3 - G Proteins & Enzyme Linked Receptors
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Metabotropic Receptors
Receptors associated with G proteins and secondary messenger systems
GPCR
G-protein coupled receptor
single polypeptide
7 transmembrane domains (a-helices)
Ligand binds to either extracellular domain or within transmembrane domain (depending on type)
What are the effects of activating a G protein?
Activates an ion channel
Activates a second messenger (eg Ca)
Examples of G-protein activated enzymes
Adenylyl Cyclase —> activated by Beta 2 adrenoreceptor (second messenger enzyme)
Guanylyl Cyclase
Phospholipase C
What products are produced in reactions involving these G-protein activated enzymes?
- adenylyl cyclase
- guanylyl cyclase
- phospholipase C
ATP -> cAMP
GTP -> cGMP
PIP2 -> DAG/IP3
What is the effect of Protein Kinase A/Protein Kinase G on cAMP/cGMP?
Phosphorylates them to cause the response
What is the effect of Phosphodiesterase on cAMP/cGMP?
Dephosphorylates them to form AMP/GMP
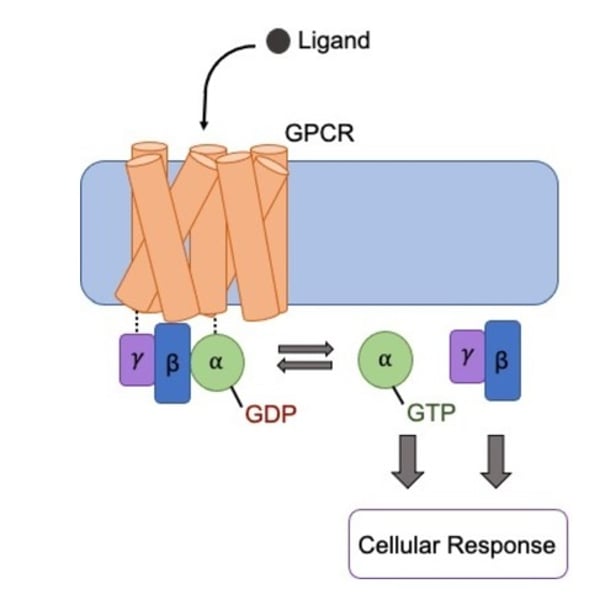
How do GPCR's work?
Ligand binds to GPCR
GDP attached to alpha subunit swaps for GTP
GTP detaches the alpha unit from beta and gamma units
This activates the cell response
What are the two mechanisms of turning proteins on?
- GTP binding to G proteins —> exchange of GDP for GTP, switched off again by GTP hydrolysing back to GDP & protein itself
- Phosphorylation —> by kinase enzyme, switched off again by dephosphorylation by phosphase enzyme
How does Noradrenaline cause bronchodilation?
NA binds to beta 2 receptor
G protein activation
Activates & increases cAMP
Inhibits MLCK (myosin light chain kinase)
Causes bronchodilation
What are the affects of
- alpha adrenoreceptors?
- beta 1 adrenoreceptors?
- beta 2 adrenoreceptors?
increased BP and bronchoconstriction
increased HR
bronchodilation
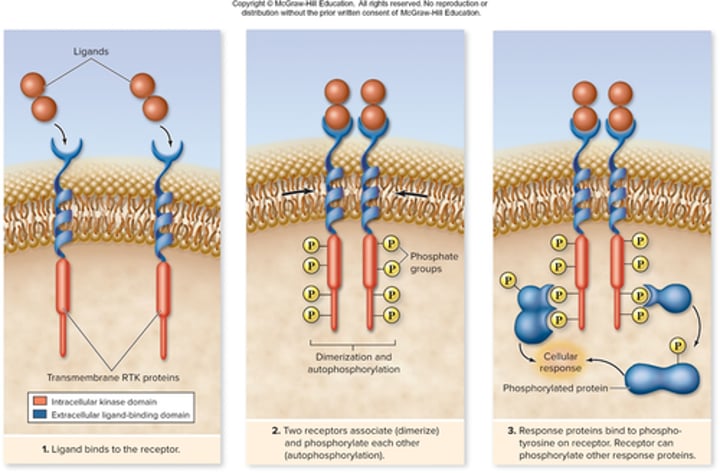
Enzyme linked receptor
Have binding domain & kinase domain
Sit as monomers in membrane
Tyrosine kinase domain embedded in tail
Noradrenaline Structural Activity Relationship (SAR)
Increasing -OH groups on noradrenaline increases its potency
How do receptor tyrosine kinases work?
2 receptors stuck together
Causes 2 monomers to stick together and to phosphorylate tyrosine kinase
Causes cellular response