Alkene/Alkyne Reactions
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Hydrohalogenation
Alkene Reaction
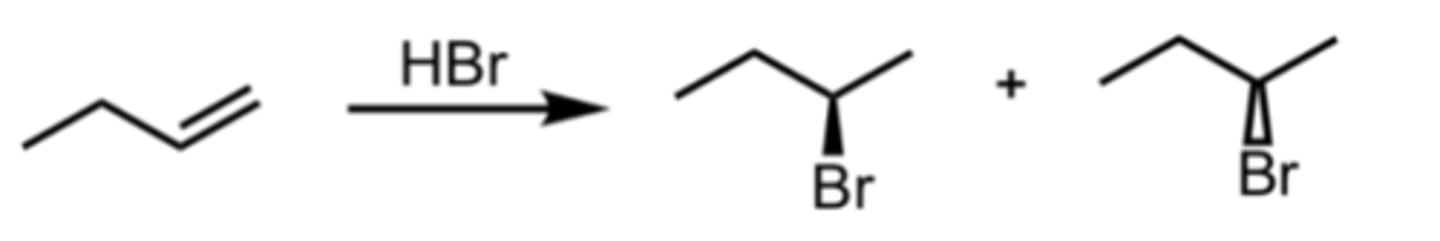
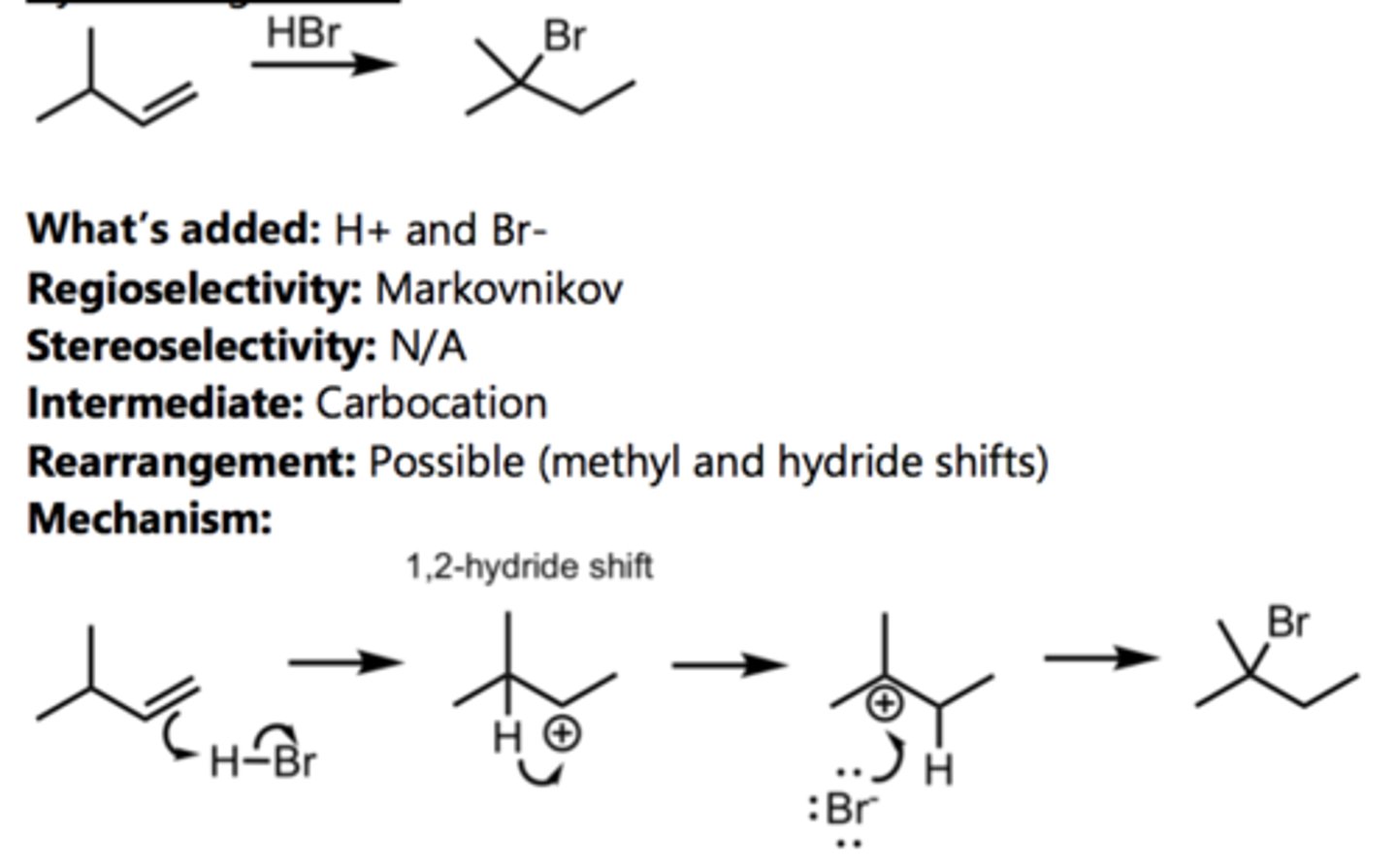
Hydrohalogenation (with Rearrangement)
Alkene Reaction
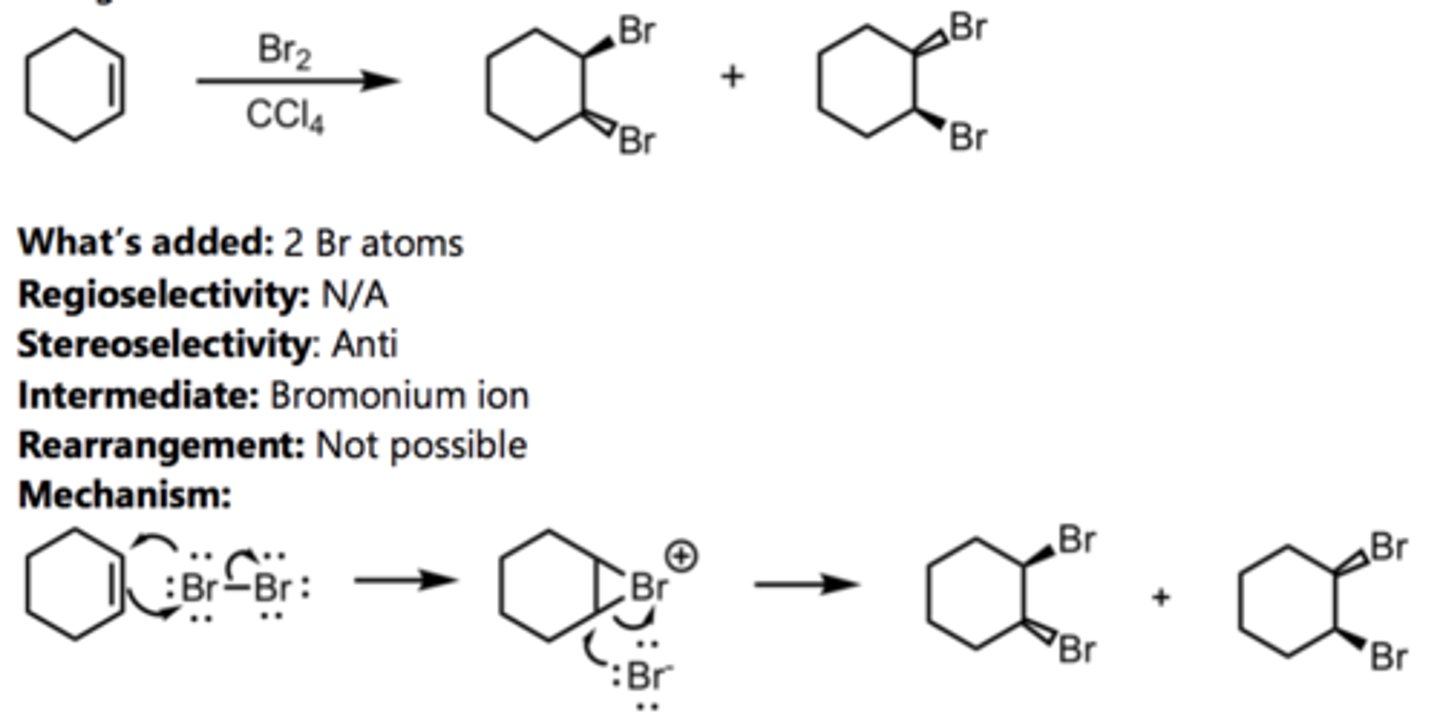
Halogenation
Alkene Reaction
Hydrobromination with Peroxide
Alkene Reaction
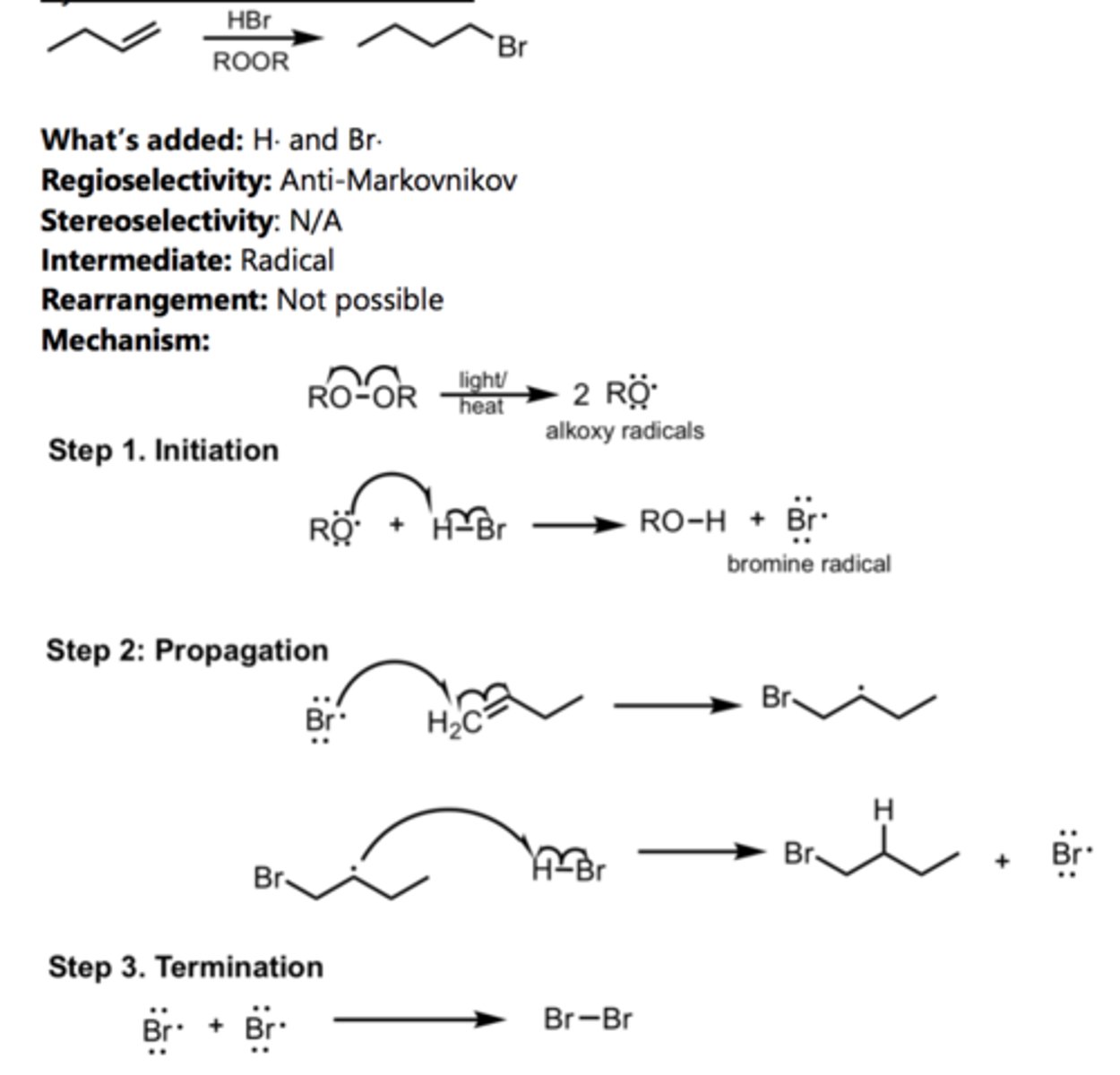
Hydration
Alkene Reaction
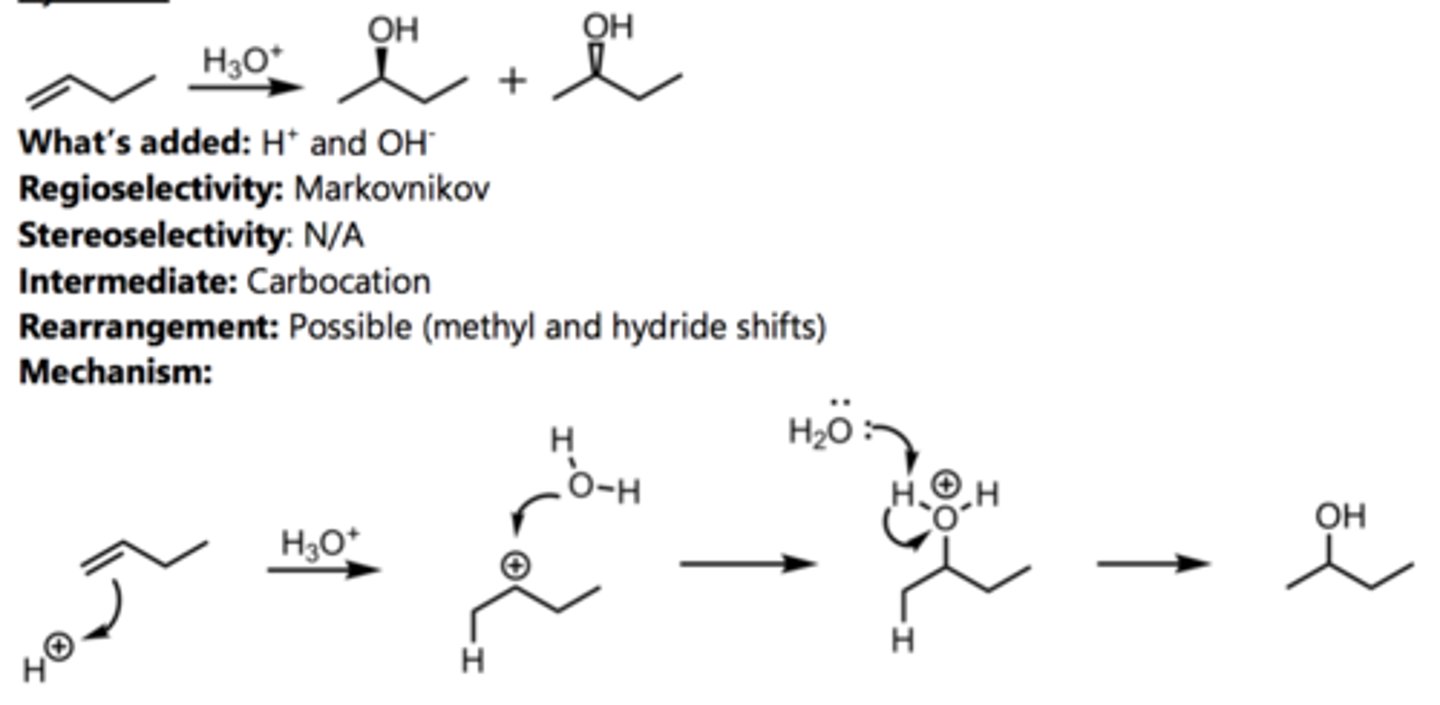
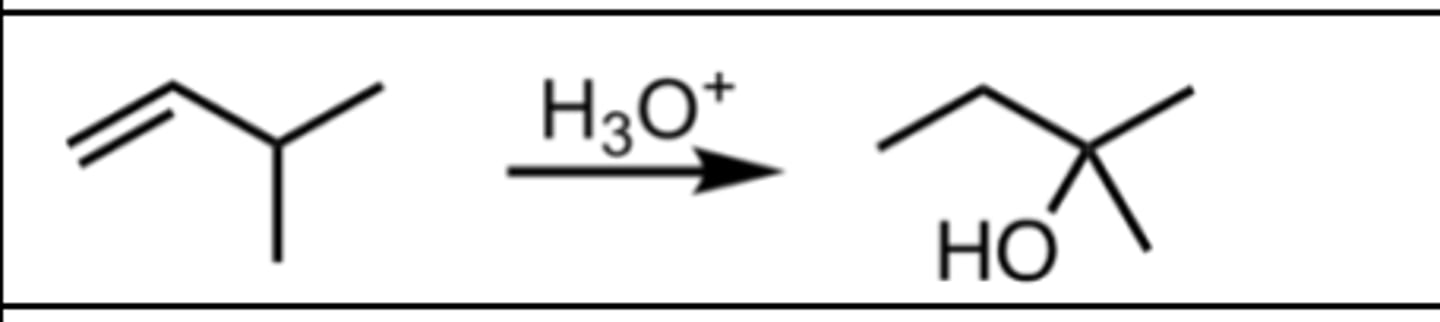
