A&P Lab Exam 1
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is the fluid portion of blood that contains plasma proteins and dissolved solutes?
Plasma
Define plasma
the fluid portion of blood containing plasma protein and dissolved solutes
What are the cells that transport carbon dioxide and oxygen?
erythrocytes, or red blood cells
What are the cells that initiate immune response and defend against potentially harmful substances?
Leukocytes, or white blood cells.
What are the cells that participate in hemostasis (stopping blood flow out of a cut)
Thrombocytes or platelets.
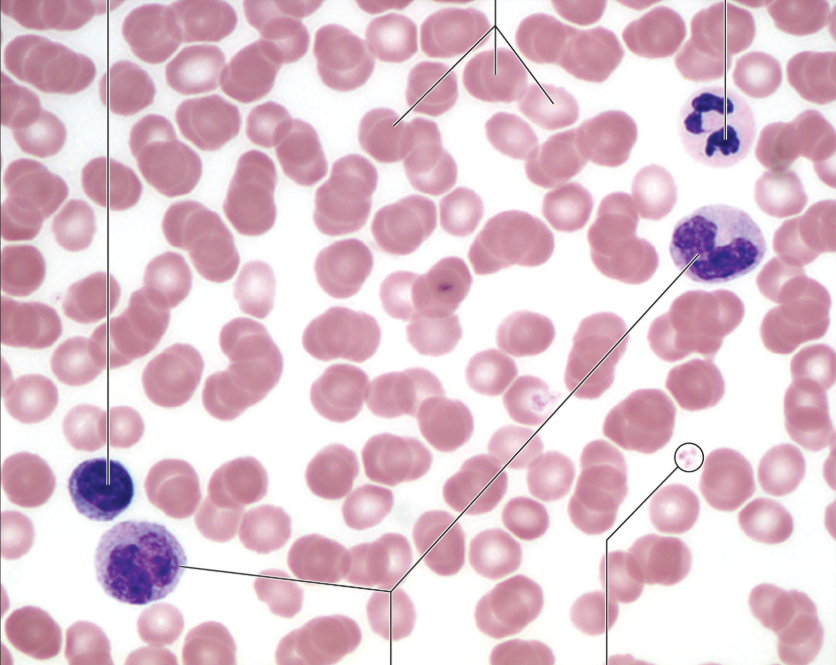
Point out the erythrocytes, leukocytes, and thrombocytes in this image
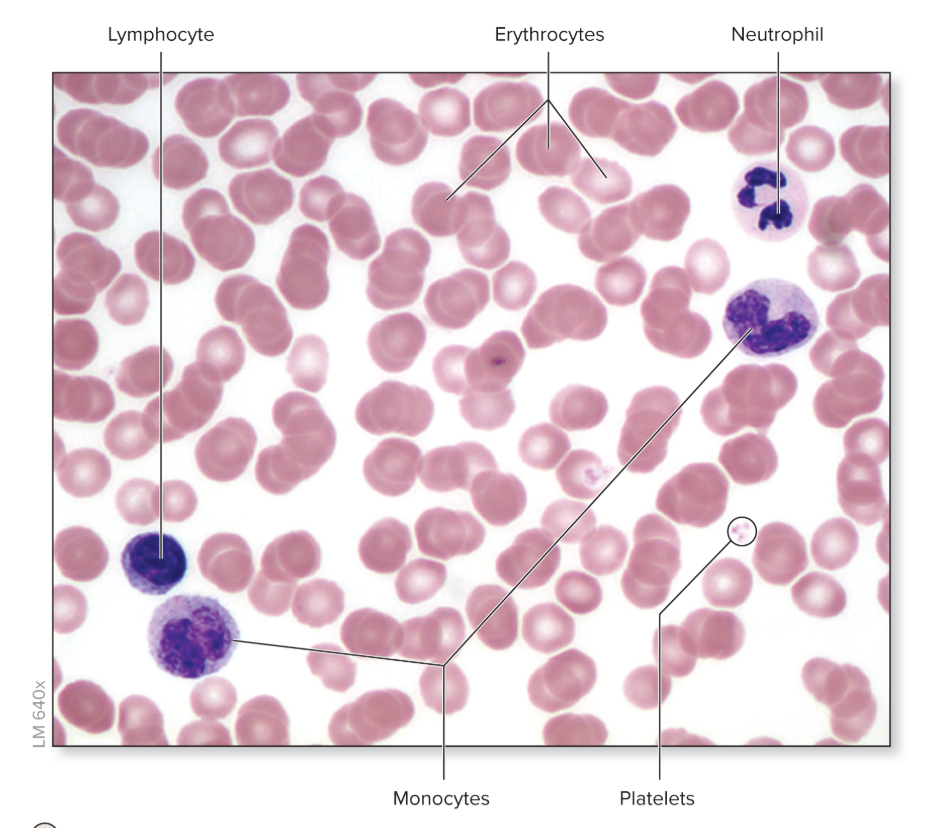
What are the three types of granular leukocytes?
Neutrophil, eosinophil, and basophil
What are the two types of agranular leukocytes?
Lymphocytes and monocytes
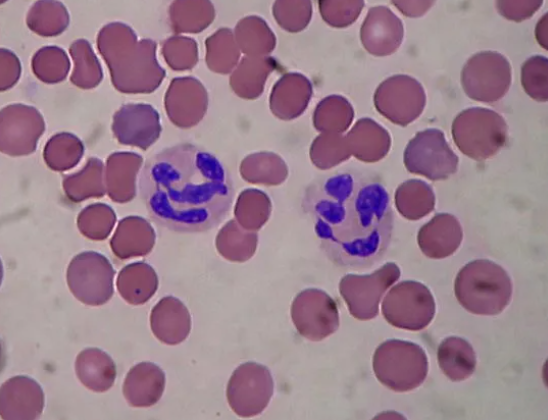
Identify the leukocyte
Neutrophil
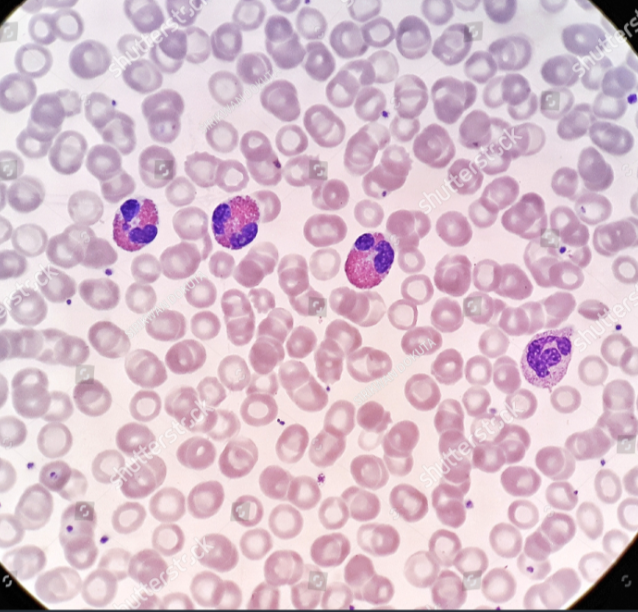
Identify the leukocyte
Eosinophil
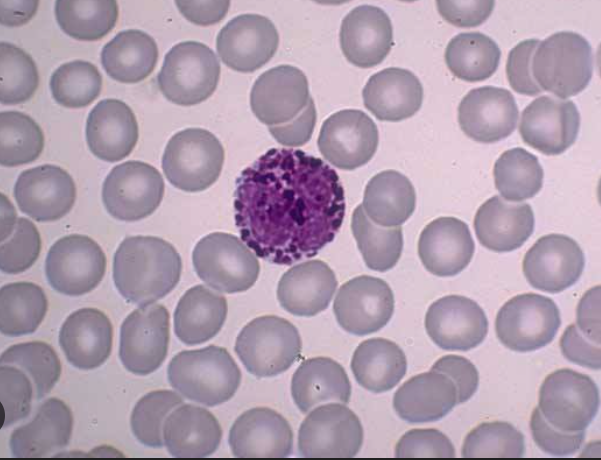
Identify the leukocyte
Basophil
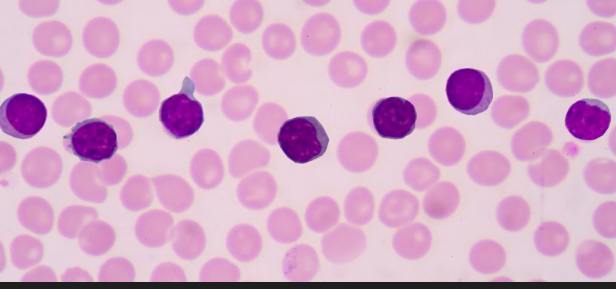
Identify the leukocyte
Lymphocyte
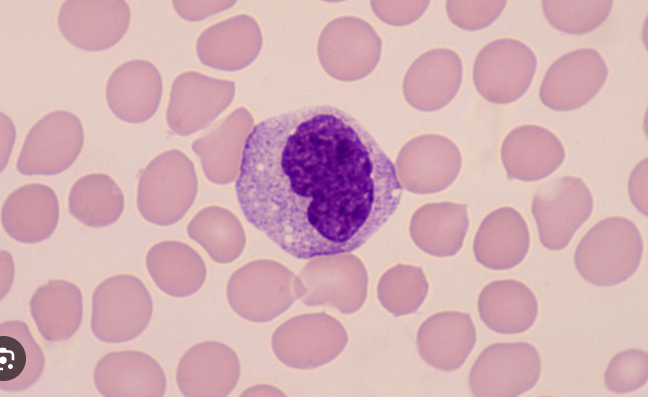
