Cell Membranes and Osmosis
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
what are the two main functions of the cell membrane?
seperates intracellular environment from extracellular environment and regulates what enters/exits a cell
what are the 3 main components of the cell membrane?
phospholipid, steroids, proteins
what are the 3 proteins in the cell membrane?
peripheral protein, integral protein, and glycoprotein
what is a glycoprotein?
a carbohydrate and protein
what is the building block steroid in cell membranes?
cholesterol
what do phospholipids do for the cell membrane?
create a waterproof and hydrophobic bilayer
what parts of the phospholips are hydrophobic vs. hydrophilic?
the head is hydrophilic and the tail is hydrophobic
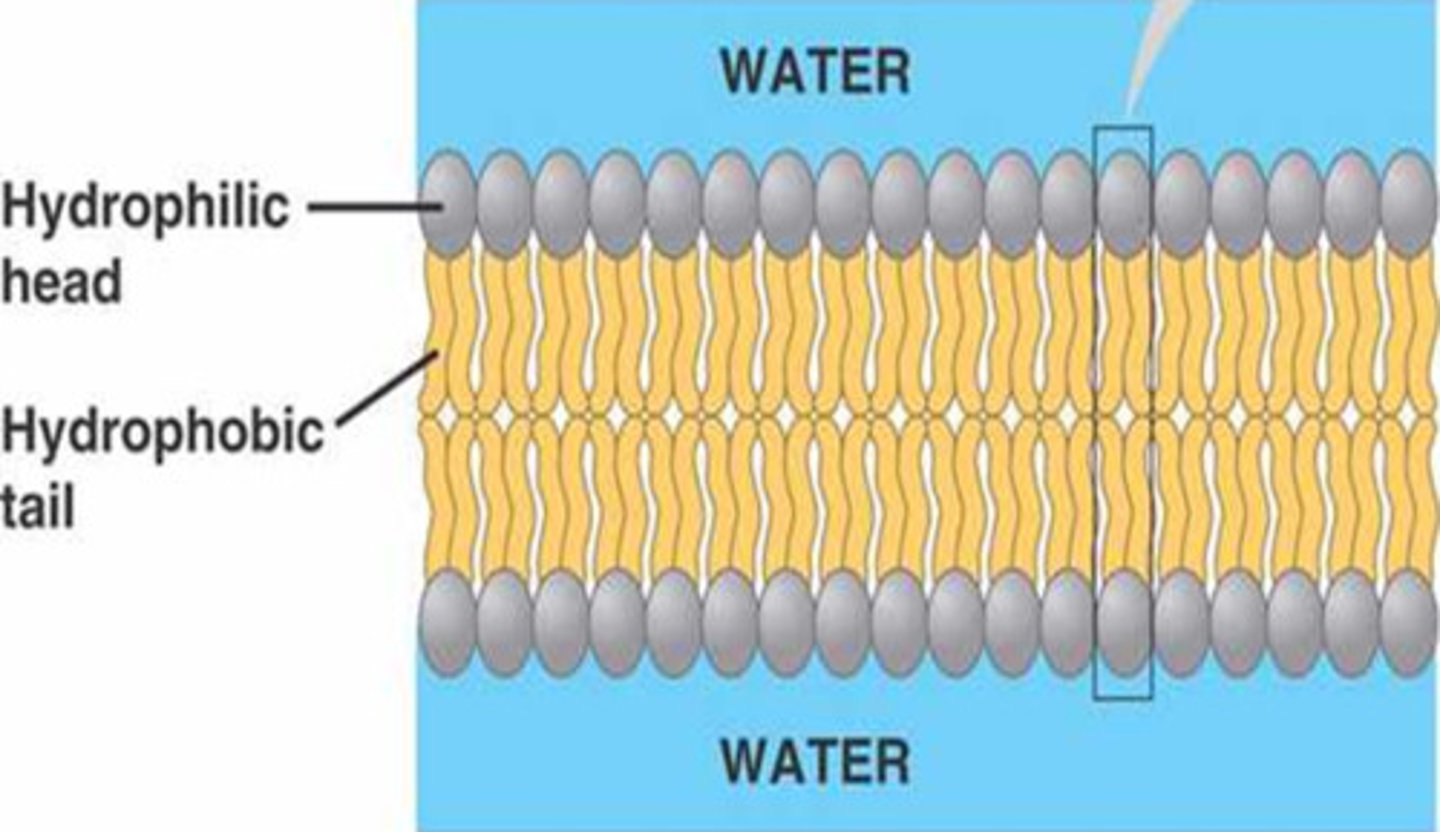
are cell membranes fluid or solid?