Hydration (with rearrangement)
Alkene Reaction
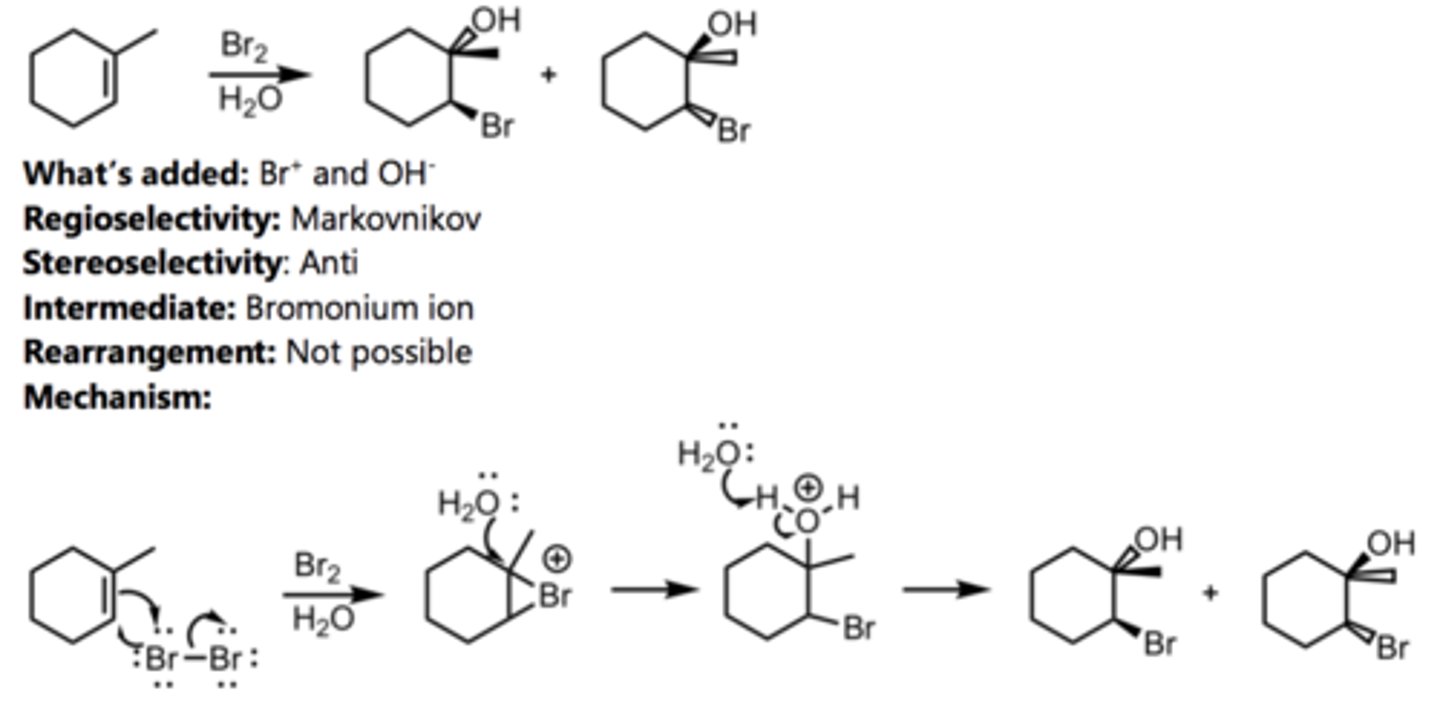
Bromination in H₂O
Alkene Reaction
Oxymercuration-Demercuration
Alkene Reaction
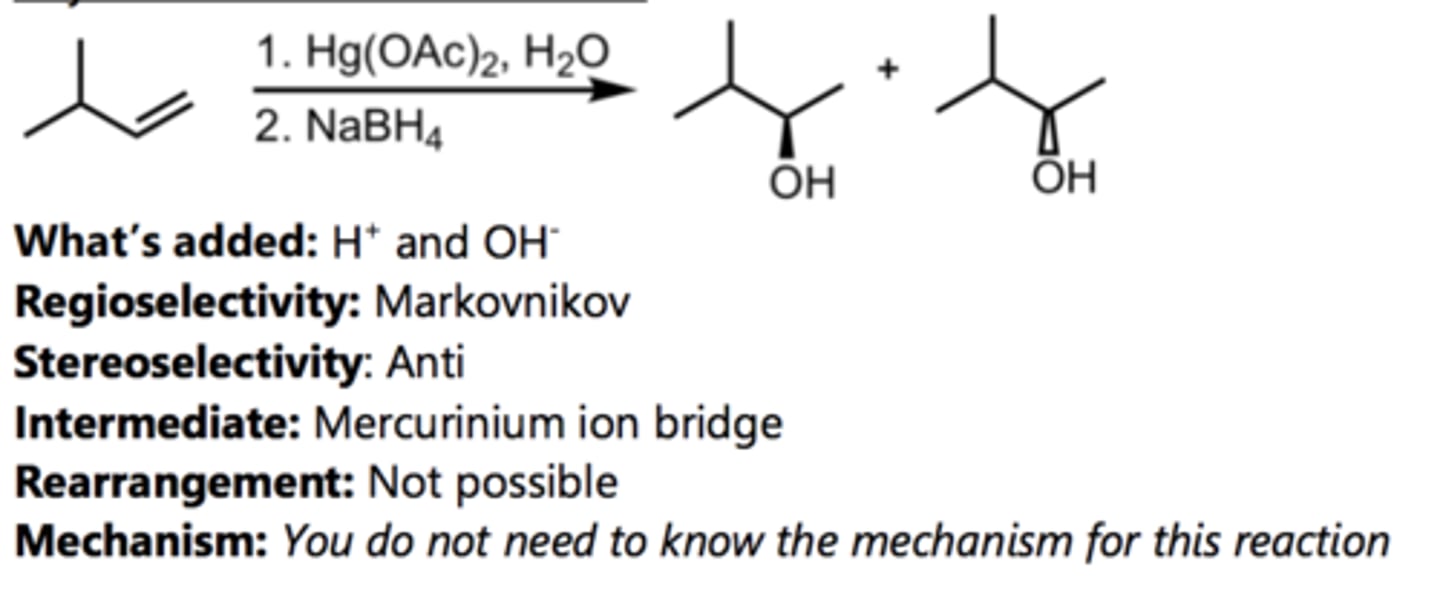
Hydroboration-Oxidation
Alkene Reaction
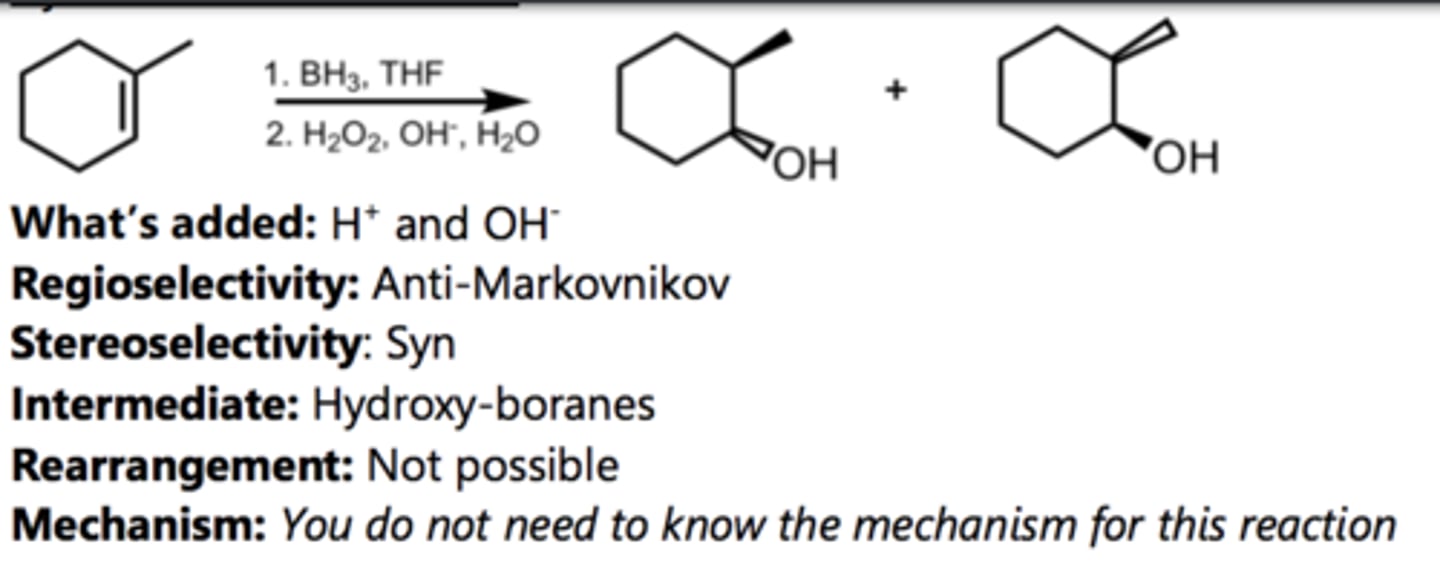
Syn-Hydroxylation
Alkene Reaction
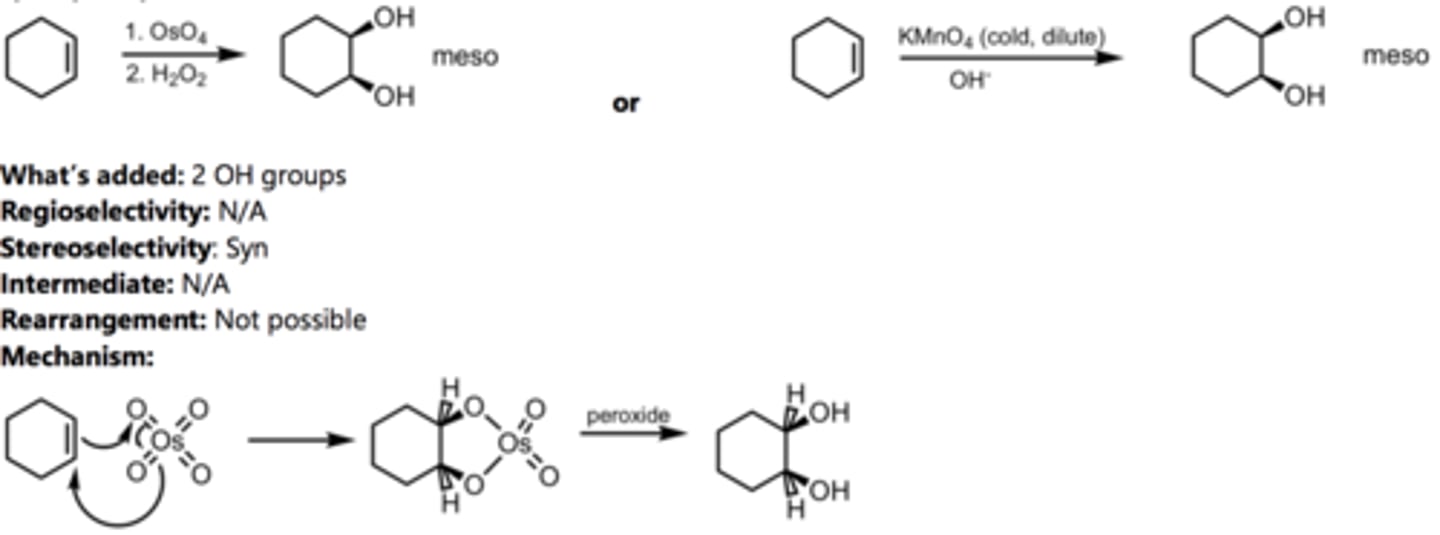
Anti-Hydroxylation
Alkene Reaction
Addition of an Alcohol
Alkene Reaction
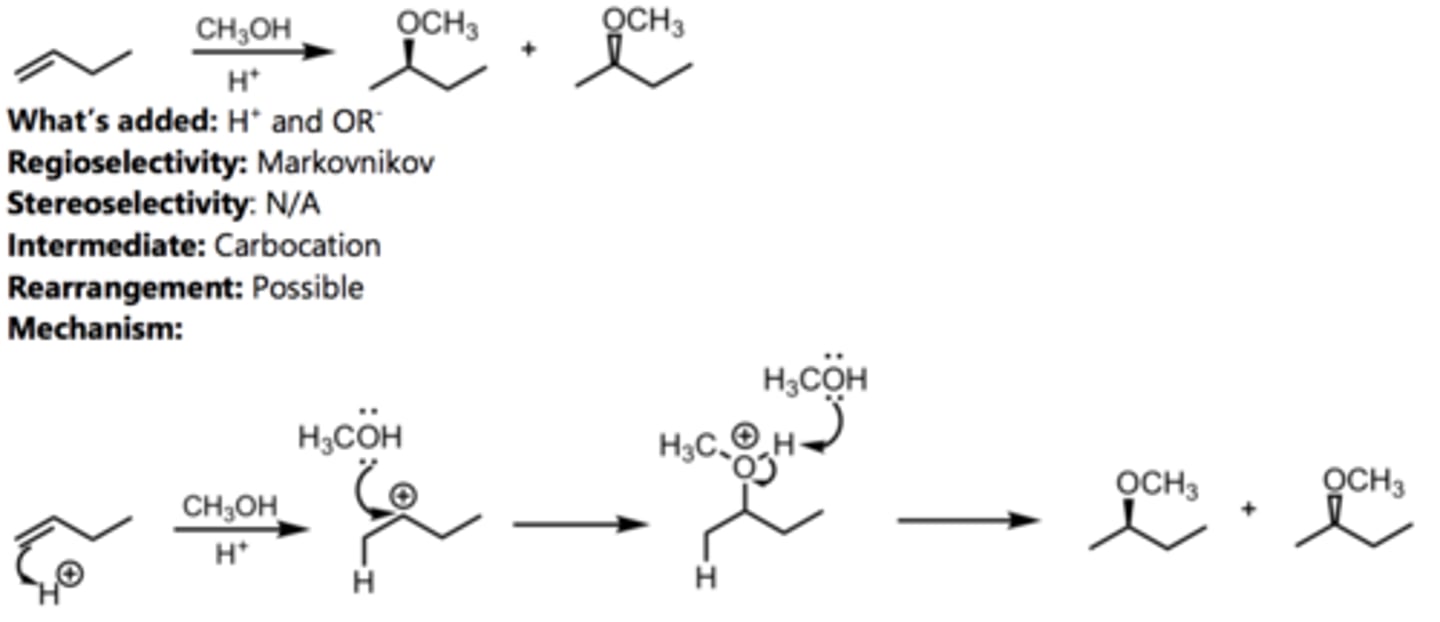
Bromination in Alcohol
