ap bio -- unit 5: cell communication
1/44
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Prophase
nucleus begins to break down. spindle fibers begin to form. DNA is condenses around histones into visible chromosomes. this is the first phase of mitosis.
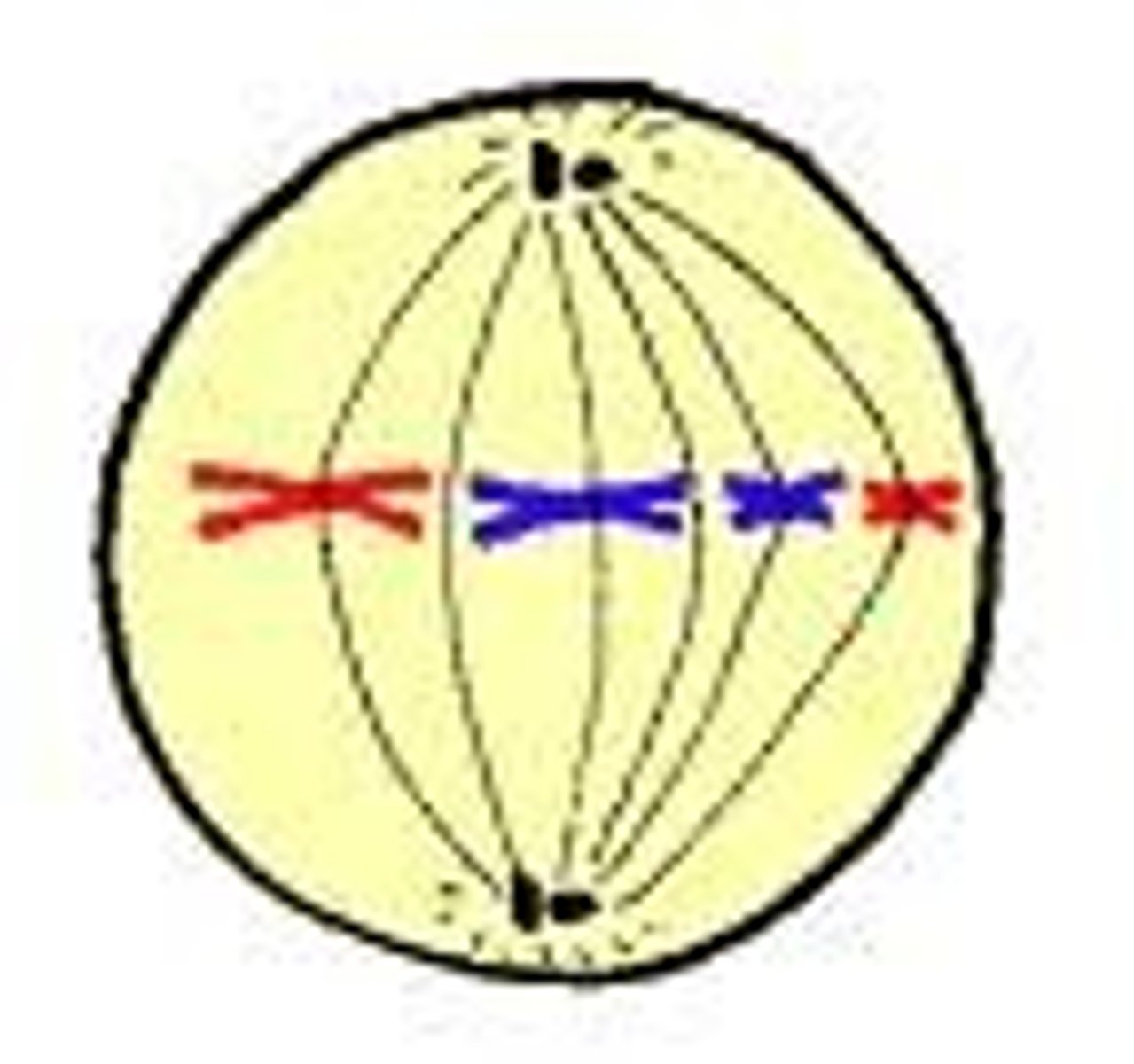
Metaphase
the duplicated chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. the spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes. a check point takes place.
