BIOSC-130 Fetal Pig Dissection
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Dorsal
back/spine
Posterior
tail end
Anterior
front of the body
Ventral
belly side
Medial
toward the midline
Lateral
side/edge of body
Proximal
near body
Distal
away from body
Caudal
tail
Cephalic/cranial
toward the head
Sagittal
divides body into left and right
Frontal
divides the body into anterior and posterior sections
Transverse
Divides body into cephalic and caudal parts
Thymus
site of T cell maturation and is larger in children and adolescents
Heart
pumps blood
Lungs
two spongy organs, located in the thoracic cavity enclosed by the diaphragm and rib cage, responsible for respiration
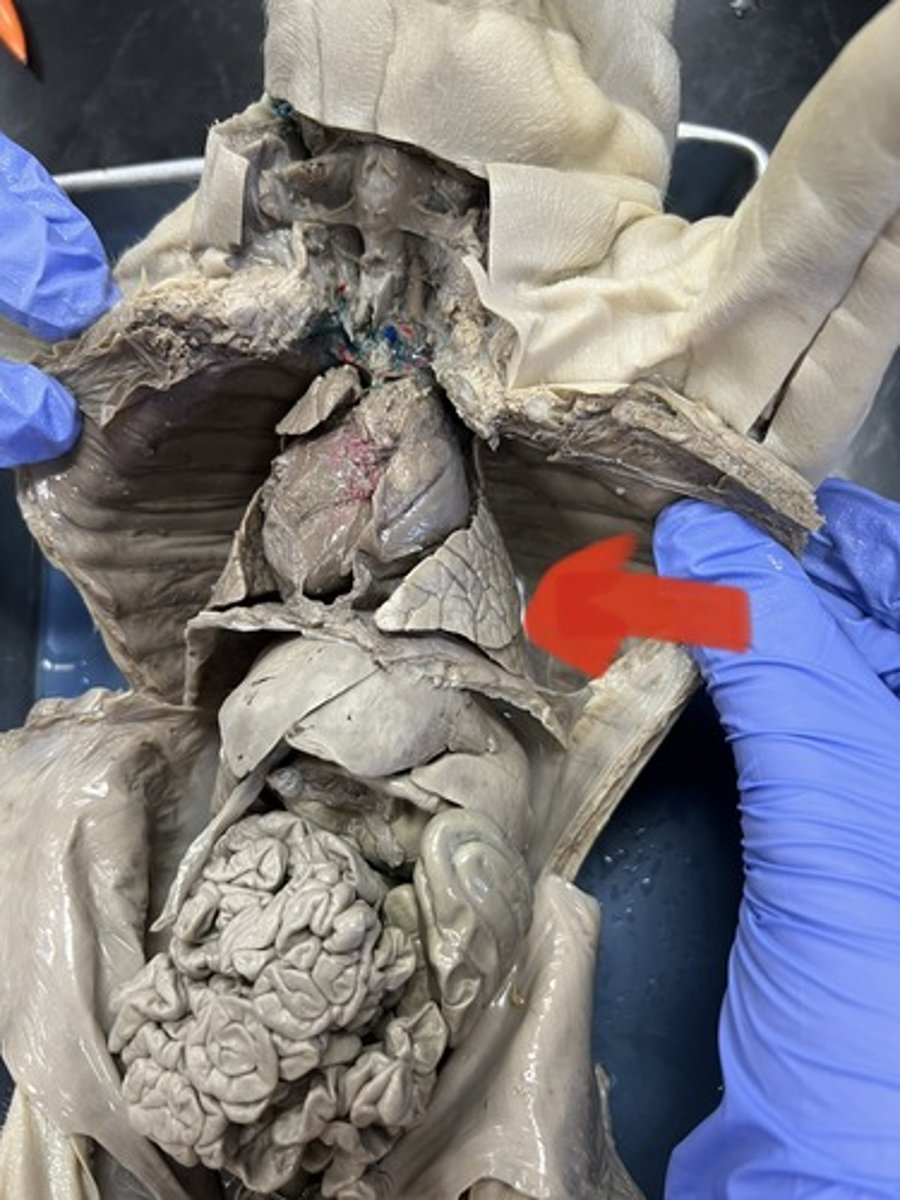
Diaphragm
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathing
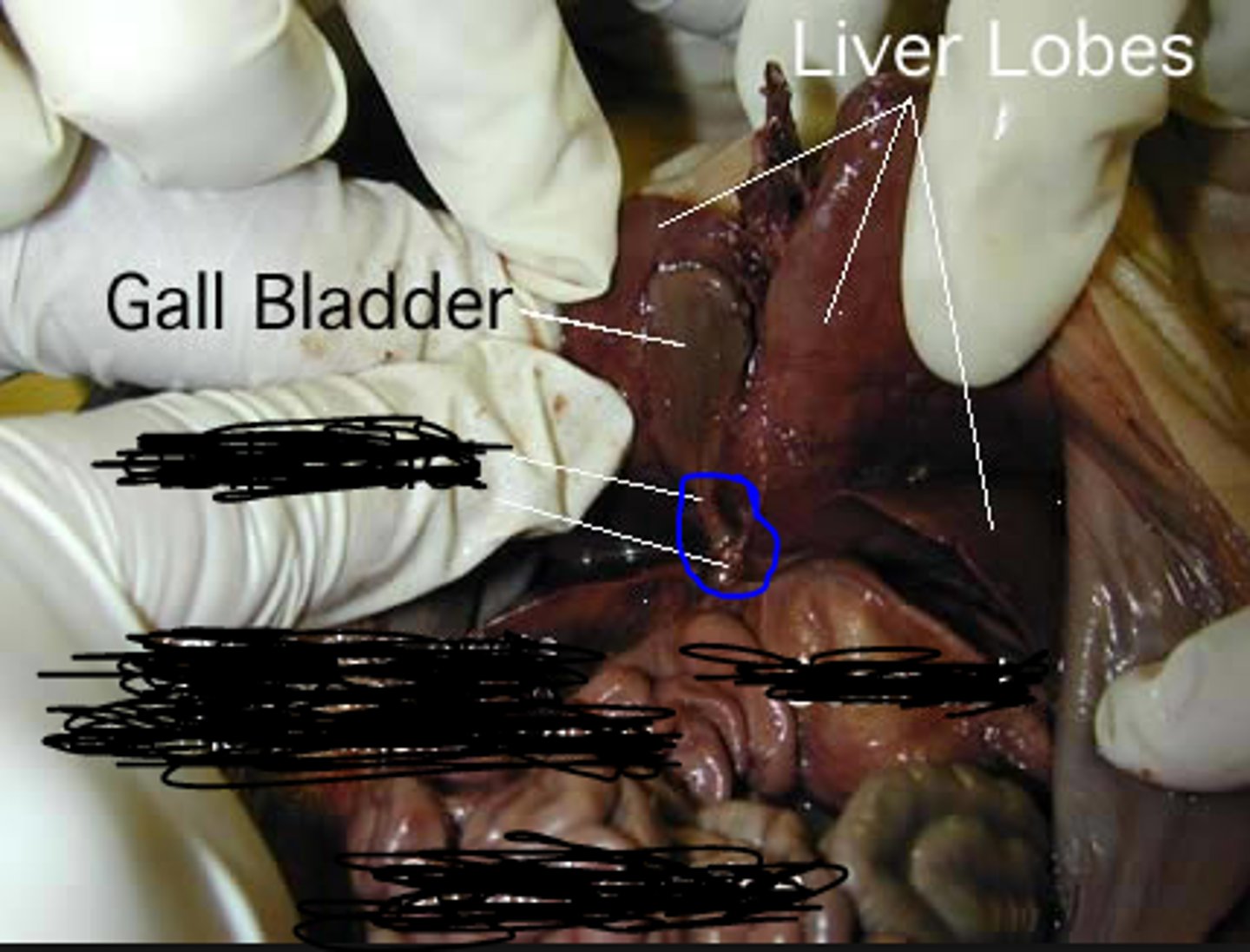
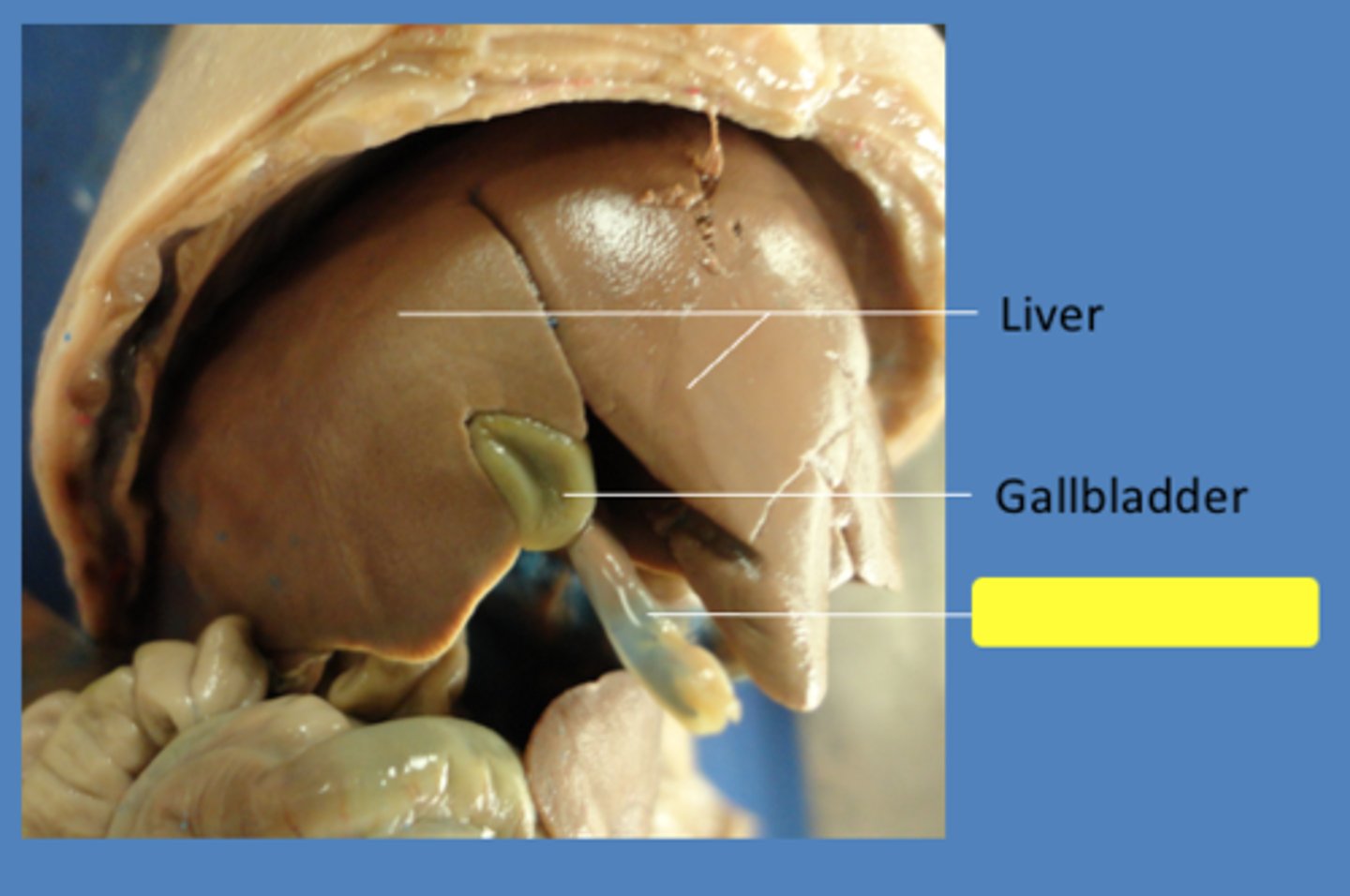
Liver
produces bile
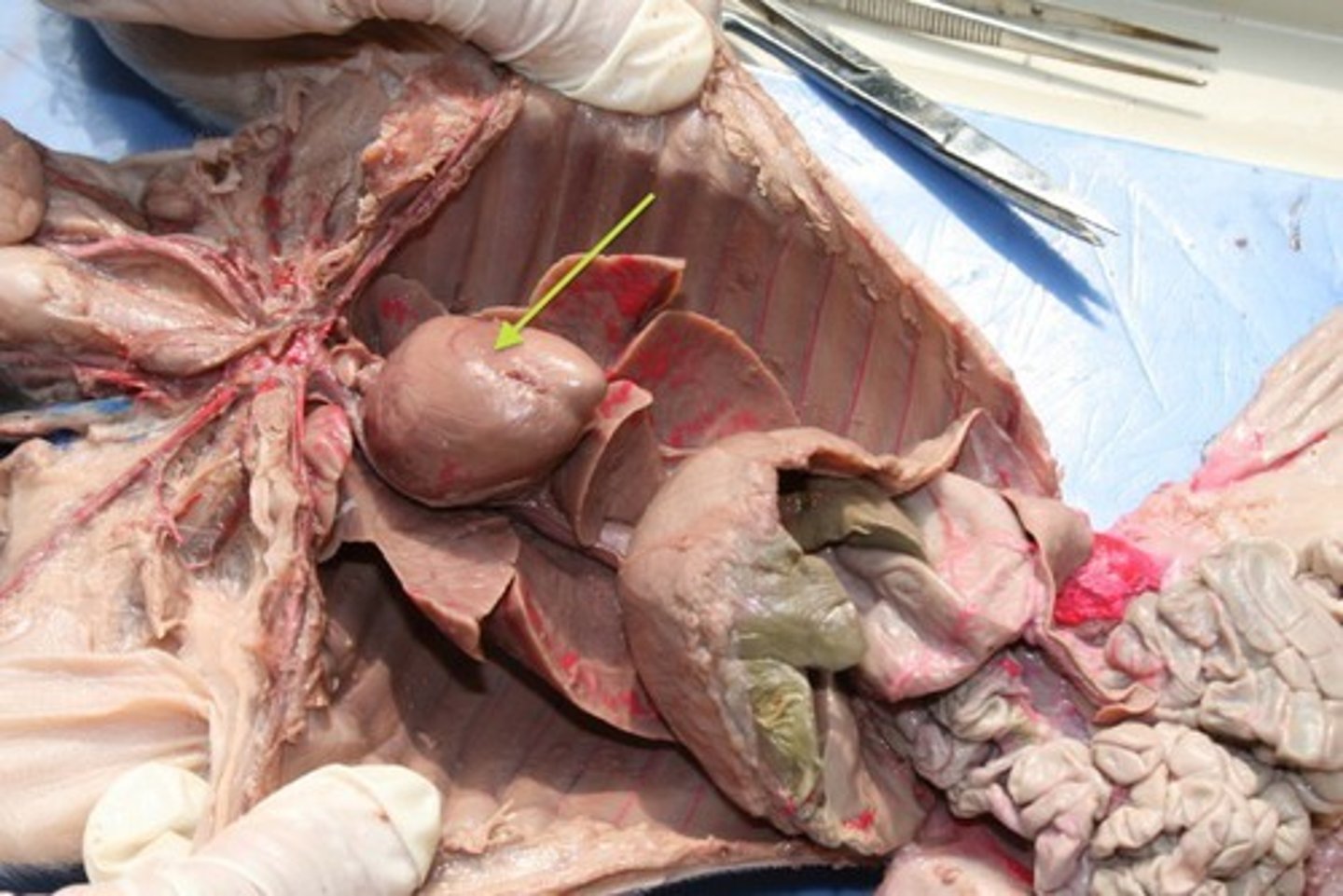
Spleen