Alkene Reaction
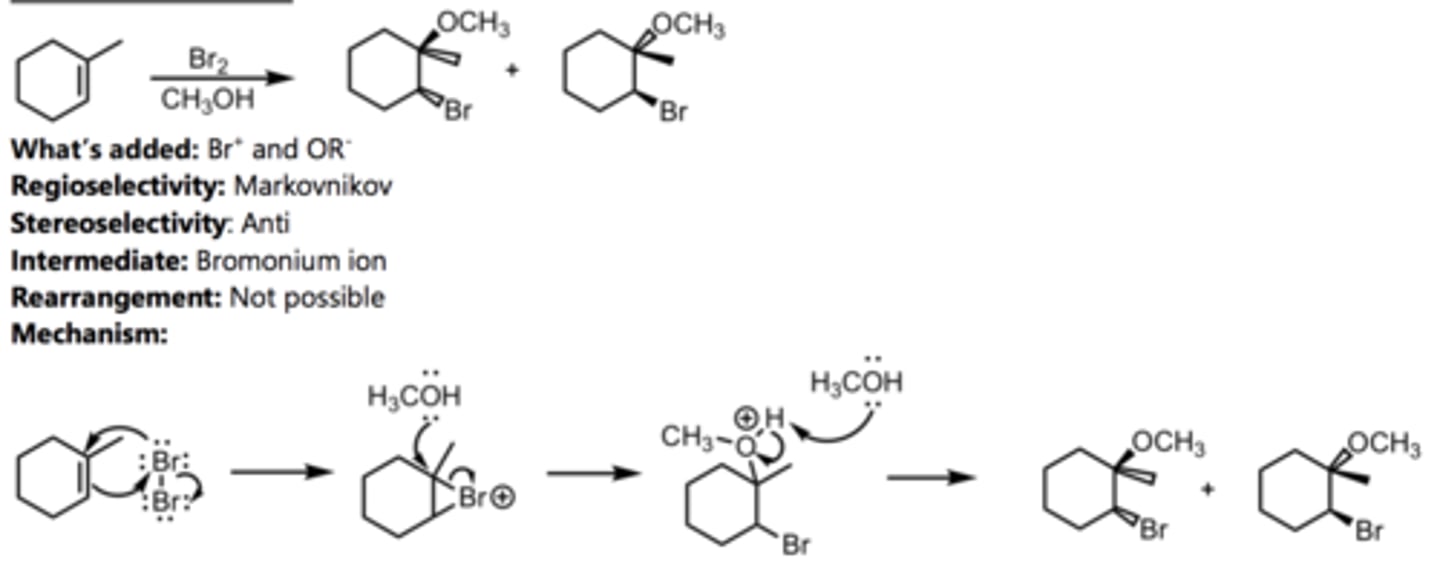
Alkoxymercuration-Demercuration
Alkene Reaction
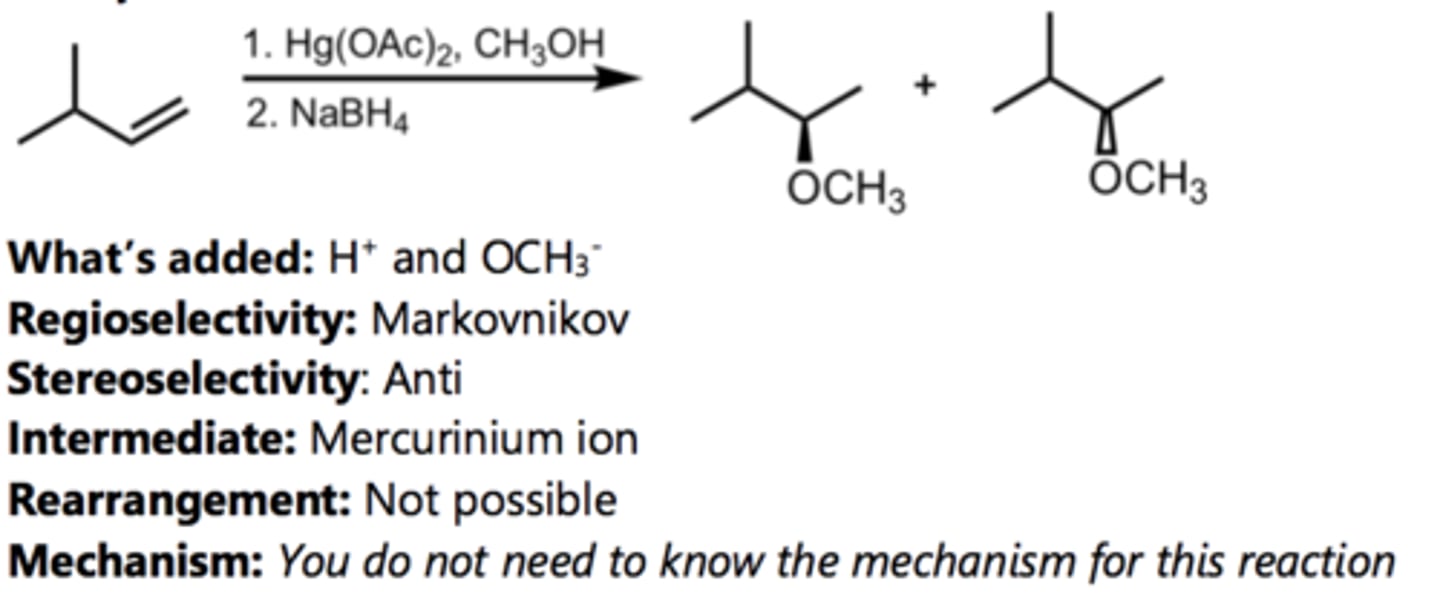
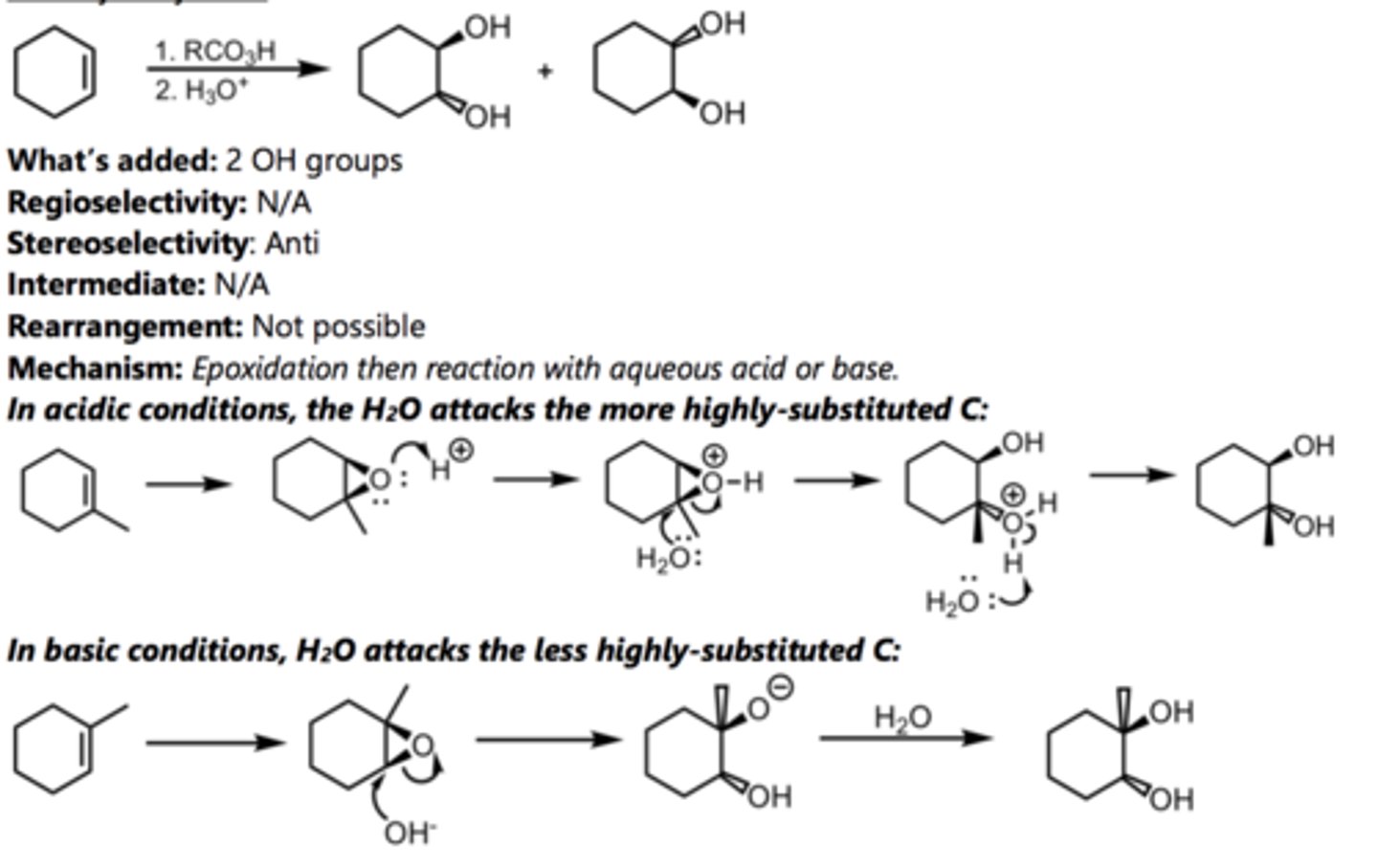
Epoxidation
Alkene Reaction
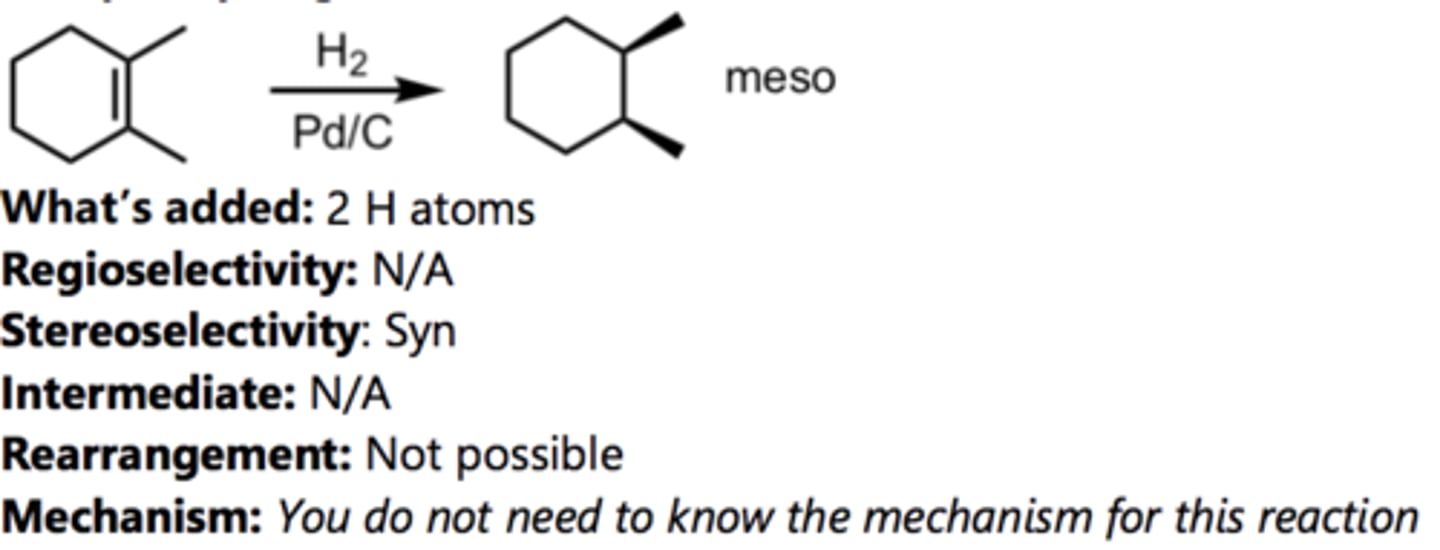
Catalytic Hydrogenation
Alkene Reaction
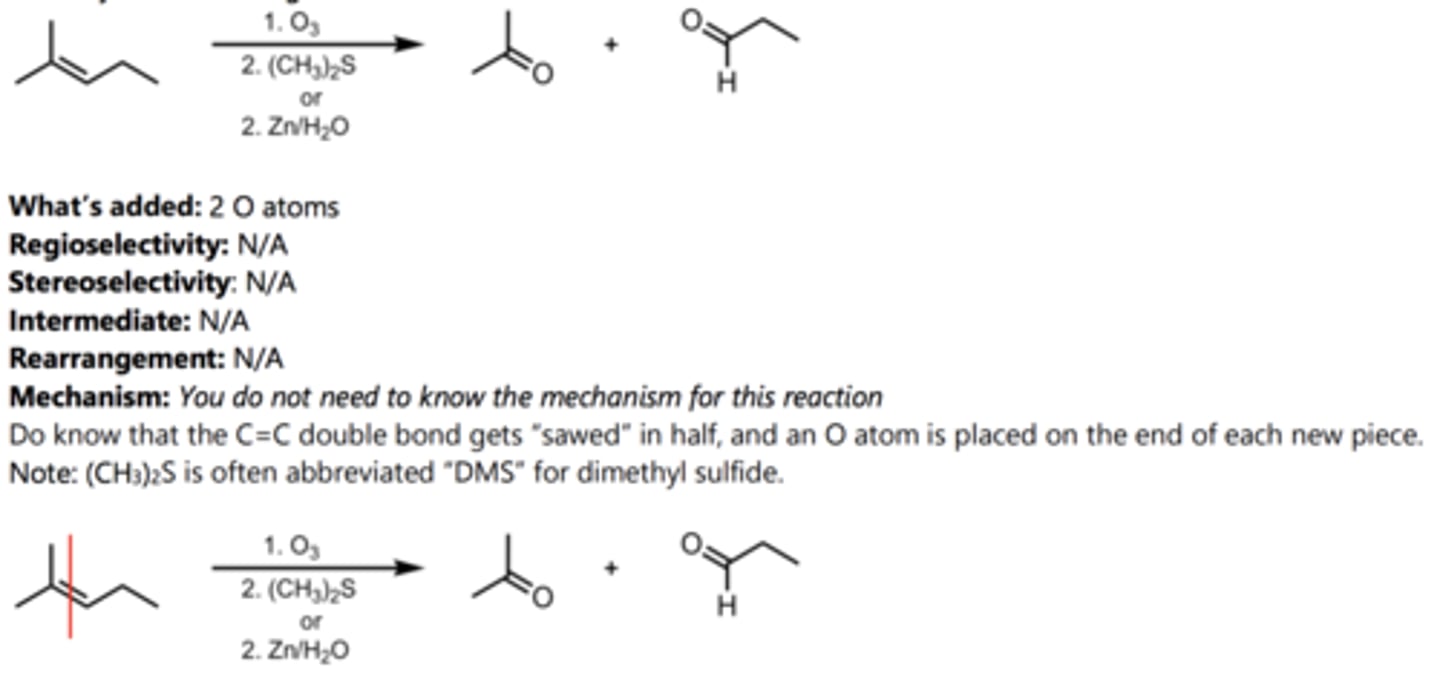
Ozonolysis (Reducing Conditions)
Alkene Reaction
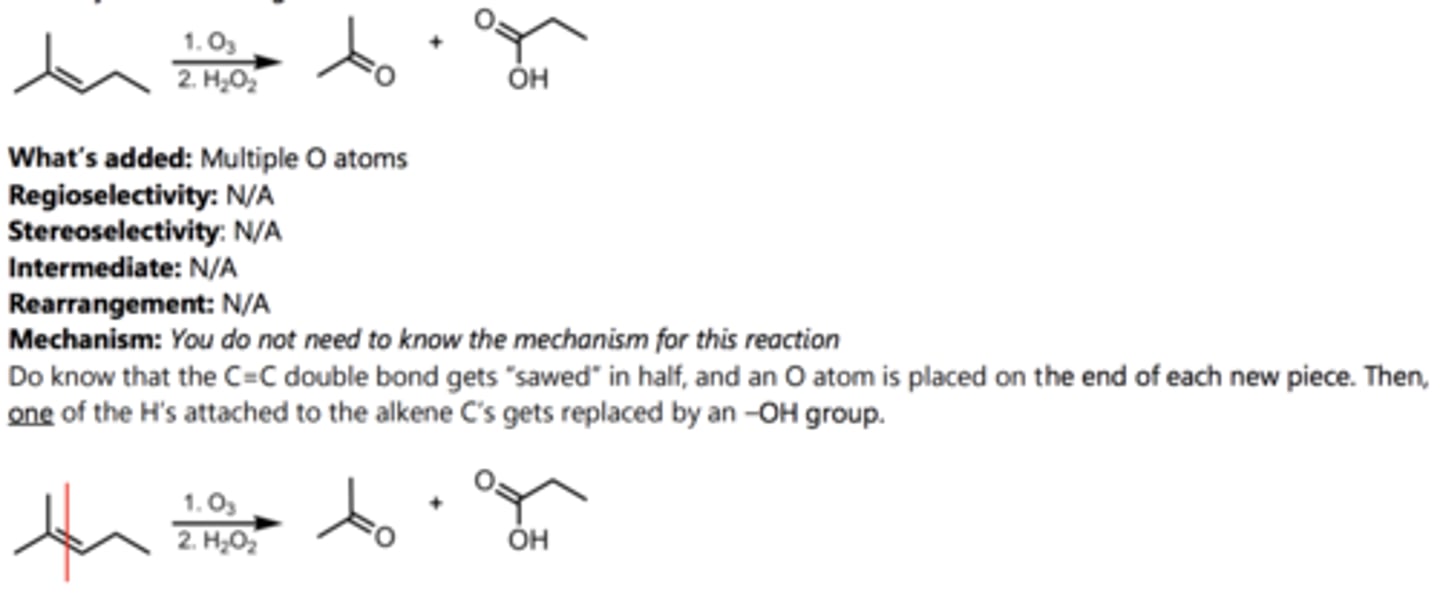
Ozonolysis (Oxidizing Conditions)
Alkene Reaction
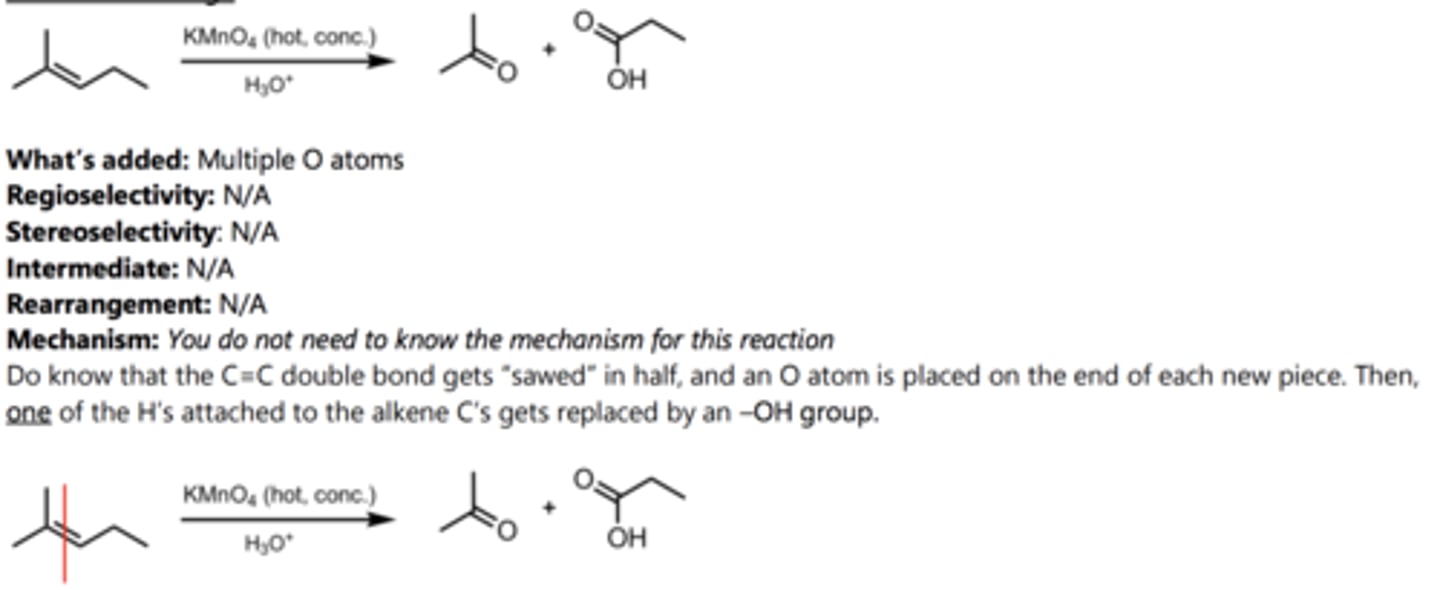
