Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Chapter 10 The Muscular System
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
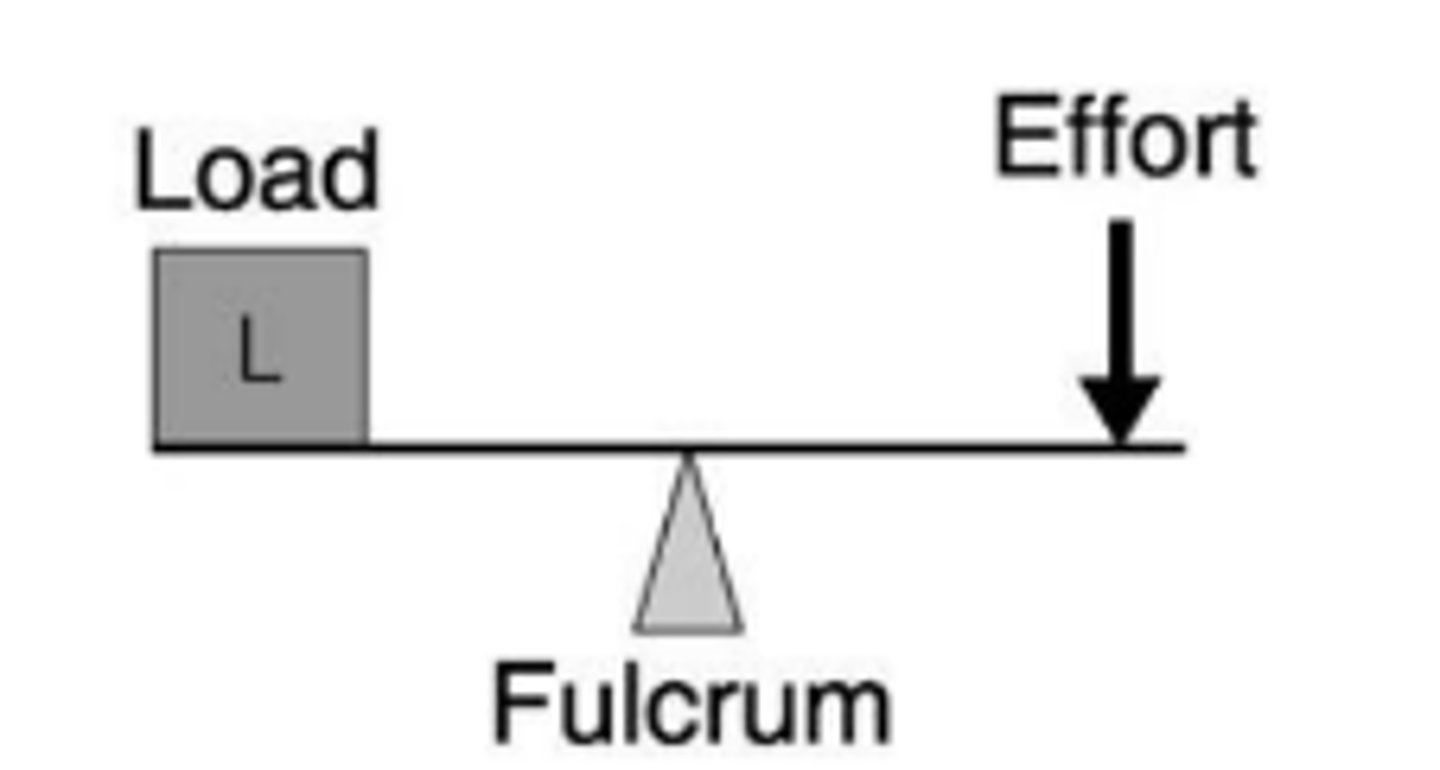
first-class lever
Atlanto-occipital joint;
demonstrated by using scissors
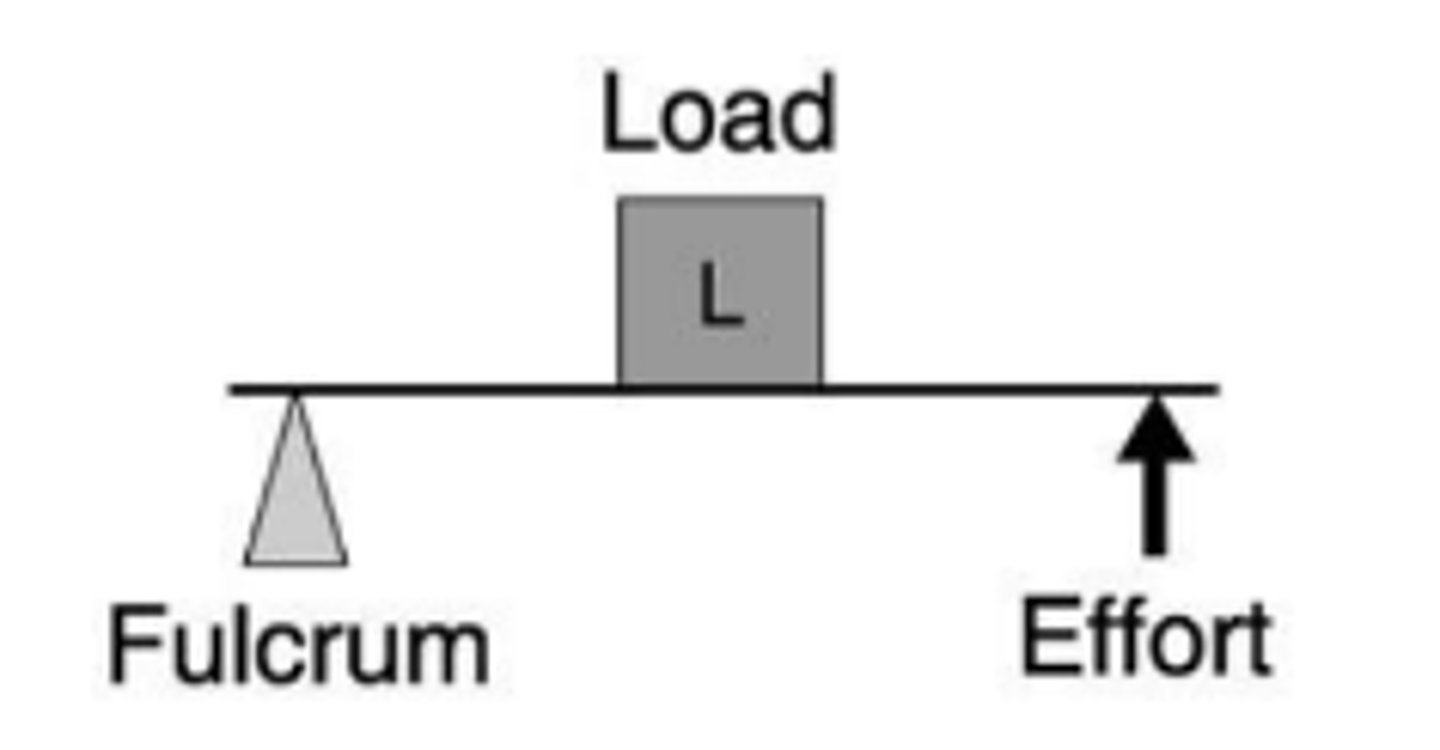
second-class lever
Tibia-calcaneus joint
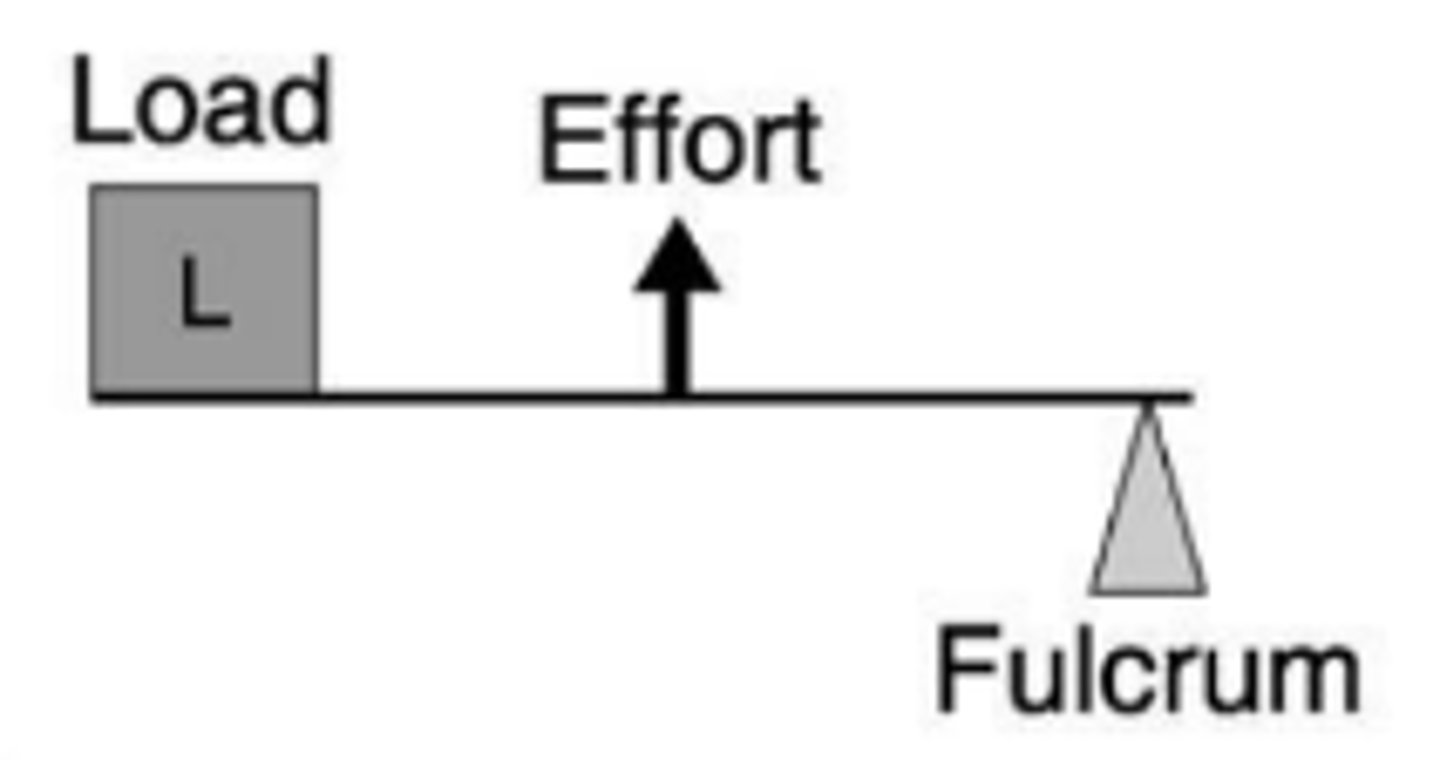
third-class lever
Humerus-ulna Joint;
shoveling snow
sternocleidomastoid
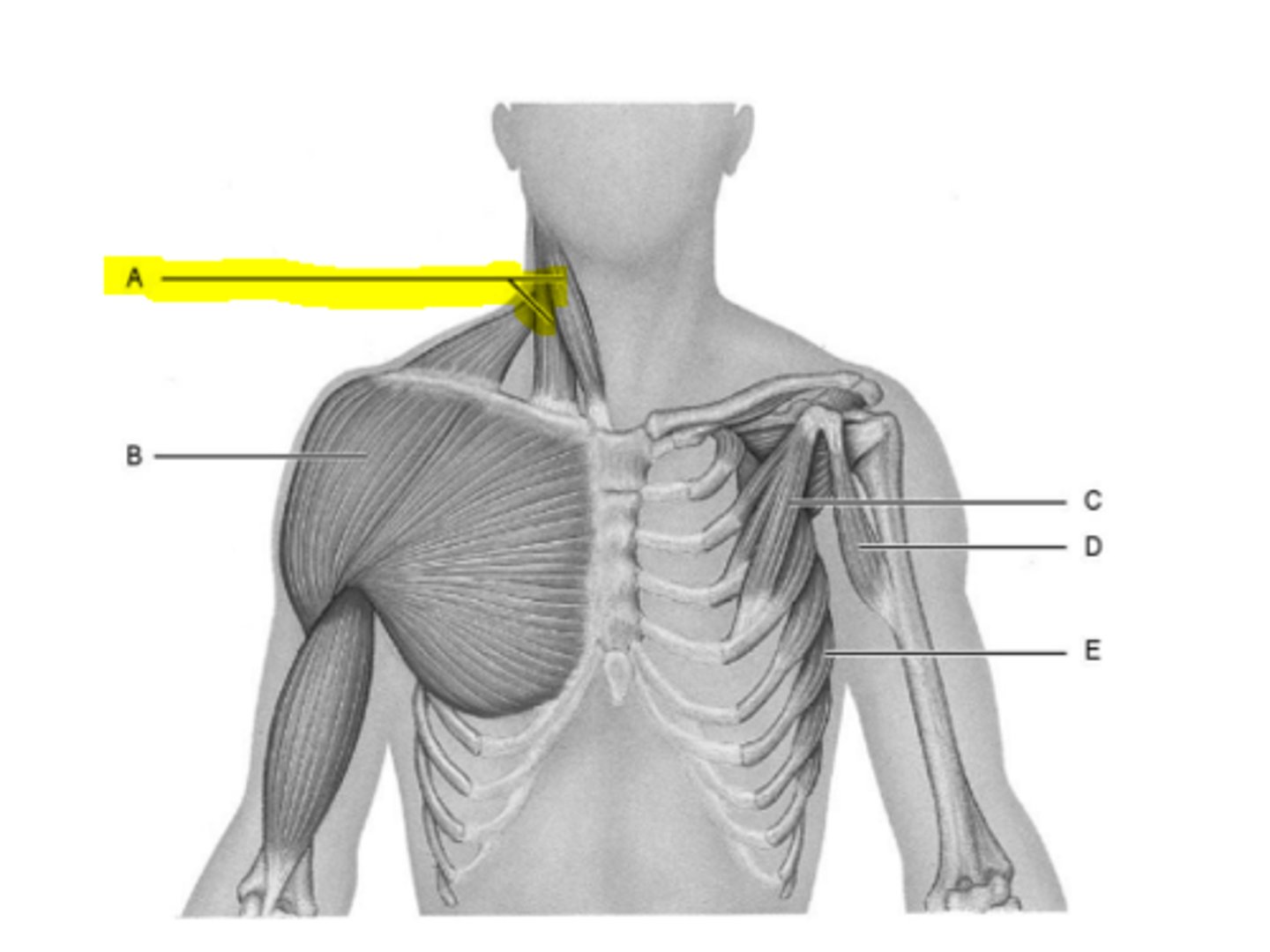
deltoid