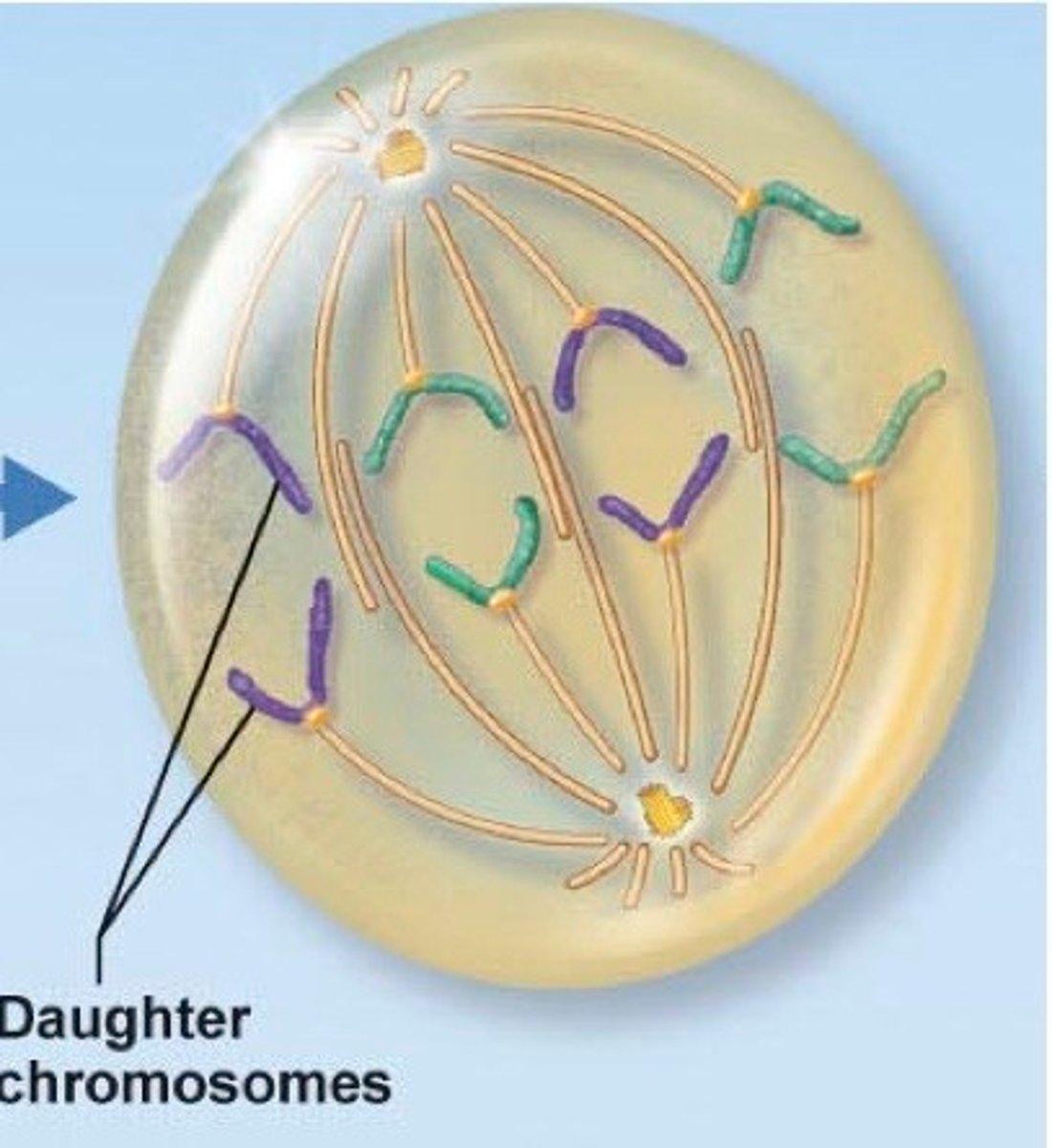
Anaphase
the sister chromatids are pulled apart from one another. the are pulled to opposite poles of the cell by spindle fibers
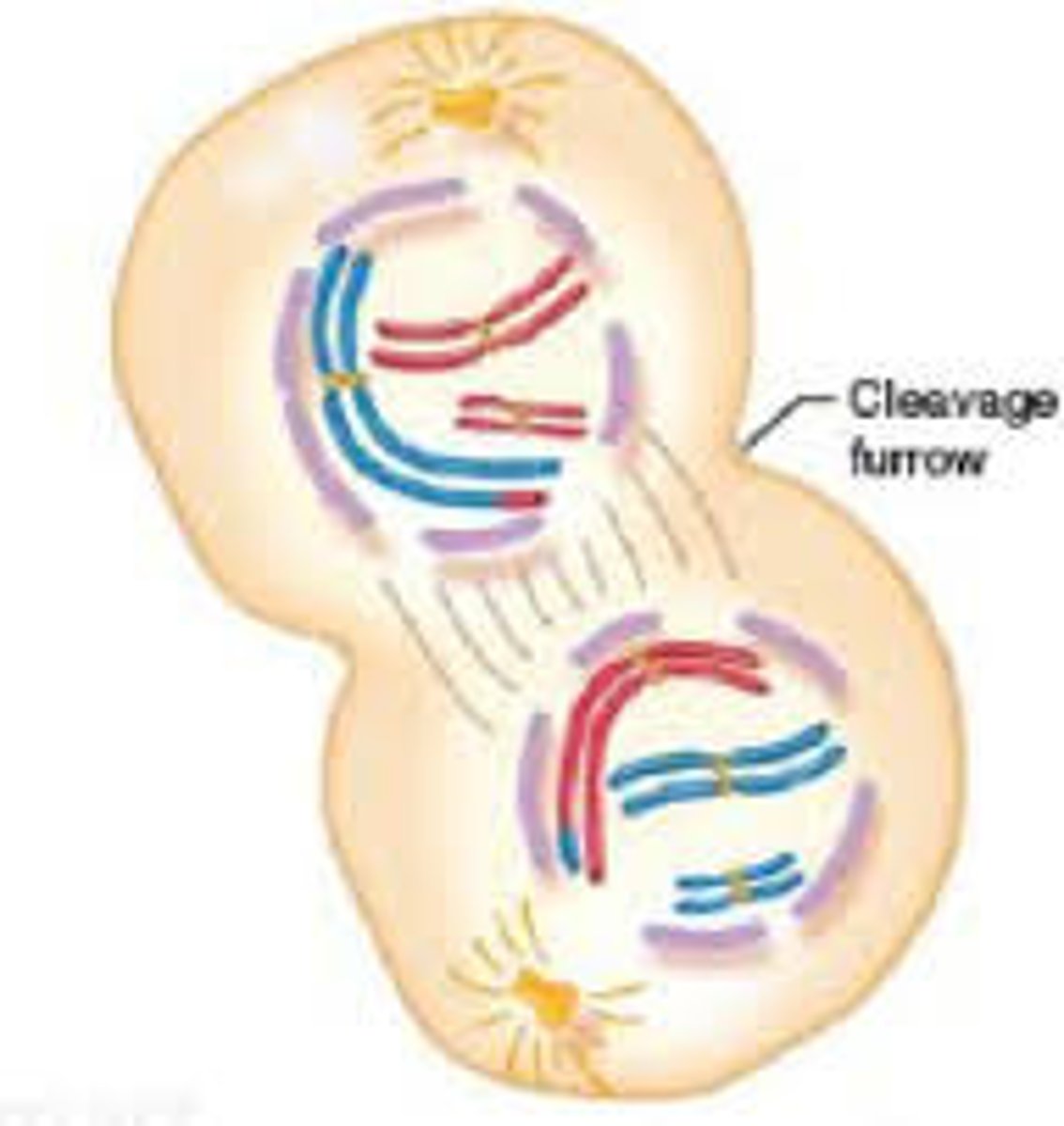
Telophase
This stage is the opposite of prophase. two nuclei are rebuilt, spindle fibers are broken down and the chromosomes decondenses. This is the end of mitosis
Mitosis
A type of cell division in which each daughter cell is genetically identical to the parent cell. makes body cells.
