Cards made from pocket prep
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
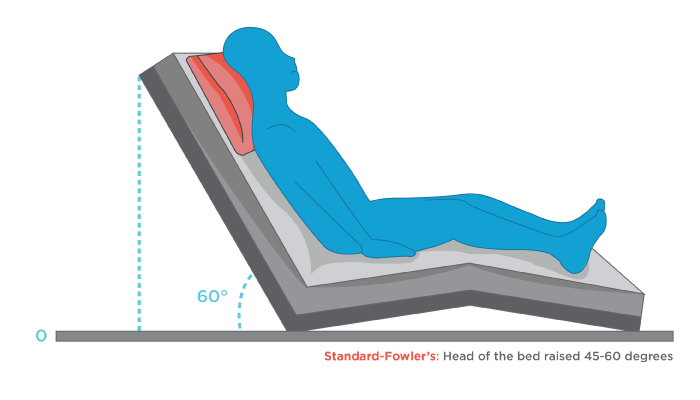
What is the fowler position?
45-60 degree angle is formed from the stretcher
Indicated when patient has chest pain or respiratory distress
Without spinal immobilization or hypotension
What is the first check in the GCS?
Eye opening:
Spontaneous
Sound
Pain
Unresponsive
What is the second check of GCS?
Verbal Response
Oriented
Confused
Inappropriate
Incomprehensible
Unresponsive
What is the third check of GCS
Motor Response
Obeys command
Localizes
Decorticate
Decereberate
Unresponsive

In an MCI, if a patient is able to walk and and have no major injuries what do you label them?
Green

In an MCI, you check RPM,
R: respirations → none after tilt-chin-lift?
→ yes after tilt-chin lift?
Over 30?
P: perfusion → radial pulse absent →
M: mental status → unable to follow commands →
All others →
R: BLACK. RED
RED
P: RED
M: RED
All others: YELLOW/ DELAYED

What are the common nerve agents and what is used to stop them?
VX
Tabun
Sarin
Soman
What to use after exposure to nerve agent
Mark 1 and DuoDote
What are the common vesicants?
Vesicants: blister agents
Lewisite
Mustard gas
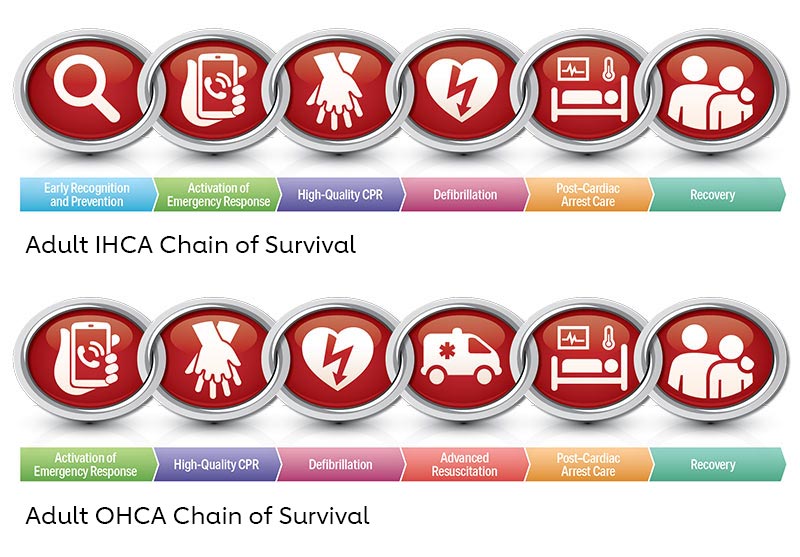
What is the AHA chain of survival?
In children, what are the early and late signs of respiratory distress?