fluid
how are cell membranes fluid?
the components constantly move past each other which = flexible
what are the two types of phospholipids?
saturated and unsaturated
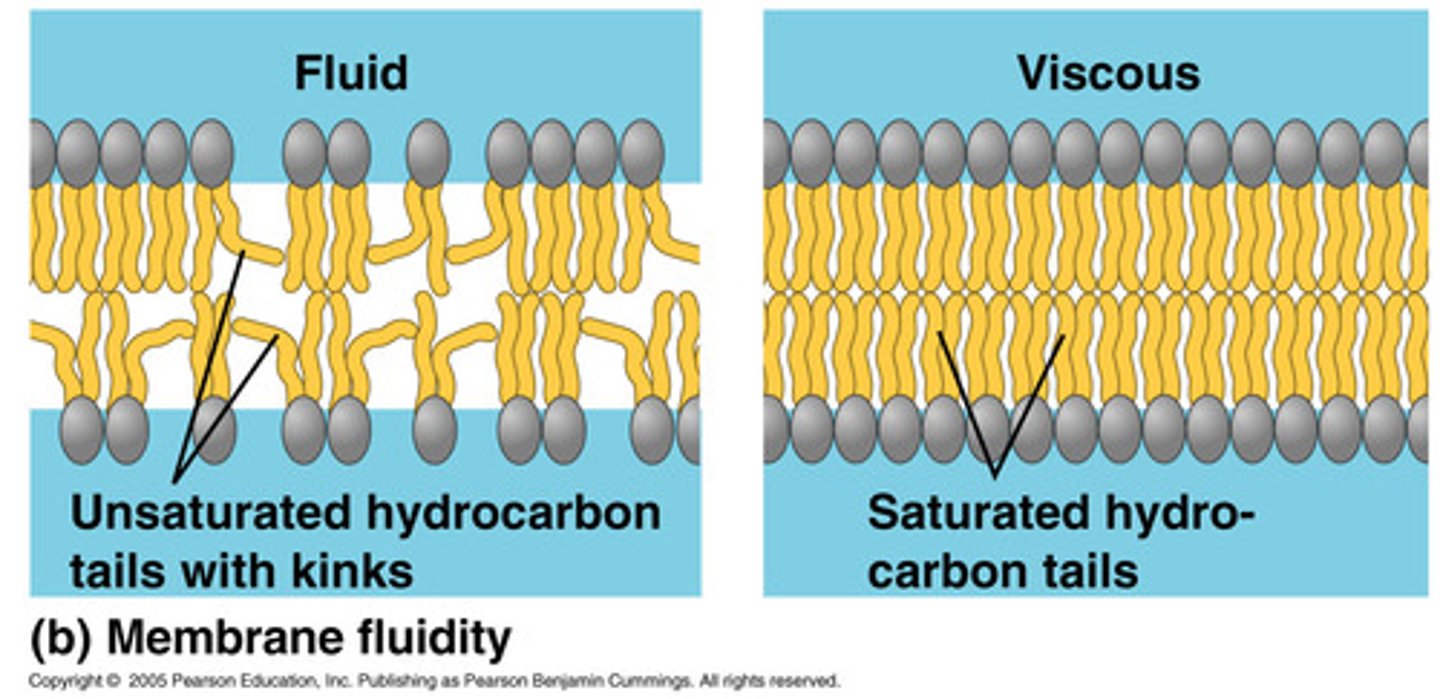
what two things make a cell membrane more fluid?
if a cell membrane has more unsaturated phospholips and more cholesterol spaces, then it is will be more fluid
does a warm or cold environment have more cholesterol?
cold, to improve fluidity
what is a Fluid Mosaic Model?
a model that describes the structure of a cell membrane: cell membranes are composed of different molecules and are fluid
what are membrane proteins?
proteins in a cell/in a membrane
what are the two structural classifications for membrane proteins?
integral and peripheral proteins
what is a transmembrane protein?
a integral protein that is on both sides of the membrane
what is a peripheral protein?
