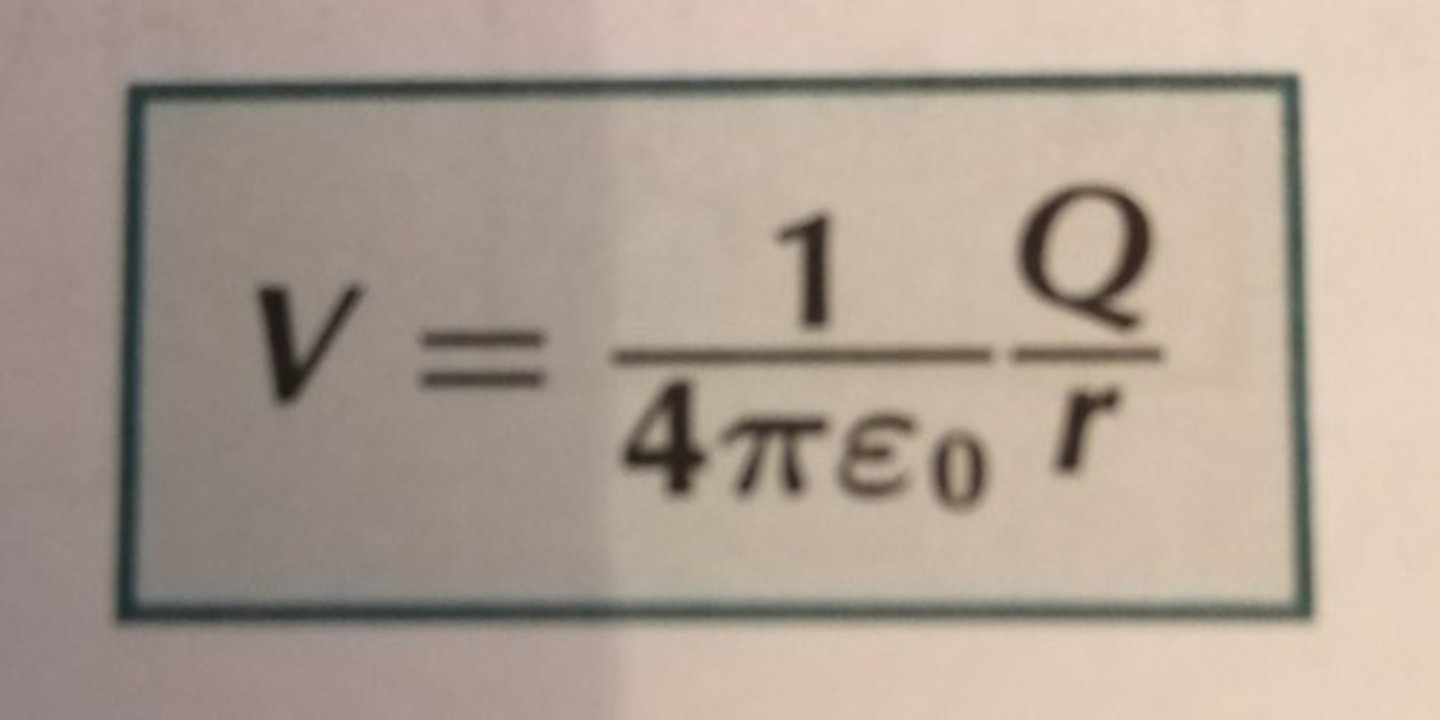
define potential difference
The work done per unit charge flowing between any two points,
or the difference in electric potential between two points