AP Chemistry Semester 1 Exam
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
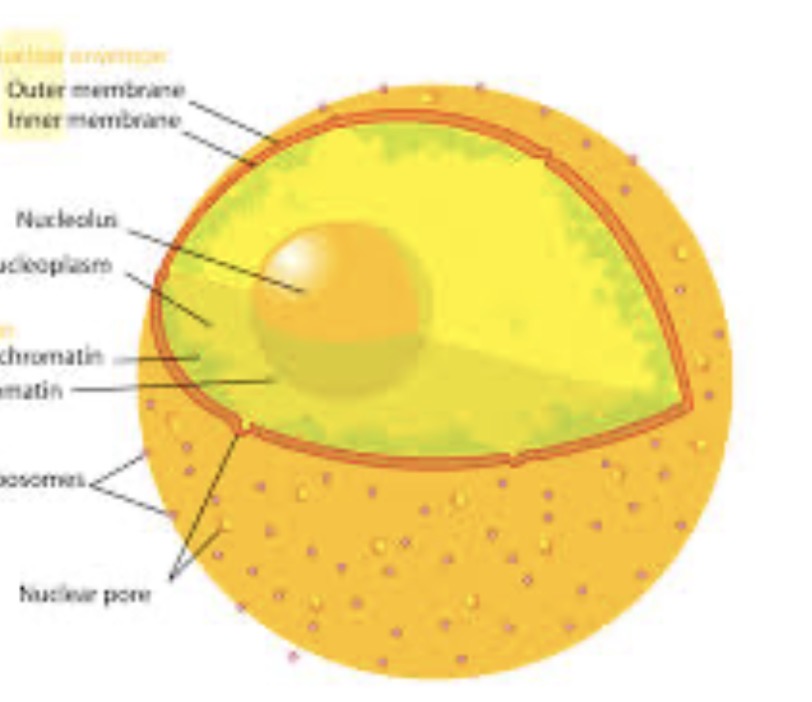
Where is the nucleus of an atom?
Center of the cell
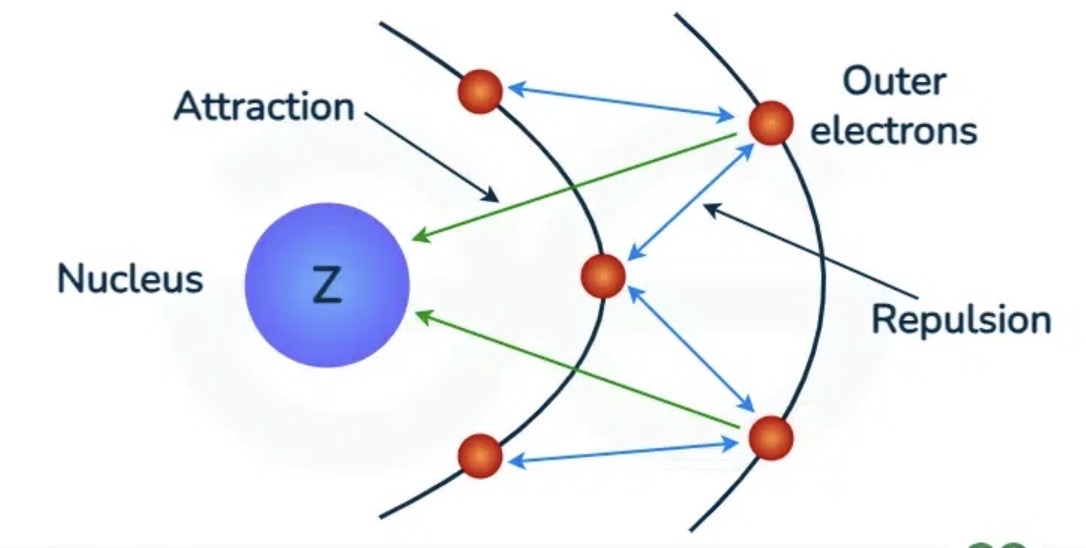
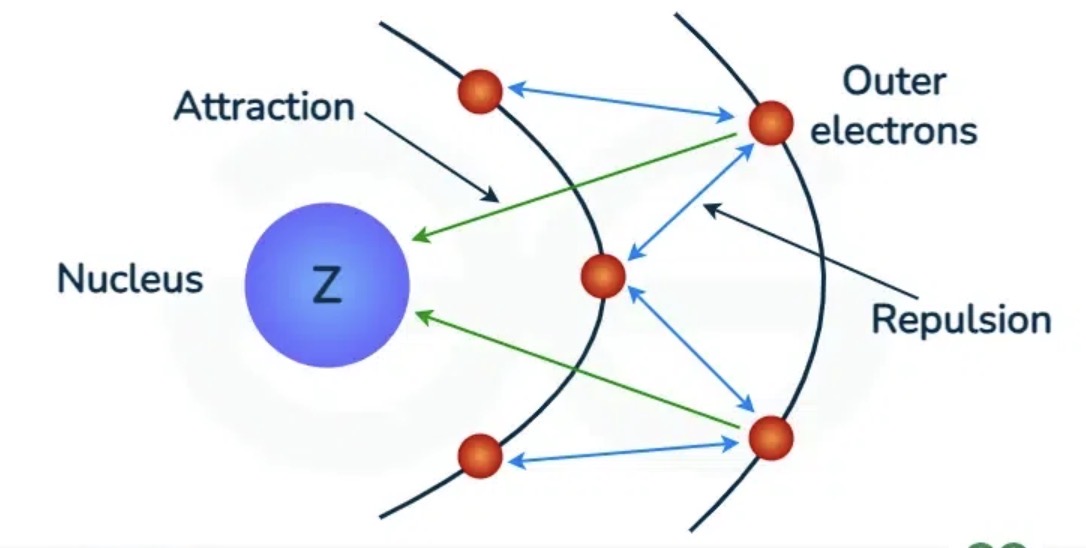
Where is the shielding electron?
