HBS 1.2.5 Synovial Joints and Movements in Human Anatomy
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Fibrous joint
A fixed, or immovable, joint that connects bones. It is made primarily of collagen.
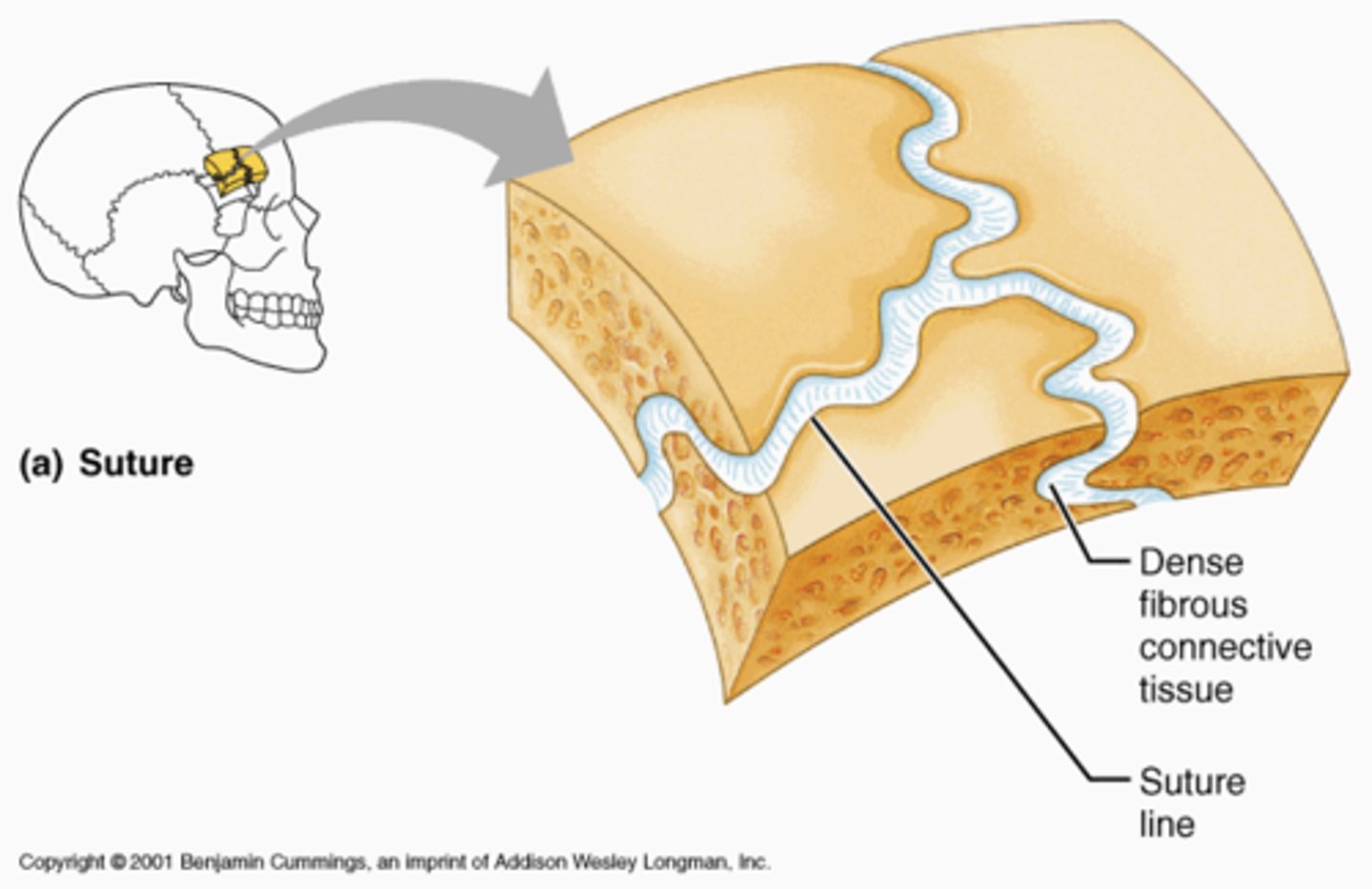
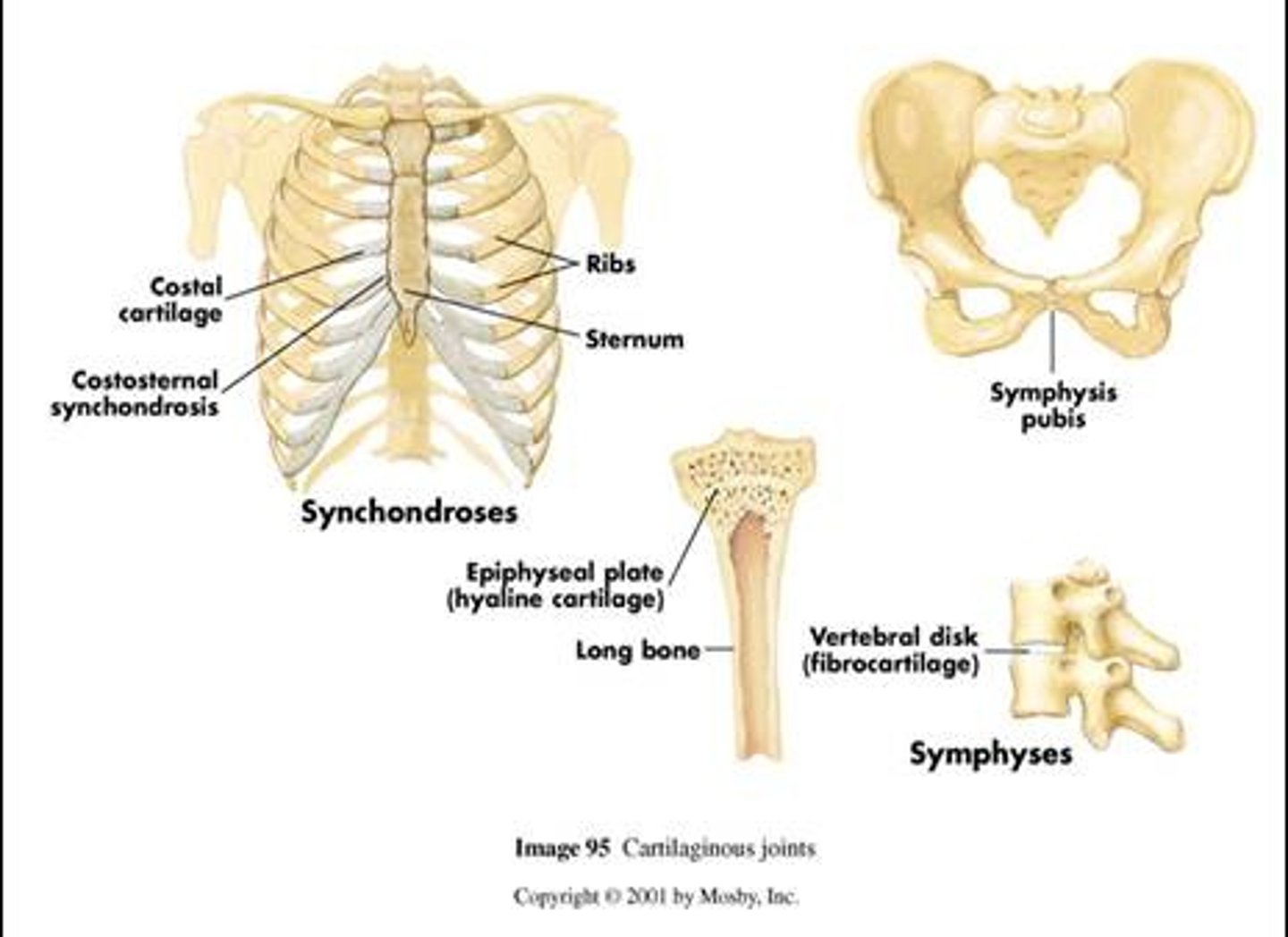
Cartilaginous joint
A joint that has some motion to it with hyaline cartilage present, in the space between articulating bones.
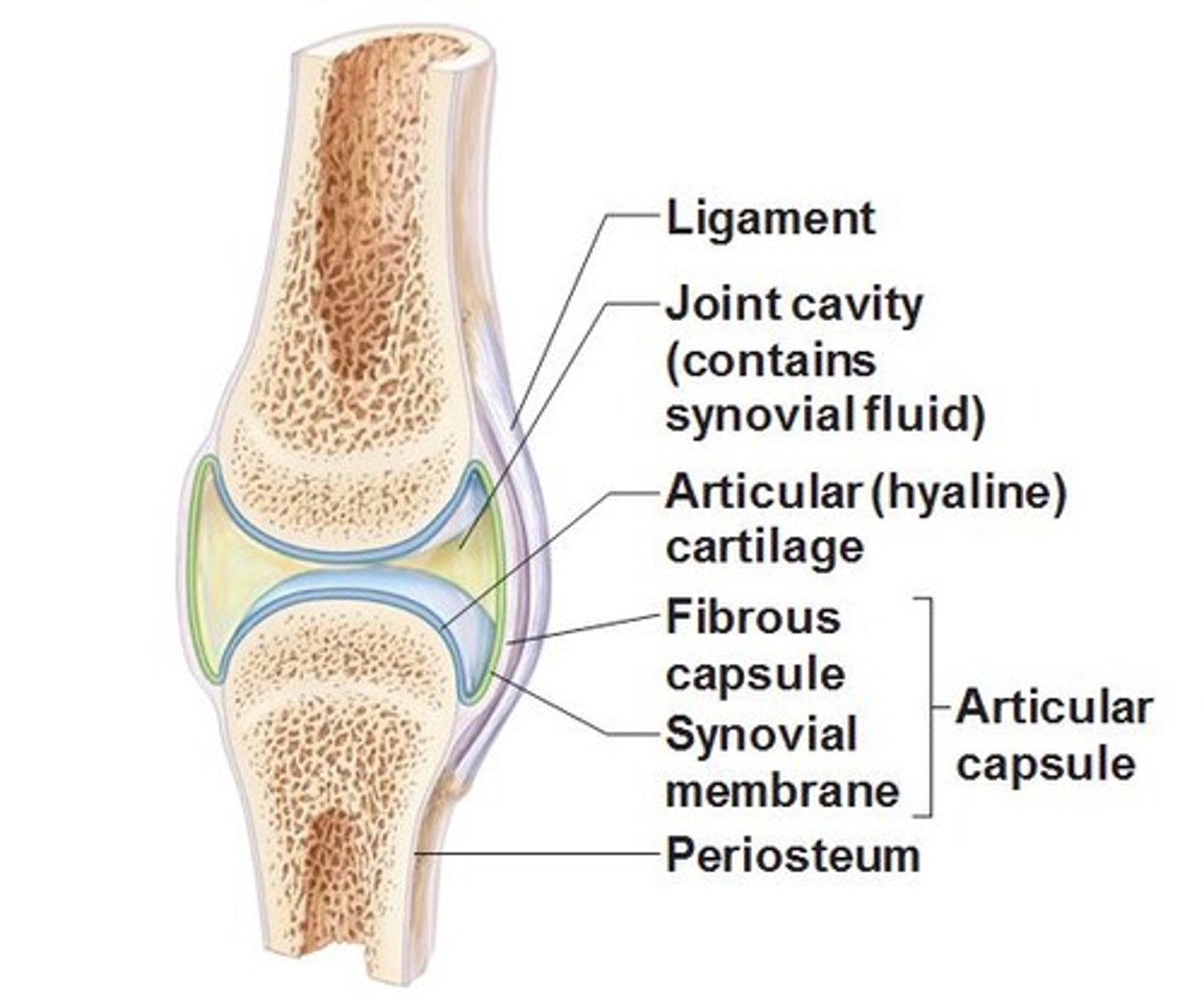
Synovial joint
A moveable joint that contains synovial fluid in the space around it to reduce friction; the most common type of joint in the body.
