Chemistry 120 Module 6
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
For chemists, the system typically refers to __________________. The surroundings include _____________________.
A chemical reaction ; everything else in the universe (including the solvent in which the reaciton occurs!)
Energy changes are described from the perspective of……
the system
Which of the following are state functions? enthalpy, internal energy, entropy, heat, free energy, work
State functions (pathway independent): enthalpy, internal energy, entropy, free energy
Not state functions (pathway dependent): heat, work
Can we measure E and H directly?
no, we can only measure changes in E and H (deltaE, deltaH)
Is the sum of heat and work a state function?
Heat and work are NOT state functions, but the SUM of them is a state function (deltaE)
Describe what is means to have negative work, positive work, negative heat, and positive heat.
Negative Work- work done by the system, on the surrounding (-w)
Positive Work- work done on the system, by the surroundings (+w)
Negative Heat- heat lost by the system, released to the surroundings (-q)(exothermic)
Positive Heat- heat gained by the system, absorbed from the surroundings (+q)(endothermic)
formulas?
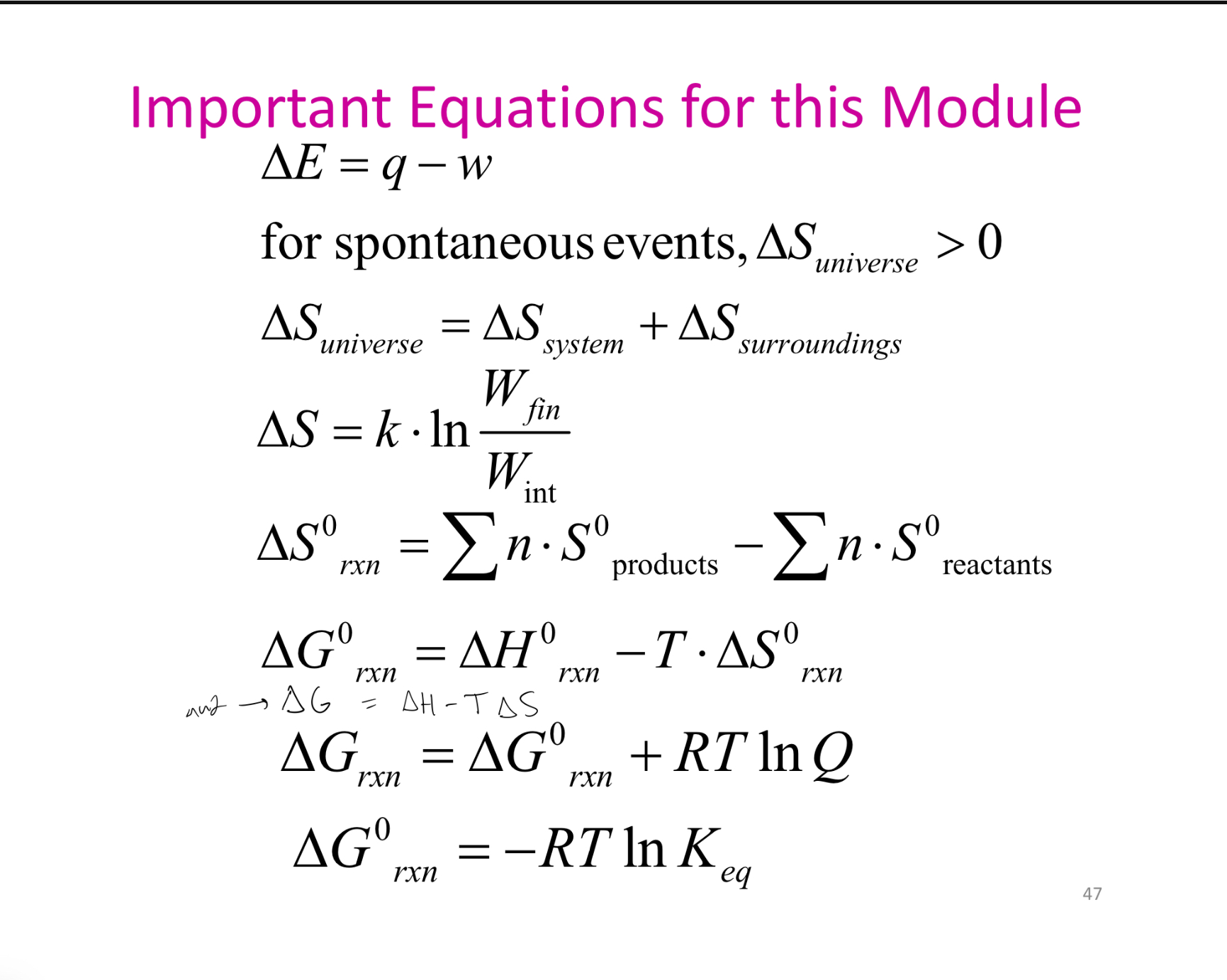
3 Laws of thermodynamics

All the energy that is currently in the universe was present at the beginning - actually immediately after the _____________
inflationary period
All “spontaneous events'“ in the Universe involve changing ___________________.
