Serology cont'd
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Legionnaire's disease, febrile agglutinins, S. aureus, GAS, M. pneumoniae, Spirochetes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Legionella: m/c are serogroup 1, 3, 4, and 6, which is most pathogenic?
serogrp 1
Legionella char
slender, pleo, GNR, faint staining in GST
req L-cysteine & iron (BCYE w/PAC or PVA): looks ground glass
Legionella epidemiology
bodies of water, air conditioning ducts, can resist disinfectants, can parasitize amoebae in water
L. pnuemophila pathogeneisis
Legionellosis: fever, chills, dry nonproductive cough → affects GI, CNS, liver, kidneys
Pontiac fever: self limiting febrile illness, hypersensitivity rxn to organism
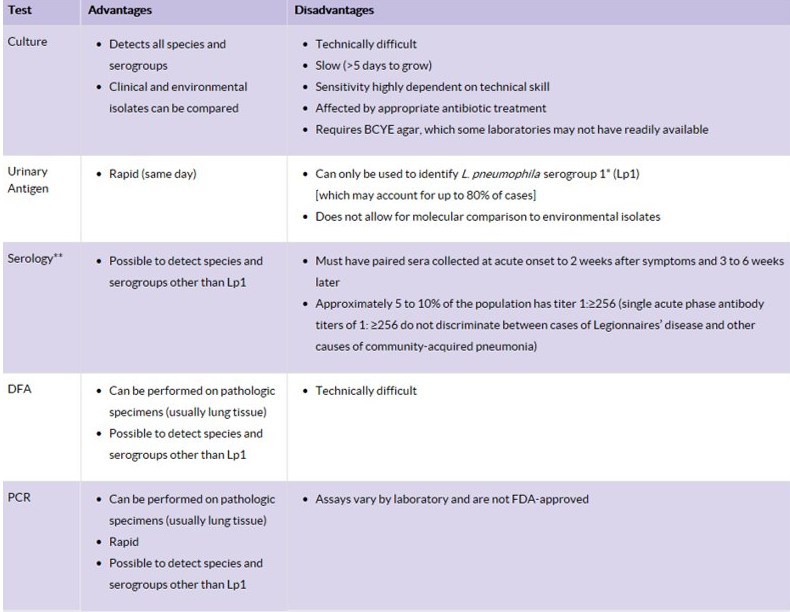
Legionella lab ID
culture
direct Ag: DFA, urine Ag
serology: indirect fluor Ab
Legionella: direct Ag DFA
rapid but less sensitive than cx
1) pt specimen + monoclonal
2) incub 30min at 37C
3) add mounting media
4) read under fluorescent microscope
Legionella: urine Ag
EIA method, 15min
Ab+Ag for L. pneumophila serogroup 1= positive line
Legionnaire’s dz → shed Ag in urine
may be false neg early in dz
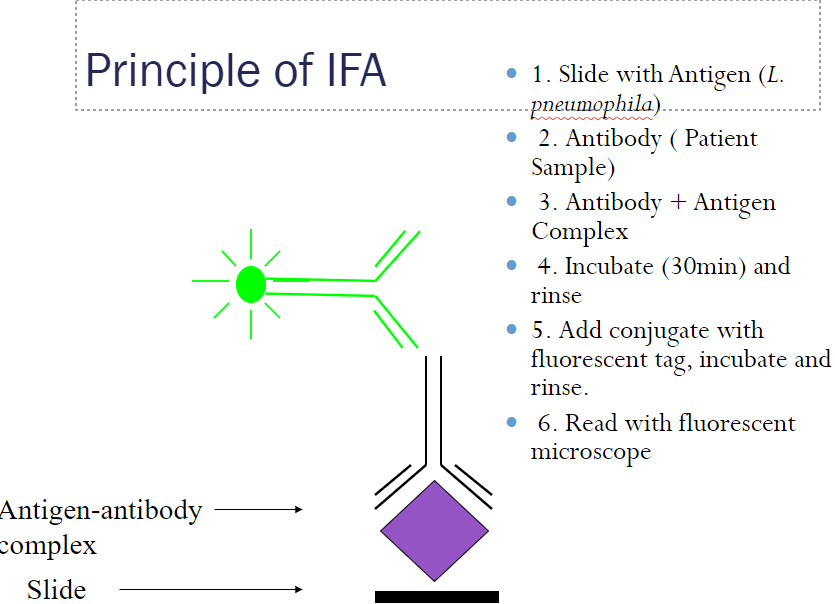
Legionella: serology IFA
sandwich assay
1) Ag (L.pneumophila) + diluted pt serum (Ab) → incubate, rinse
2) Ag-Ab complex + anti-human globulin w fluorescent tag → incub, rinse → read
results: highest dilution of pt serum showing 1+ fluorescence = pts positive titer
sample: acute serum should be obtained w/in 1 week pre or post onset & convalescent from 3 to 6 weeks after onset.
