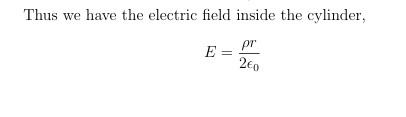Physics 2 Midterm 1
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
What is principle of conservation of charge
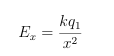
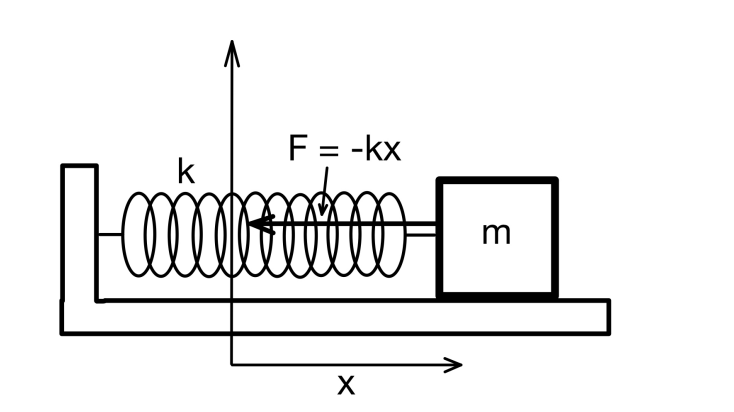
What is a ideal spring
An ideal spring has no mass and loses no energy (it is perfectly elastic, and therefore a conservative force, we will talk about conservation forces later). We are now considering a point mass on a spring (ignoring friction) that is oscillating back and forth,

What is this a figure of
Ideal
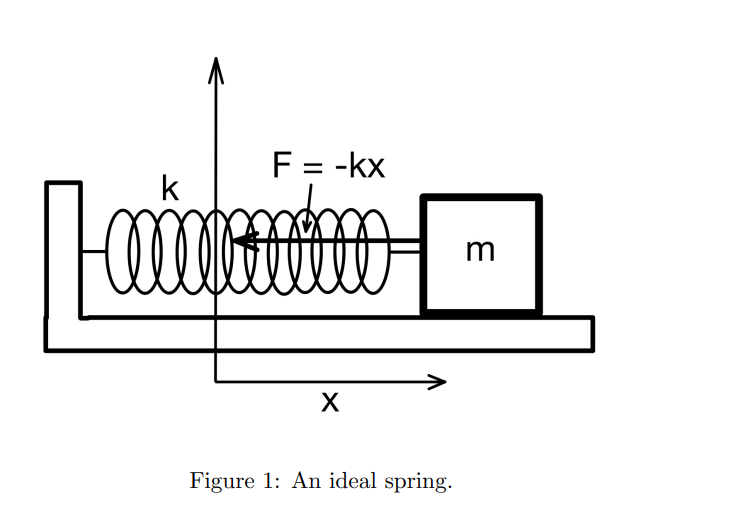
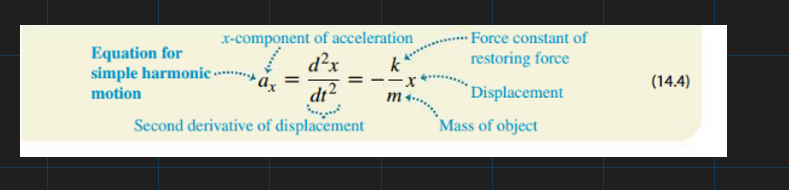
What does the negative sign indictate on the spring force
That it is a restoring froce
What are ODES

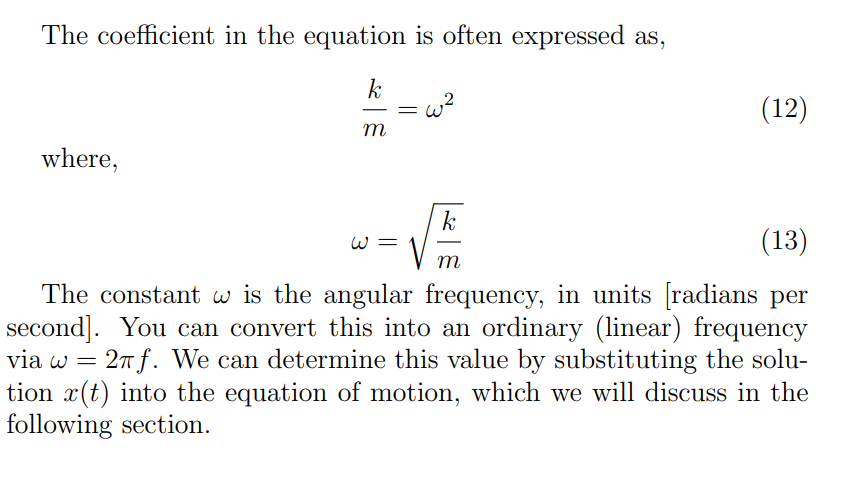
Whats the equation for angular frequecny and what does it reprssent
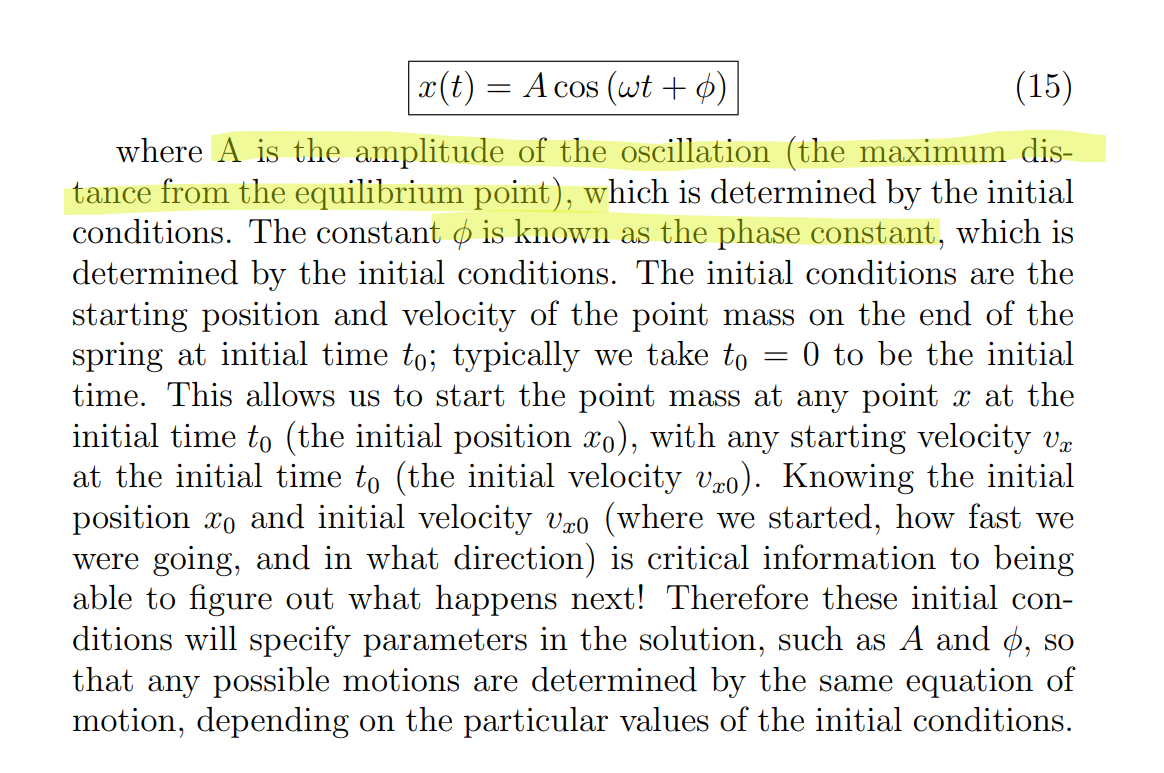
What is the solution for the ideal spring equation