organ near the stomach that produces, stores, and eliminates blood cells
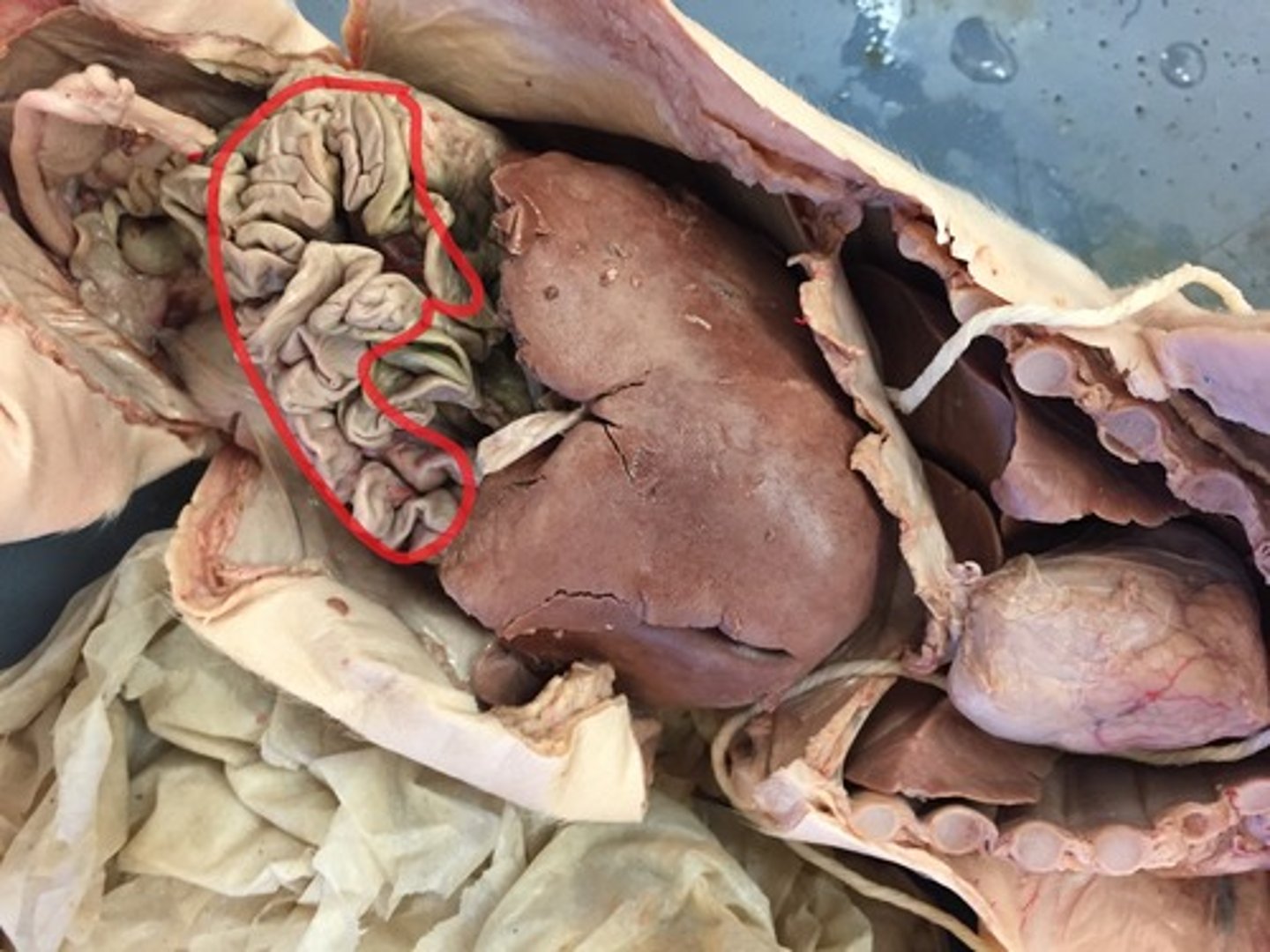
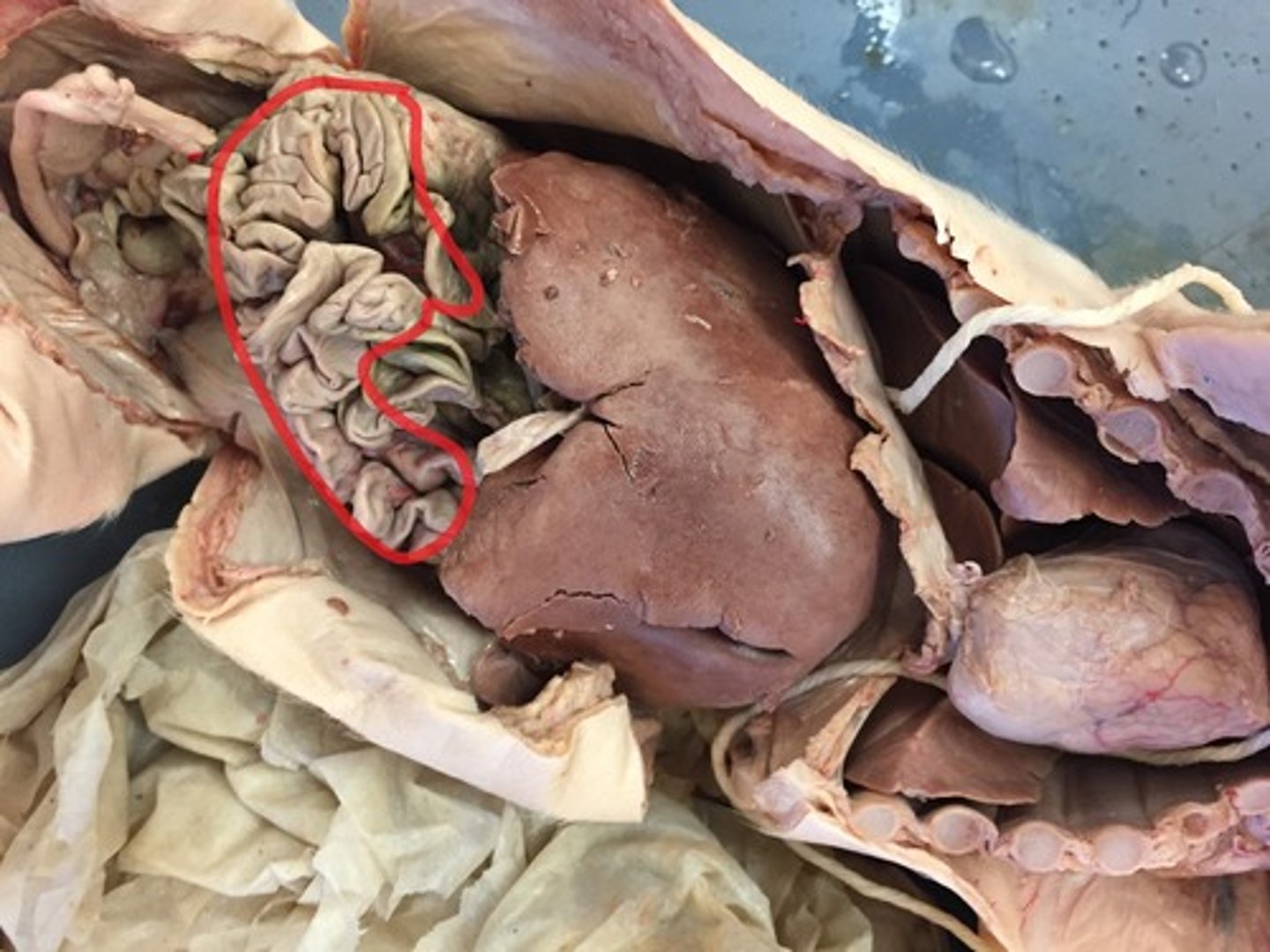
Large Intestine
last section of the digestive system, where water is absorbed from food and the remaining material is eliminated from the body
Small Intestine
Digestive organ where most chemical digestion and absorption of food takes place
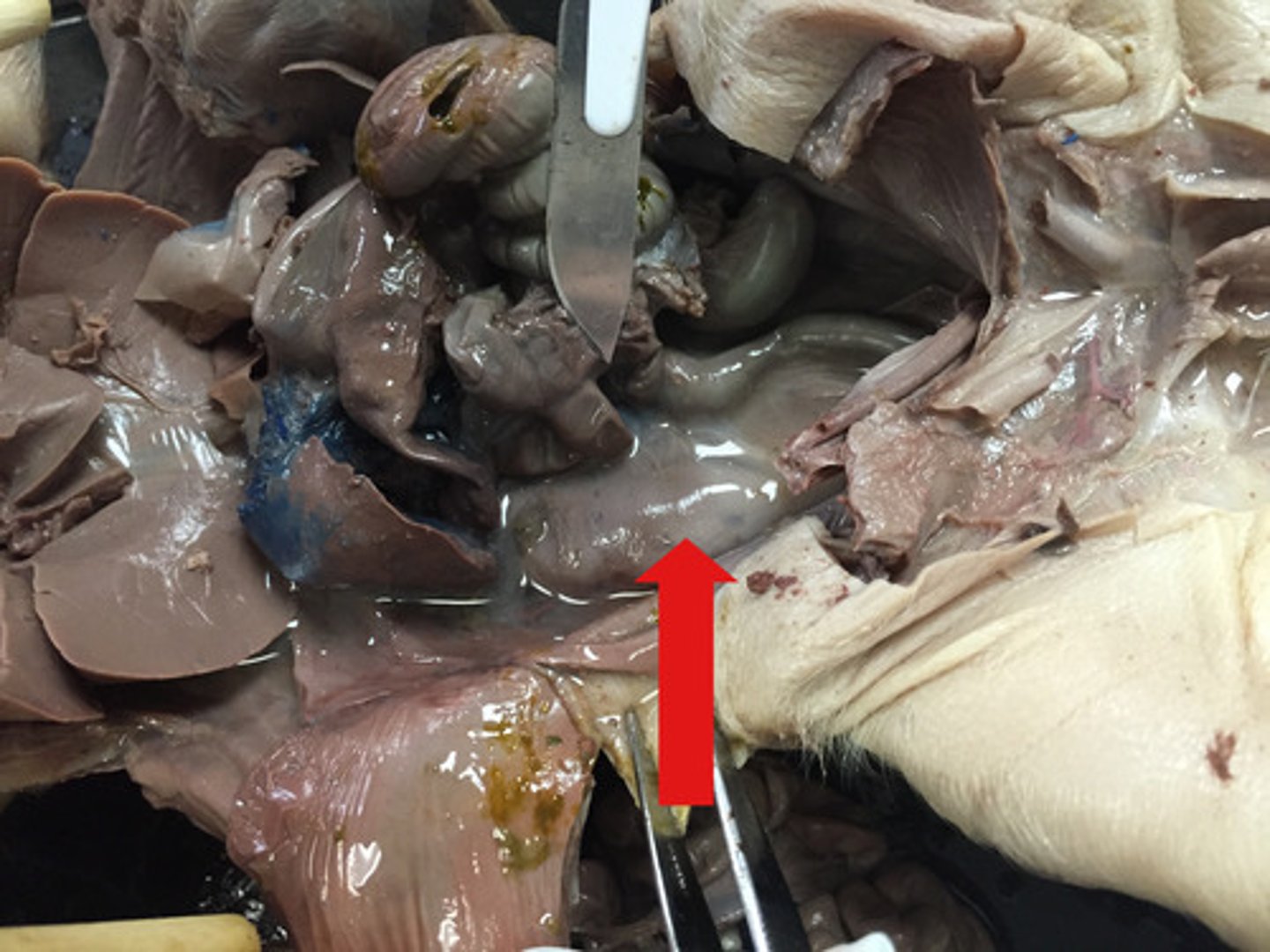
Stomach
large muscular sac that continues the mechanical and chemical digestion of food
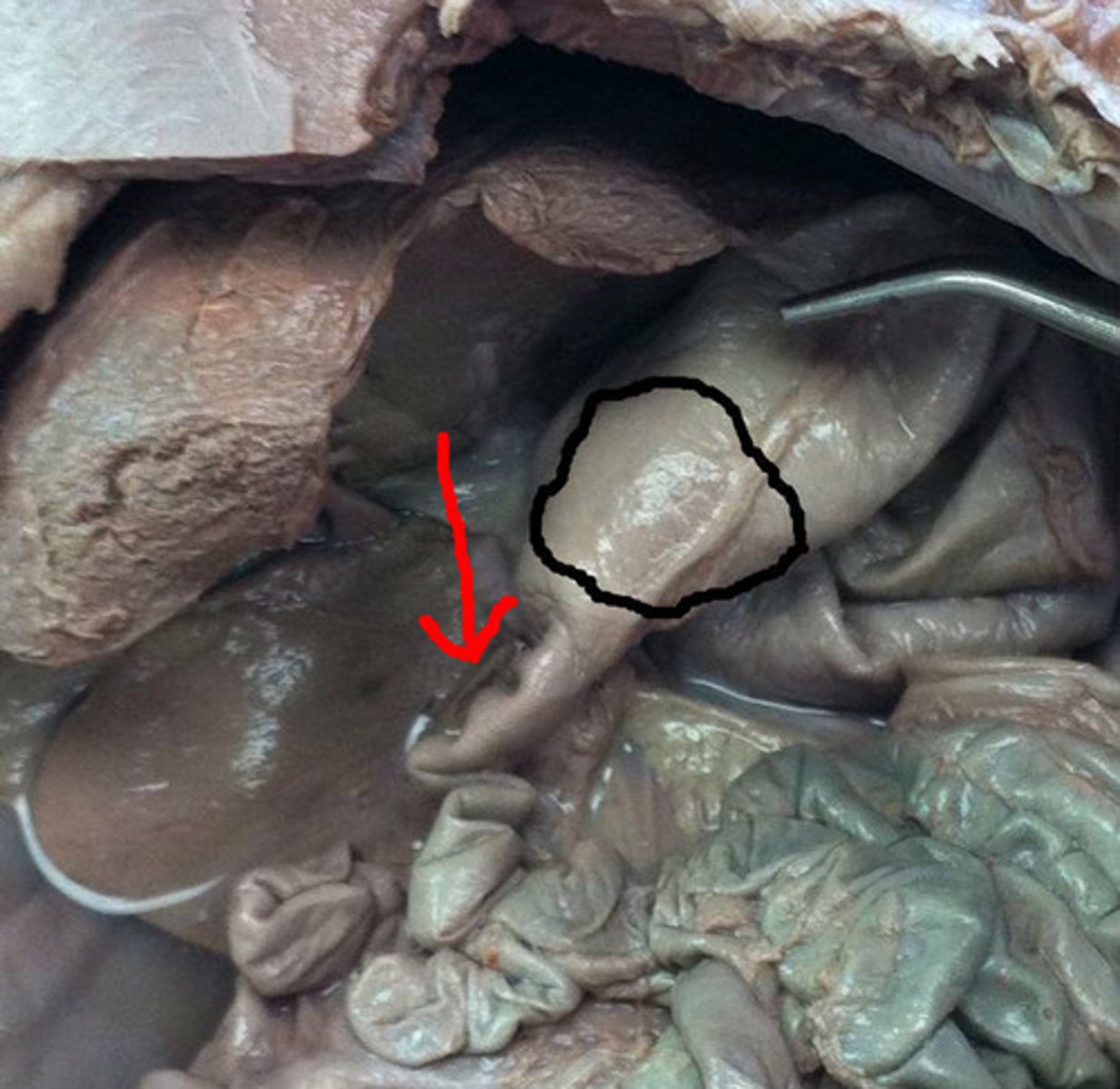
Kidney
filters waste from the blood like urea, water, salt and proteins.
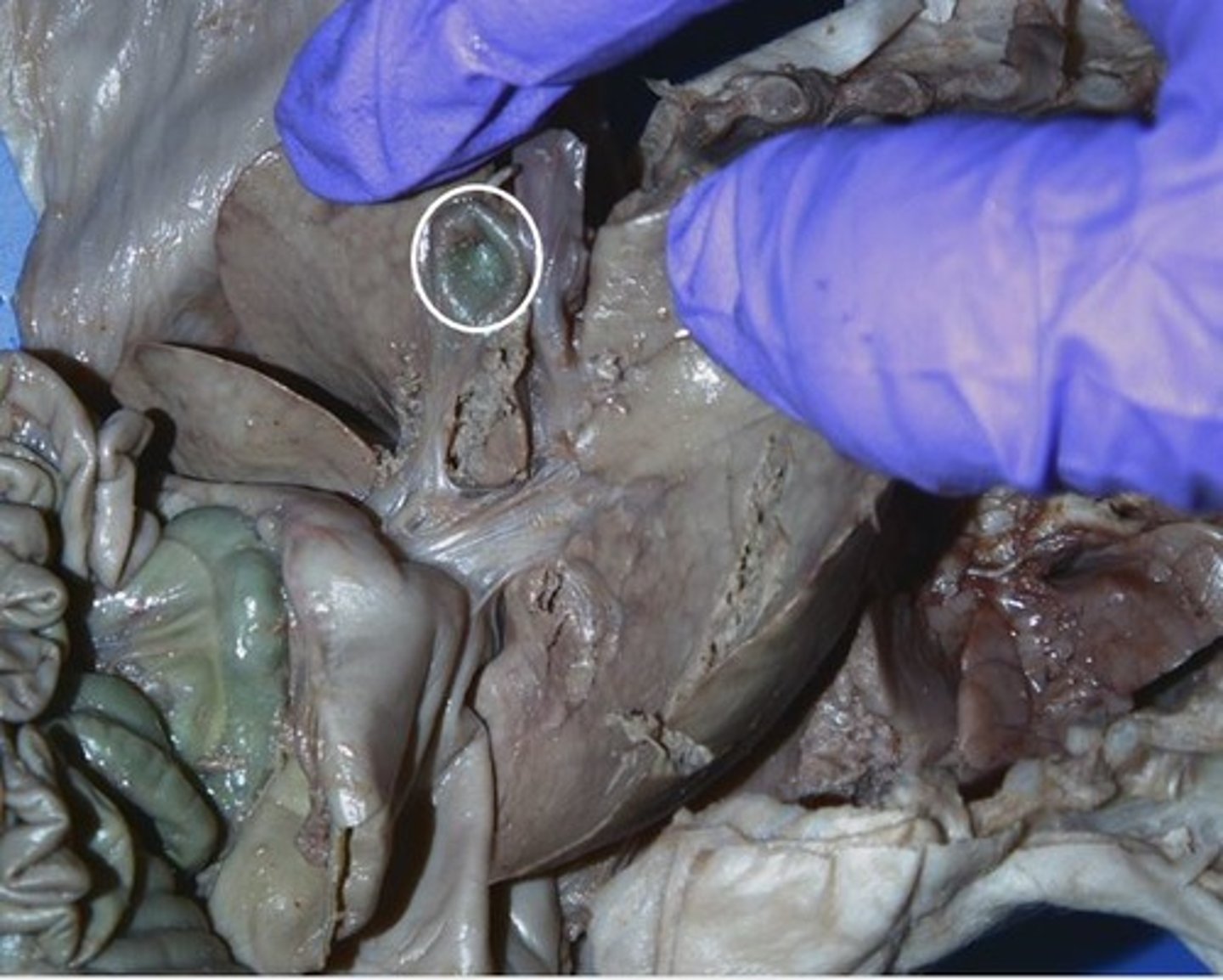
Gall Bladder
the organ that stores bile after it is produced by the liver
Pharynx
throat; passageway for food to the esophagus and air to the larynx
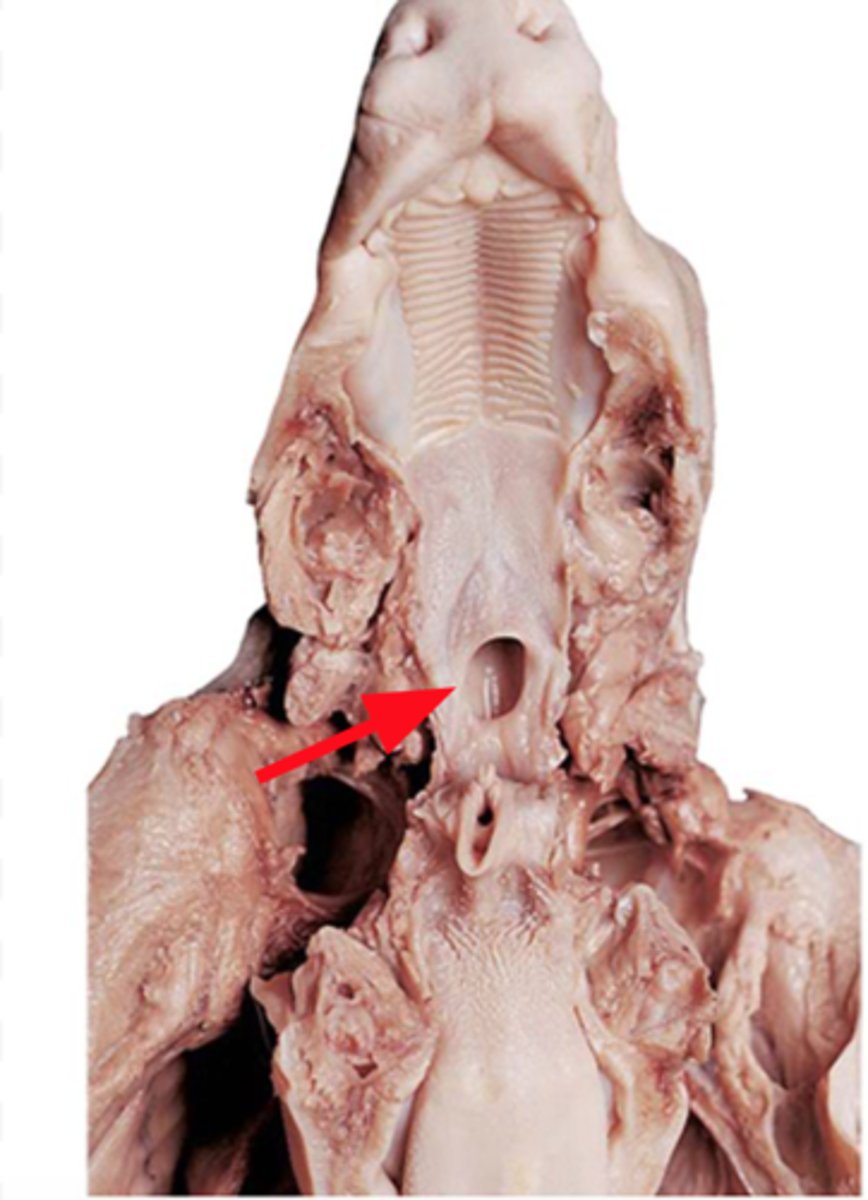
Mouth
where digestion begins

Esophagus
muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach.