other lab tests for L. pneumophila
molecular assay: PCR or nucleic acid test are available but v $$, usually confirmatory
immunological methods: latex agglutination allows rapid elimination of NEG samples, POS can be checked out w more targeted tests
also not FDA-approved
Legionella lab ID adv vs disadv
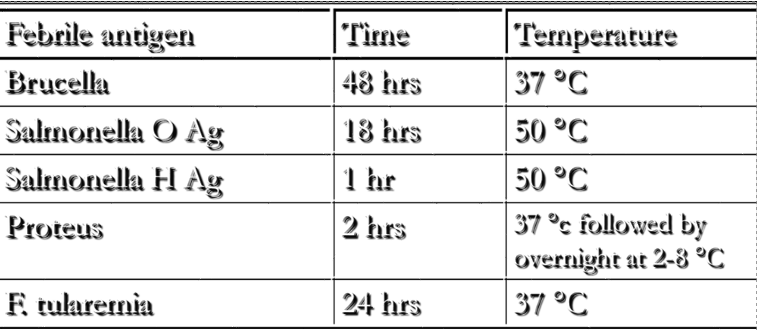
febrile agglutinin
agglutinating-Ab that arise from infns from orgs that induce FEVER
often used to dx dz where bug is difficult to grow in vitro
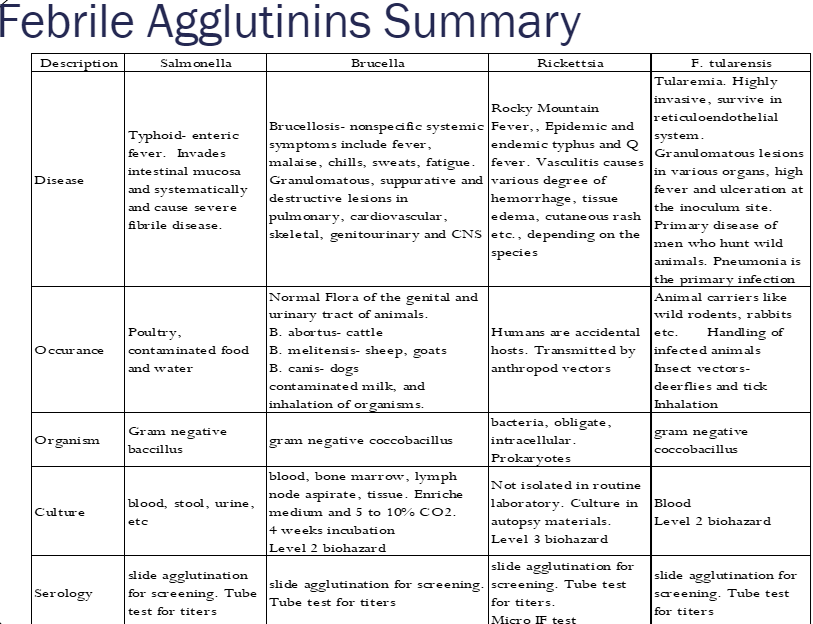
ex) Francisella (tularemia),
Rickettsia (typhus),
Brucella (brucellosis),
Salmonella (typhoid fever)
febrile Agglutinin test (FAT): Widal test
detects Ab to typhoid & paratyphoid fever caused by Salmonella spp.