Oxidative Cleavage
Alkene Reaction
Catalytic Hydrogenation (Catalytic reduction)
Alkyne Reaction
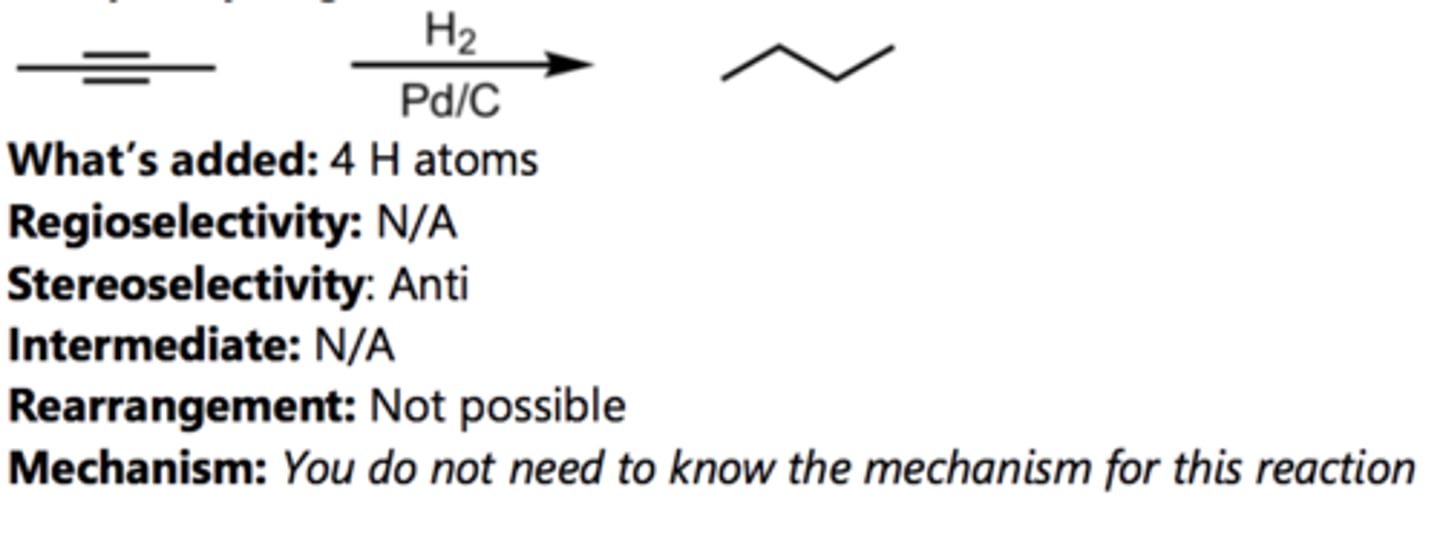
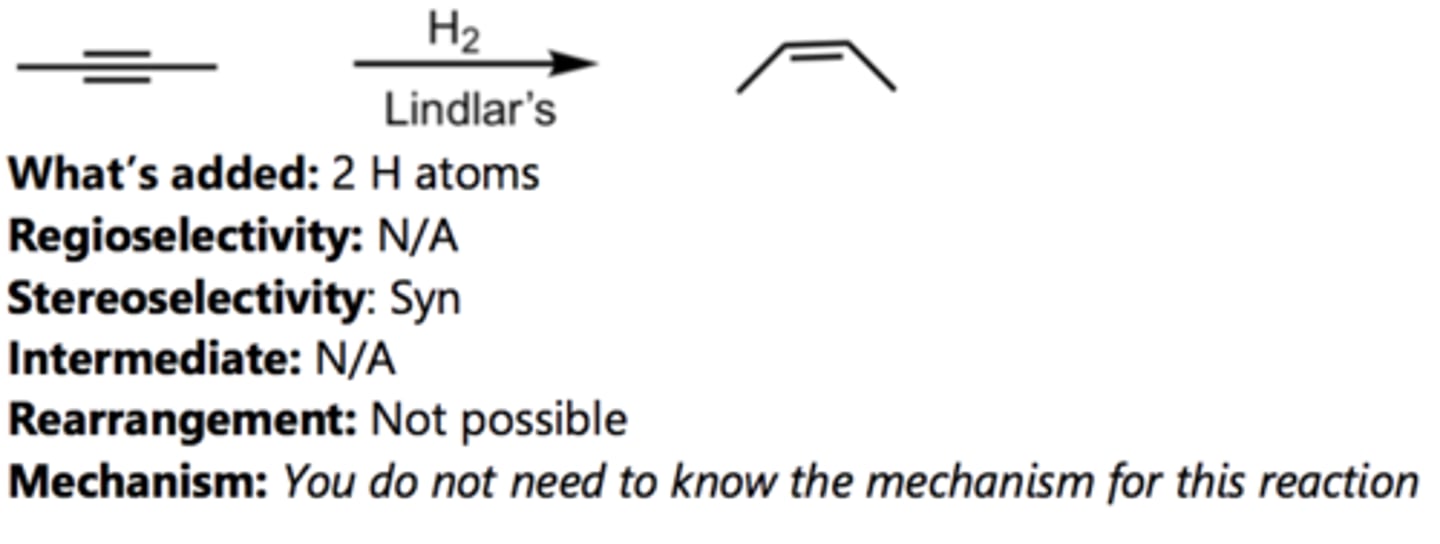
Reduction to Cis-Alkene
Alkyne Reaction
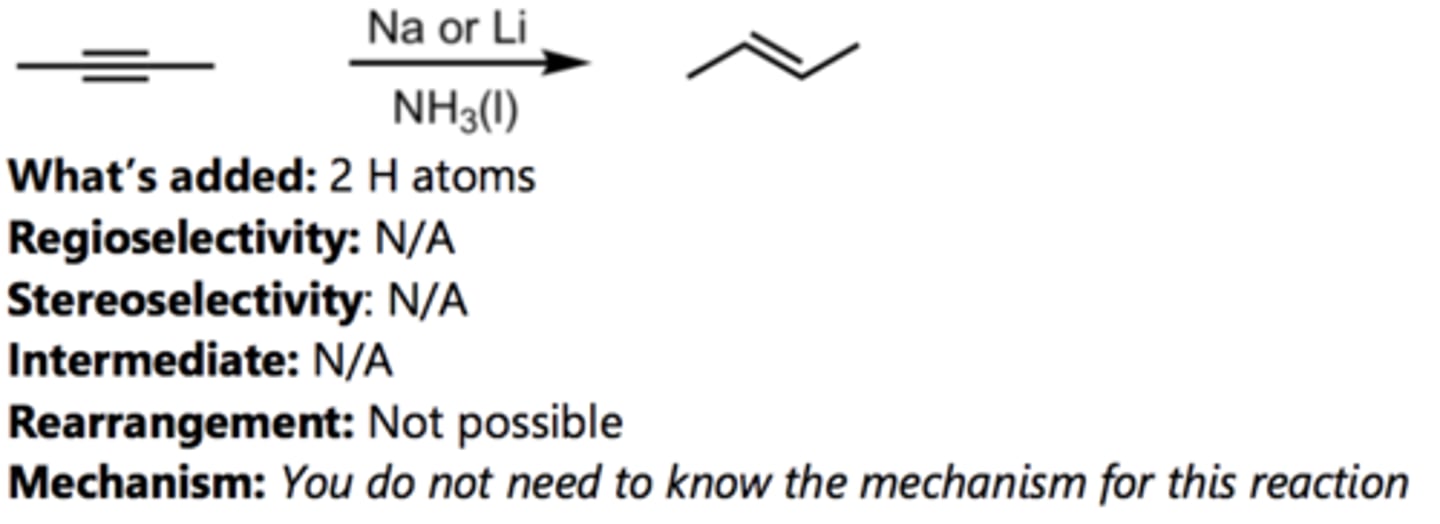
Reduction to Trans-Alkene
Alkyne Reaction
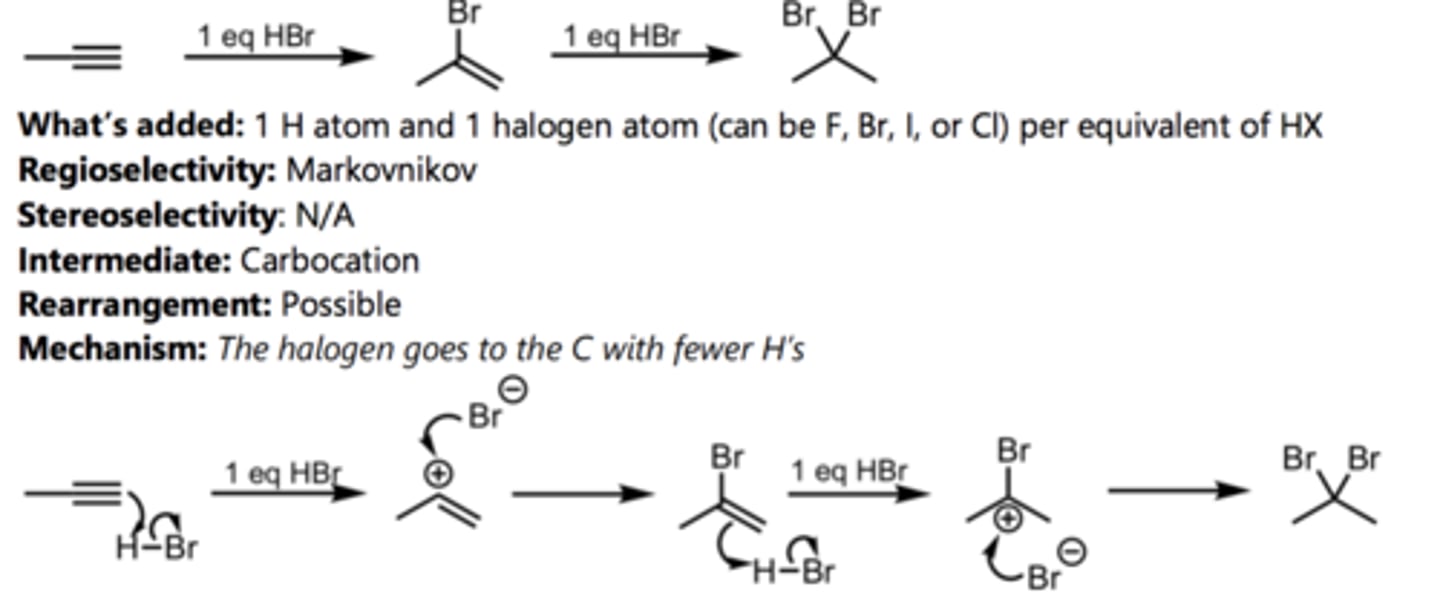
Hydrohalogenation with HBr (Terminal Alkyne)
Alkyne Reaction
Hydrohalogenation with HBr (Internal Alkyne)
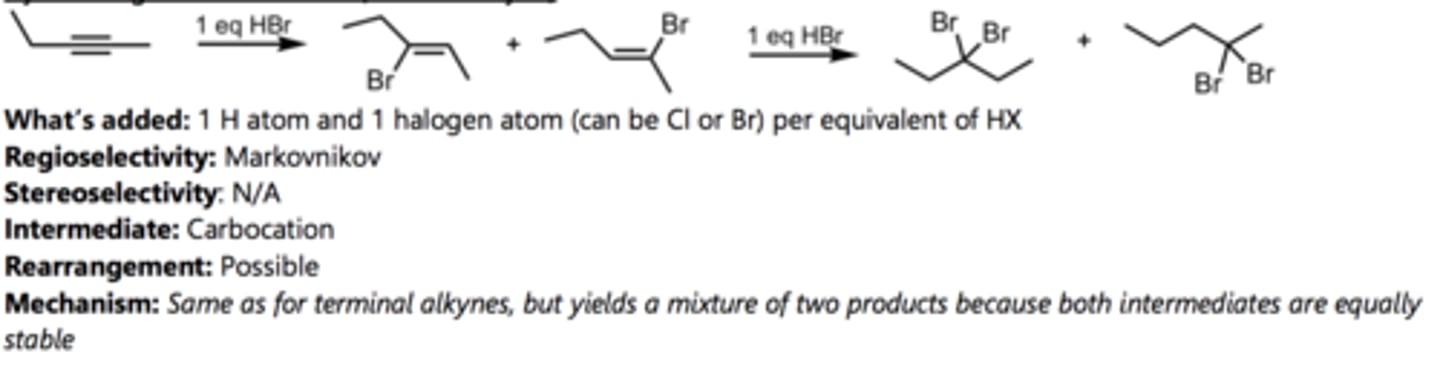