Identify the leukocyte
monocyte
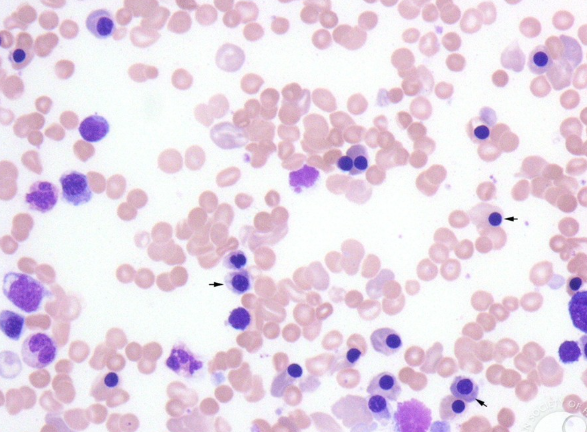
Identify the disease and the cause
Erythroblastosis fetalis, blood incompatability due to Rh positive infant in Rh - mother causing anemia or death bc of erythrocyte destruction
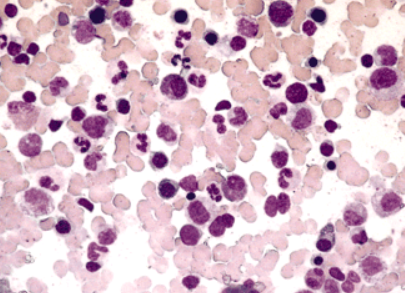
What disease is shown
Leukemia
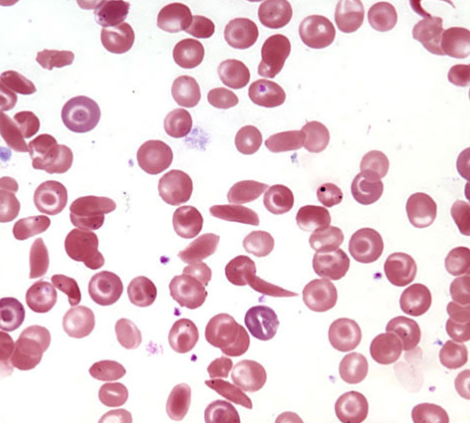
Identify the disease
Sickle cell anemia
What is the term that refers to the percentage of the volume of all formed elements in blood? And what are the formed elements
Hematocrit, and erythrocytes, leukocytes, and thrombocytes
antigens
agglutinogens, the identifying protein things on red blood cells that cause A or B type blood
antibodies
agglutinins, the response created to “fight off” unknown antigens or other unknown substances.
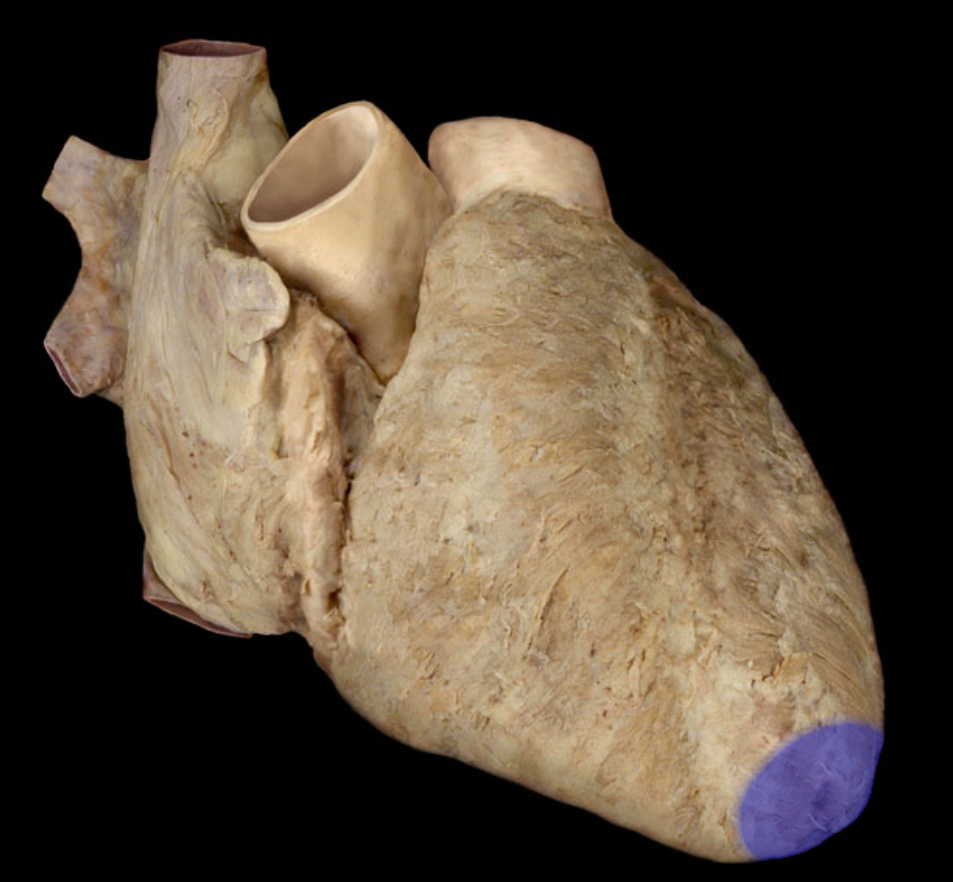
Name the structure
Apex of heart
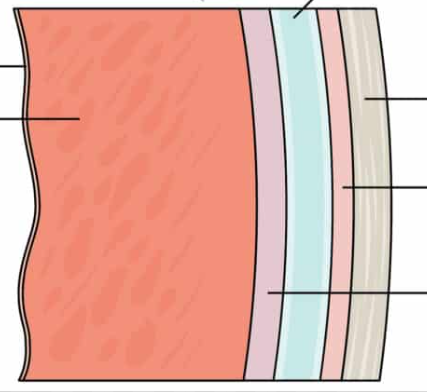
Identify the layers, from left to right.
Endocardium, myocardium, Epicardium (visceral layer of the serous pericardium), pericardial cavity, parietal layer of pericardium, and fibrous pericardium
What is the pericardial sac made up of?
Two main layers, the serous (visceral and parietal) pericardium and fibrous pericardium.
