Lab quiz: Epidemiology & Isolation Techniques
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
WHY IS THIS SO LONG
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Epidemiology
the study of how microbes spread within a group or
population
Portal of entry
the way a microbe enters and infects a new host (Like an entranceway)
i accidentally made this
idk how to get rid of it on mobile ❤
Portal of entry examples
• Direct contact
• Respiratory route
• Ingestion
• Vector
• Skin
• Gastrointestinal tract
Opportunistic pathogen
Acquired from another person or may have already been in or on that individual
Who is more likely to develop infections from opportunistic pathogens?
Immunosuppressed patients
Where is Staphylococcus aureus commonly found, and what can it cause?
It commonly occurs on human skin but can cause staph infections
Normal biota (flora)
Microbes found on our skin that are usually harmless and difficult to remove
Which microorganisms are examples of normal biota?
Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus
Transient organisms
Organisms found on the skin for a short periods of time but do not grow there
How do transient organisms usually get on the skin?
Through contact with contaminated surfaces
Are transient organisms easily removed from the skin?
yes
Are transient organisms easily removed from the skin?
Yes, some transient organisms can cause disease
Why don’t transient organisms stay on the body for long?
They have difficulty competing with established resident microbes and are eliminated by the immune system
Vector
A living organism that transmits disease
Biological Vector
An organism in which a parasite undergoes part of its life cycle before being transmitted to another organism
How do biological vectors transmit disease?
Directly, often through biting
What is an example of a biological vector?
The female Anopheles mosquito.
Mechanical Vector
An organism that transmits a parasite but is not part of its life cycle
How do mechanical vectors transmit disease?
Indirectly, by carrying disease organisms on their bodies
What are examples of mechanical vectors?
Fleas and ticks
What bacterium causes Tuberculosis?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
What does the term “tubercle” mean?
Nodule or growth
When did Tuberculosis become a major problem?
During the Industrial Revolution
Who identified Mycobacterium tuberculosis and when?
Robert Koch in 1882
How long can it take for Tuberculosis to develop?
years
Can an infected person spread Mycobacterium tuberculosis before showing symptoms?
yes
What is Mycobacterium tuberculosis sensitive to?
Ultraviolet ray(ioli)s
Reservoir of Infection
An Object that allows a microbe to grow, reproduce, and maintain the ability to infect a new host
Fomite
n object that allows a microbe to survive and pass to a new host
How does soap help clean the skin?
It breaks down oils on the skin, allowing trapped bacteria to be washed away
What are micelles?
Spheres of lipids that form in aqueous solutions and help lift dirt and oils from the skin
What role does friction play in hand washing?
It physically removes emulsified skin oil and bacteria
What is an antiseptic?
A chemical that kills microbes
What are examples of antiseptics?
Hydrogen peroxide and triclosan.
Aseptic Technique
Handling microbes and materials in such a way that minimizes contamination
What does the aseptic technique prevent?
prevents the microbes you are transferring from contaminating the work area or yourself
prevents the microbes being transferred from getting contaminated
Contamination
Presence or possible presence of microbes where they do not belong
Aseptic Technique examples:
wearing lab coats, hand washing, cleaning all work surfaces, using incinerators
Who developed many of the techniques used to isolate bacteria in pure cultures?
Robert Koch and his team
What is agar and where is it derived from?
Agar is a gelatin-like substance derived from seaweed
At what temperature does agar melt?
100 °C
At what temperature does agar solidify?
42–45 °C
Is agar considered a medium or an additive?
Agar is an additive
What purpose does agar serve in culturing bacteria?
It provides a solid surface for bacterial growth, allowing isolated colonies to form
What is a colony?
A clump of bacteria growing on a solid surface
Colony Forming Unit
The bacterial cell in a colony that arose from a single original cell
Every cell in the colony is _____ _____.
Genetically identical
What is the goal of isolating bacteria?
To obtain a pure culture
Pure cultures are needed to:
Carrying out biochemical testing
Determining antibiotic sensitivity
Developing vaccines
Determining nutritional requirements
Studying organisms that cause disease
Are bacteria autotrophic or heterotrophic?
Heterotrophic
Where are bacteria grown in a laboratory setting?
On media
Growth media
Substrate for bacteria to grow in or upon
Complex media (undefined)
Media that use extracts from other organisms such as animals, plants, or fungi
What are the characteristics of complex media?
They are rich in nutrients and support a wide range of bacterial growth
What is an example of complex media?
Tryptic soy media
What does tryptic soy media contain?
Enzymatic digests of casein and soybean in undefined amounts
Chemically defined media
Media that contain pure organic and inorganic compounds added in exact, known amounts, with narrow range of bacteria growth
Enriched media
Media to which specific nutrients are added to support bacterial growth
What type of microbes does enriched media allow to grow?
Fastidious microbes
Fastidious microbes
those with complex nutritional requirements
What are examples of enriched media?
Blood agar and Brain-Heart Infusion (BHI) agar.
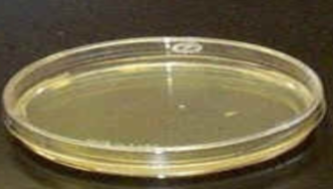
Name the media form
Agar plate

Name the media form
Broth

Name the media form
Agar slant
How is powdered media prepared?
It is dissolved in distilled water
What is an autoclave?
An instrument that sterilizes media using steam under pressure
What temperature does an autoclave reach during sterilization?
121 °C
What pressure does an autoclave use?
15 pounds per square inch
How long must materials be autoclaved to ensure sterilization?
20 minutes—to kill all bacteria, fungi, spores, and viruses