Biology Heart + immunity + cells test review
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
6.1 defense against infectious disease
Innate immunity (non-specific immunity)
these are barriers against infection and prevent entry of any pathogen
does not target specific pathogens
EX: the skin provides a physical barrier to prevent entry of pathogens
pathogen
any biological agent that causes illness or disease
typically, a virus (flu), bacteria(e-coli), fungi (athletes’ foot) or protists (malaria)
sebum
oily/waxy substance produces by the skins sebaceous glands
slightly acidic to prevent infection
Mucous membranes
openings (orifices) produce mucus to trap pathogens
contains lysozyme an anti-bacteria enzyme
Phagocytes
a type of white blood cell
provide nonspecific immunity (do not learn to recognize and attack specific pathogens
they exhibit ameboid movement, recognize foreign pathogens, engulf them by endocytosis, then digest the pathogens using lysosomes
at the sight of injury, inflammation will cause the phagocytes to leak out of the capillaries to fight off infection.
blood contains:
white blood cells
erythrocytes (red blood cells)
platelets
clotting factors
blood clot formation
vessel is damaged
exposed molecules in damaged vessel cause binding of platelets
binding activates the platelets
these activated platelets release clotting factors
fibrin forms strands
these fibrin strands form a mesh that stabilizes the clots, and captures more erythrocytes, forming a clot
prothrombin
is a zymogen- a precursor to an active enzyme
is inactive however becomes active thrombin
this thrombin is converted to a soluble fibrin
the soluble fibrin becomes insoluble
this become an insoluble polymer that is a netlike structure that causes the clot to from
adaptive immune response 6.1.2
antigens
proteins found on cells that are used for recognition
most are glycoproteins
each type of pathogen will have specific antigens. the adaptive immune system learns to recognize these antigens
antibodies
proteins made by the immune system, that bind to specific antigens
they are monoclonal- specific to one antigen and made by one type of parent cell
(same recognition process as to why different blood types are incompatible)
the main weapon against pathogens
lymphocytes
cells of the adaptive immune system that cooperate to produce antibodies
travel in the blood and are also concentrated in lymp nodes
humans have around 1000-4800 lymphocytes
B and T cells
types of lymphocytes
many b cells are stored in lymph nodes with genetic instructions to make a specific type of anti-body
they wait dormant ready to make antibodies if/when infiltration occurs
when infiltration occurs ……
the pathogen enters and the macrophage engulfs it
the macrophage deactivates it and it presents the antigen to a helper T Lymphocyte
these helper T cells activate specific B cells
the B cells divide by mitosis making clones (these clones are plasmacells)
Plasma cells make antibodies to fight off the infection
this process
occurs in the lymphnodes
after this process….
some B cells remain
these are called memory cells and may have a very long-life span
retaining memory cells provides immunity
vaccinees aim to form memory cells without causing disease
Types of Vaccines
Attenuated virus- contains the weakened virus that can replicate but not cause disease
inactivated virus- the bacteria is killed, or virus cannot reproduce
subunit virus- contains only the antigen
mRNA virus- contains mRNA which our cells use to make the appropriate antigen (used this in covid)
Penicillin
is a non-competitive inhibitor and targets bacterial cell walls therefore has no effect on human cells
Zoonosis
most pathogens infect only one host species however sometimes an infection can cross species barriers
these are Zoonotic infections (like the bird flu)
Industrial antibody production
monoclonal antibodies (mAB’s) are used for diagnosis
inject an animal with antigens (usually a rat)
the animal will make plasma cells
harvest the plasma cells from the spleen
using a cancer cell to splice the antibody cell
this is a hybridoma cell
mAB’s
are used to make pregnancy test
HCG (human chorionic gonadotrophin) is a hormone produced in early pregnancy
this is detected in Urine hence the pregnancy
HIV cause AIDS