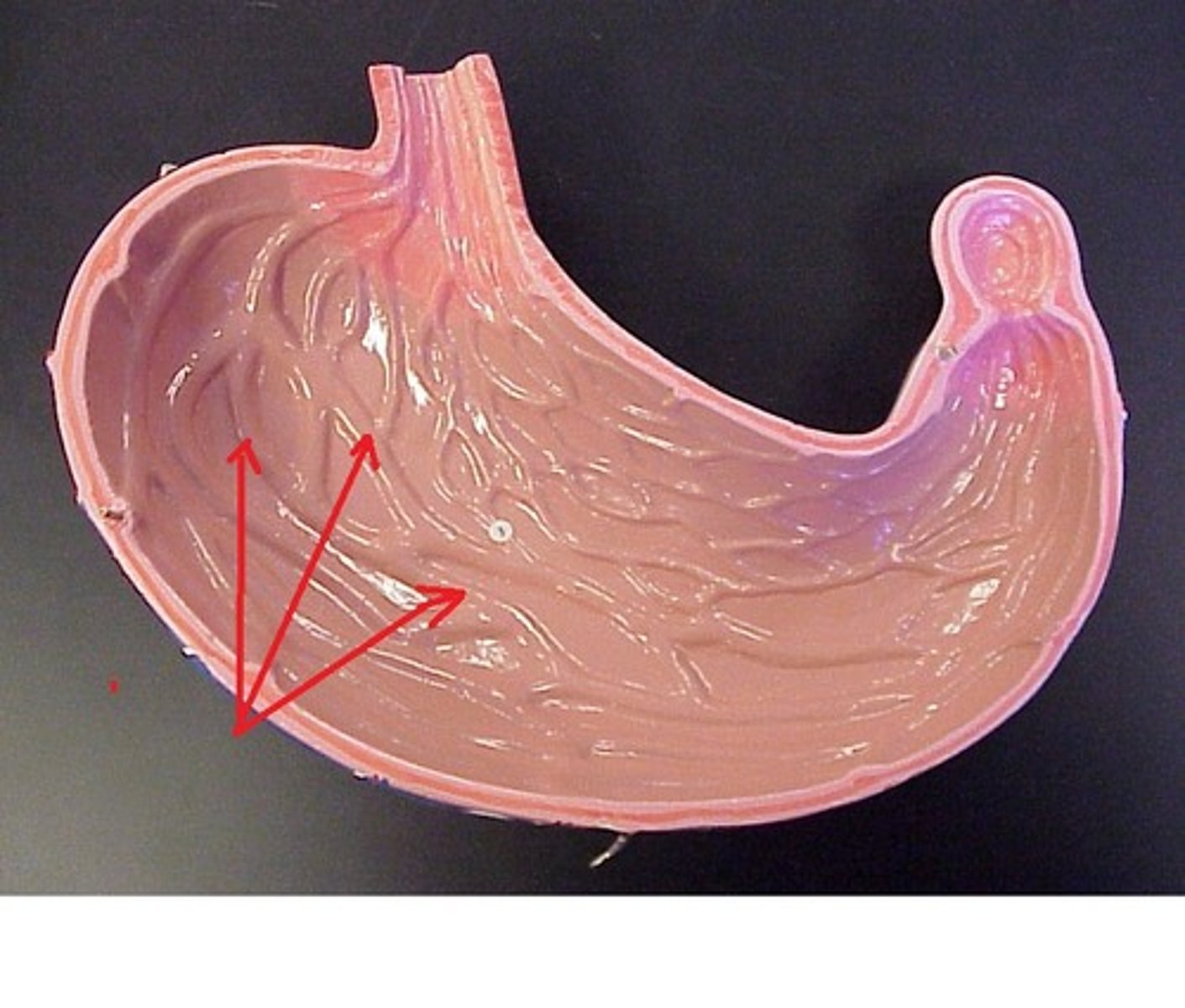
Gastric Rugae
visible folds on the inner stomach which allow the walls to stretch
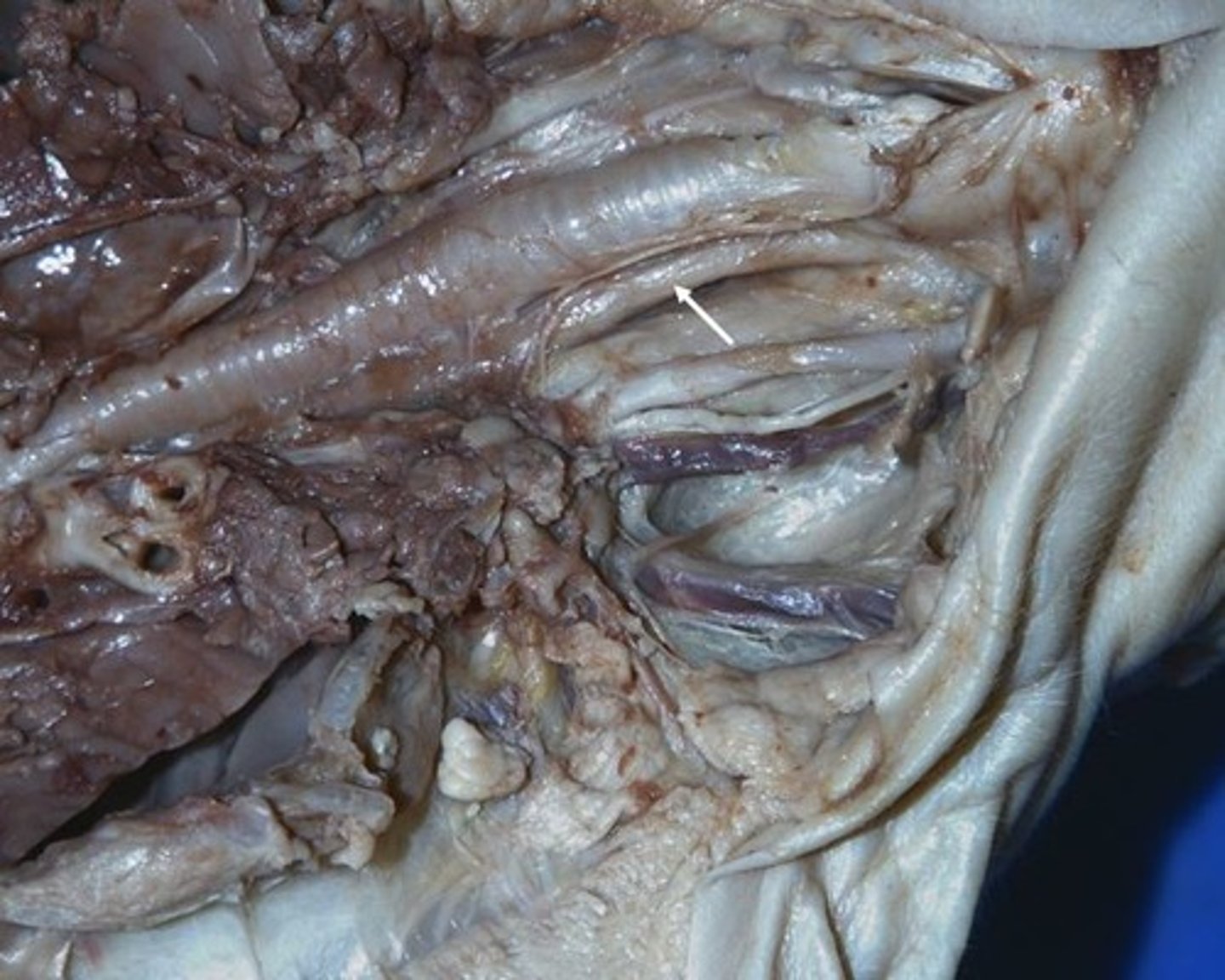
Cardiac Sphincter
opening from the esophagus to the stomach
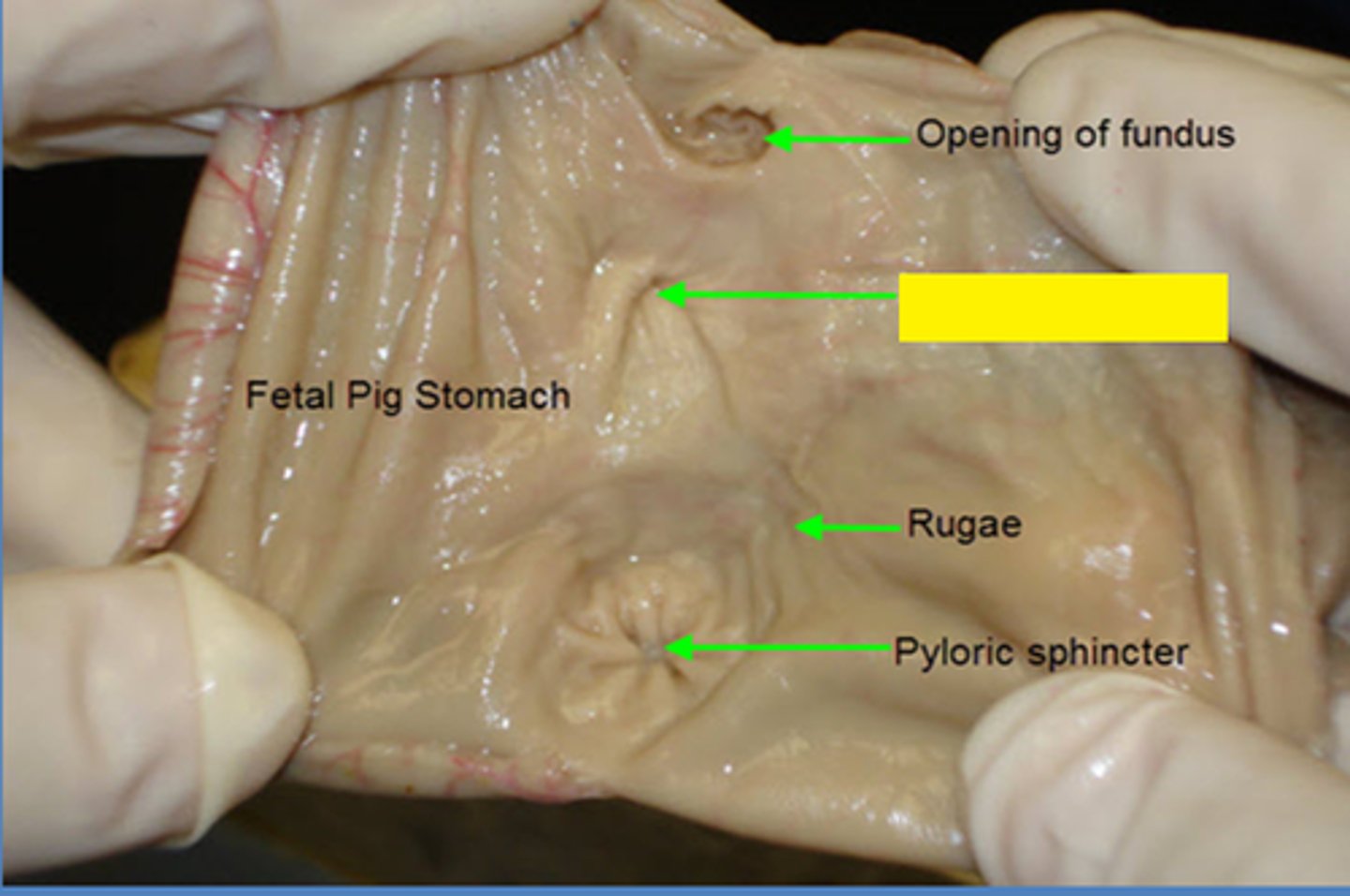
Pyloric Sphincter
ring of muscle that guards the opening between the stomach and the duodenum
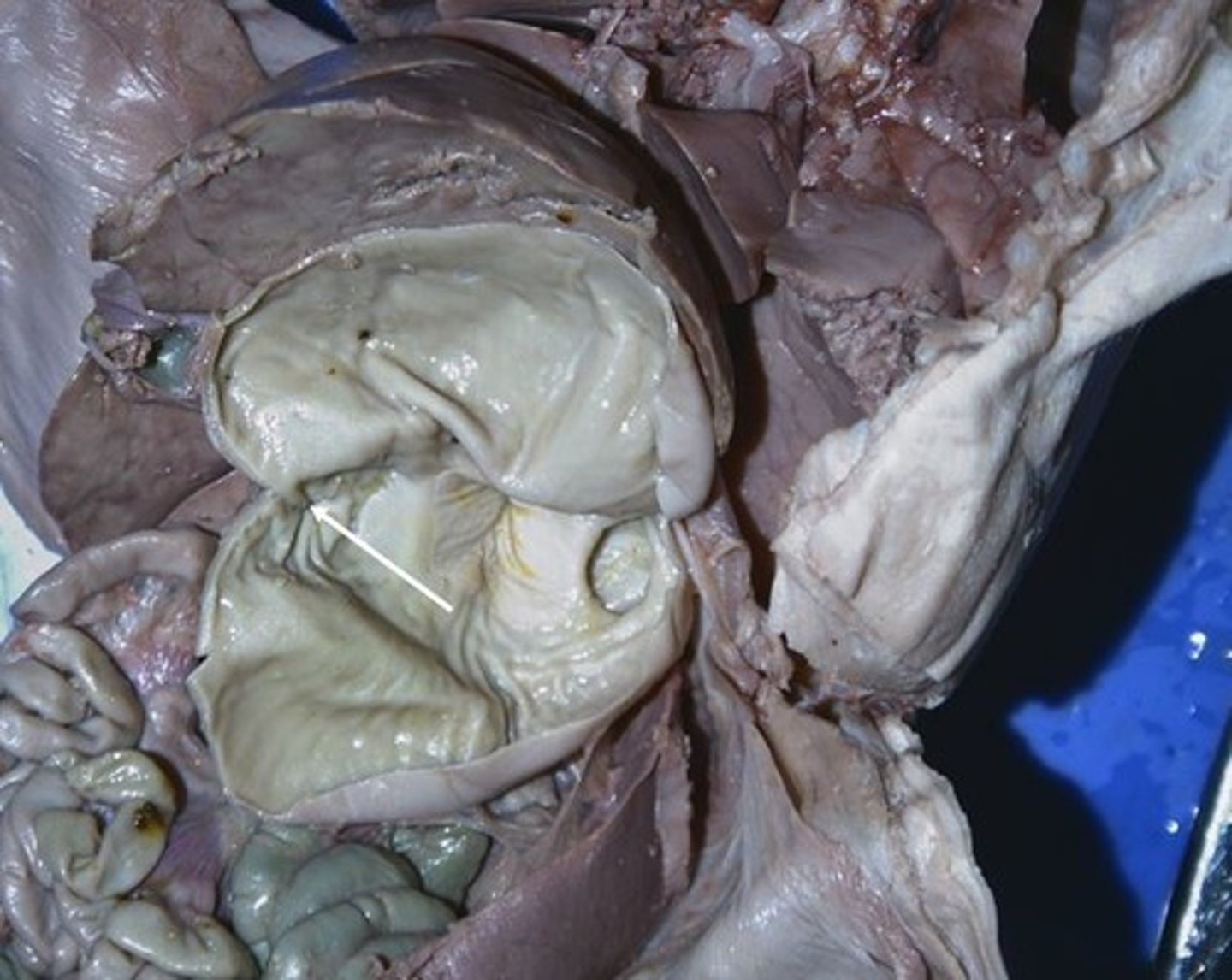
Pancreas
Regulates the level of sugar in the blood/insulin and glucagon
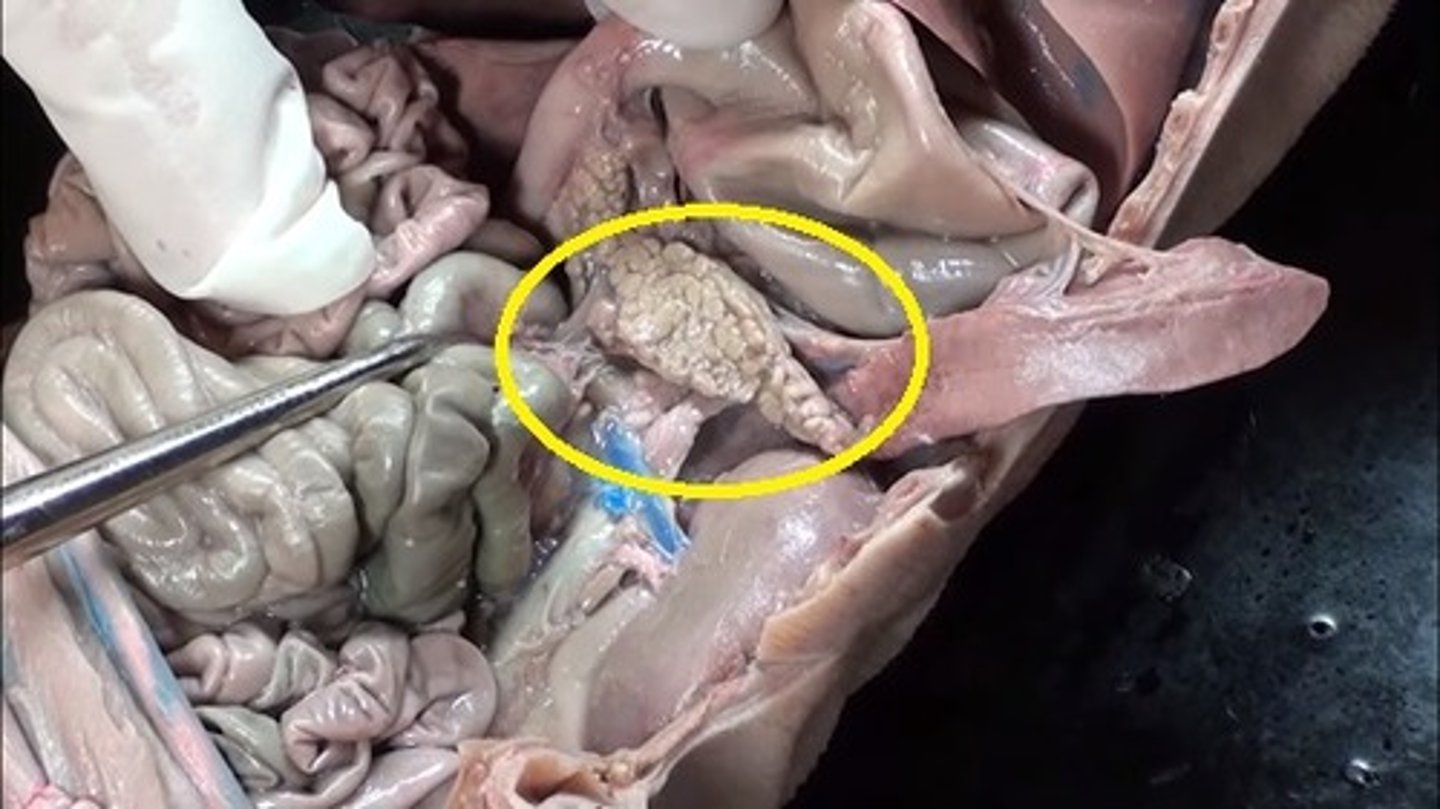
Cecum
the cavity in which the large intestine begins and into which the ileum opens
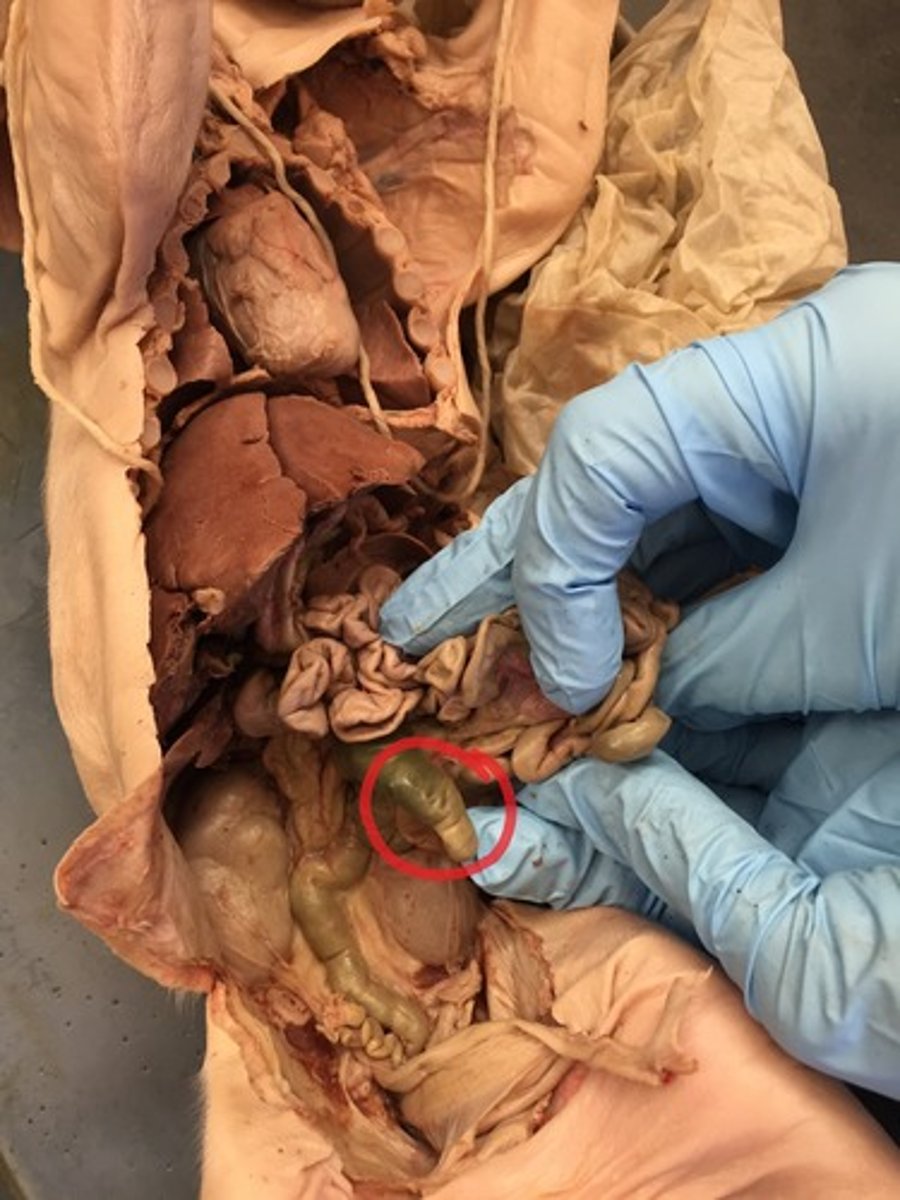
Rectum
short tube at the end of the large intestine where waste material is compressed into a solid form before being eliminated
Anus
muscular opening at the end of the rectum through which waste material is eliminated from the body
Duodenum
first portion of the small intestine which receives secretions from the gallbladder and pancreas
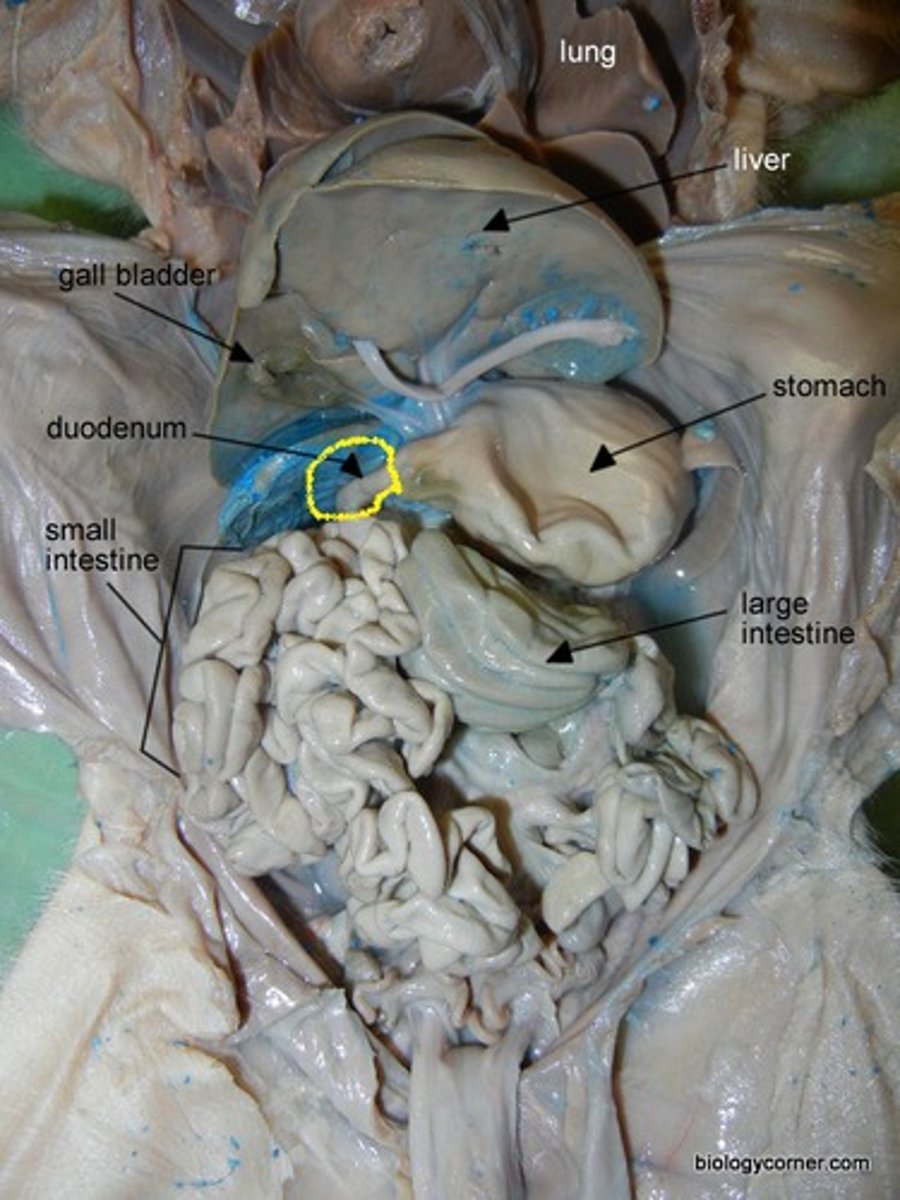
Jejuno-ileum
All of the small intestine except the duodenum
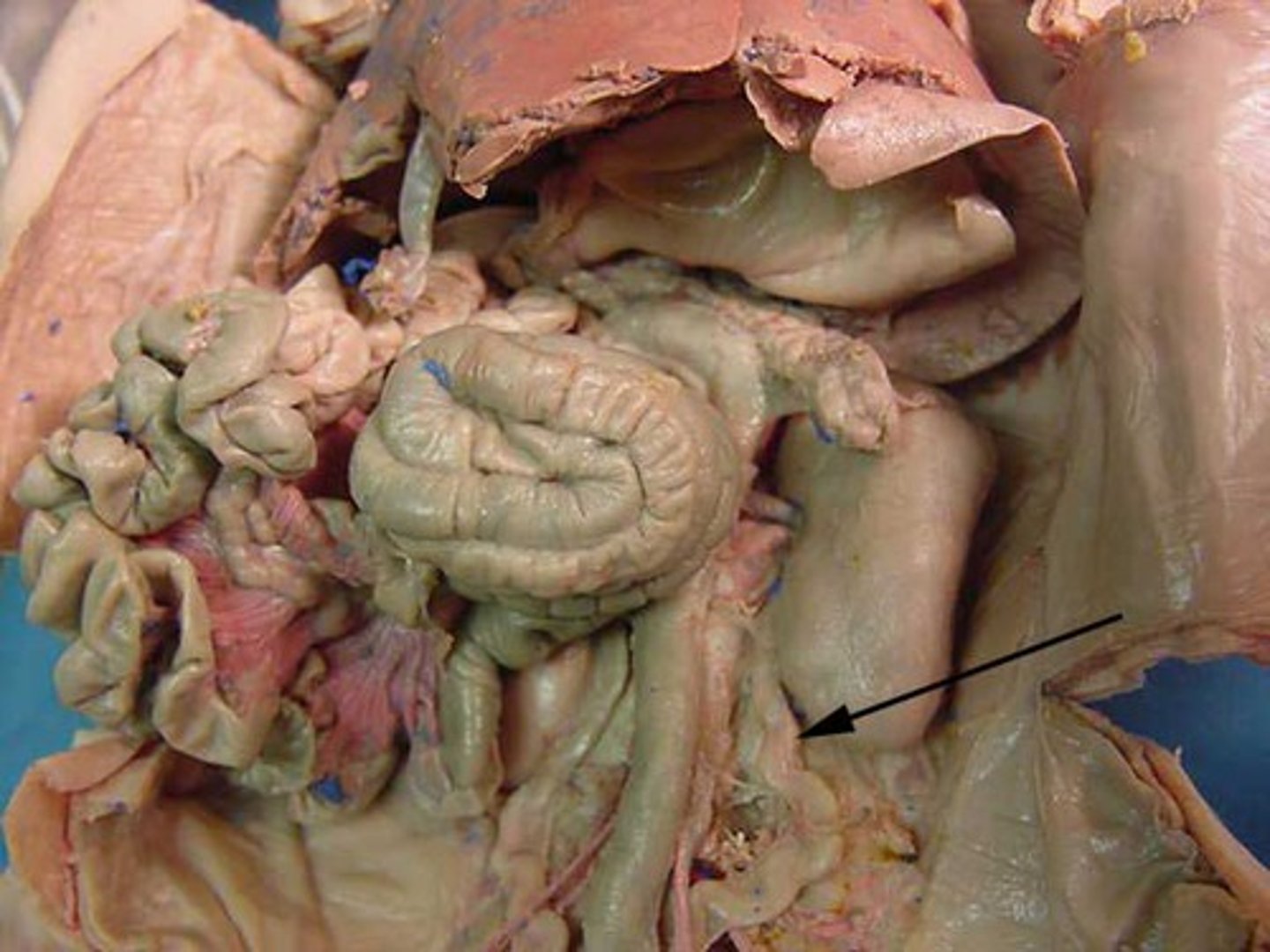
Ureter
duct leading from the kidney to the urinary bladder
Bladder
elastic, hollow, muscular organ that provides temporary storage for urine.
