Final Exam Stars, Galaxies and the Universe
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
171 Terms
What is the cosmic calendar?
a scale on which we compress the history of the universe into 1 year
When did human civilization and life on earth start on this calendar
Last minute of the calendar
Asterism
patterns of stars often called constellations
Constellations
regions in the sky with well defined borders (88)
celestial sphere
Imaginary sphere around the earth where astronomical object are projected
What are the celestial poles and celestial equator
alines with earths poles and equator
ecliptic plane
-The plane of Earth's orbit around the Sun
-doesn't line up with equator because of the tilt of the earths axis
What are the 3 important celestial motions
1. Rotation: Earth spins on its axis
2. Revolution: earth orbits its sun
3. Moon orbits earth: causes lunar phases, tides, eclipses
Sidereal period (earth to sun)
-cycle of motion measured with respect to the stars
-sidereal day: 23hr, 56 min, 4secs
-sidereal year: 365.25 days (shorter than solar day)
Solar day?
cycle of motion measured with respect to the sun
-24 hrs
Why do the constellations we see depend on the time of year?
Sun blocks them
Why do the constellations we see depend on our latitude?
The visible constellations vary with time of year because our night sky lies in different directions in space as we orbit the sun. The constellations vary with latitude because your latitude determines the orientation of your horizon relative to the celestial sphere. The sky does not vary with longitude.

Why do we have seasons
results from the tilt of the Earth and its revolution around the Sun
Explain the position of the Earth in the northern hemisphere during the summer and winter solstices
Summer=tilt towards the sun, winter=away from the sun
Will Polaris always be the North Star?
no, because of the precession of earths axis
Equinoxes
-when the ecliptic intersects the celestial equator
-equal light and dark hours
Solstices
-when the sun reaches the max declination
-summer- longest
-winter- shortest
What is precession?
the slow change in the direction in which Earth's axis tilts (26,000 years)
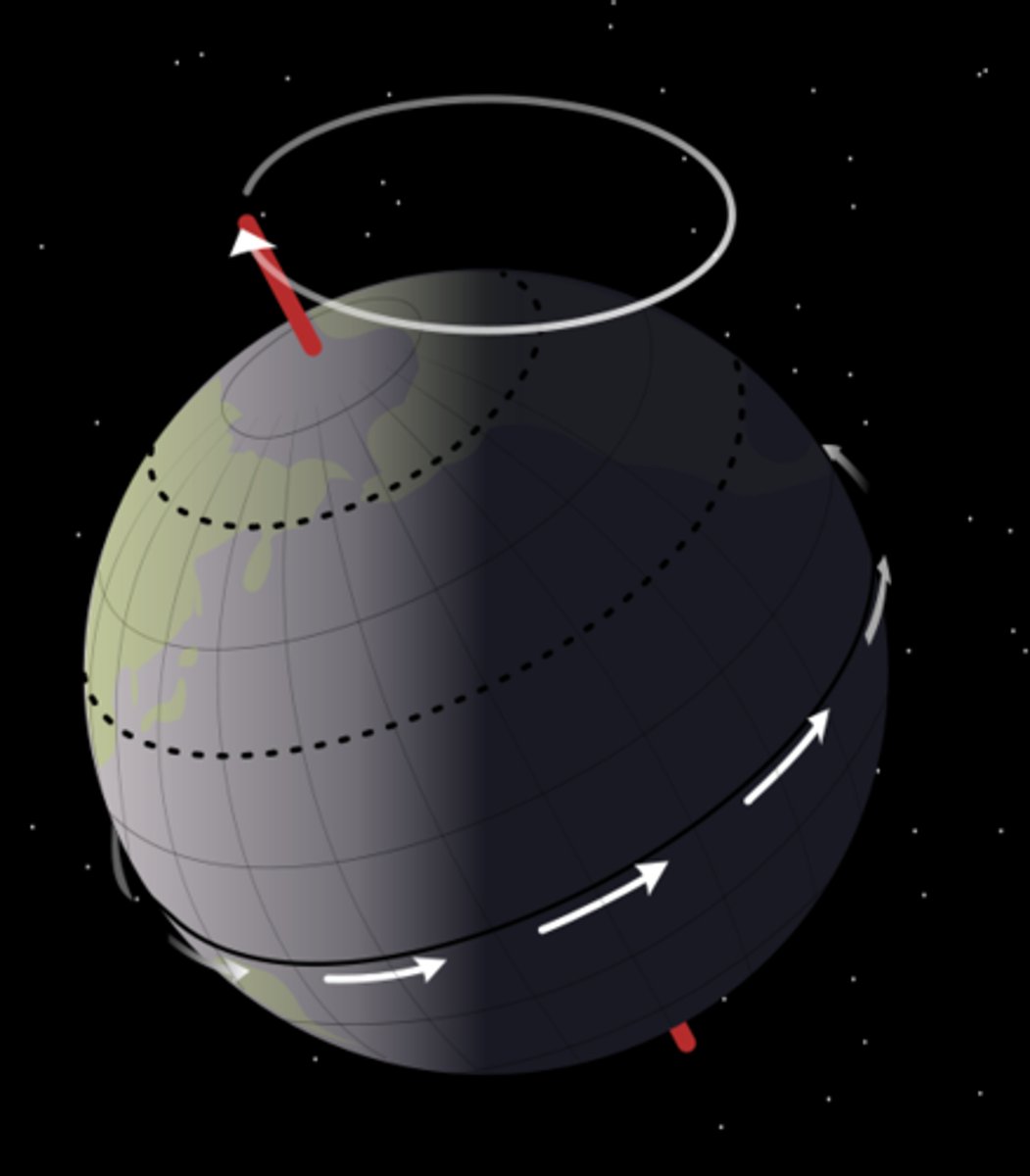
synchronous rotation
Rotational periods equal the orbital period
-this is why we only see one side of the moon
Full or new moon for solar eclipses
new
full or new moon for lunar eclipses
full
Umbra
The darkest part of the moon's shadow
Penumbra
lighter part of the shadow
3 types of lunar eclipse
1. penumbra eclipse
2. partial eclipse
3. total eclipse
3 types of solar eclipses
1. annular solar eclipse
2. partial solar eclipse
3. total solar eclipse
what are the 3 hallmarks of science
1. natural causes
2. progress through testing of ideas
3. scientific models must make testable predictions
Who made the heliocentric solar system model
Nicolaus copernicus (1473-1543)
What is the heliocentric solar system model
-assumed orbits were circular
-sun was center
-simplified the solar system model (Occam's razor)
-observations of retrograde motion
What did Tycho Brahe do?