Identify the structure
Right atrium
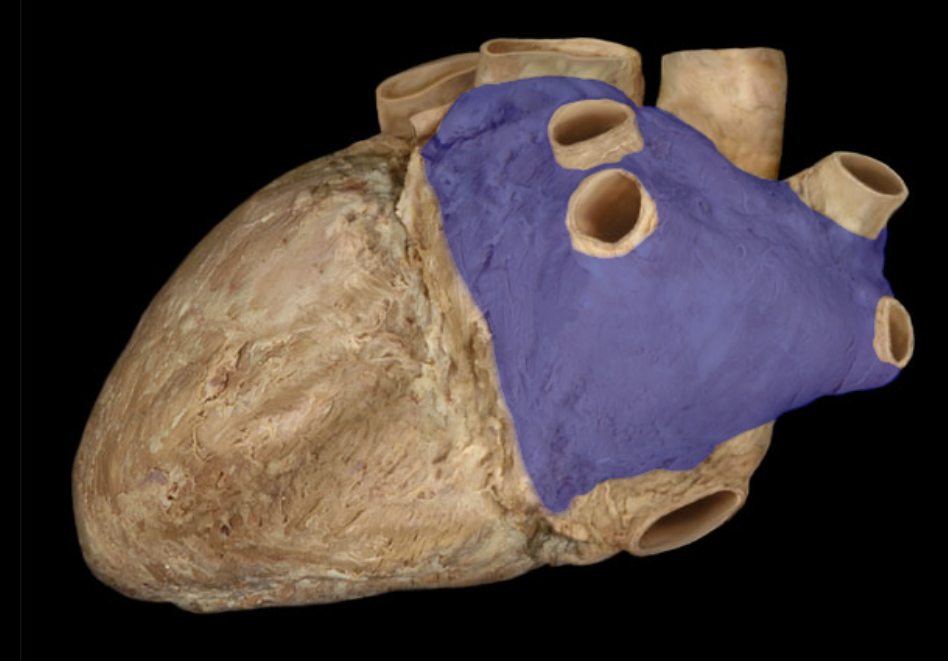
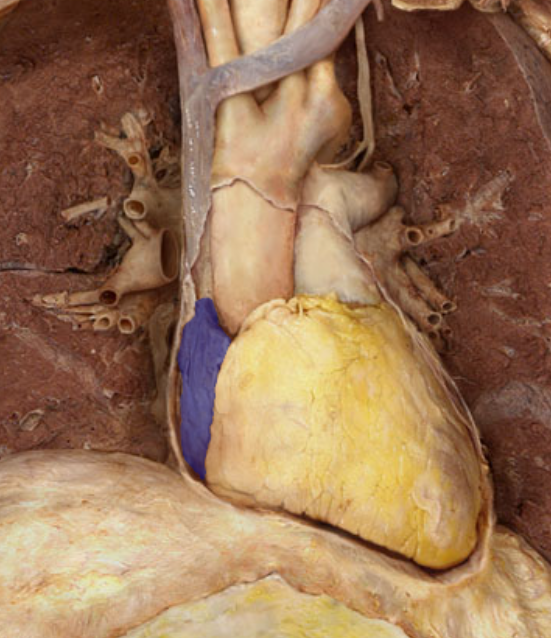
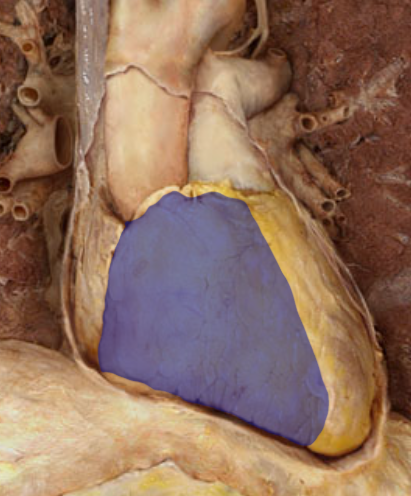
Identify the structure
Left atrium
Identify these structures
Right and left auricles
Identify this structure
Right ventricle
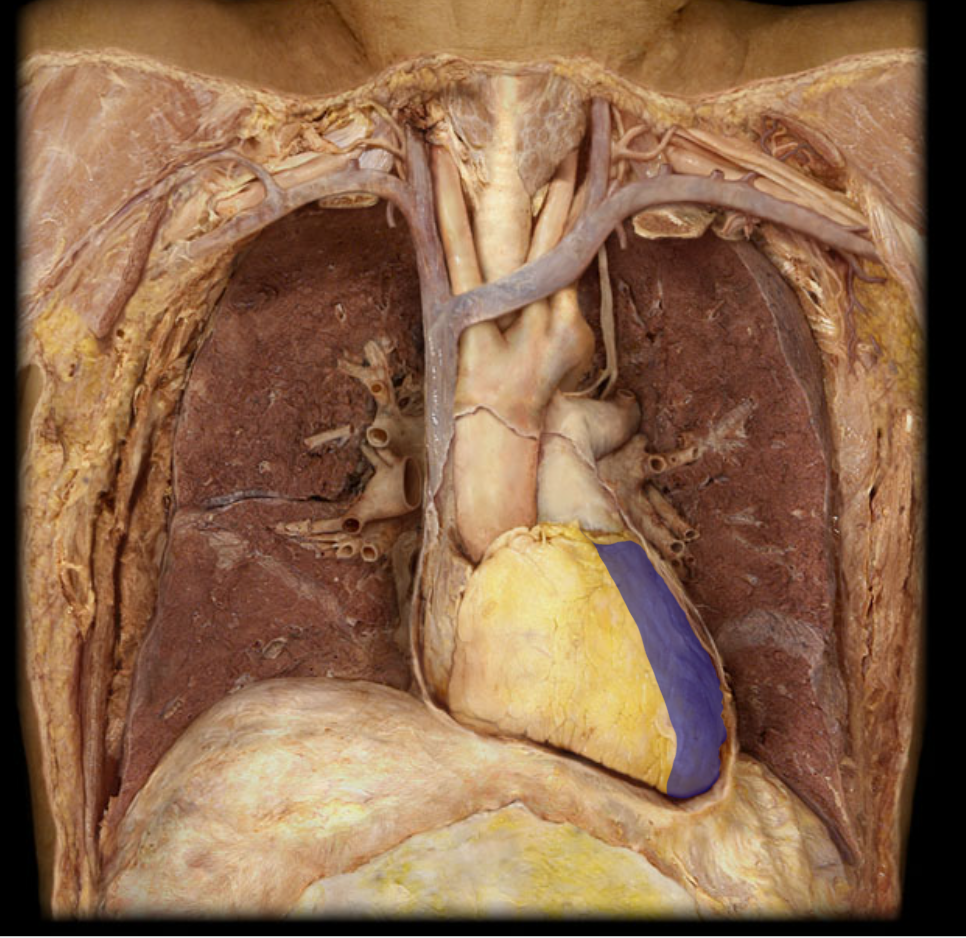
Identify the structure
Left ventricle
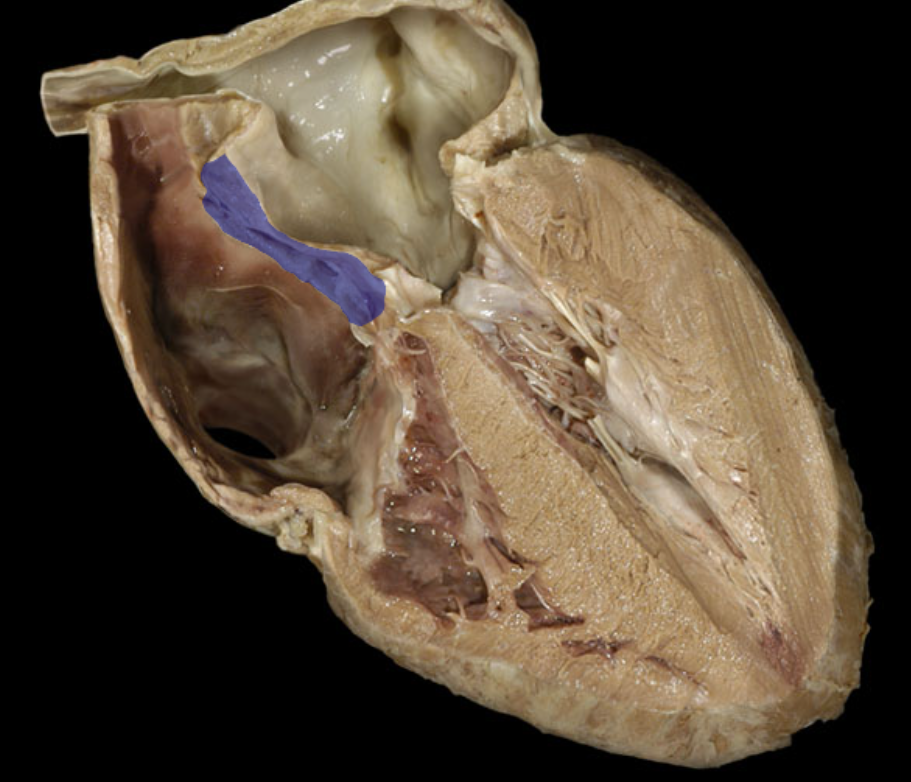
identify the structure