Peripheral proteins are hydrophilic on their surface, so are not embedded in the membrane.
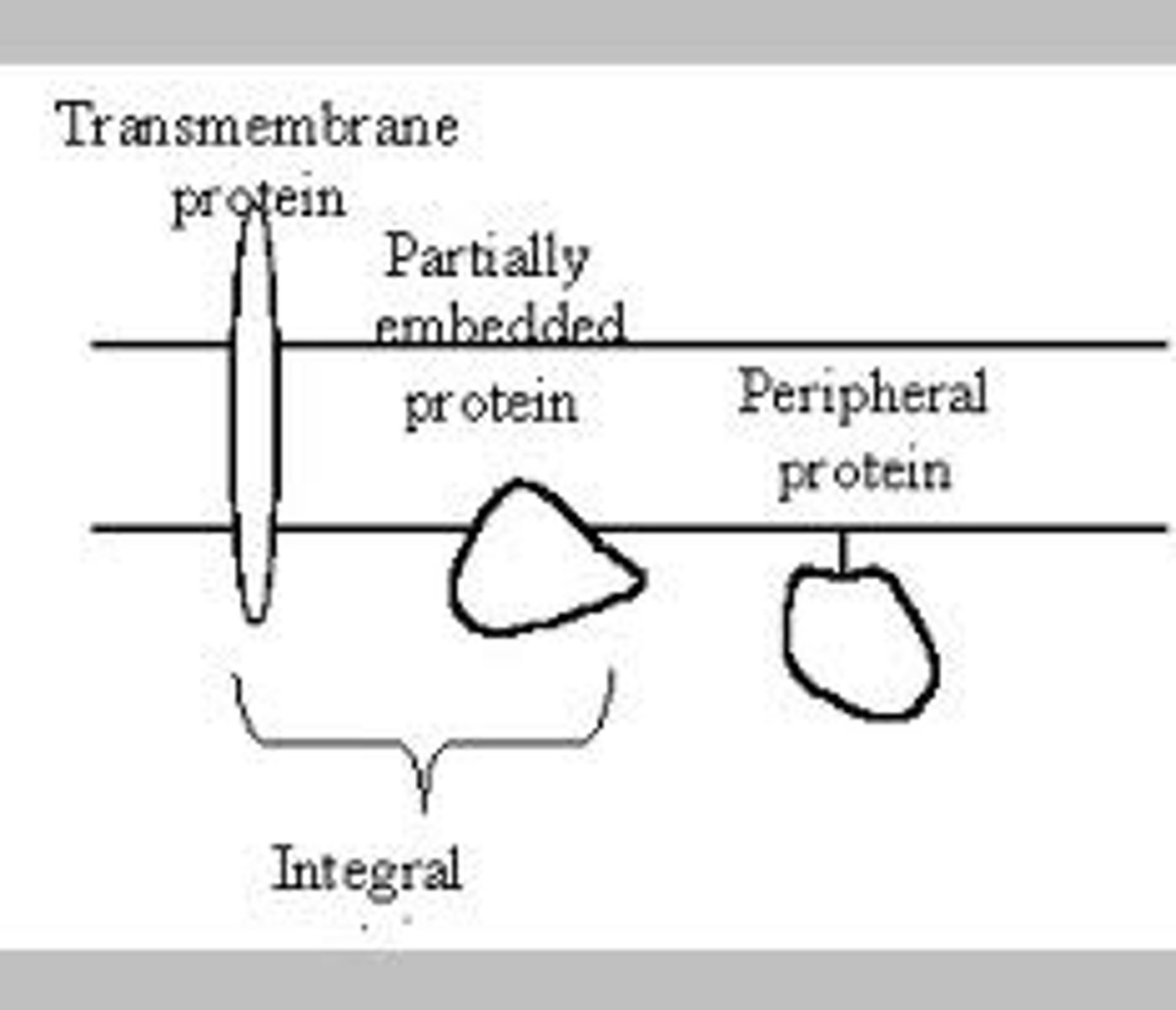
what is a integral protein?