someone who is HIV positive may not may not develop aids
HIV attacks T cells and other t cells that signal antibody production in B cells
HIV attacks various cell types, AIDS will result is helper T cells are targeted
over time it reduces t cell production and weakens immune system
6.2 The blood system
Blood
55% of total blood is Plasma (water, O2, CO2, salts, proteins, and waste)
<1% of blood is a Buffy coat (platelets and leukocytes)
45% of blood is Erythrocytes (red blood cells)
circulation happens in two circuits
Pulmonary- from heart to lungs and back to the heart
systemic- from the heart to the rest of the body
arteries
carry blood away from the heart
contain muscle and elastic fibers that constrict and stretch to pulsate (this regulates blood flow)
veins
carry blood to the heart
they contain thinner walls and less muscle tissue
they are close to skeletal muscles so they can be squeezed and allow blood flow
that have closed valves to prevent backflow of the blood
6.3 Regulation of the cardiac cycle
Cardiac cycle
the activity of the human heart from the beginning of a heart beat to the beginning of the next
the cycle involves the contraction of the atria followed by the contraction of the ventricles
pace of the Cardiac cycle
the pace is the heart rate
heart rate is controlled by a bundle of nerves called Sinoatrial node (SA node for short)
SA node
initiates contraction in the right atrium
slight Dely between atrial contraction and ventricular contraction
heart muscle is Myogenic- it will continue to beat without a nerve impulse
brain communicates wirh the SA node to set the pace
Cardiovascular center
Brain stem holds cardiovascular center- and receives impulses from different receptors
communicates about the bodies Ph, blood pressure, and oxygen
if these are low the heart beats faster, if high heart beats more normally
nerves that aid in heart rate
vagus nerve slows heart rate
sympathetic nerve increases heart rate
epinephrine
the fight or flight hormone made in the adrenal gland
SA node responds to epinephrine when in the blood
Blood pressure
Standard: 120/80
systaltic blood pressure (top number) - measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats
diastolic blood pressure (bottom number)- measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart rests between beats
Atherosclerosis
the development of fatty tissue (atheroma) in the arterial walls
atheroma is found on all people
occlusion
the narrowing of arteries
increases the risk of heart disease
causes heart rate and blood pressure to increase
additionally, an increased risk of blood clots therefore strokes and heart attack
if the coronary arteries are clogged it can cause heart attacks
Risk factors of Atherosclerosis
high LDL levels
chronic high blood pressure
consumption of trans fats
may be a microbial component
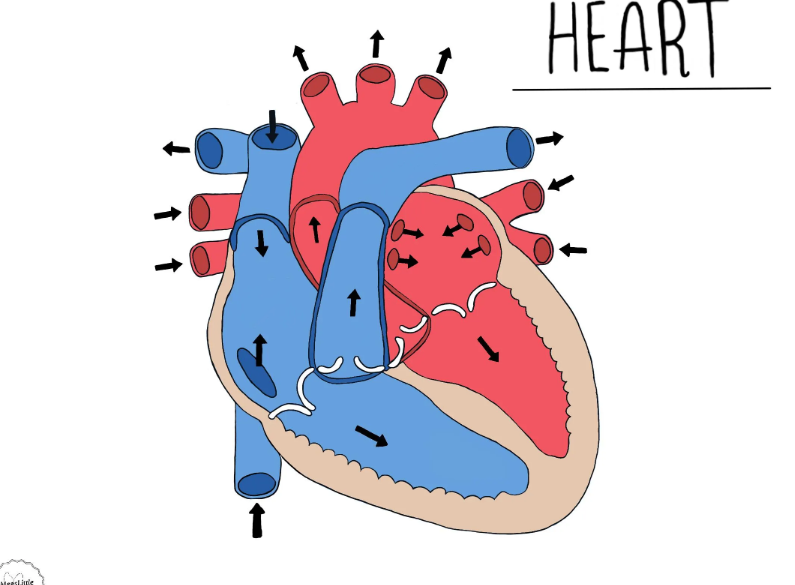
identify the aorta, superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, the atriums, the ventricles, (both of the semi-lunar parts of the) pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins and the 4 valves.
answers here
capillaries
have adaptations to allow the exchange of materials between blood and tissues
large surface area due to branching
venule- small vein
arteriole- small artery
narrow diameter and thin walls
some are fenestrated- small holes that increase permeability
in arterials
an increased pressure forces fluid out of the capillaries
but large molecules remain the plasma
in venules
a decrease in pressure allows for the uptake of fluids
the fluid that leaks out of the capillaries is
tissue fluid
tissue fluid allows for passive diffusion
glucose and O2 diffuse into cells
CO2 and cellular diffuse out of cels
small substances and proteins remain in plasma, but amino acids may move
excess fluid
drains into lymph ducts- have thin with gaps to increase fluid absorption
called lymph when inside lymph duct
similar to veins- also contain valves for one way movement of lymph fluid
all lymph ducts converge+ lymph empties into subclavian vein to be returned to the blood supply( now called plasma)
humans and animals have a
double circulation system to divide oxygenated blood from deoxygenated blood
bony fish have
single circulation meaning all of their blood in the fish’s heart is deoxygenated