The form of energy (approx. work —> heat)
Spontaneous events require a shift from ___________ to __________
From work-energy to heat-energy
Which forms of energy are useful for doing work, and which are not useful for doing work?- Concentrated forms / dispersed forms
Concentrated forms- useful for doing work
Dispersed forms- not useful for doing work
Only a portion of heat can be used to do work- related to the _________________________________
size of the temperature gradient involved (more work can be done when the temperature gradient is large)
As the universe expands, what happens to the temperature gradient? What eventually happens?
The temperature gradient declines, less work can be done, and the ability for spontaneous events declines. At the end….. the universe will be at or very near absolute zero… at this point, no work can be done as there will be no temperature gradient and no way for randomness to increase. Thus, no spontaneous events can occur. This is the “Great Freeze” or the end of the universe.
Which is concentrated energy and which is dissipated energy? (heat and work)
Heat- dispersed energy
Work- concentrated energy
In practice, they found… what percentage of energyy could be converted into heat? and what percentage of heat-energy can be converted into work?
100% of the energy could be converted to heat
at best, 30% of heat-energy can be converted into work
Microscopic vs. Macroscopic
Microscopic- Refers to energy-related properties of INDIVIDUAL MOLECULES that compose the system. Ex: kinetic & potential energy of an atom / molecule… also includes vibrational, rotational, and translational motion of a molecule
Macroscopic- Refers to energy-related properties of THE ENTIRE ENSEMBLE (or population) of molecules that compose a system. Ex: heat, work, deltaE, deltaH, deltaS, deltaG
Who invented Statistical Thermodynamics
Maxwell (Max—> Maximum value—> Statistical Thermo)
True/False- The greatest work effieciency for a reaction occurs when it is reversible and at equilibrijm.
True.

More work can be done if the temperature gradient is ______ (small or large)
large!
A goal of thermodynamics to to explain ____________ properties of chemistry at the _____________ level (microscopic/macroscopic)
macroscopic properties at the microscopic level
Is a spontaneous event a statistical trend?
yes
Is entropy a form of energy? Is enthalpy a form of energy?
entropy- NOT a form of energy
enthalpy- is a form of energy
spontaneous events are associated with a(n) ___(increase/decrease)_________ in the entropy of the universe
increase- this is stated by the 2nd law of thermodynamics
What did Ludwig Boltzman do?
-He is responsible for the 2nd Law of thermodynamics
-He invented the concept of Entropy
-equation with the Boltzman constant….. solves for entropy
Can the 2nd Law of thermodynamics be violated?
In principle, yes
In practice, no.
If humans didn’t need to eat, would they violate the 2nd law?
Yes
Can the ΔSsystem be >0 and the ΔSsurroudnings also be >0
yes!
What is a microstate?