What do the different variables in the wave function represent
In the general solution for a simple harmonic oscillator (like your mass on a spring), the position $x$ at any time $t$ is:
x(t) = A \cos(\omega t + \phi)
A(Amplitude): The maximum distance from equilibrium.
omega (wt):The portion of the cycle that has passed due to time.
phi: (Phase Constant): The "offset" or "shift" applied to the starting point.
What is the sin version of the ideal spring formula, and whats differetn

Whats the equation for mechanitcal energy for an ideal spring
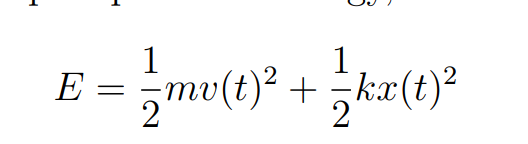
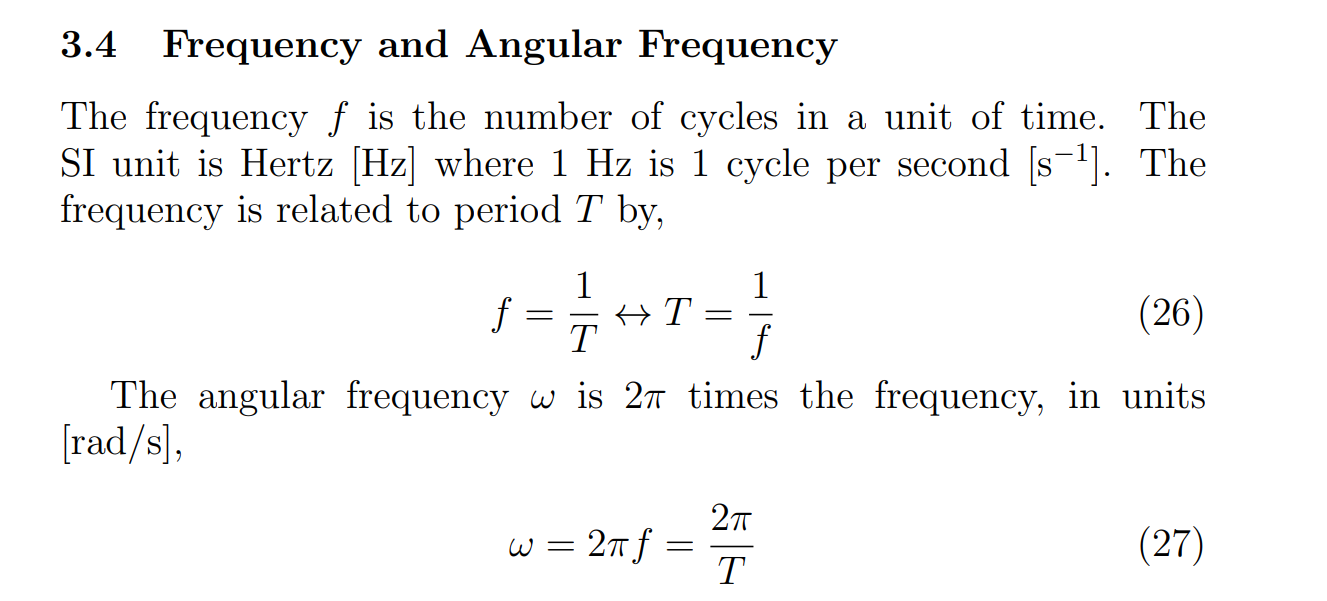
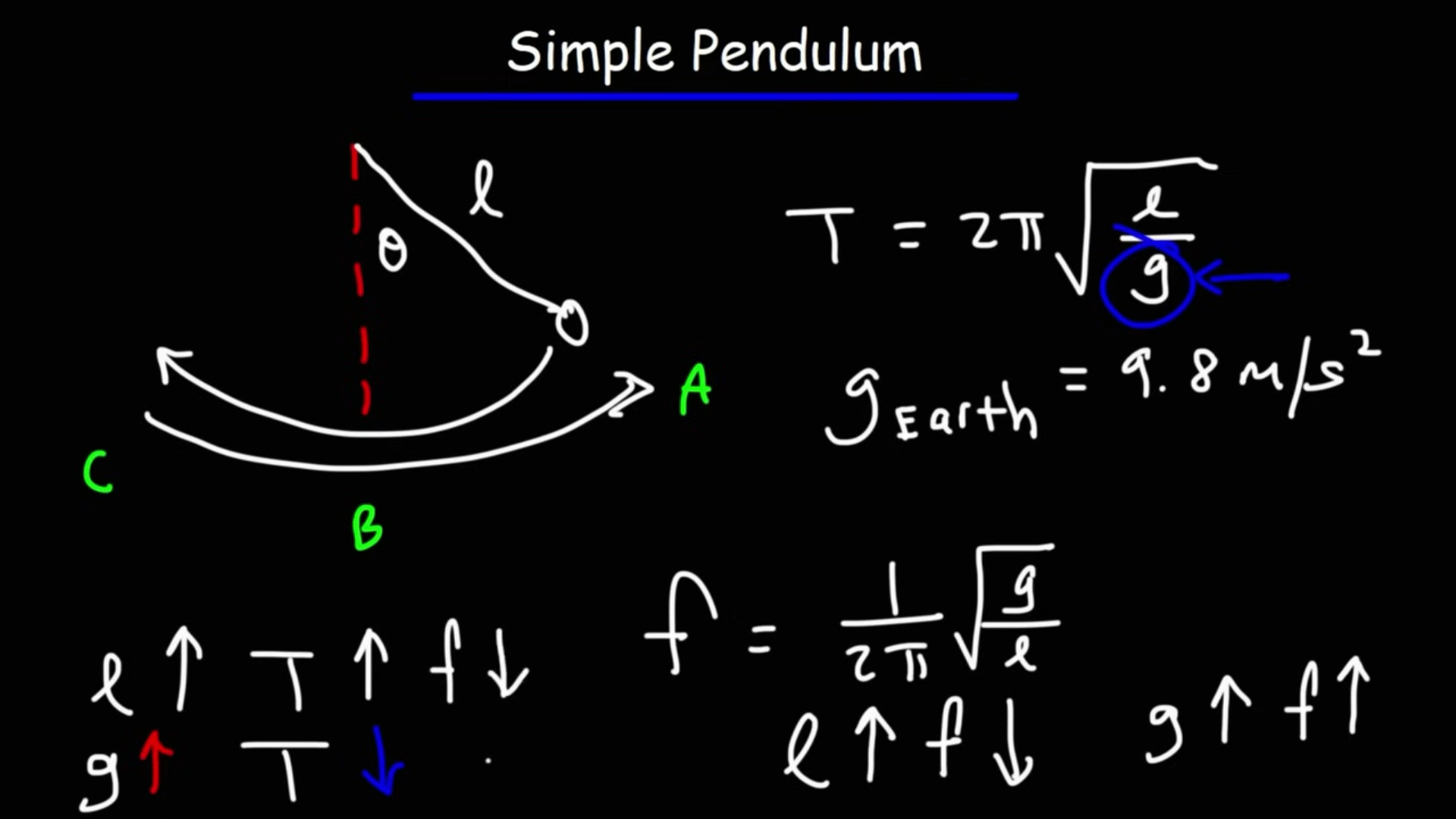
What is the formula for Frequency and period, and angular frequency
How do you solve for Amplitude