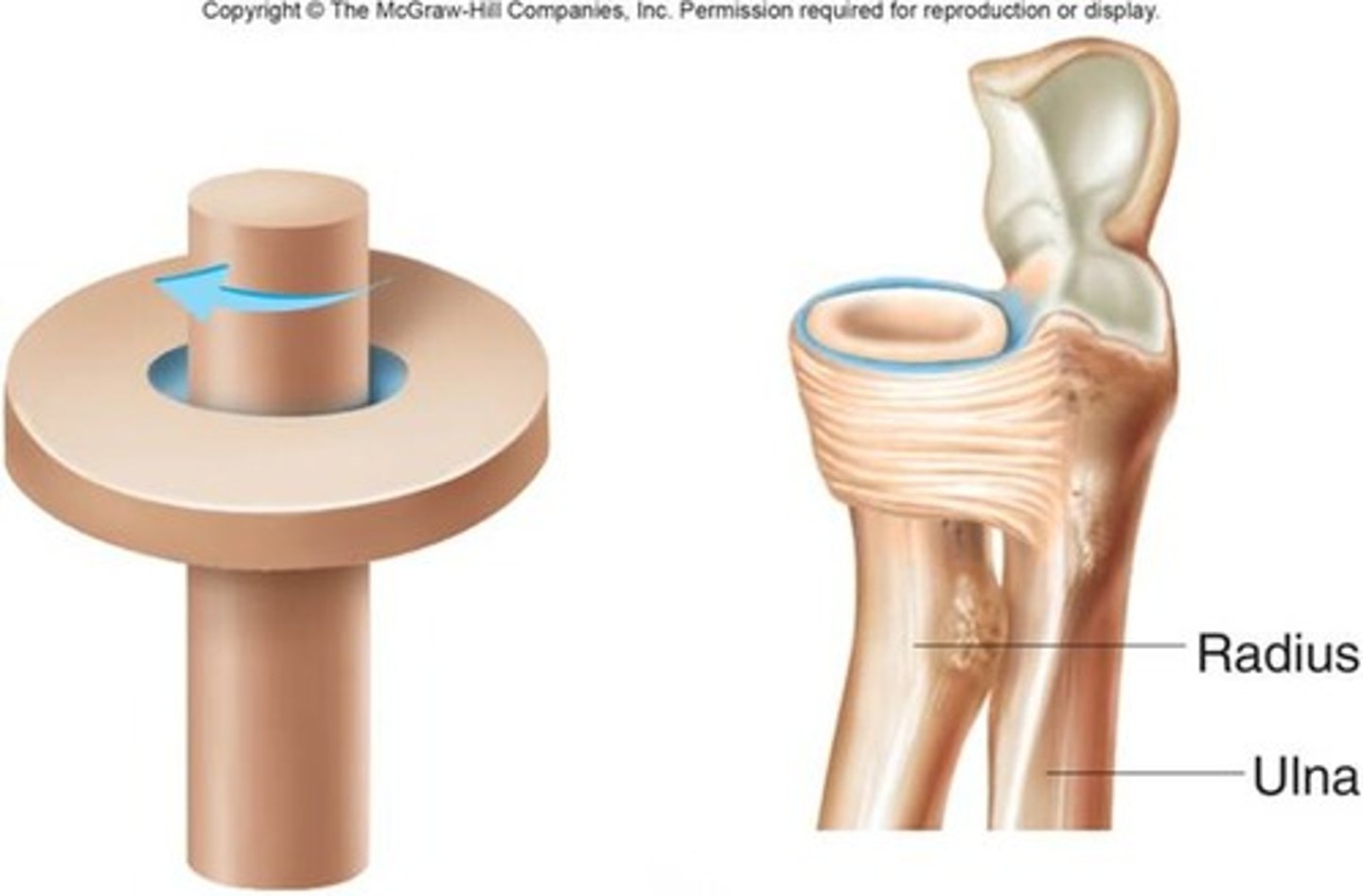
Pivot Joint
rotating bone turns around an axis; i.e. connection between radius/ulna and humerus
Hinge Joint
Joint between bones (as at the elbow or knee) that permits motion in only one plane (Monoaxial)
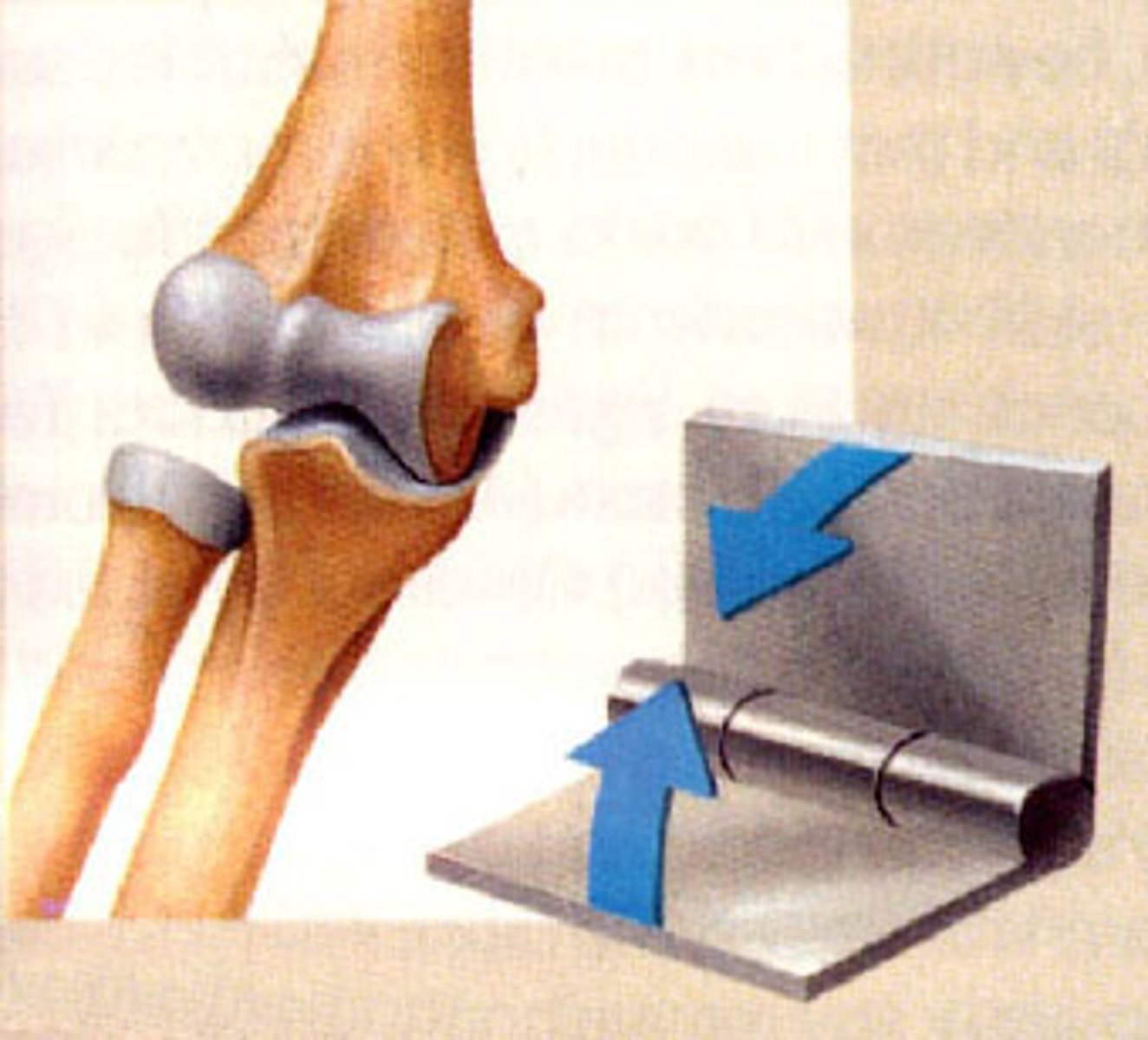
Gliding/Plane Joint
type of joint in which the articular surfaces are only slightly convex and concave. Slight nonaxial or multiaxial
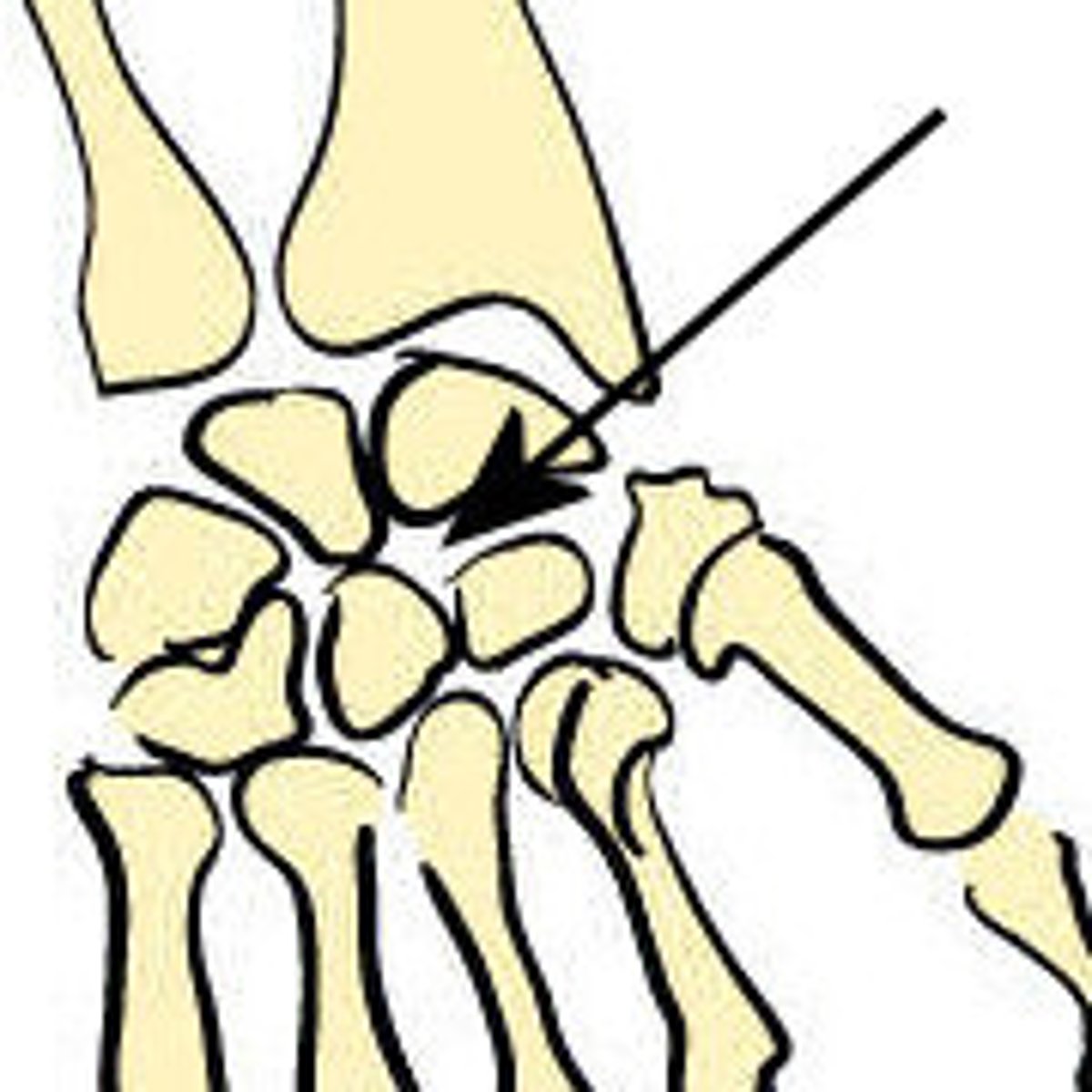
Saddle Joint
type of joint found at the base of each thumb; allows grasping and rotation. Biaxial.