a protein embedded into the cell membrane
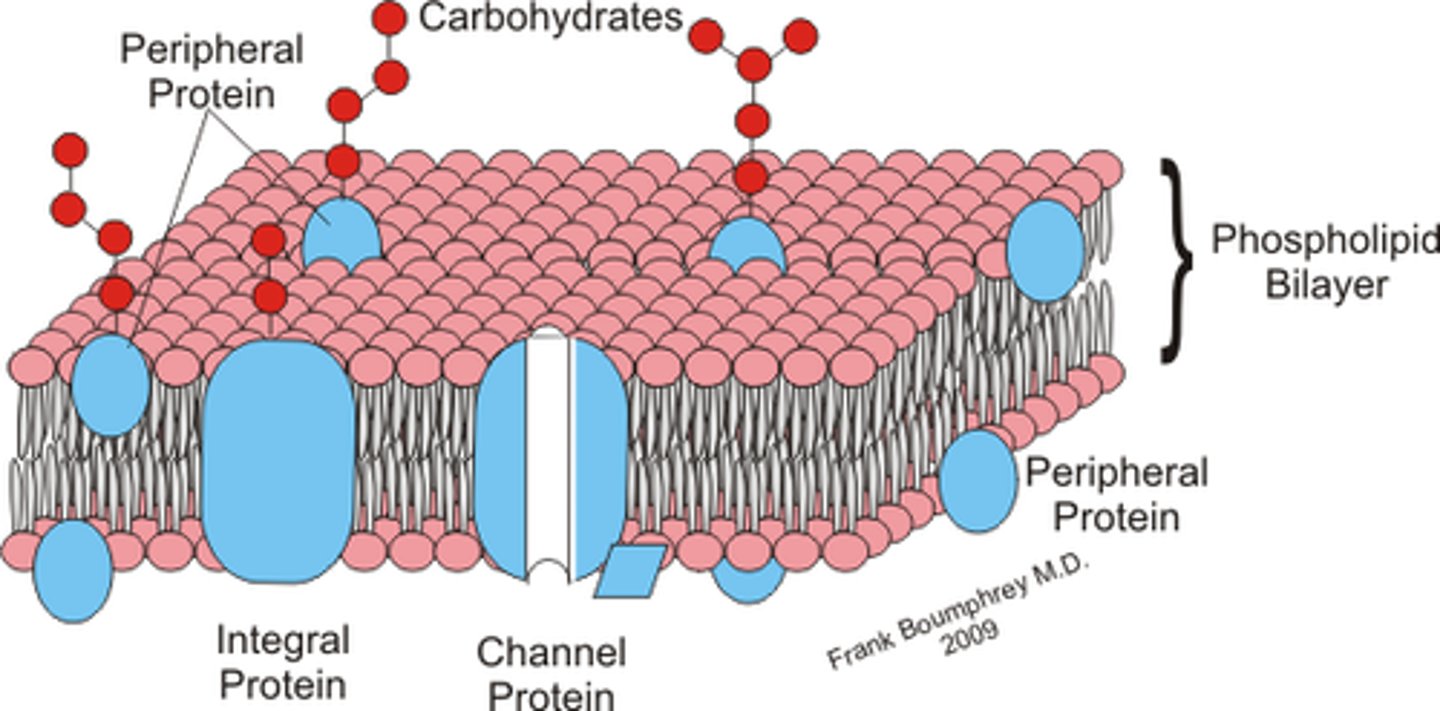
what are the 6 function classifications of membrane proteins?
Transport protein, Enzymatic activity, Anchors cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix, signal transduction, cell-cell recognition, intracellular joined proteins
what is the function of a transport protein?
move things in between intercellular and extracellular environments
what does it mean to say a transport protein is substrate specific?
only works on one substrate
what is a substrate?
a molecule a protein acts on
what does enzymatic activity protein do?
catalyze chemical reactions
enzymatic activity proteins are metabolic processes, what does this mean?
two are next to each other to catalyze one after another faster (one goes and that energy is used to catalyze the second one)
what do signal transduction proteins do?