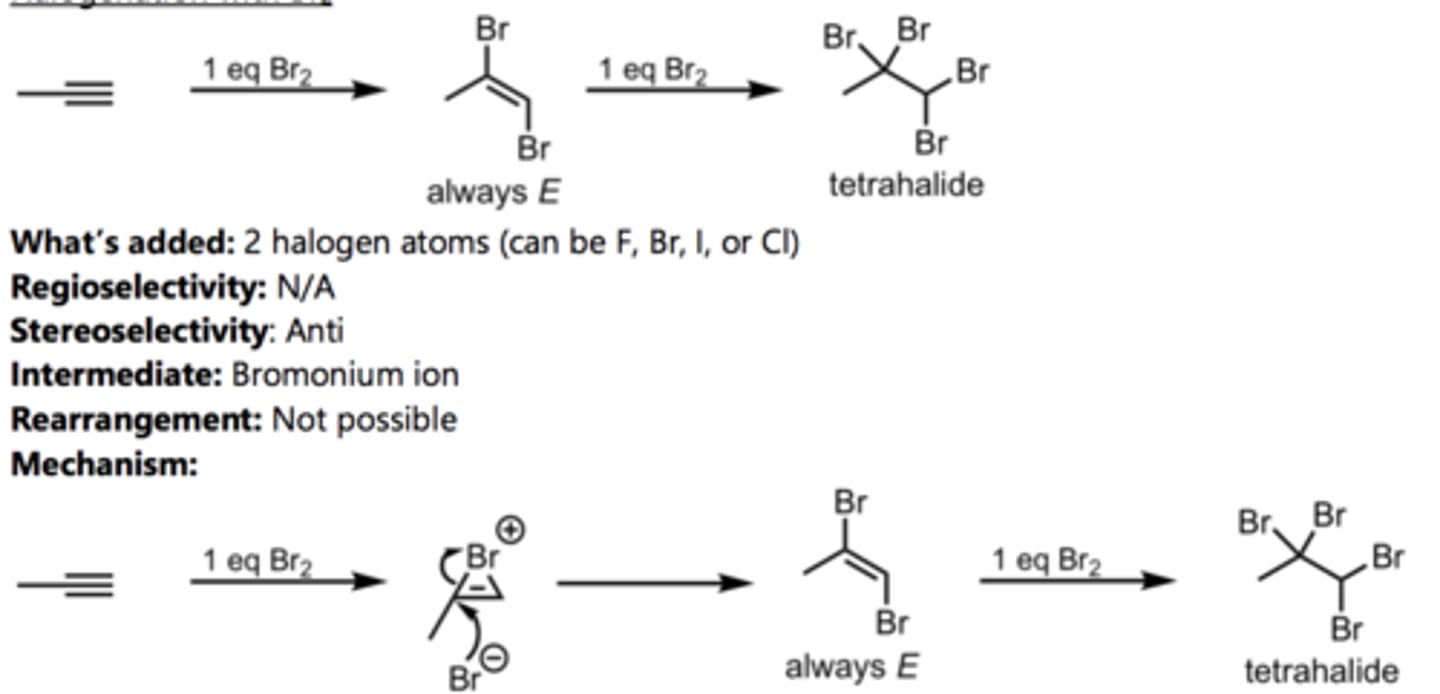
Halogenation with Br₂
Alkyne Reaction
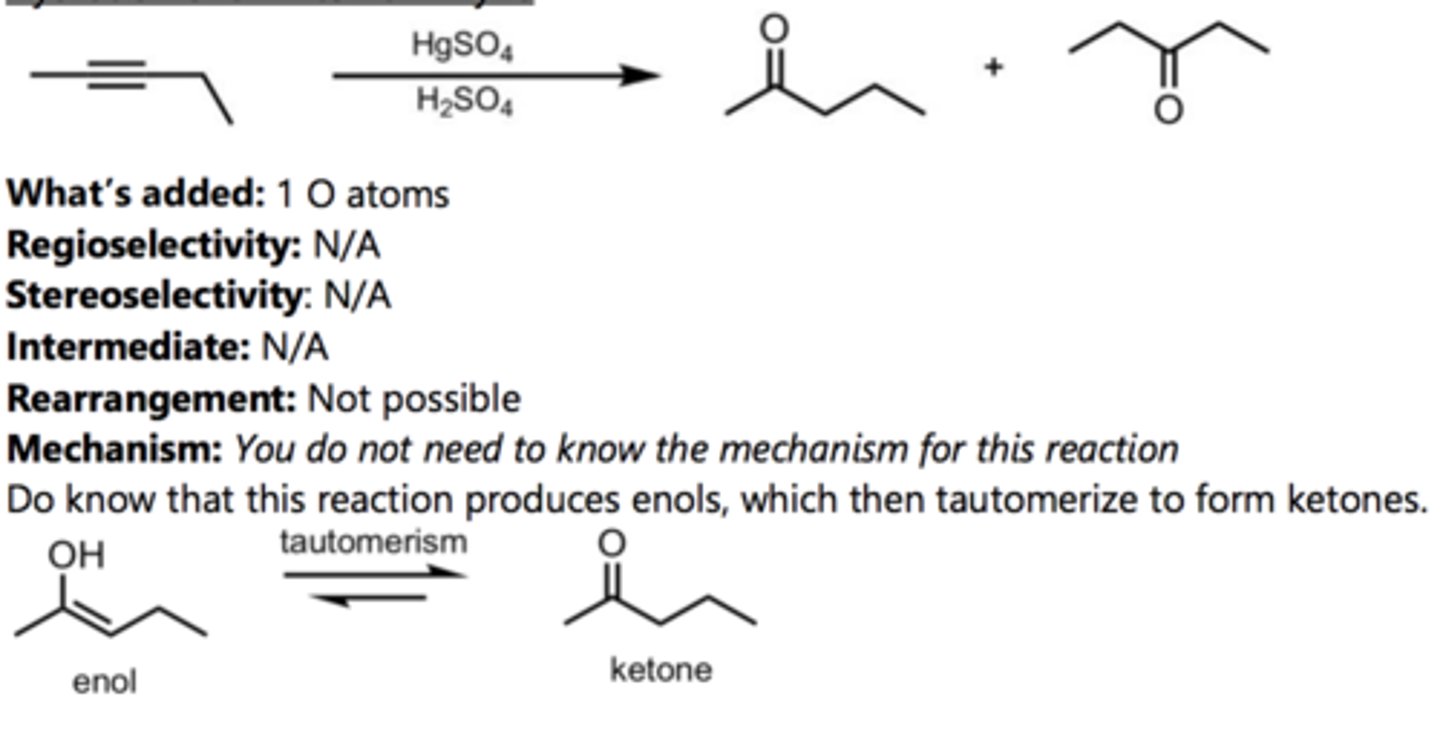
Hydration of an Internal Alkyne
Alkyne Reaction
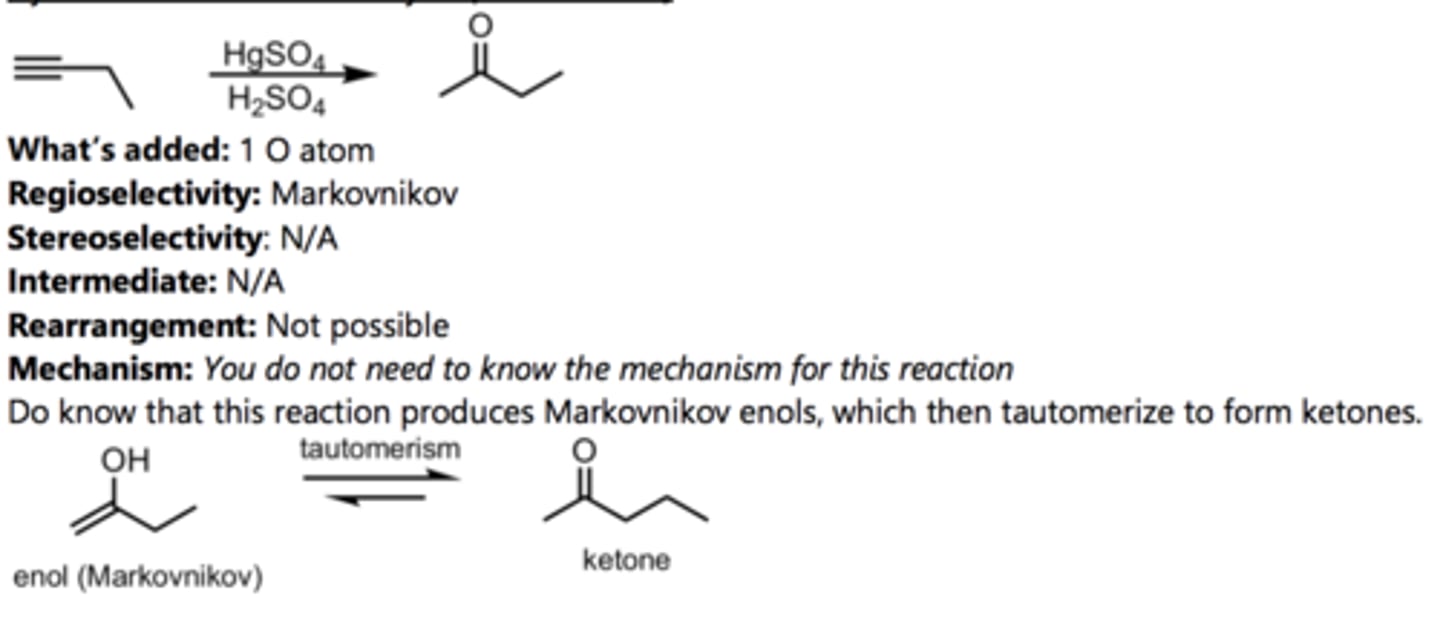
Hydration of a Terminal Alkyne (Markovnikov)
Alkyne Reaction
Hydration of a Terminal Alkyne (Anti-Markovnikov)
Alkyne Reaction
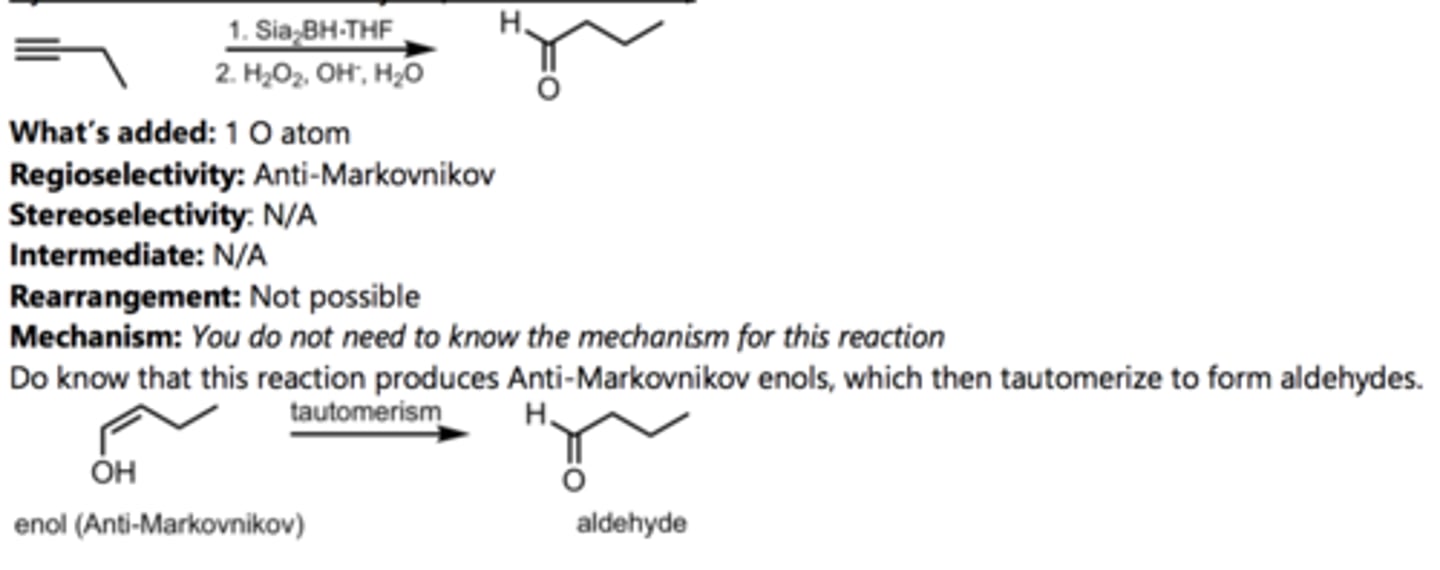
SN2 Addition of an Acetylide Ion to an Alkyl Halide
Alkyne Reaction
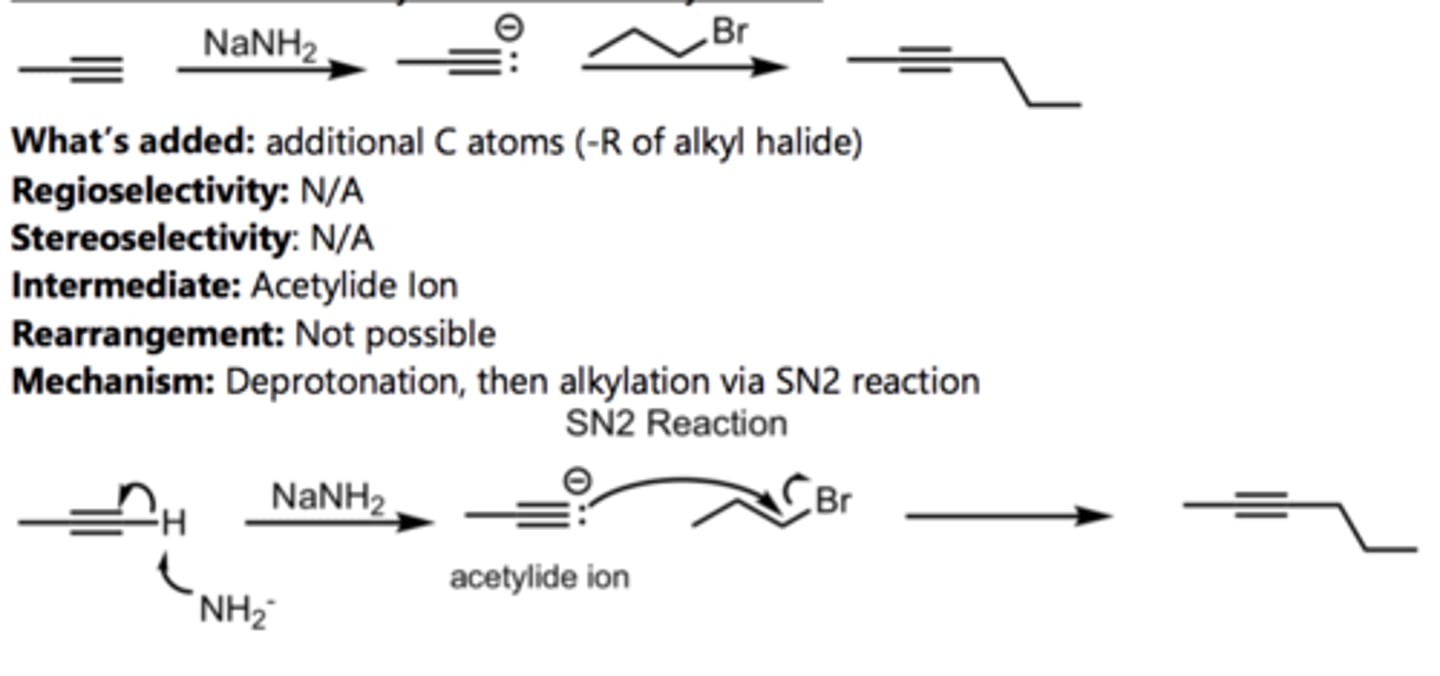
SN2 Addition of an Acetylide Ion to a Ketone