interatrial septum
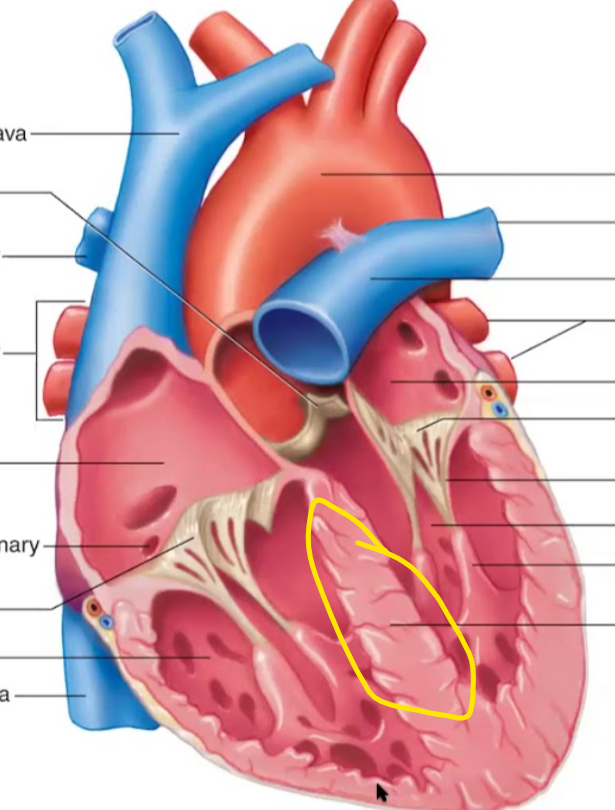
Identify the structure
Interventricular septum
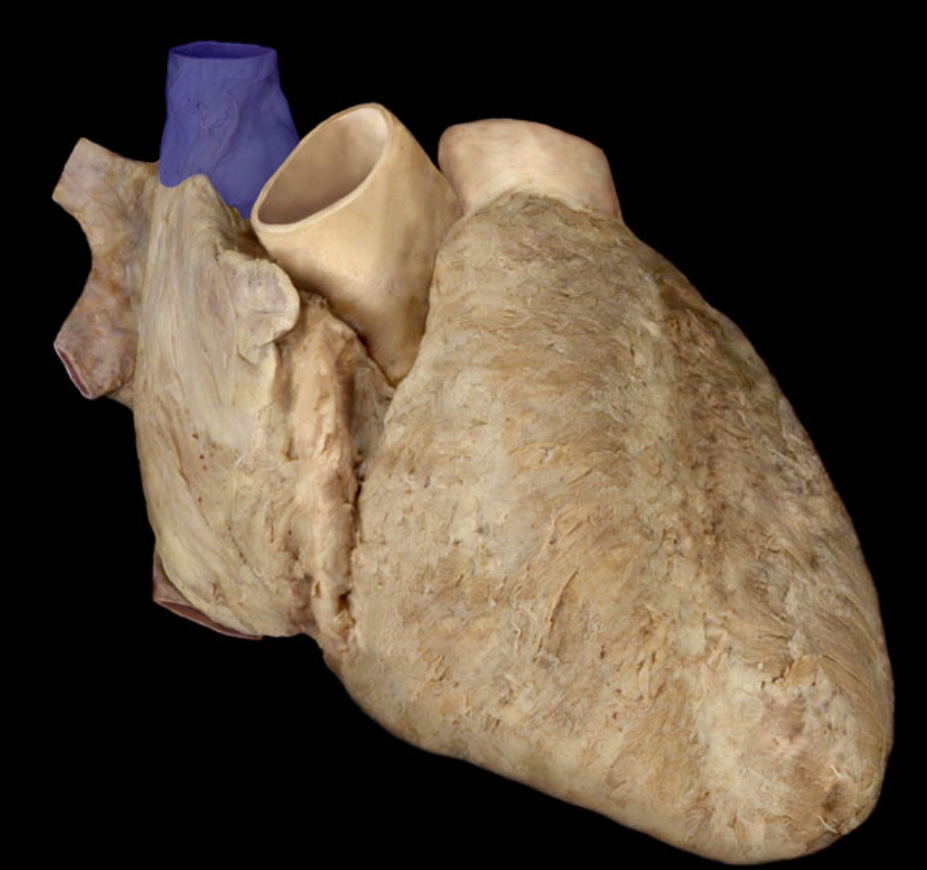
Identify the structure
Superior vena cava
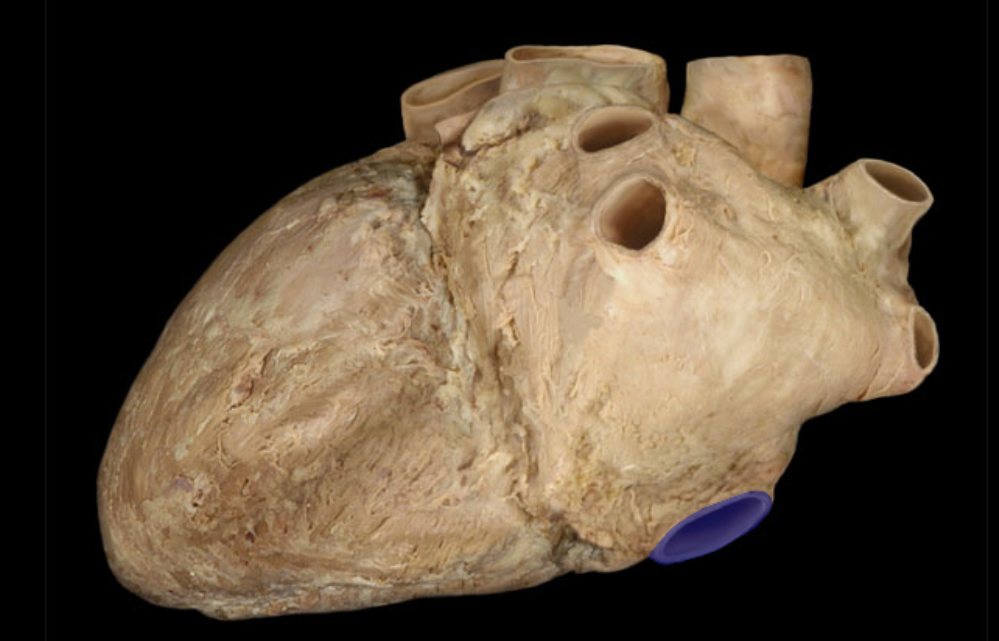
Identify the structure
Inferior vena cava
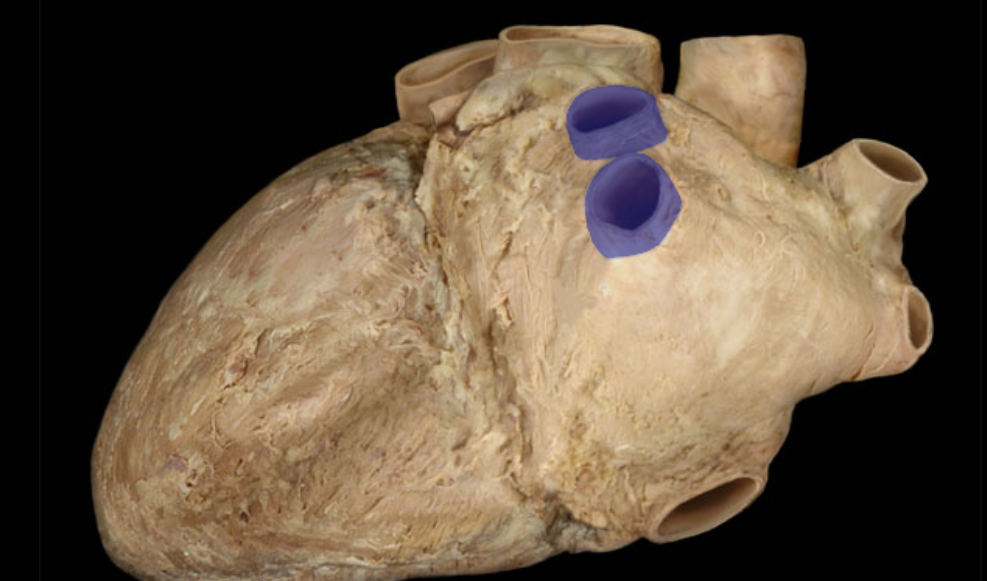
Identify the structure
Pulmonary veins
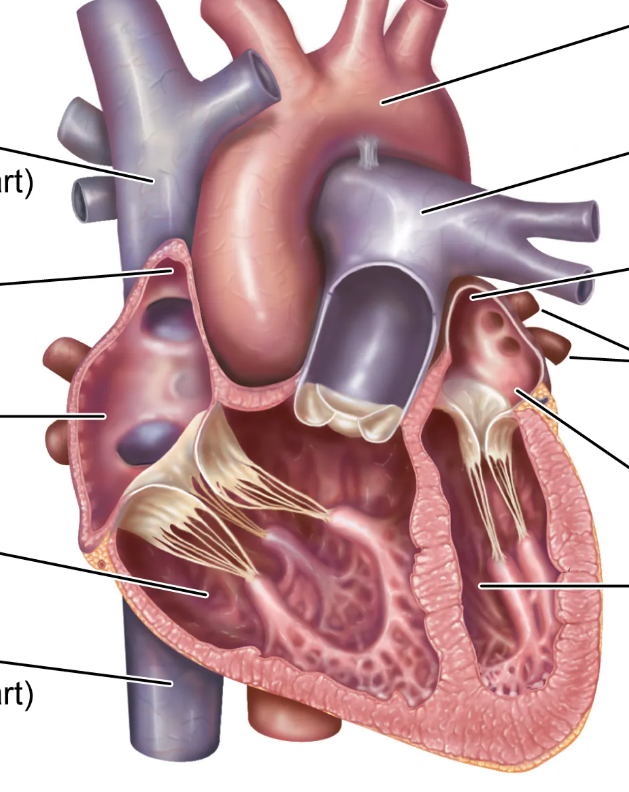
Identify the pulmonary veins