-used the parallax method
-"new star" corrected
What are Keplers 3 Laws
1'st law: The orbit of each planet around the sun is an ellipse with the sun at one focus
2nd law: As a planet moves around in it's orbit, it sweeps out equal areas in equal times
3rd law: The squares of the periods of any 2 planets have the same ratio as the cubes of their semi major axes (p^2=a^3)
Newton's Law of Gravitation
More massive objects pull harder, and the pull gets weaker very quickly as they get farther apart, explaining why planets orbit stars and why things fall to Earth
-(Force = G (m1m2)/r²)
Why doesnt planets fall into the sun
they are falling towards the dun but they have enough speed to stay in orbit
angular momentum
related to the speed of the object in motion is conserved (doesn't change)
What is light?
Electromagnetic wave and particles called a photon
-wave-particle duality
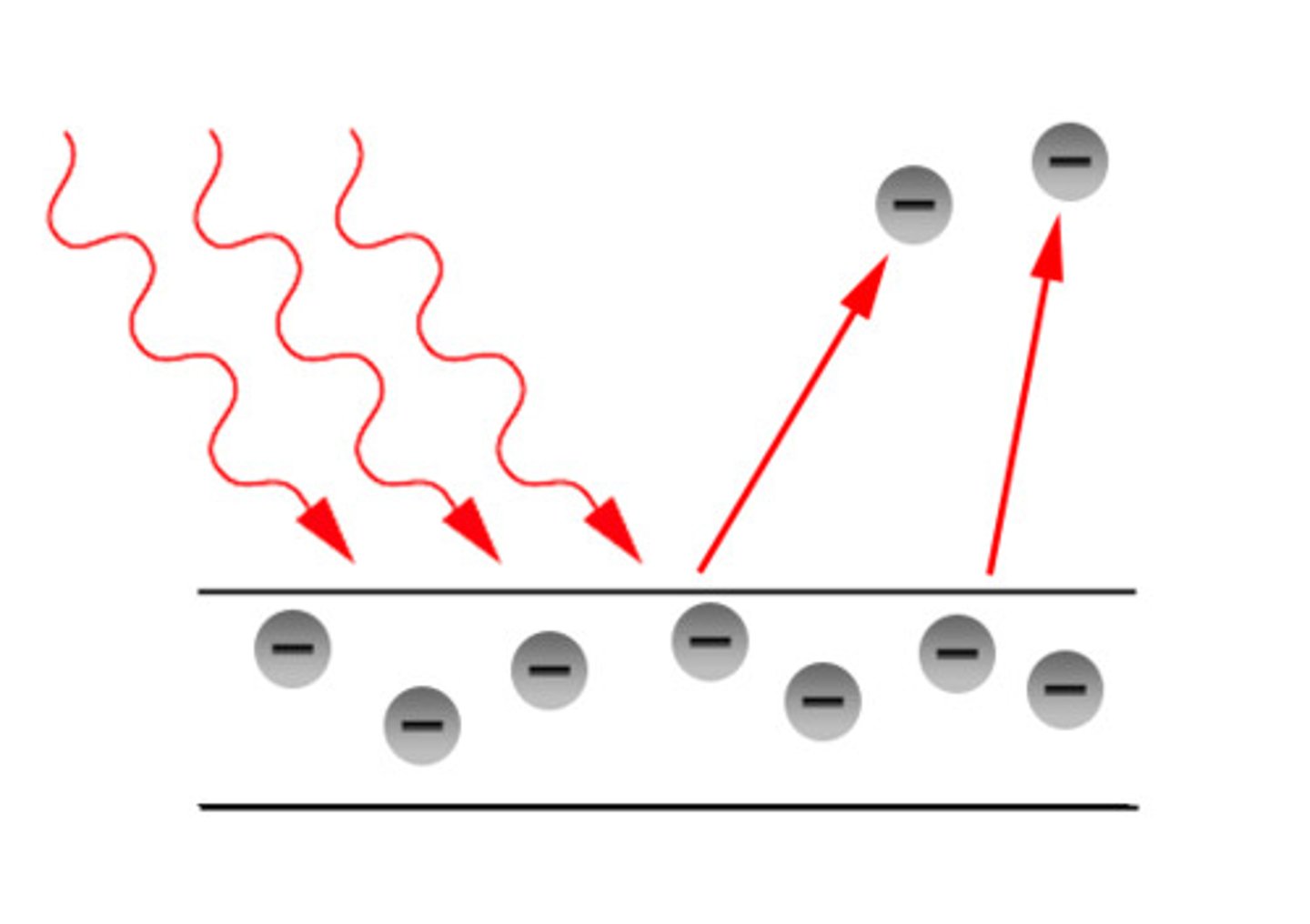
photoelectric effect
The emission of electrons from a metal when light shines on the metal
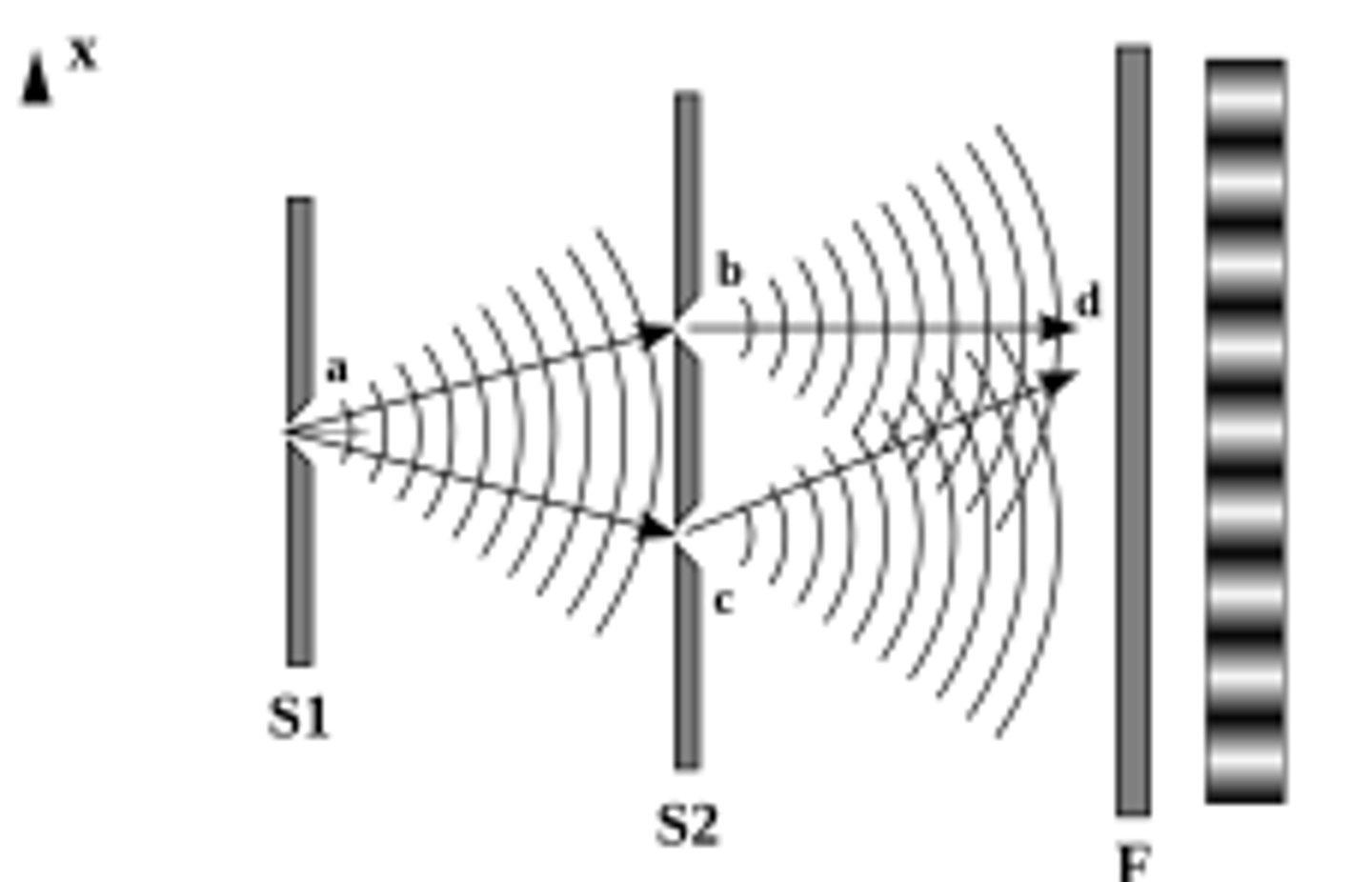
What is Young's double slit experiment?
A single source of light directed towards a double slit, which creates two coherent beams of light. This interferes as it hits the screen and creates an interference pattern.
The double slit experiment and the photoelectric effect showed what about light?
It acts as a wave and particle (duality)
What is the EM spectrum?
radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, gamma rays
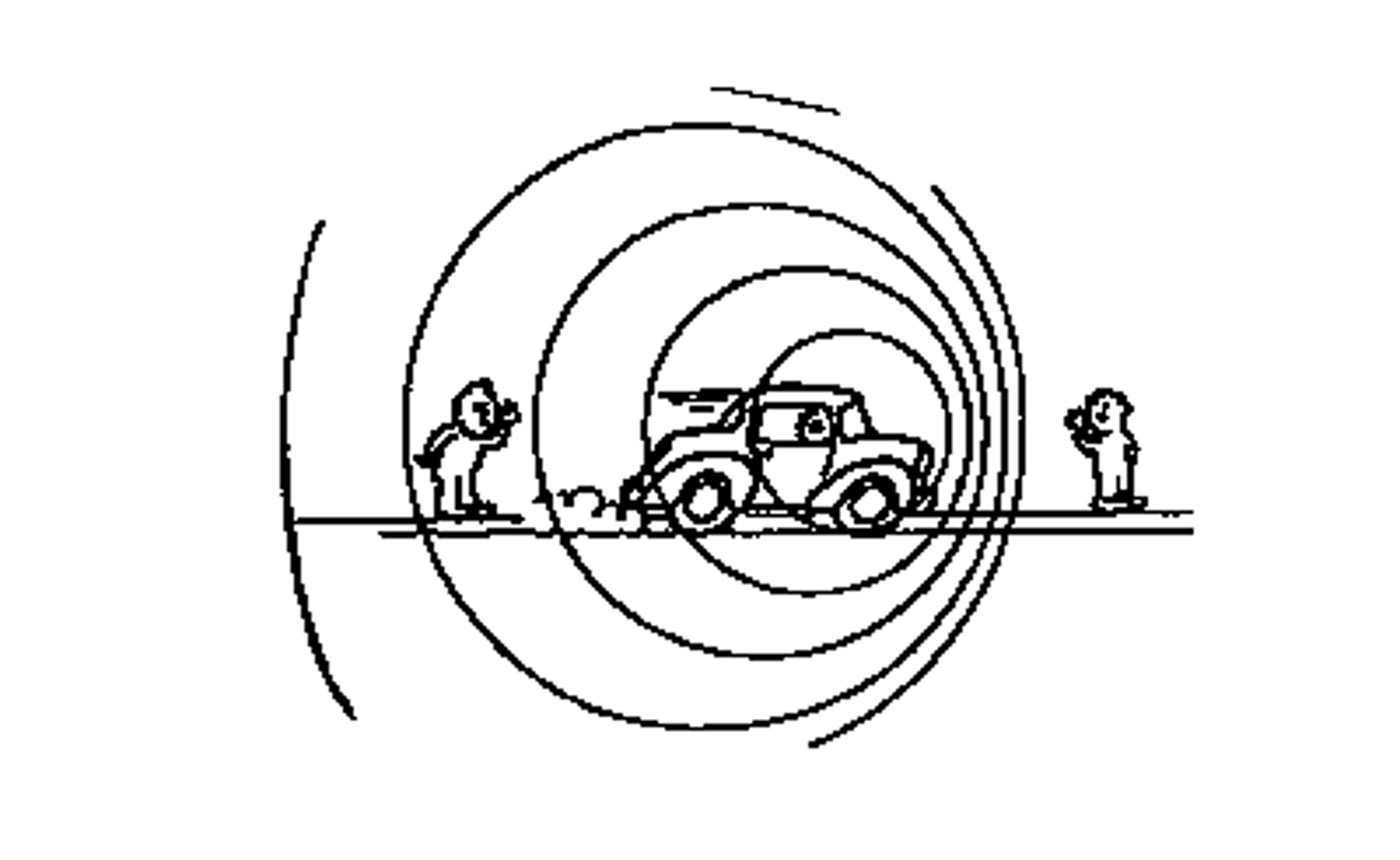
What is doppler effect
A change in sound frequency caused by motion of the sound source, motion of the listener, or both.