The arrangement of atoms or molecules in a single instant. (The ball could be located in each of the four boxes with equal probabilities. The system has four microstates.)
Fewer microstates means what about entropy?
Fewer microstates means lower entropy
What does molecular complexity mean about microstates and entropy?
Greater molecular complexity means more microstates, and therefore, greater entropy
3 moles of gas form 2 moles of gas… what has happened to entropy?
The entropy has decreased.
Can you have a negative entropy for a spontaneous reaction?
yes, this is possible because it only refers to the entropy change for the system.
Explain Anabolism vs. Catabolism
Anabolism- the process of building larger molecules from smaller ones, often requiring energy. (this is negative entropy) (ana has a cat, the cat is always BREAKING stuff, and she has to build it back together)
Catabolism- the process of breaking down larger molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy. (this is positive entropy)(this energy is used to drive anabolism) (ana has a cat, the cat is always BREAKING stuff, and she has to build it back together)
Does entropy change with temperature?
yes!
Does entropy change with state of matter?
Yes!
Rank the states of matter from greatest entropy to least entropy.
Most entropy- gas
Least entropy- solid
What does the 3rd law say?
A perfect crystal of any molecular species at 0 K has zero entropy.
Is standard molar entropy equal to 0 at standard state?
NO
What did Willard Gibbs do?
one more equation………
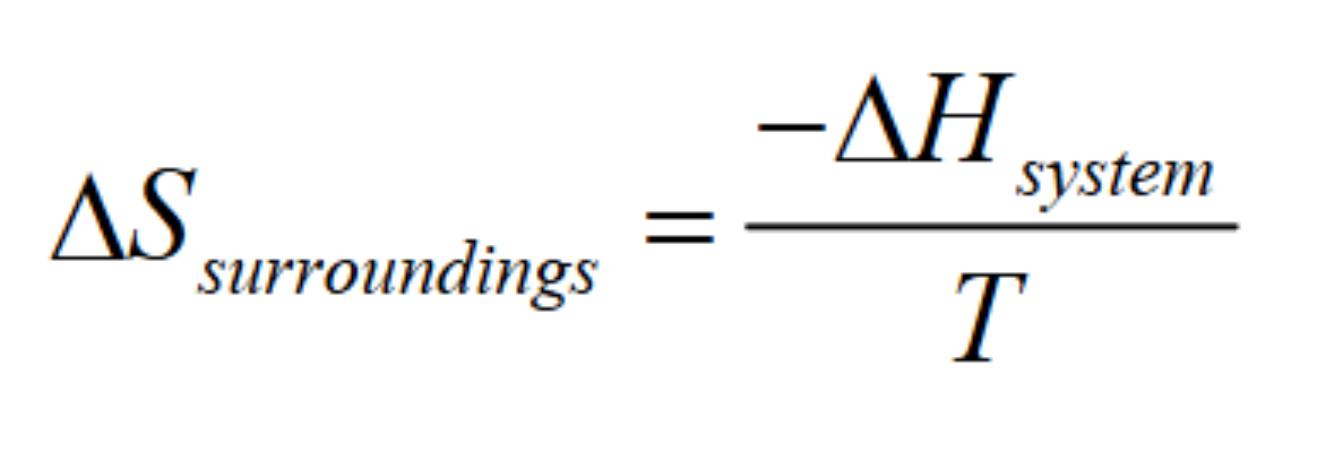
Does the importance of entropy increase or decrease at high temps
increase!
