Bio 232: Exam 4
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/589
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
590 Terms
1
New cards
the synapse
neuron - neuron communication
2
New cards
Multiple bits of information to a
single neuron
3
New cards
spinal motor neuron
Soma
4
New cards
Presynaptic Neuron
“sending” impulse towards synapse
5
New cards
postsynaptic neuron
“receiving” impulse away from synapse
6
New cards
chemical synapses:
step 1: presynaptic cell
step 1: presynaptic cell
electrical signal at axon terminal
depolarization
Open VG Na+ & Ca2+ channels
depolarization
Open VG Na+ & Ca2+ channels
7
New cards
chemical synapses:
step 2: NT released by exocytosis
step 2: NT released by exocytosis
synaptic vesicles fuse w/ membrane
release NT to synaptic cleft
release NT to synaptic cleft
8
New cards
NT released by
exocytosis
9
New cards
chemical synapses:
step 3: postsynaptic cell
step 3: postsynaptic cell
NT binds to NT receptor
10
New cards
chemical synapses:
step 4: NT/NT receptor channels open
step 4: NT/NT receptor channels open
conformational change - opens
ions flow changes membrane potential (graded)
excitation or inhibition
ions flow changes membrane potential (graded)
excitation or inhibition
11
New cards
signal size
higher frequency at the presynaptic neuron
12
New cards
higher frequency at the presynaptic neuron =
more NT released
13
New cards
Bigger electrical signal at
postsynaptic membrane
14
New cards
chemical synapses - review
step 1
step 1
electrical signal - presynaptic
VG Na+ and Ca2+ increases in Ca2+
VG Na+ and Ca2+ increases in Ca2+
15
New cards
chemical synapses - review
step 2
step 2
NT released by exocytosis - presynaptic
synaptic vesicles fuse with membrane
synaptic vesicles fuse with membrane
16
New cards
chemical synapses - review
step 3
step 3
post synaptic cell - NT binds to NT receptor
17
New cards
chemical synapses - review
step 4
step 4
post synaptic cell - receptor channel opens
changing MP of postsynaptic neuro
changing MP of postsynaptic neuro
18
New cards
gap junction =
electrical junction
19
New cards
drugs (toxins) block release of
NT - presynaptic cell
20
New cards
drugs block release of the
vesicle containing the NT
21
New cards
example of blocking NT at neuromuscular junction
Neurons controlling muscles “motoneurons”
NT and ACh
neuron releases ACh to muscle
NT and ACh
neuron releases ACh to muscle
22
New cards
termination of NT response is a __________ response
transient (temporary)
23
New cards
If the process f termination was not transient
paralysis
24
New cards
termination:
enzyme degrades
enzyme degrades
at synaptic cleft or postsynaptic neuron
25
New cards
termination:
“reuptake”
“reuptake”
of NT by presynaptic neuron
26
New cards
Termination:
diffusion of NT
diffusion of NT
out of synaptic cleft
dilution of the NT
dilution of the NT
27
New cards
Excitatory Post Synaptic Potential
depolarization
28
New cards
small stimulus - EPSP
small depolarization in PSC
no AP as K+ flows out (LEAK CHANNELS) prevents excessive '“+” charge in cell
no AP as K+ flows out (LEAK CHANNELS) prevents excessive '“+” charge in cell
29
New cards
small or below threshold
no AP
30
New cards
large stimulus
EPSPs move down dendritic process/cell body to axon hillock - graded potential
generate an AP on the axon (LARGER POSITIVE CHARGE)
generate an AP on the axon (LARGER POSITIVE CHARGE)
31
New cards
at or above threshold
AP
32
New cards
inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs)
cause hyperpolarization - reduces MP
will not cause an AP at axon
bigger depolarization needed to fire an AP
will not cause an AP at axon
bigger depolarization needed to fire an AP
33
New cards
EPSPs can
summate
add together
add together
34
New cards
Multiple excitatory presynaptic neurons induce EPSPs on
a single postsynaptic neuron
35
New cards
EPSPs are more likely to reach
threshold - induce AP
36
New cards
Axon hillock “integrates” all
EPSPs and IPSPs
37
New cards
Axon hillock “integrates” all EPSPs and IPSPs determines
response
threshold or sub-threshold
threshold or sub-threshold
38
New cards
example of integration
graded potential
39
New cards
criteria 1 for a NT
NT present presynaptic terminal and released w/stim
40
New cards
criteria 2 for a NT
NT applied to postsynaptic neuron produces response (EPSP or IPSP)
41
New cards
criteria 3 for a NT
natural mechanism exist to terminate response
42
New cards
if all 3 are met,
substance is a NT
43
New cards
new messenger
nitric oxide (NO)
nitric oxide (NO)
diffuses across membranes
44
New cards
new messengers (NTs) ________ neuron to _________ neuron
postsynaptic neuron to presynaptic neuron