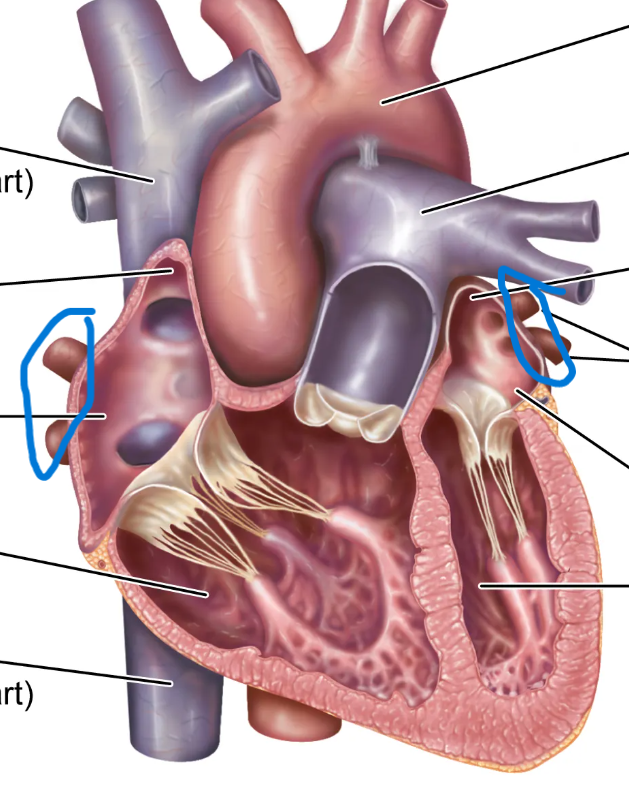
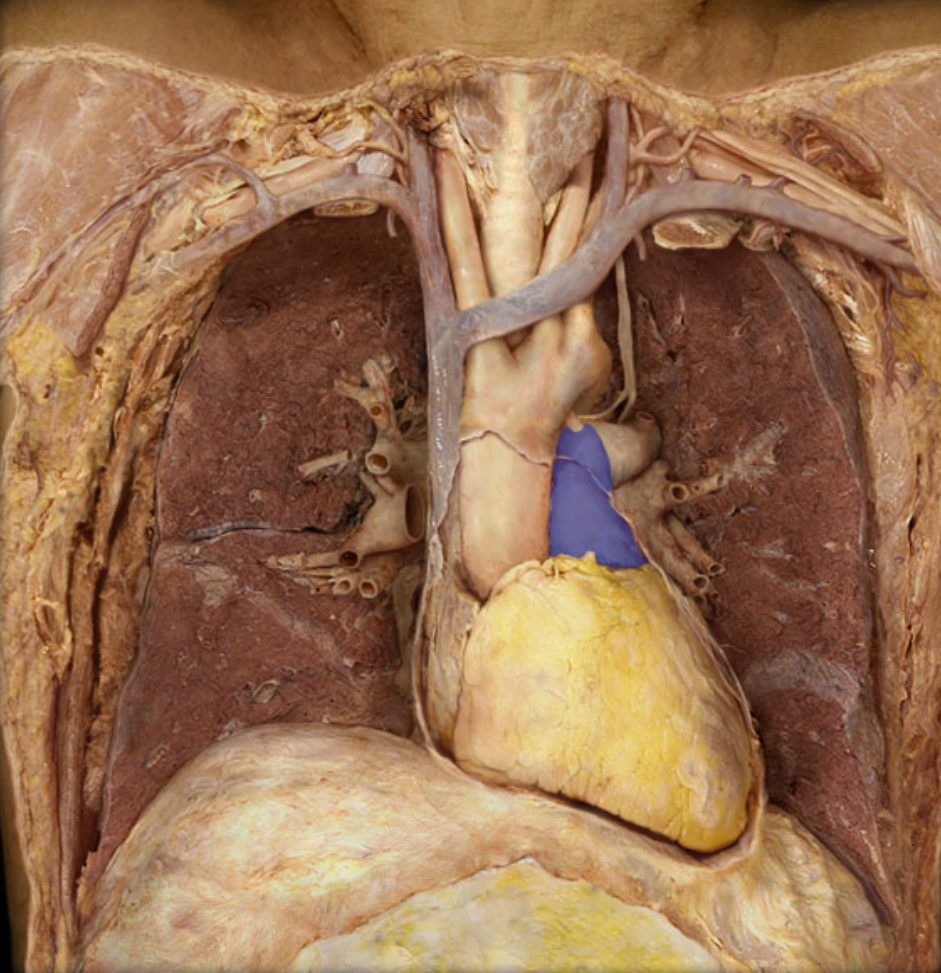
Identify the structure
Pulmonary trunk
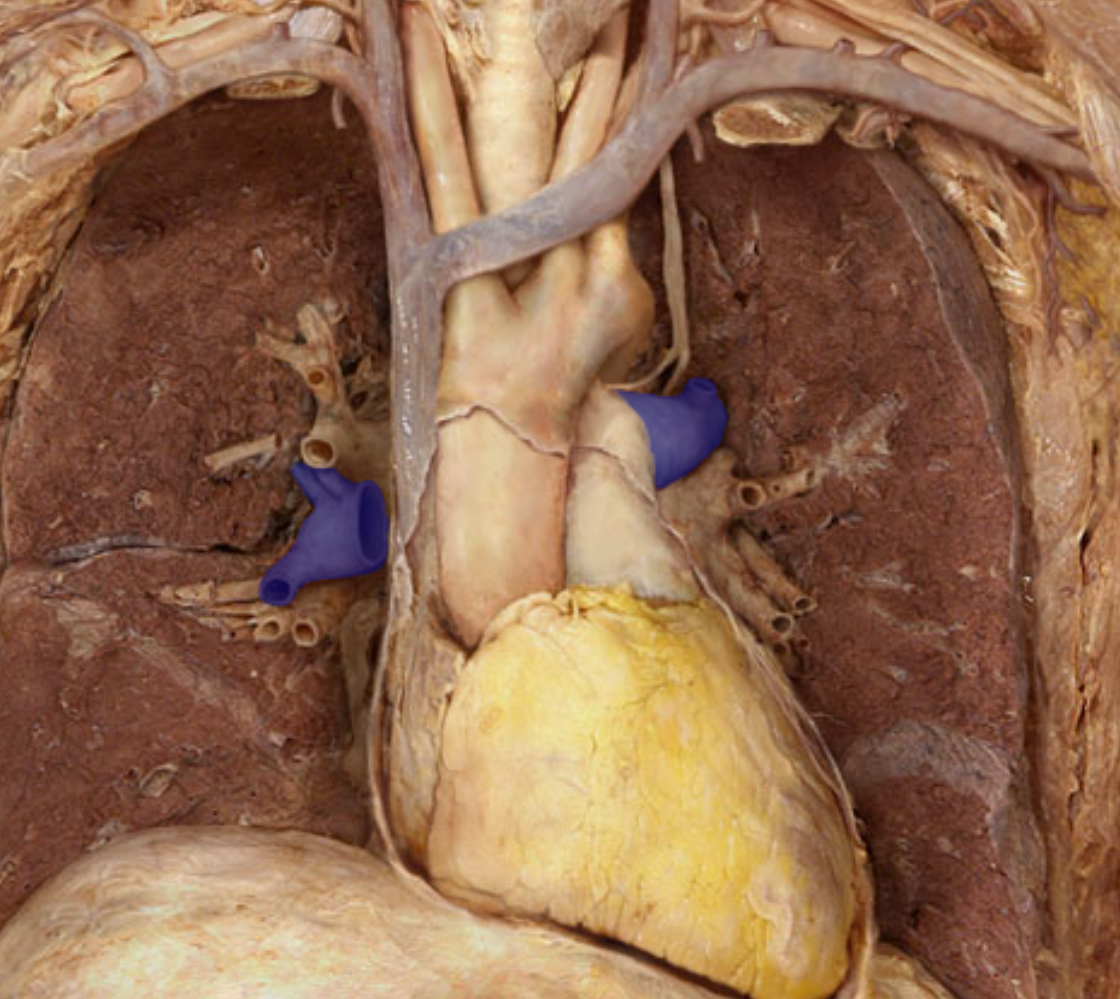
Identify the structure
Pulmonary arteries
Visualize where the aorta is
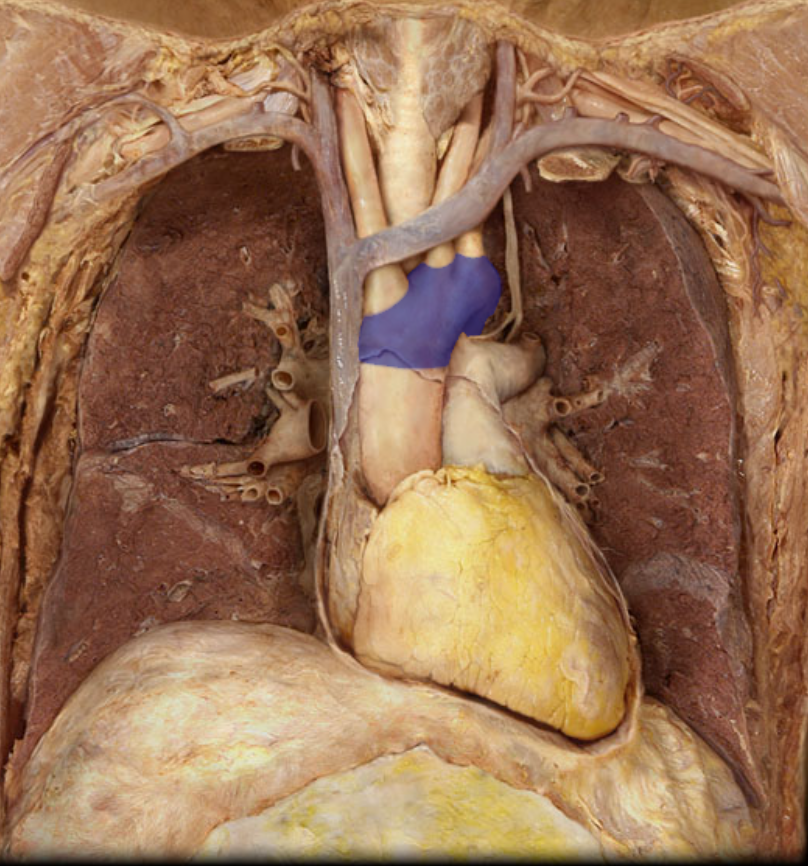
Identify the structure
Aortic arch
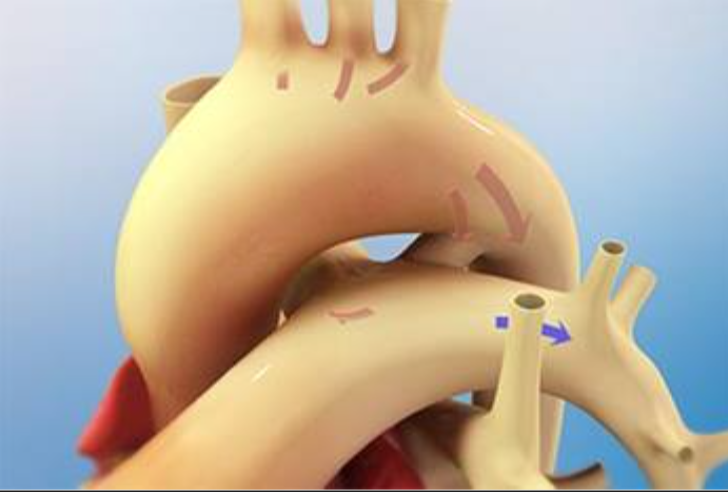
Identify the structure that is unusual, and when it is present. And what does this structure turn into?
