Free radical substitution
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is a free radical
Free radicals are species that have an unpaired electron and they are highly reactive.
What is heterolytic fission
bond breaks unevenly and both electrons from the bond go to one atom.

What is homolytic fission
bond breaks evenly and each bonded atom gets one electron, forming free-radicals.

Under what conditions does FRS occur
Alkanes can react with halogens in the presence of ultraviolet (UV) light. A halogen is substituted for a hydrogen atom in the alkane to form a halogenoalkane.
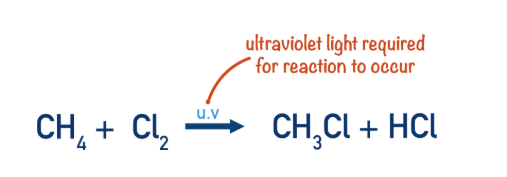
Initiation step in the reaction between chlorine and methane
A halogen and an alkane will not react without UV light. The UV light is required to form a halogen radical.
In this example, the UV light gives energy to the covalent bond in Cl2, so that it undergoes homolytic fission (see above). Producing two Cl• radicals.
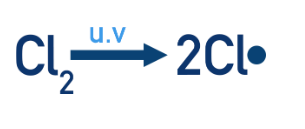
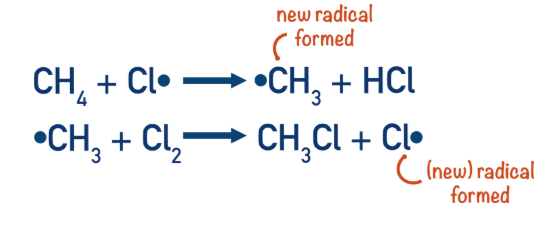
Propagation steps
Termination steps
When two radicals react together, two unpaired electrons come together and a covalent bond forms. This means a neutral product ( that isn't a radical) get produced and the chain reaction ends at this point. Any two radicals can react to end the chain process at any time.
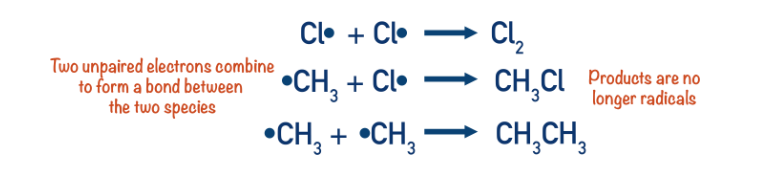
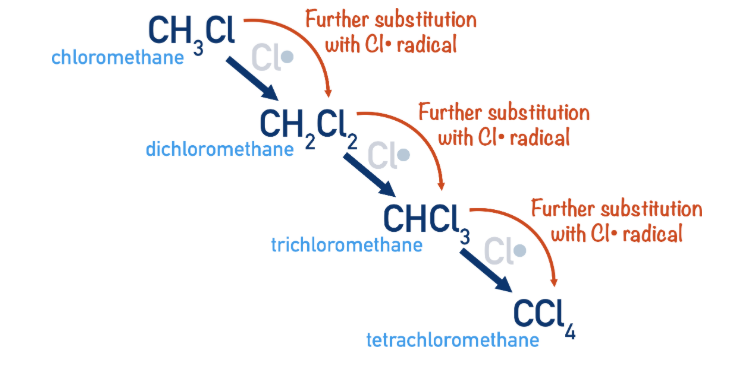
What is further substitution
Further substitution involves the FRS happening till there are no hydrogens left in the original compound.
Initiation step in the destruction of ozone

Propagation steps
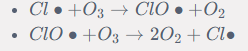
Termination step

Why is ozone useful
Absorbs harmful U.V
CFCs were used in aerosols, as coolants in fridges and as solvents in industry.
Scientists collected evidence in the 1970s that they were damaging the ozone layer.
This led to bans, beginning with Sweden in 1978, and the development of safer alternatives like hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and hydrocarbons.