Sign that respiratory problems are impending: Bradypnea
Early: Agitation
Late: Cyanosis, Bradycardia
Signs of Anti-cholinergic (bendaryl) poisoning
HRDBM hardBM →
Hot as a hare
Red as a beet
Dry as a bone
Blind as a bat
mad as a hatter
Causes of altered mental status:
AEIOU-TIPS
Alcohol
Epilepsy
Insulin
Opiates
Uremia
Trauma, Temperature
Infection
Poisoning
Shock
Stroke assessment:
FAST
Face
Arms
Speech
Time
Signs of Intracranial pressure increase
Cushing’s triad
Irregular respiration
Widened pulse pressure
Bradycardia
Pressure on ocular nerve leads to possible change in pupil size
Sign of Abdominal aortic aneurysm
the aorta pops →
Loss of blood pressure
Loos of perfusion → cool skin
How to be safe when entering a helicopter
wait for the pilot to let you know it is safe
Enter from positions 10 and 2

Has important info about transported hazardous material
On a highway transport truck
Bill of Lading:
Chain of command:
Medical director
Incident commander
Liason+Public information officers
Pulmonary edema vs Asthma vs Pulmonary embolism:
Pulmonary edema: Jugular vein distention + Bilateral lower extremity edema
Asthma: prolonged expiratory phase + expiratory wheezing
Pulmonary embolism: Chest pain + shortness of breath
Hypoglycemia symptoms
Hypo→ less
Slow breathing
Weak pulse → leads to faster beat so tachycardia
Pale, cool skin
Altered mental status and rapid onset of symptoms
Acute coronary syndome (ACS): which conditions are categorized in this?
Acute myocardial infarction
Stable and Unstable Angina pectoris
How to perform secondary assessment in 3 steps
SAMPLE OPQRST
Baseline vital signs
Focus on chief complaint physical exam
What is the occlusive dressing for?
prevent air and liquids from entering or exiting a wound
Uses:
To prevent Tension pneumothorax (chest wound)
To prevent mesenteric necrosis and hypothermia (abdominal evisceration)
Prevent peritonitis (Open back wounds)
Prevent mediastinitis (Neck injuries)
What should you first do if you have a patient who is profusely bleeding? 3 steps optional
Apply direct pressure
Apply a pressure dressing
Apply a tourniquet proximal to the injury
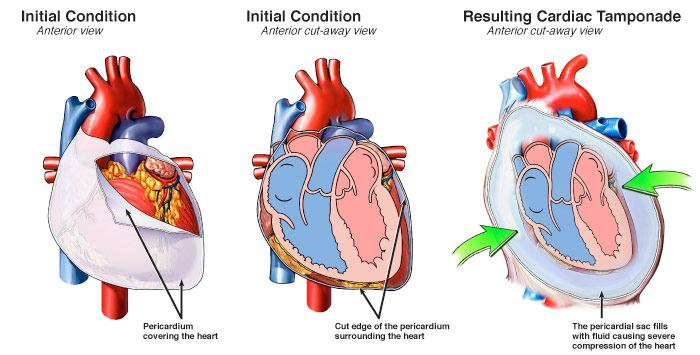
Cardiac tamponade
Why does it happen?
What are symptoms of this?
Fluid buildup around the sac of the heart
Associated with chest trauma
Muffled heart tones, jugular venous distension and hypotension
Can’t pump as well → Can’t hear it pumping, Veins cannot drain blood into the heart, so it backs up, and lack of blood in arteries leads to less pressure.
Nitroglycerine administration and contraindications
List side effects
Vasodilator
Contraindicated for patients with systolic BP less than 90 mmHg
Side effects: Headaches, Hypotension, Tachycardia OR Bradycardia.