Whats the formula to solve for phase constant
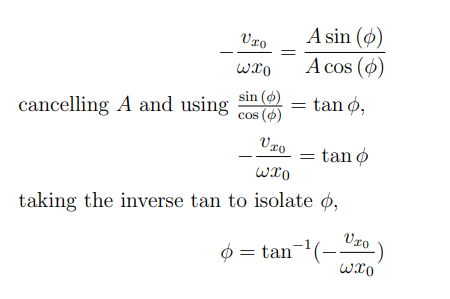
What is the damped harmomic oscillator solution
What does the energy expression reduce to nergy expression reduces
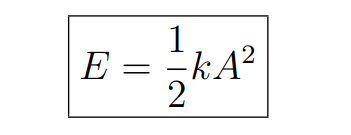
True or False: The total energy of the spring is awlays constant
True
True or False: Potential energy and kinetic energy exactly compensate each other, as one icnreases, the other decreases, for a constant total
True
What is Max at the amplitude,
The potential energy function
1/2kA²
What is Max at equlilbruium
The kinetic energy is at a maxikimum
1/

Whats the equation for simple harmonic motion
Whats the formula for period for spring
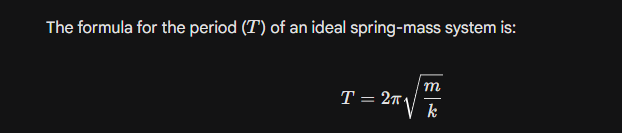
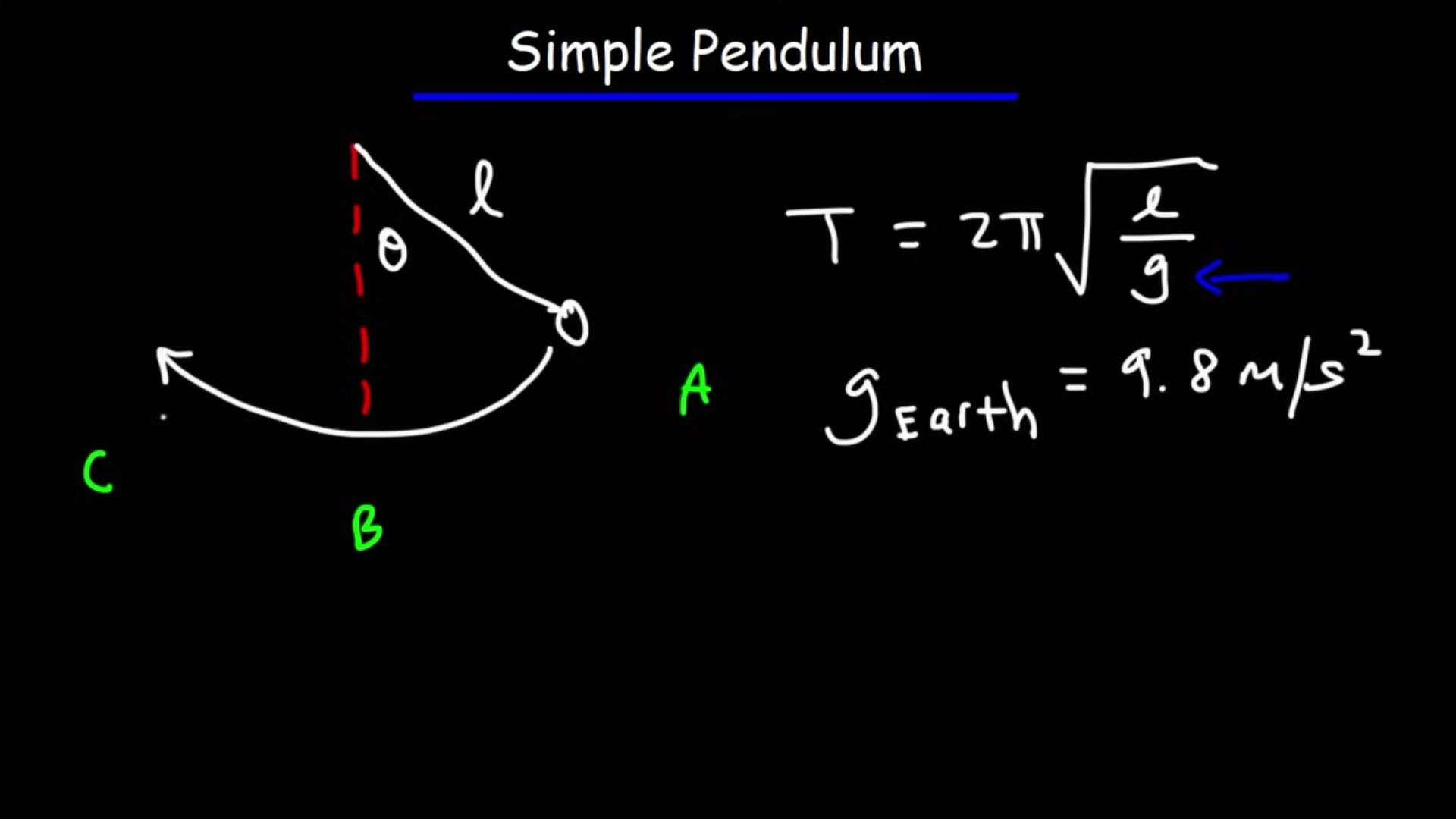
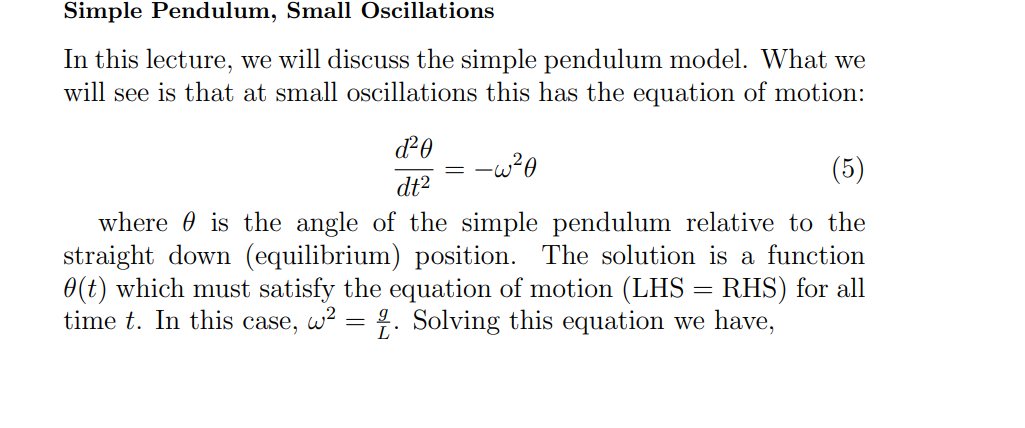
What is the equatino for a simple pendulum, and what is w = to?
and what does the Amplitude become
g (Acceleration due to gravity): This represents the gravitational pull acting on the pendulum bob, which provides the restoring force necessary for oscillation. On Earth, this is approximately $9.8 \text{ m/s}^2$.
