OPT 224 Drugs Affecting the Pupil
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
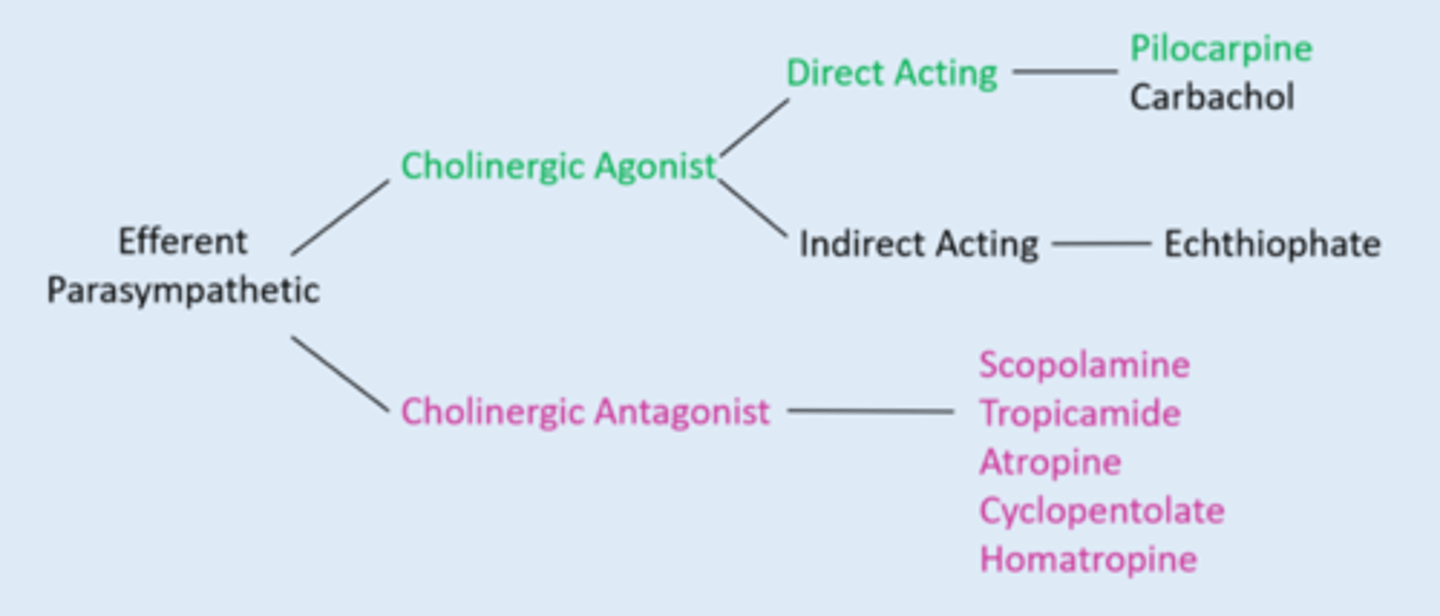
What is the 1 miotic / cholinergic agonist?
pilocarpine
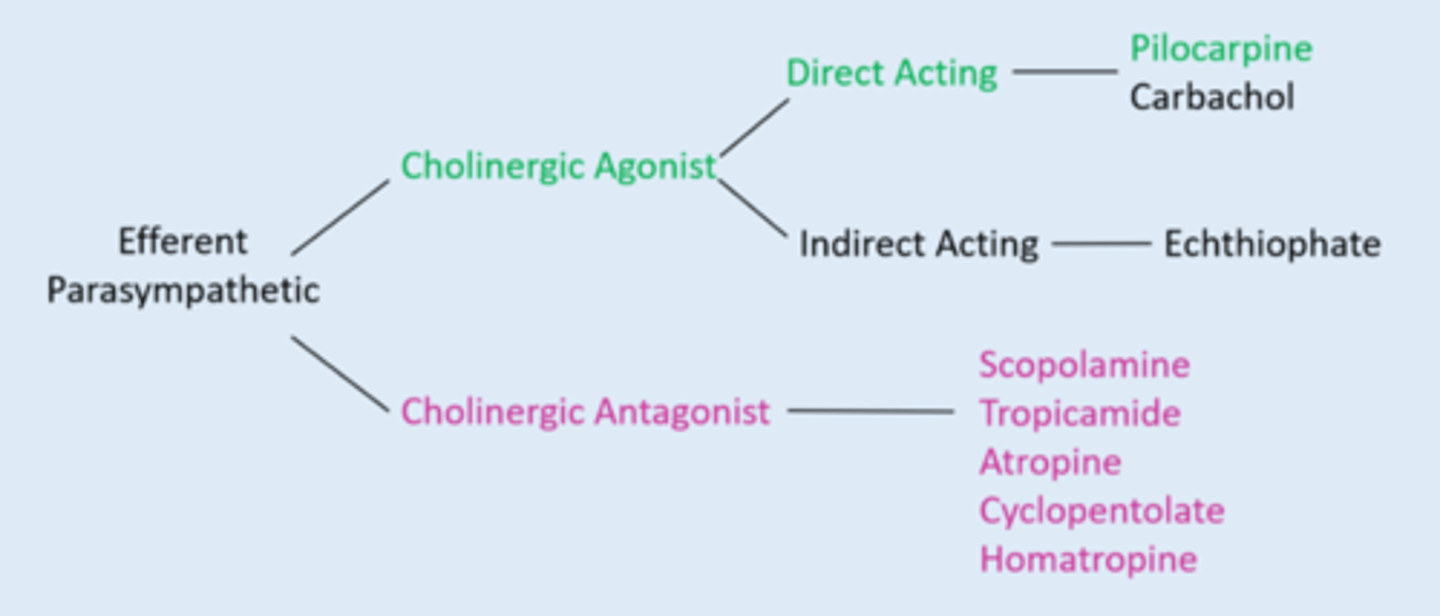
What are the 5 cycloplegic / cholinergic antagonists?
scopolamine
tropicamide
atropine
cyclopentolate
homatropine
What are the 3 mydriatics / adrenergic agonists?
phenylephrine
hydroxyamphetamine
cocaine
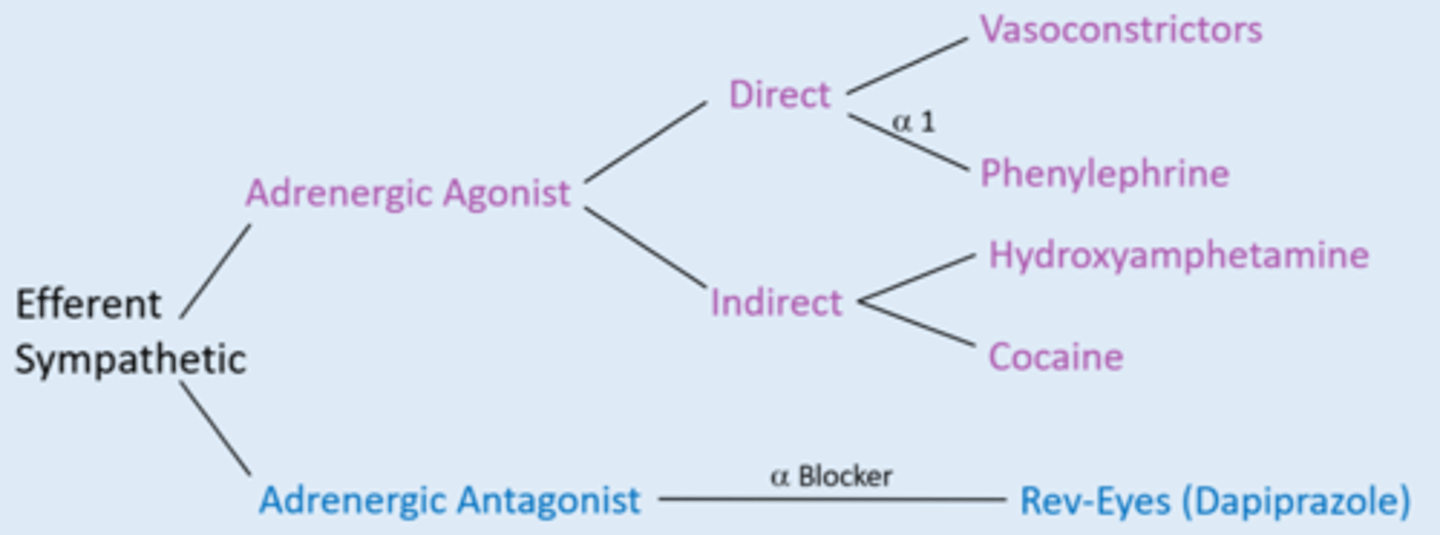
What is the 1 mydriolytic / adrenergic antagonists?
dapiprazole
Which CN is involved in the parasymp efferent pupillary pathway?
CN III
Explain the parasymp efferent pupillary pathway.
EW nucleus = preganglionic fibers synapse at ciliary ganglion = ACh = postganglionic fibers synapse on iris sphincter mm and CB = ACh
Explain the symp efferent pupillary pathway.
hypothalamus = 1st synapse in sp cord = preganglionic neuron synapses at sup cervical ganglia = ACh = postganglionic neuron enters cavernous sinus to join CN V = synapse on iris dilator mm, Muller mm, conj arterioles, face sweat glands = NE
What is the MOA and eye effects of pilocarpine (Vuity)?
muscarinic cholinergic agonist = iris sphincter contracts, CB contracts:
pupil constricts
accom
increased aq outflow (opens TM)