Interphase
Includes G1, Synthesis, and G2. The cell grows and DNA is replicated. Cells spend most the time in this phase.
Cytokinesis
cell pinches in on itself to split the cytoplasm in two.
G1
The cell grows, duplicates organelles, make DNA rep proteins
G2
Cell grows, makes proteins for mitosis
S Phase
The cell replicates all DNA.
sister chromatids
identical copies of a chromosome. made during S phase. they are joined together at the center and are eventually separated during mitosis.
Prophase drawing
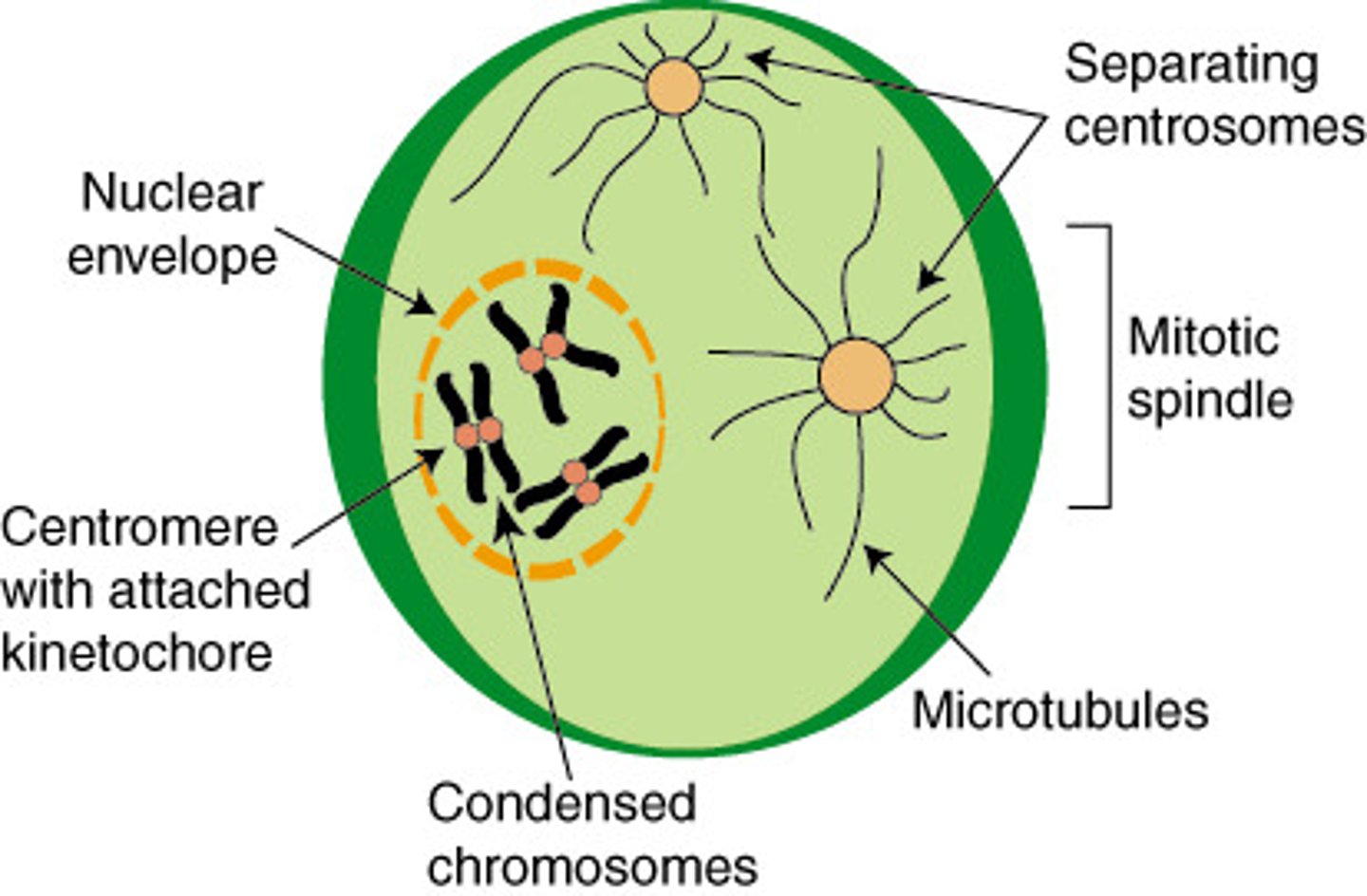
Metaphase drawing
Anaphase drawing
Telophase drawing
Interphase drawing
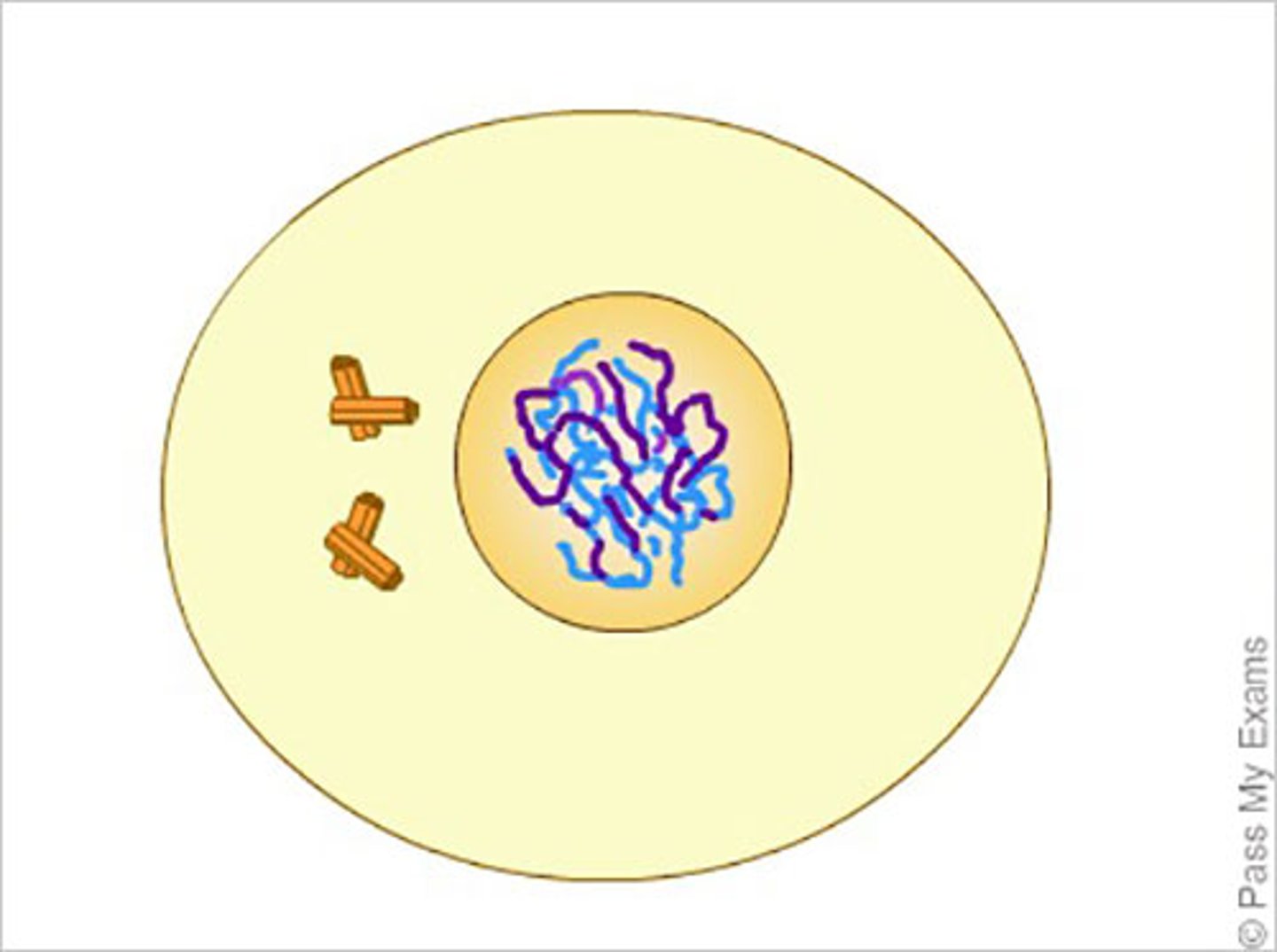
Histones
DNA is wrapped up around these protein molecules so they are condensed and organized.
G1 checkpoint
checks for cell size, nutrients, and DNA damage
G2 checkpoint
checks for cell size; checks that all DNA has been replicated correctly.
G0
The nondividing, resting state of cells. Cell carries out its typical functions in this state. differentiated cells remain in this phase.
M Checkpoint
the cell ensures all sister chromatids are attached to a spindle fiber.
Apoptosis
programmed cell death, initiated if there are mutations or infection
spindle fibers
Protein structures which move the chromosomes during cell division. made of microtubules.