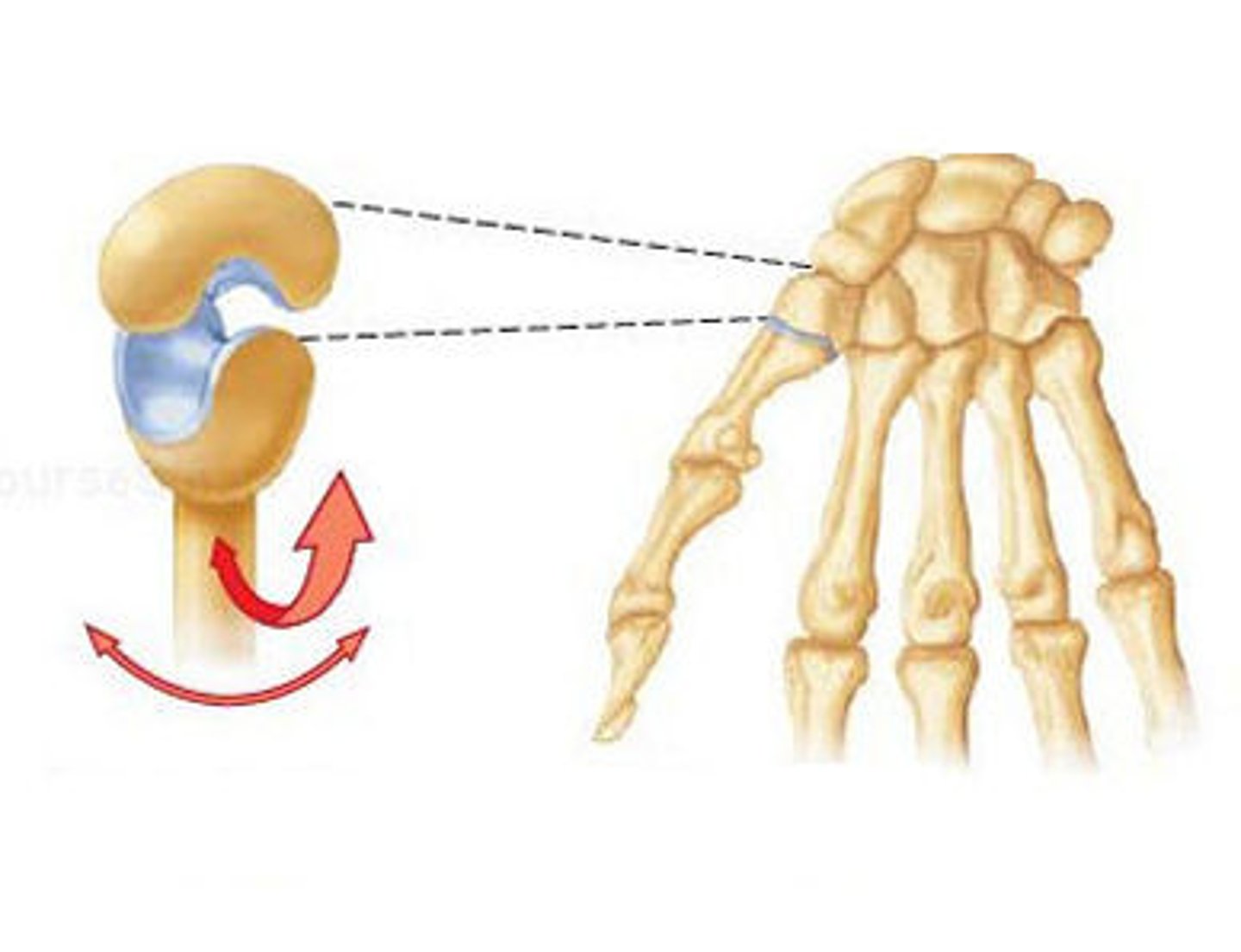
Condyloid/Ellipsoidal Joint
Description: Oval-shaped projection fits into an oval-shaped depression. Biaxial
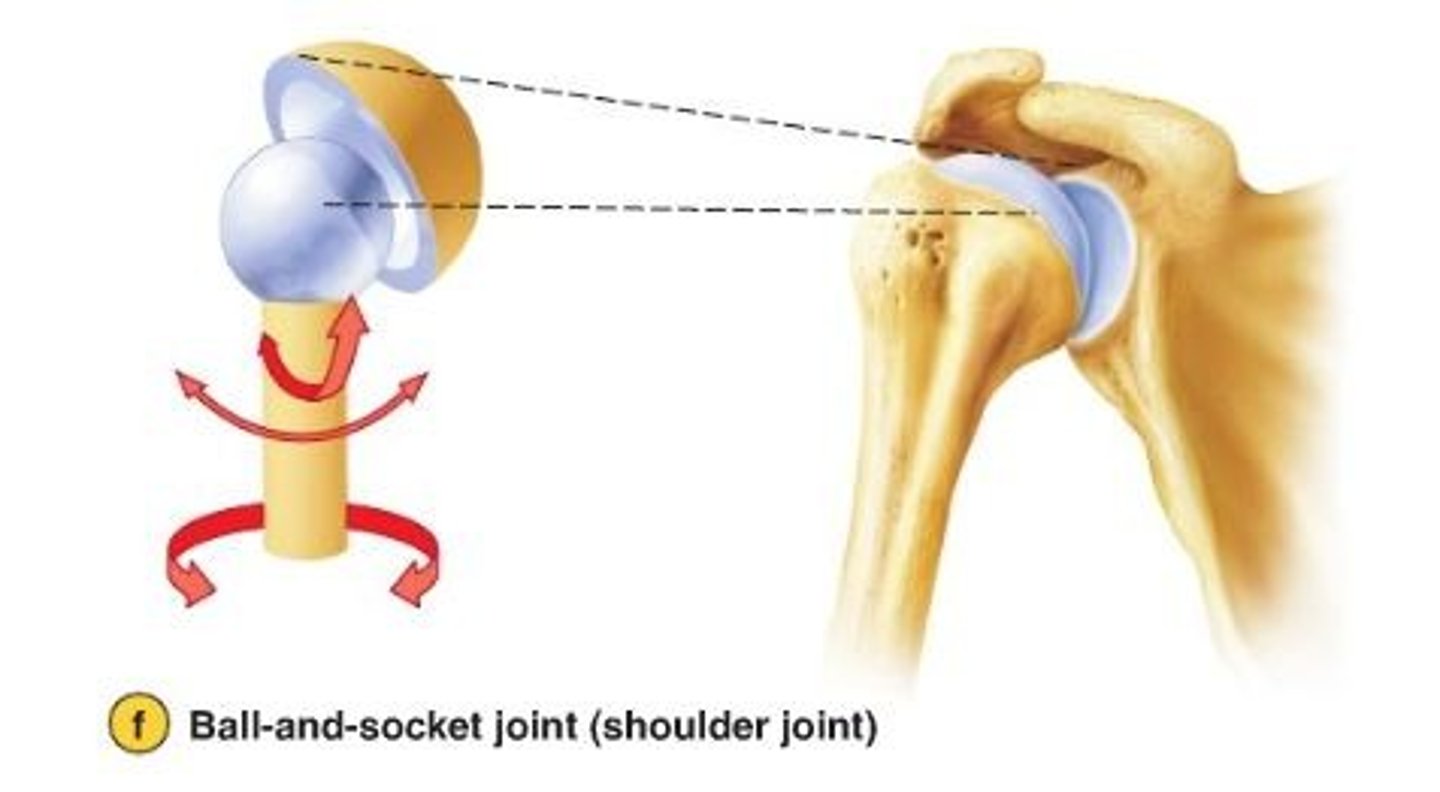
Ball and Socket Joint
A joint that allows internal and external rotation, as well as bending. Triaxial
Rotation