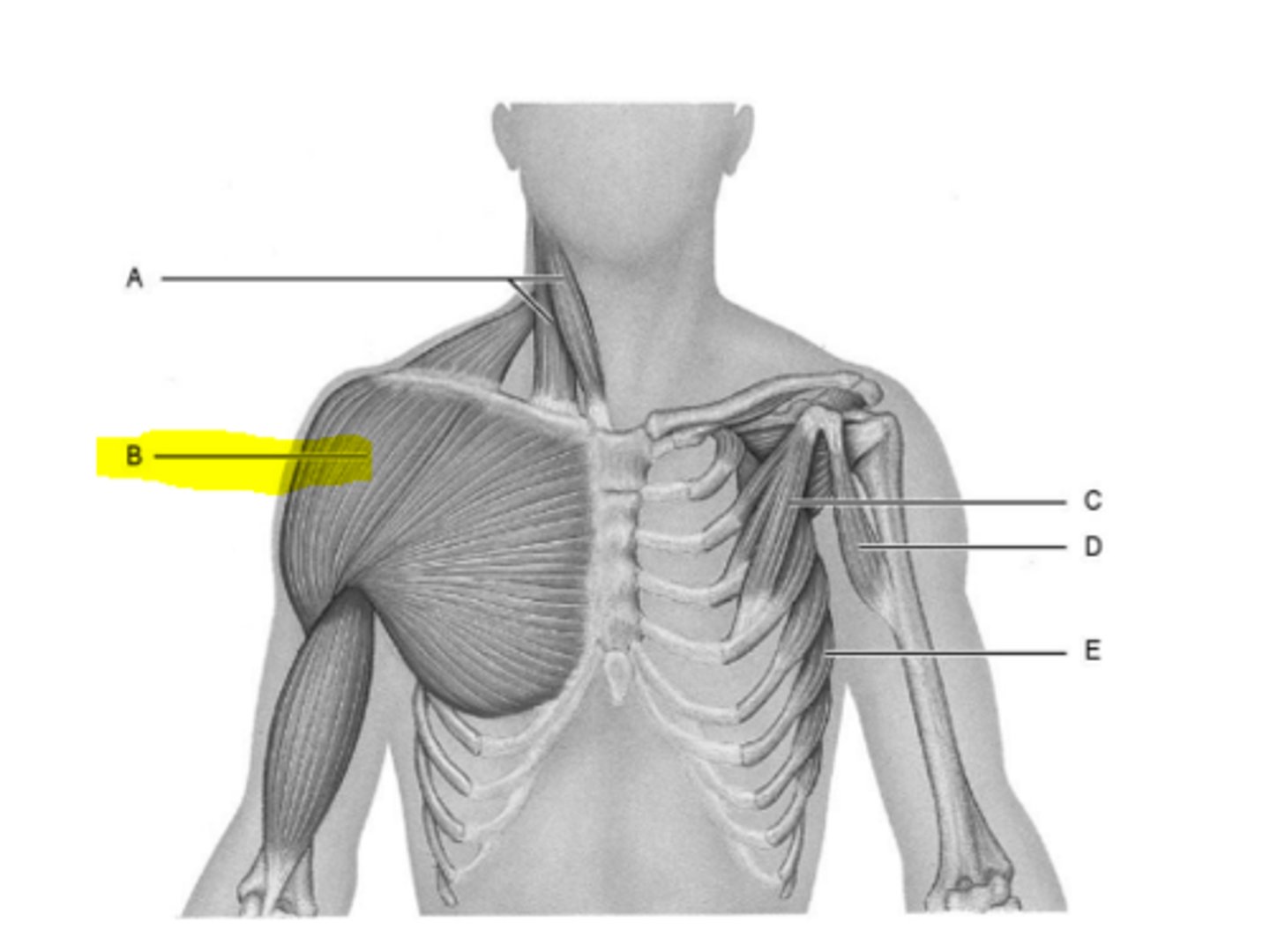
pectoralis minor
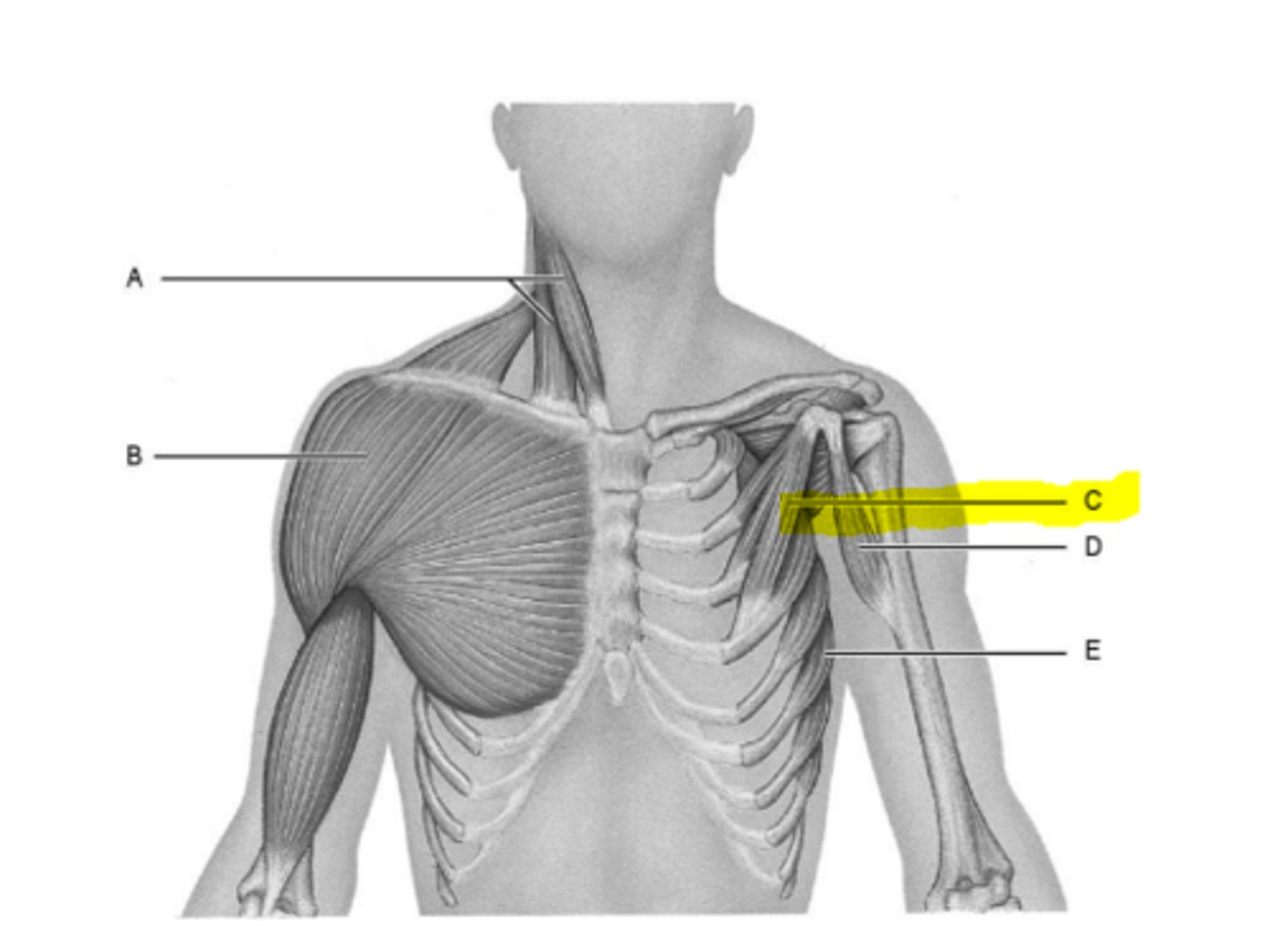
coracobrachialis
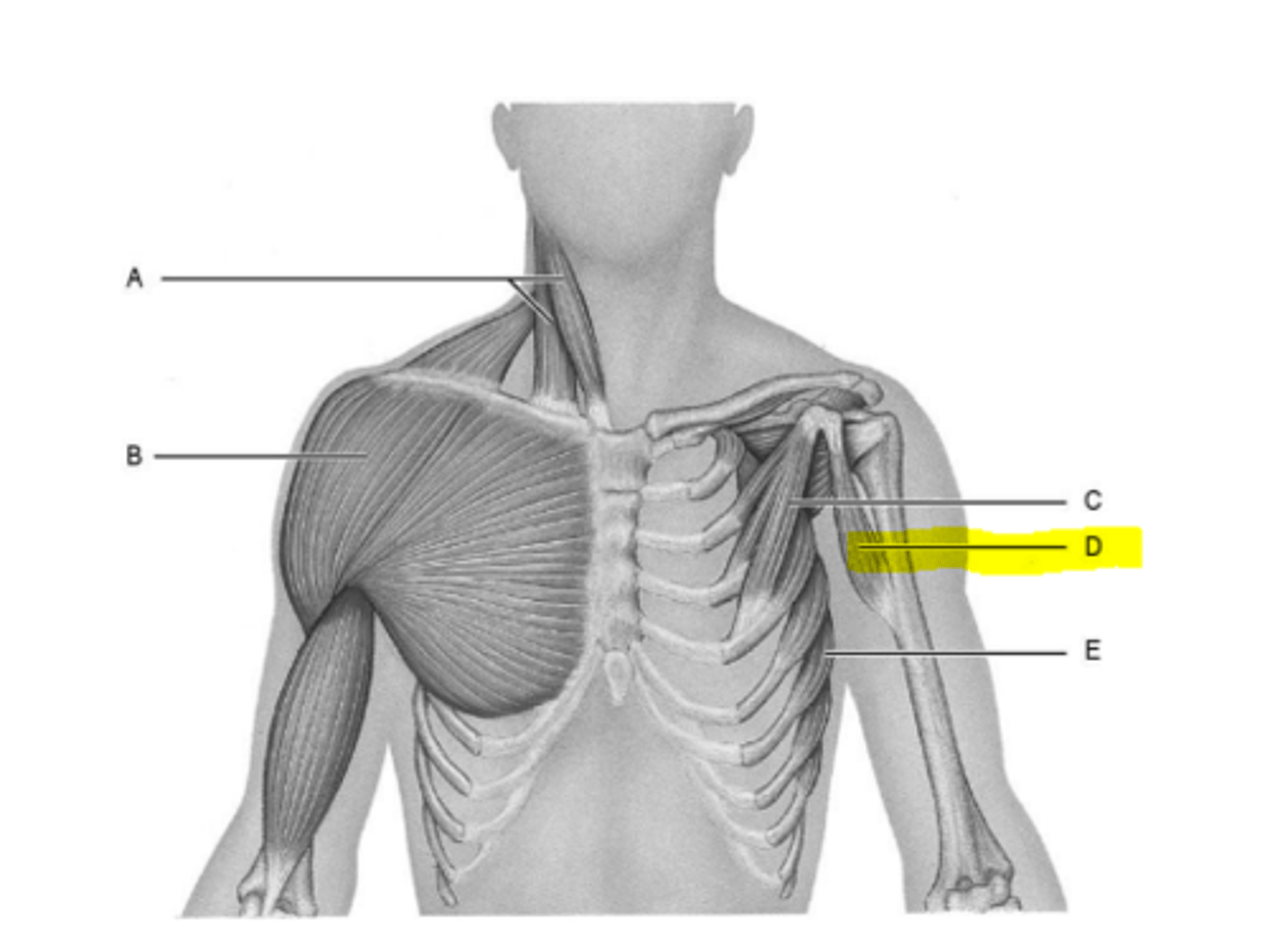
sterratus anterior
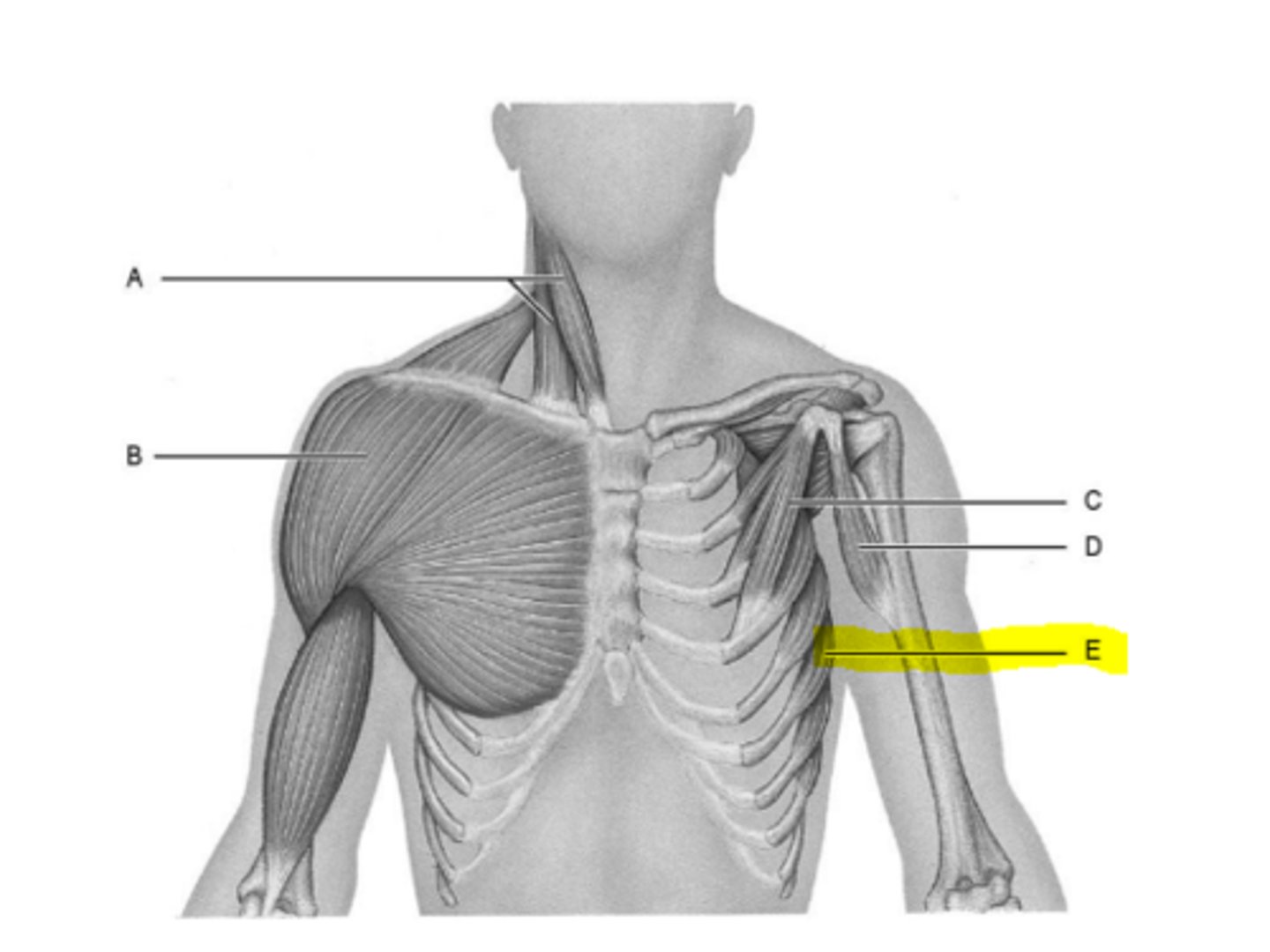
levator scapulae
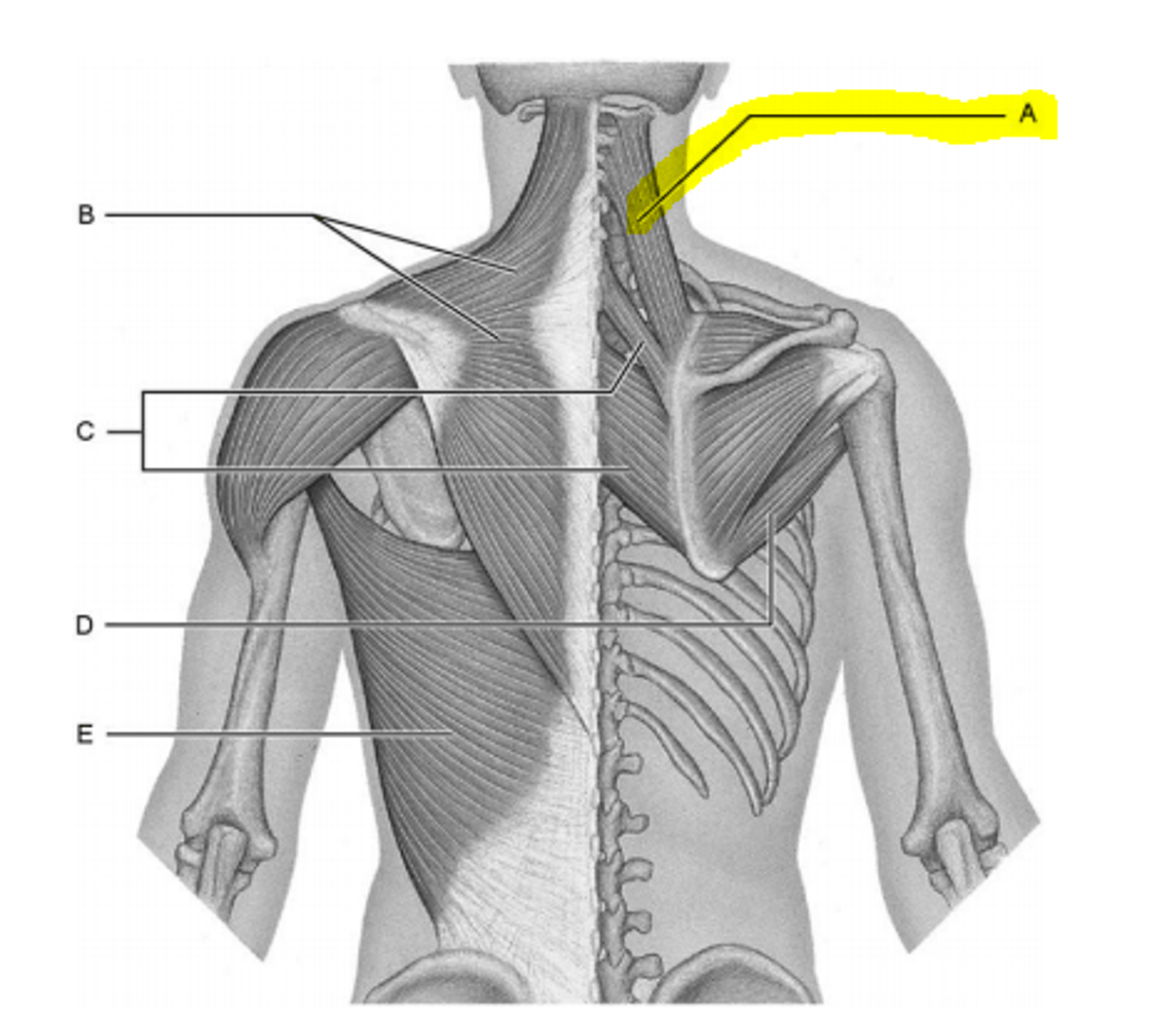
trapezius muscle
rotates scapula
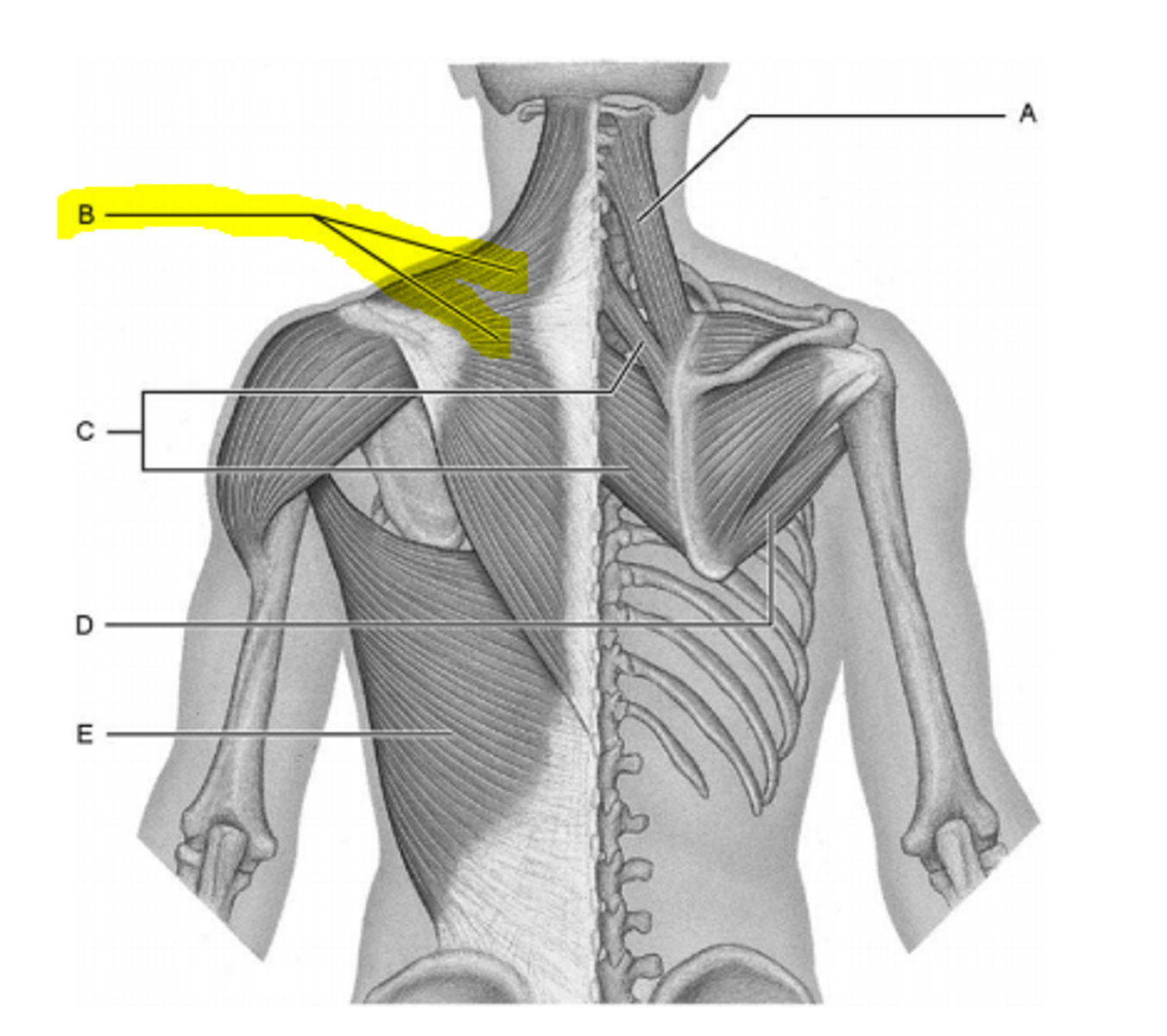
retract scapula
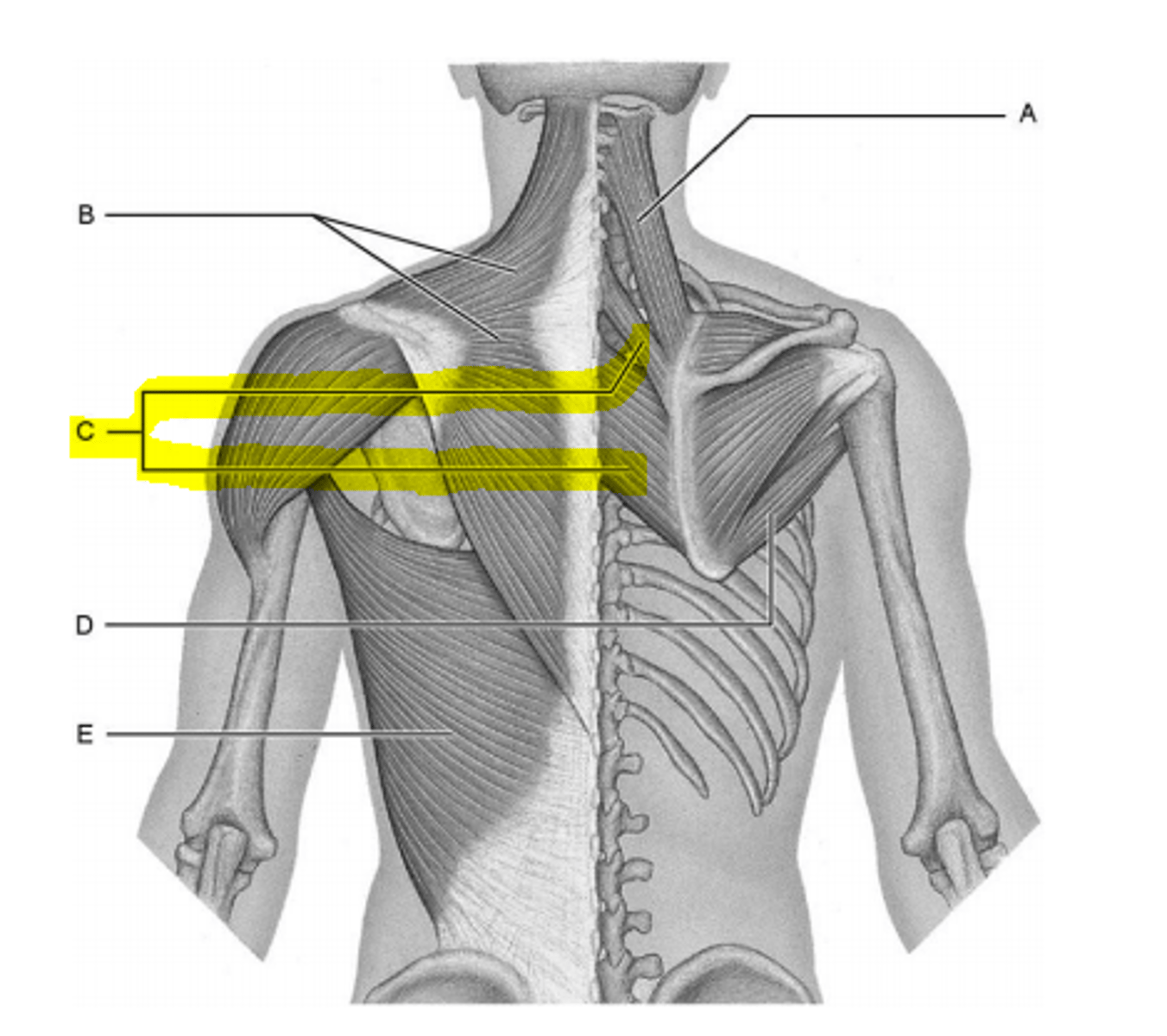
teres major muscle
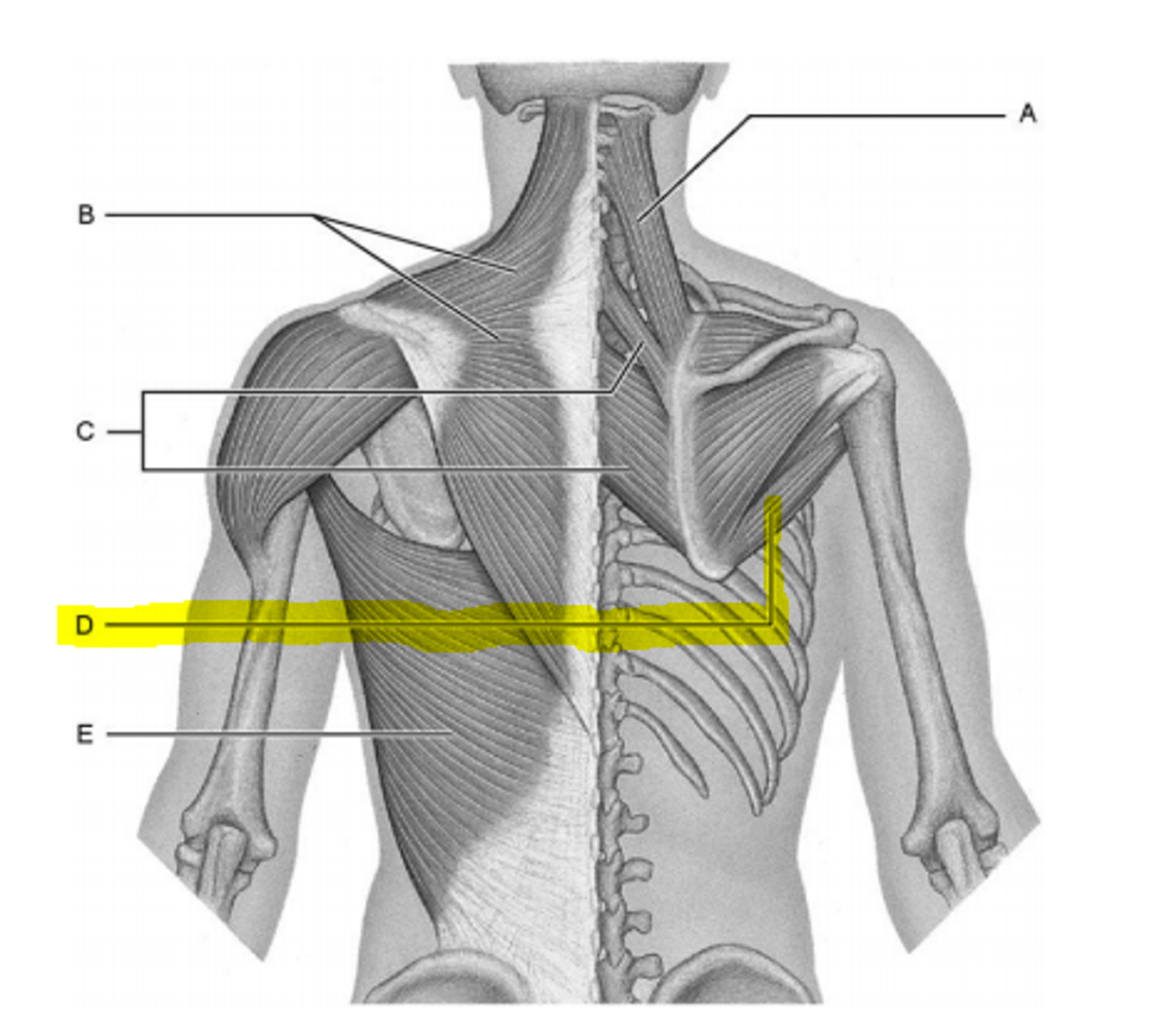
latissimus dorsi
Broadest muscle of the back