What EM radiation can reach earths surface?
visble light, radio waves, mircowaves, short-wave infrared, long wave ultraviolet
What are the 2 type of optical telescopes
reflecting and refracting
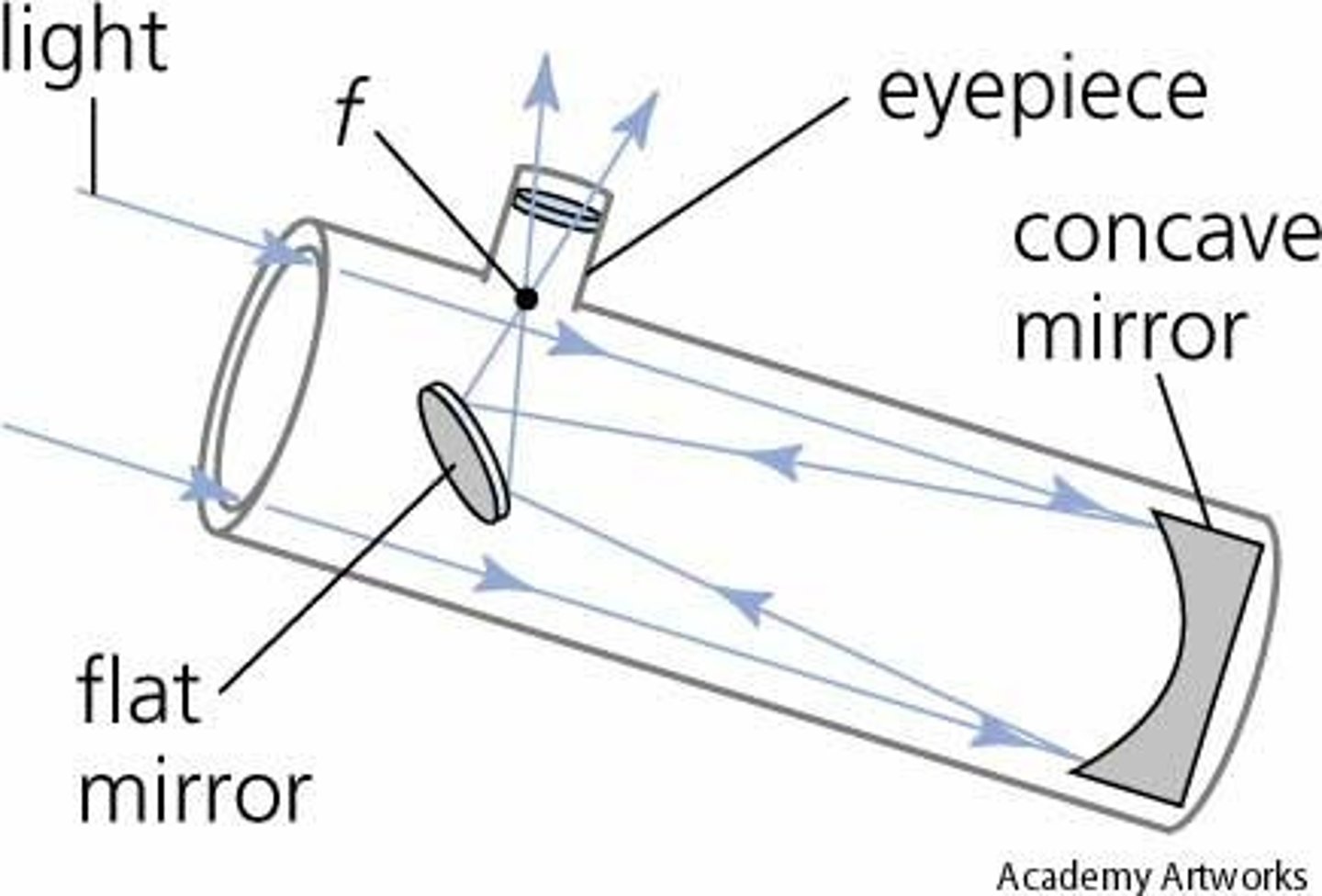
What is a reflecting telescope?