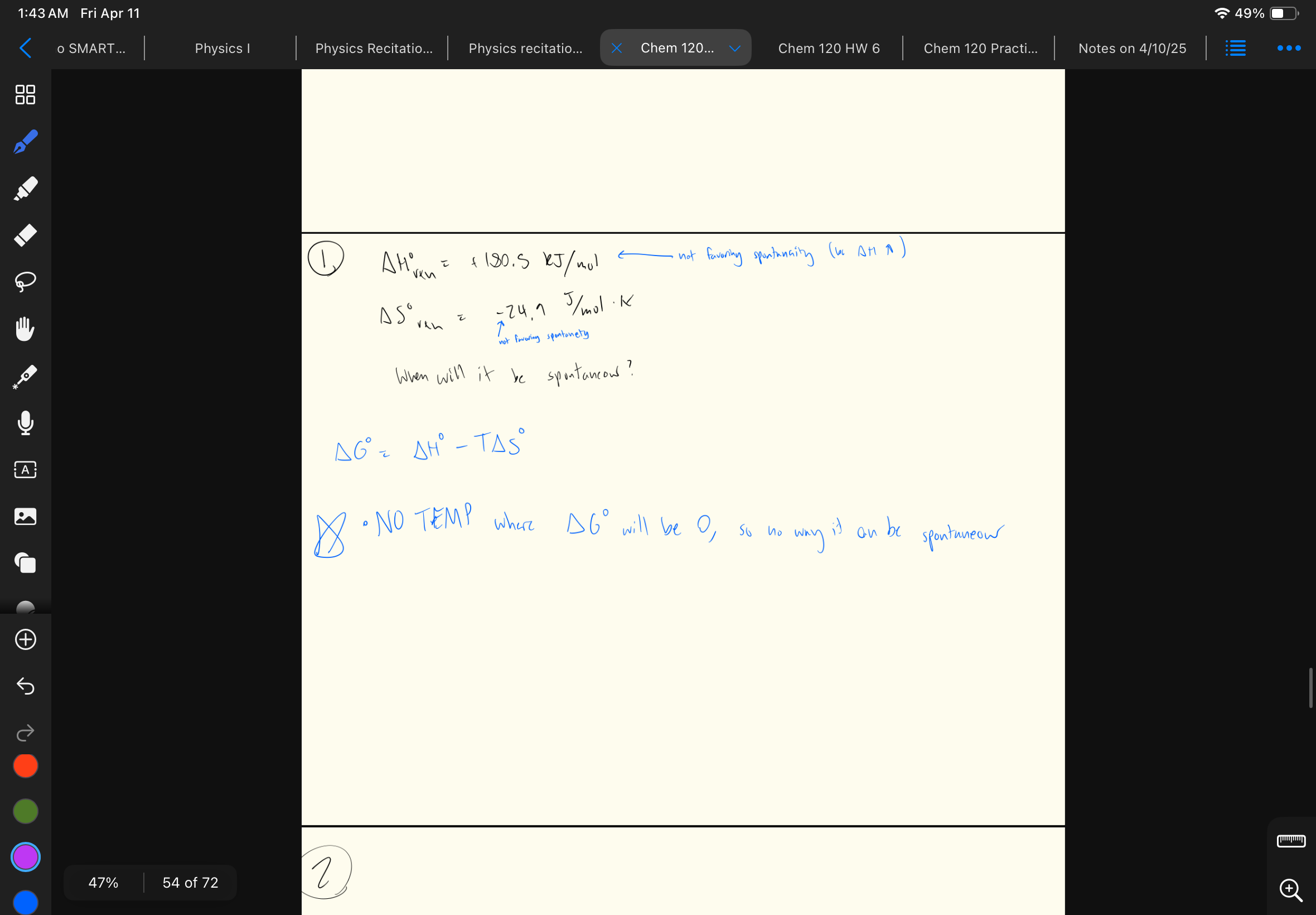
take a look at this to find out another possible way to find info about delta G maybe… idk

Not all free energy is used to do work… the remaining energy ends up as ______
heat
How does reversibility play a role in the amount of free energy that can be used for work?