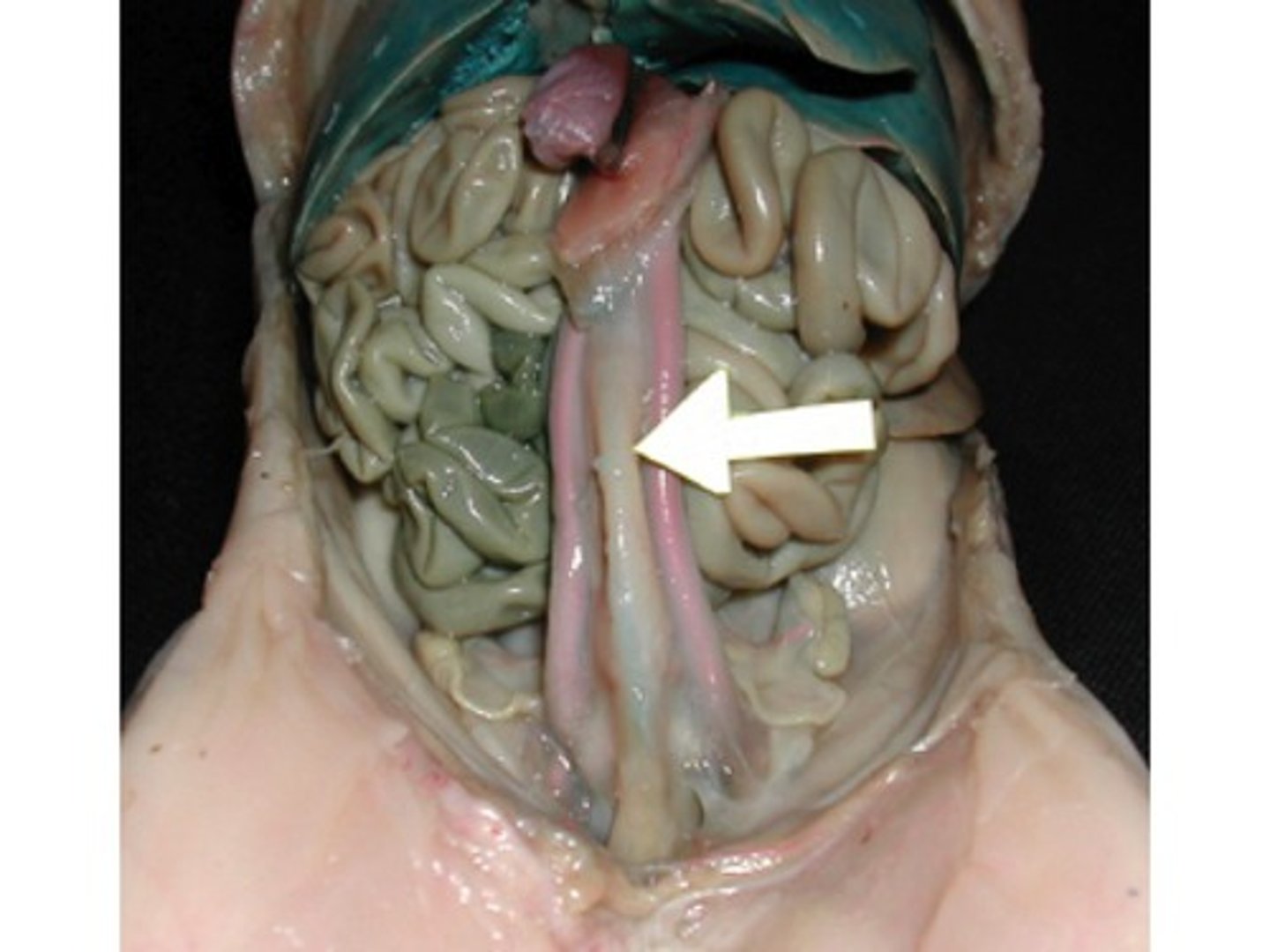
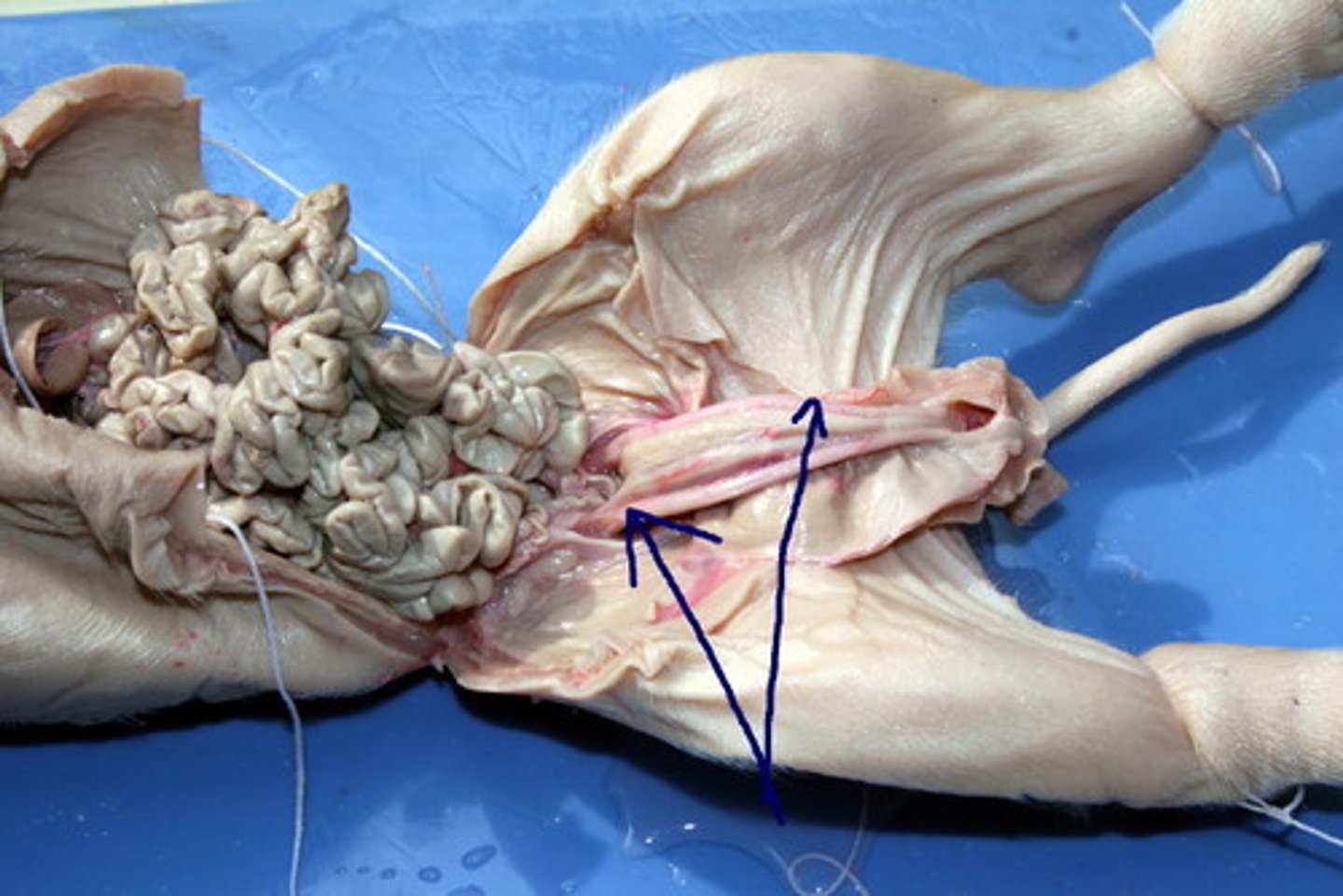
Umbilical vein
carry oxygenated blood from placenta to fetus
Umbilical arteries
carry deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta
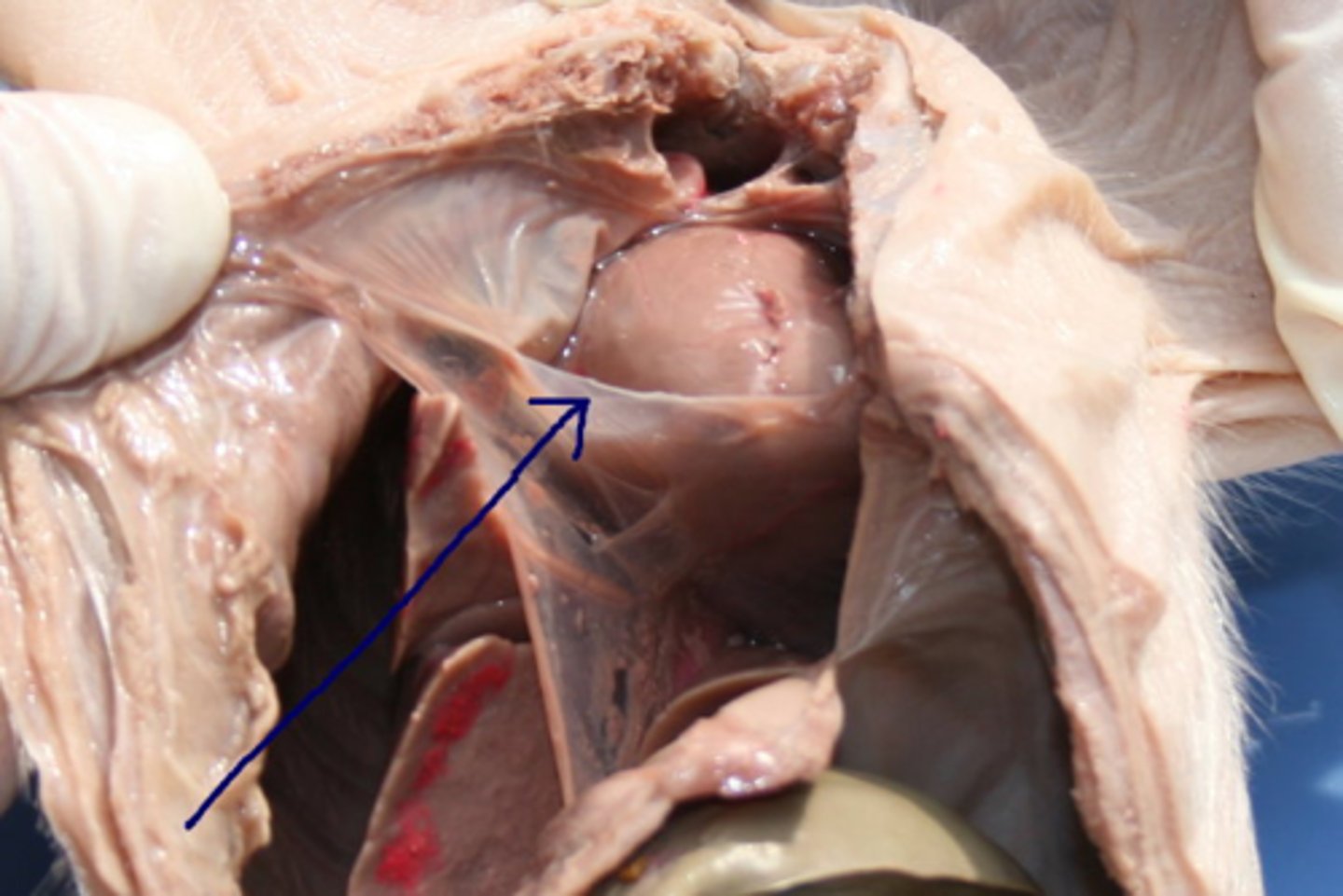
Pericardial sac
surrounds the heart and helps prevent overfilling
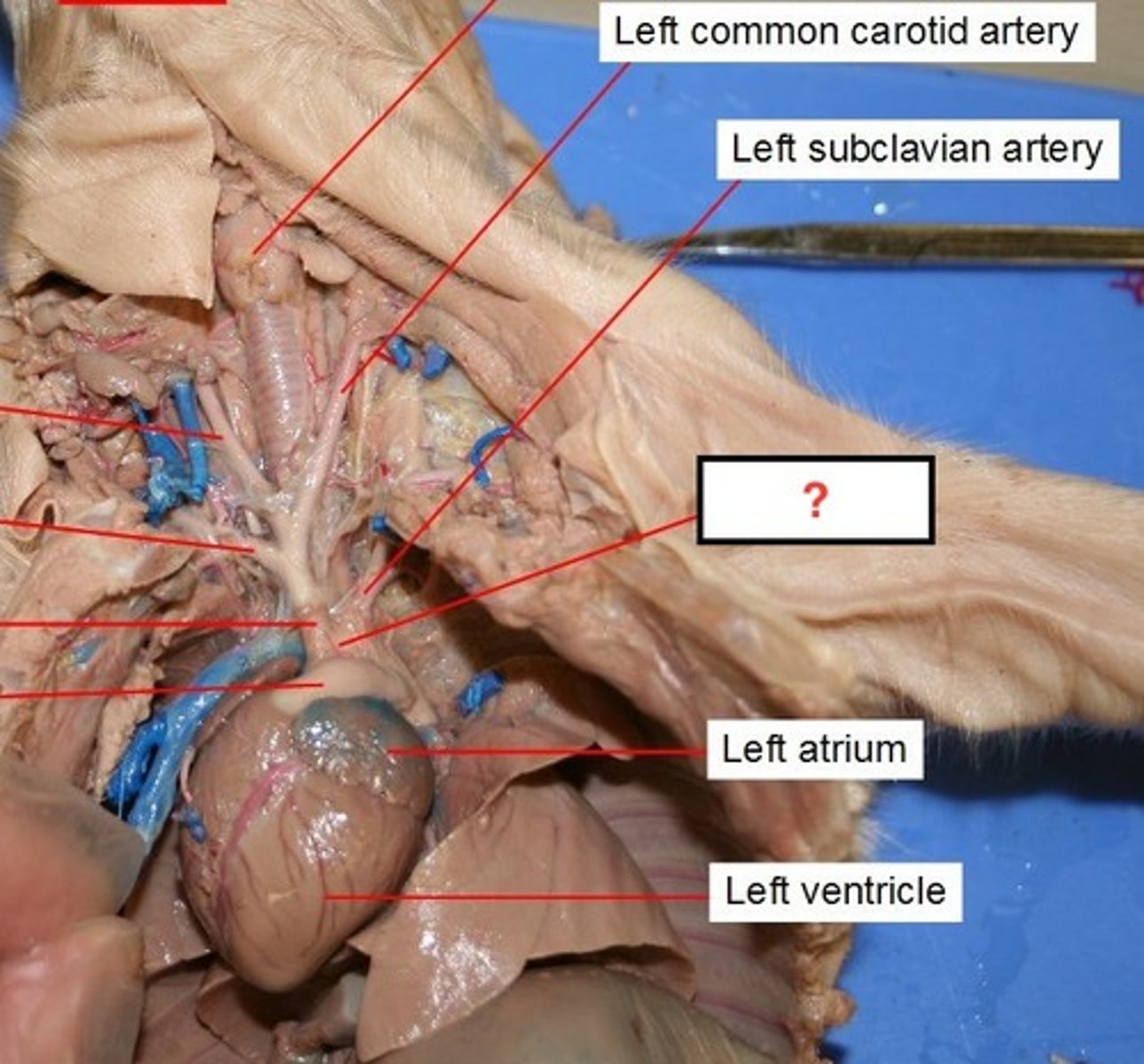
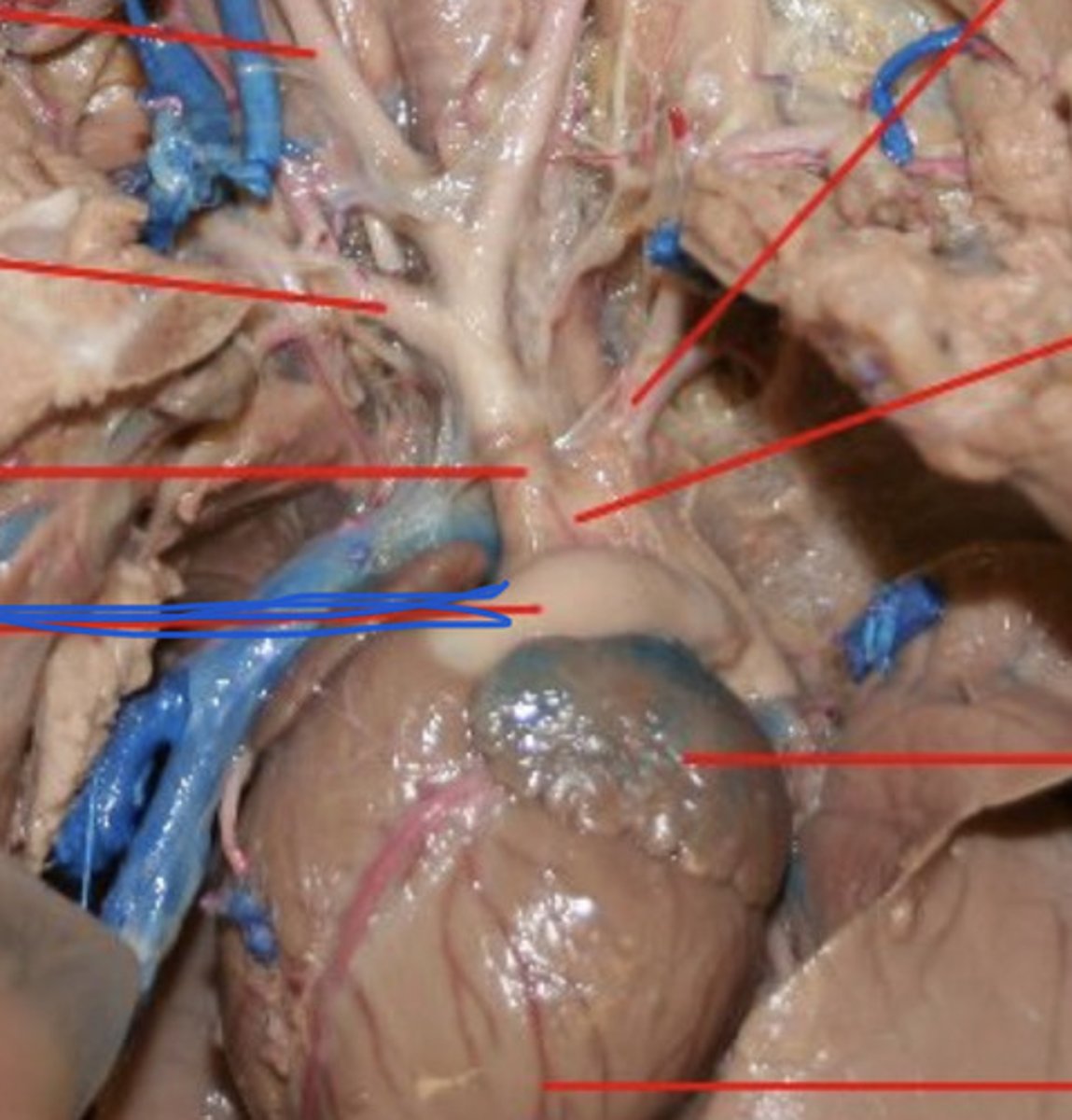
Atrium
two upper chambers of the heart that receives blood that comes into the heart
Ventricles
two lower chambers of the heart, and they pump blood out to the lungs and body
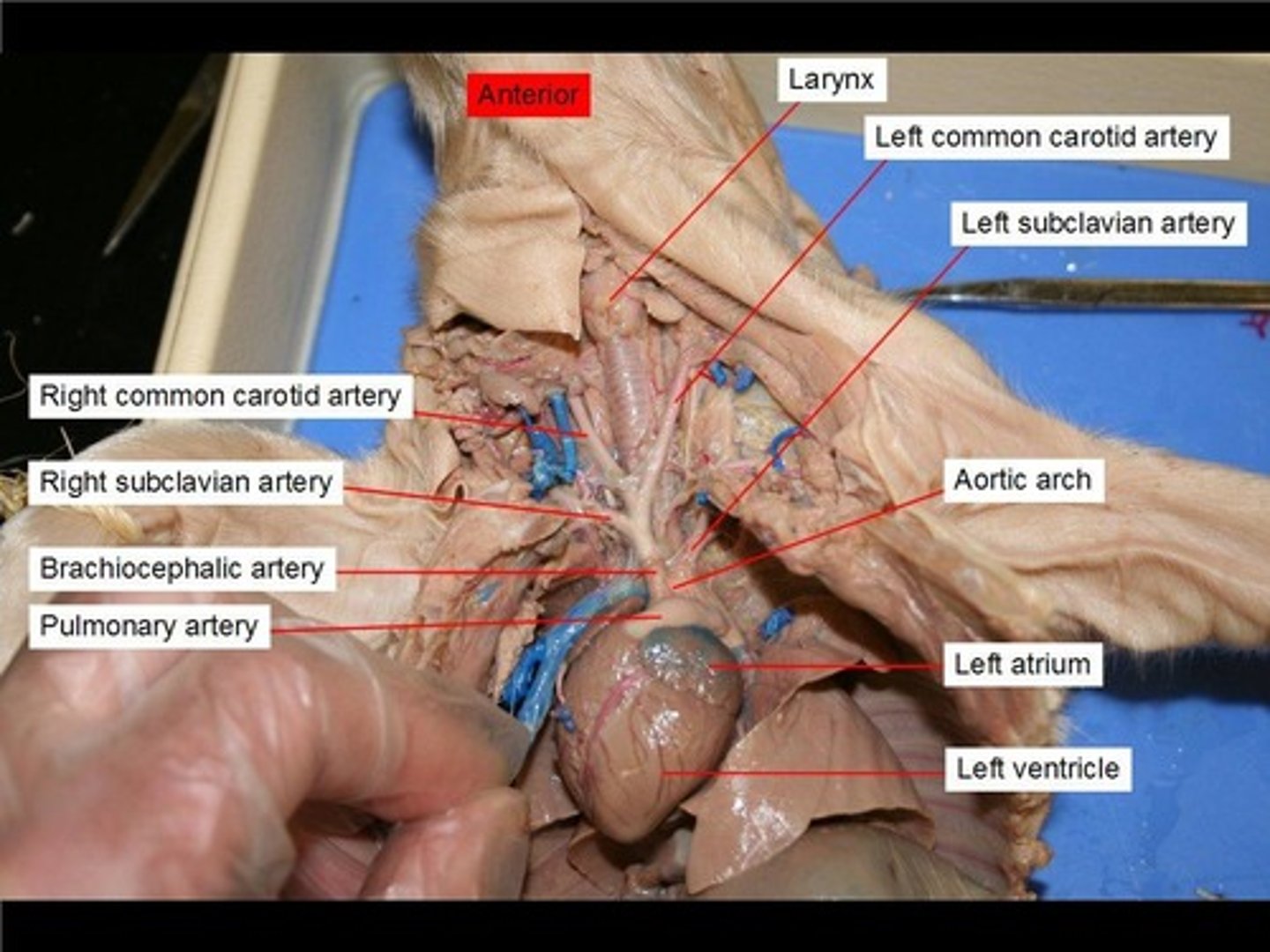
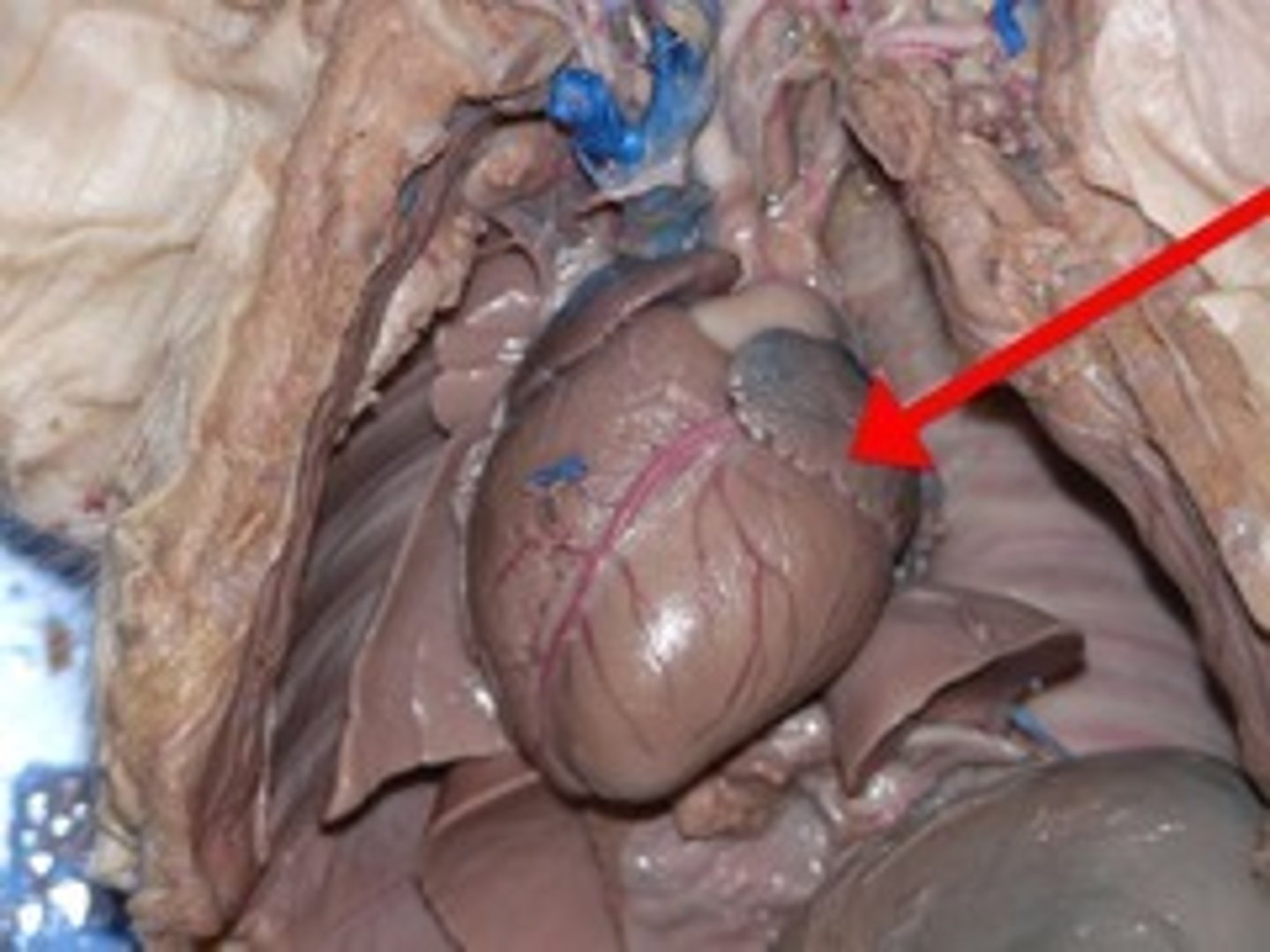