lets the inside of the cell know whats happening outside of the cell
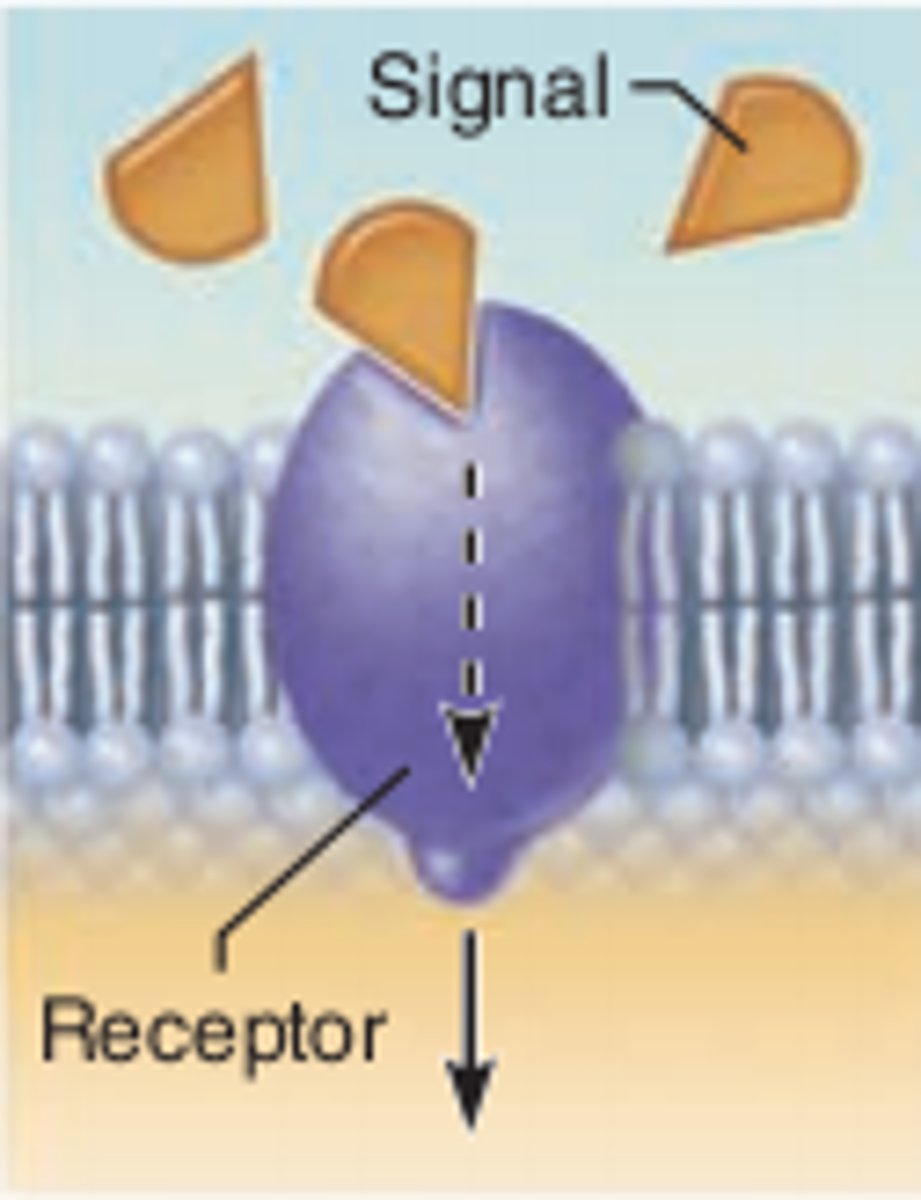
what is a signal transduction protein also called?
a receptor proein
what are the two parts of a signal transduction protein?
signaling molecule and receptor
what does the signaling molecule do?
messenger between cells (hormones)
what does cell-cell recognition do?