L (Length of the pendulum): This is the distance from the pivot point to the center of mass of the pendulum bob.
g/L (The Ratio): Together, these physical properties determine how fast the pendulum swings. Specifically:
Higher Gravity ($g$): A stronger gravitational pull results in a faster swing (higher frequency).
Longer Length ($L$): A longer pendulum results in a slower swing (lower frequency).
This relationship is used to satisfy the differential equation of motion:
\frac{d^2\theta}{dt^2} = -\left(\frac{g}{L}\right)\theta
here θA is the “amplitude”, that is, the maximum angle in the periodic oscillation
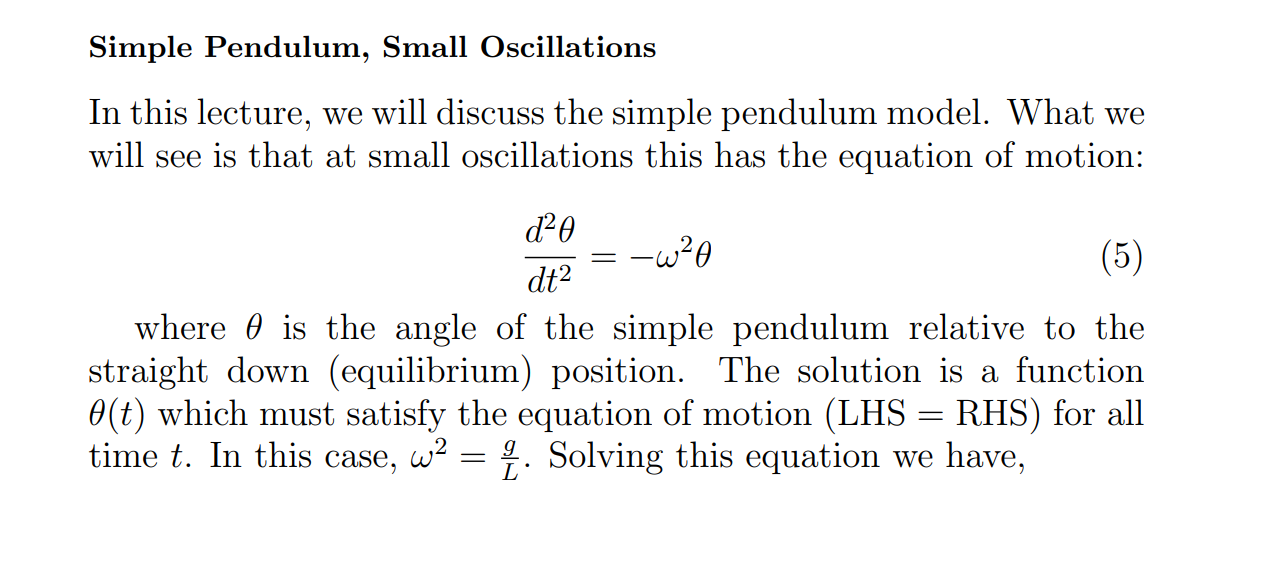
What is the equation for LC Circuit, and is the w equal to, and what does the Amplitude become
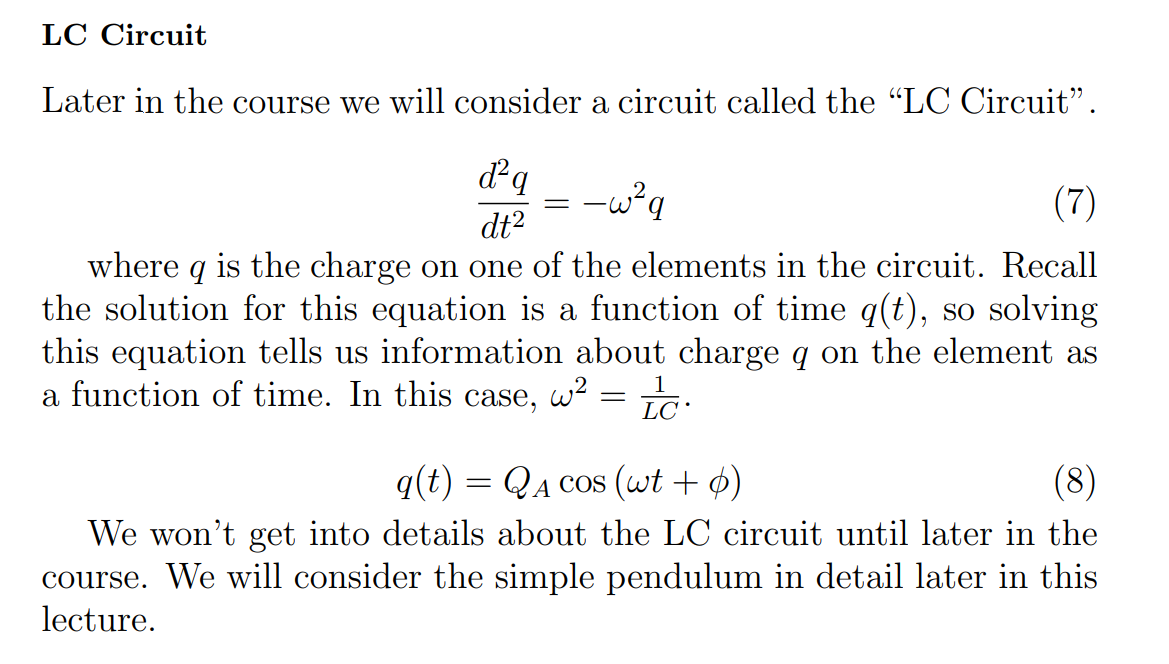
Whats the the relationship between force and potential energy and the deritative of this potential energy function
Describe the realtionshipe between kinetic, potential, and total energy. and when they are maxed