In energy levels between the nucleus and valence electrons
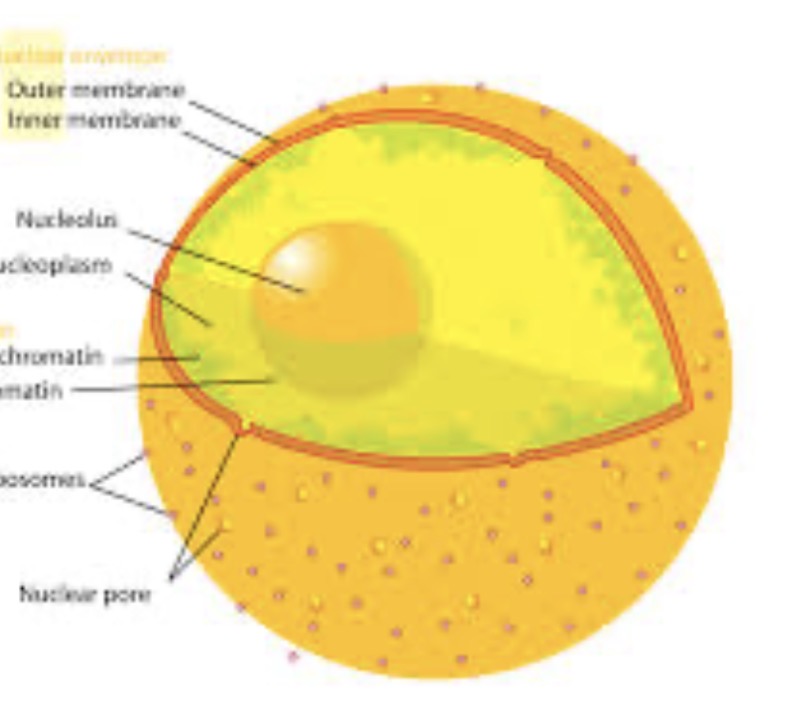
Where are the valence electrons?
Outermost shell
What charge does the nucleus have?
Neutral
What charge does an electron have?
Negative
Where is the attractive force in an atom?
Between electrons and protons in the atoms nucleus
What is the relationship between distance and force?
Distance is inversely proportional to force
What is the relationship between magnitude of charge and force?
Magnitude of charge is directly proportional to force
Explain how Coulomb’s law applies to atomic structure?
Coulomb’s law applies to atomic structure through the attraction force between particles of opposite charges (protons & electron)
Where are the periods vs groups on the periodic table?
Periods are on the left hand vertically on the chart (energy levels). The groups are on the top of the chart (valence electrons).
Use Coulomb’s law to explain how atomic radii of atoms change across a period. USE CER
C: According to Coulomb’s law, as you move across periods the atomic rasii decreases
E: B/c the increase number of protons pull valance electrons closer
R: This Columbic force reduces the distance between the nucleus and outermost shell
Use Coulomb’s law to explain how atomic radii of atoms change down a group. USE CER
C: According to Coulomb’s law, as you move own a group, atomic radii increases.
E: B/c each period adds an electron shell.
R: This columbic forces places valence further from the Nucleus, which increases the distance, it weakens the attractive force
What is ionization energy?
Amount of energy required to remove an electron.
Predict the family of the periodic table…
This belongs to group … because that is where the jump takes place. This is B/c once we elimate that valence electrons outer shell, we are left with atoms closer to the Nucleus. Meaning it requires more energy to remove
Explain the following observations in terms of atomic structure and periodicity
Ex) Ca has a lower second ionization energy than K
Ca has a lower second ionization energy because it is further away from the Nucleus. The Columbic force reduces the distance between the Nucleus and outermost shell
Explain the following observations in terms of atomic structure and periodicity
Ca²+ ion has a smaller radius than the Ca atom
Ca²+ ion has a smaller radius than the Ca atom because it would take less energy to remove the electrons than the Ca atom.
Ionic
Transfer electrons (Metal + Non-metal)
Covalent
Shares electrons (Non-metal + Non-metal)
Explain what determines polarity using the terms electronegativity, dipole, and equally
What determines the polarity is the electronegativity between atoms and the overall shape. The Dipole atoms point toward the more electronegative atom, which shows if the molecule is asymmetrical or symmetrical. In this case, the Dipoles causes for this to be asymmetrical (unequally shared)
How does Coulomb’s law impact ionization energy?
Stronger coulombic attraction between the nucleus and an electron means higher ionization energy.
What impacts coulombic attraction?
The magnitude of the charges and the distance between the,
Why do we balance chemical equations? What law do we have to uphold
We balance chemical equations to ensure both the reactant and product reflect that matter is neither created or destroyed during the reaction. This upholds the law of conversion mass.
How do you find formal charge?
(Valence electrons) - (Non bonding electrons) - (Bonding electrons / 2)
What makes a solute soluble in a solvent
When their intermolecular forces are similar.