A telescope that uses a curved mirror to collect and focus light
-popular
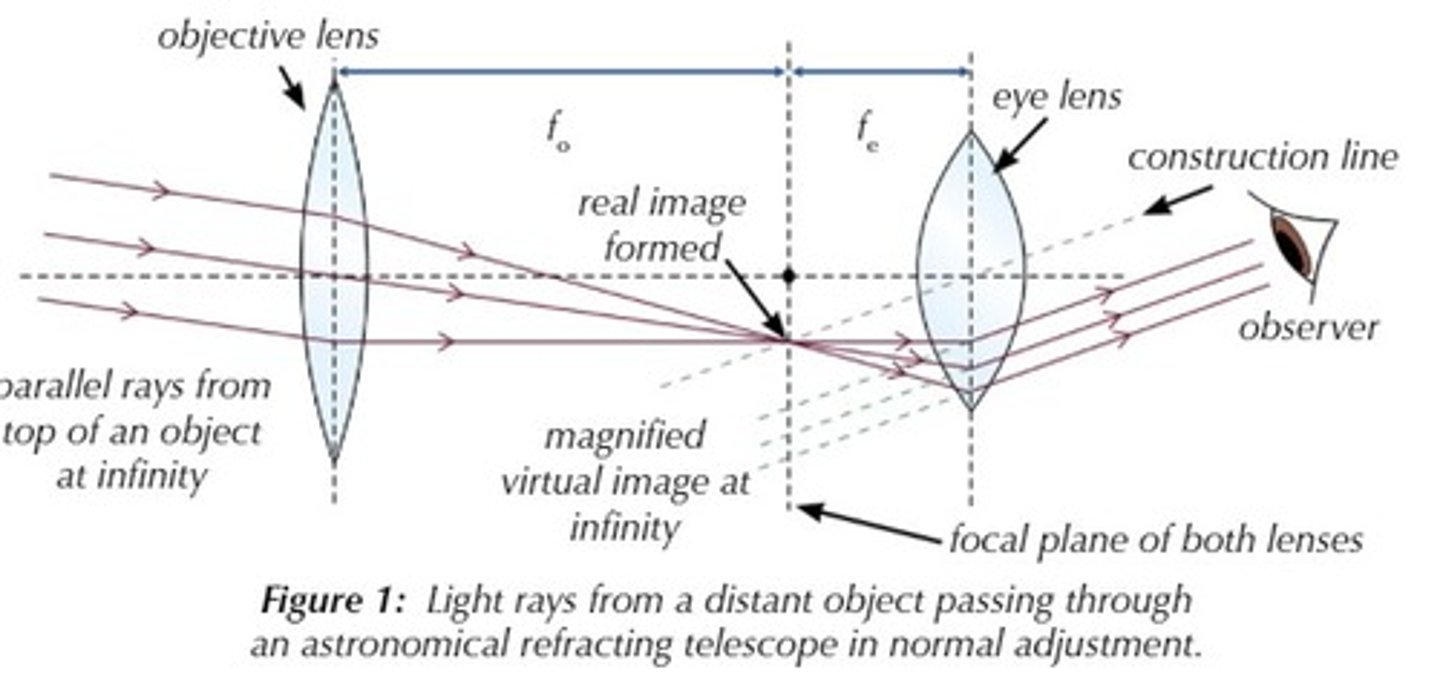
what is refracting telescope
a telescope that uses a set of lenses to gather and focus light from distant objects
The bigger the primary mirror the more ______ your telescope is
powerful (brighter, greater resolution and greater max magnification
What are non-optical observations?
radio telescopes, cosmic ray observation, neutrino observories
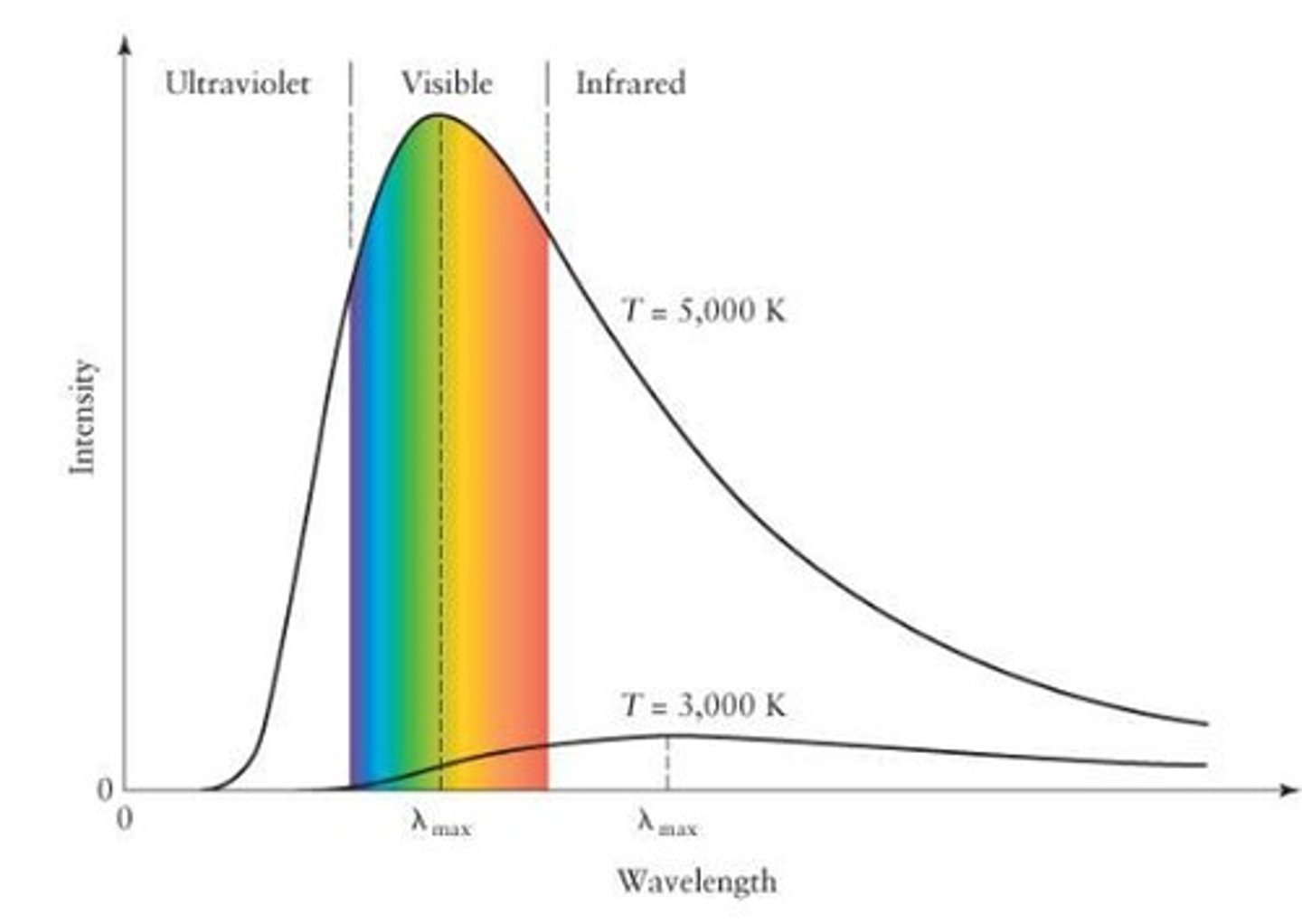
What is blackbody radiation?