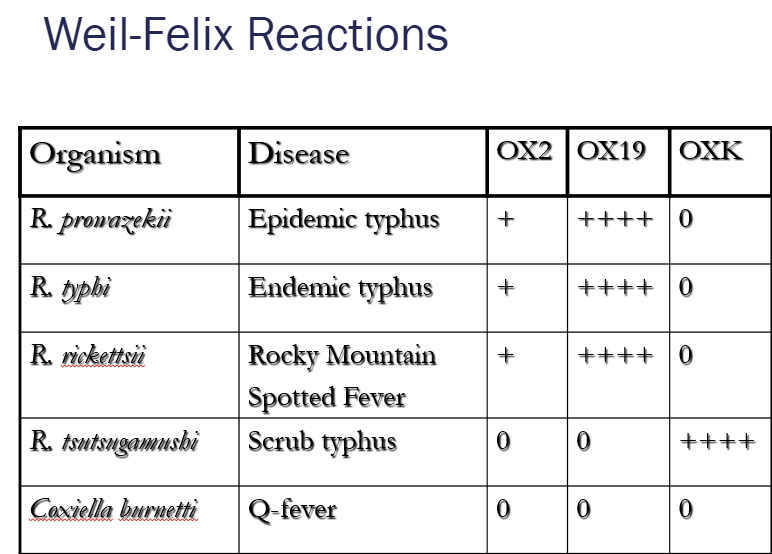
FAT: Weil Felix test
based on x-reaction of Ricketssia -Ag w O-Ag polysaccharide in Proteus vulgaris strains OX2/19/K
→ measures anti-rickettisial Ab in pt serum by agglutination w/Proteus bacteria
**cannot distinguish b/t R. prowazekii, typhi, rickettsii
FAT: slide agglutination test
test Ab in pt’s serum
steps: 80uL test sample + 1 drop of Febrile Ag (40 uL) → mix & rotate → read after 30 sec
no agglutination = NEG → titer is <1:20
agglutination 2+ or greater = POS → set up tube agglutination for confirmation
FAT: tube agglutination test
steps: serial dilutions of POS pt’s serum in saline, 1:10 → 1:2560 → add 0.5mL Ag & incubate in water bath
tube agglutination results
what are the 2 types of agglutination rxns?
read degree of clarity in supernatant
gently tap tube to suspend agglutinated particles
somatic agglutination: usually granular & will settle quickly to bottom of tube
flagellar agglutination: more floccular , fluffy agglutinate that are readily dispersed
tube agglutination interpretation
Ab due to infn may not be detected early in infn
max titer levels occur usually at convalescence
neg test are NOT conclusive
pos result may be due to vaccination
most conclusive serological evidence of infn = at least 4-fold inc in serum drawn b/t acute & convalescent phase of illness or a single titer >1:80 to 1:160
febrile agglutinins table
after infn w/S.aureus → body produces Ab to key cell wall component called __.