What are the 6 main diseases treated by pilocarpine?
1. POAG
2. ocular hypertension
3. acute angle closure glaucoma
4. pigmentary dispersion glaucoma
5. Dx Adie's pupil, CN 3 palsy
6. presbyopia

Explain how we use pilocarpine to treat primary open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension.
QID or less = CB contracts = pulls on scleral spur = pulls on TM = TM opens = increased aq outfow = IOP decreases 15-25%
NOTE: not as common for tx as there are better drops now

What is the pilocarpine dose used for primary open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension?
QID or less (start QID with low [ ] and can increase [ ] as needed)
![<p>QID or less (start QID with low [ ] and can increase [ ] as needed)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/48e6bcc6-5f7c-4d19-bd9f-3882928ae319.jpg)
Pt's on pilocarpine will have trouble with _______________.
dilation

What is the dose of pilocarpine used to treat acute angle closure glaucoma?
1 gt up to TID over 30min
NOTE: not as common for tx as there are better drops now

When can we NOT use pilocarpine to treat acute angle closure glaucoma?
IOP > 50mmHg bc iris is ischemic and won't respond to pilocarpine

Explain how we use pilocarpine to treat pigment dispersion glaucoma.
iris moves away from lens zonules = no longer rubs on zonules = prevents release of iris pigment

Explain how we use pilocarpine to treat presbyopia.
pupil constricts = increased depth of field = VA improves 3 lines, only 1 line of distance VA lost
What is the dose of pilocarpine used to treat presbyopia?
1 gt OU 1-2x daily
What is present in the vehicle of Vuity pilocarpine that makes it so comfortable?
pHast technology = adjusts to pt's physiologic pH
What are some side effects of pilocarpine?
miosis
accom spasm = blur
HA
conj hyperemia
RD (esp high myopes)
AC shallowing due to iris diaphragm moving forward
BAB breakdown

What are 3 cautions of using pilocarpine?
pt's < age 40 bc causes accom spasm
pt's at risk for RD like high myopes, aphakia, etc.
pt's with uveitis bc of BAB issue

What are 2 contraindications of using pilocarpine?
pt's with angle closure secondary to...
1. lens-induced mechanism
2. aqueous misdirection

What is the MOA of eye effects of atropine?
cholinergic antagonist = pupil dilation, accom paresis

Atropine is the _______________ of all the cholinergic antagonists.
strongest/most potent

What are the 6 main conditions treated with atropine?
1. ant uveitis/corneal injury
2. posterior synechiae
3. cycloplegic refraction
4. pupillary dilation
5. myopia control
6. occlusion therapy (amblyopia)