What happens when you plot a x(t) vs v(t)
you get an ellipse
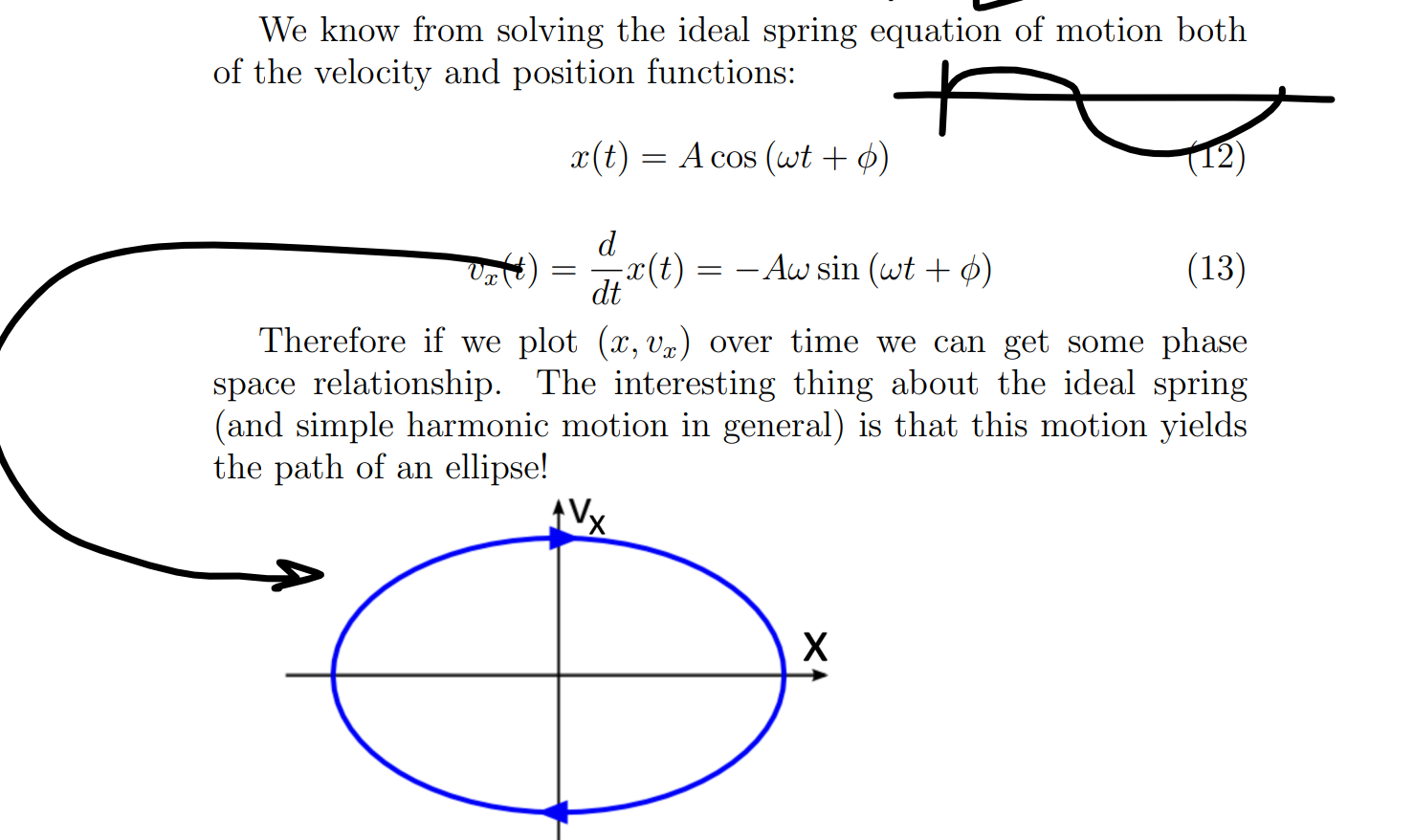
Whats One way to show that the path is an ellipse formula