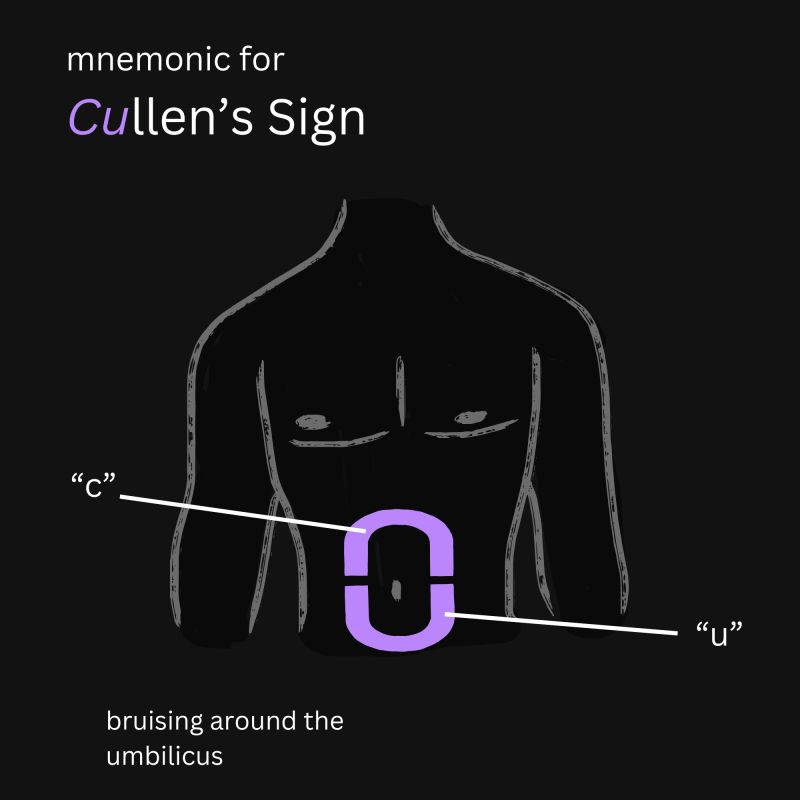
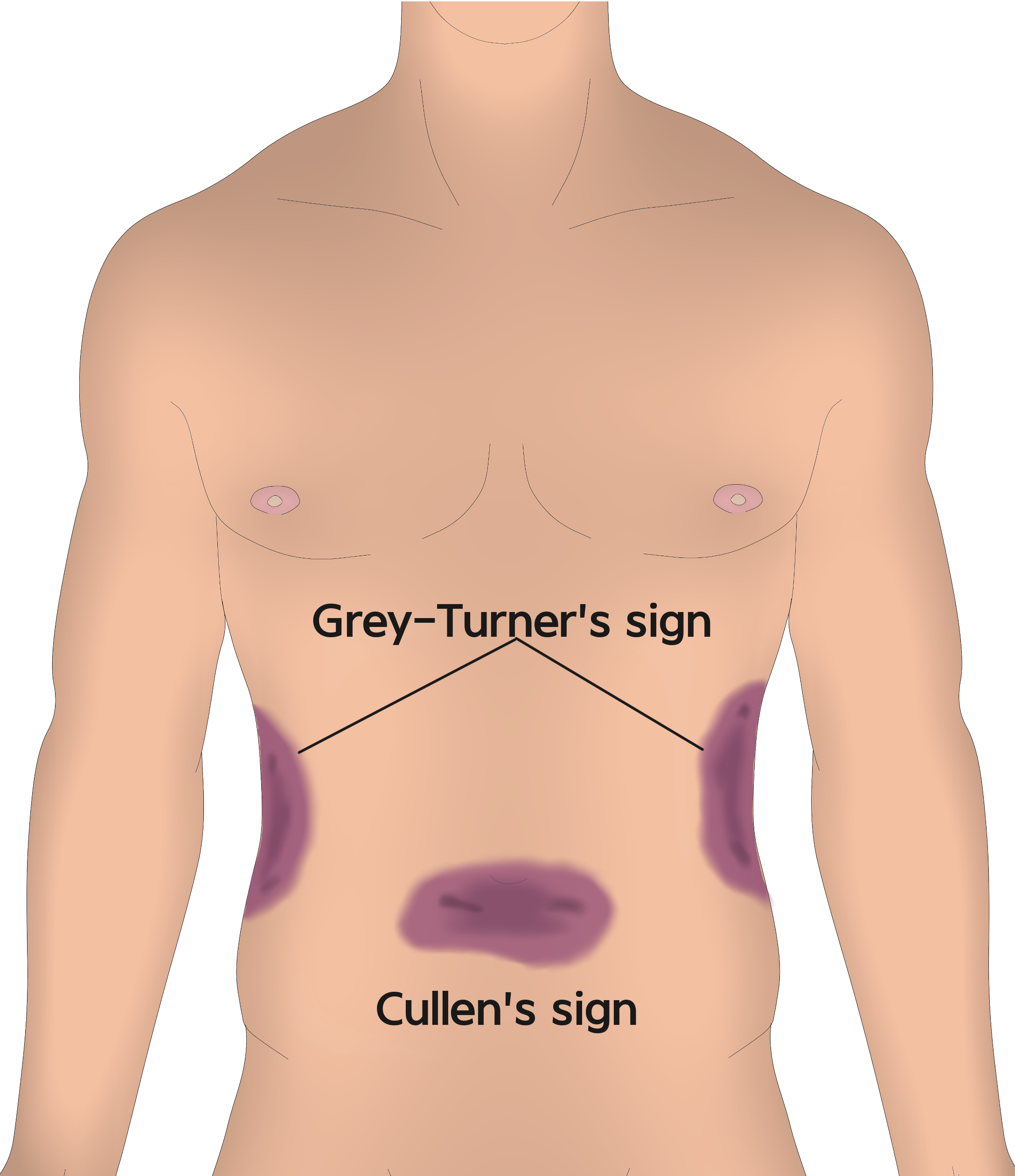
Cullen’s sign?