How does atropine work to treat anterior uveitis/corneal injury?
relax CB = relieves pain
inhibit iris sphincter = reduce sticky inflam cells = prevent post synechiae
reduces BV permeability = stabilizes BAB = reduces cells + flare
What is the dose of 1% atropine used to treat anterior uveitis/corneal injury?
1 gt 1% BID or TID
What is the dose of 1% atropine used to break posterior iris synechiae attached to the ant lens?
1 gt 1%
Explain how atropine is used for a cycloplegic refraction.
inhibits CB = prevents accom = helps to Dx accom esotropia
While the traditional dose was 1% atropine 3 days before exam, what is the new dose of atropine for a cycloplegic refraction?
0.5% ung BID for 1 day before exam
mostly age 1-6
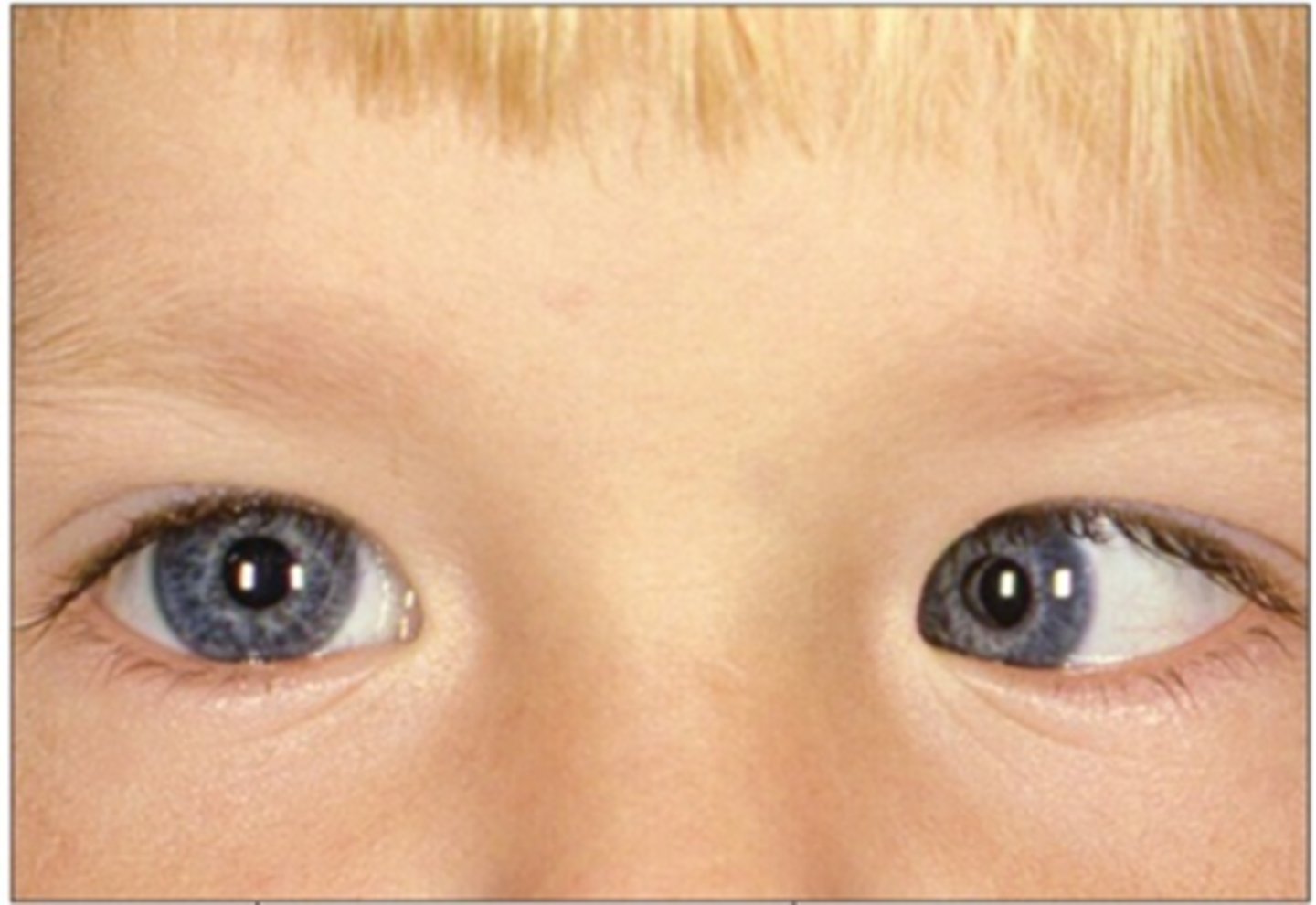
How does 0.1% atropine work for myopia control?
accom mechanism to reduce axial elongation