teichoic acid
Teichoic acid assay: method
Ouchterlony double diffusion technique
Ag & Ab diffuse in medium
→ bands forming = Ab-Ag complex formation, density of lines indicate amount of complex
teichoic acid assay titers
1:2 seen in normal individuals, transient S. aureus infns, pts w other G+ infns
1:4 or greater have been seen in: EC pts, deep seated infns, non-EC pts
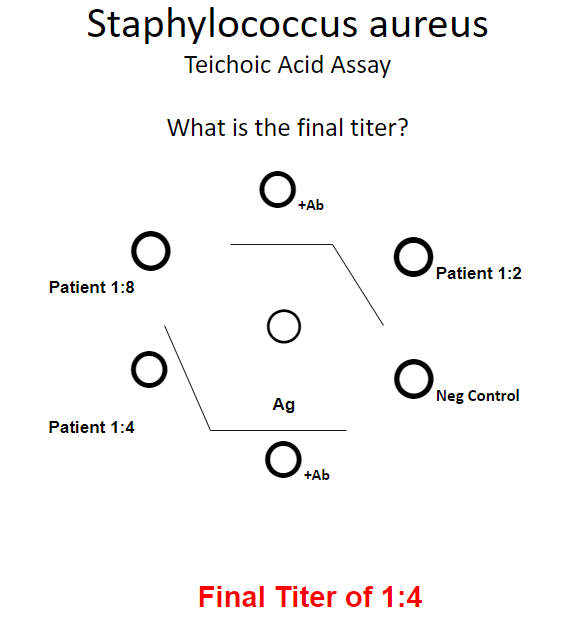
titer = highest titer w/ band of ID
Strep pyogenes: pathogenesis
m/c cause of bacti pharyngitis
after inital infn → Ab made x-react w skeletal, smooth muscle, and myocardial fibers causing 2 sequelaes: rheumatic fever & glomerulonephritis
What is S. pyogenes main virulence factor?
M-protein = limits phagocytosis
sequelae to GAS infn: rheumatic fever
assoc’d w GAS pharyngitis (NOT w skin infns)
usually in kids 6-15 y/o, occurs 20 days after scarlet fever or strep throat
symptoms include joint pain, fever, heart problems, shortness of breath → permanent heart damage
serological findings are assoc’d w elevated ASO, anti-DNase, and/or anti-hyaluronidase
acute glomerulonephritis
assoc’d w respiratory AND skin infns → 10 days after GAS infn
caused by deposition of Ag-Ab complexes in glomerular capillary walls → edema, hypertension, hematuria, proteinuria
GAS lab ID relies on 3 Ab produced:
1) streptolysin O (ASO)
2) deoxyribonuclease B (anti-DNase B)
3) anti-hyaluronidase (anti-AHT)
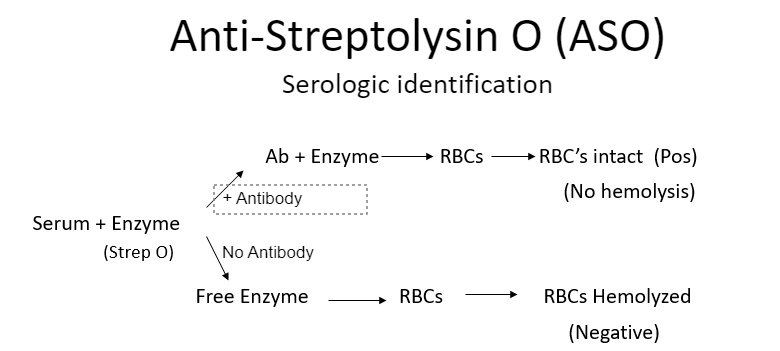
anti-streptolysin O (ASO)
O2-labile enzyme from most GAS throat/respiratory infns; is a hemolysin that lyses rbc, wbc, plt, cultured cells
b/c ASO is irreversibly inhibited by cholesterol in skin lipids, pts w GAS skin infn do NOT develop anti-ASO Ab
other GAS extracellular enzymes formed
Streptolysin S = O2-stable, non-antigenic (no Ab)
