concepts of infectious diseases
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
infection: occurs when ___
-most don’t cause symptoms & go unnoticed
-ex: asymptomatic but PCR positive for covid
pathogen/ parasite enters/ begins to grow in/ on host
disease: disruption of ___
-specific signs & symptoms
-ex: HIV infection progresses to AIDs disease
normal structure/ function of any body part, organ or system
pathogenicity: ____
think: “___“
pathogen’s ability to make host sick, CAN it make host sick
virulence: _____
think: “__”
level of harm caused by pathogen following infection, HOW sick can it make host
types of pathogens
-primary pathogens: disease-causing microbes that ______
-opportunistic pathogens: cause disease only in hosts that are ____
break defenses of healthy hosts, immunocompromised
virulence can be measured by:
-lethal dose 50% (LD50)
-infectious dose 50% (ID50)
-# of pathogens needed to kill (LD) or infect (ID) of hosts
-the lower the LD50 & ID50, the ___ (higher/ lower?) the virulence
higher
latent infections: ____ (sympatomatic/ nonsymptomatic?) when virus is undetectable?
chronic infections: _____ (symptomatic/ nonsymptomatic?)
-symptoms that gradually develops & may resolve ___ (quickly/ slowly?)
-some infections have a latent state: pathogen can’t be found in culture (bc they’re in dormant state) but persist in body & can reactivate
acute infection: symptoms develop & resolve rapidly
ex: common cold
nonsymptomatic, symptomatic, slowly
primary infection: new infection in __ ___ ___
secondary infection: another infection w/ a diff ____ that follows ___ infection (due to weakened immune system from primary infection)
-ex: damaged tissues more succeptable to infection by diff organism; bacterial lung/ ear infection following primary infection with flu virus
-ex: ear infections after respiratory viruses, and skin infections like cellulitis following boils or other breaks in the skin
previously healthy individual, pathogen, primary
signs: ____
ex: fever, rash,
symptoms: ____
ex: pain, fatigue, dizziness
observable & measurable, experienced only by the patient
syndrome: collection of ___ & ___ that occur together & collectively _________ (can be multiple diseases)
sequelae: pathological consequences after ____
ex: immune response to strep infection can cause heart damage after infection
signs, symptoms, characterize a condition, a disease resolves
phases of disease
-incubation: between ___ & ___ of disease, host may/ may not be ___ & pathogen trying to ___
-prodromal: ___ symptoms of general ___, similar to most diseases
-illness: typical __ & __ develop & are most severe: _____ battle at its peak
-decline: # of __ decreases and __ & __ decline
-convalescent: symptoms have disappeared, __ at its peak, host is recovering
-long-term: immunity (memory of pathogen) ___ over time
-infection, signs, infectious, replicate quickly
-vague, discomfort
-sign, symptoms, pathogen-host
-pathogen, signs, symptoms
-immunity
-wanes
modes of transportation
direct
infected → uninfected host through: skin contact, air (aerosols, droplets, etc)
-from __ to new host
-vertical transmission: ___ → ___
indirect
through , ___ which means LIVING carrier
through ___ (fomite, food, water, aerosols)
-reservoir, mom, offspring
-vector, vehicle
reservoir: _____
-asymptomatic carrier harbors ___ ___ agent by doesn’t have the disease
ex: Neisseria meningitidis is an important cause of meningitis. It has no animal reservoir and is maintained in the human population by asymptomatic hosts.
-animal (including humans) or environment that normally harbors & maintains pathogen
-potential disease
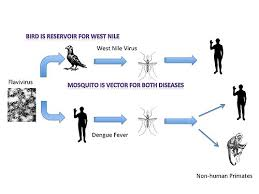
reservoir vs vector
.