What is period equal to
Time/ cycles
Formula for simple pendulm for 1 compelete swing (go there then back to norma) T
mass doesn’t matter
Formula for simple pendulm for 1 compelete swing (go there then back to norma) f
Whats the equation for torque on simple pendulm
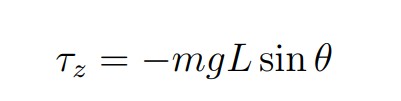
Whats net torque equal to
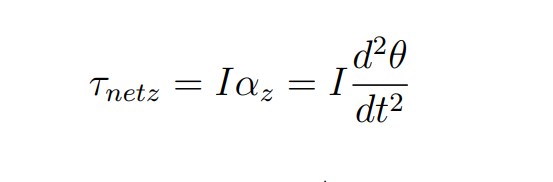
Whats the equation of motion for pendulm

For a physical pendulm how could we find the angular requency
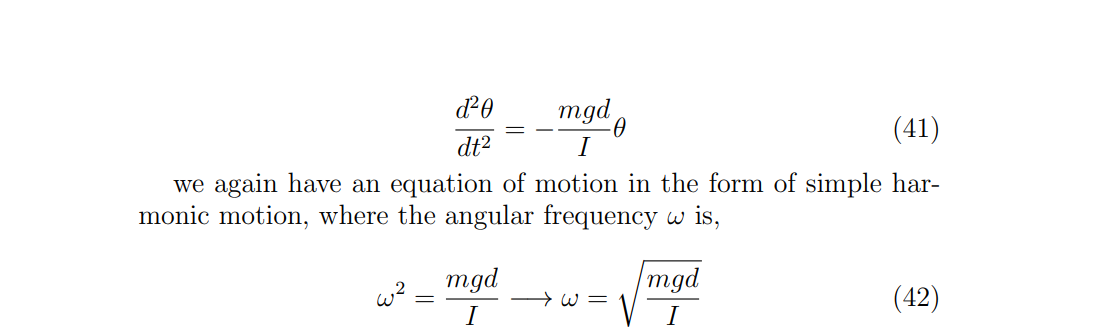
For a physical pendulm how could we find the Period
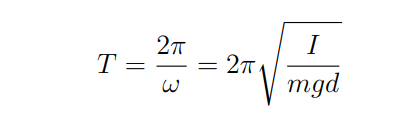
What is w equal to on a simple pendulm
What is the difference and what are we accounting or the damping ossiclaitons

What happens to the motion of a damped harmonic oscililator

For a damped oscillator what is the force Fd (damping force) equal to
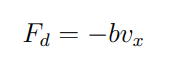
What is the no damping frequncy formula and, what is the damping coefficient?
b is the damping coeffienct and m is the mass

What is angular frequency formula for damped ossilations

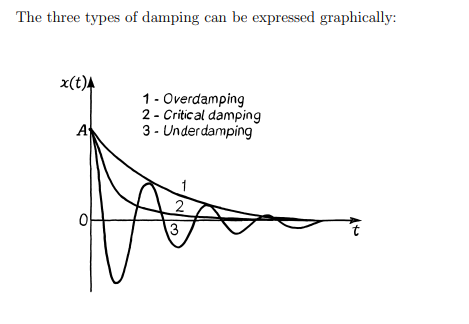
What are the 3 possibilities for angular frequency for damped oscillations, and what are the conditions for each
Real damping the w is larger than the y/4 (light damping)
Imaginary value y²/4 > w (Heavy Damping)
If w=y²/4 we have a zero value for w (Crtiical Damping)

What kind of damping is each one here
1. Underdamped (Real)
In this scenario, the damping is "light." The system still oscillates, but the amplitude gradually decreases over time until it eventually stops at equilibrium.
The Angular Frequency: The frequency is slightly lower than the natural frequency: $\omega_d = \sqrt{\omega_0^2 - \gamma^2}$.
Behavior: You see recognizable "bouncing" or "swinging," but each peak is lower than the last.
2. Critically Damped (Zero)
This is the "sweet spot" where the damping is exactly strong enough to prevent oscillation entirely.
The Angular Frequency: In this case, $\omega_d = 0$.
Behavior: The mass returns to its equilibrium position ($x=0$) in the shortest amount of time possible without ever crossing over to the other side.
Application: This is the ideal setting for car shock absorbers or self-closing doors, where you want a fast return to "rest" without any bouncing.
3. Overdamped (imaginary)
In this state, the damping is "heavy." The system is so thick with resistance that it can't oscillate at all.
The Angular Frequency: The value of $\omega_d$ becomes imaginary because the term under the square root is negative.
Behavior: The system slowly "crawls" back toward equilibrium. It takes much longer to return to rest than it does in a critically damped system.
What is the formula for the angular frequency for the damped oscillator
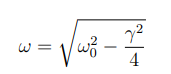
What is the solution for light damping
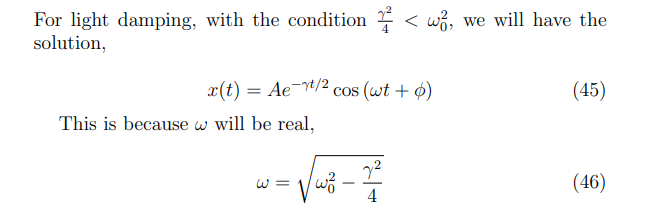
What is the cosine way to express the light damping solution
basically broke into 2 functions

What is the ratio of amplitude decay formula
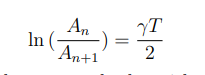
Whats the heavy decay solution
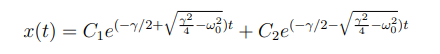
What is forced undamped oscillations
Motion is maintained indefinetitly, depsite the presenecesn of damping
Imagine a swing and someone pushing it in order for that motion to continue
Whats the formcula for undamped forced osccilations
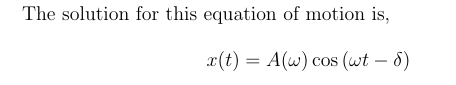
What is the solution formula for the forced osscillations
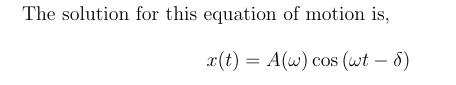
What is resonance in a forced osscilation
It reaches its maixmium value . Also lim w→w_0 = would be infinitiy

What is resonance (given defintion)

What is natural frequency
How

When does reasonance occur
When the frequency of the natural frequency is equal to the added freqeucey (frequency of the driving force matches the natural frequency), which will produce maximum amptlitude

Whats the differenced between undamped and damped oscillations
Nothing about the soltuion is different, only what happeneds to the amptlitude, and forceing frewquencnyes, and phase constand change

Whats the equation for A(w) for damped harmonic osillator with any driving (forced) frequency w.