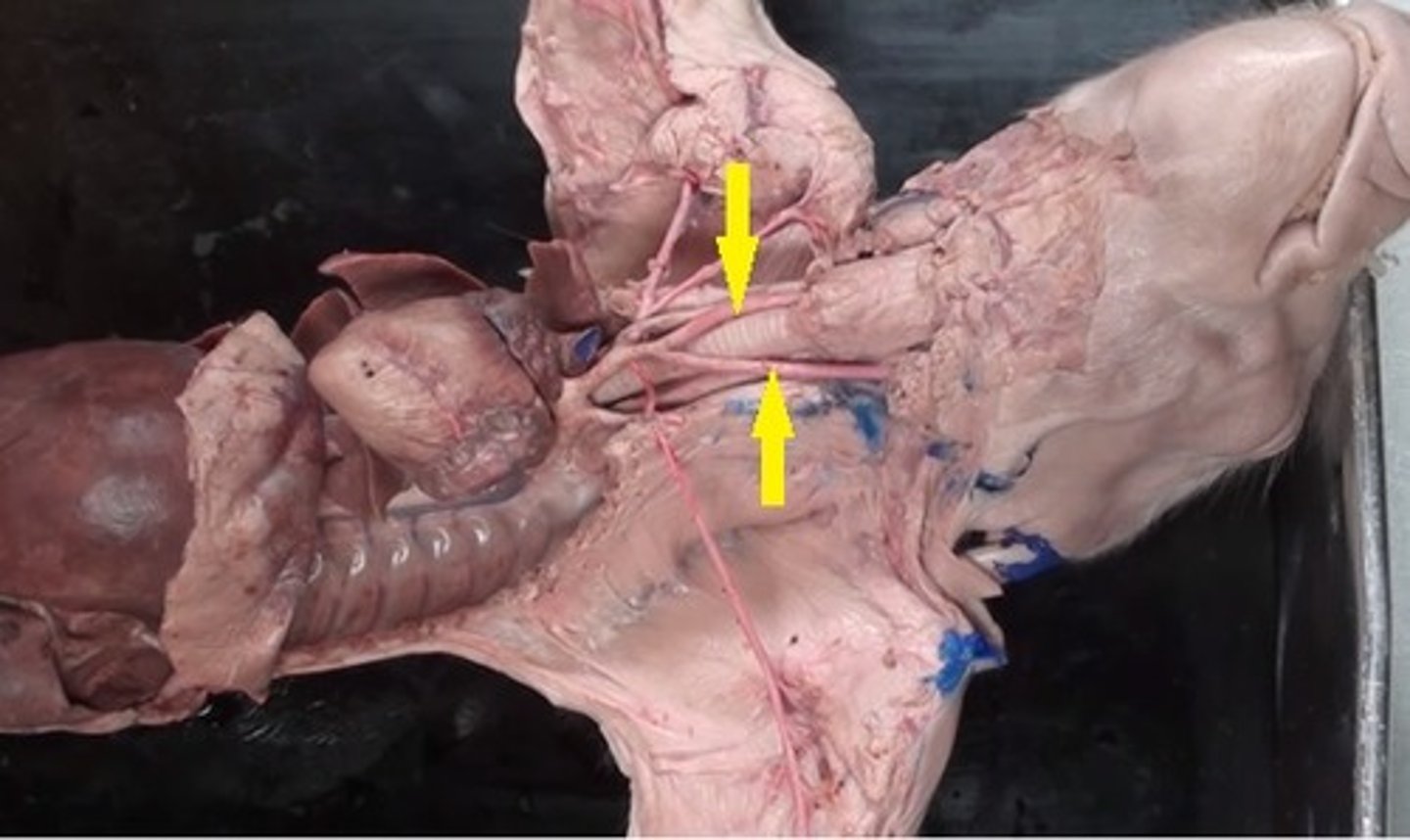
Carotid arteries
the major arteries that carry blood upward to the head
Aorta
large arterial trunk that carries blood from the heart to be distributed by branch arteries through the body.
Pulmonary Trunk
carries blood from right ventricle to pulmonary arteries
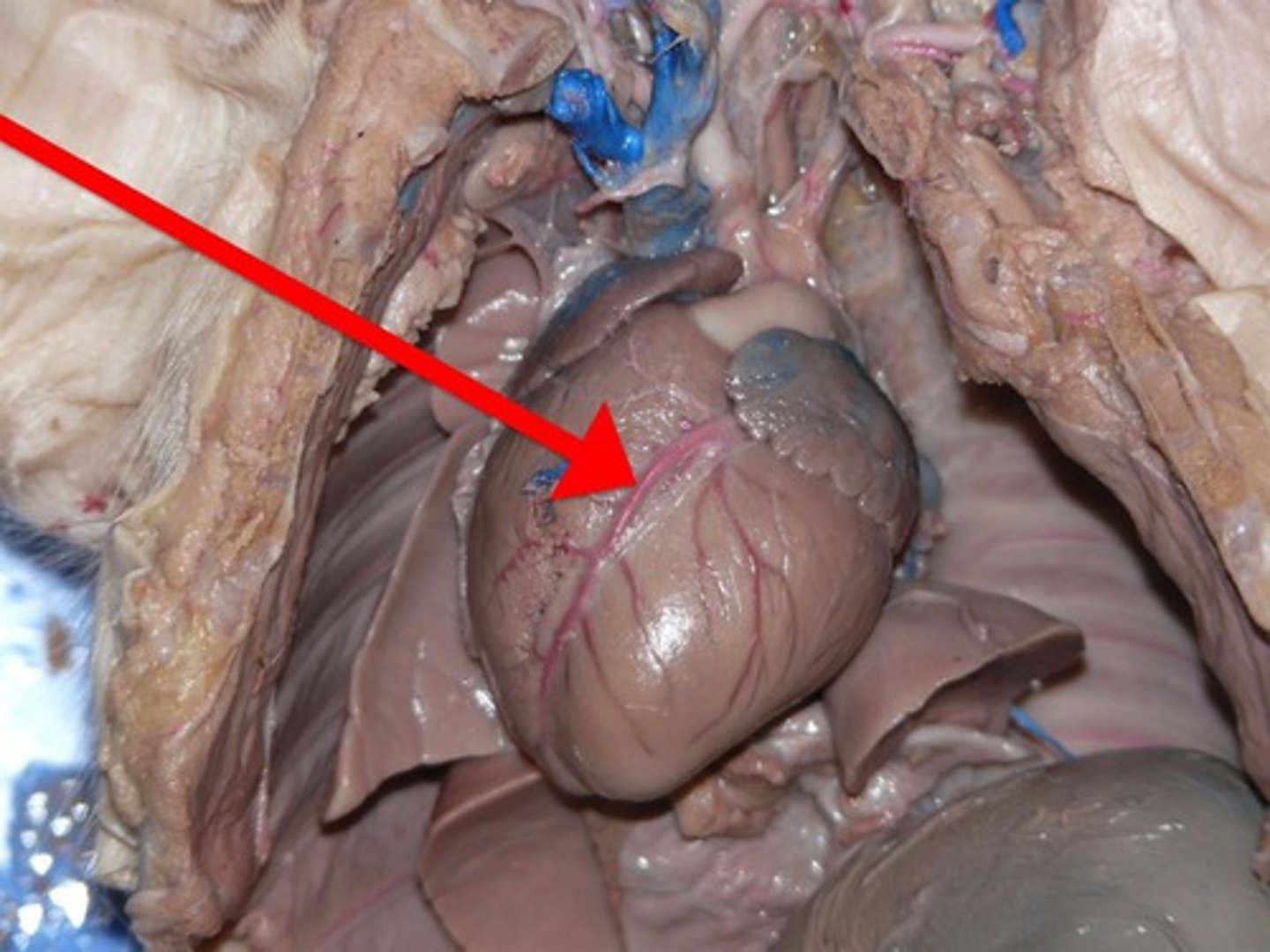
Coronary artery
The artery that supplies heart tissue with blood
Pulmonary artery
artery carrying oxygen-poor blood from the heart to the lungs (#22)
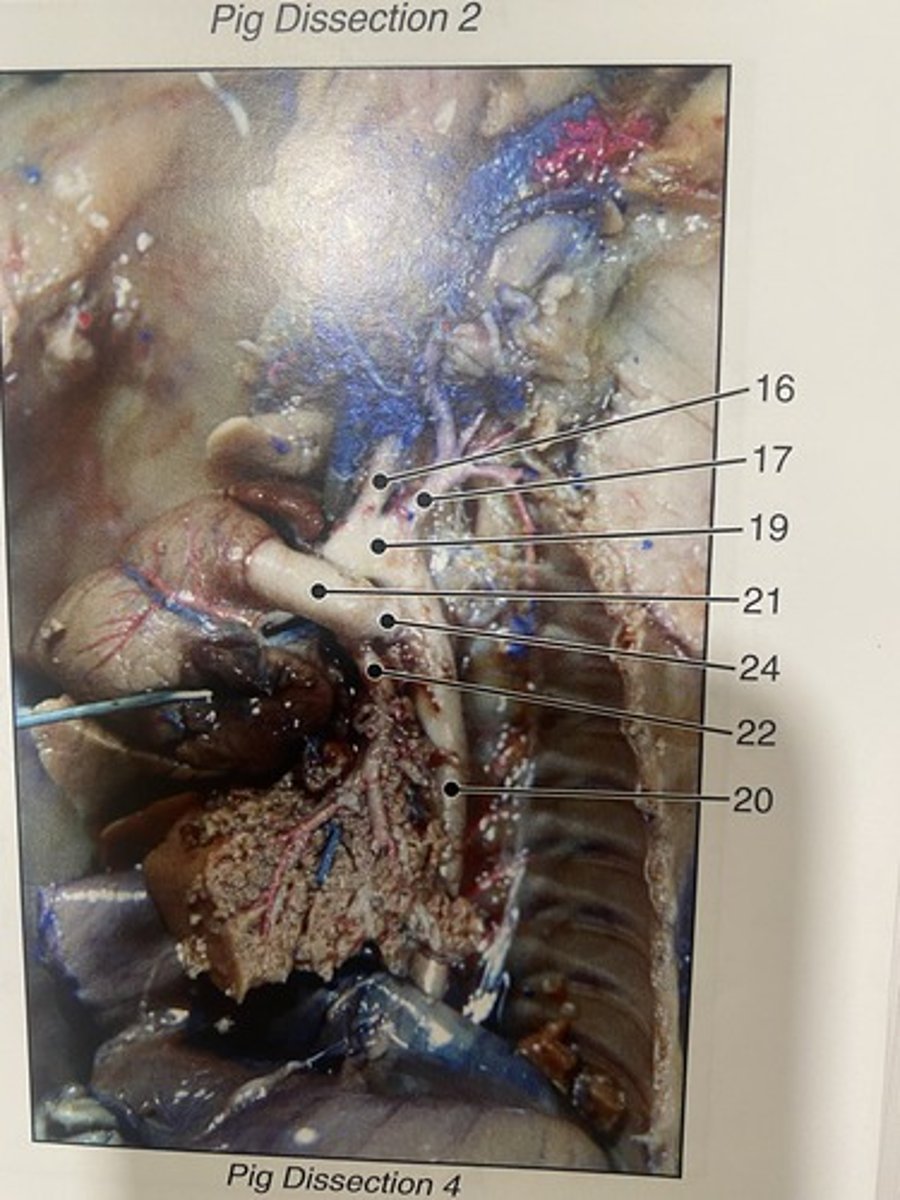
venae cavae (vena cava)
two large blood vessels that drain oxygen-poor blood from the veins into the right side of the heart
Ductus arteriosus