circular movement around an axis such as the shoulder joint
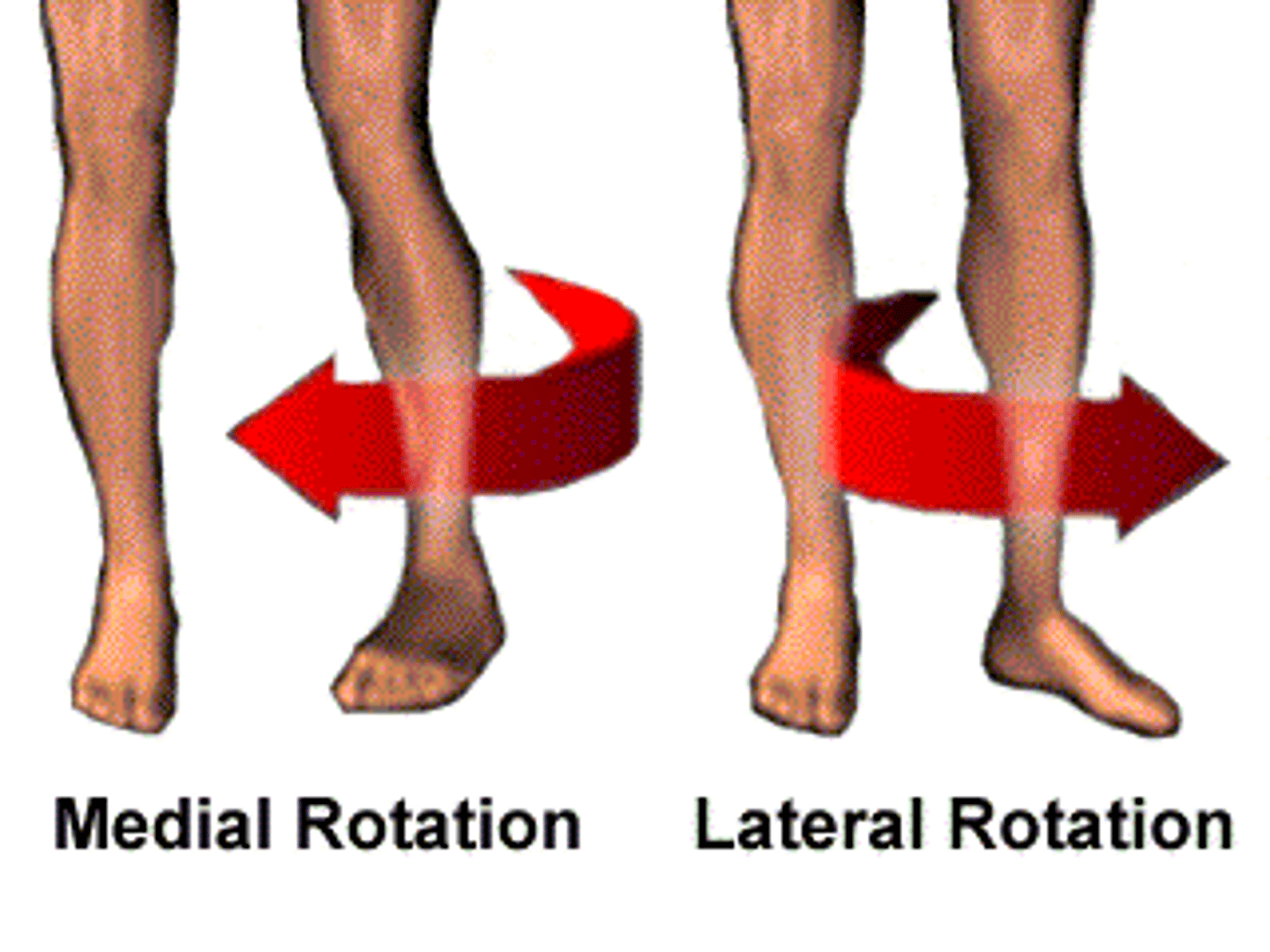
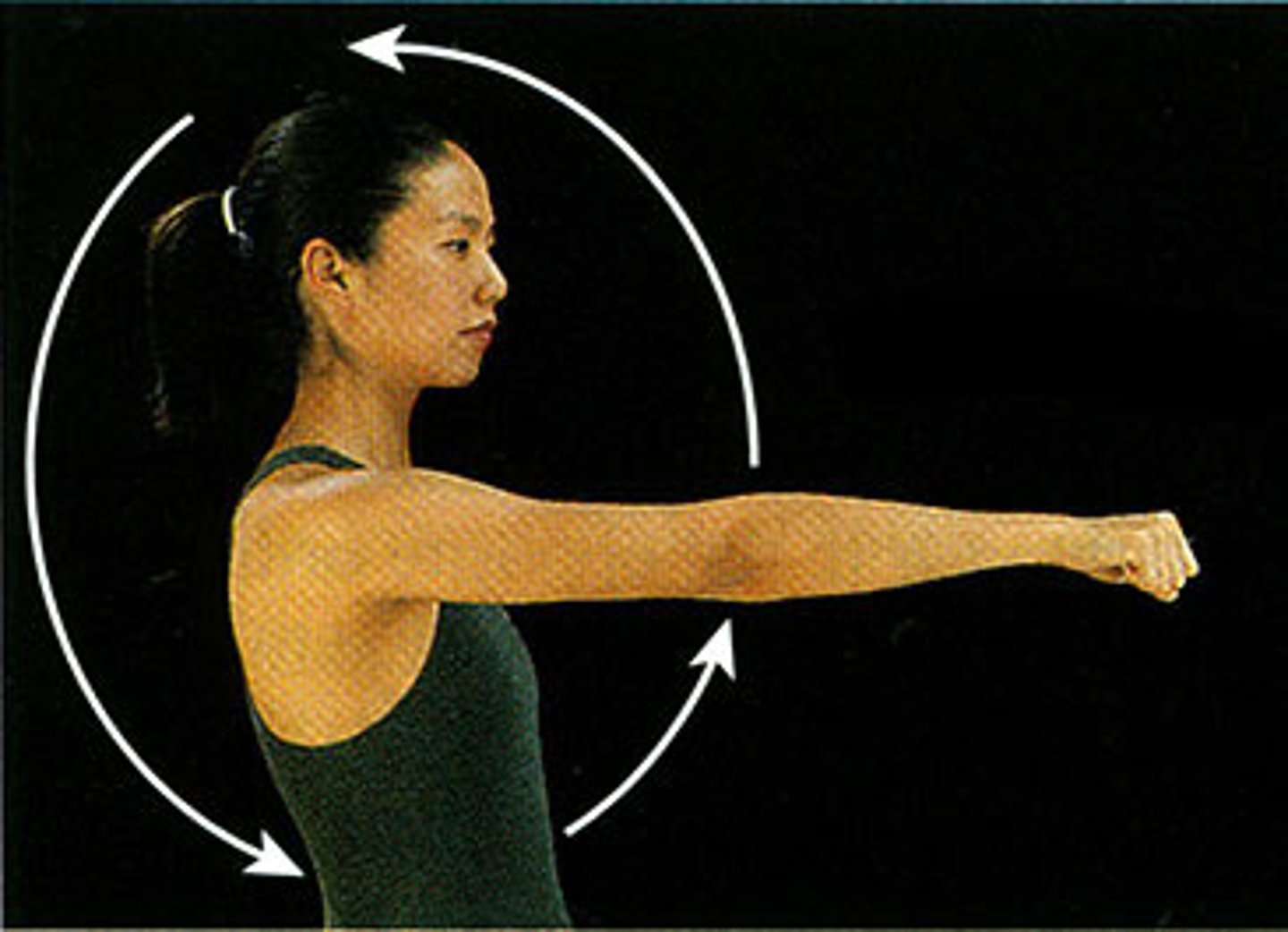
Circumduction
circular movement of a limb
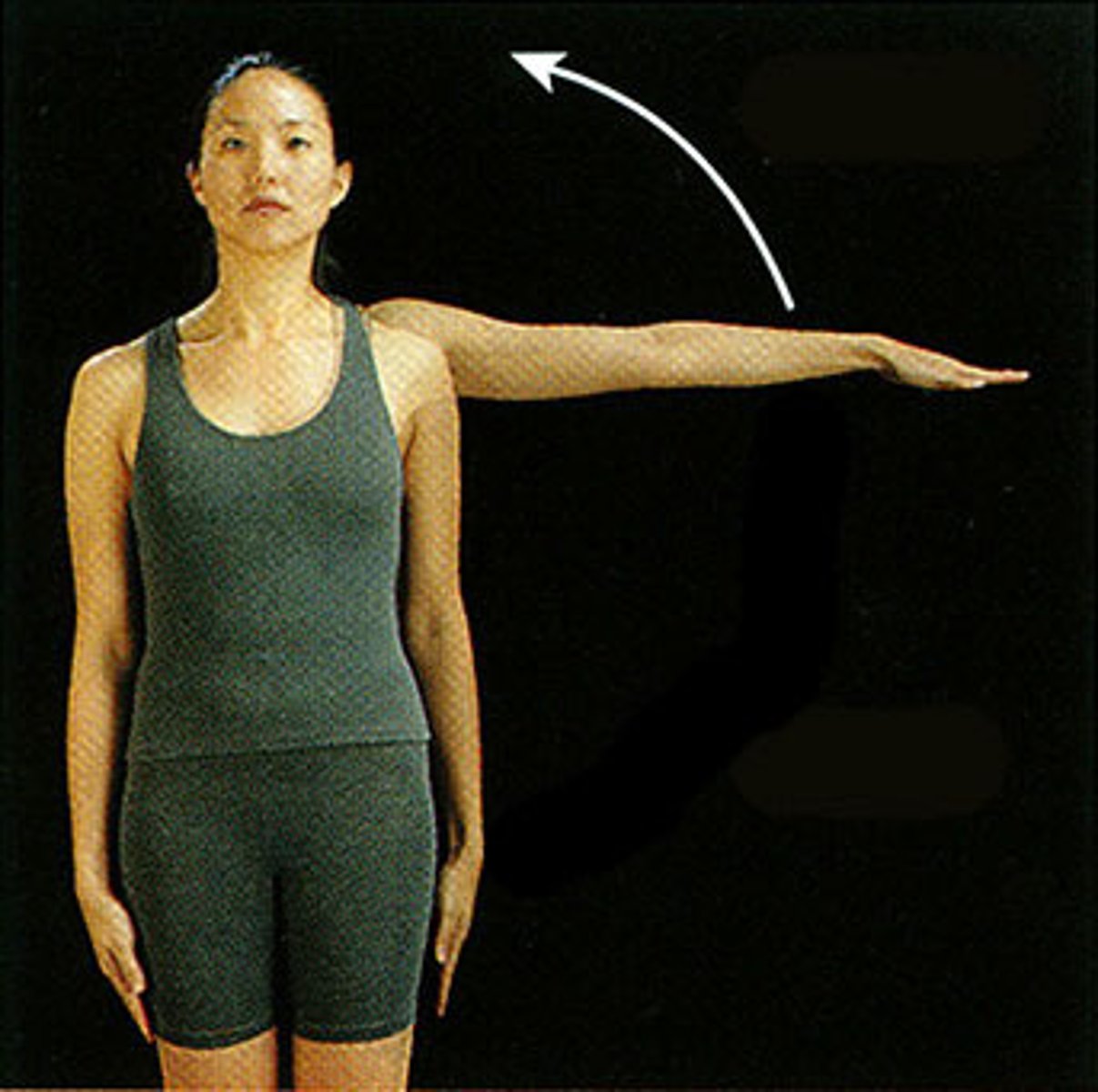
Abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body in the frontal plane
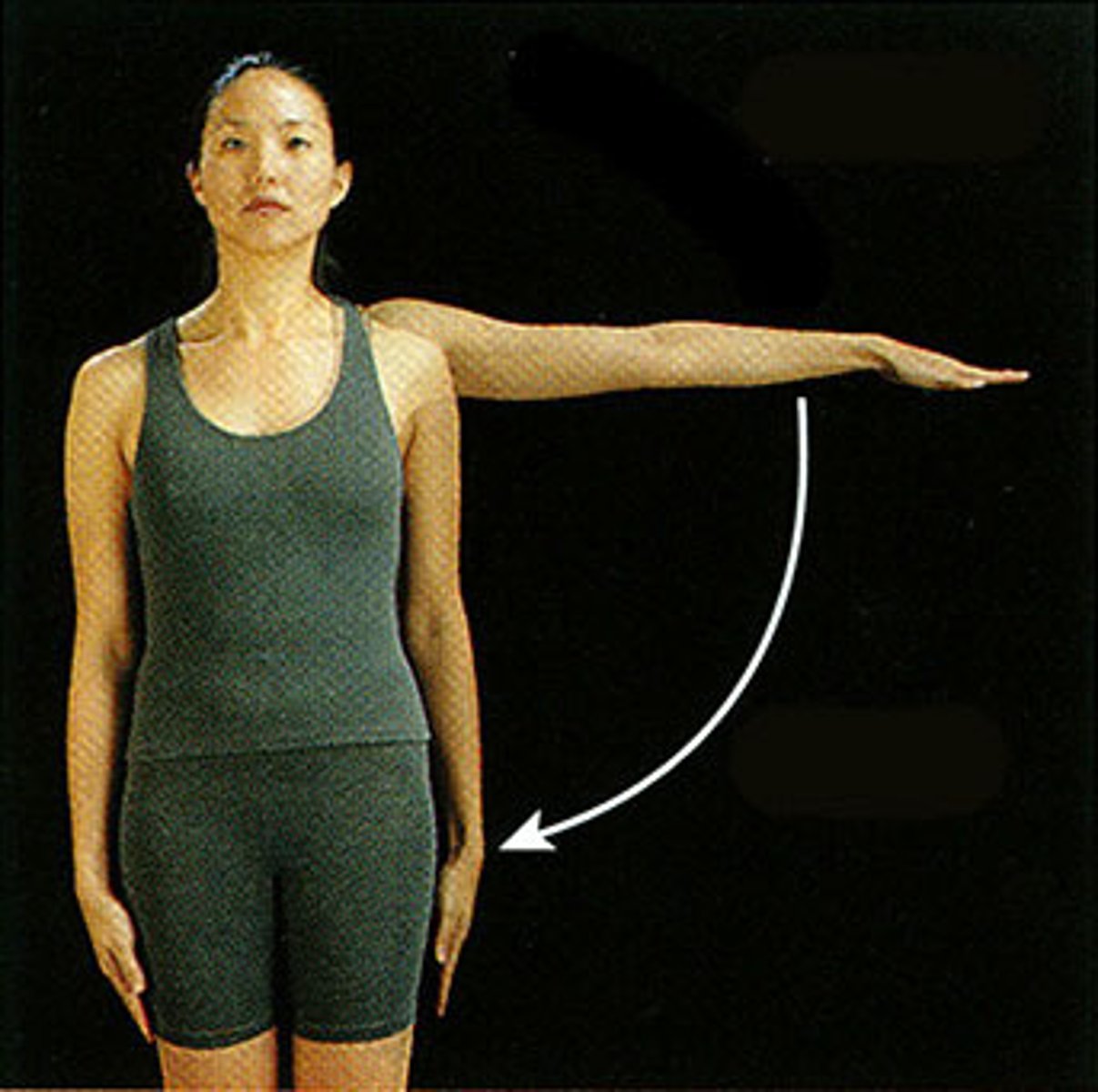
Adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body in the frontal plane

Depression
movement of body part downward
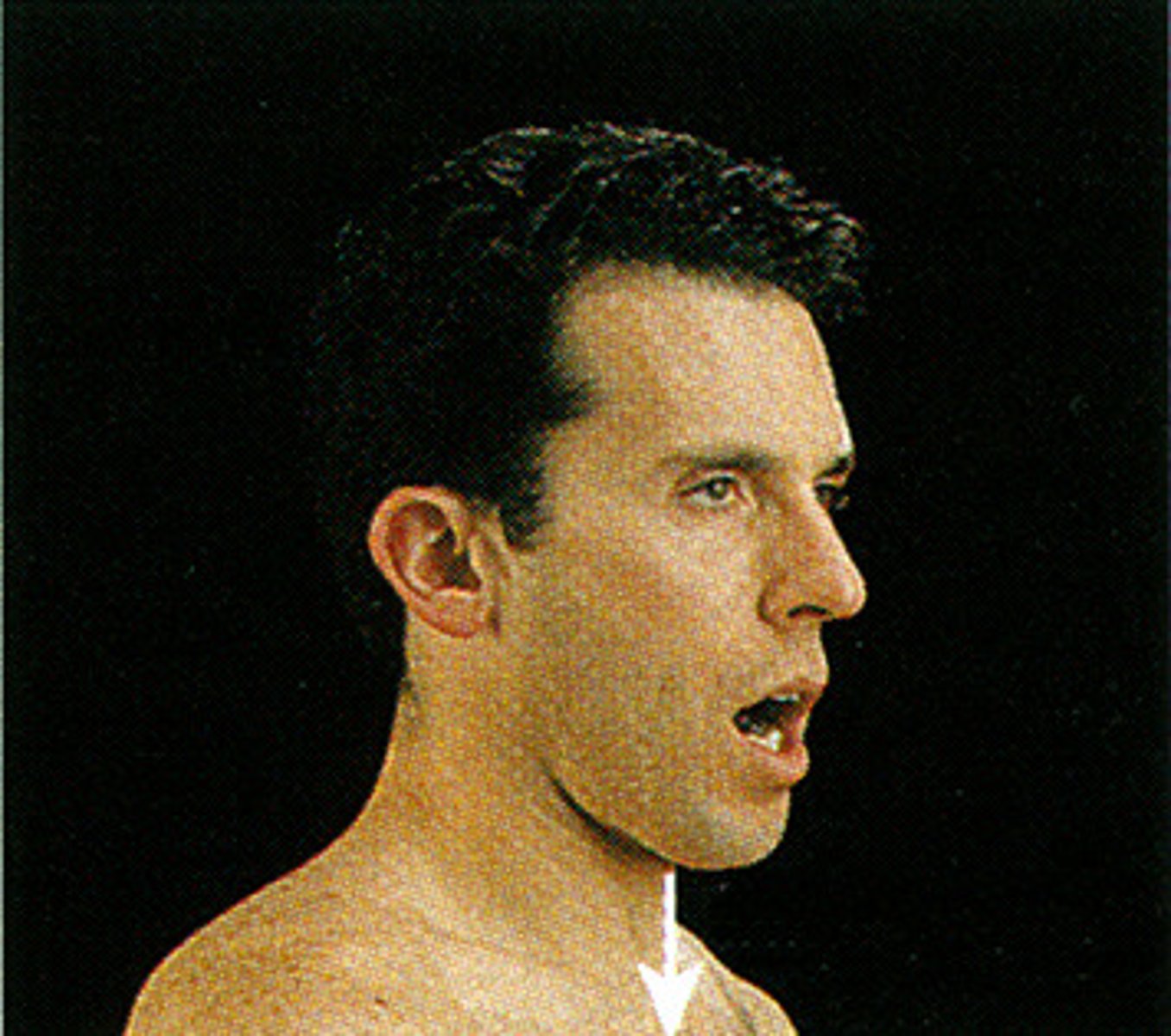
Elevation
movement of a body part upward in a frontal plane
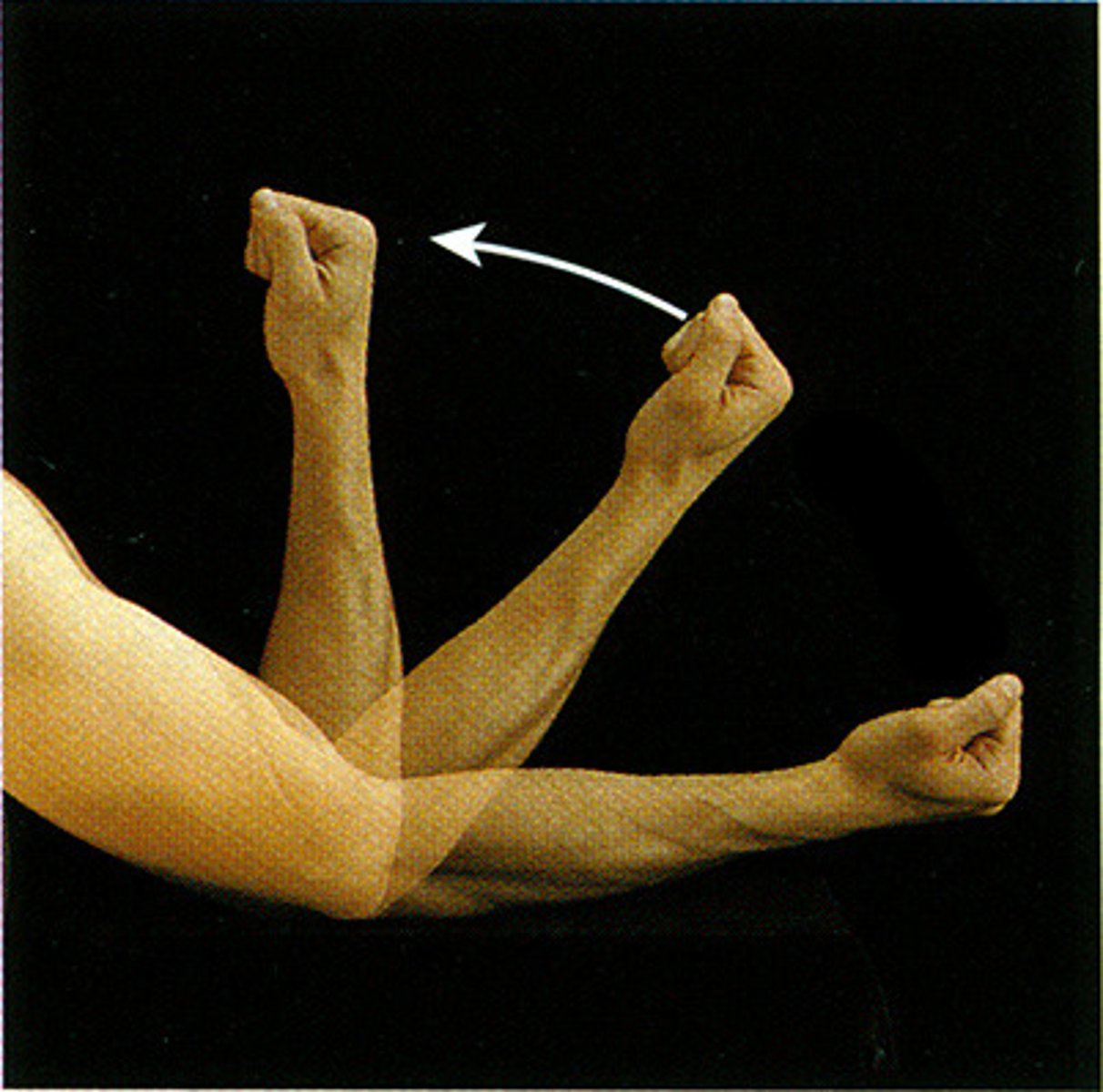
Flexion
Decreasing the angle between two body parts.