Strepokinase = lyses formed clots
anti-Streptolysin O (ASO) test
neutralization tube test: v time consuming
latex agglutn test: rapid, false pos/neg are common
nephelometry: measures light scattered from Ab-Ag
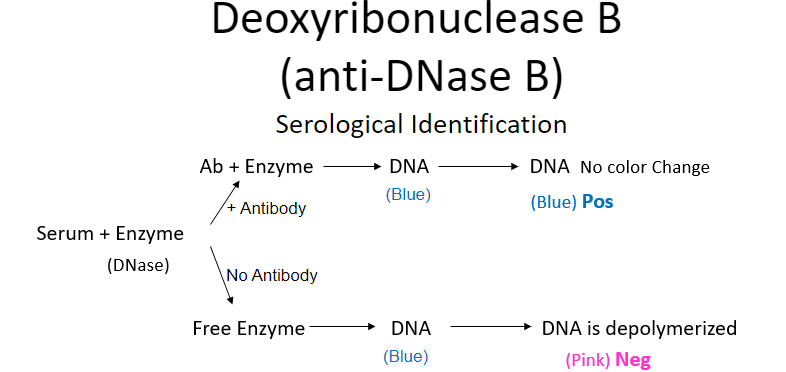
deoxyribonuclease B (anti-DNase B)
DNase enzymes that degrades DNA, not cytolytic → reduced viscosity of abscess material → facilitates spread of bug
** marker for GAS skin infns since fail to make anti-ASO
Ab remains elevated for months & dec slowly
deoxyribonuclease B assay
titers inc after skin infns
test measures Ab ability to neutralize DNase → which has a end point color indicator
POS = blue (no change, enzyme neutralized by Ab)
NEG = pink = DNA is depolymerized
can make serological titers (quantitative)
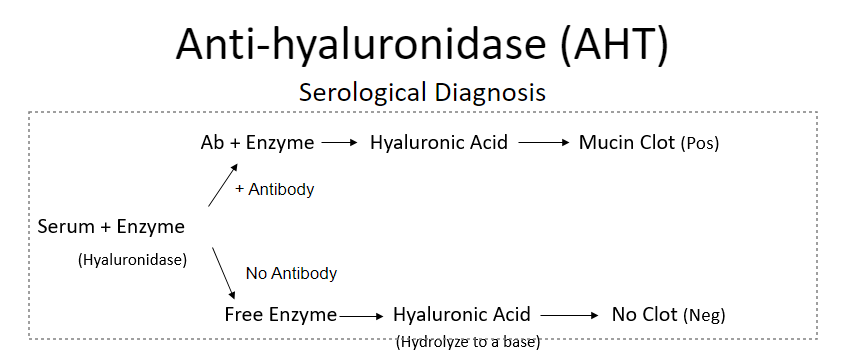
anti-hyaluronidase (AHT) (aka “spreading factor'“)
inc after GAS throat & skin infns
depolymerize hyaluronic acid (constituent of synovial fld & other connective tissue), one produced by GAS is immunologically distinct (is heat-stable & doesn’t req Mg2+)
POS result = important for rheumatic fever dx
AHT assay
when hyaluronidase is present → will hydrolyze hyaluronic acid if no Ab to neutralize → no mucin clot
POS for Ab = mucin clot
NEG = no clot
titer = reciprocal of highest pt dilution showing a clot
better indicator of rheumatic fever than ASO test
pt w rheumatic fever may have titer of 1:1024 and greater
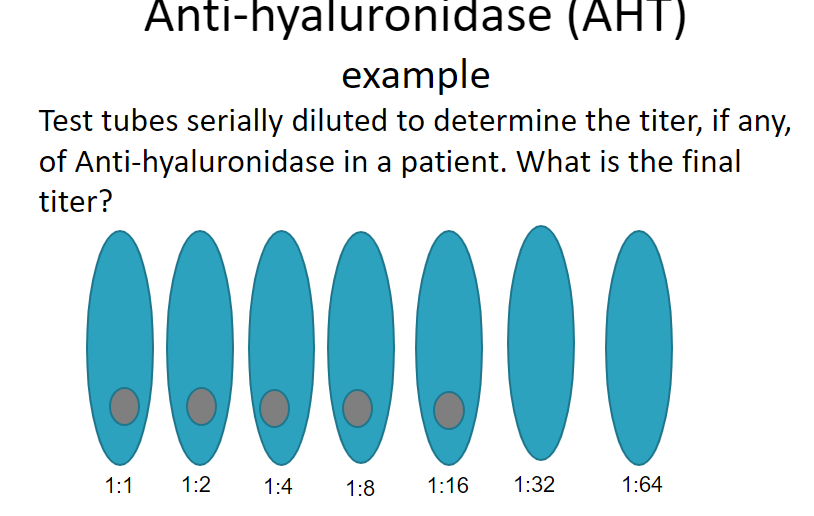
titer = 1:16
Mycoplasma pneumoniae char
smallest free-living bacteria, doesn’t GST
no cell wall → penicillin-R
v fastidious to grow
“fried egg” colony morph
→ causes “walking pneumonia”
Mycoplasma pneumoniae serological ID
standard is complement fixation (CF) → poor sensitivity