Ductus arteriosus, present in infants because blood doesn’t go to their lung. Turns into ligamentum arteriosum
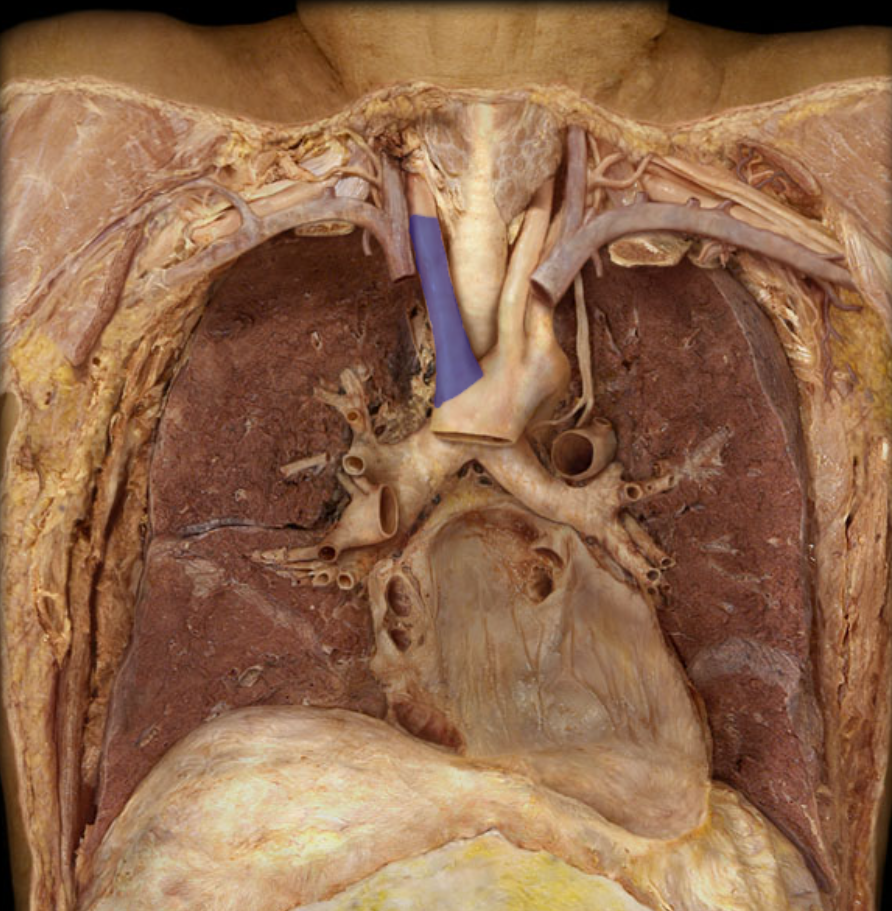
Identify the structure
Brachiocephalic trunk
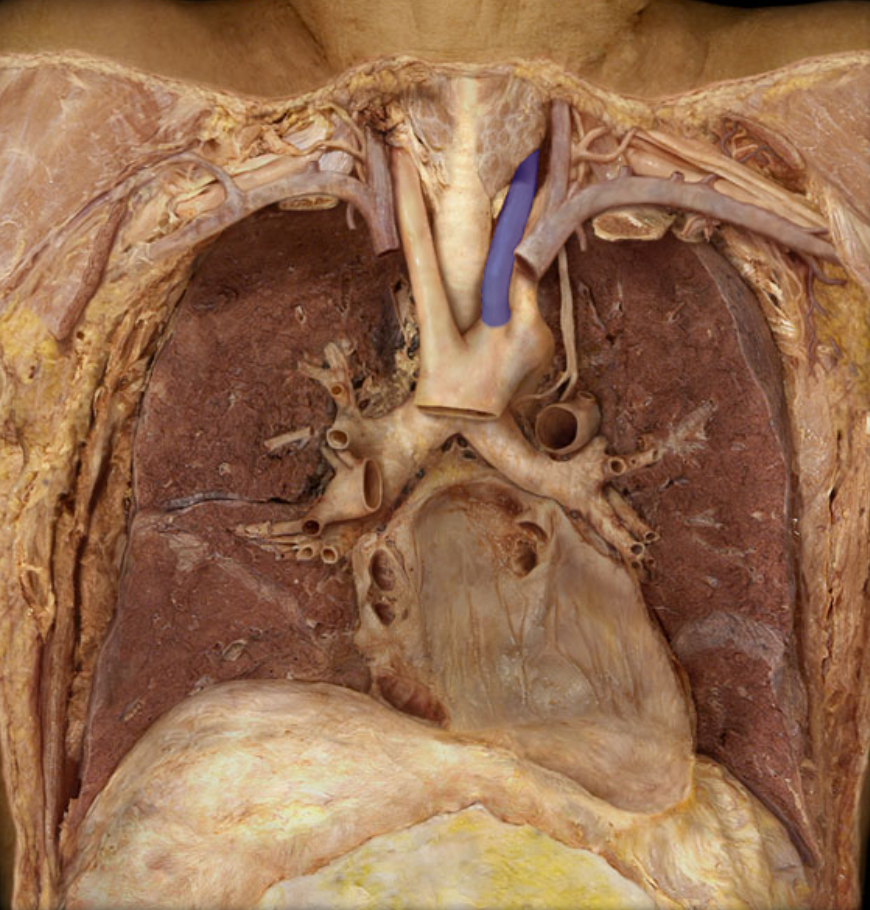
Identify the structure
Left common carotid atery
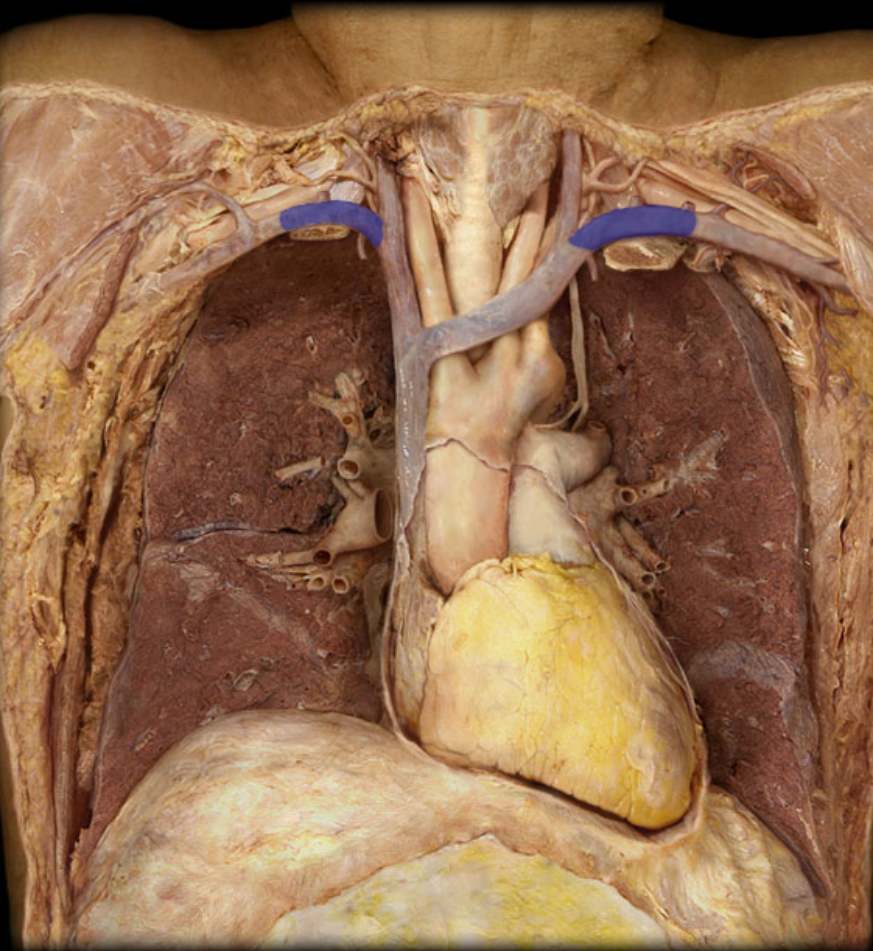
Identify the structure
Right and left subclavian arteries
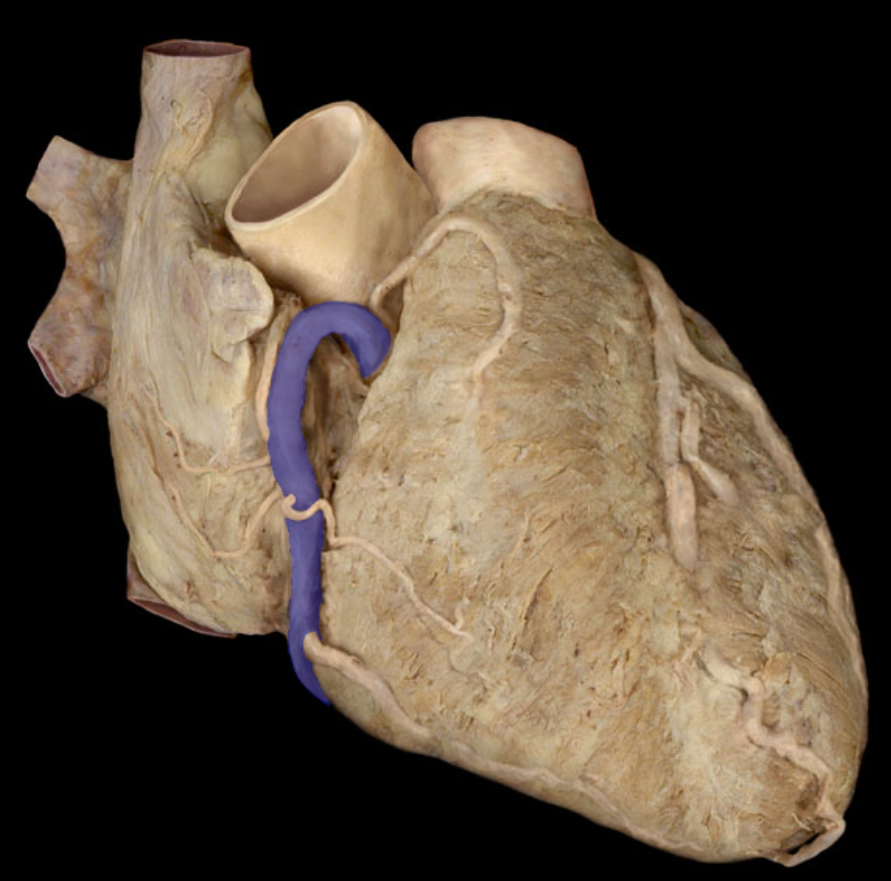
Identify the structure
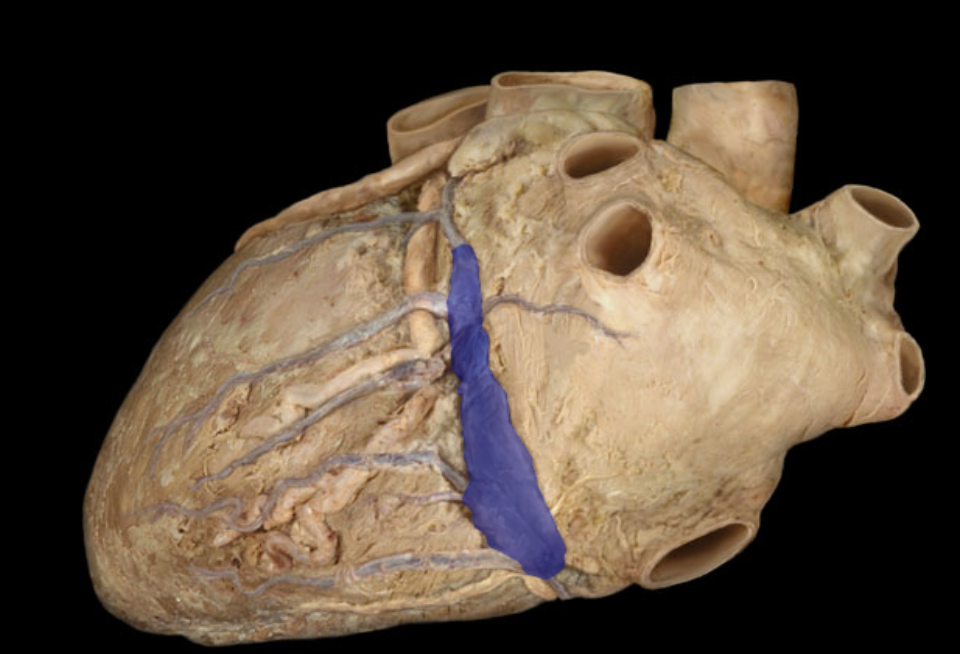
Right coronary artery
What are the branches of the left coronary artery, and what is its length compared to the right?
Anterior interventrucular artery, circumflex artery