How does atropine work for low to moderate amblyopia occlusion therapy?
similar to direct occlusion, we put atropine in the non-amblyopic eye to "turn on" the other eye
NOTE: parents say atropine was easier to maintain than patching

What is the MOA of homatropine?
cholinergic antagonist = pupil dilation, accom paresis (same as atropine but less strong)
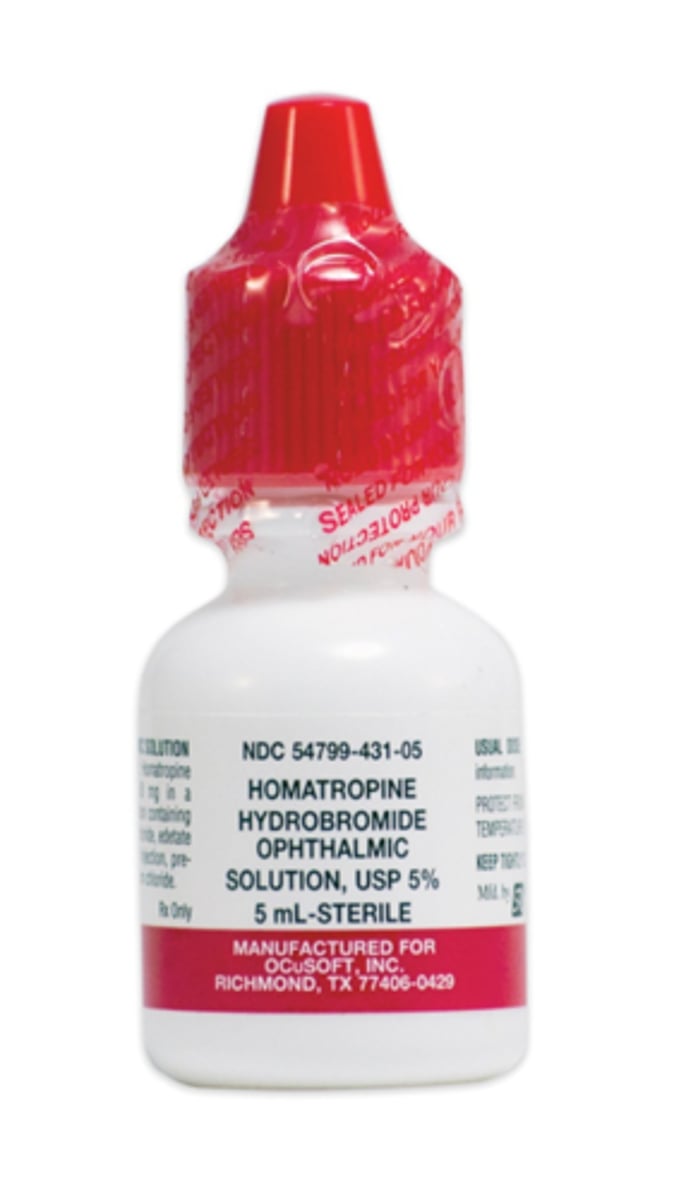
What is 1 gt BID homatropine the drug of choice for?
anterior uveitis/corneal injury = same MOA as atropine above
While it can be used, homatropine is NOT the drug of choice for which 2 clinical uses?
cycloplegia bc low potency
pupil dilation bc lasts 2 days
What is the MOA of cyclopentolate?
cholinergic antagonist = pupil dilation, accom paresis (same as atropine but less strong)

Can cyclopentolate be used to tx anterior uveitis like the 2 previous cholinergic antagonists?
yes - mild cases

What is 1 gt 1% cyclopentolate the drug of choice for?
cycloplegic refraction

What is the residual accom left after cyclopentolate refraction?
1.00D to 1.75D

What is the MOA of tropicamide?
cholinergic antagonist = pupil dilation, accom paresis (same as atropine but weak)