Radiation emitted by a body that absorbs all the radiation incident on it
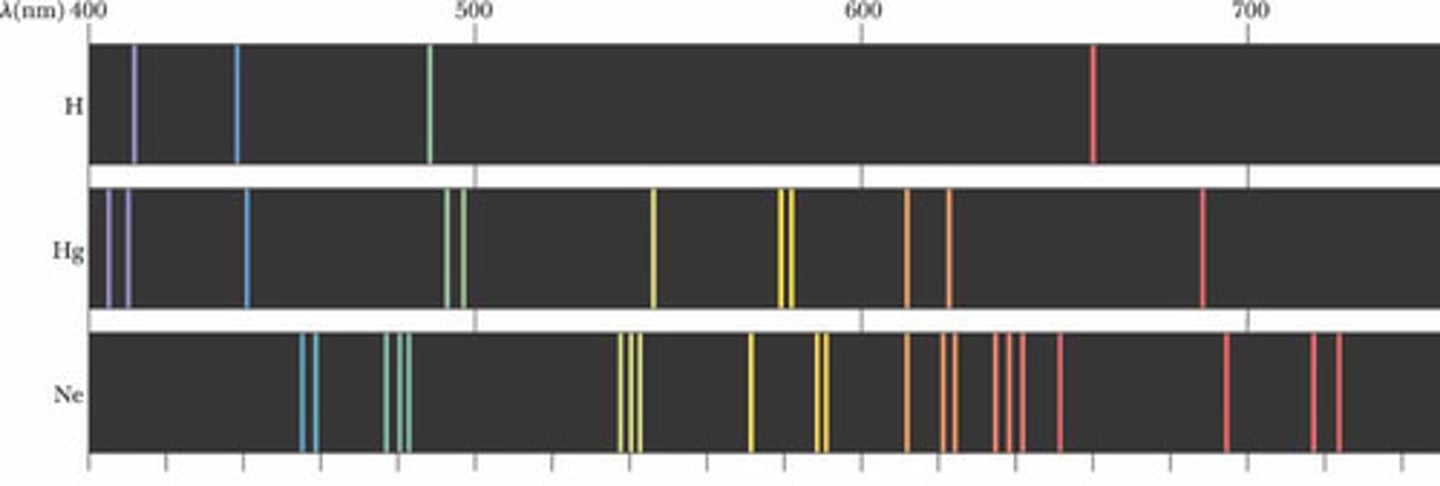
Chemical "fingerprint"
emission spectra are unique to individual elements
What is a hotter object in relation to EM radiation and spectra
emit more, peaks shift to smaller wavelengths
_____ are close to ideal blackbodies and why?
Stars because you can figure out their surface temps by their colors
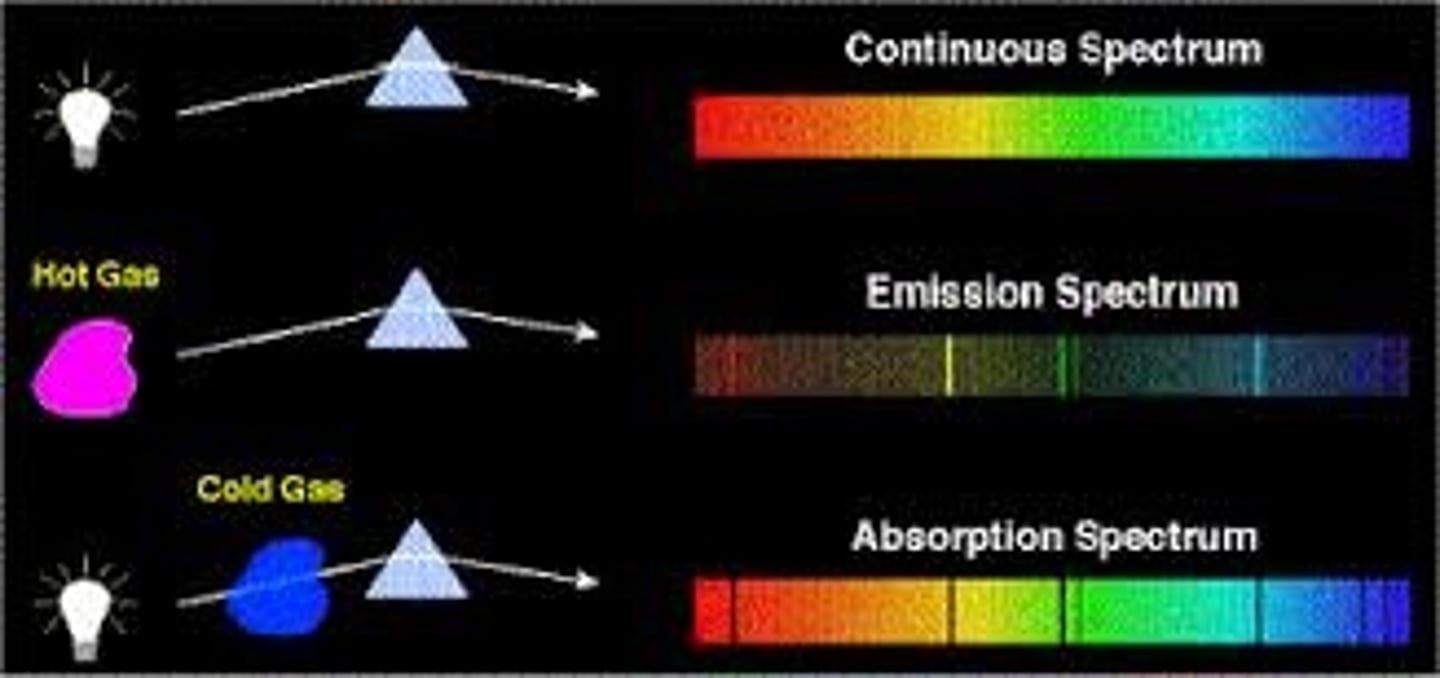
What are the three different spectra types
1. continuous spectrum
2. emission line spectrum
3. absorption line spectrum
What did rutherford scattering experiment show?
there existed a dense nucleus in the atom
What is the planetary model?