a blood vessel in a fetus that bypasses pulmonary circulation by connecting the pulmonary artery directly to the ascending aorta (#24)
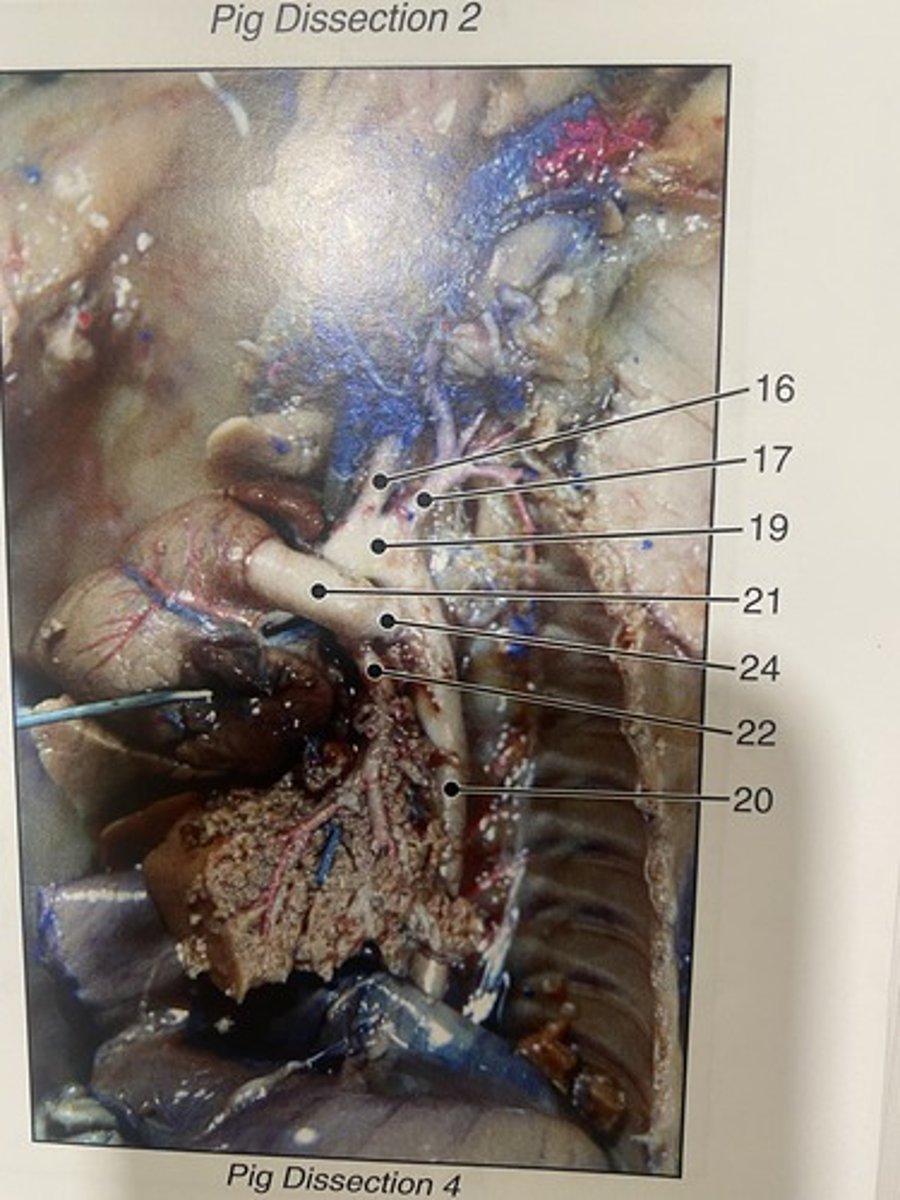
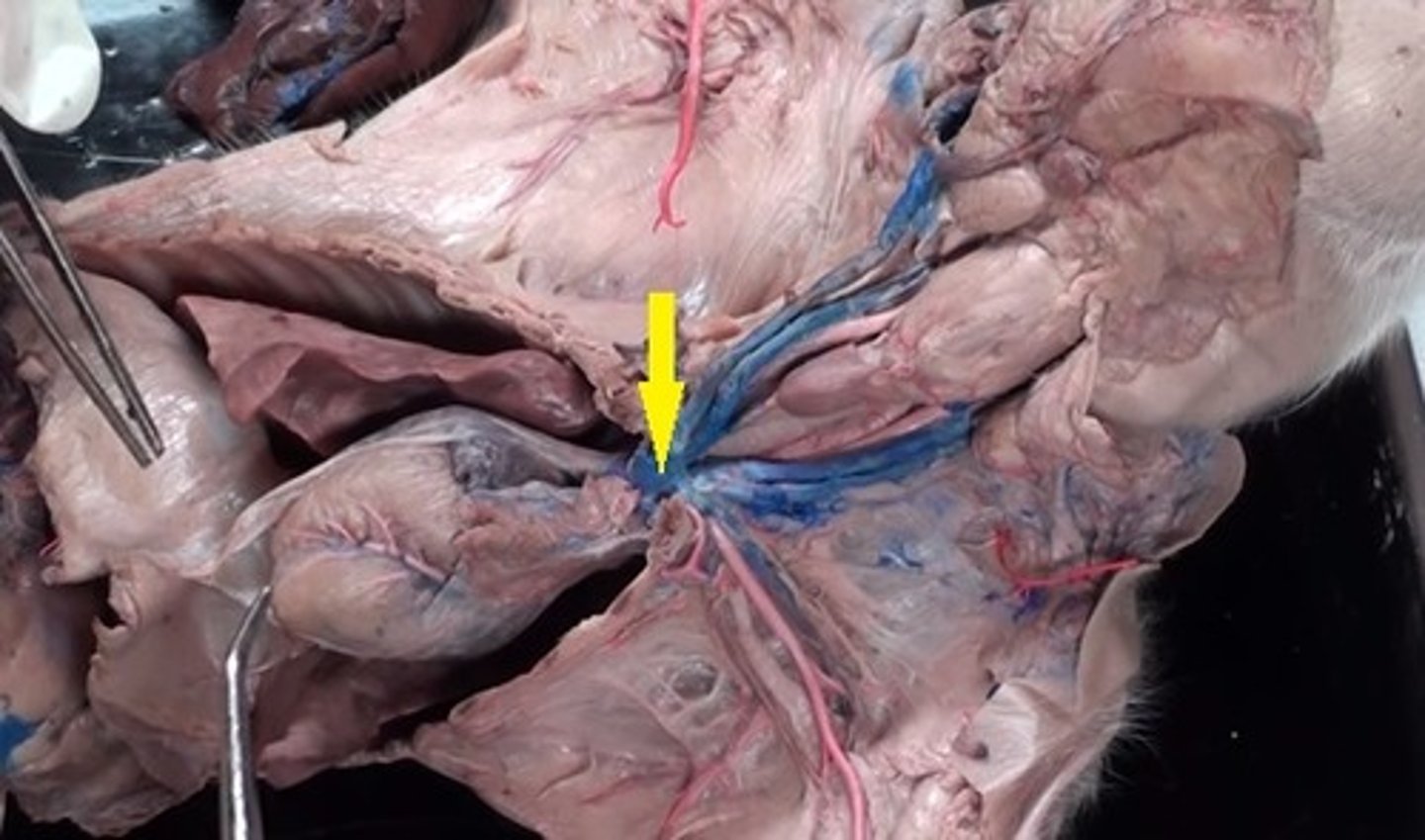
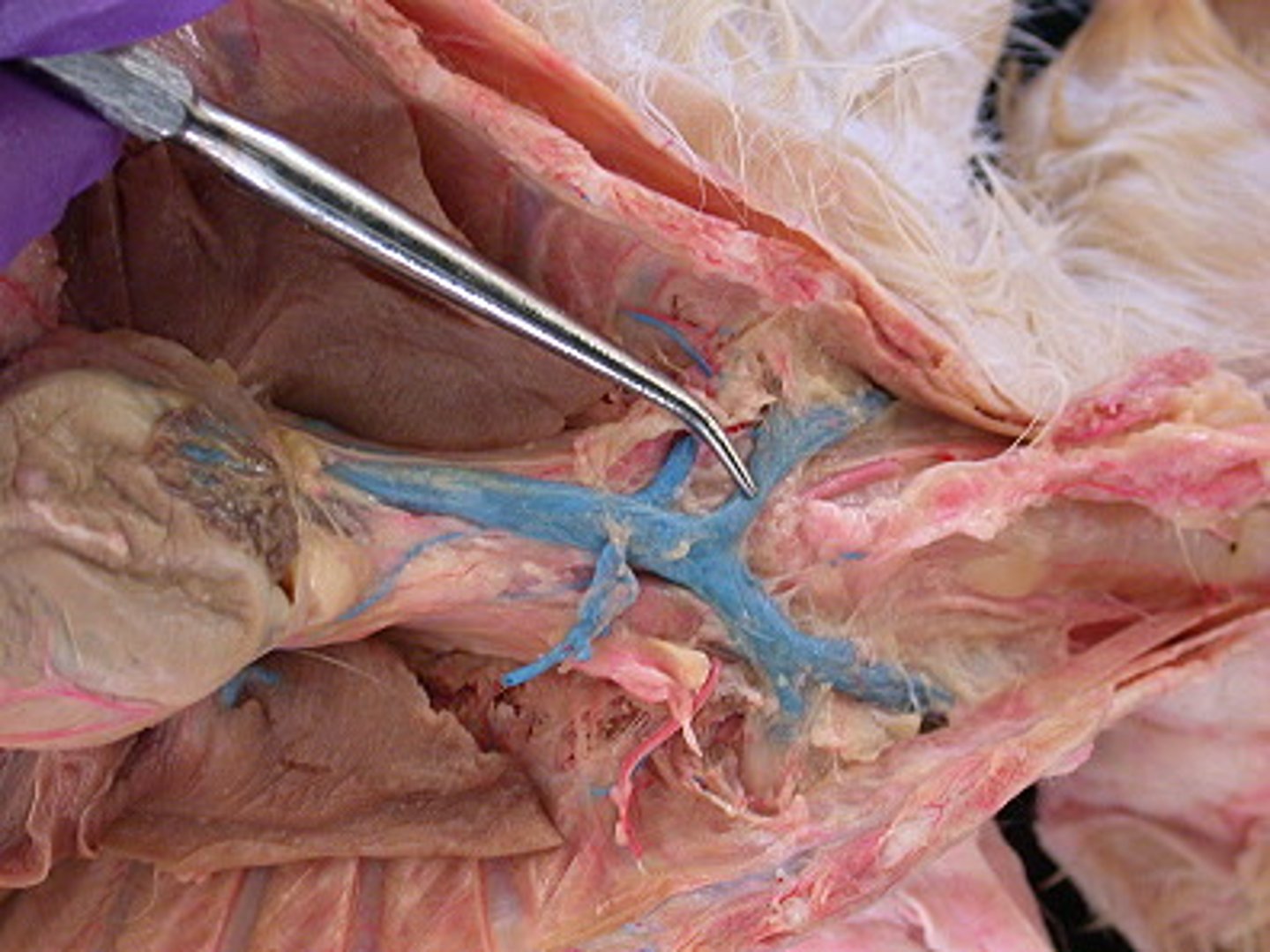
Brachiocephalic veins
carry blood from the cephalic, subclavian, and jugular veins to the cranial vena cava
Brachiocephalic artery
first major branch off of the aorta and the major artery to the forelimbs and head (#16)
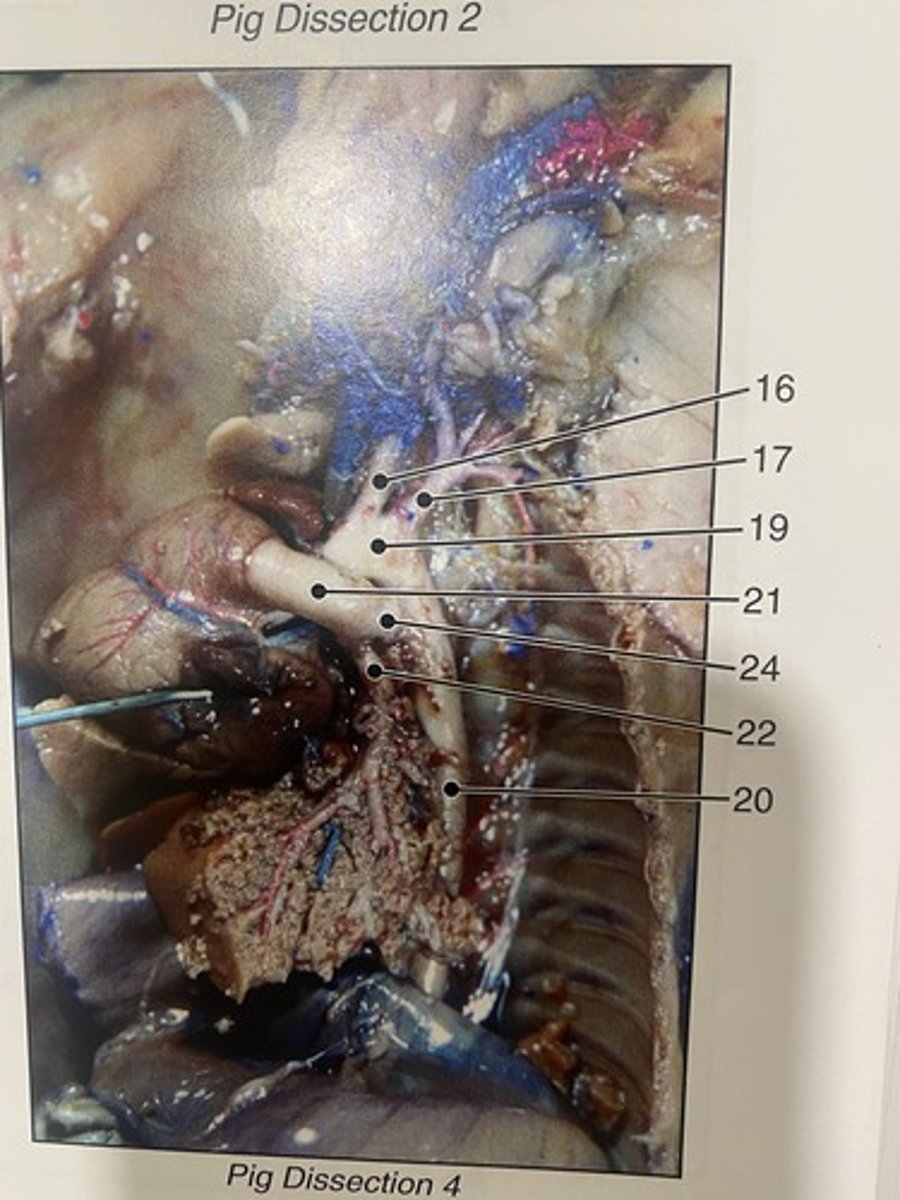
External and internal jugular veins
drain the head and neck into the superior vena cava
Subclavian arteries
carry oxygenated blood from the aorta to the arms (#17)