More reversible reactions allow more free energy to be used as work (and a reaction near equilibrium is most reversible)
Reactions with negative ΔG are called “_______”
Reactions with positive ΔG are called “_______”
-ΔG = exergonic (spontaneous, release, exer, more entropy, NON-spontaneous)
+ΔG= endergonic
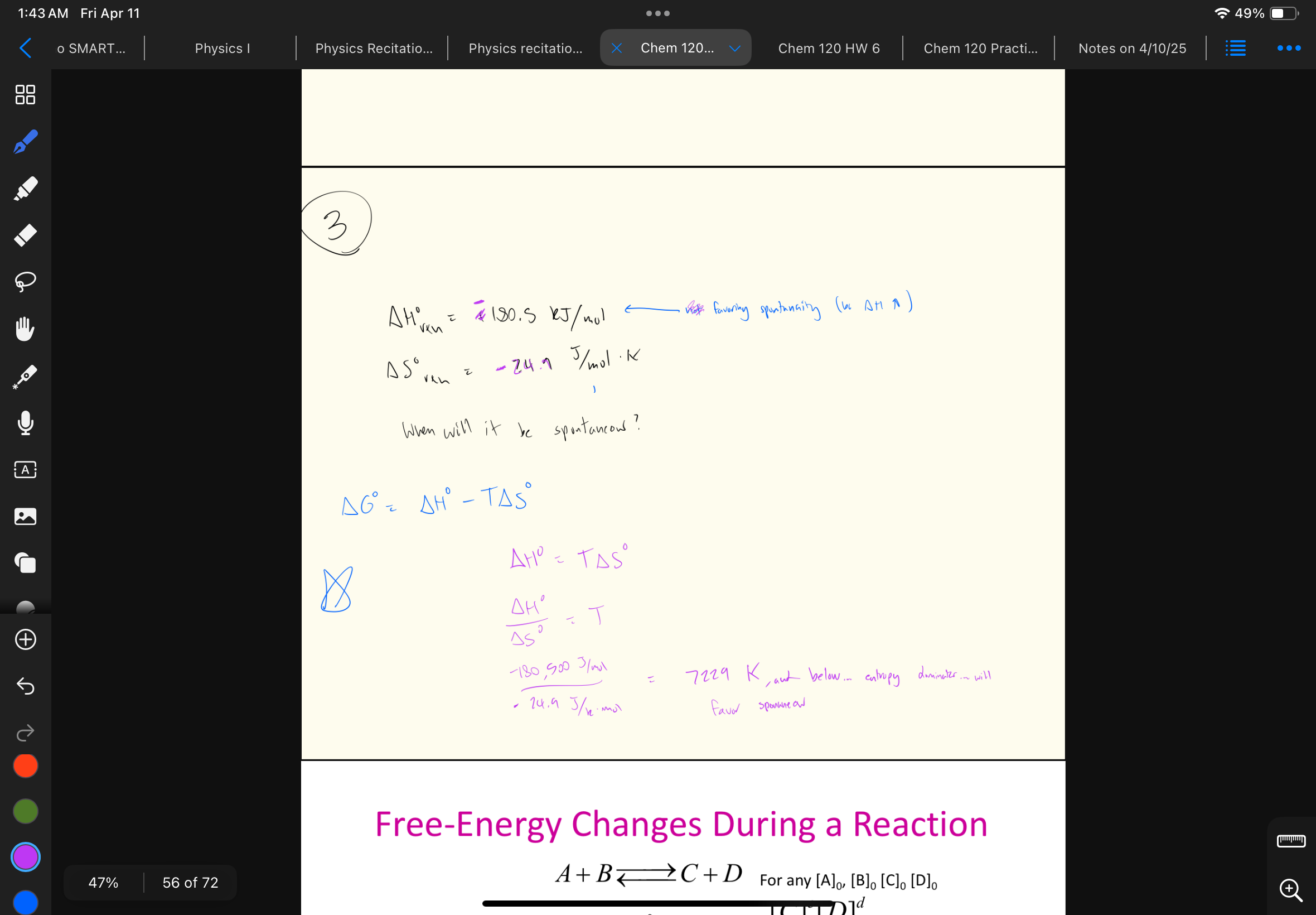
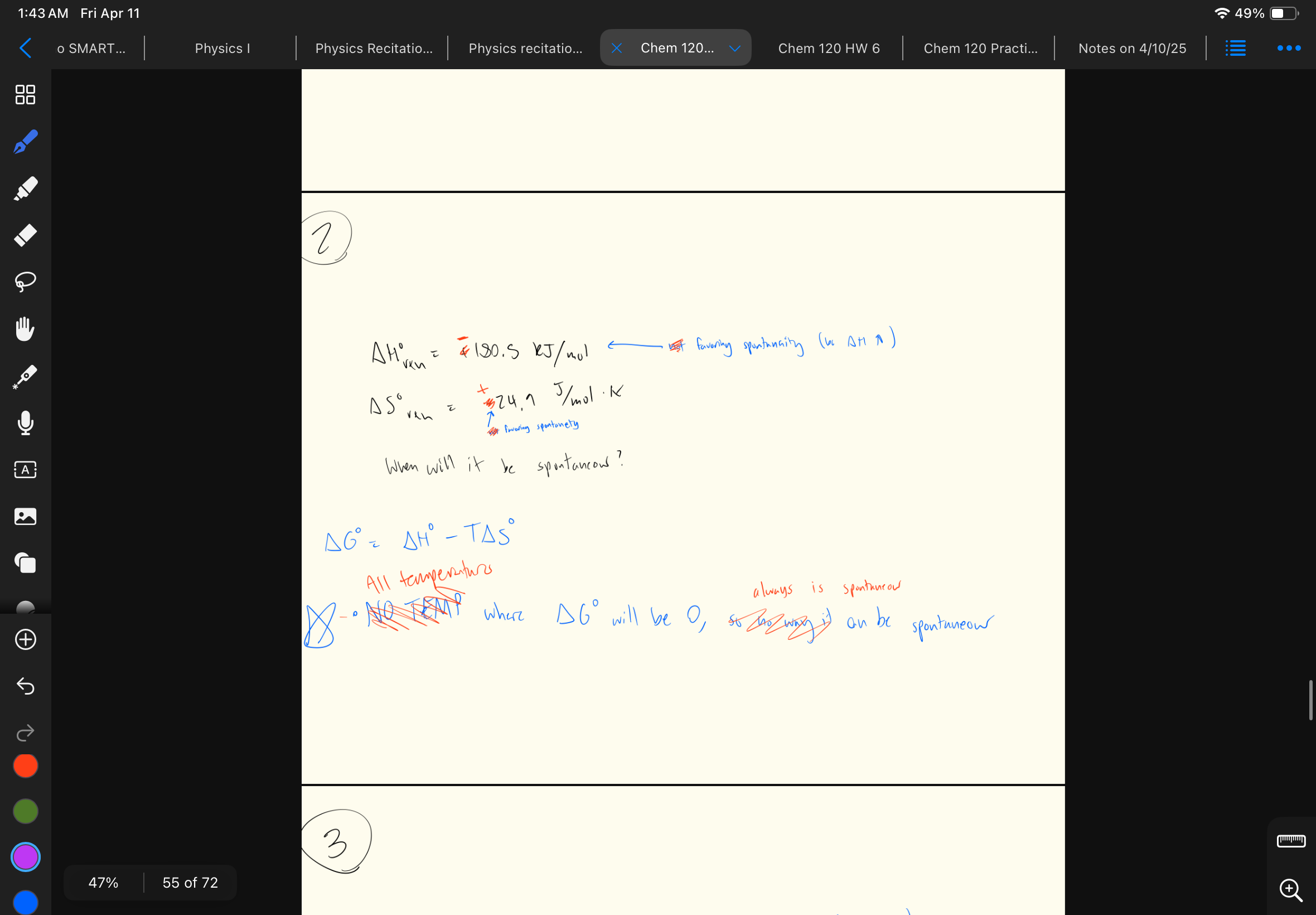
When ΔG < 0… compare Keq and Q
Q < Keq
Take a look at this problem… comparing Keq and Q (Q/Keq)
