CHE 2C Midterm 2
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
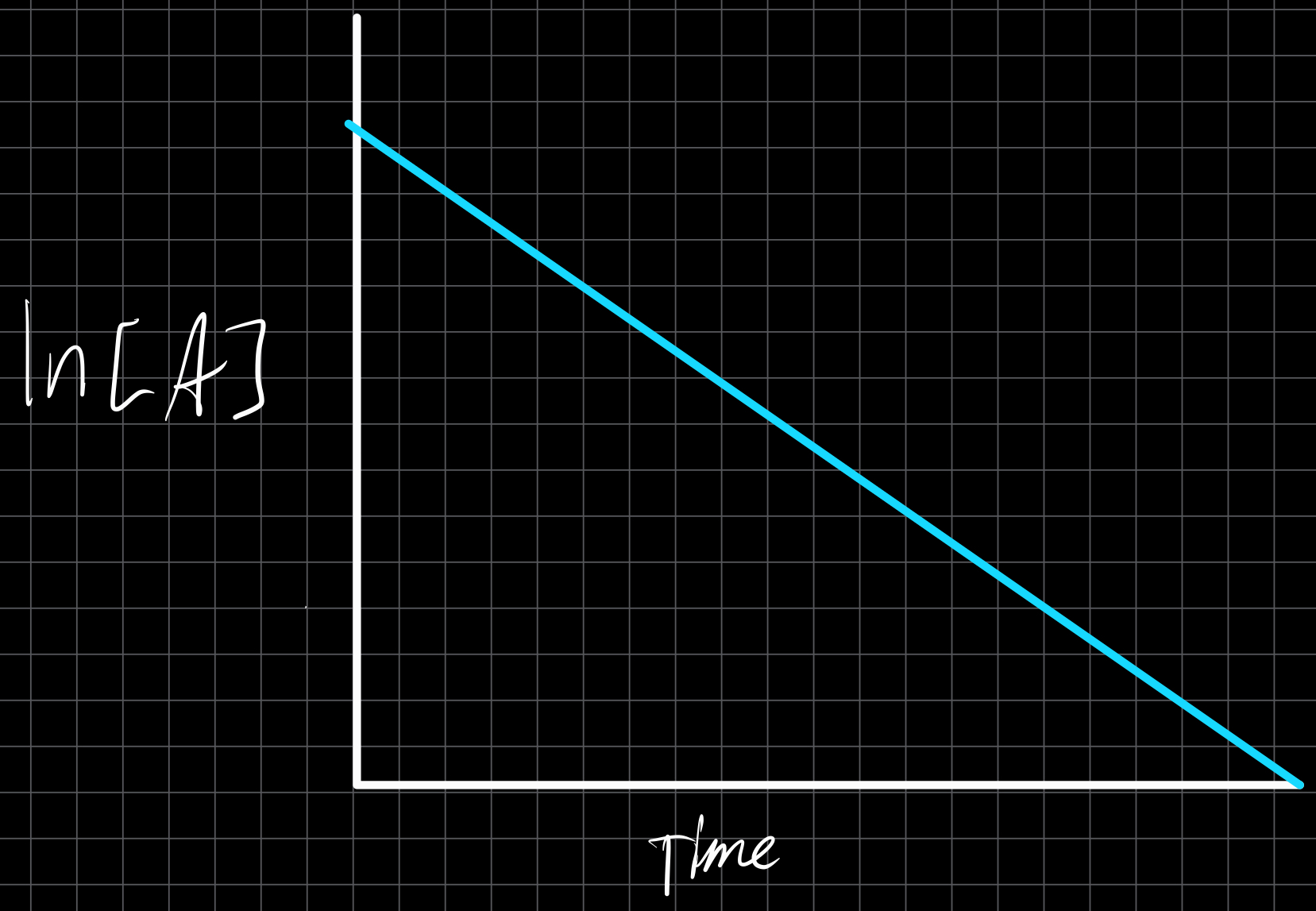
First Order
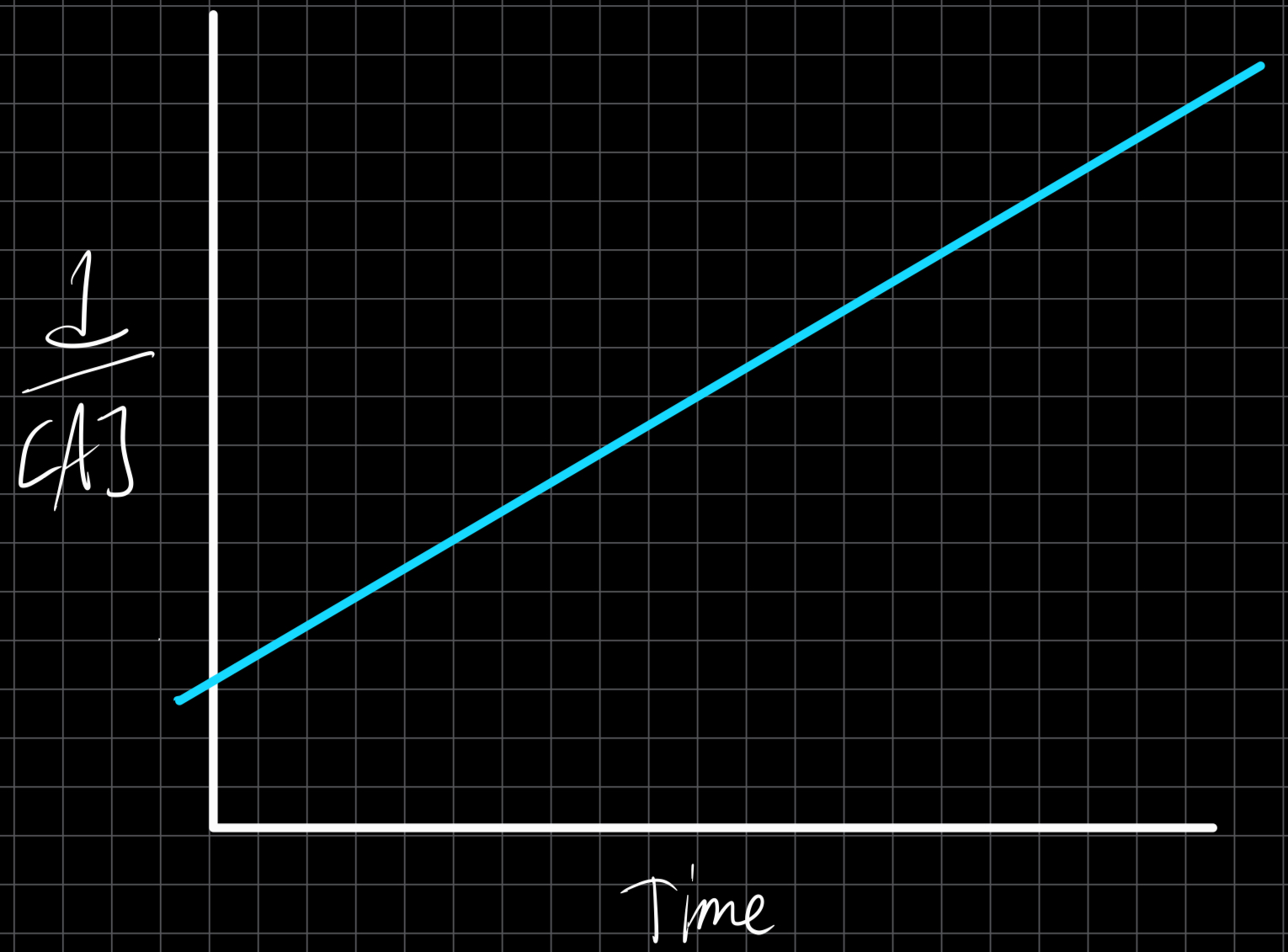
Second Order
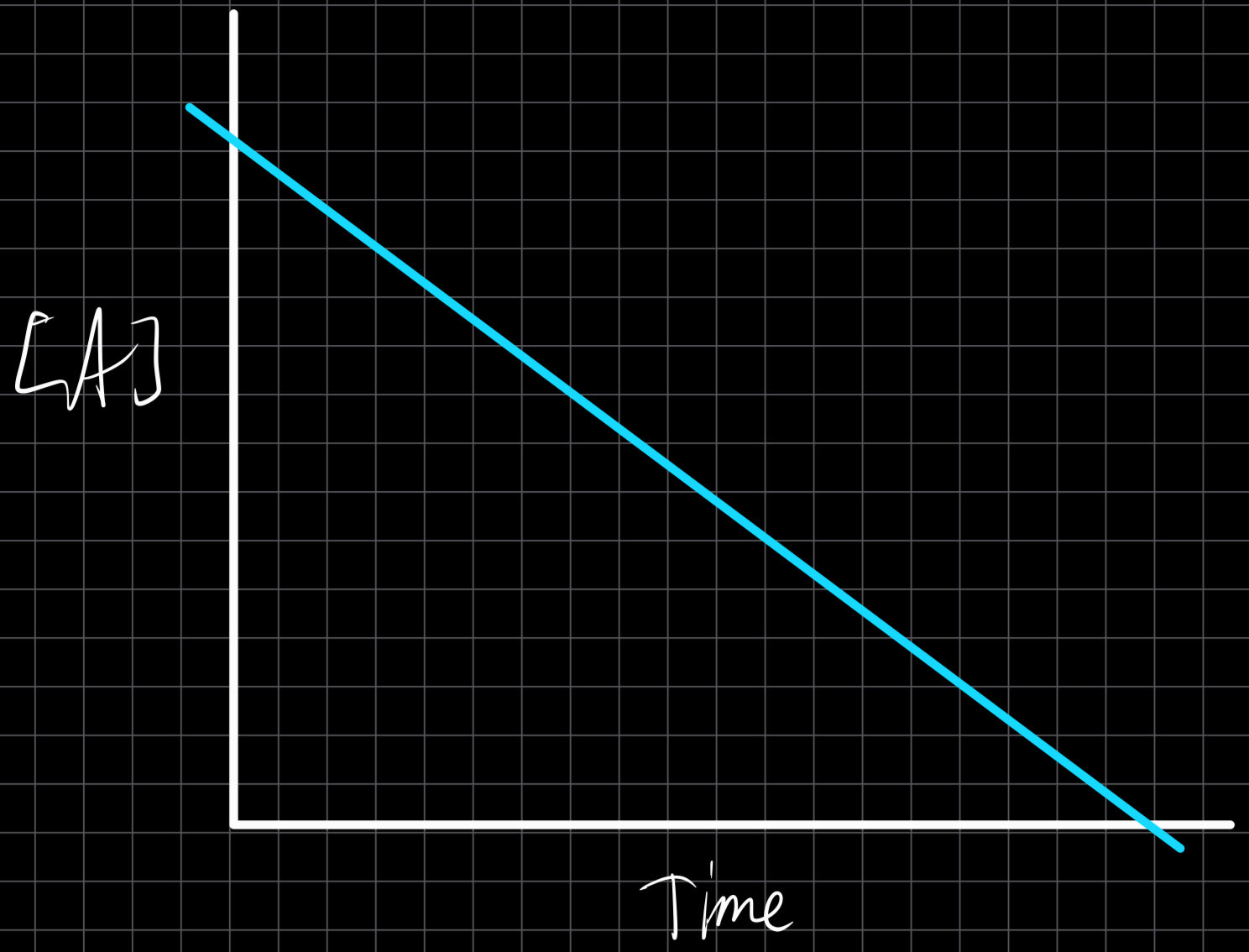
Zero Order
Things needed for reaction to occur
Correct orientation
Enough Kinetic Energy to overcome Activation Energy