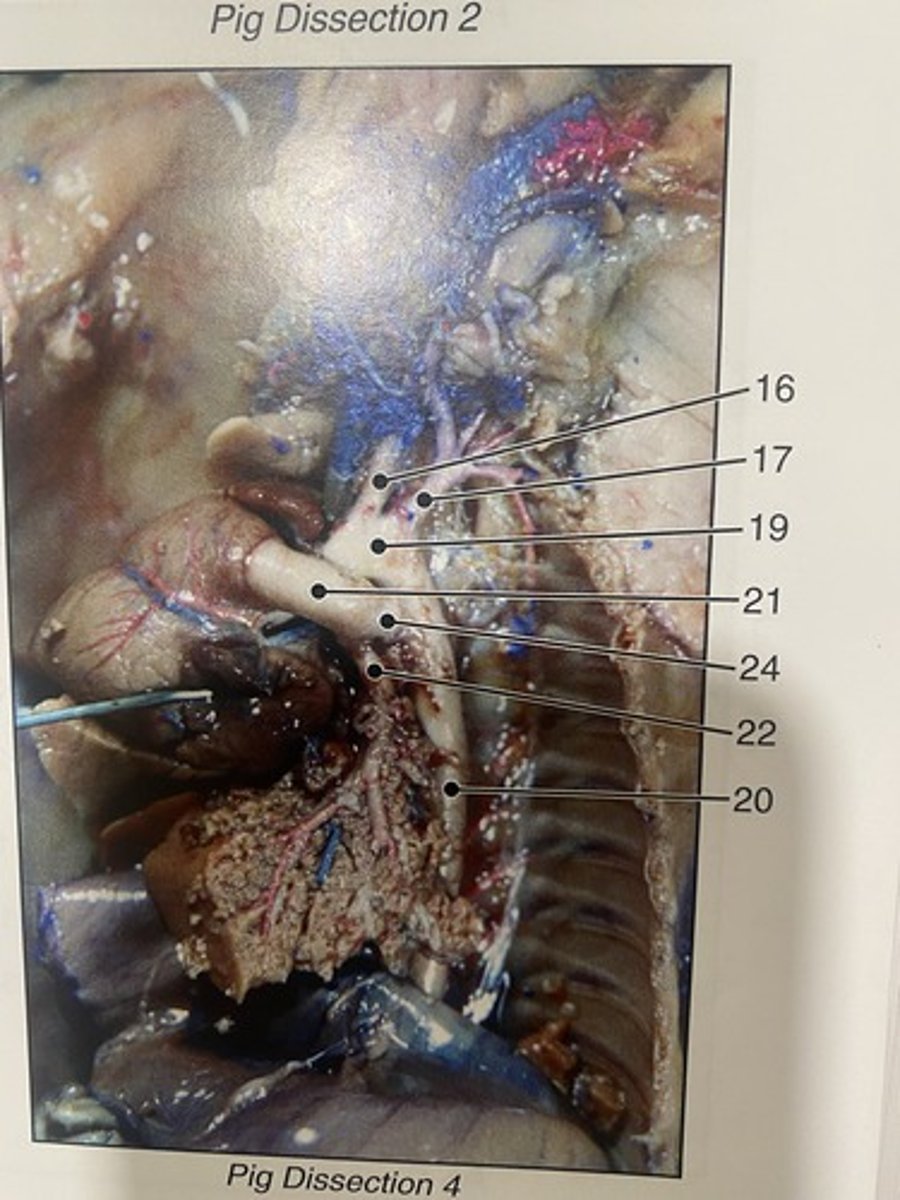
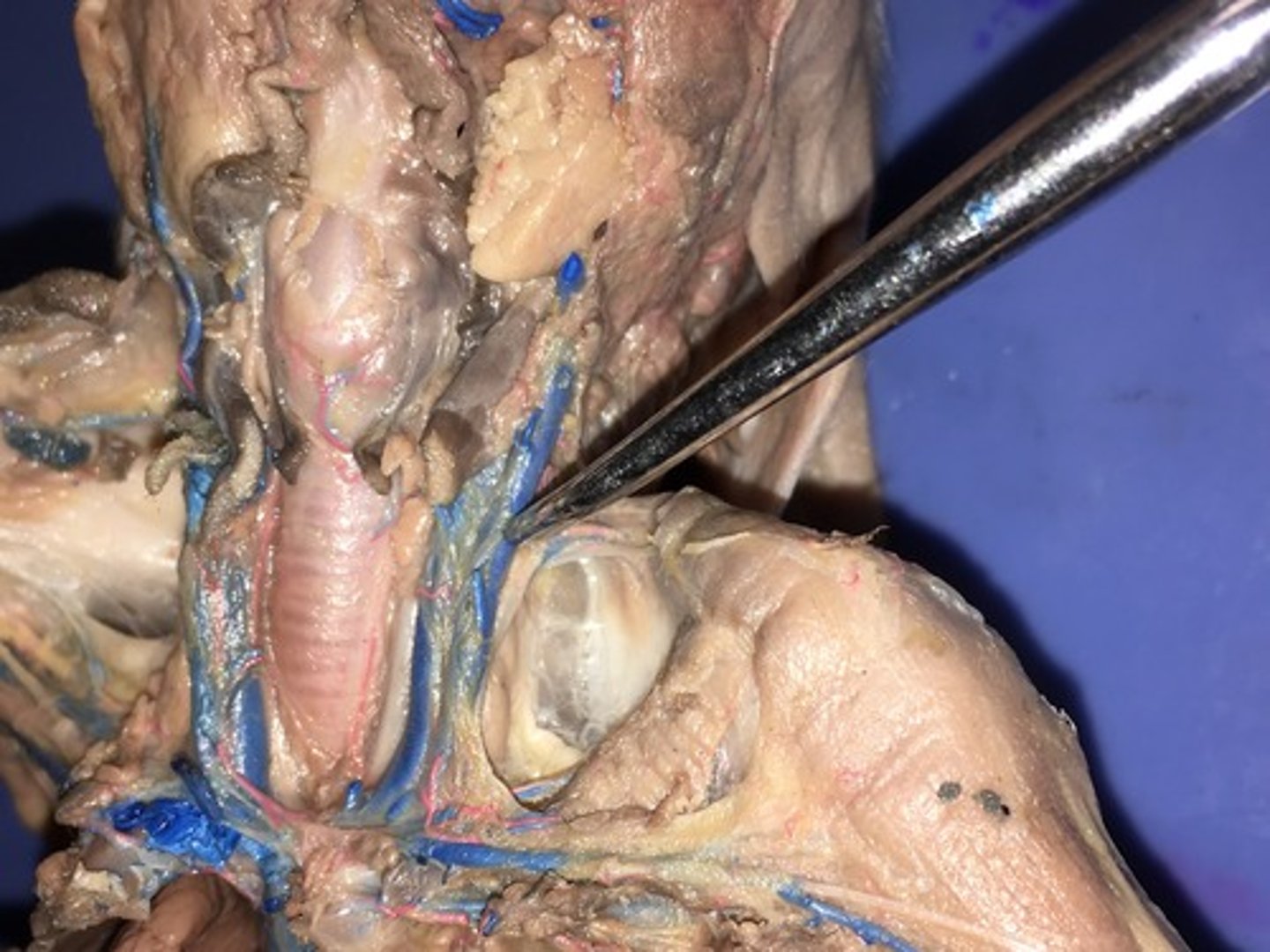
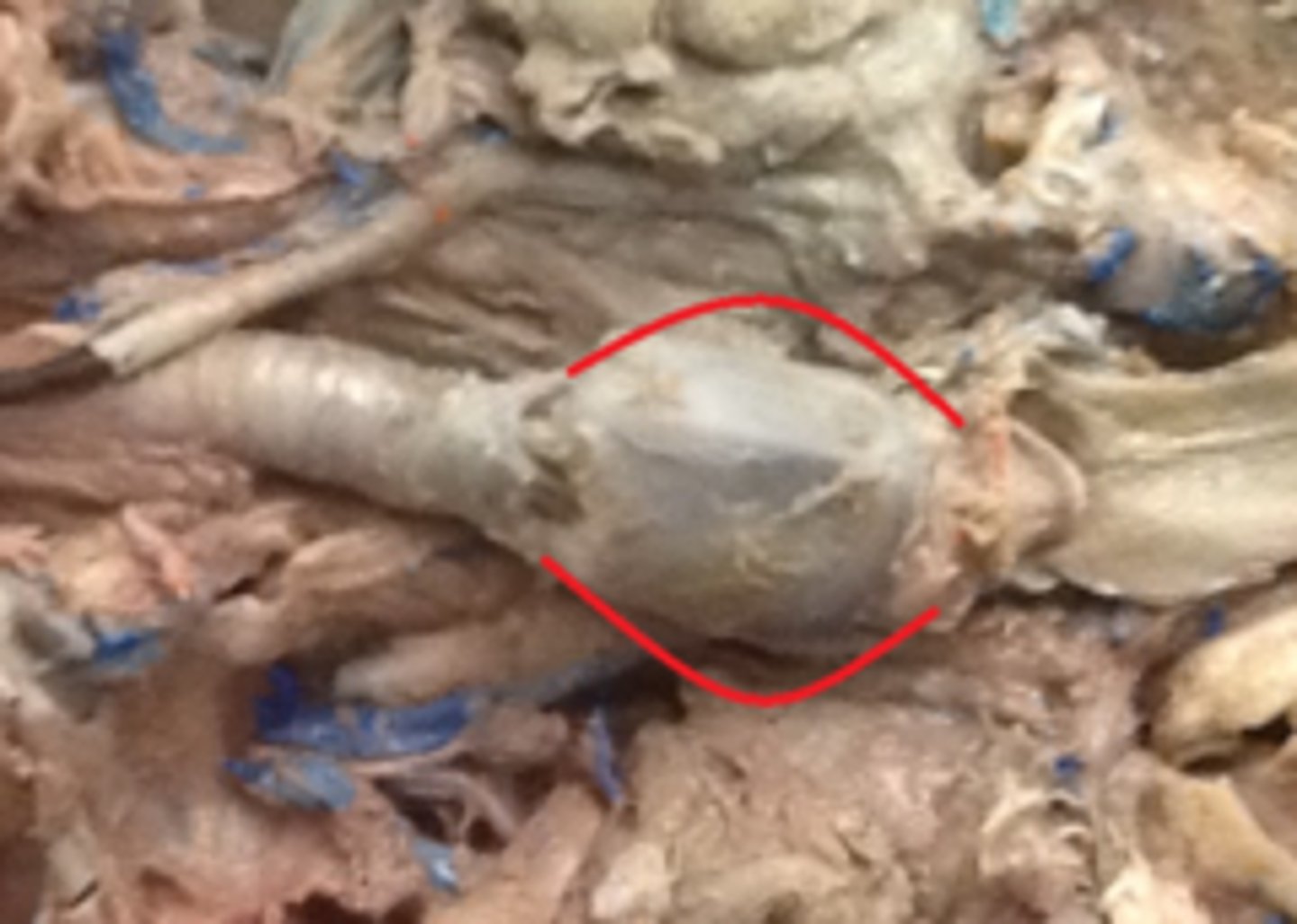
Larynx
voice box; passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea; contains vocal cords
Trachea
Allows air to pass to and from lungs
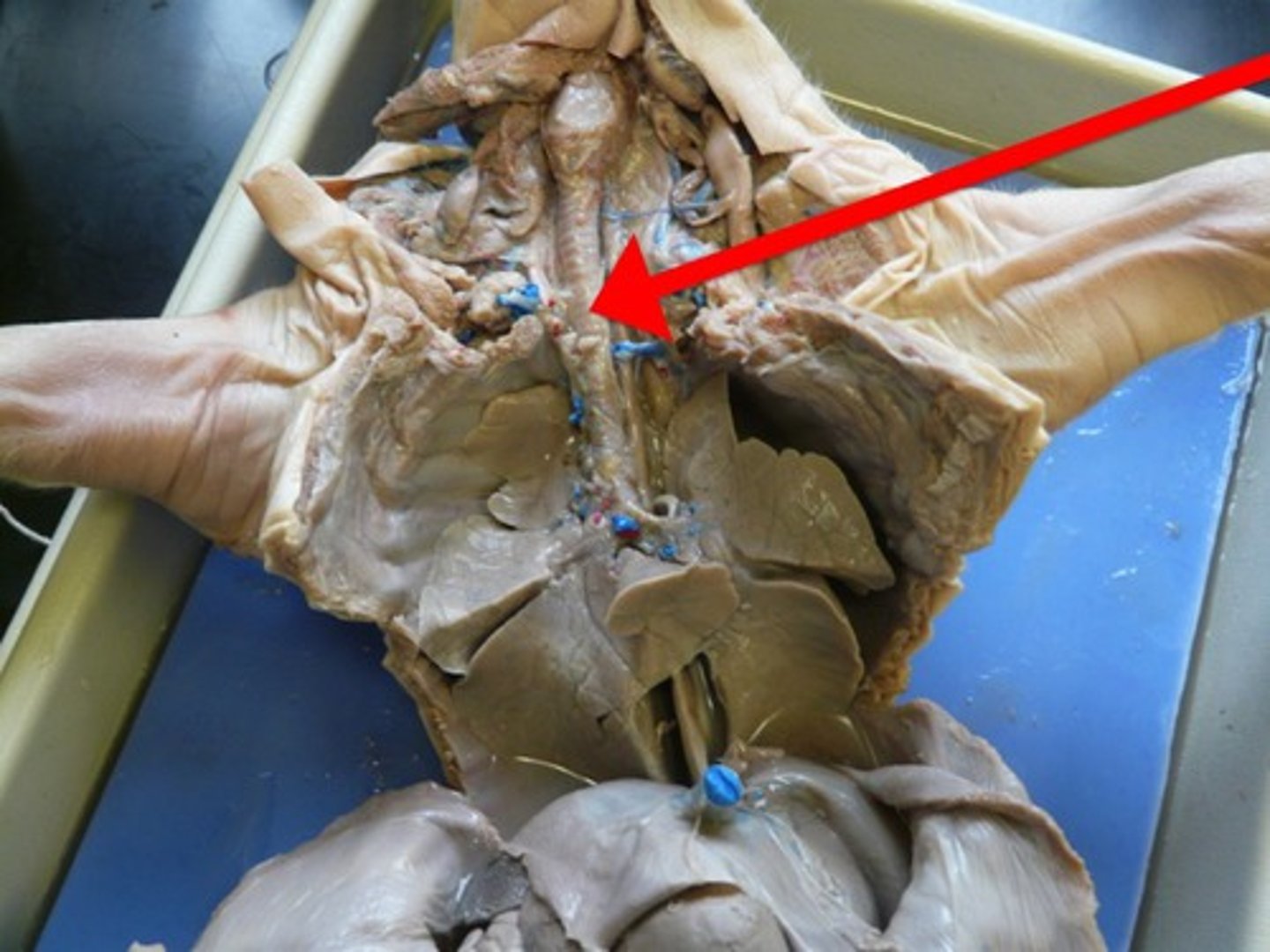
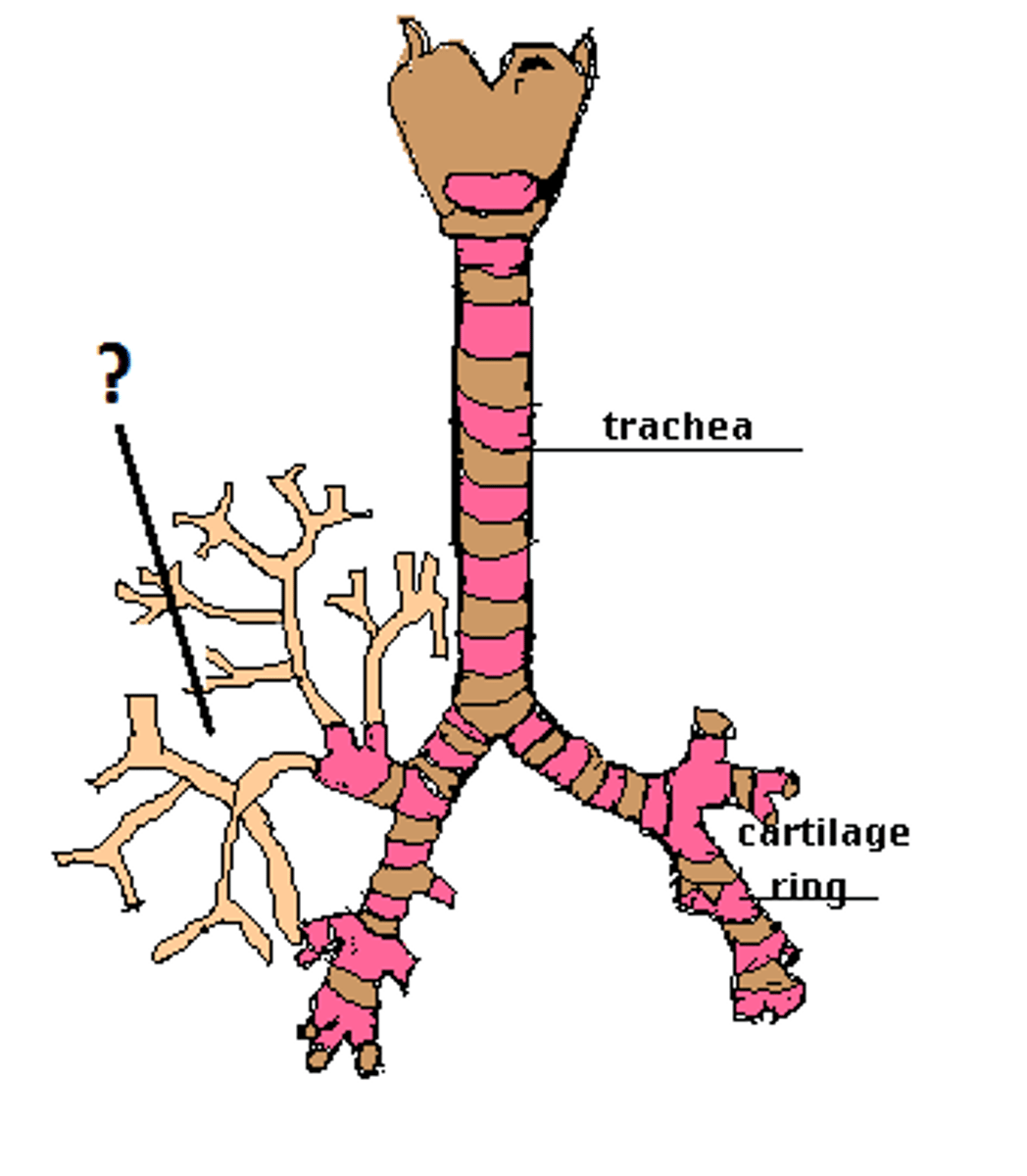
Bronchi
The passages that direct air into the lungs
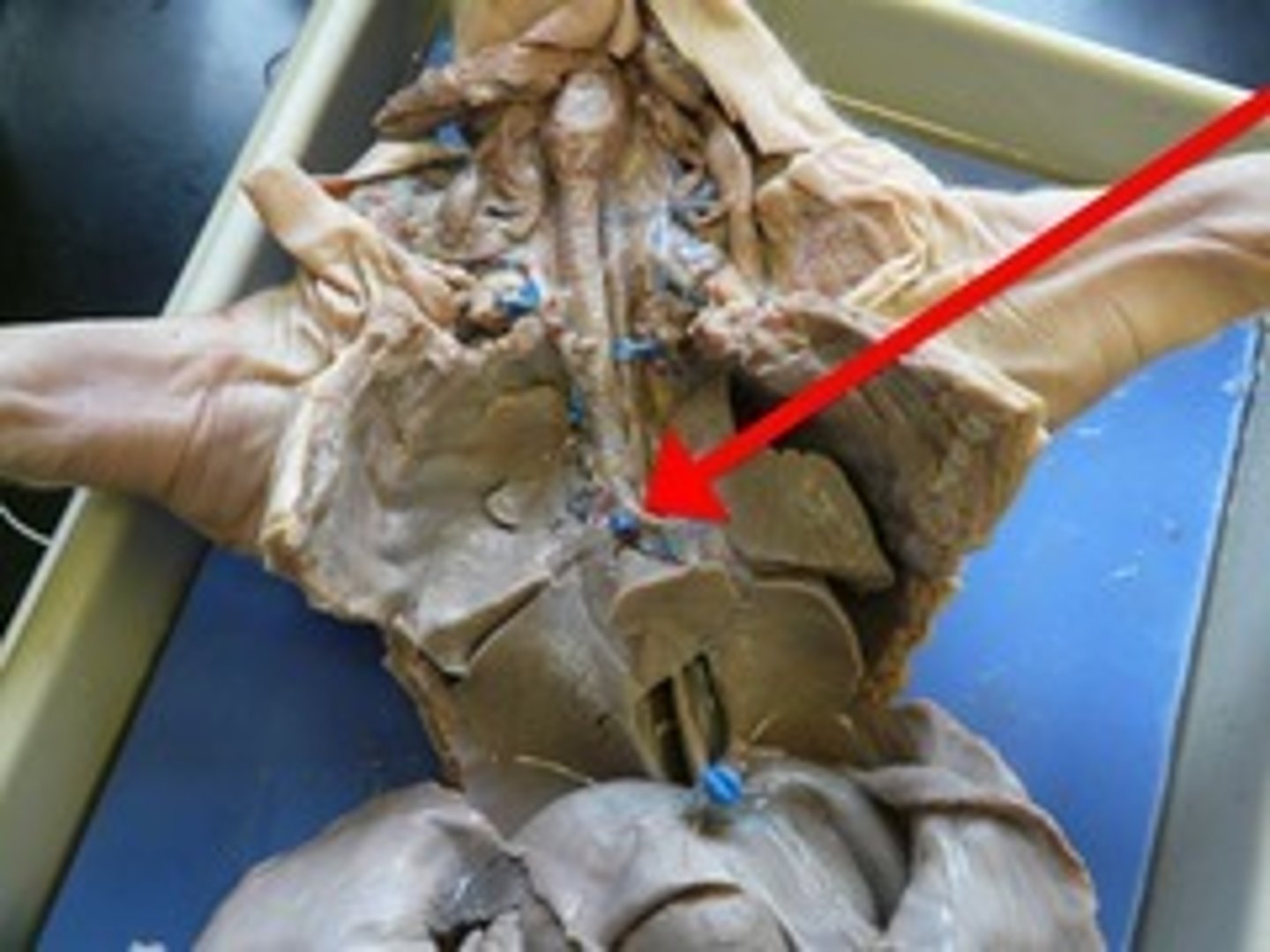
Bronchioles
smallest branches of the bronchi
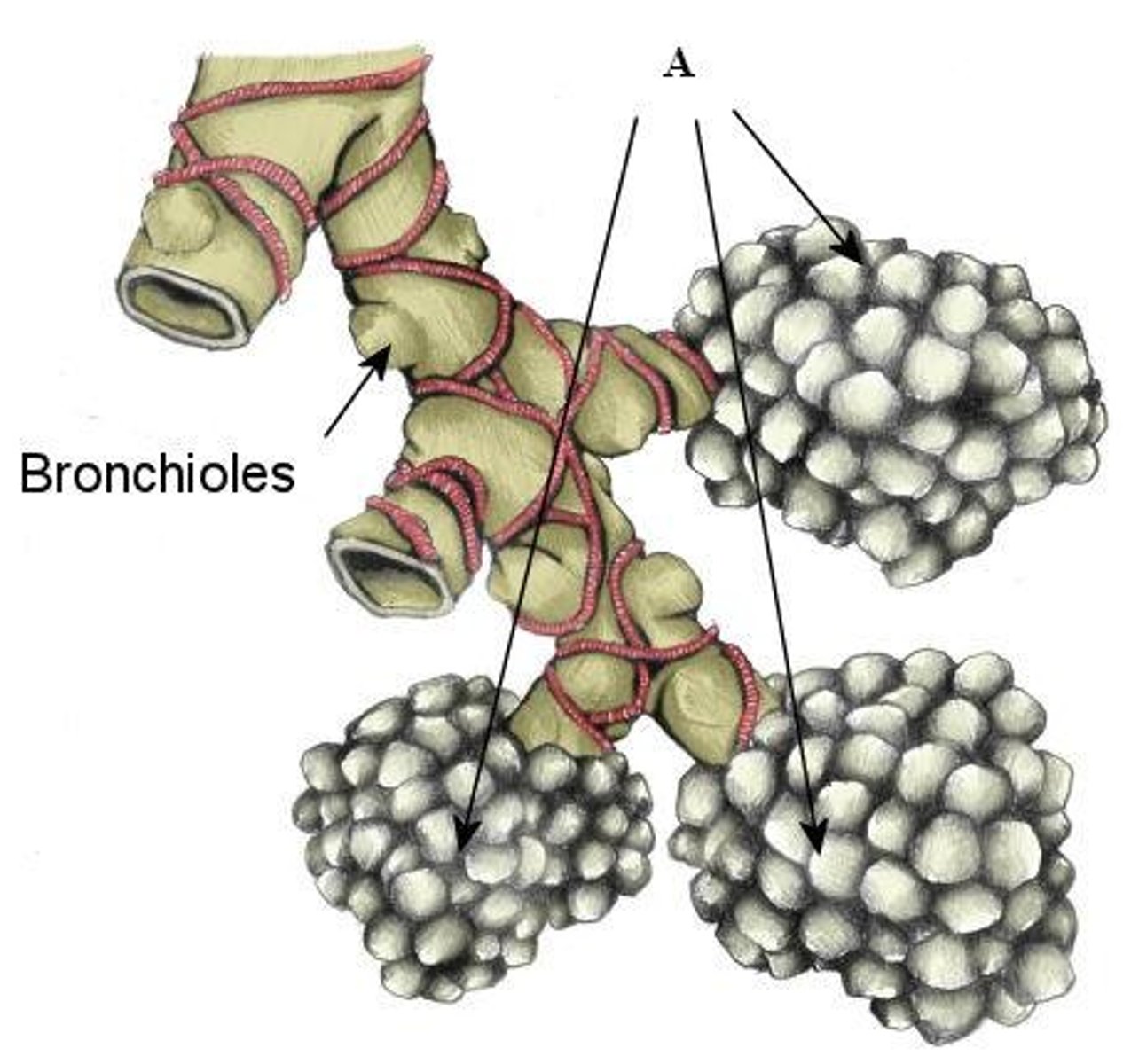
Alveoli
tiny sacs of lung tissue specialized for the movement of gases between air and blood
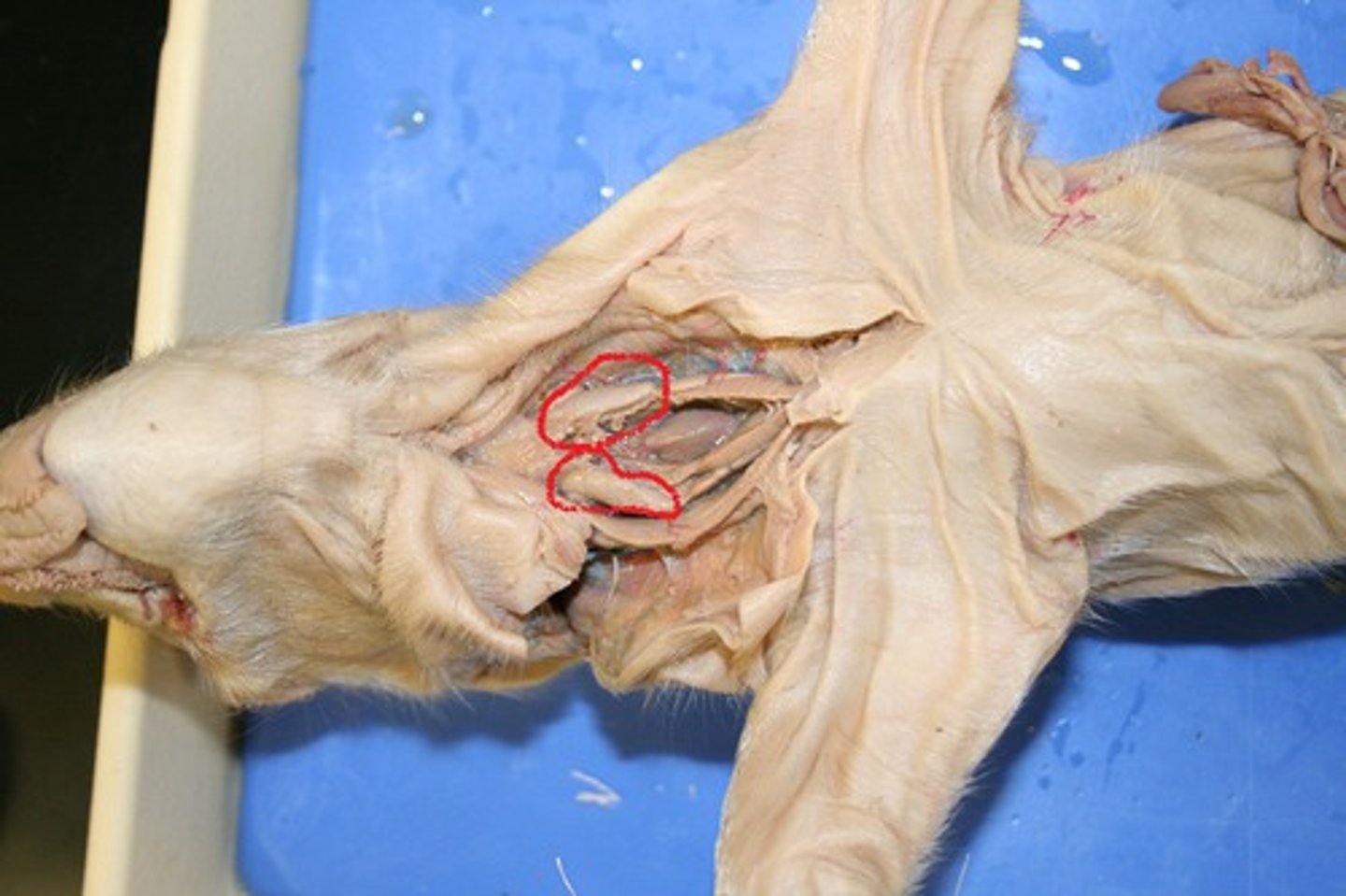
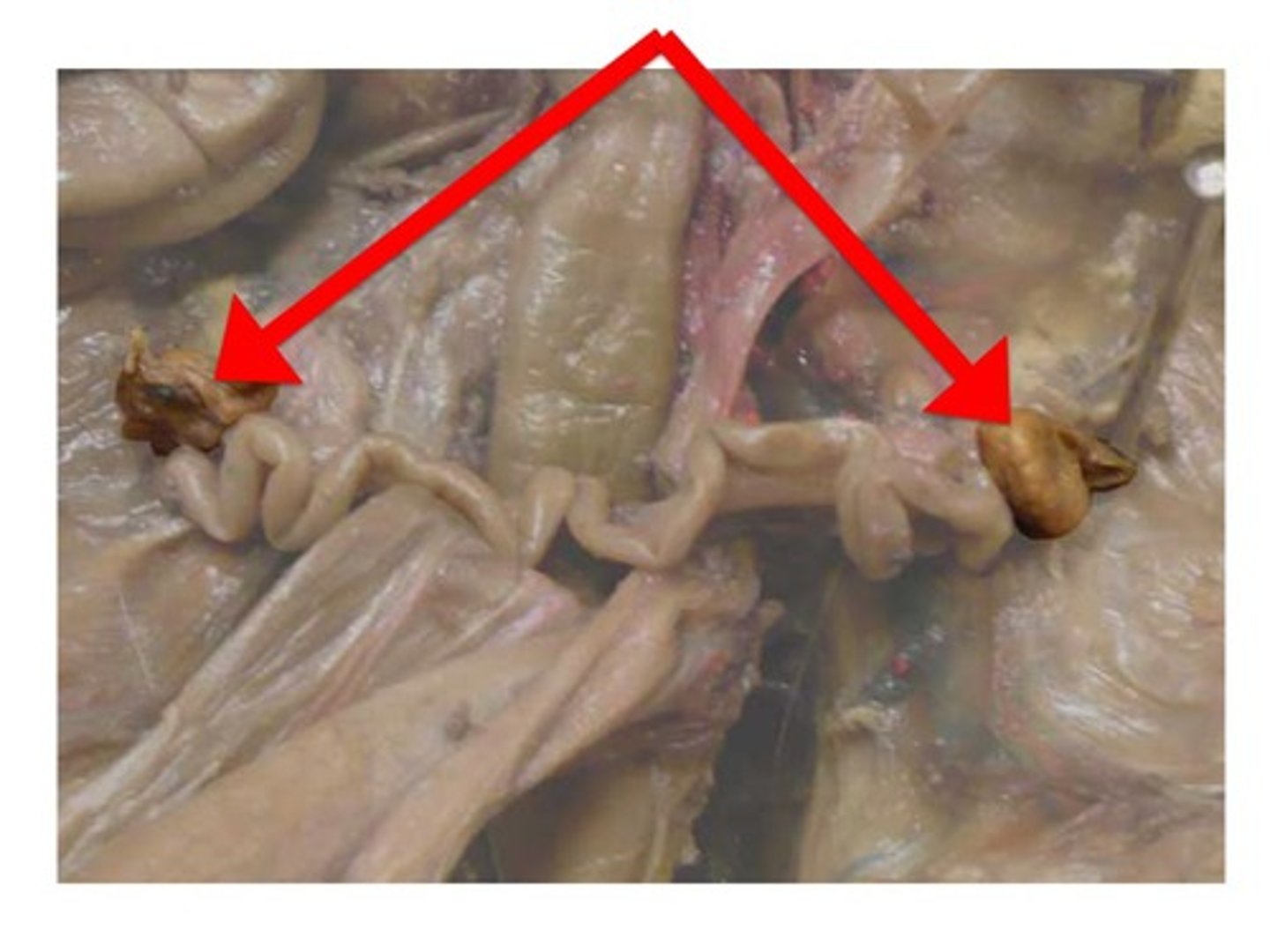