ligase
An enzyme that connects two fragments of DNA to make a single fragment, joins okazaki fragments
Okazaki fragments
Small fragments of DNA produced on the lagging strand during DNA replication
DNA polymerase
Enzyme involved in DNA replication that joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule
primase
An enzyme that adds RNA nucleotides to indicate the starting region for replication
Topoisomerase
corrects "overwinding" ahead of replication forks by unraveling the DNA double helix
antiparallel
The opposite arrangement of the sugar-phosphate backbones in a DNA double helix. they run in opposite directions
ligand
A molecule that binds specifically to a receptor site of another molecule.
Recpetor
protein that detects a signal molecule and performs an action in response
Phosphorylation cascade
A series of enzyme-catalyzed phosphorylation reactions commonly used in signal transduction pathways to amplify and convey a signal inward from the plasma membrane.
Responses to cell signaling
turn a gene on or off, apoptosis, undergo mitosis
Plasmadesmata
an open channel in a plant cell wall that connects the cytoplasm of adjacent cells
gap junctions
provides cytoplasmic channels between adjacent animal cells
Homeostasis
A tendency to maintain a balanced or constant internal state; the regulation of any aspect of body chemistry, such as blood glucose, around a particular level
positive feedback loop
feedback loop that causes a system to change further in the same direction; the response amplifies the signal
negative feedback loop
A feedback loop that causes a system to change in the opposite direction from which it is moving; WEAKENS THE STIMULUS
signal amplification
turns one signal molecule into multiple second messenger molecules; happens during transduction
Second messenger
A small, nonprotein, molecule or ion, such as calcium ion or cyclic AMP, that relays a signal to a cell's interior in response to a signal received by a signal receptor protein.
G protein
a protein coupled to a receptor; conveys messages to other molecules when a ligand binds with and activates the receptor
adenylyl cyclase
Converts ATP to cyclic AMP in response to an extracellular signal.
Kinase
an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to a specified molecule.
Cyclin
one of a family of closely related proteins that regulate the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells by binding to CDKs
CDK
Cyclin-dependent kinases. A protein kinase that is active only when attached to a particular cyclin. Activity rises and falls depending on the concentration of the cyclin partner.