Tropicamide is the drug of choice for what clinical use?
pupillary dilation

In which patients are their pupils resistant to dilation unless phenyl is added?
DM

True or False: Higher concentration of tropicamide improves mydriatic response.
false = more about iris colour

While it can be used for this clinical use, tropicamide is not the drug of choice for which use?
cycloplegia

What are 4 ocular side effects of the cycloplegics?
stinging
SPK
increased in IOP (transient)
conj hyperemia
What are the rare systemic side effects of the cycloplegics?
reduced GI motility
fever
cutaneous flush
tachycardia
dry skin/mucous memb
urinary incontinence
CNS disturbances = ataxia, incoherent speech, restlessness, hallucinations, seizures
While usually self-limiting, how can we counteract the systemic side effects of the cycloplegics?
physostigmine (1-2mg IV or IM q5-15 min) given at the ER - indirect cholinergic agonist

Cycloplegics are contraindicated in which pt's?
untreated narrow angle glaucoma
untreated anatomically narrow angles
Cycloplegics are cautioned in which pt's?
Down syndrome bc increased risk of side effects (but ideas are changing)
pregnant pt
Rank the cholinergic antagonists in order of longest to shortest duration.
atropine = 7 days
scopolamine = 3 days
homatropine = 1 day
cyclopentolate = 24 hrs
tropicamide = 6 hrs
What is the MOA and eye effects of phenylephrine?
direct alpha1 agonist = mimics NE = stimulates iris dilator, conj vasoconstriction

What are the 6 main clinical uses of phenylephrine?
1. pupil dilation
2. reduce redness
3. differentiate scleritis vs episcleritis
4. palpebral widening for ptosis
5. break post synechiae
6. determine location of Horner's lesion

Explain how phenylephrine is used for pupil dilation.
directly stimulates iris dilator for 6 hrs

Can phenylephrine be used for cycloplegic refraction?
no - does not cause cycloplegia

What are 2 downsides to using phenylephrine (visine) to reduce redness?
while it causes vasoconstriction, will have...
rebound redness with chronic use
pupil dilation if corneal integrity not intact or CL wear

Explain how phenylephrine is used for differentiating scleritis vs episcleritis.
if episcleritis, superficial BV will blanch/vasoconstrict while deeper scleral BV will not

Explain how phenylephrine is used for ptosis.
increased symp innervation of Muller mm = palpebral widening

Explain how phenylephrine is used for breaking post synechiae.
10% phenyl can break

Explain how 1% phenylephrine is used for determining Horner's lesion location.
mydriasis = lesion is postganglionic
no mydriasis = lesion is central or preganglionic

What are 3 ocular side effects of phenylephrine?
stinging
photophobia
release iris pigment granules into aq (with 10%, mostly in elderly)

What are some rare systemic side effects of phenylephrine?
CV effects = increased BP, syncope, MI, tachycardia, arrhythmia, subarachnoid hemorrhage

In which pt's is phenylephrine use cautioned?
CV disease bc CV and BP effects
pt's < age 5 bc BP effects
hyperthyroidism
narrow angles

In which pt's is phenylephrine use contraindicated?
HTN
thyrotoxicosis
pt's < age 1

What is the MOA and eye effect of hydroxyamphetamine?
indirect adrenergic agonist = inhibits NE reuptake = net increased NE = pupil dilation
Similar to phenyl, what are the 2 main clinical uses of hydroxyamphetamine?
pupil dilation
determining Horner's lesion location
Recall: what is the MOA and eye effects of cocaine?
indirect adrenergic agonist = inhibits NE reuptake = net increased NE = 2mm of pupil dilation, vasoconstriction
What are the 2 main clinical uses of cocaine?
topical anesthetic
Dx Horner's syndrome
Explain how cocaine can help to Dx Horner's syndrome.
Horner's pupil will NOT dilate with topical cocaine
What is the MOA of dapiprazole?
adrenergic antagonist = blocks receptors
What is the eye effect and clinical use of dapiprazole?
miosis = can be used to reverse dilation (especially with phenyl and/or hydroxyamphetamine)
Dapiprazole does not really work to reverse dilation from __________________.
tropicamide
True or False: while no longer commercially available, there is a new version of a med similar to dapiprazole coming soon.
true