simplified and outdated because it incorrectly depicts electrons in orbits, fixed circular paths
Label
A=number of protons and neutrons
Z=number of protons
X=element
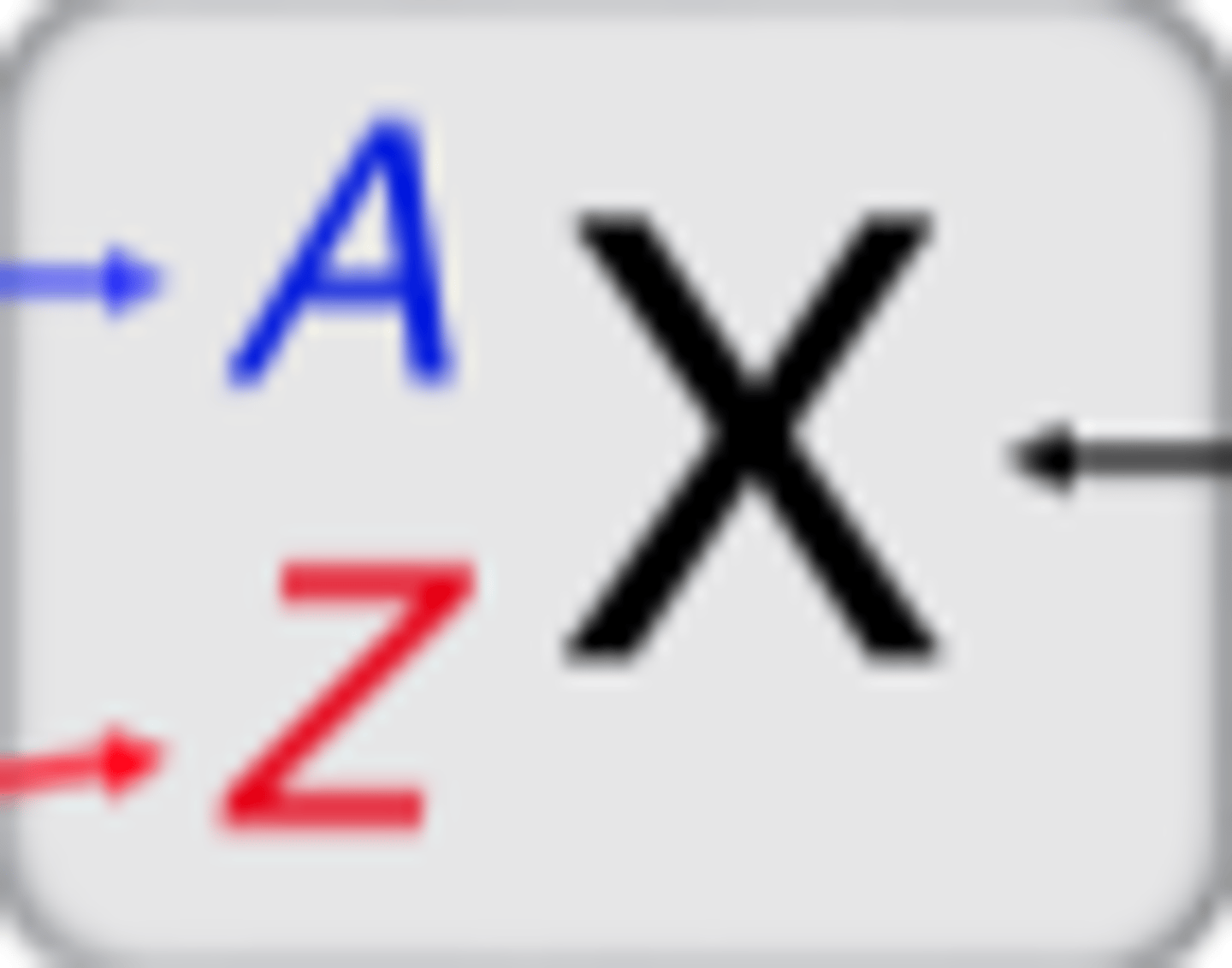
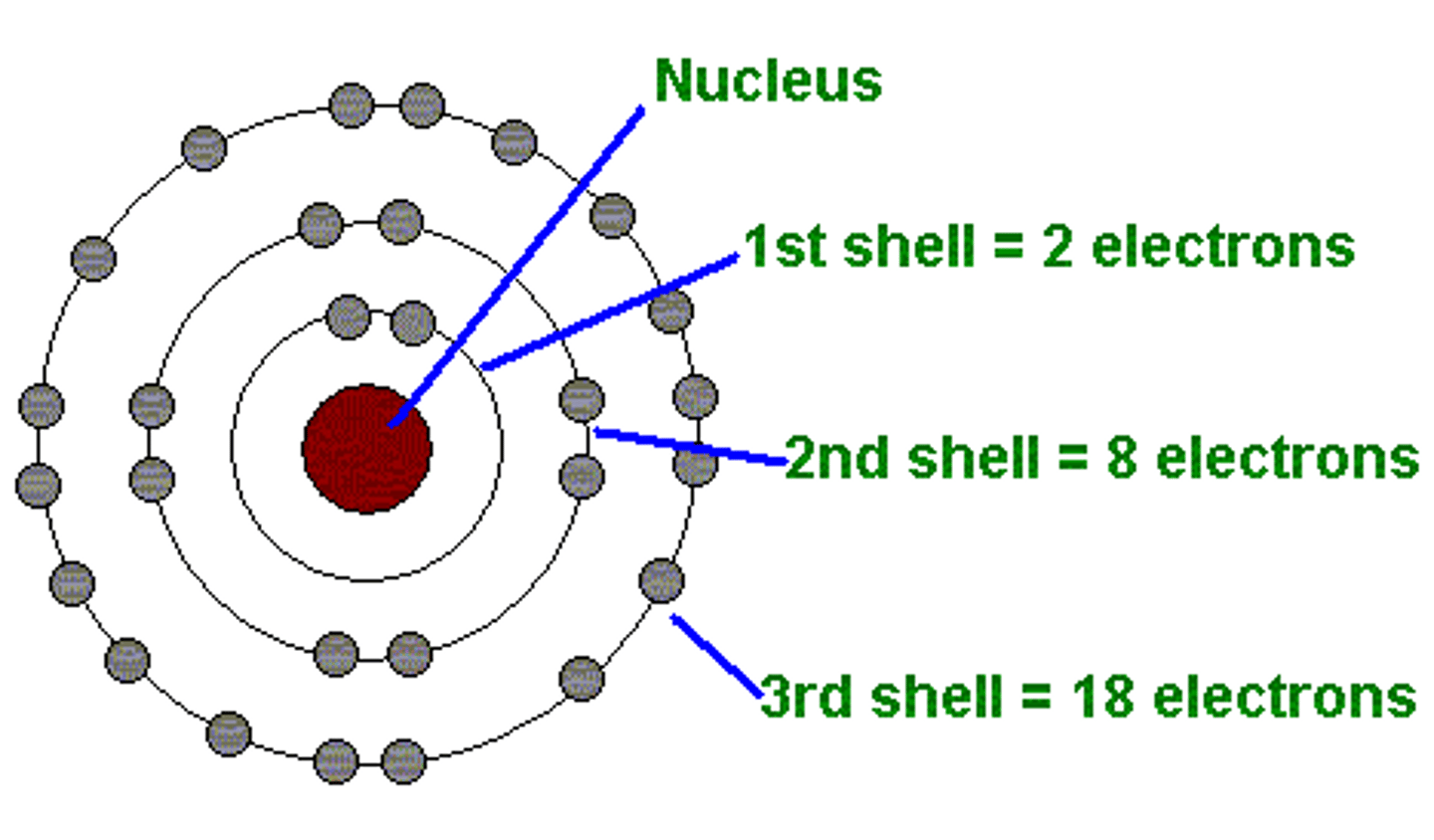
Bohr Model of the Atom
A dense, positively charged nucleus is surrounded by electrons revolving around the nucleus in orbits with distinct energy levels
-not correct but useful for describing the H atom
What spectra are caused by electrons transitioning to a different energy level
Emission and absorption
Exoplanet
A planet outside of our Solar System.