Bruising around the umbilicus,
sign of intraperitoneal hemorrhage
Pancreatitis or ectopic pregnancy
“Umbilicullen”
Grey-Turner’s sign?
bruising of the flanks
Sign of retro peritoneal hemorrhage
SEVERE pancreatitis
Turn to your side
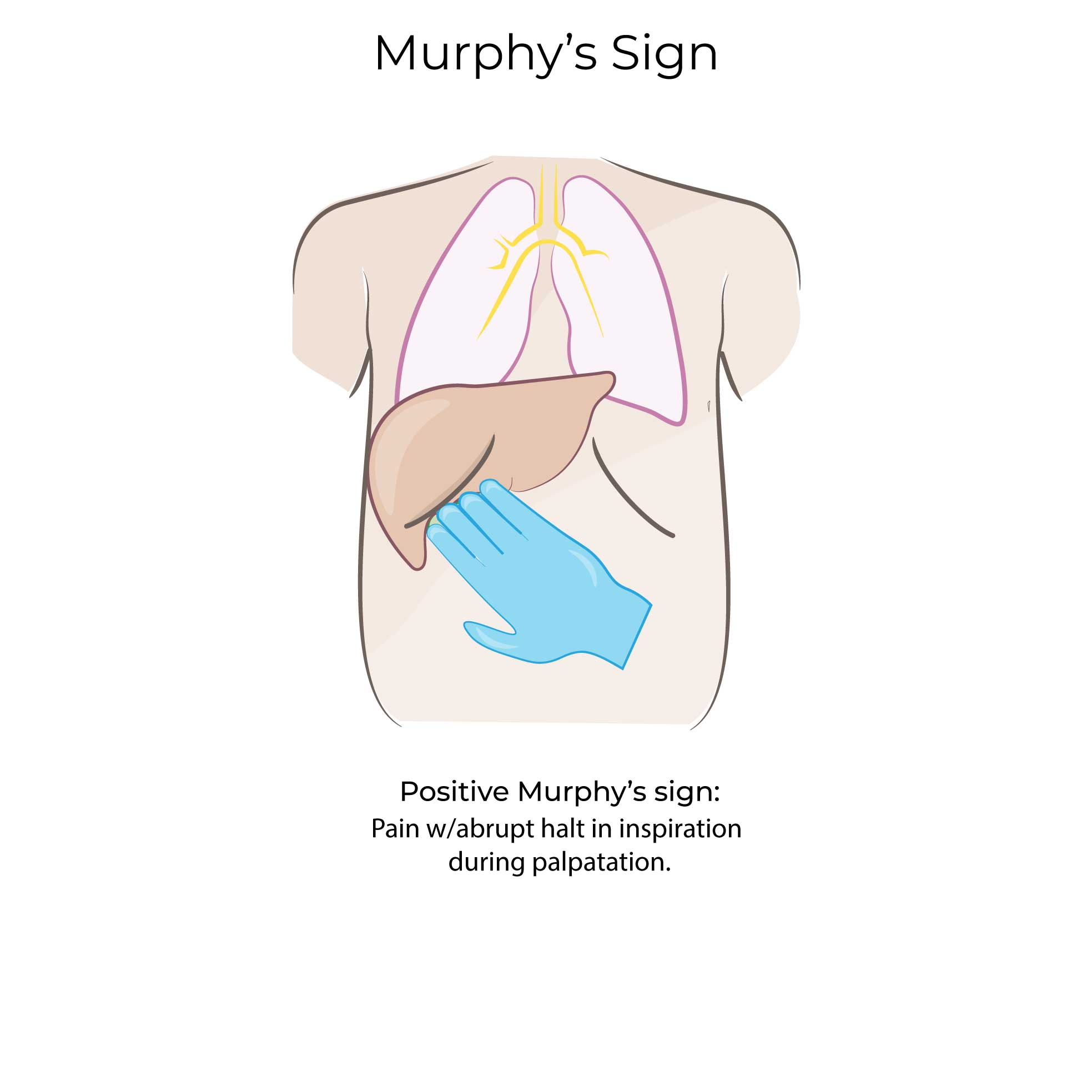
Murphy’s sign
Pain upon palpation of right upper quadrant (RUQ) during inspiration
cholecystitis—inflammation of the gallbladder
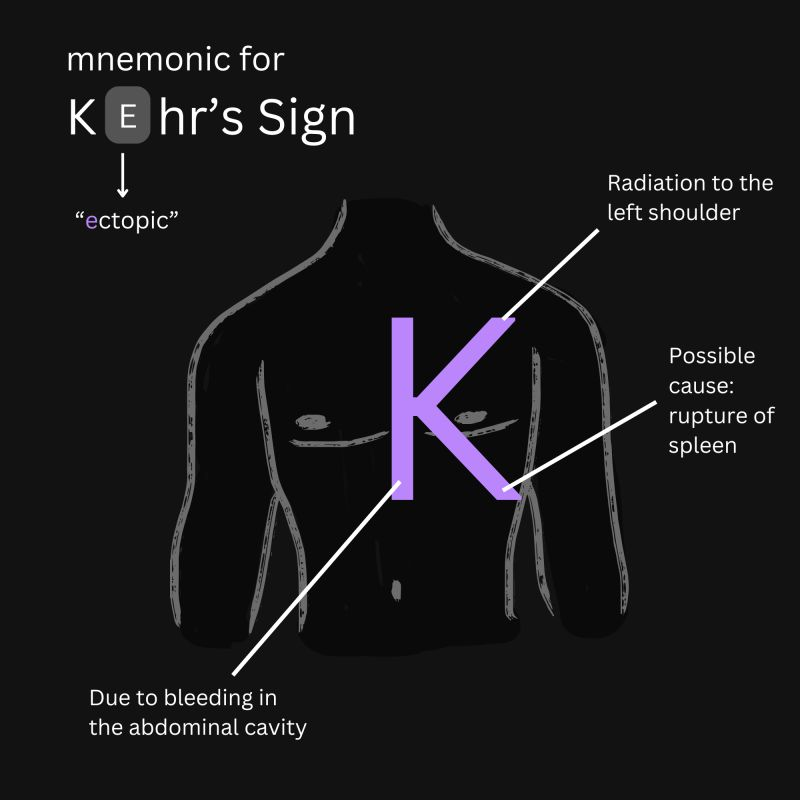
Kehr’s sign?
Pain at the tip of the left shoulder
Intra-abdominal bleeding affecting the spleen
Blood or other fluid enters the peritoneal cavity, irritating diaphragm and then the shoulder
Kehr-bear gives a hug on top of shoulder→ah! my spleen!
OR: Imagine a K on the patient. One line radiates the shoulder. One line goes the to spleen.
What does RICES stand for?
Rest, ice, compression, elevation, splinting
How should a patient be transported while in shock?
Supine
How should a pregnant patient be transported?
On her left side
When is the traction splint mainly used?
Mid-femur fracture
What are the sympathomimetics?
Mimic the Sympathetic nervous system (Dilate pupils, tachycardia, hypertension, seizures, agitation, hyperthermia)
Cocaine
MDMA (ecstasy)
Methamphetamine
Caffeine
Treatment for acute abdomen:
Supplemental oxygen, and Lay on left side to prevent aspiration of vomitus.
Oxygen for possible shock due to internal bleeding.
What is in the LUQ of the abdomen?
Stomach, spleen and part of the pancreas
What is in the RUQ of the abdomen?
Liver, gallbladder, duodenum, and part of the pancreas
What is in the LLQ of the abdomen?
Descending colon and left half of transverse colon
Small intestine
What is in the RLQ of the abdomen?
Appendix, Ascending colon, and right half of transverse colon
Small intestine
How much blood is in the human body?
How much loss results in hypovolemic shock?
Tell Me some signs of Hypovolemia:
6 Liters
10% is generally well-tolerated (tachycardic compensation)
20-25% leads to loss of compensatory mechanism
40% is overt shock (hypotension, decrease cardiac output)
Tachypnea, tachycardia (weak), Hypotension, AMS, cyanosis, cool & clammy skin
Difference between Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS)?