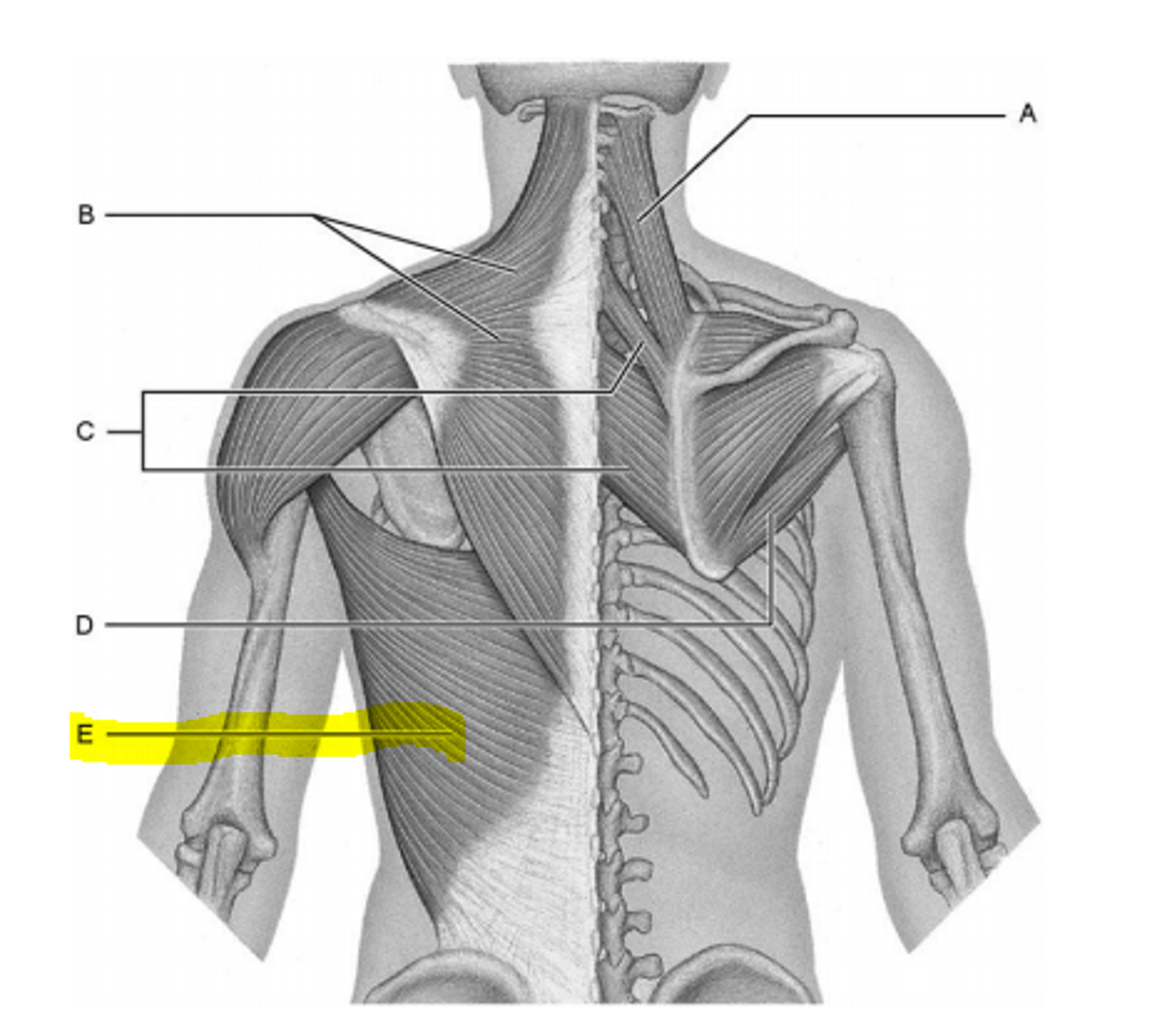
flexor carpi ulnaris
powerful flexor and adductor of hand;
stabilizes the wrist during finger extension
flexor digitorum profundus
flexes distal interphalangeal joints
extensor carpi radialis brevis
extends and abducts the hand
extensor pollicis longus and brevis
extends the thumb
fixator
Muscle that stabilizes the origin of another muscle.
antagonist
Muscle that opposes and reverses the action of another muscle.
synergist
Muscle that is primarily responsible for bringing about a particular movement.