How did planets come to be?
1. Raw materials were forged in 1st generation of stars
2. Raw materials were then released by the stars
3. New star formation gathers the raw materials
4. New star formation contains a protoplanetary disk that may become a planet
Methods of detecting exoplanets
All of them are based on either or both
-exoplanets affecting the light coming from a star (or bright object)
-gravitational effects of the exoplanet on the star (or bright object)
Direct observation" gathering light directly from exoplanet
Transit Method: This is currently the most successful method, finding the most planets.
Scientists watch a star's brightness. If a planet crosses in front of it (transits), it blocks a tiny bit of light, causing a temporary dip in brightness that repeats periodically.
Radial Velocity (Wobble) Method: This was the first method to find planets and remains crucial.
A planet's gravity pulls on its star, causing the star to wobble slightly. This wobble shifts the star's light towards blue (blueshift) and red (redshift) as it moves towards and away from us, revealing the planet's presence.
Astrometry (exoplanet)
Similar to radial velocity, the planet's gravity makes the star "wobble," but astrometry measures these tiny side-to-side shifts in the star's position over time, rather than changes in its light.
Exoplanets display great variation:
-range in size
-hot jupiters and super earths
-variation in the atmosphere and orbits
-few in the habitable zone
The current understanding of the formation of the solar system is _________ model
Nice 2
The formation of the solar system:
1. Protosun forms from collapsing gases and dust
2. Jupiter formed and migrated closer to the protosun than it is today
3. Saturn pulled Jupiter away from the inner solar system
4. Gravitational attraction between planets and conservation of energy changed their orbits over time
5. Inner planets were formed from collisions of metal-rich planetesimals inside the snow line
Formation of our Moon
1. Large planetesimal (Theia) collided with Earth
2. Large amount of debris was ejected into orbit in a disk
3. This debris clumped together to form the Moon
Where is there a lot of debris in the solar system
Oort Cloud, Kuiper belt, asteroid belt
asteriod
mostly rock and metal of at least 10 m
meteoriods
space debris smaller than asteroids
comets
equal mixture of rock and ice
What defines a planet?
1. orbits a star
2. massive enough to be spherical
3. massive enough to clear out its orbit
Define moons/natural satellites
orbits a body that in turns orbits the sun
Smaller solar system body (SSSB)
everything else orbiting the Sun except satellites, providing a catch-all term for the many rocky and icy remnants of solar system formation.
What does it mean that all the planets orbut roughly in the same plane and in the same direction
Indicates that all the planets formed from the same rotating disk
All orbits are ____________
counterclockwise
What are the 3 layers of the suns atmosphere
photosphere (surface), chromosphere, and the corona
-hottest is the corona
What is the suns "surface" made out of?
plasma (ionized gas)
Photosphere
-inner layer
-visble layer of the sun
-sphere of light
-granules
What are granules
form and decay in 20-min cycles and the center is hotter than the edges
Chromosphere
-spikes of gas called spicules
-sphere of color
-can release the trapped gas when the magnetic field opens up
Spicules
spikes of gas jets that are trapped by the suns magnetic field
Cornona
-very hot
-outermost layer
What produces the heliosphere that surrounds the solar system
solar wind
solar wind?
gas and high energy particles that are ejected from the sun
Solar wind interactions with ______ to create the heliosphere
interstellar wind
Boundary of the heliosphere is called?
heliopause
What is Earths magnetosphere
The region of Earth's magnetic field shaped by the solar wind.
The frequency of sunspots are on a _______
11-year cycle
sunspots?
regions of the photosphere that appear dark because they are cooler than the regions around them
-tend to be grouped toegther
What creates the sunspots
the suns magnetic field
-the conductive plasma is moved out of the way by local magnetic fields creating colder regions (sunspots)
Differential rotation of the sun
the equatorial regions of the sun rotating more rapidly than the polar regions.
The suns magnetic cycle is _______
22-years
The magnetic field is produced by a magnetic dynamo
-magnetic field caused by the movement of charged particles
Solar flares
violent, eruptive events that release vast quantities of high energy radiation (faster the CMEs)
Coronal mass ejections
huge, balloon-shaped plumes of high-energy gas ejected from the corona
Space weather
-solar activity can affect electrical equipment on and near the earth
-recent push to predict space weather events
What makes the sun shine?
Thermonuclear fusion at the Sun's core is the source of the Sun's energy
Thermonuclear fusion happens where
the core
Radiative zone
s where photonscollide with atoms and getreemitted.
Convective zone
is where the hotgas carries the energy to the surfaceand cools and falls back down
What is hydrostatic equilibrium?
Hydrostatic equilibrium is a balance between the outward gas pressure in the Sun and the inward pull of gravity. The Sun supports its own weight by its outward gas pressure, so that it is neither contracting nor expanding.