DKA: Normally happens to type 1 diabetics
Blood glucose concentration is lower and ketones are present
HHS: Normally happens to type 2 diabetics due to insulin resistance
Blood glucose concentration is higher and ketones are absent
What is the use of Aspirin?
What is the max dose?
In a patient presenting with suspected acute coronary syndrome, Aspirin inhibits platelet aggregation, which can limit the progression of coronary artery thrombosis and reduce myocardial damage.
324 mg
Do not give it to children
Don’t give it to asthmatics, causes bronchoconstriction
What is the use of Nitroglycerin?
What is the max dose?
Used for ischemic chest pain relief. It is contraindicated for patients who have taken phosphodiesterase inhibitors (PDE5) like cialis or viagra
1.2 grams or three 0.4 mg tablets
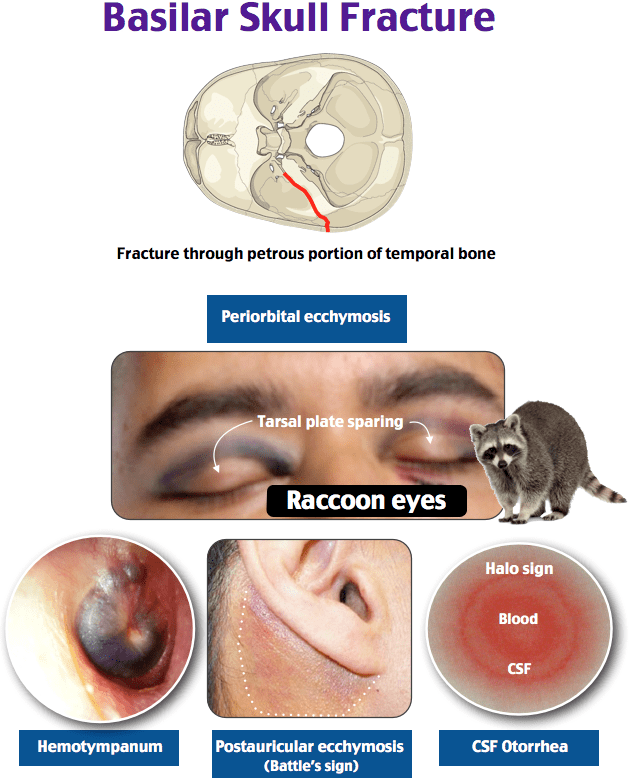
What are the signs of a Basilar Skull Fracture?
Cerebrospinal Fluid Otorrhea (Clear fluid from ears)
Hemotympanum (blood behind tympanic membrane
Retroarticular Ecchymosis (Battle Sign or Mastoid bruising)
Periorbital Ecchymosis (Raccoon eyes)
CHRP → “Chirp” → With the ears that were fractured in the petrosal, you hear a chirp
What are the signs of a Hemothorax
Diminished breath sounds
Asymmetrical chest movement
Tachycardia
Shortness of breath
“DATS a hemothorax”
What are some signs of Hypoglycemia?