Hit directly and be going fast enough for bond to form
rate formula for aA + bB → cC + dD
r = k [A]^a [B]^b
formula for order
sum of coefficients or exponents
what direction can the transition state go in
forwards and backwards
what mechanics is assumed for kinetics
classical mechanics
what do catalysts do
Lower Activation Energy
No effect on Keq
Inversely correlated with k
homogeneous
reaction and catalyst are at same phase
heterogeneous
reaction and catalyst are at different phases
building block of life
organic compounds (carbons)
how many bonds does C form
4
sp3 orbital diagram
4 sigma bonds
Linear
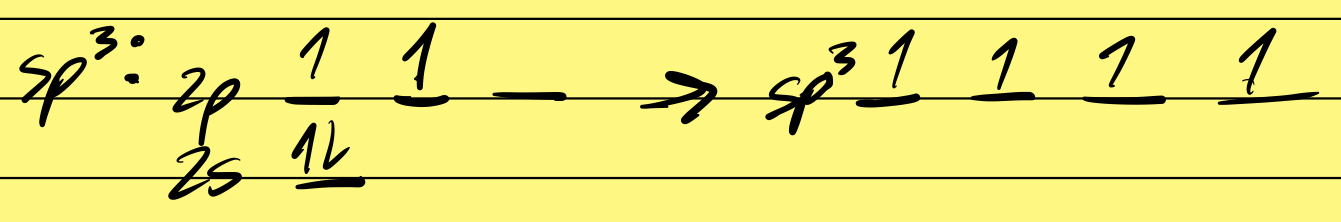
sp2 orbital diagram
3 sigma bonds & 1 pi bond
Trigonal Planar