identify self or non-self cells
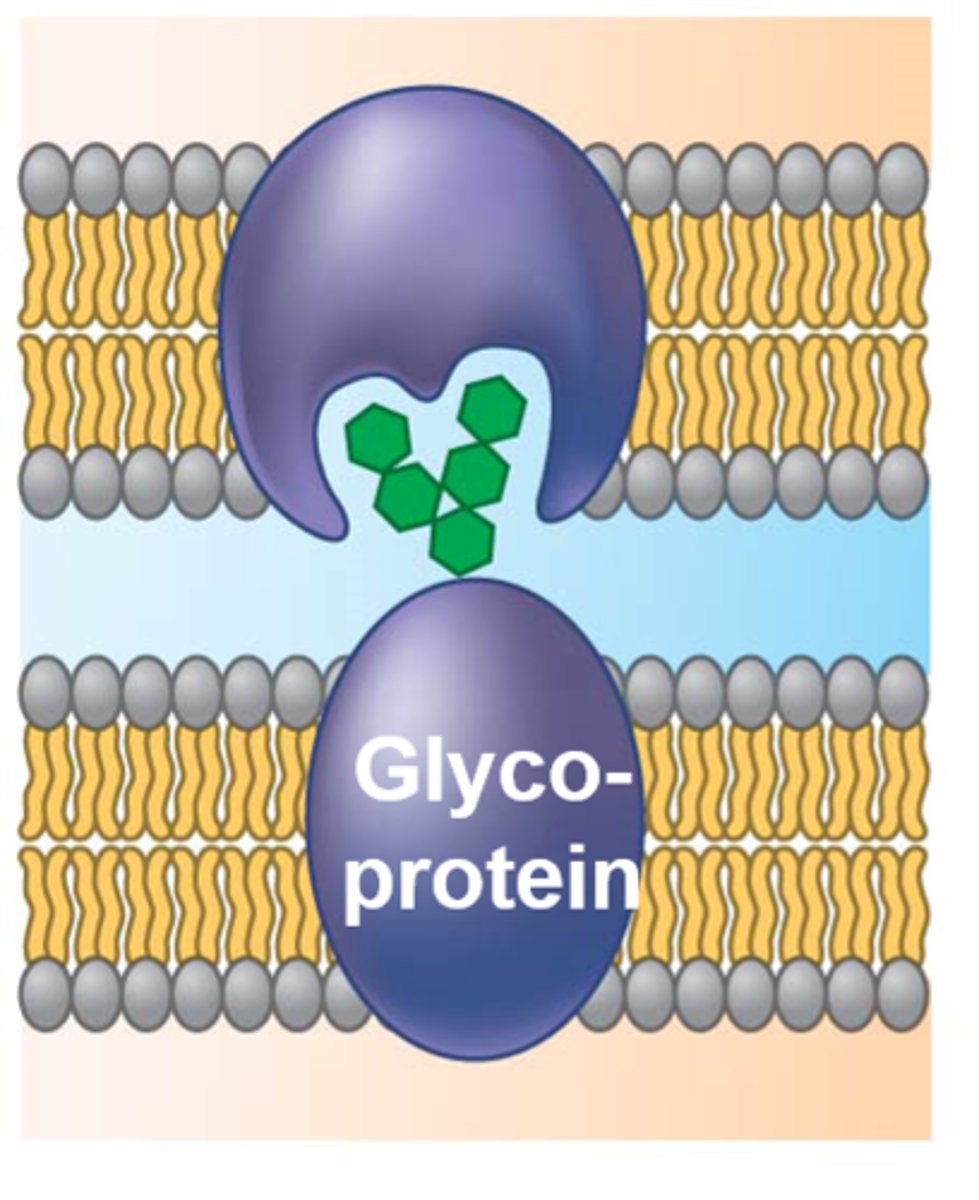
what is the immune function of cell-cell recognition?
identify harmful, foreign cells
what is blood type determined by?
glycoproteins (A, B, AB, etc.)
what do intracellular proteins do?
attach membranes of 2 cells together, important in tissue
cell membranes are Selectively Permeable, what does this mean?
decides what goes in and out of a cell
what needs/is permeable to enter a cell?
water, food/nutrients(glucose, amino acids, etc.), oxygen
What needs to exit the cell?
electrolytes and carbon dioxide
what is the cell membrane always permeable to?
nonpolar and small molecules
what is simple diffusion?
moves straight in between the phospholipid bilayer
what is transported by transport proteins?
moves larger polar and non polar molecules
what are the active transport proteins?
carrier/pump proteins
what are the passive transport proteins called?
channel proteins
what channel protein transports water?
aquaporin
what are the two ways to regulate transport?
"lid" and get rid of transport protein
how do cell membranes get rid of a transport protein?
brings transport protein to vesicle inside cell
what does it mean to say something is aqueous?
base=water
where do solute particles move too?
down there concentration gradient, to somewhere more dilute
what happens after reaching equilibrium in concentration?
cells move at a net rate
how do you move solutes against their concentration gradient?
active transport
what is osmosis?
movement of water through a selectively permeable membrane
what is tonicity?
making a comparison of two solutions concentration