bio005 Ch14 Cardiac Output, Blood Flow, and Blood Pressure
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Cardiac Output (CO)
Cardiac output is volume of blood pumped/min by each ventricle
Stroke volume (SV) = blood pumped/beat by each ventricle
Heart rate (HR) = the number of beats/minute
CO = SV x HR
Total blood volume is about 5.5L
Cardiac Output (CO) equation
CO(mL/min)= SV(mL/beat) X HR(beat/min)
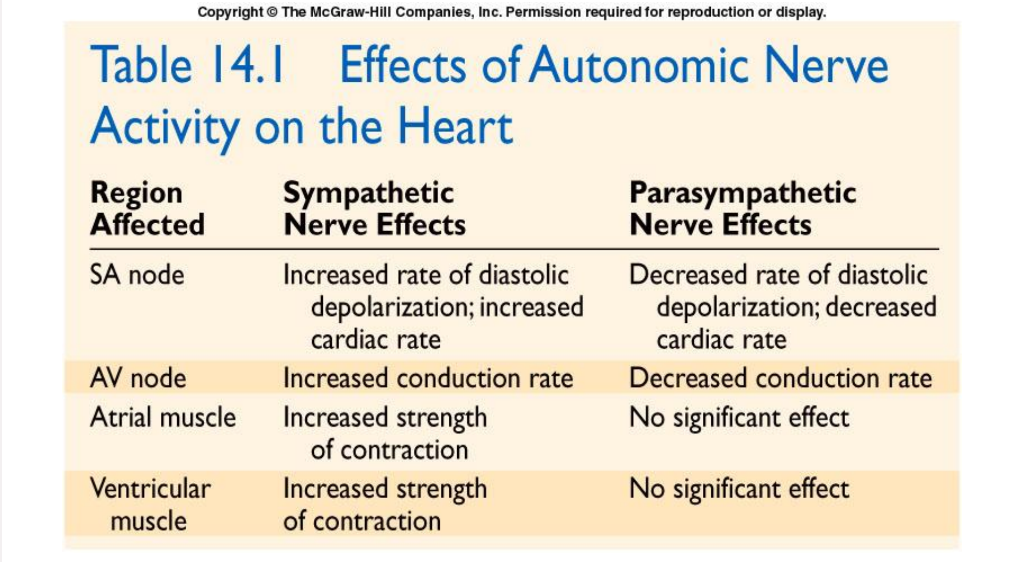
Regulation of Cardiac Rate
Without neuronal influences, SA node will drive the heart at a rate of its spontaneous activity
Autonomic innervation of SA node is the main controller/regulator of HR
The sympathetic nervous system increase heart rate.
The parasympathetic nervous system decrease heart rate.
Cardiac control center of medulla oblongata coordinates activity of autonomic innervation
Regulation of Cardiac Rate: Sympathetic
Norepinephrine and epinephrine (“adrenaline”) increase opening of pacemaker HCN (hyperpolarization- activated cyclic nucleotide) channels
This depolarizes SA node faster,increasing HR
Regulation of Cardiac Rate: Parasympathetic
ACh promotes opening of K+ channels
Result: K+ outflow counters Na+ influx, slowing depolarization and decreasing HR
Effects of autonomic nerve activity on the heart
Stroke Volume
Determined by 3 variables:
End diastolic volume (EDV) = volume of blood in ventricles at the end of diastole which is also called preload
Total peripheral resistance (TPR) = resistance to blood flow in arteries which is also called afterload
Afterload measures as the pressure required for ventricular ejection
Contractility = strength of ventricular contraction
Regulation of Stroke Volume
Preload/EDV is workload on the heart prior to contraction
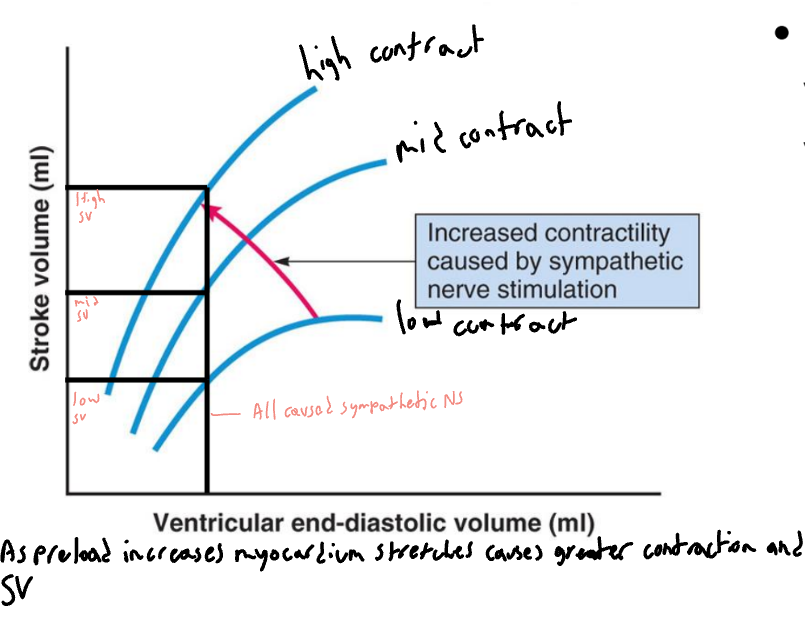
Stroke volume is directly proportional to preload and contractility (as preload and contractility increase, so does stroke volume)
Afterload/TPR impedes (make it harder for) ejection from ventricle
Ejection fraction
Ejection fraction is stroke volume / preload
Normally, EF is 50-70%, average 60%; a useful clinical diagnostic tool.