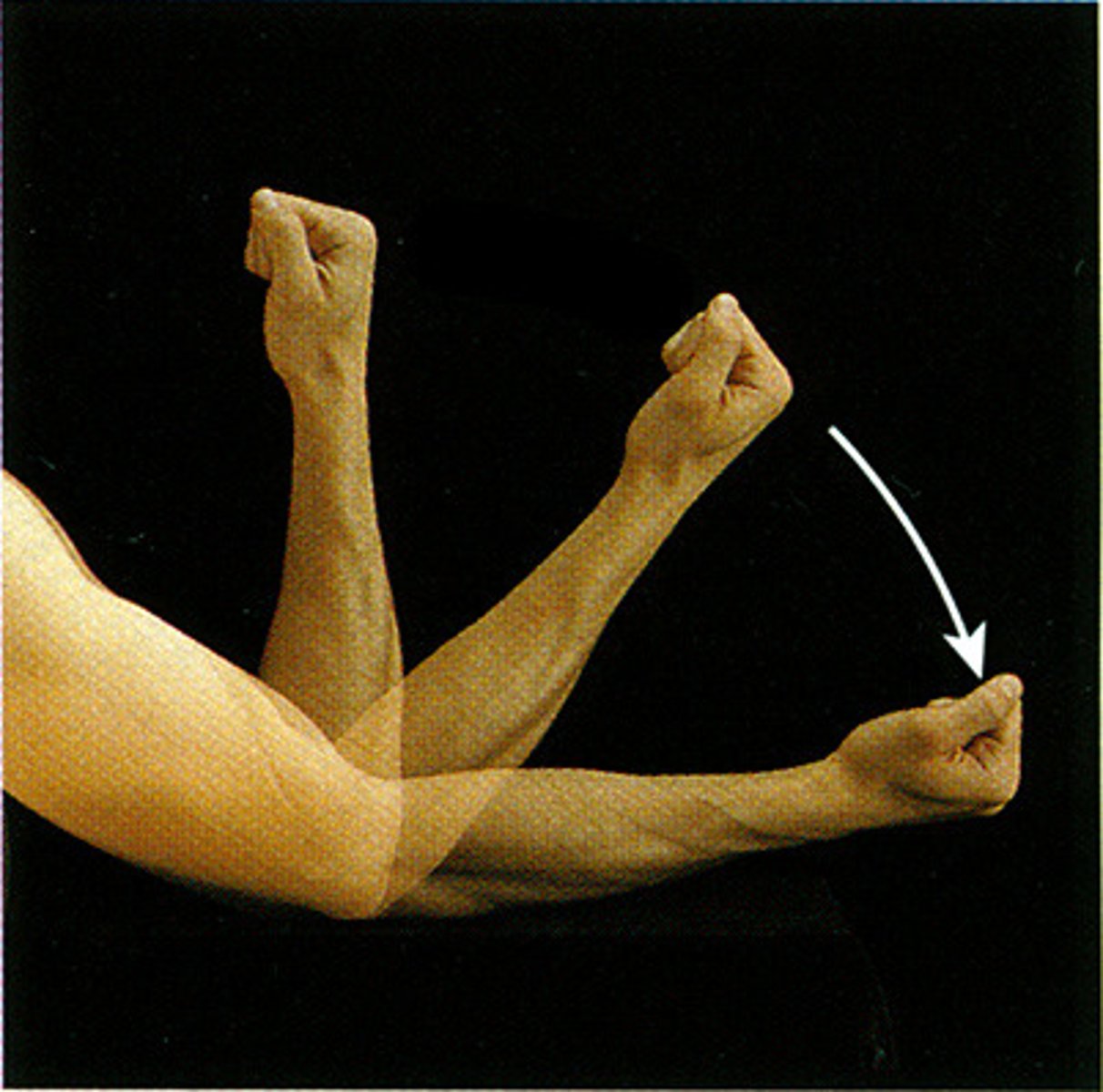
Extension
Increasing the angle between two body parts.
Hyperextension
Extension beyond the normal range of motion.
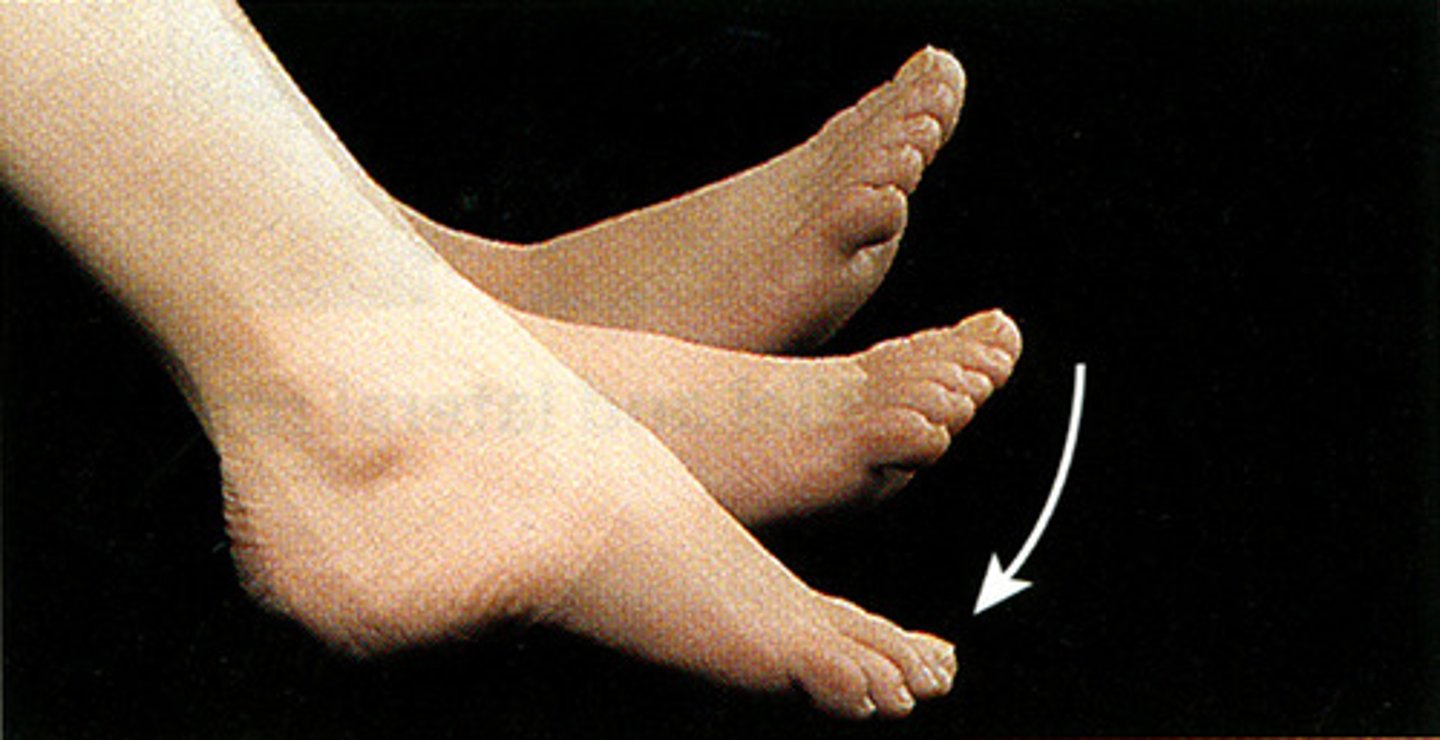
Plantar flexion
bending of the sole of the foot by curling the toes toward the ground. Movement that decreases the angle between the foot and the leg.
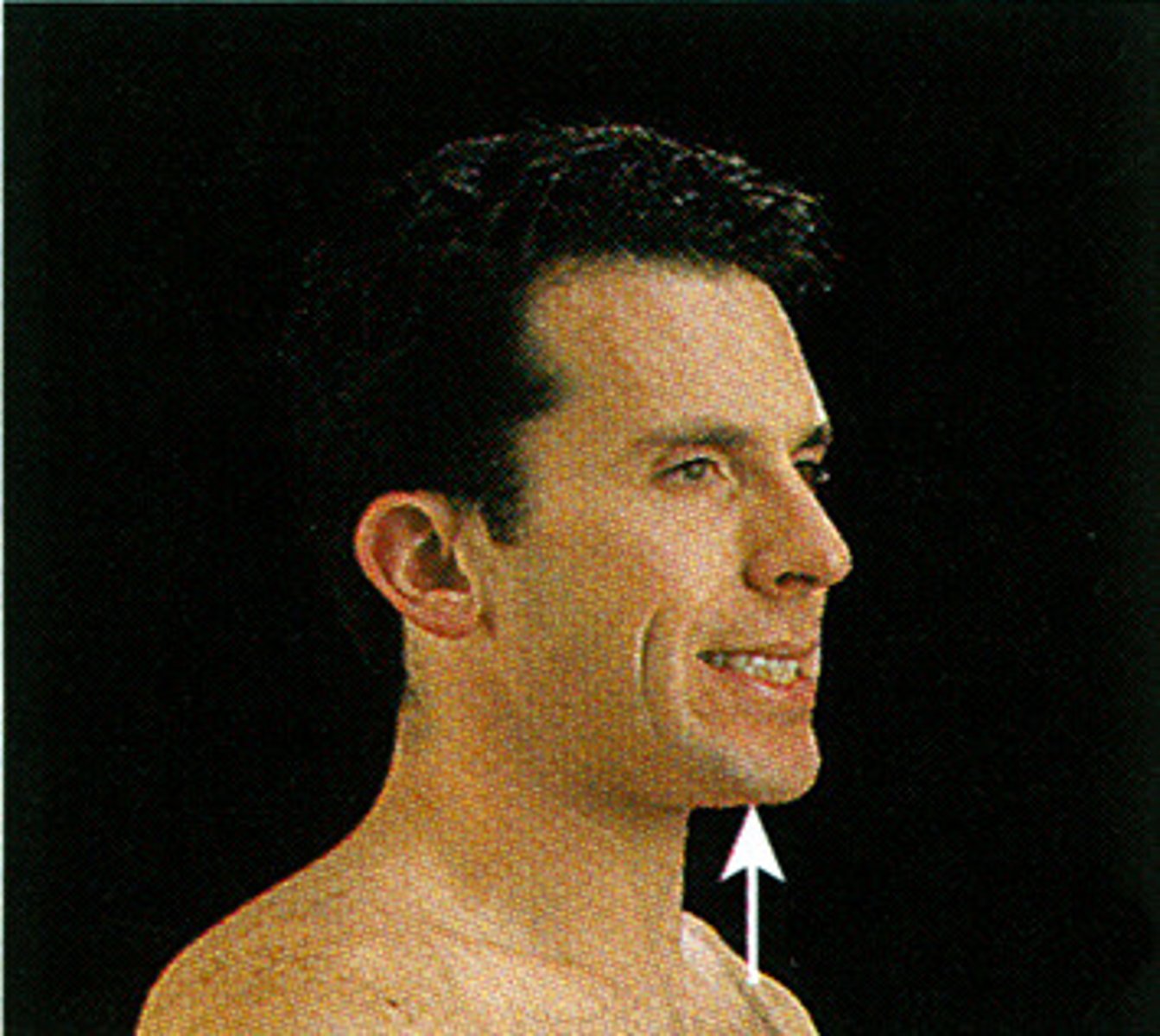
Dorsiflexion
Backward flexion, as in bending backward either a hand or foot. Movement that increases the angle between the foot and the leg.