Alkyne Reaction
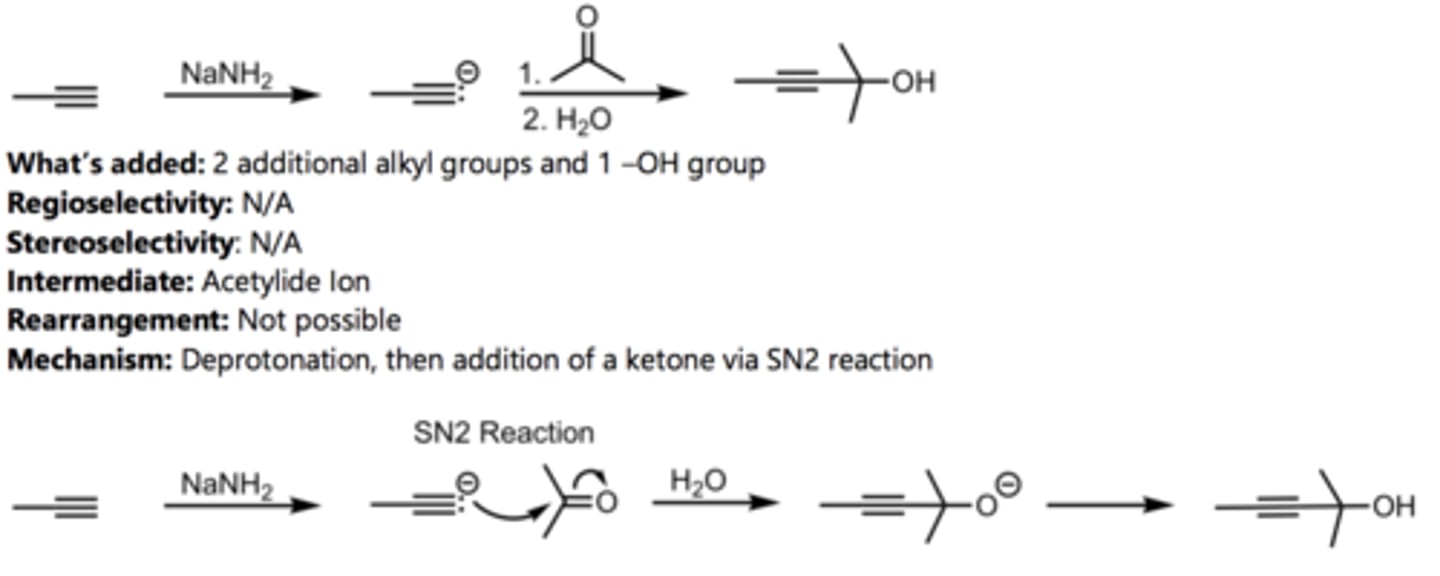
SN2 Addition of an Acetylide Ion to an Epoxide
Alkyne Reaction
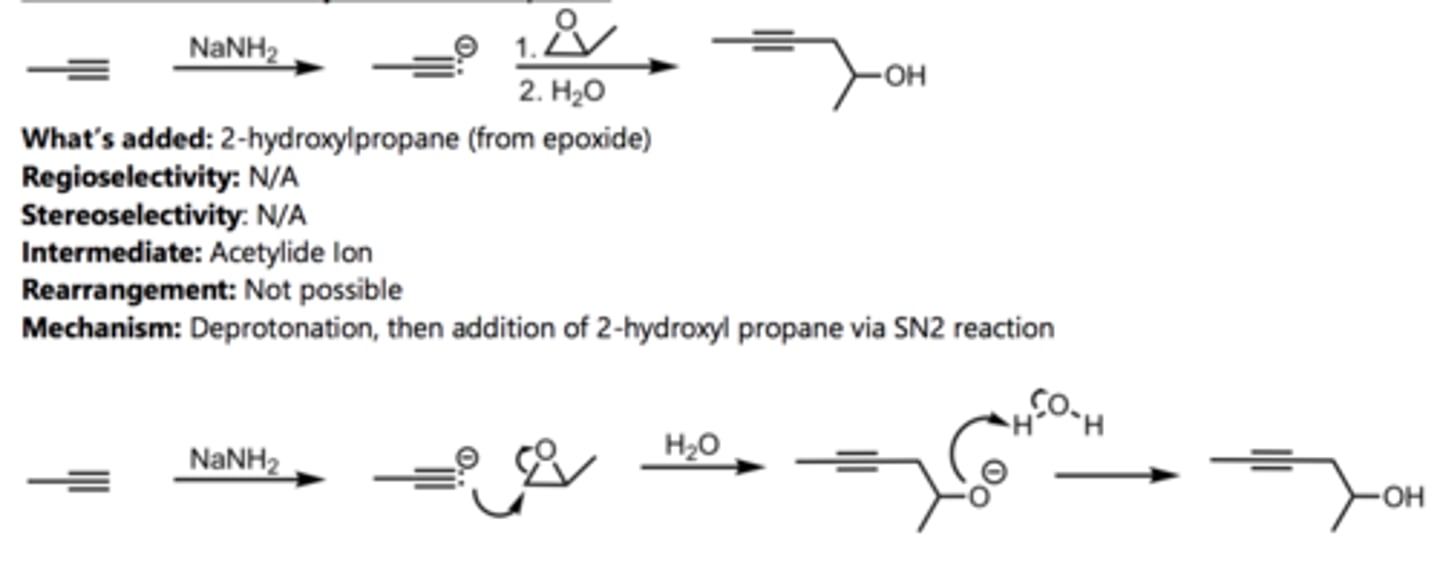
Ozonolysis
Alkyne Reaction
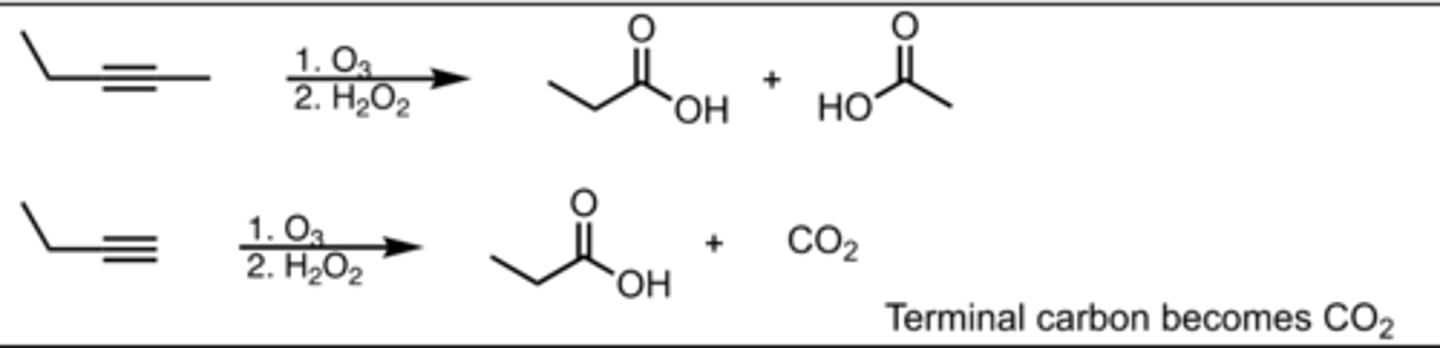
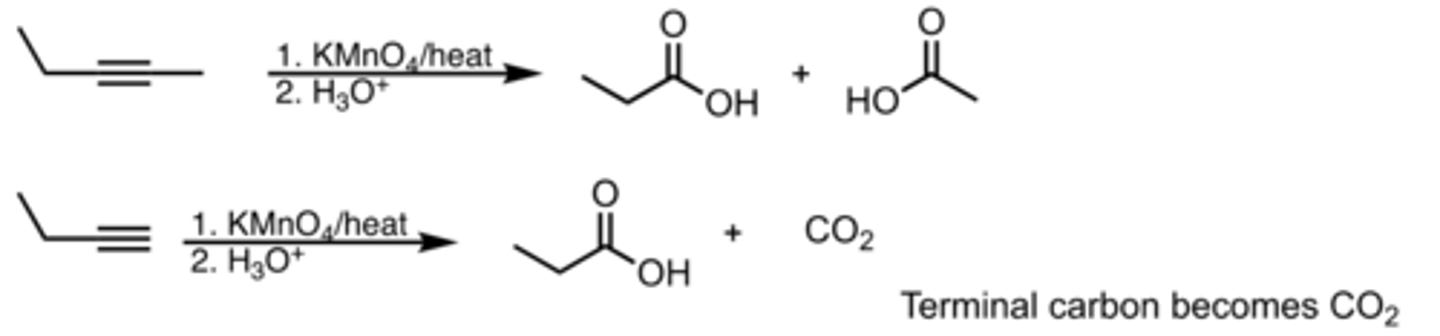
Oxidative Cleavage
Alkyne Reaction
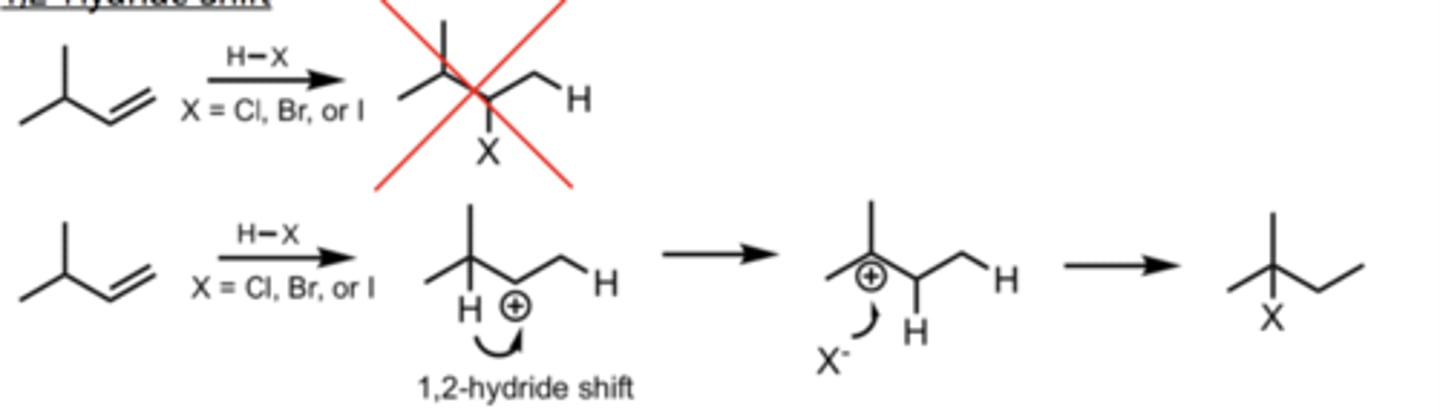
1,2-Hydride Shift
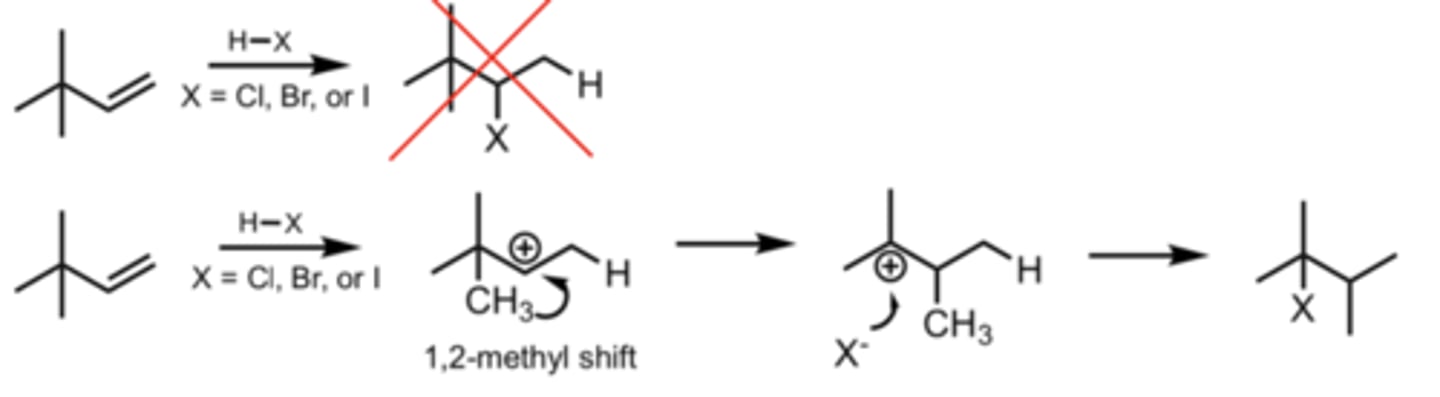
1,2-Methyl Shift
Allyl
Contains Resonance
Which carbocations are too unstable to form?