agonist (prime mover)
Muscle that aids another by promoting the same movement.
FALSE
True/False
A pair of tweezers is a good example of a second-class lever. True/False
FALSE
True/False
Although all skeletal muscles have different shapes, the fascicle arrangement of each muscle
is exactly the same. True/False
FALSE
True/False
Both first- and second-class levers operate at a mechanical disadvantage. True/False
True
True/False
Muscles are only able to pull, they never push.
TRUE
True/False
Regardless of type, all levers follow the same basic principle: either mechanical advantage or mechanical disadvantage.
mechanical advantage
effort farther than load from fulcrum
mechanical disadvantage
effort nearer than load to fulcrum
True
True/False
The buccinator muscle compresses the cheek and is well developed in nursing infants.
True
True/False
Muscles that help maintain upright posture are fixators.
True
True/False
Deep muscles of the thorax promote movements for breathing.
False
True/False
The deltoid is a prime mover of the arm that acts in adduction.
True
True/False
The soleus is a synergist of the gastrocnemius during plantar flexion.
False
True/False
Muscles that help to maintain posture are best described as synergists.
True
True/False
In order to propel food down to the esophagus, the pharyngeal constrictor muscles are used.
true
true/false
The major head flexors are the sternocleidomastoid muscles, with the help of the muscles
attached to the hyoid bone.
true
True/false
The arrangement of a muscle's fascicles determines its range of motion and power.
True
True/False
Muscle power depends mostly on the total number of muscle fibers (cells) in the muscle.
achilles (calcaneal) tendon
What is the largest tendon in the body?
diaphragm
The ____ flattens and moves inferiorly during inspiration
erector spinae
Muscle spasms of the back often are due to the ____ ____ contraction.
hyoid bone
Muscles connecting to the ___ ___ are important for swallowing and speech.