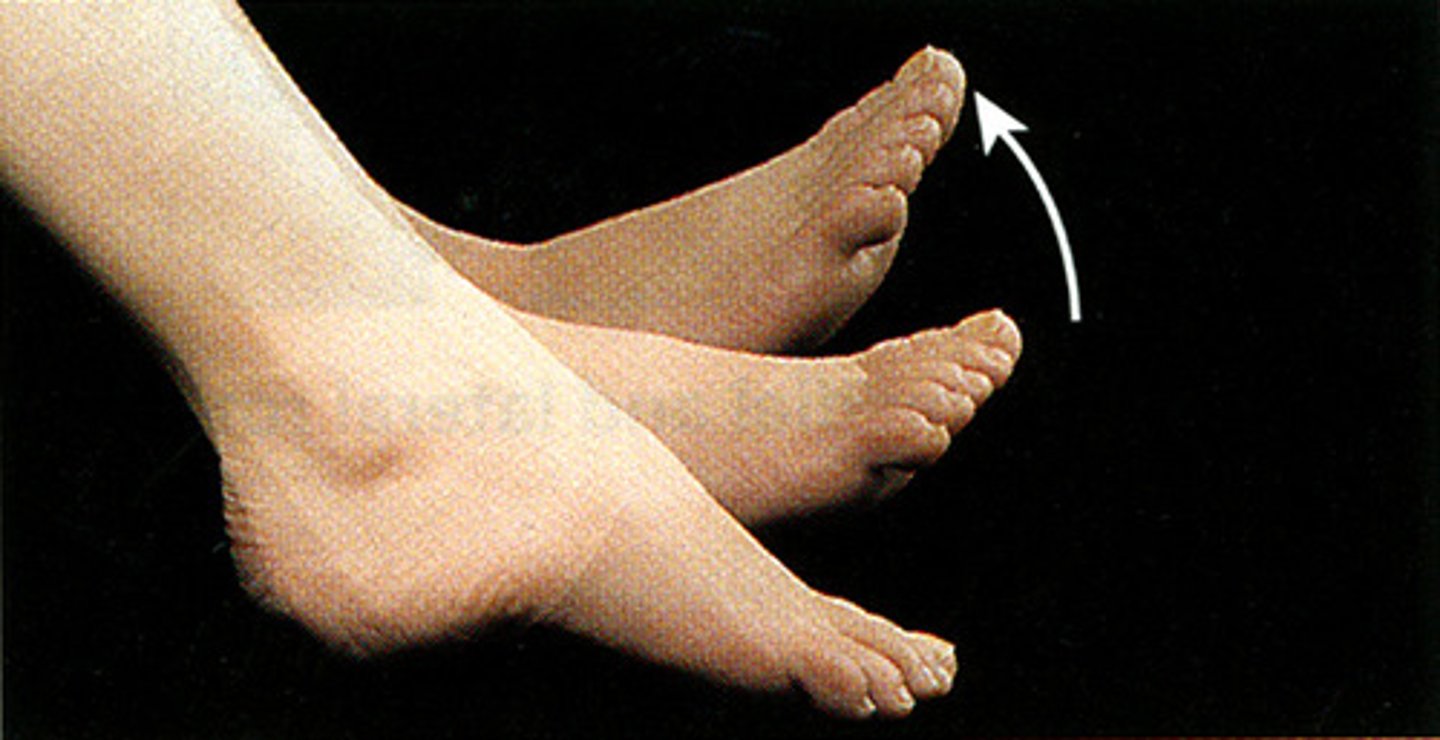
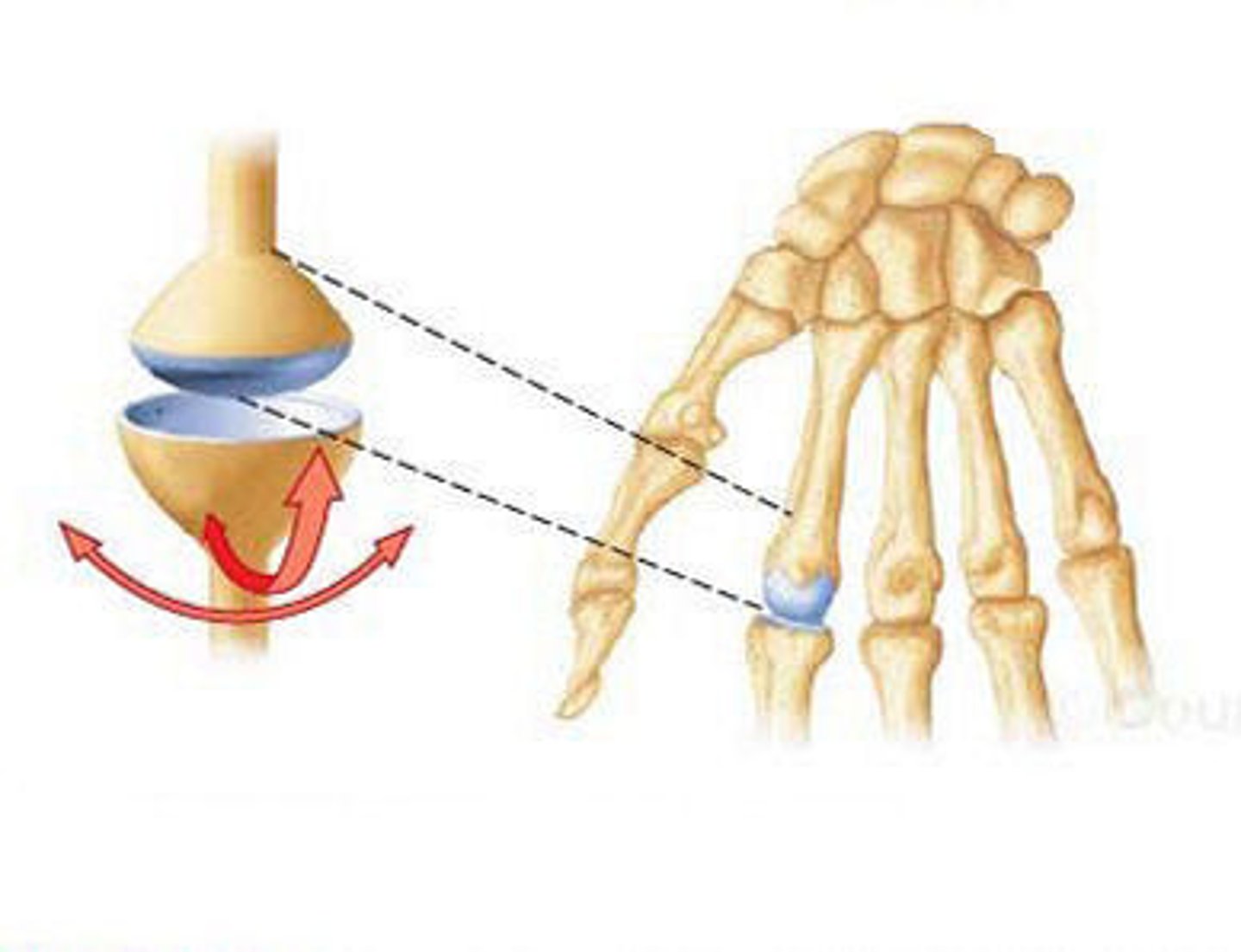
Condyloid Joint
synovial joint that does everything except rotating. Biaxial joint allowing Flexion, Extension, Abduction, Adduction, and Circumduction, but not rotation around an axis.
