AP bio macromolecules
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Carbohydrates
Function as a primary source of energy; examples include sugars and starches.
Monosaccharides
Single sugar molecules; examples are glucose and fructose.
Disaccharides
Carbohydrates formed from two monosaccharides; examples include sucrose and lactose.
Polysaccharides
Complex carbohydrates formed from long chains of monosaccharides; examples include glycogen and cellulose.
Lipids
Function primarily as long-term energy storage, insulation, and chemical signaling; examples include fats and oils.
Saturated fats
Solid at room temperature, found in animal products; examples include butter and lard.
Unsaturated fats
Liquid at room temperature, found in plant oils; examples include olive oil and canola oil.
Phospholipids
Form cell membranes; consist of a glycerol backbone, two fatty acids, and a phosphate group.
Proteins
Function as structural components, enzymes, and signaling molecules; examples include enzymes and hemoglobin.
Amino acids
Building blocks of proteins; there are 20 different types.
Peptide bonds
Link amino acids together to form proteins.
Enzymes
Biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in the body; examples include amylase and lactase.
Nucleic Acids
Function in storing and transmitting genetic information; examples include DNA and RNA.
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
Double-stranded nucleic acid that stores genetic information.
RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
Single-stranded nucleic acid involved in protein synthesis.
Nucleotides
Building blocks of nucleic acids; consist of a sugar, phosphate group, and nitrogenous base.
Hydrophilic
Refers to molecules that are attracted to water; often seen in carbohydrates.
Hydrophobic
Refers to molecules that repel water; commonly found in lipids.
Functional groups
Specific groups of atoms within molecules that determine the characteristic reactions of those molecules.
Identifying carbohydrates
Look for the presence of -OH (hydroxyl) groups and ring or linear structure.
Identifying lipids
Check for long chains of carbon and hydrogen with few oxygen atoms.
Identifying proteins
Presence of amino acid chains and peptide bonds indicated through specific tests.
Identifying nucleic acids
Detect the presence of nucleotide sequences with complementary base pairing.
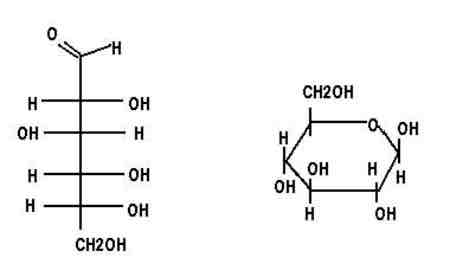
What macromolecule is this?
Carbohydrate
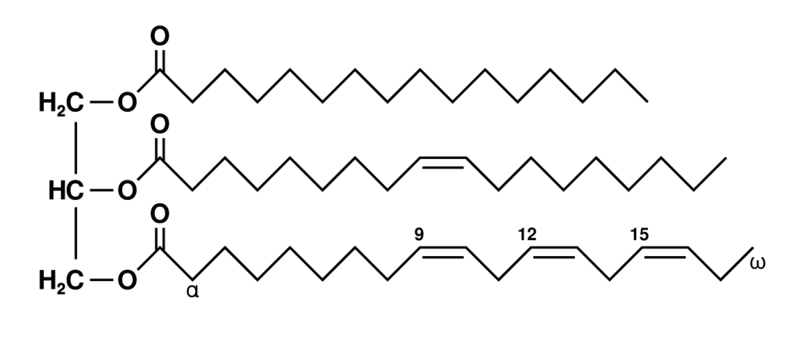
What macromolecule is this?
Lipid
2 unsaturated fatty acids
1 saturated fatty acid
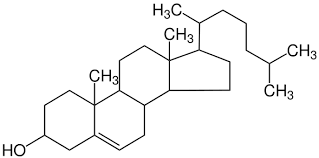
What macromolecule is this?
Lipid
steroid
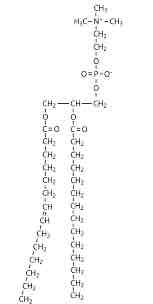
What macromolecule is this?
Lipid
phospholipid
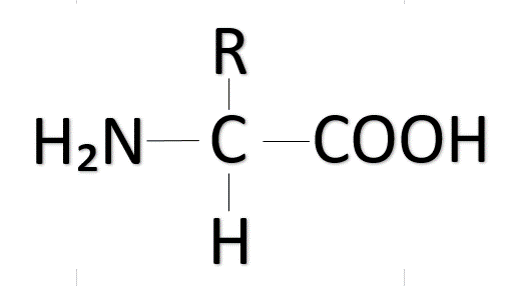
What macromolecule is this?
Amino Acid
Protein
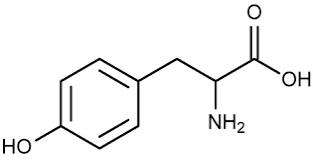
What macromolecule is this?
Amino Acid
Protein
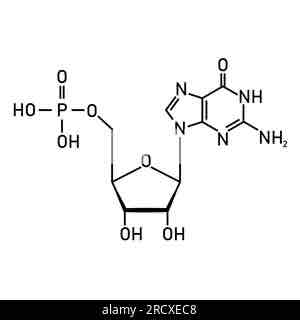
What macromolecule is this?
Amino Acid
Nucleotide