17.1-17.3 Quiz
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What is a buffer?
consists of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base
How to determine salt & weak acid that make buffers?
common ion + WB and WA; are not strong acids/bases
Equilibrium equation for a weak acid
WA + H2O ←→ H3O+ + A-

How does the addition of an acid to an equilibrium will affect the concentrations of ions?
H+ is added and X- is consumed to produce HX; pH does not significantly change; shifts to produce more WA
How does the addition of a base to an equilibrium will affect the concentrations of ions?
OH- reacts with HX to produce X- and water; no significant pH change; more conjugate base (X-) is made
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
use to relate pKa to pH and pH to the initial concentration of the WA and CB
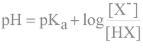
When are pH and pKa equal?
at ½ of the equivalence point
What is the relationship between pH and pKa?
pH is within ± 1 unit of pKa in a (ideal) buffer
How can you determine the combination of WA and CB that has the greatest buffering capacity?
the greater amounts of conjugate acid-base pair (molar concentration); most effective within 1 pH unit of pKa
Buffer Capacity
the amount of acid or base neutralized by the buffer before there is a significant change in pH
SA/SB titrations curve
initial pH = 1; sharp and long Inflection points; equivalence point is 7
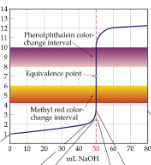
WA/SB titrations curve
initial pH between 2 and 3; excess of acid before equivalence point; smaller Inflection point; equivalence point around 8
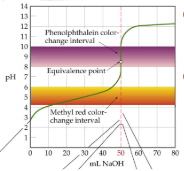
Stronger the acid with _____ the inflection point
longer
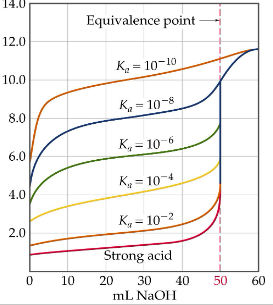
How do you determine the initial concentration of the given solution?
WA- use Ka to determine initial pH since solution only contains weak acid; pH of the dissociation of the acid/base
Given a list of indicators, which would be the best one for the titration?
dramatic color change in the desired range; phenolphthalein
How do you determine the hydronium ion concentration or pH of the solution after x mL of acid or base has been added to the solution of known volume and molarity?
do neutralization; find moles of each; BCA charts to determine what is in excess; find total volume; find molarity of excess substance; find pH or pOH then pH
What is the pH at the equivalence point in the titration?
SB/SA- pH = 7.00; WA/WB- pH > 7.00 (around 8.00)
titration curve
plot of pH vs. volume of acid/base added
equivalence point
point at which the acid and base are present in stoichiometric quantities
End point
observed point
titration error
different between equivalence point and end point
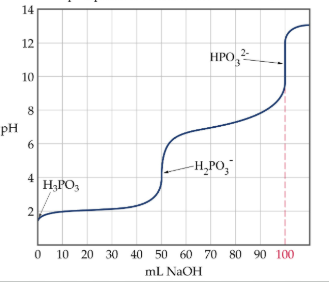
Polyprotic Acid Titrations
each ionizable proton dissociates in steps; n equivalence point corresponding to each ionizable proton