Recombinant DNA in Medicine
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What are the four recombination techniques used in medicine?
amplification (PCR, RT-PCR)
seperation by size (gel electrophoresis)
detection of specific sequences: hybridization
Northern/southern
FISH
microarrays
analysis of nucleic acids
restriction endonucleases: recognize and cleave specific sequences
Reading the sequence of nucleotides – Sanger method or NGS
Describe how PCR is done
Components: thermostable DNA polymerase, nucleotides, synthetic primers, and DNA
Each cycle:
melting of double-stranded templates
annealing of synthetic primers
DNA polymerase begins the synthesis of complementary DNA
What is RT- quantitave PCR (RT-PCR)? How is it done?
The use of a fluorescent probe allows real-time detection of PCR product at the end of each cycle.
A special dye, which fluorescence increases upon binding to a dsDNA, is used for quantitation. (template could also be RNA)
A special software can calculate the number of copies in analyzed samples by using a control sample with the known number of DNA templates.
Can be used to compare the expression of genes in different cell types or tissues.
Describe how gel electrophoresis work
Nucleic acids migrate in electric field during gel electrophoresis from negatively charged cathode to positively charged anode.
Fragments are separated by size: shorter fragments move faster, and longer fragments move slower.
A mixture of the fragment of known sizes is used as a reference to determine the size of analyzed samples
How does hybridization work?
uses labeled probes, single- stranded DNA or RNA molecule to detect complementary DNA or RNA sequences.
used to detect a sequence of interest.
What are northern/southern blots used for? FISH? microarrays?
Northern (RNA) or Southern (DNA) blot: determine presence and size of nucleic acid molecule.
The nucleic acids should be separated using gel electrophoresis.
FISH: detect location of specific sequence(s) on the chromosome.
Microarrays: allow quantitative detection of multiple sequences in the analyzed sample.
What are the steps for the northern/southern blots
A. Separate DNA or RNA on agarose gel.
B. Transfer separated nucleic acids on nitrocellulose paper.
C. Remove nitrocellulose paper from the gel.
D. Hybridize separated nucleic acids with radiolabeled probe
E. Visualize probe hybridized to complementary DNA by autoradiography.
What is FISH used for clinically?
identification of numerical and structural chromosomal abnormalities.
characterization of marker chromosomes.
tracking the origin of cells after bone marrow transplantation.
identification of regions of deletion or amplification
Describe the Philadelphia chromosome
specific abnormality of chromosome 22, which is unusually short and is most commonly associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML).
The Abl gene expresses a membrane-associated tyrosine kinase.
Translocation of Abl into chromosome 22 forms a fusion gene BCR-Abl.
The fusion protein BCR-Abl is "always on" or constitutively active, which results in unregulated cell division (i.e. cancer).
how does restrictive endonucleases work?
recognize palindromic sequences and cuts it there → makes sticky ends
What are the three techniques we use to detect Disease-causing mutations
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP)
– Allows detection of point mutations that destroy or create restriction site(s). (Sickle cell anemia)
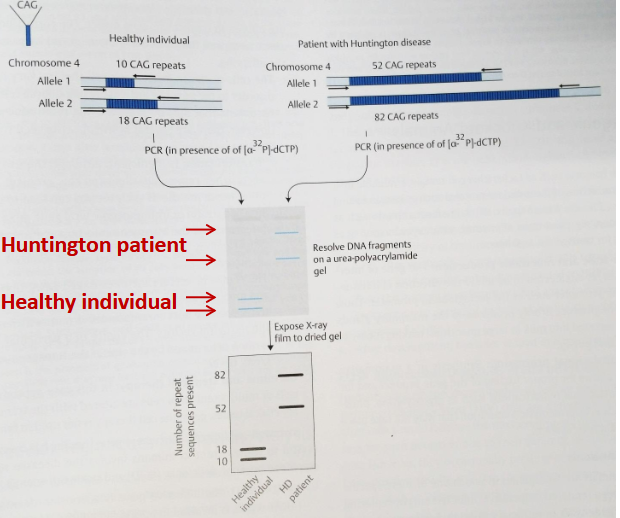
Detection of Variable Number of Tandem Repeats (VNTR)
Can be performed by PCR amplification of the repetitive DNA.
Used in genetic testing, forensic, DNA fingerprinting
Microarrays is a variation of hybridization-based technique that uses tens of thousand of synthetic probes
– Allows screening of many gene expression simultaneously.