Less than 40% = heart failure, more than 75% = heart hypertrophy
Frank-Starling Law of the Heart
States that strength of
ventricular contraction
varies directly with
preload/EDV
It’s an intrinsic property of the myocardium
As EDV increases,
myocardium is stretched more, causing greater
contraction and SV
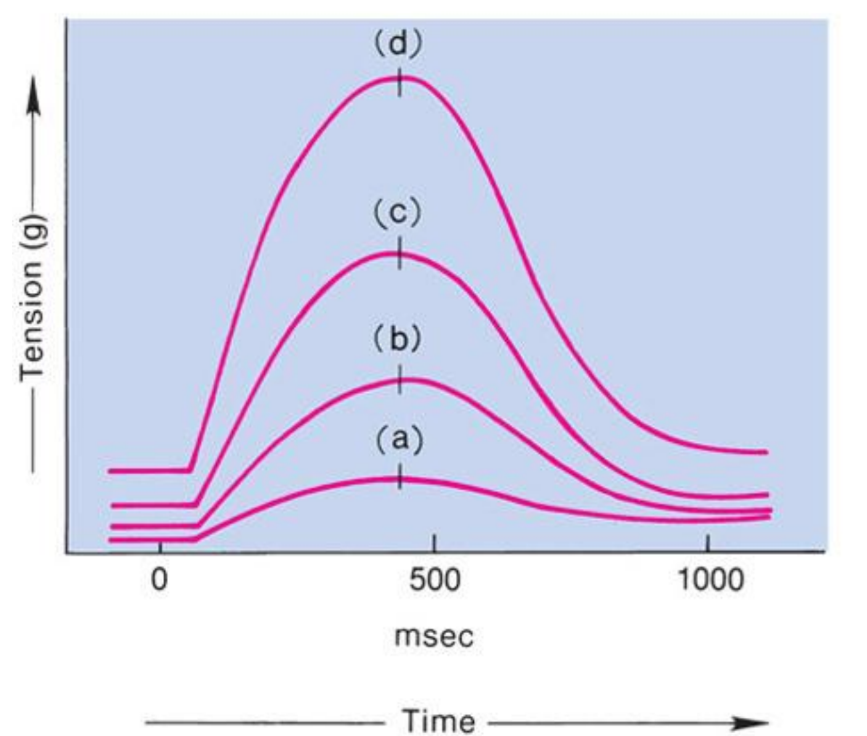
Frank-Starling Law of the Heart
(a) is state of myocardial
sarcomeres just before filling
Actins overlap, actin-myosin interactions are reduced, and contraction would be weak
In (b, c and d) there is increasing interaction of actin and myosin allowing more force to be developed
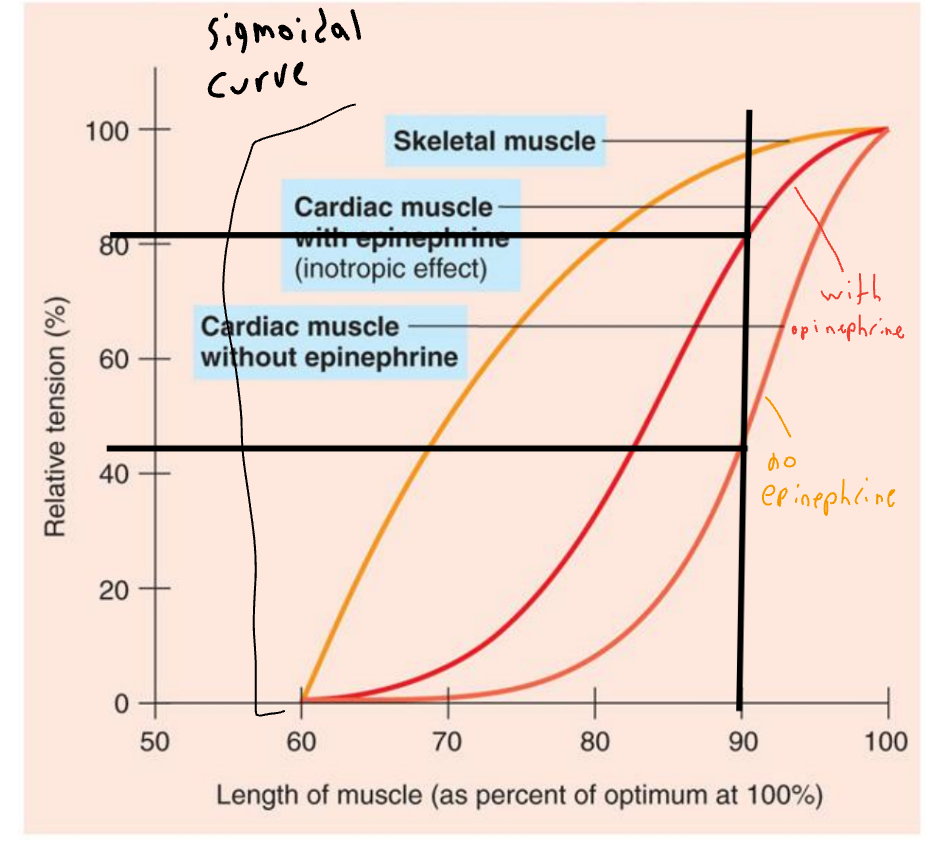
Extrinsic Control of Contractility
At any given EDV, contraction depends upon level of sympathoadrenal activity
Norepinephrine and epinephrine produce an increase in HR and contraction (positive ionotropic effect)
Due to increased Ca2+ in sarcomeres
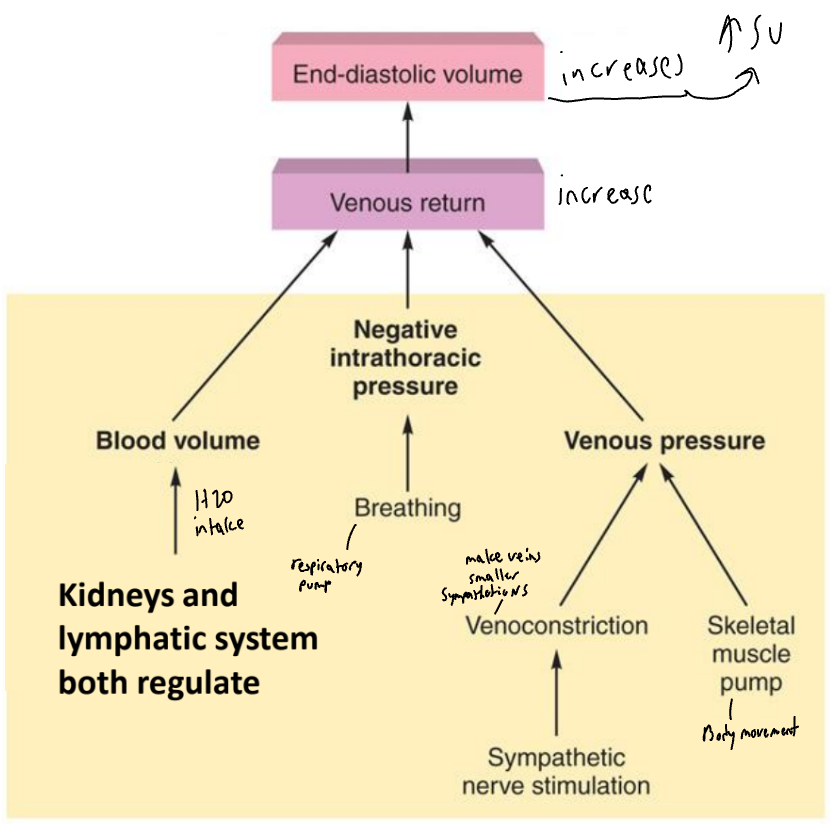