45
New cards
new messengers:
retrograde signal
retrograde signal
helps us understand learning/memory in “long term potentiation”
46
New cards
NO is released and goes to
PSN
47
New cards
NT ACh
Causes muscles to contract
If stim, ACL will release into the synaptic cell
Transient
48
New cards
glutamate
depolarization (excitatory)
49
New cards
GABA
hyperpolarization (inhibitory)
50
New cards
ACh
binds to 4 different Ach receptors
51
New cards
ACh neuromuscular junctions
excitatory
52
New cards
ACh cardiac muscle
inhibitory
53
New cards
channel-linked receptors
ionotropic or metabotropic
ionotropic or metabotropic
ionotropic
54
New cards
G Protein-linked NT receptors
ionotropic or metabotropic
ionotropic or metabotropic
metabotropic
55
New cards
channel-linked receptors
direct or indirect
direct or indirect
direct
56
New cards
G Protein-linked NT receptors
direct or indirect
direct or indirect
indirect
57
New cards
Channel-linked receptors - direct action
open an ion channel
allows ion to cross membrane
allows ion to cross membrane
58
New cards
channel-lined receptors
rapid or slow
rapid or slow
rapid response localized, brief
59
New cards
G Protein-linked NT receptors - indirect action
via second messenger
60
New cards
G Protein-linked NT receptors
rapid or slow
rapid or slow
slow response, prolonged, complex
61
New cards
facilitated zone
subthreshold stim
stim from other sources can induce AP
stim from other sources can induce AP
62
New cards
discharge zone
closely lined to presynaptic input
likely to reach threshold
likely to reach threshold
63
New cards
circuits
pattern of connections of neuronal pools
64
New cards
divergence
amplification
single sensory receptor
single sensory receptor
65
New cards
divergence - single sensory receptor
up signal cord and multiple brain regions at once
66
New cards
convergence - multiple presynaptic inputs
concentrated effect
67
New cards
convergence increases
response
68
New cards
convergence results
multiple stimuli causes same response
69
New cards
Example of convergence with a new mother
loving feeling
sound, seeing, and hearing her baby
sound, seeing, and hearing her baby
70
New cards
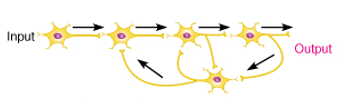
what circuit is this
reverberating or parallel
reverberating or parallel
71
New cards
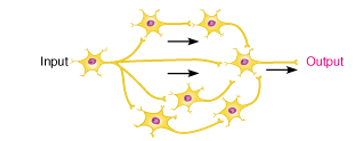
what circuit is this
reverberating or parallel
reverberating or parallel
72
New cards
serial processing
predictable all-or-none manner
73
New cards
neural processing pieces
receptor
sensory neuron
CNS integration
Motor neuron
Effector (muscle)
sensory neuron
CNS integration
Motor neuron
Effector (muscle)
74
New cards
parallel processing
inputs into many different pathways (processed simultaneously)
75
New cards
One stimulus travels through multiple pathways can provide
multiple - unique responses
76
New cards
parallel processing is important in
higher mental function
77
New cards
examples of parallel processing in higher mental function
problem solving or connecting parts to a whole
78
New cards
function of PNS
information conveyed to and from the CNS
79
New cards
PNS includes all
neuronal tissue outside the brain and spinal cord
80
New cards
Everything outside of
CNS is PNS
81
New cards
components of the PNS
1. sensory receptors
2. peripheral nerves (and ganglia)
1. efferent motor ending (from the CNS)
82
New cards
mechanoreceptors
skin (afferent) tip of finger to CNS
mechanical pressures - nerve impulse
mechanical pressures - nerve impulse
83
New cards
thermoreceptors
temperature
84
New cards
chemoreceptors
chemicals in solution
85
New cards
nociceptors
pain damaging stimuli
tissues
tissues
86
New cards
nerve structure is like
a fiberoptic cable
87
New cards
outer coating of nerve
epineurium has blood vessels and fascicles
88
New cards
outer layer of bundle/fascicle
perineurium
89
New cards
each tube inside fascicle iis wrapped in
endoneurium
90
New cards
after endoneurium
myelinated axon
91
New cards
ganglia
neuron cell bodies and supporting cells
92
New cards
Dorsal Root Ganglia
ganglia with afferent nerve fibers - outside back to CNS
touch or pain receptor
touch or pain receptor
93
New cards
Dorsal Root Ganglia cell bodies from
sensory neurons
94
New cards
reflex arcs
reflexes occur over specific neuronal pathways
95
New cards
reflex arcs steps:
step 1:
step 1:
receptor
96
New cards
reflex arcs steps:
step 2:
step 2:
sensory neuron
97
New cards
reflex arcs steps:
step 3:
step 3:
CNS integration center
98
New cards
reflex arcs steps:
step 4:
step 4:
motor neuron
99
New cards
reflex arcs steps:
step 5:
step 5:
effector
100
New cards
receptor
site of stimulation