cold agglutinin assay shows 65% sensitivity (but poor specificity)
cold agglutinins for M. pneumo
cold autoimmune IgM Ab that bind at 2-4C → cause rbc to clump tg when person is exposed to cold temps → inc chance affected rbc will be destroyed by the body
bind to blood group I/i-Ag found in rbcs (auto anti-I can be stimulated by org that carry an I-like Ag on their surface, ie M. pneumo or anti-i in infectious mono)
cold agglutinins not specific bc
x-reactivity w EBV (mono), CMV, adenovirus, other disease lymphoma
strong reactive cold agglutinin titer of 1:128 or significant titer increase = recent infn w M. pneumo
Syphilis mode of transmission
cannot grow in vitro
spread via direct contact (via sex) 30-50% chance if partner has active lesion
congenital infns also
primary syphilis
lesion = chancre, painless
usually outside penis, vagina or cervix
secondary syphilis
40% pt have neurologic signs ie visual disturbances, hearing loss, tinnitius facial weakness
stage where org is most numerous
all sero tests = POS
latent (hidden) syphilis
after 12 mo
pt are non-infectious (except pregnant women)ter
tertiary syphilis
gummatous syphilis
cardiovascular
neurosyphilis
gummas
localized areas of granulomatous inflammation
cardiovascular syphilis
ascending aorta → aortic aneurysm
neurosyphilis
m/c complication of tertiary syphilis, acute MG → tabes dorsalis
large rise in HIV+ pt
congenital syphilis
fetal death 10%
60-90% develop cluttons joints, deafness, Hutchinson’s teeth, mulberry molars & bone abnormalities
EIA test for syphilis
used for large vol testing → lowers manual labor; detects Ab to lipoproteins from damaged cells & cardiolipin from treponemes & thus are NOT specific for Treponema (Liason IgG & IgM)
is it non-trep OR trepeneme specific?