Variables that affect venous return and thus end-diastolic volume

venous return
Venous return = return of blood to the heart via veins
Controls EDV and thus SV and CO
Dependent on:
Blood volume and venous pressure
Venoconstriction caused by sympathetic stimulation
Skeletal muscle pumps
Blood Pressure (BP)
Blood pressure is controlled mainly by:
HR, SV, Peripheral resistance
an increase in any of these can result increased BP
Sympathoadrenal activity raises BP via arteriole vasoconstriction and by increased CO
Kidney plays role in BP by regulating blood volume
and therefore stroke volume
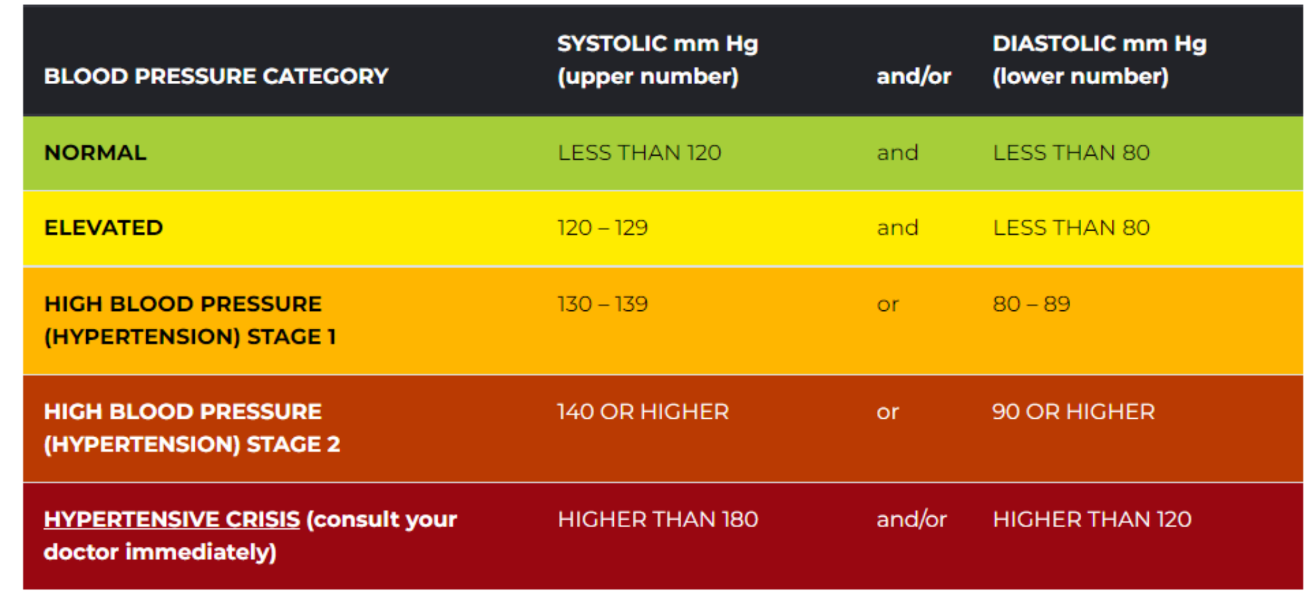
Hypertension
Blood pressure in excess of normal range for age and gender > 120/80 mmHg (2021 guidelines by ACA and AHA)
Afflicts 47% of adults in the U.S.
Most common type is primary/essential hypertension
Caused by complex and poorly understood
processes but to do with sodium consumption
Secondary hypertension is caused by known disease
processes (examples next slide)
Hypertension (BP Chart)
Possible Causes of Secondary Hypertension
Kidney disease – kidney disease; renal artery disease
Endocrine disorder – excess catecholamines; excess aldosterone
Nervous system disorder – including intracranial pressure; damage to vasomotor center
Cardiovascular disorder – complete heart block; arteriosclerosis of aorta
Dangers of Hypertension
Patients are often asymptomatic until substantial vascular damage occurs
Contributes to atherosclerosis
Increases workload of the heart leading to ventricular hypertrophy and congestive heart failure
Often damages cerebral blood vessels leading to stroke
silent killer
Treatment for hypertension
Often includes lifestyle changes such as cessation of smoking, moderation in alcohol intake, consistent exercise, reduced Na+ intake (less than 5 g daily), eating fruits/vegetables etc
Drug treatments include diuretics to reduce fluid volume, beta-blockers to decrease HR, calcium blockers