What is the equation for maximum amplituded for damped forced ocsillatiosn

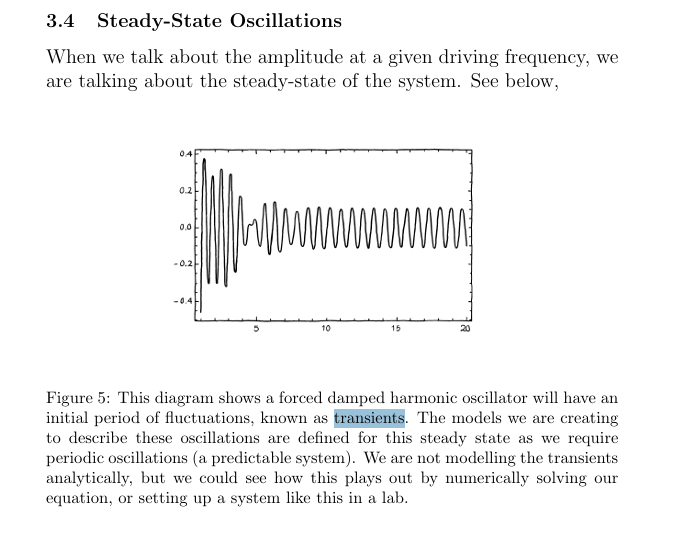
What are transients
Intial period of flucations, before they start becoming “normal”
What is the unit of measurment for Electric charge q
Columbs - C
It can tell us weather or not motion will ocur when an objeect is placed in a alectromagnetic field
What is the units for electric field
N/C Newton per Coulomb or
Volts/Metre
What is the formula for a electrostatic field given off by a single stationary charge 1
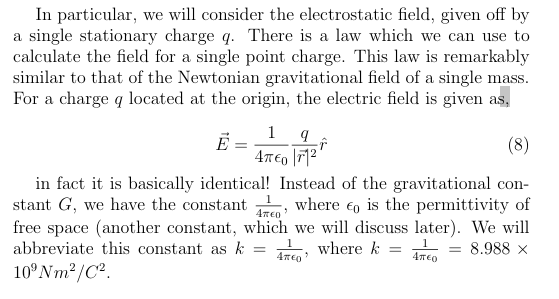
What is the formula for for electric field and how do you calculate R
Vector differences, R is the unit vector

What is the vector R equal to in terms of charge q and the point
From the charge q to the point P
Feild point - charge location
What happens when the charge is postive and what happens when its negative
If q is postiitve poitns away
Negative arrow points forward
Whats the formula of electrif field
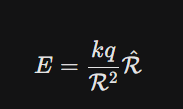
What is the formula for Force acting on particle Q is a electrif field
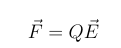
What is the F = ma (Newtons second law) version for electric fields), and what is it also equal to

What is the inverse Square Force Law that effects Coulombs Law
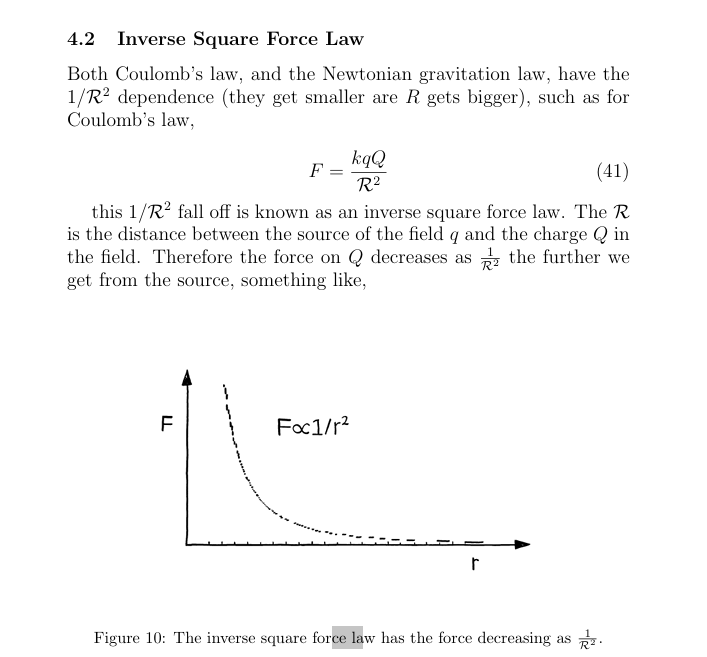
What is coulobs Law
F = k (q1 q2/r²)
What is the formula for coulombs law, and what can it do
it represents the force experienced by a charge (Q) when it is placed within an existing electric field created by another charge Q
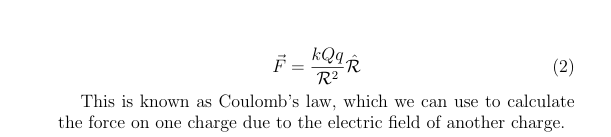
What does big R and little r represent.
Big R is distance from point/P to vector
r is just the vectors
R→ is = Sumed position - start
What does a negative Coulombs Law represent
An attractive force

What is the integration formula
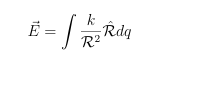
What is lambda equall to and represetnts for integrations for lienar charge distribution

Whats the calculation for dl and what happens when its along an axis

What does the superposition find

What does lambda represent
Charge per length
lambda = dq/dl
Whats the formula for the electric charge on a ring
sing trigonometry, cosα = dEx dE −→dEx =dEcos
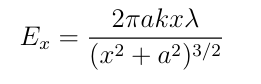
What is the aproximate of E on ring of charge formula
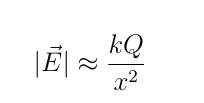
What is flux
Flux is the amount of something passing through a surface
When is flux maximized