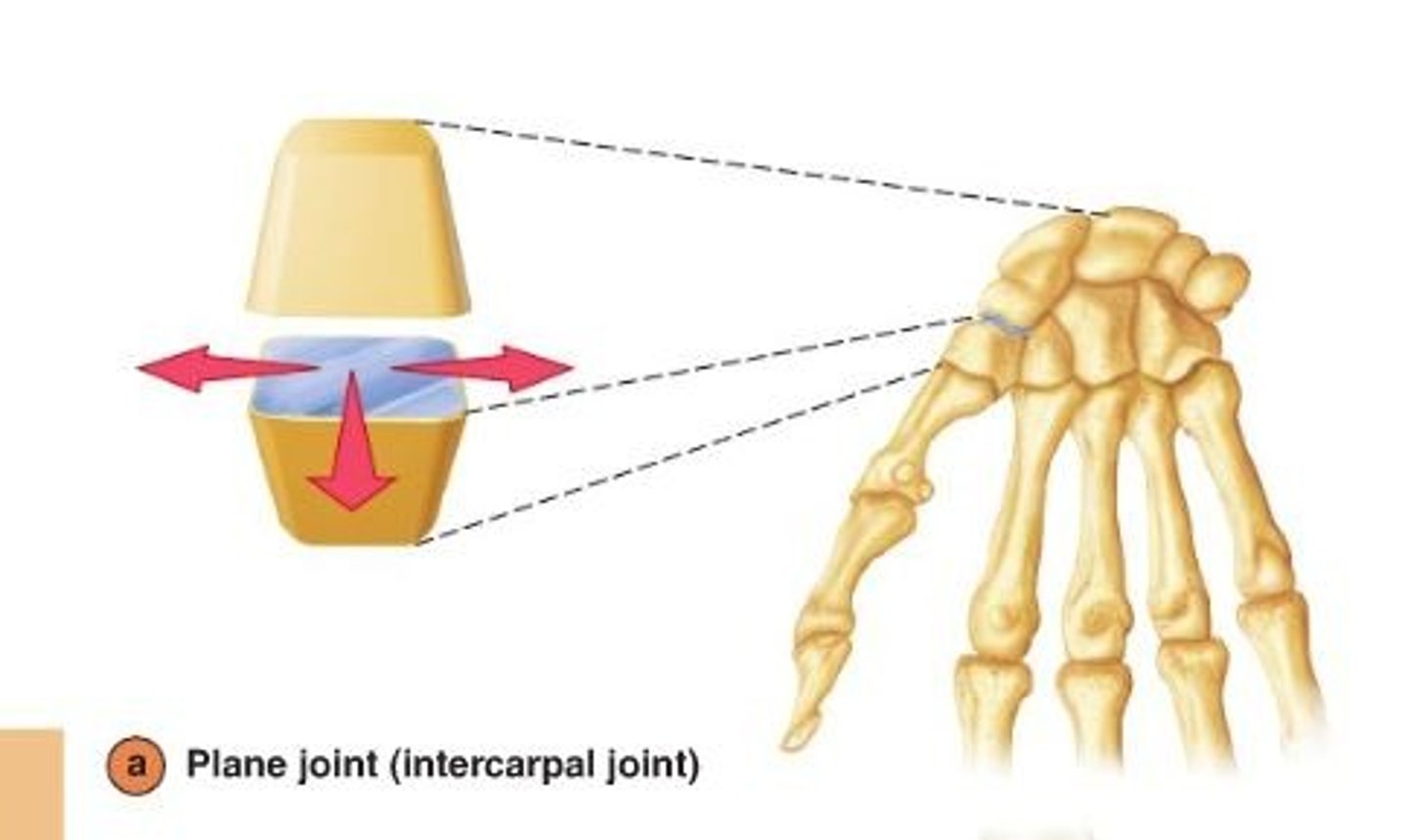
Plane Joint
short slipping or gliding movements; i.e. carpals. Multiaxial joint allowing Gliding or Sliding movements.
Articular Cartilage
Covers the ends of bones (condyles) to cushion the joint and allows for easy bending/straightening motions.
Elastic Cartilage
Found in the ear, epiglottis, and upper respiratory tract.
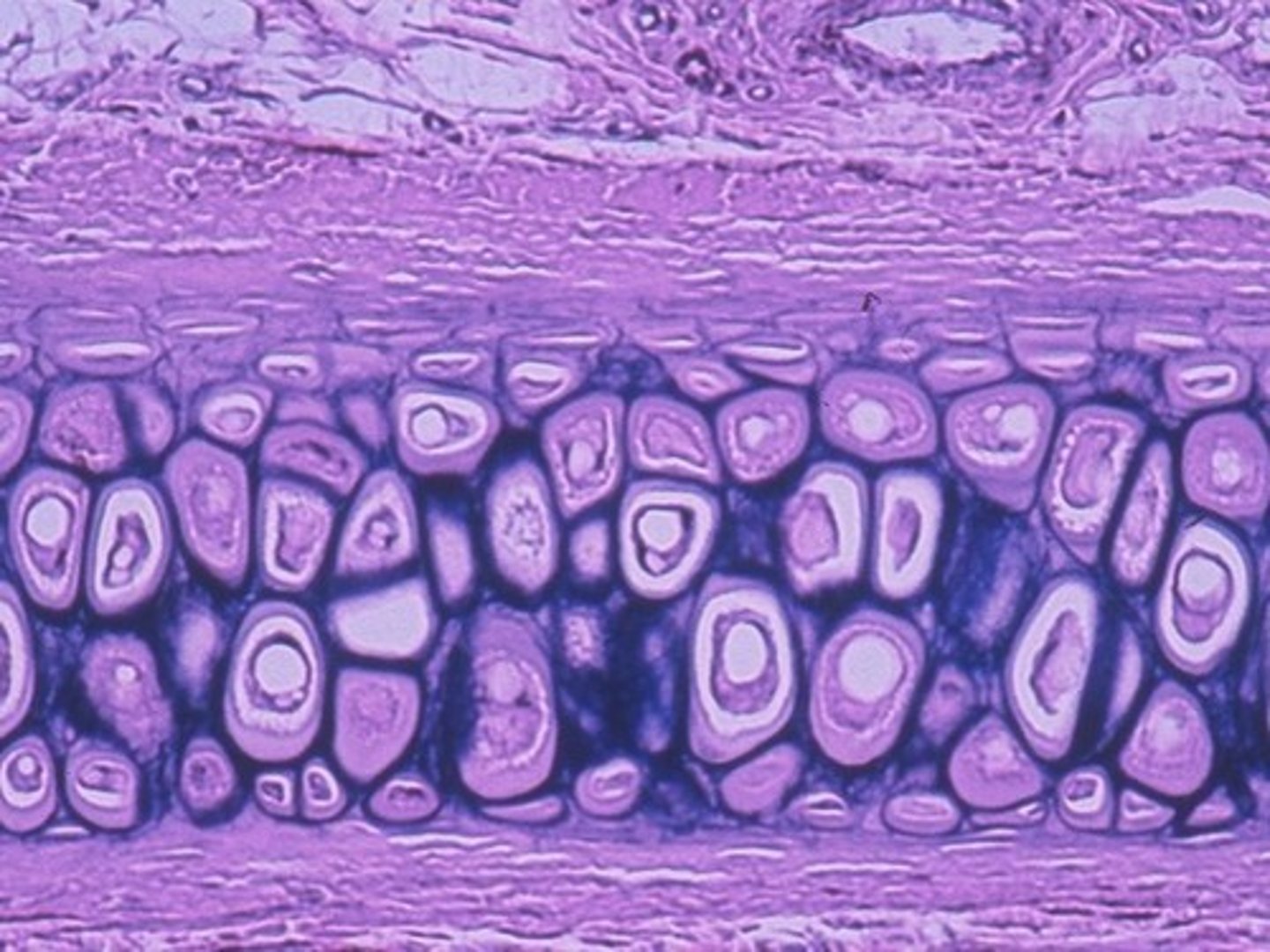
Fibrocartilage
Found in the intervertebral discs and pubic symphysis.
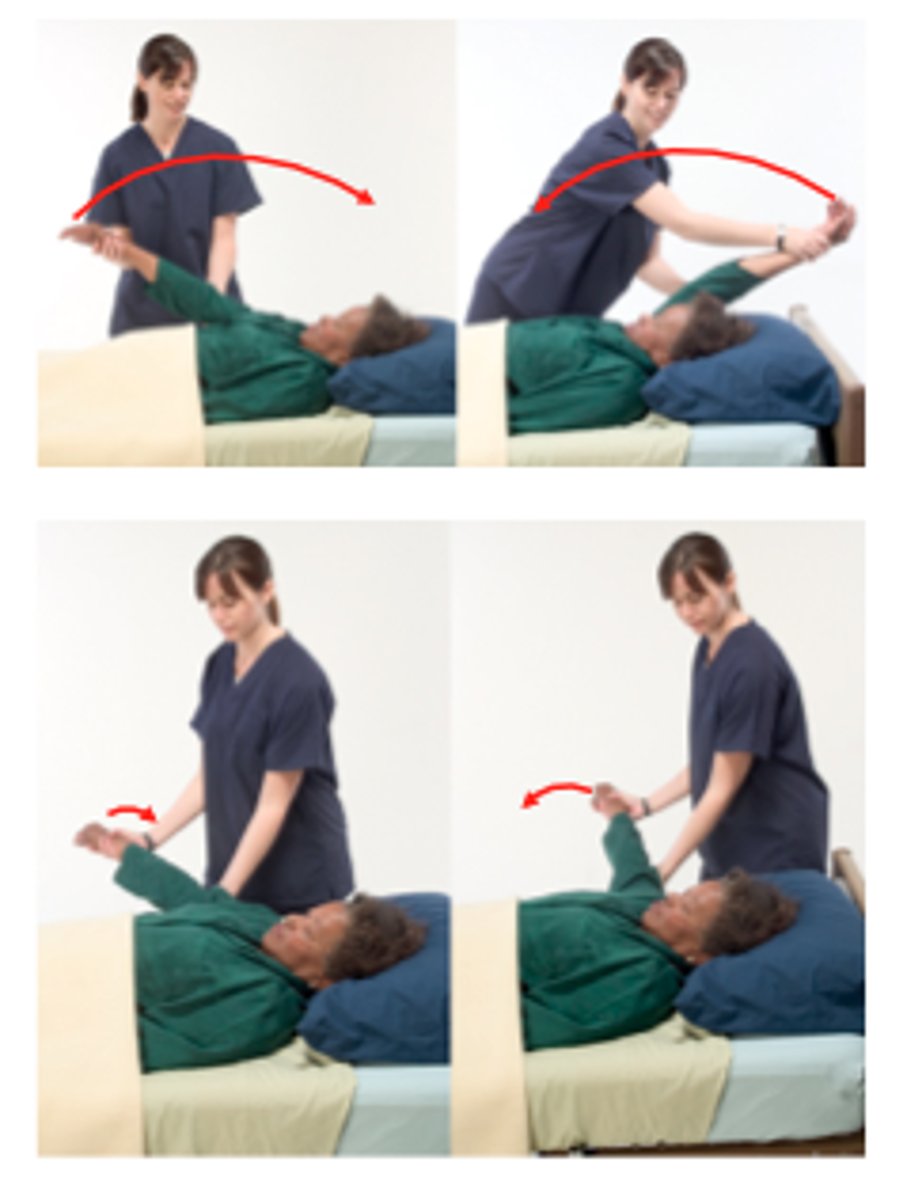
Range of Motion (ROM)
An important measurement to track to help determine whether a treatment plan is working.
Dislocated Shoulder
Condition where the ball part of the joint has fallen out of place from the cup/socket portion of the joint.
Movement Types
The ball and socket joint allows for the greatest amount of movement because its structure permits multi-axial movement in nearly all directions.
Gravity Effect on Cartilage
The cartilage between bones gets compressed with gravity, causing a person to get shorter during the day.
Recovery of Cartilage
By the time a person wakes up the next morning, their cartilage has recovered and they are back to their full height.
Bones, Muscles, and Joints Function
Bones provide support and shape, muscles provide movement, and joints attach bones to provide flexibility.
Running Activity Joints
Running requires the ball and socket joint, and the hinge joints in the knees and ankles.