True
True/False
The muscles of facial expression insert into skin or other muscles, not bones.
true
True/False
Most superficial thorax muscles are extrinsic shoulder muscles.
the difference in the positioning of the effort, load, and fulcrum
What is the major factor controlling how levers work?
What is the major factor controlling how levers work?
the difference in the positioning of the effort, load, and fulcrum
Which of the following is NOT a muscle primarily involved in the breathing process?
A) diaphragm
B) latissimus dorsi
C) external intercostal
D) internal intercostal
latissimus dorsi
What is the main factor that determines the power of a muscle?
the total number of muscle fibers (cells) available for contraction
What is a muscle that provides the major force for producing a specific movement called?
an agonist (prime mover)
When the term biceps, triceps, or quadriceps forms part of a muscle's name, what does it tell you about the muscle?
The muscle has two, three, or four origins, respectively.
The most powerful muscle in the body is the ________.
quadriceps femoris
The names of muscles often indicate the action of the muscle. What does the term levator mean?
The muscle elevates.
Which of the following describes the suprahyoid muscles?
They are a group of muscles that lie superior to the hyoid bone and help form the floor of the oral cavity.
The supraspinatus is named for its location on the posterior aspect of the scapula above the spine. What is its action?
to initiate abduction of the arm, to stabilize the shoulder joint and to help prevent downward dislocation of the humerus
Which of the following muscles is involved in producing horizontal wrinkles in the forehead?
the frontal belly of the epicranius
At the grocery store a cute, little curly-haired child is standing behind you in line. You turn around for a moment and she sticks her tongue out at you. Which tongue muscle did she use?
genioglossus
Which group of muscles elevates the first two ribs and flexes and rotates the neck?
the scalenes
Which of the following muscles is involved in crossing one leg over the other to produce the cross-legged position?
the sartorius
Which of the following muscles inserts to the posterior calcaneus via the calcaneal tendon?
the gastrocnemius
If a lever operates at a mechanical disadvantage, it means that the ________.
load is far from the fulcrum and the effort is applied near the fulcrum
Which of the following muscles fixes and depresses the ribs and stabilizes the pelvis during walking?
rectus abdominis
What type of muscle assists an agonist by causing a like movement or by stabilizing a joint over which an agonist acts?
a synergist
Which of the following is NOT a member of the hamstrings?
gracilis
The sternocleidomastoid muscle inserts on the ________.
mastoid process of the temporal bone
In general, a muscle that crosses on the anterior side of a joint produces ________.
flexion
Which of these is NOT a way of classifying muscles?
the type of muscle fibers
Which of the following muscles is NOT a member of the hamstrings group?
A) biceps femoris
B) semimembranosus
C) semitendinosus
D) vastus intermedius
vastus intermedius
Which of the following best describes the orbicularis oris?
It closes, purses, and protrudes the lips.
Which muscle group is involved when a "pulled groin" occurs?
thigh adductors
What are the levers that operate at a mechanical advantage called?
power levers
Which muscle(s) is (are) contracted to exhale forcibly?
internal intercostals and rectus abdominus
Paralysis of which of the following would make an individual unable to flex the thigh?
iliopsoas and rectus femoris
First-class levers ________.
in the body can operate at a mechanical advantage or mechanical disadvantage, depending on specific location
What do the genioglossus, hyoglossus, and styloglossus muscles have in common?
All act on the tongue.
If L = load, F = fulcrum, and E = effort, what type of lever system is described as LEF?
third-class lever
Which of the following muscles is a flexor of the thigh?
adductor magnus
Which of the following muscles is involved in inversion at the ankle joint?
tibialis anterior
Which of the following muscles serves as a common intramuscular injection site, particularly in infants as the buttocks and arm muscles are poorly developed?
the vastus lateralis
Paralysis of which of the following muscles would make an individual unable to flex the knee?
hamstring muscles
Which of the following muscles does NOT act in plantar flexion?
popliteus
________ is a powerful forearm extensor.
Triceps brachii
The ________ is known as the "boxer's muscle."
serratus anterior
The ________ runs deep to the internal oblique.
transversus abdominis
The ________ helps keep food between the grinding surfaces of the teeth during chewing.
buccinator
The ________ tightens the neck and draws the corners of the mouth downward as in expressing horror.
platysma
The ________ is the main chewing muscle.
masseter
The abnormal protrusion of the small intestine through a weak point in the muscle of the abdominal wall is called a ________.
hernia
The quadriceps femoris is composed of three "vastus" muscles and the ________.
rectus femoris
The ________ is a synergist of the latissimus dorsi; it extends, medially rotates, and adducts the humerus.
teres major
The ________ extends the great toe.
extensor hallucis longus
From superficial to deep, order the transversus abdominis, external oblique and internal oblique muscles. Describe the orientation of the muscle fibers for each of these as well as for the rectus abdominis muscles.
Fibers of the external oblique muscle run downward and medially (like outstretched fingers in pants pockets) and at right angles to those of the internal oblique that runs just deep to it. Under these is the transversus abdominis whose fibers run horizontally across the abdomen at an angle to both oblique muscles. The rectus abdominis muscles run medially from the pubis to the rib cage.
Bodybuilders are known for their "great quads." Describe the quadriceps muscles.
These are the muscles of the front and sides of the thigh, and include the rectus femoris and the lateral, medial, and intermediate vastus muscles.
A woman mentions to her friend that another person on the beach has "great abs." What is she talking about?
The woman is referring to well-developed rectus abdominis muscles. This is a term coined by bodybuilders and refers to the bulging muscles between the tendinous intersections.
How does an antagonist differ from a prime mover (agonist)? How is it the same?
A prime mover is the muscle that causes the desired movement to occur. An antagonist is a muscle that opposes the action of the prime mover in a given movement. If, however, the
direction of movement reverses, the former antagonist is now the prime mover and the former prime mover is now the antagonist.
An elderly woman, with extensive osteoarthritis of her left hip joint, entered the hospital to have a total hip joint replacement (prosthesis implantation). After surgery, her left hip had to be maintained in abduction to prevent dislocation of the prosthesis while healing was occurring. An abduction pillow was used to keep the legs apart, especially when lying on her side. Name the abductor muscles and describe the action of each that need to be strengthened in order to help maintain abduction.
Gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus. These muscles originate on the pelvis; they act as major extensors of the thigh and abduct and rotate the thigh as well. The tensor fascia lata also abducts the thigh.
A wide receiver for a college football team pulled a hamstring muscle. What muscles could be affected and what would the effect be?
The muscles include the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus. They are important flexors of the leg and extensors of the thigh. Injuries here could make it impossible to run properly or to extend the thigh.
How can a lever system work at a mechanical disadvantage but still be of use to us?
A lever that operates with the load far from the fulcrum and the effort applied near the fulcrum is operating at a disadvantage in terms of power, but the advantage is that the load can move over large distances at a rapid rate. Wielding a shovel is an example.
The muscle tissue type that consists of single, very long, cylindrical, multinucleate cells with very obvious striations is:
skeletal muscle only
Which one of the following does NOT compress the abdomen:
A) rectus abdominis
B) internal oblique
C) latissimus dorsi
D) external oblique
E) transversus abdominis
external oblique
Neurotransmitters are released upon stimulation from a nerve impulse by the:
sarcolemma of the muscle cell