Primary and Methyl carbocations
Markovknikov Product
Alkene addition product from most stable carbocation intermediate
Angle Strain
When rings deviate significantly from ideal bond angles
Most stable carbon ring sizes
5 - 6 membered rings are most favorable - 109.5 Degree bond angles
Oxygen bonds in a neutral state
Oxygen has 2 Bonds in a neutral state
Oxygen with a positive charge
Oxygen with 3 bonds
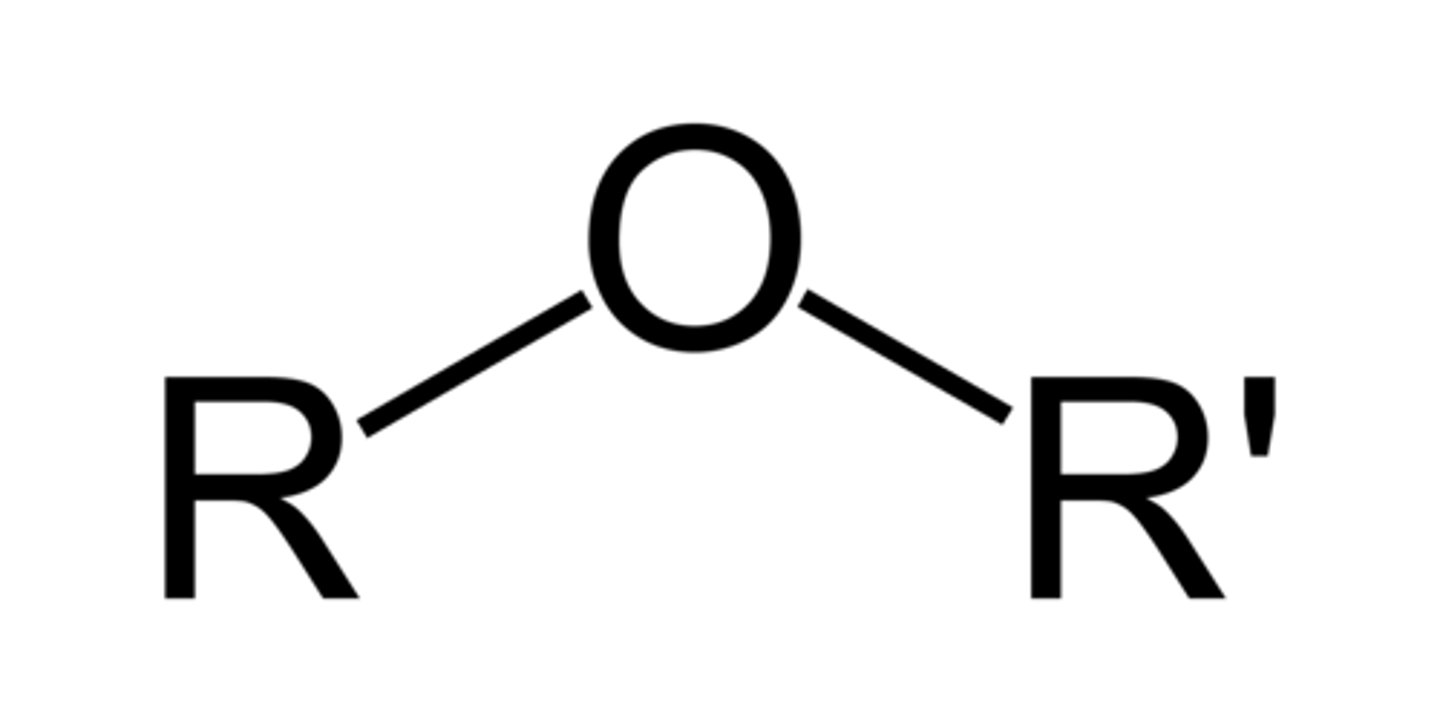
Ether
Carbon Groups on e(i)ther sides of an Oxygen
Anti-Markovknikov Product
Alkene addition from the LEAST stable carbocation intermediate
Peroxide
Oxygen single bonded to an Oxygen
ROOR
Peroxide
H₂O₂
Hydrogen Peroxide
H₃O⁺
Acid
CH₃OH
ROH
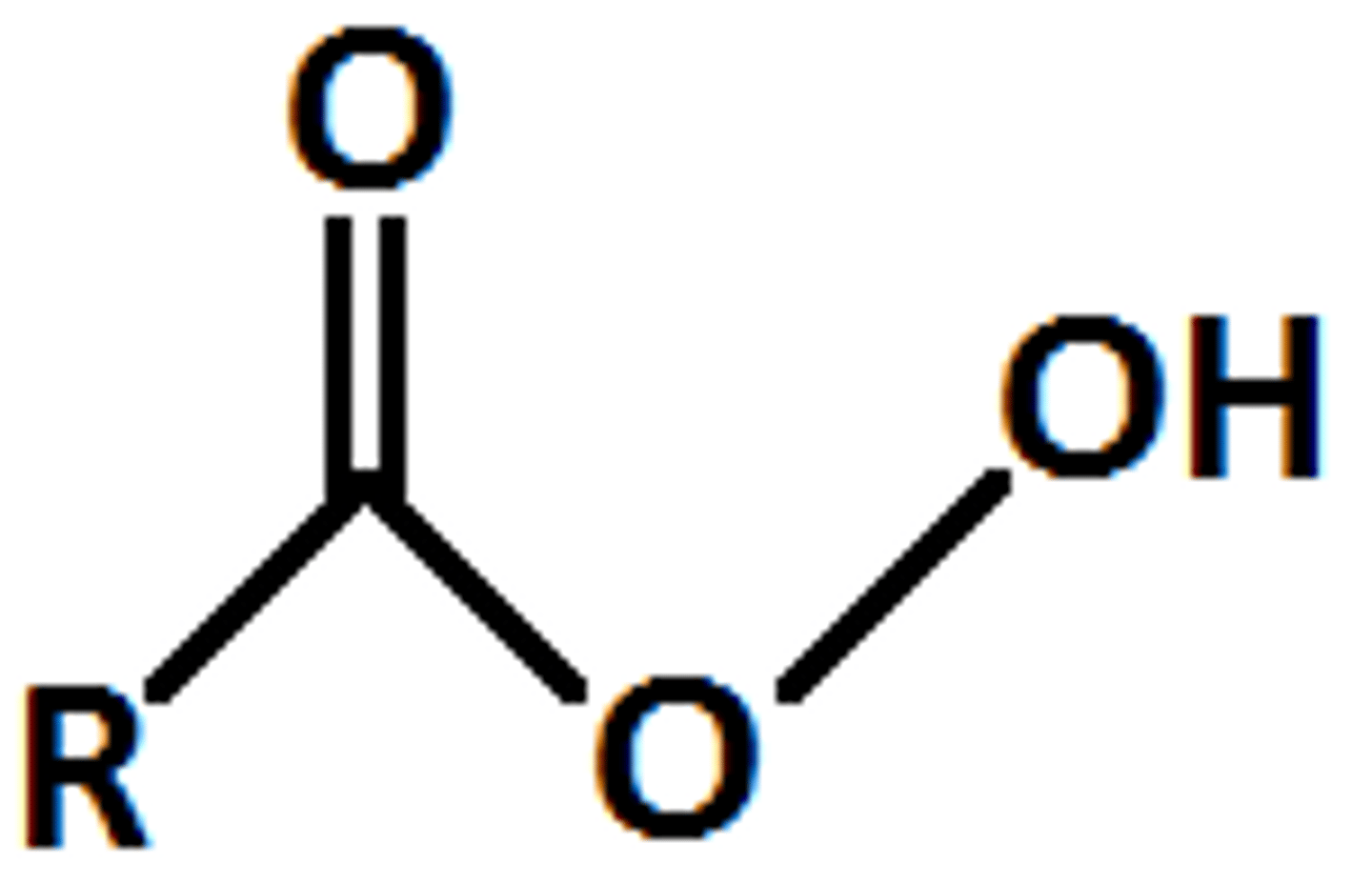
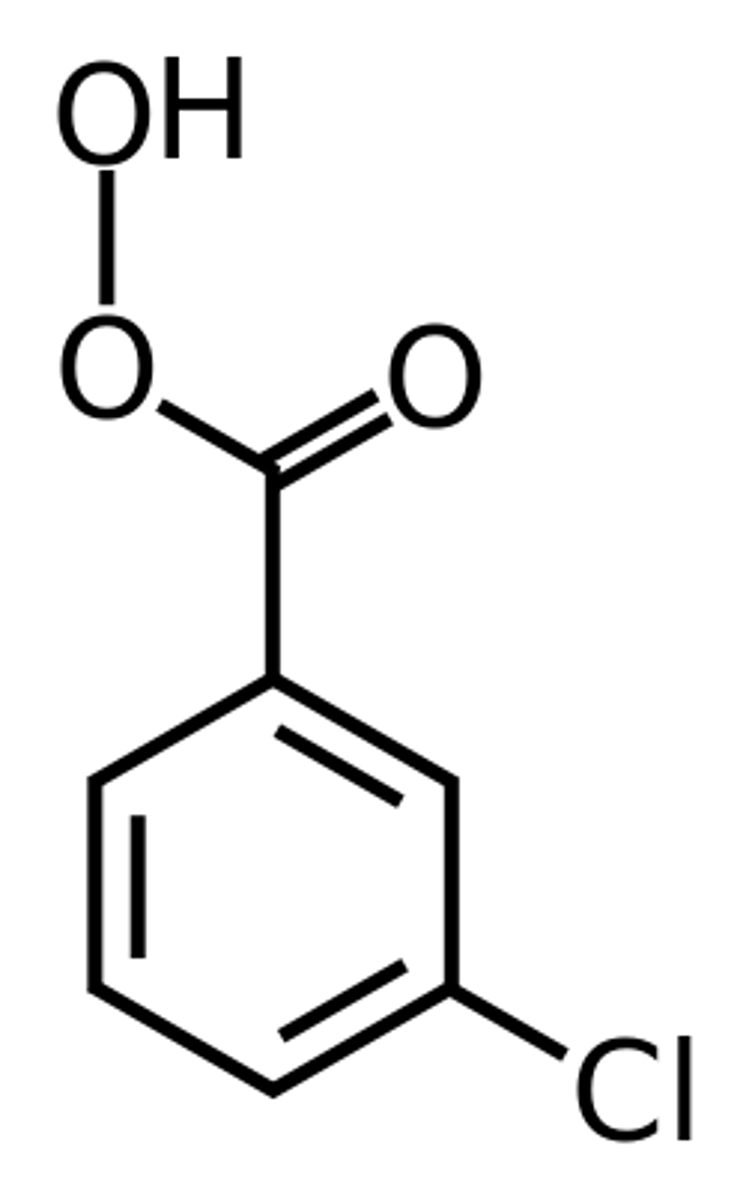
Peroxy Acid