Ovaries
Glands that produce the egg cells and hormones
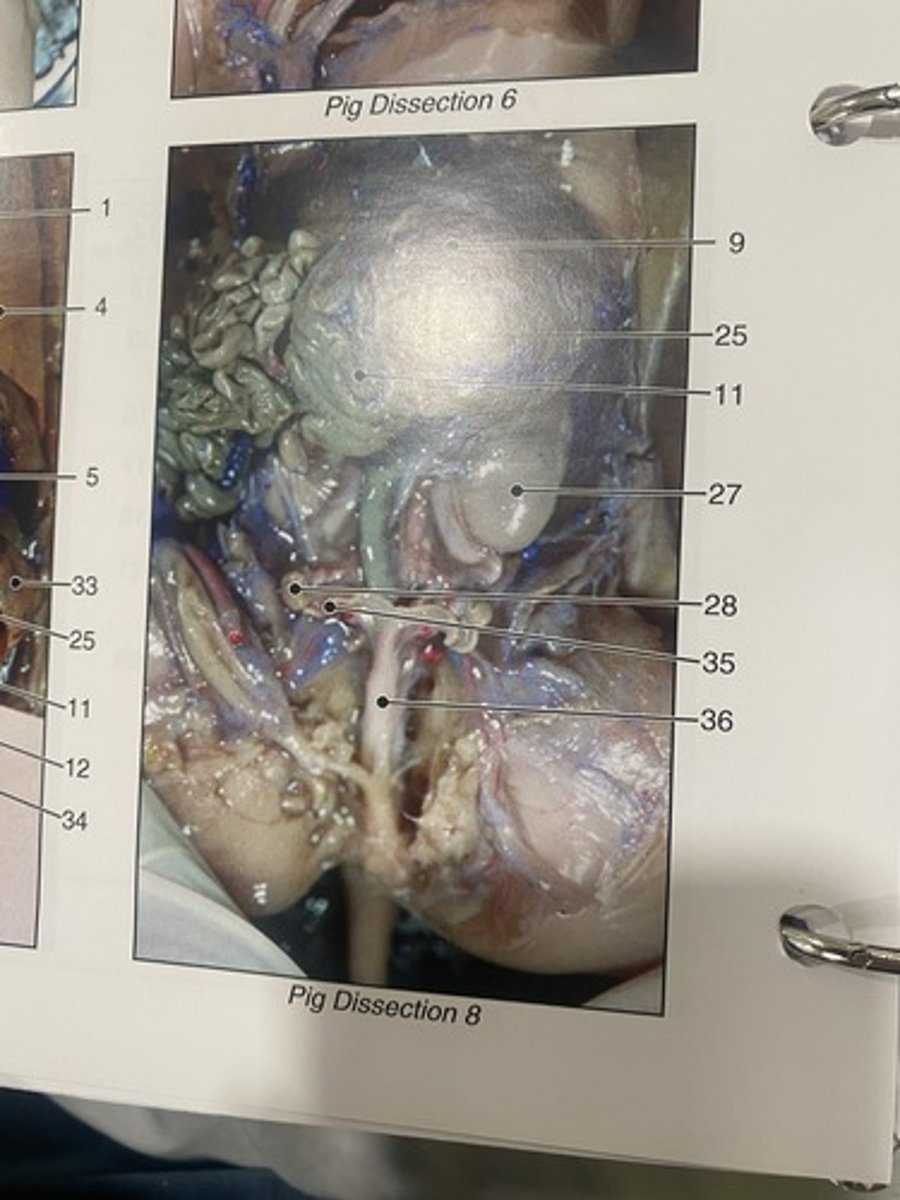
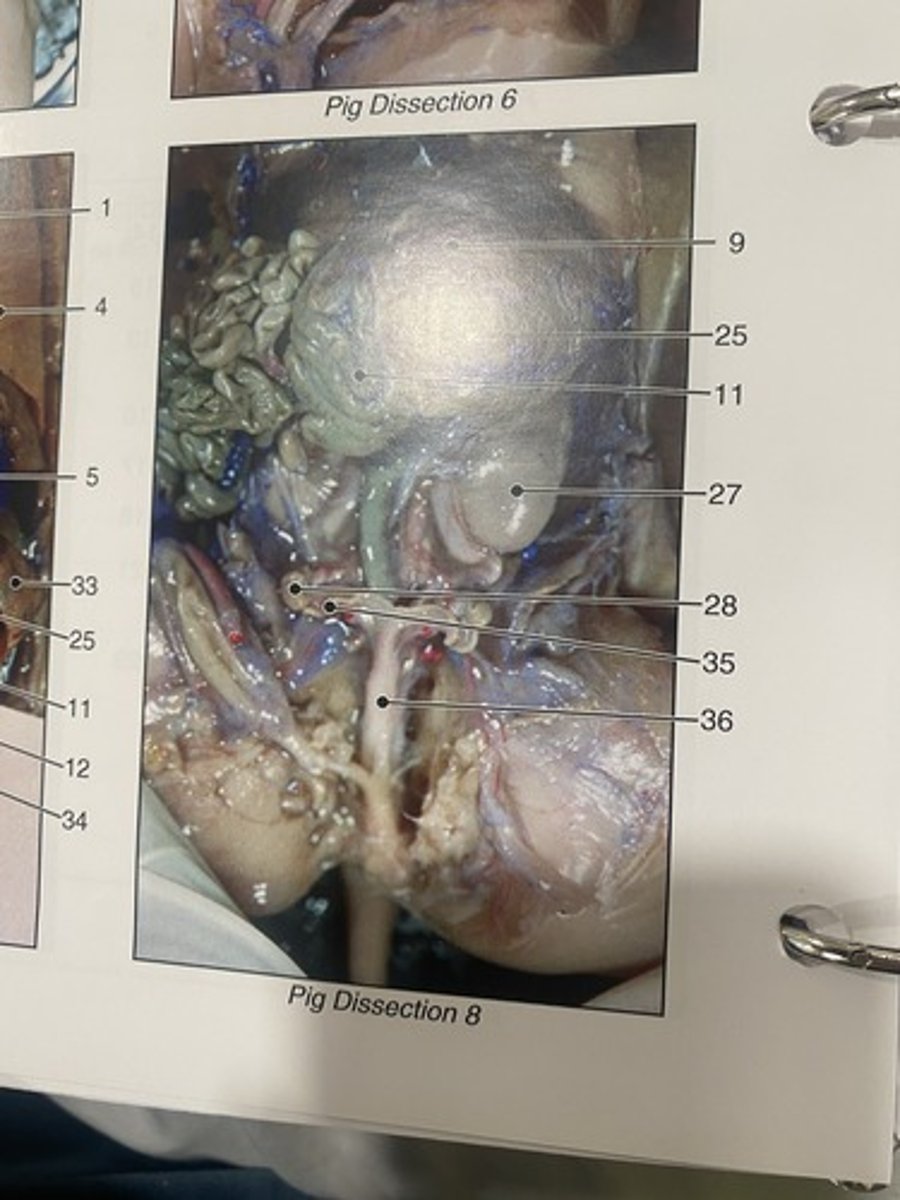
Uterus body
major portion of uterus (#36)
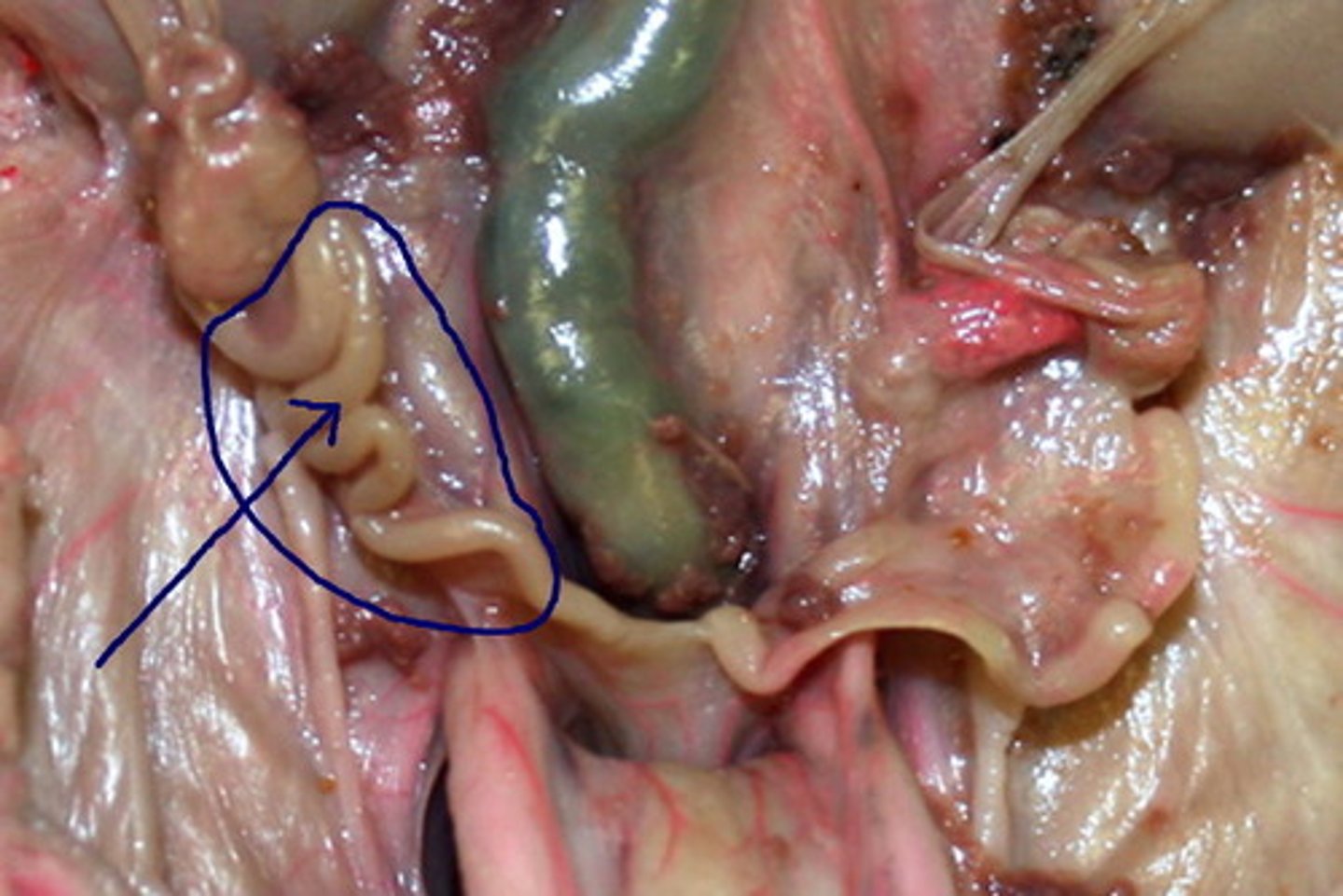
Fallopian tubes
tubes which carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus and which provides the place where fertilization occurs
Uterine horn
the points where the uterus and the fallopian tubes meet (#35)
Testes
male gonads that produce sperm
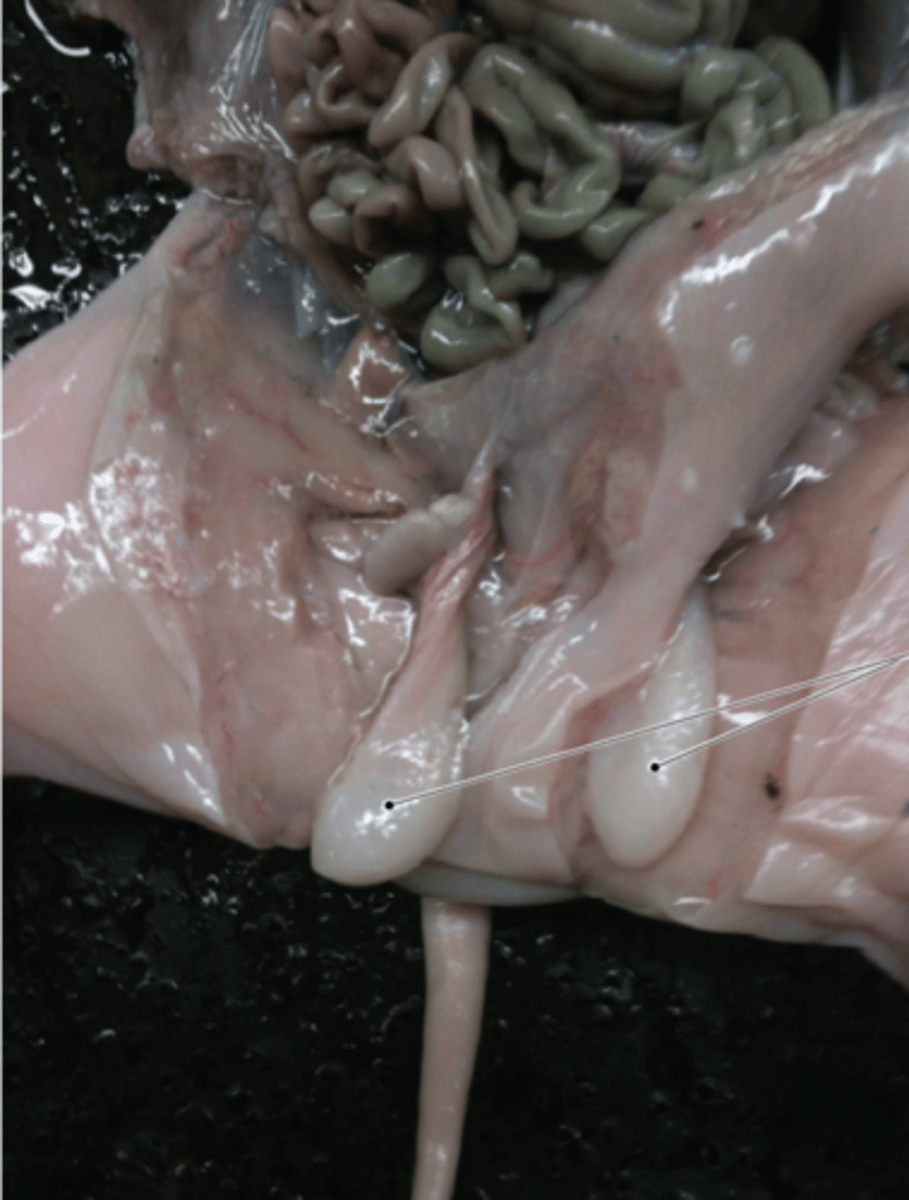
Thyroid
regulates metabolism
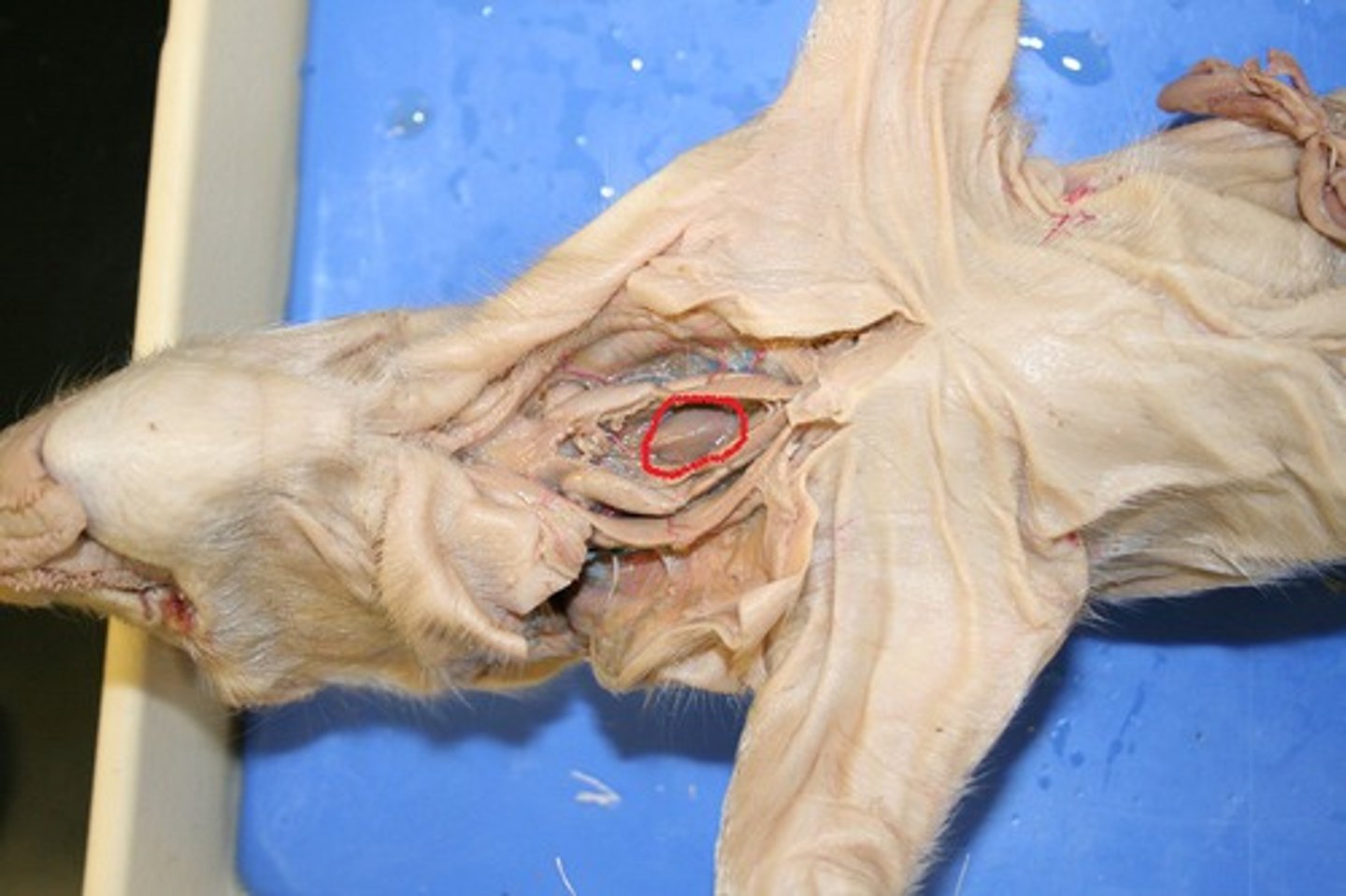
common bile duct
carries bile from the liver and gallbladder to the duodenum