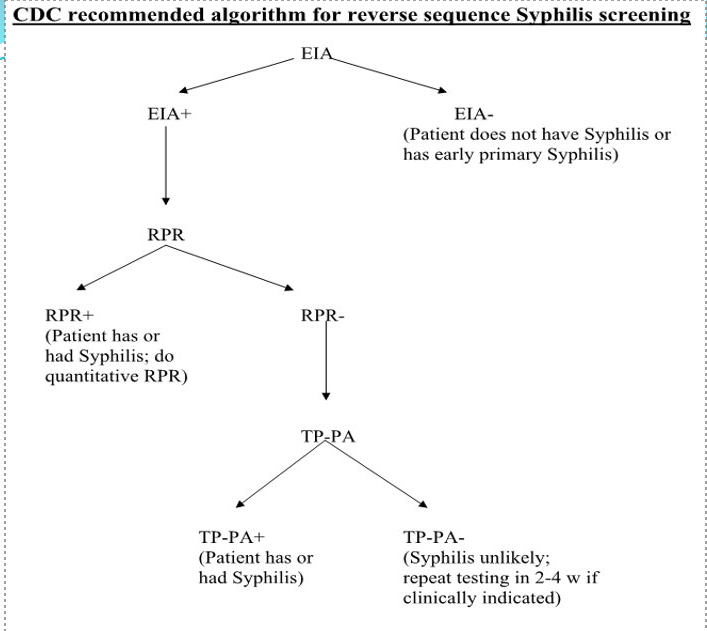
syphilis EIA results
if EIA POS → RPR (rapid plasma reagin)
if NEG → do TPPA (confirmatory test)
if RPR POS → titer RPR via serial dilutions of serum (but can have false POS due to infectious mono, lupus, pregancy)
nontreponemal sero tests: RPR
CANNOT perform on CSF
Ag = cardiolipin (w choline chloride), cholesterol, lecithin, charcoal added for macroscopic viewing
nontreponemal sero tests: VDRL
venereal disease research laboratory
performed on CSF (or serum) → use for neurosyphilis dx
Ag = cardiolipin, cholesterol, lecithin
microscopic flocculation 100x
nontreponemal sero tests
Ab appear 1-4 weeks after primary chancre, usually highest in titer during secondary syphilis, titer gradually dec after 1st year
used to screen/monitor course of dz, efficacy of treatment
4-fold change in titer = change of 2 dilutions → considered necessary to demonstrate a clinically significant difference
from 1:16 to 1:4 or from 1:8 to 1:32
reagin
an antibody-like substance present in serum from pt w/syphilis
binds to Ag cardiolipin-lecithin coated particles → flocculation
neurosyphilis dx
need POS serum treponemal test & POS VDRL in CSF
CSF VDRL is specific, but not sensitive
treponemal test
detect Ab directed against T.pallidum organism
more difficult to perform, used for confirmation
types
- fluorescent treponemal Ab absorbed (FTA-ABS)
-agglutination test
darkfield microscopy for syphilis dx
organism present in lesion & exudates, false NEG if transport to lab is delayed (dies easily)
pathogenic treponemes are ID’d based on corkscrew motility & flexing motility = live specimen req’d
fluorescent Ab for syphilis dx
utilizes fluorescent-labeled Ab
sensitive & specific compared to darkfield
live specimen NOT req’d
but x-reactivity w related treponemes
fluorescent treponemal Ab absorbed (FTA-ABS)
slides have Nichols strain of T.pallidum
uses Reiter Treponemes to remove reactivity w lupus Ab → prevents x-reactivity w Ab to other treponemes
fluro 2+ or greater = POS
highly specific for treponemal Ab, 100% reactive in secondary/latent syphilis
agglutination treponemal test: TPPA
Treponema pallidum particle agglutination
performed if RPR=NEG for confirmation
pt serum is incubated w either sensitized T. pallidum gel particles or unsensitized gel particles as a control
POS= smooth mat that covers well’s surface due to formation of lattice-like structure
NEG = form compact button
Lyme disease caused by
Borrelia burgdorferi
loosely-coiled spirochete
can be cx w Barbour-Stoenner-Kelly media
vector = Ixodes tick
arthritis → skin, heart, joint involvment
Lyme disease stages
1) localized rash: erythema migrans, bullseye rash, fades untreated
2) early dissemination: in blood, skin, CNS, heart, joints afected
3) late dissemination: arthritis, late neuroborreliosis
Lyme dz dx: immunofluorescence
detects IgM or IgG, v subjective
Lyme dz dx: EIA
rapid, specific, insensitive in early stage of dz
Lyme dz dx: Western blot
confirmation test after POS EIA/IFA
Lyme dz dx: PCR
highly specific, but specificity varies by source; most sensitive in synovial fluid
least sensitive in CSF