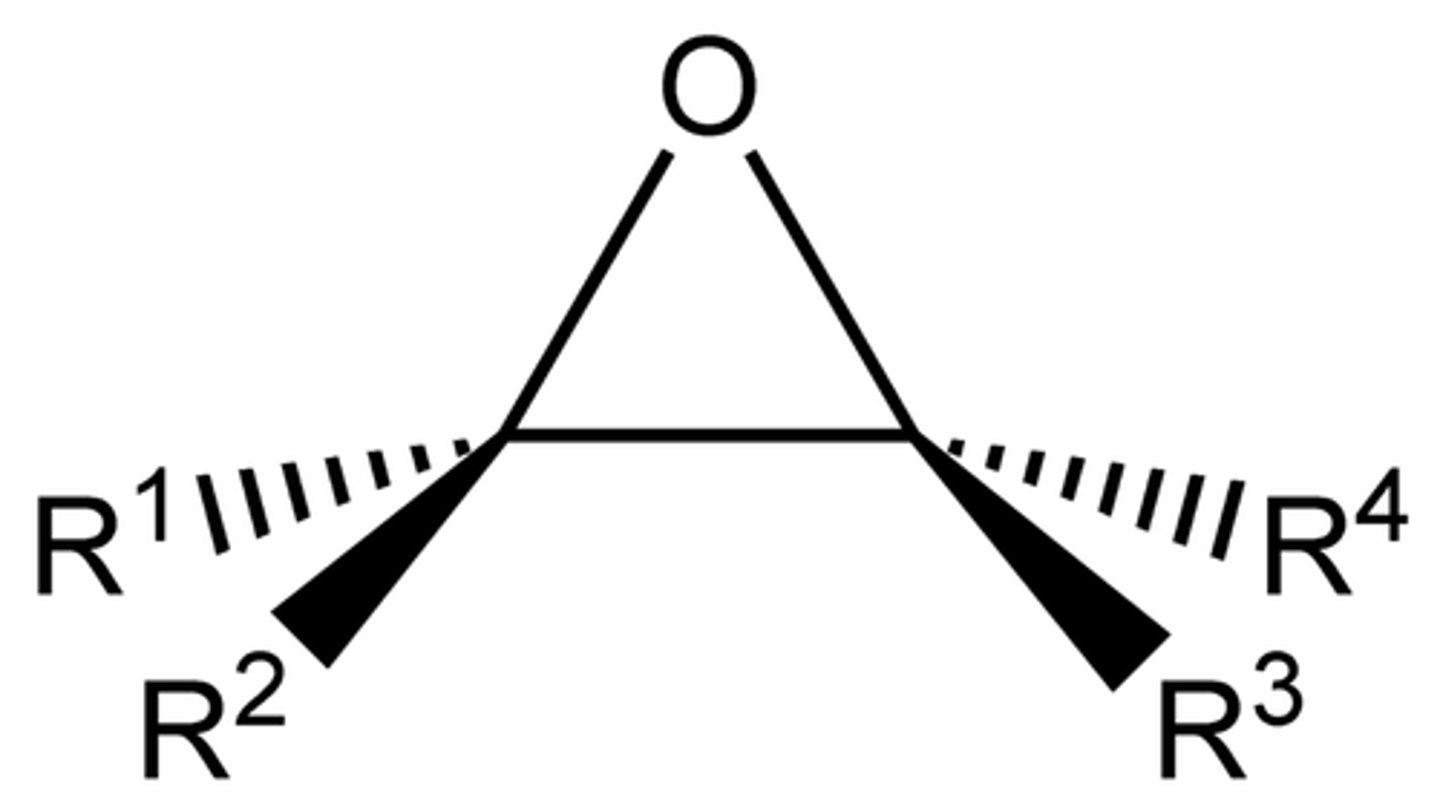
Epoxide
3 Membered ring, with two carbons and an Oxygen
mCPBA
Peroxy Acid
O₃
Ozone
(CH₃)₂S
DMS
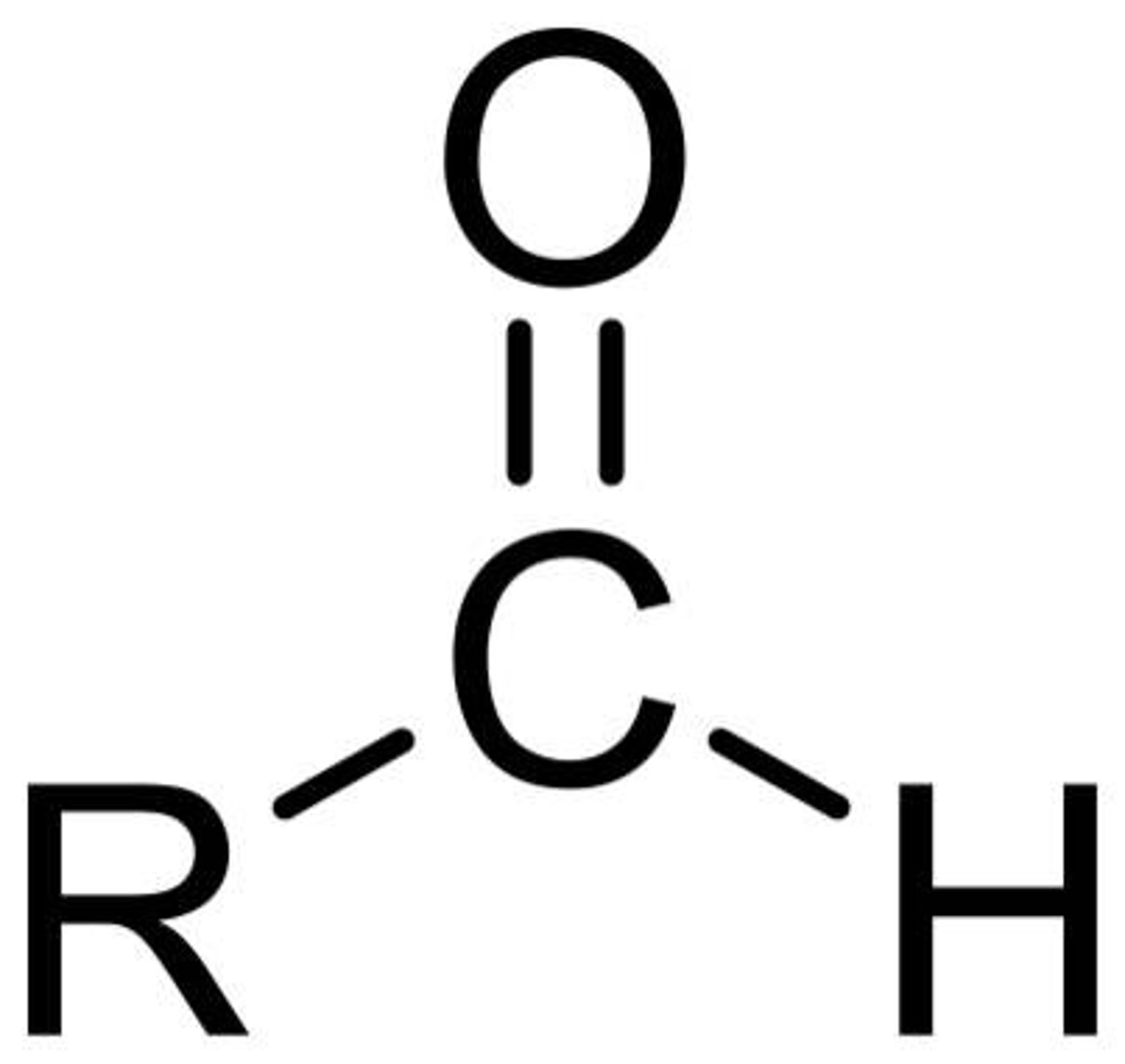
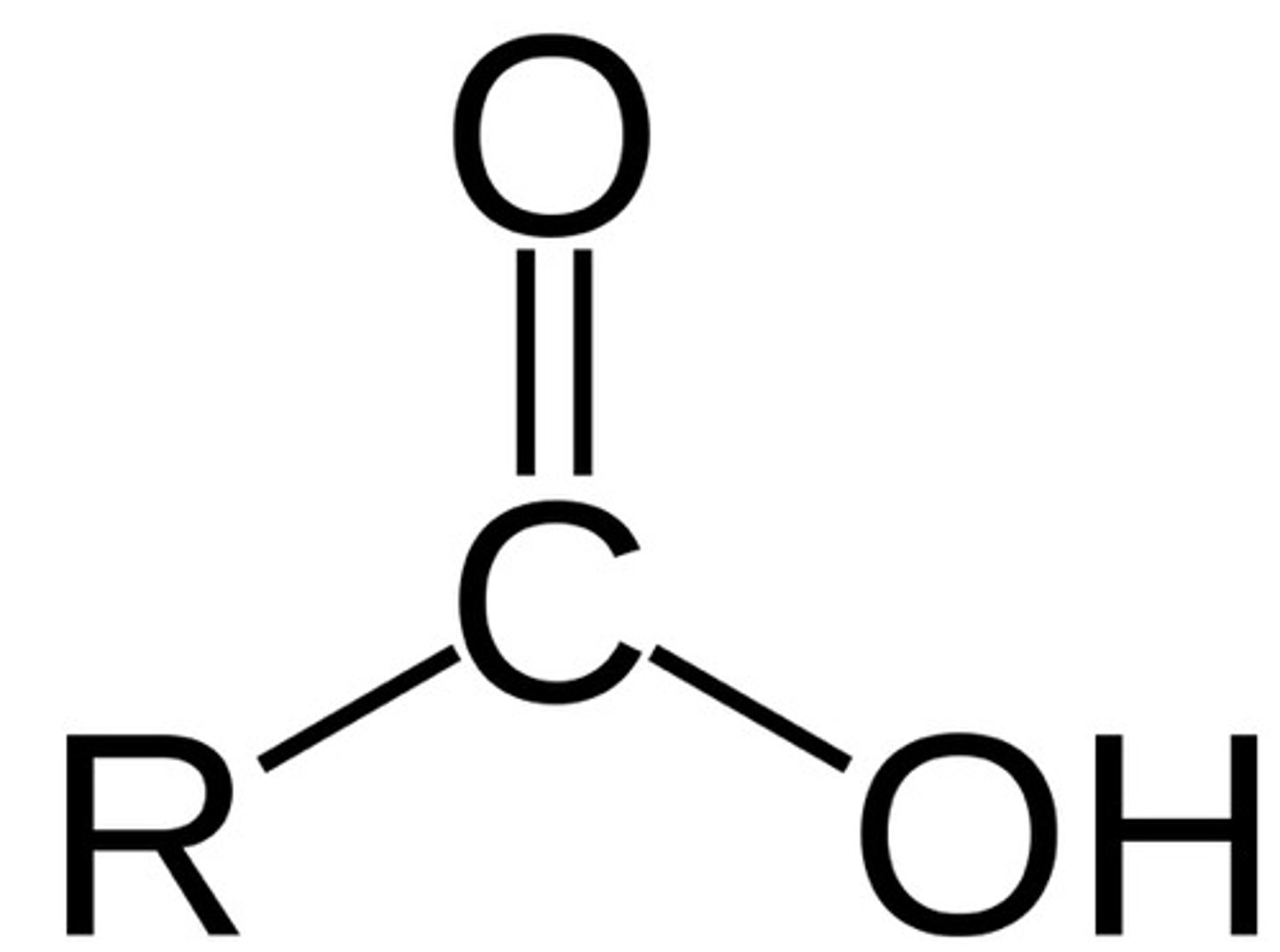
carboxylic acid
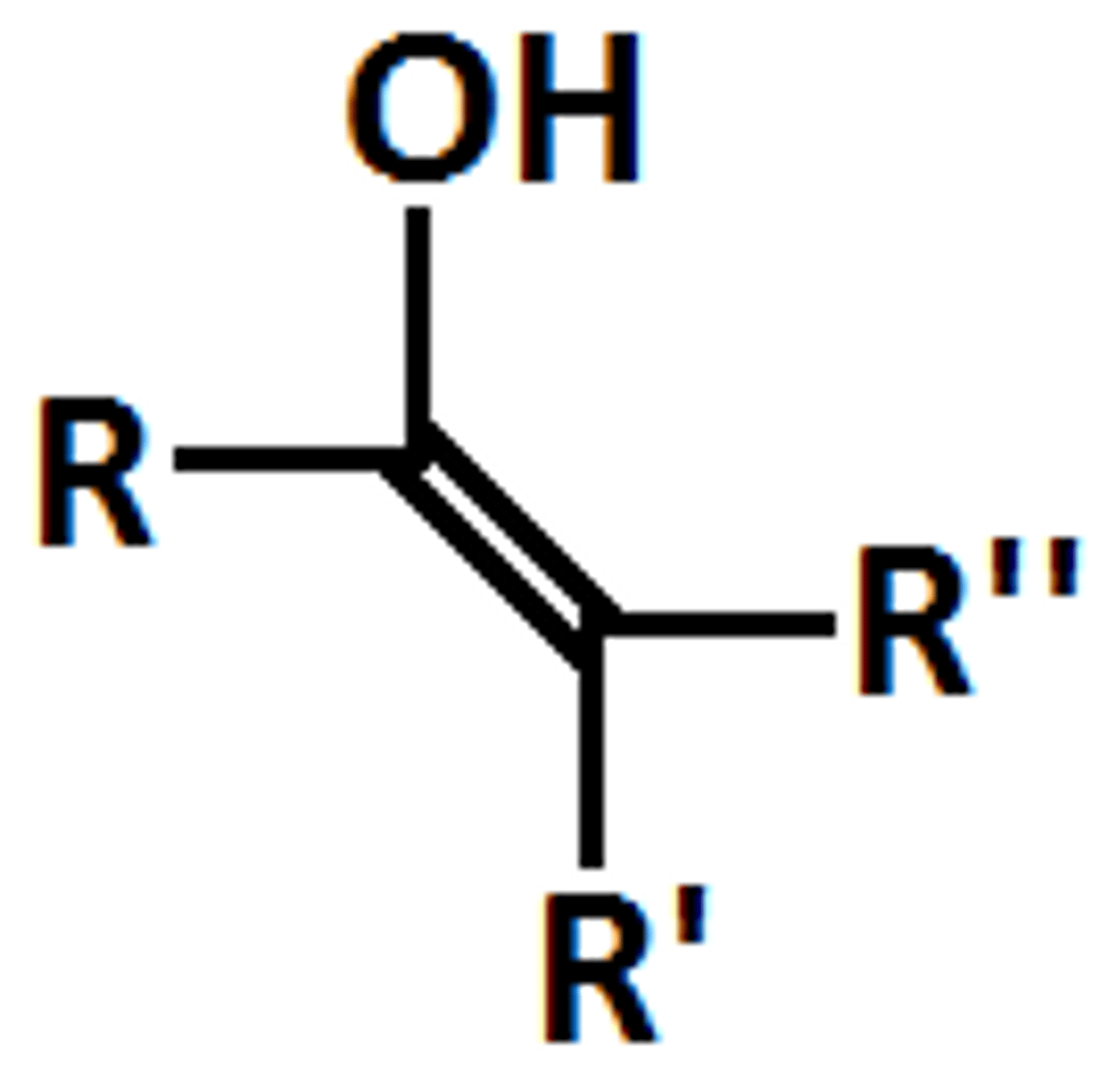
Enol
OH Bonded to Carbon, double bonded to another carbon
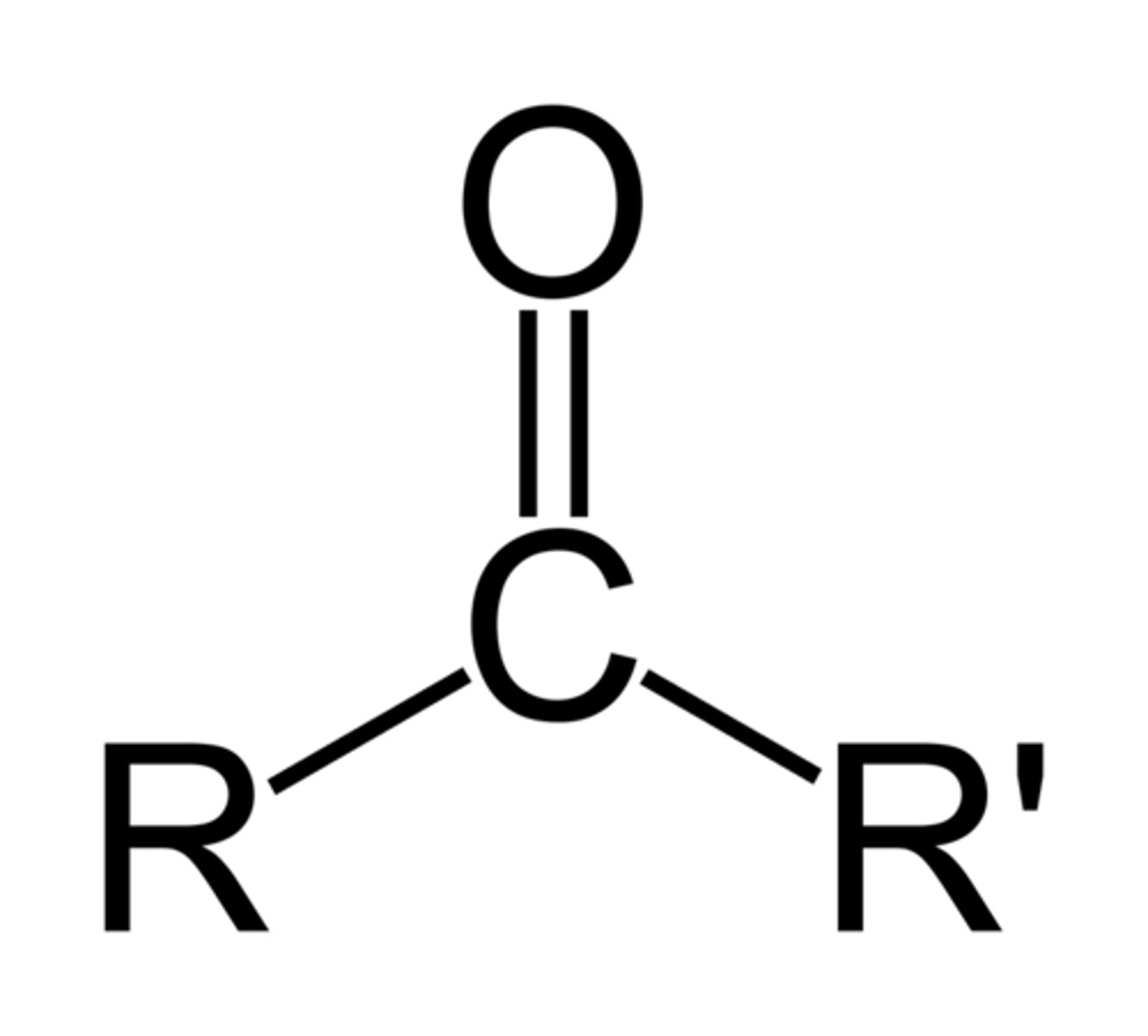
Ketone
O double bonded to Carbon
Peroxide with OH⁻, and H₂O
Basic Peroxide
aldehyde
alkylhalide
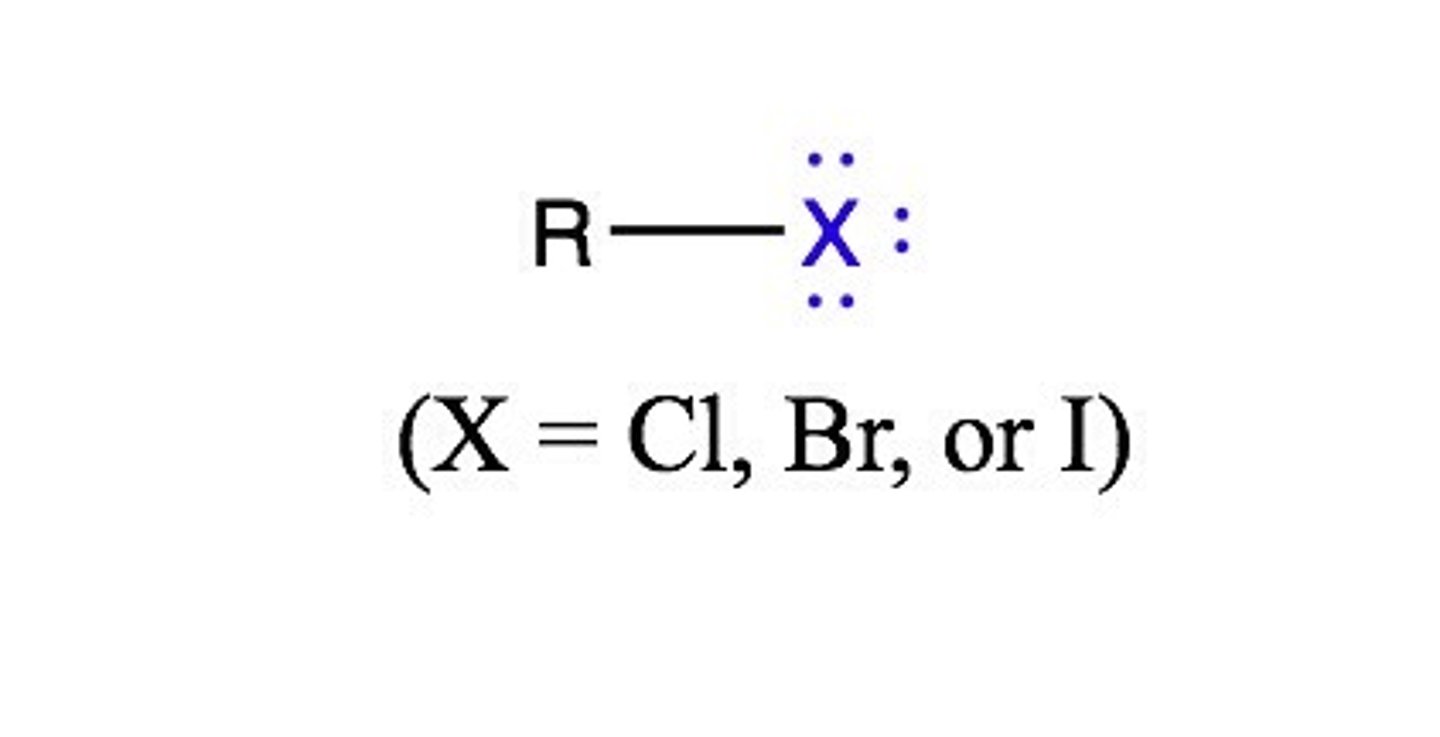
Hydrobromination with peroxide of Alkynes
Br will go to least stable Carbon, producing Anti-markovnikov Product
mCPBA/H₂O₂/Peroxy acids form:
Epoxide
CH₃MgBr Acts as:
H3C-
Lithium is a
Electrophile, gives away its electrons
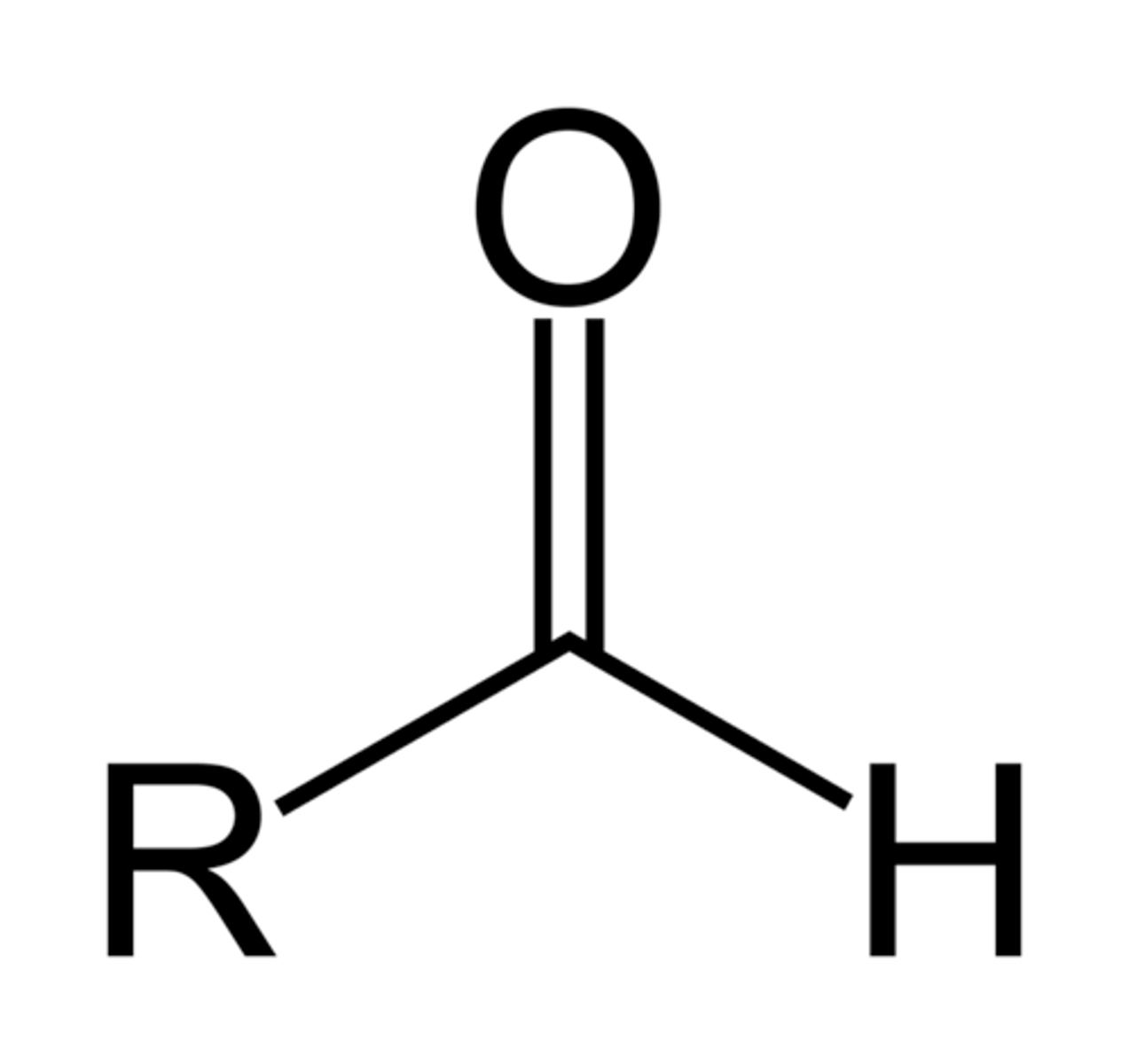
CHO
Aldehyde