Lesson 12: Vaccines
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Definition Vaccine
Vaccines are the most effective biological tools for the prevention of certain infectious diseases.
What is the purpose of vaccines?
Vaccines are used for the prevention of certain infectious diseases by inducing a specific immune response that destroys or inactivates the pathogenic infectious agent.
Why are vaccines important in public health?
Vaccines decrease morbidity and mortality, exist in all countries with a vaccination calendar, increase the number of available vaccines, allow elimination or eradication of diseases such as measles and polio, and modify the epidemiological behavior of diseases.
What are vaccines made of?
Vaccines are composed of proteins, polysaccharides, or nucleic acids of pathogenic microorganisms, delivered alone, as part of a complex particle, or by live attenuated agents or vectors.
What is immunity?
Immunity is the system that protects the body against diseases through antibody and cellular immune responses.
What is Immunogenecity?
The ability of an infectious agent to trigger an immune response within a host
What is the primary immune response?
The primary response occurs when a virus or bacteria first enters the body, is recognized as foreign, and antibodies are produced to destroy the agent.
What is the secondary immune response?
The secondary response occurs when the host comes into contact with the same microorganism again, and antibodies rapidly and effectively destroy it due to immunological memory.
What types of immunity exist?
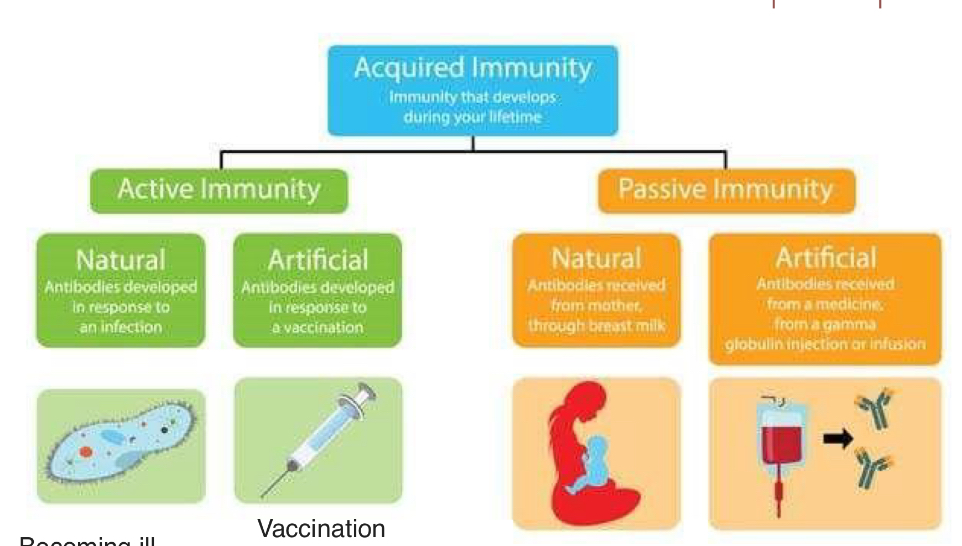
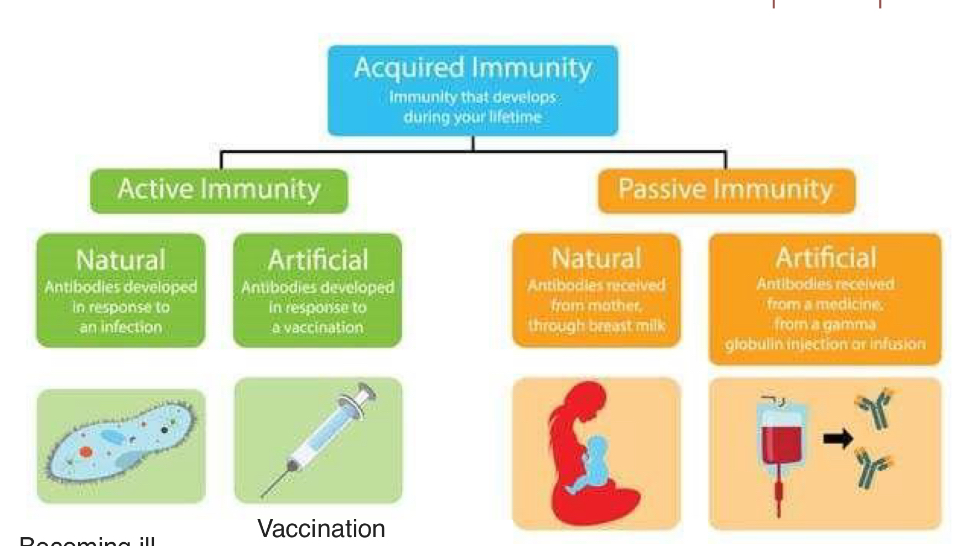
Immunity can be natural or artificial, and passive or active.
What is active immunity?
Active immunity is the body’s own production of specific antibodies or cellular responses after infection or vaccination, resulting in long-lasting and intense protection.
What is active natural and articial immunity?
Antibodies developed in response to an infection
Antibodies developed in response to a vaccination
What is passive immunity?
Passive immunity is acquired from immunoglobulins from another host, provides immediate protection, is short-lasting, and does not generate immunological memory.
What is passive natural and artificial immunity?
Antibodies received from mother through breast milk
Antibodies received from a medicine, injection or infusion
What is immunization?