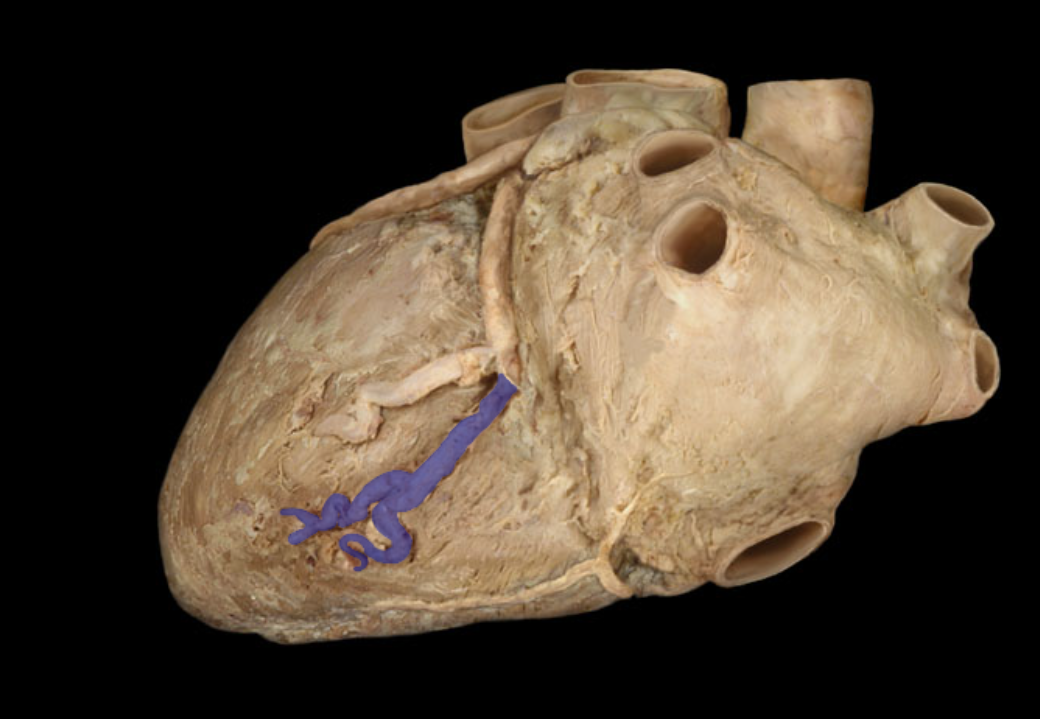
Identify the structure
Anterior interventricular artery
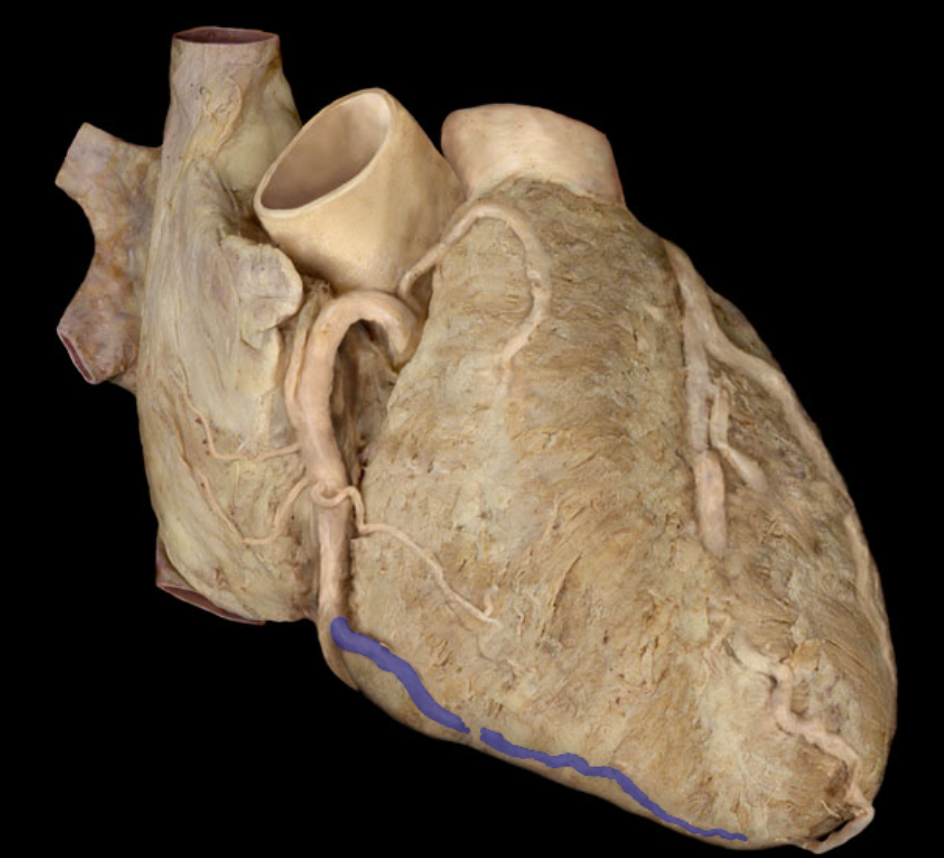
Identify the structure
Posterior interventricular artery
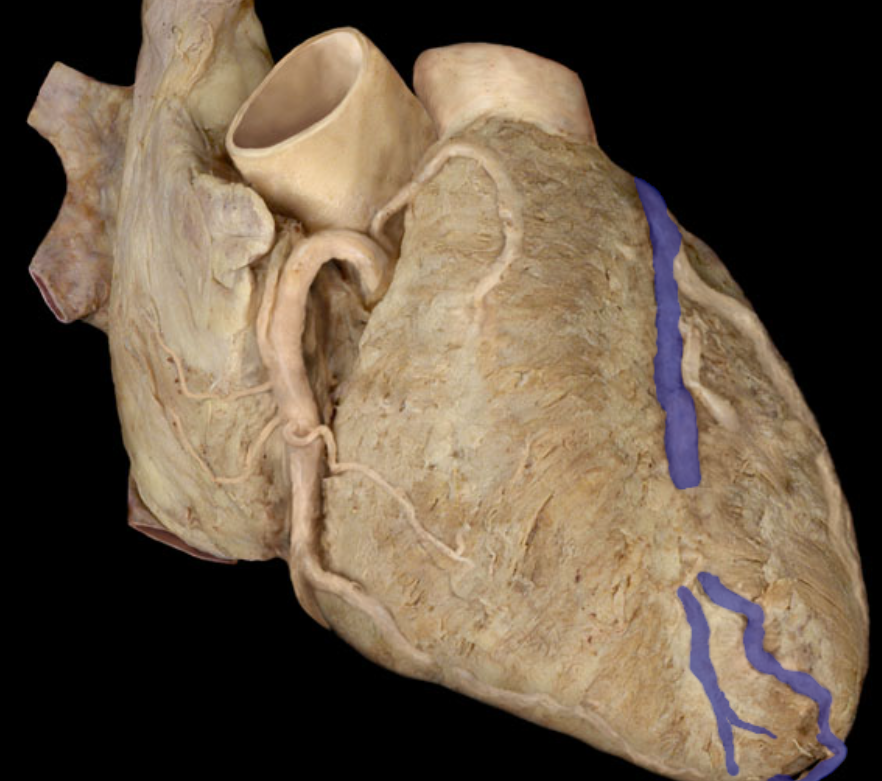
Identify the structure
Right marginal artery
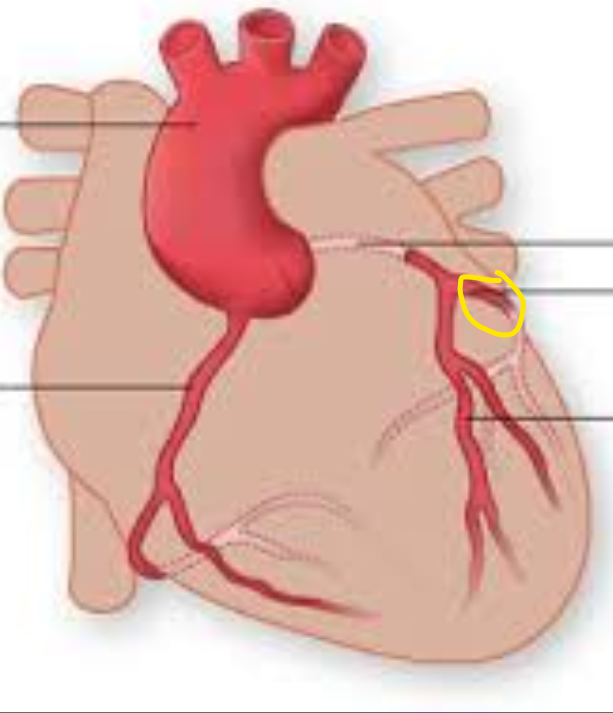
Identify this structure
Circumflex artery
Identify this structure
Coronary sinus (main vein drain)
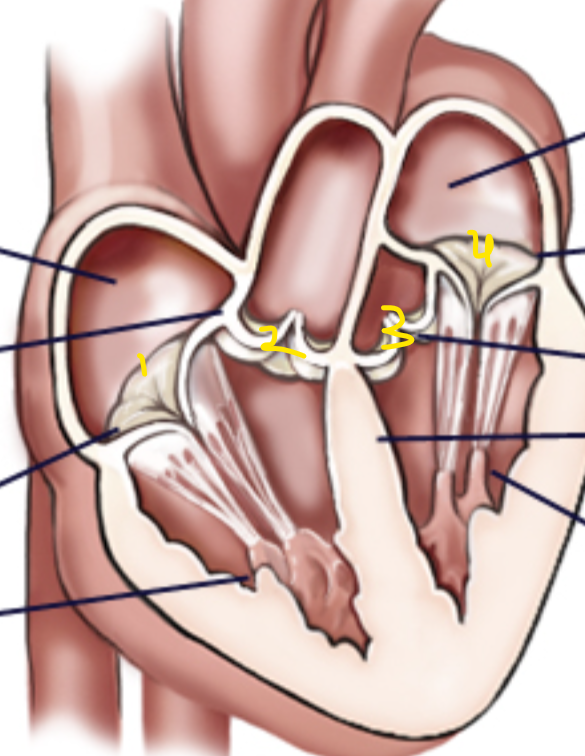
Name the structures in order
Right tricuspid (atrioventricular) valve, pulmonary semilunar valve, mitral/bicuspid (left atrioventricular) valve