Neuroglycopenic symptoms due to insufficient glucose in the brain:
Confusion
Slurred speech
Also: Seizures, coma, irritability, difficulty speaking
Adrenergic activation:
Pale, Cool, Diaphoretic Skin
Tremors, anxiety, tachycardia
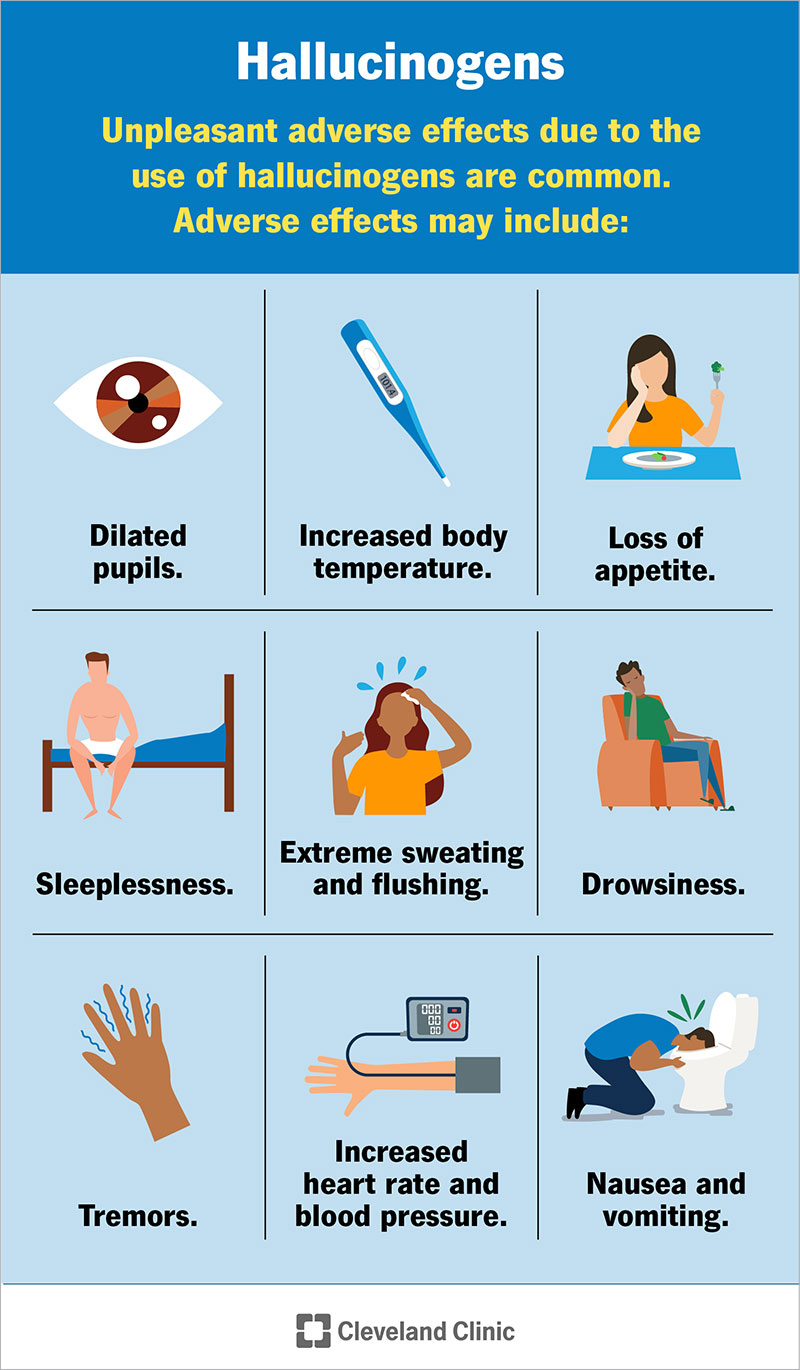
What are some signs of hallucinogenic intoxication?
Dilated pupils
Hypertension
Warm, Dry skin
Also: Tachycardia
When should you start CPR on an unresponsive infant?
When there is no palpable pulse or when the pulse is less than 60 bpm
What is the bends and the squeeze?
Scuba diving condition:
The bends: Decompression sickness
The squeeze: descent pains
Compare the airway of a pediatrics and adults
Children: have smaller trachea, faster respirations, Larger tongue, rely on diaphragm more to breath
Adults: Use chest muscles more for breathing
What is the target oxygen saturation of these three conditions?
ACS:
Stroke:
Post-cardiac arrest:
ACS: 90%
Stroke: 95% to 98%
Post-cardiac arrest: 92% to 98%
What are causes of obstructive shock?
Tension pneumothorax
Cardiac tamponade (Fluid buildup prevents heart from filling with blood)
Pericardial effusion (Just fluid buildup)
What is the operations section of the ICS?
Manages tactial, hands on activities during an incident
Traige, treatment, transport, rescue
What is the command staff section of the ICS?
Handles information, safety, and inter-agency coordination
Liaison officer
Incident commander
Public information officer
Safety officer
The command staff has a lisp
What is the planning section of the ICS?
Analyzes document information, tracks resources and status, and produces the Incident Action Plan (IAP).
Decision making
What is the Finance/Adminstration section of the ICS?
Manages costs, timekeeping, contracts/procurement, and reimbursement/claims
What is burn shock and when does it occur?
Capillary leakage leads to poor perfusion
After 30% of total body surface area (TBSA) is affected by burns.
Pulse becomes weak
Normal response to full-thickness burn would be leathery but not weak pulse.