Immunization is the process by which an individual becomes immune or resistant to an infectious disease, generally through vaccination.
What is an antigen and what is an antibody?
An antigen is a substance capable of binding to an antibody or T-cell receptor and initiating an immune response, while an antibody is a defense protein developed by the immune system.
Which substances can produce passive immunization and for how long?
Passive immunization can be produced by breast milk (1 week), serum, serum or plasma from immune response (3–4 weeks), and hyperimmune gammaglobulins (4–8 weeks).
What are heterologous sera or antitoxins?
Heterologous sera are solutions of antibodies obtained from immunized hosts, used to provide passive immunity and to treat infectious diseases after they appear..
What is homologous sera?
Obtained from people who have suffered from the disease
What are immunoglobulins?
Immunoglobulins are proteins produced by the immune system to attack antigens, obtained from plasma fractionation, and include five major types: IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE, and IgD.
What is Zoonosis?
Diseases where agents living in animals jump from animal to human
How are vaccines classified?
Vaccines are classified as live attenuated, inactivated (dead), subunit, toxoid, conjugate, or genetically engineered vaccines.
What characterizes live attenuated vaccines?
Live attenuated vaccines contain weakened agents that can reproduce in the body, stimulate humoral and cellular immunity, usually require one dose, are less stable, and may cause disease in immunocompromised individuals.
What are the main advantages and disadvantages of live attenuated vaccines?
The main advantage is contact with the whole agent and multiple antigens; the main disadvantage is the risk of infection in individuals with weakened immune systems.
What characterizes inactivated or dead vaccines?
Inactivated vaccines contain microorganisms modified to lose infectivity while maintaining immunogenicity, cannot cause disease, require multiple doses, are more stable, and require adjuvants.
Subunit vaccines
Virus: specific fragment of virus
Bacteria: Component of bacteria with a carrier protein able to increase immunogenicity
Toxoid Vaccines
Made up of toxins from a microorganism that are detoxified
Pathogenic power is eliminated but immunogenic capacity is preserved
What is a conjugate vaccine?
1 Vaccine against 2 pathologies
What is engineered or genetically modified vaccine?
It is genetically engineered vaccine
What is an adjuvant?
An adjuvant is a substance that non-specifically potentiates the immune response to an antigen.
Examples of live attenuated vaccines
Chickenpox
Oral polio
BCG
Examples of dead or inactivated vaccines
Rabies
Influenza
Hepatitis A and B
What is group immunity?
Group immunity occurs when a high proportion of the population is vaccinated, limiting disease spread and protecting unvaccinated individuals.
What fundamental characteristics must a vaccine meet?
A vaccine must meet the characteristics of safety, immunogenicity (ability of infectious agent to induce specific immunity), efficacy and efficiency in protection, and stability.
What factors are considered before incorporating a new vaccine?
Relevance of the disease, cost and cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with other vaccines.
What are the correct needle insertion angles for vaccination?
Intramuscular injections use a 90° angle, subcutaneous injections use a 45° angle, and intradermal injections use a 15° angle.
How are interrupted vaccination schedules handled?
Vaccination schedules are never restarted; they are only continued, and the total number of doses is what matters.
Adminstration of vacciines and intervals between them
Several vaccines in one appointement insterted in different regions Of the body and not mixed inside the same syringe
Other times its necessary to have intervals between adminstrations
What are false contraindications to vaccination?
Fever, diarrhea and Allergies
What are true contraindications to vaccination?
-anaphylaxis to a previous dose or vaccine component,
-hyperthermia,
-acute severe illness,
-pregnancy with live attenuated vaccines.
What are vaccination considerations during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
Live vaccines are contraindicated during pregnancy, flu, pertussis and covid vaccination is recommended, breast milk does not interfere with infant immunity, and vaccinating breastfeeding mothers does not pose a risk to the child.
Only after 2. trimester
Reasons against vaccines
Religious, Risks, Lack of efficiency, Anti-vaccine groups
Which vaccines are contraindicated in immunocompromised individuals?
Live attenuated vaccines are contraindicated in immunocompromised individuals.
Why should adults be vaccinated?
Adults should be vaccinated due to lack of childhood vaccinations, need for booster doses, influenza risk, and higher mortality compared to infants in developed countries.
Vaccination for age group 38-64
Hepatitis A and B, Flu, Diphtheria
Which vaccines are recommended for health professionals?
Health professionals should receive MMR, chickenpox, hepatitis B, influenza, and tetanus vaccines.
Zoo staff and veternaries
Rabies and tetanus
Vaccines in patients with chronic diseases
Asplenia: Hepatitis B and flu
Cardiac: flu
What adverse reactions can vaccines cause?
Vaccines can cause local, systemic, and allergic adverse reactions.
What are examples of severe adverse vaccine reactions?
Vaccine induced
Defect in vaccine
Programm errors -handling or storage
Syncope and anxiety
Coincident events
Idiosyncratic - unknown cause
They can be caused by:
Animal proteins, Antibiotics and preservaties
What is the cold chain?
The cold chain is the system that ensures vaccine potency from manufacturing to administration, including development, manufacturing, distribution, and vaccination.
2-8 degrees
• Human resources (planning, management, implementation of vaccination programmes)
• Material resources (cold rooms, thermometers, insulated boxes, thermographs, electronic indicators)
What is the series of elements?
Developement and clinical trials
Manufacturing
Distribution
Vaccination