sp orbital diagram
2 sigma bonds & 2 pi bonds
Tetrahedral

#C = 1
Meth-
#C = 2
Eth-
#C = 3
Prop-
#C = 4
But-
#C = 5
Pent-
#C = 6
Hex-
#C = 7
Hept-
#C = 8
Oct-
#C = 9
Non-
#C = 10
Dec-
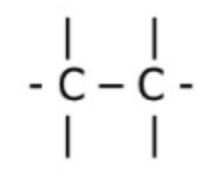
Alkane
C(n) H(2n+2)
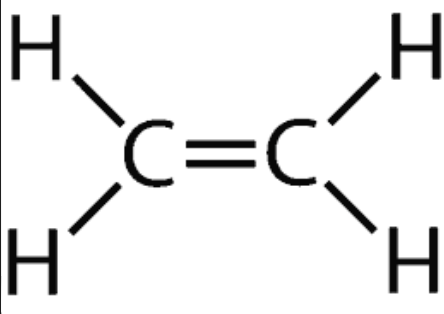
Alkene
C(n) H(2n)
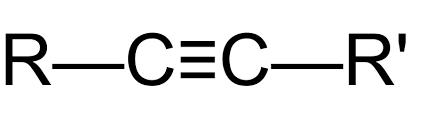
Alkyne
C(n) H(2n-2)
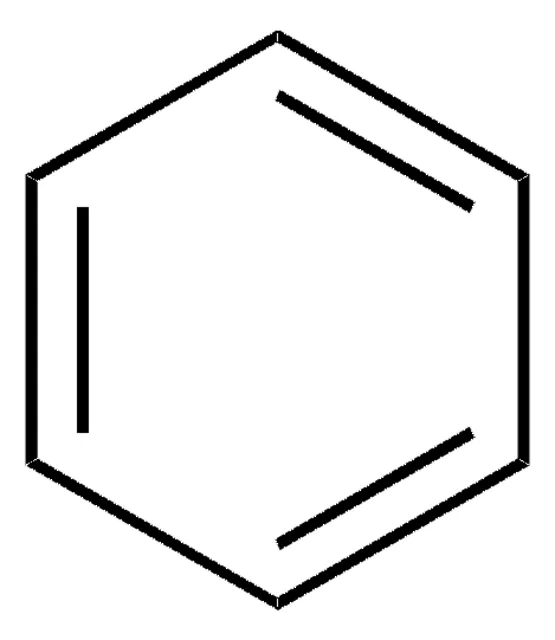
Benzene
Arene
Aromatic

Halide
…CX

Alcohol
…COH

Phenol
…COH

Ether
…COC…

Amine
…CNH2
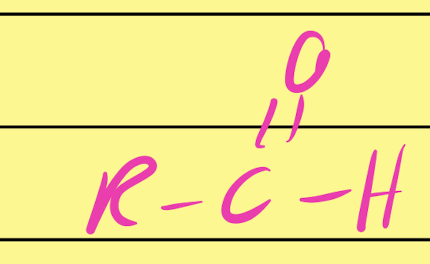
Aldehyde
…CHO
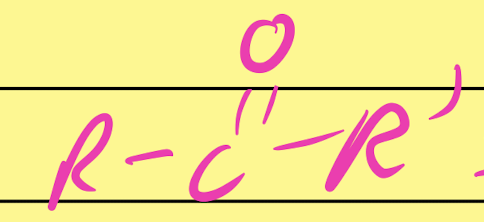
Ketone
…CO…
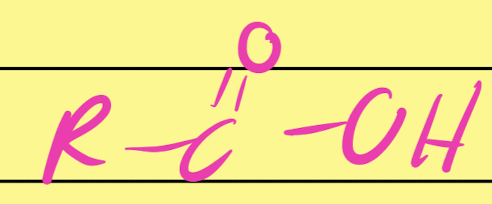
Carboxylic Acid
…COOH
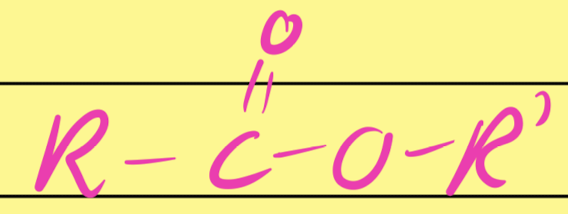
Ester
…COO…
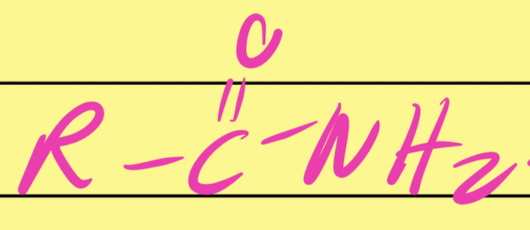
Amide
…CONH2…
Can also have R group instead of one of the H
conformations
identical molecules differing only by rotation
primary carbon
1 carbon neighbor
secondary carbon
2 carbon neighbors
tertiary carbon
3 carbon neighbors
quaternary carbon
4 carbon neighbors
chiral
carbon with different groups
most saturated
alkanes
unsaturated degree formula
#H missing / 2
halogenation
halide replaces hydrogen
steps to determine R or S
Rank groups based on molar mass
1 = Highest & 4 = Lowest
Make sure 4 is pointing away
Redraw if necessary
Trace groups from 1 to 2 to 3 to 4
CW = R
CCW = S
Opposite direction if molecular is redrawn in 2