What are the heart strings real name and purpose?
Chordae tendinae, to hold the flaps of the valves shut to prevent backflow
What are the nipple like muscles that hold work them valves called
Papillary muscles
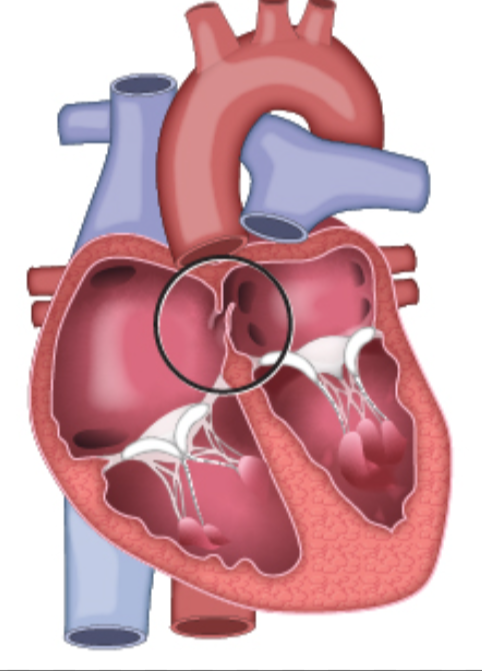
Identify this birth “defect” and what does it turn into
Foramen ovale, turns into fossa ovalis.
Pulmonary circuit describe, systemic circuit describe
Pumps blood from the right side of heart to lungs then back to left sid. Pumps blood from left side of heart to body then back to vena cavas on right side.
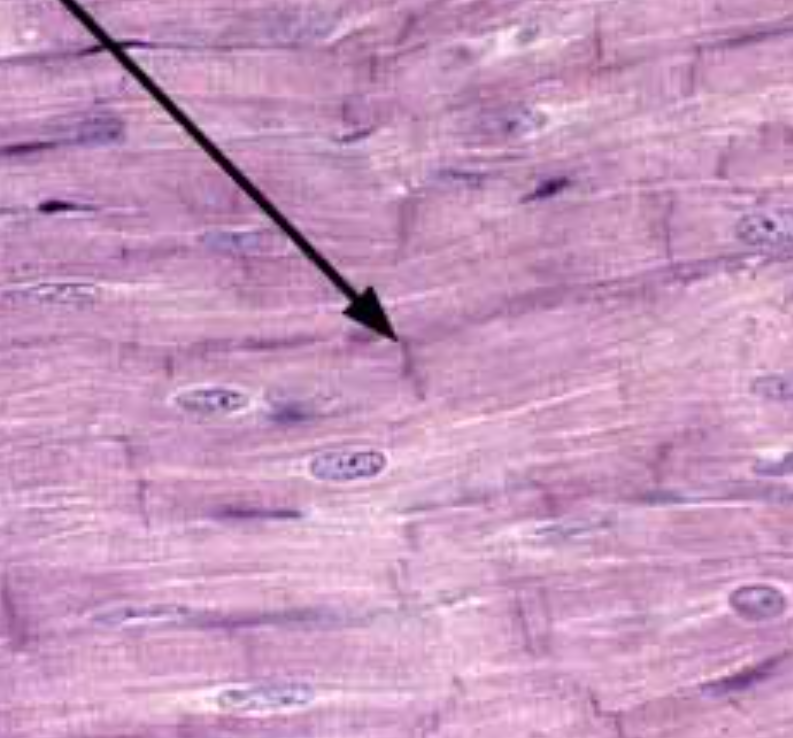
Identify this trait of cardiac muscle
Intercalated discs