What does a negative flux represent

What is the formula for flux

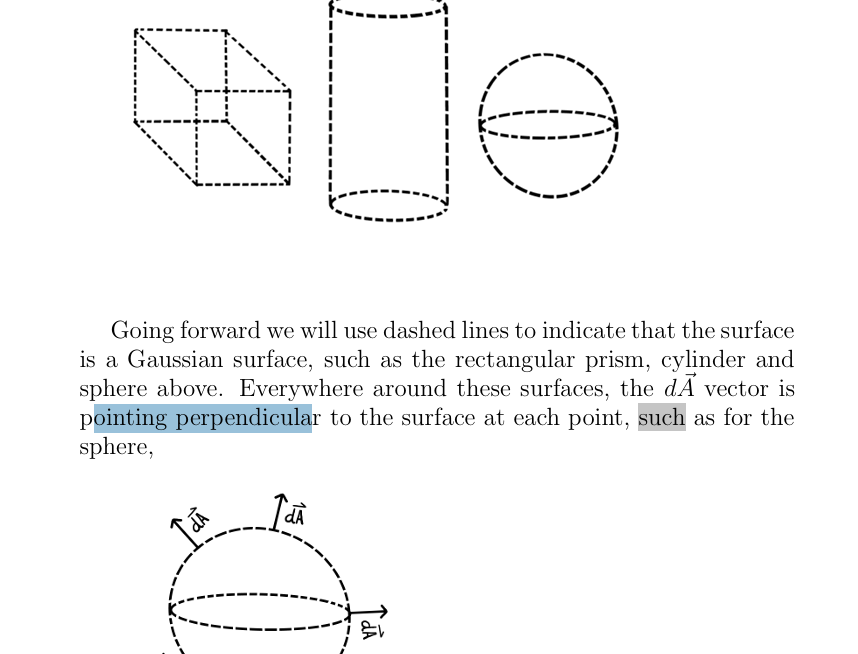
What is a gaussian surface
A Gaussian surface is an imaginary, closed surface that you define in space to calculate the electric flux passing through it. It is the "stage" where you apply Gauss's Law to determine the electric field created by a charge distribution.
NO HOLESSSS YEYSSSIR
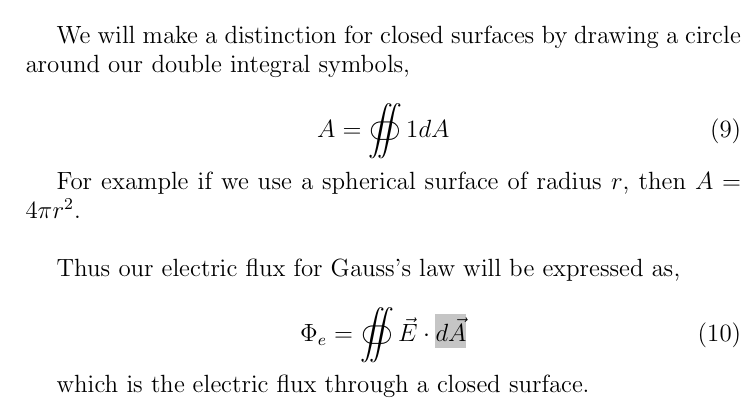
What does this circle around our double integral mean
It means that we have a Gaussian surface (no holes), therefore making the E*dA a constant (same everywhere)
How are the lines of a Gaussian surface drawn, and where are the dA vectors pointoign
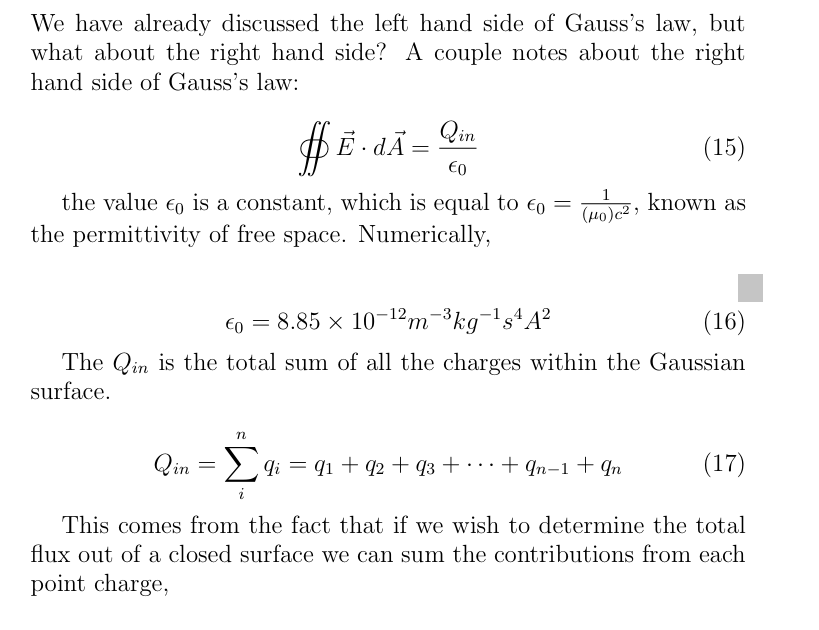
What is the final equation for Gausses Law (2 versions of it = eachother)


What is Q here?
What is EA (gauss law) equal to when cos =1
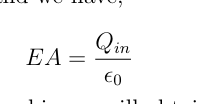
What is the formula for Sphere of Charge
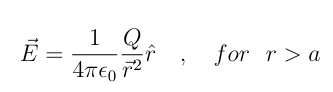
What is the formula for Infinite Wire of Charge
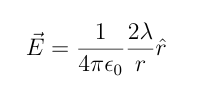
What is the equation for an infinite plane of charge
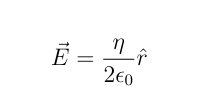
What is n —→ The surface charge density formula
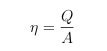
Whats the formula for the change field outside of sphere
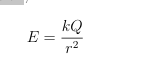
Whats the formula for E for Infinite Wire of Charge Example
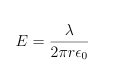
Whats the formula for E for Infinite Plane of Charge Example

Whats the formula for E for Infinite Charged Cylinder Example- Field Outside of Cylinder
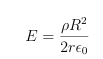
E formula for Charged Sphere Example- Field Inside of Sphere
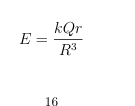
E formula for Infinite Charged Cylinder Example- Field Inside of Cylinder