– Can be used to compare expression profiles in different tissues or in the same tissue under different conditions.
– Requires a special scanner and software for analysis of experimental data.
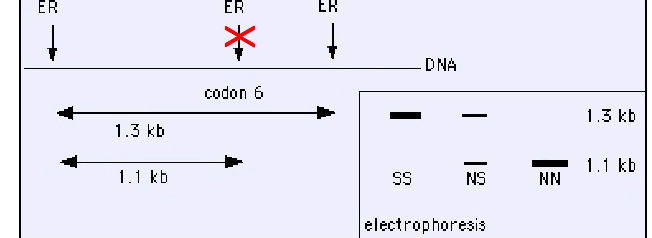
explain how we detect sickle cell anemia with RFLP
The site (ER) is normally recognized and cleaved by restriction enzyme at the 6th codon in B-globin, producing a DNA fragment of 1.1 Kb.
• The mutation eliminates this site at codon 6 that leads to generation of 1,3 Kb fragment.
• Sothern blot can discriminate between the normal homozygotes (NN), heterozygotes (NS) and affected homozygotes (SS) individuals.
explain how we can use VNTR in hunting disease by PCR
How do microarrays work?
They comprise synthetic probes corresponding to different genes spotted on a glass slide.
The analyzed samples are labeled with a fluorescent dye and hybridized with microarray.
The experimental sample is compared to the control, using red and green fluorescent tags.
The intensity of the signal corresponds to the gene expression levels in that tissue
What are the two major methods for DNA sequencing and describe them
Sanger sequencing uses termination of DNA synthesis at specific nucleotides during DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase.
• Uses a mixture of dNTPs and a specific ddNTP
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS):
• Uses DNA synthesis termination principle as in Sanger
• Allows simultaneous sequencing of millions of DNA fragments
• Human genome can be sequenced in one hour!
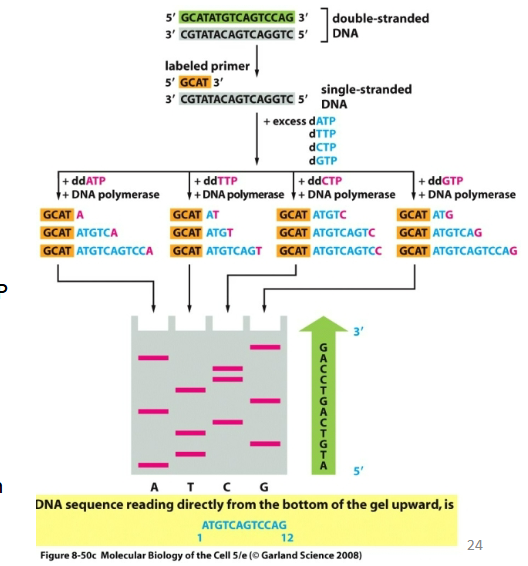
Describe how Sanger sequencing works
Random incorporation of ddNTP terminates DNA synthesis.
Low concentrations of ddNTPs in nucleotide mixtures allows to obtain a set of DNA fragments of different lengths.
ddNTPs labeled radioactivily or flourescently
Can be separated in one lane if four different fluorescently labeled ddNTP are used.
Can be detected in automated sequencing machines.
You can read the sequence after the
separation of DNA fragments.
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) can read an entire human genome in 4-8 hours
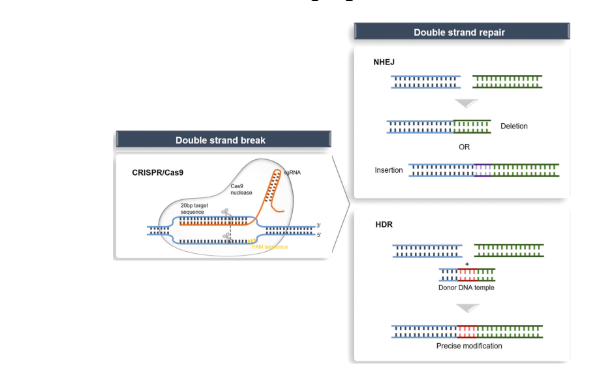
Describe how CRISPR/CAS9 work
Gene therapy
induces double-stranded breaks (DSBs) at targeted sites
this is repaired by:
Nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ) leads to the formation of insertions or deletions
Homology-directed repair (HDR) in the presence of a donor template
CRISPR/Cas9 - clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat-associated 9 nuclease
What are the two Proteomics Techniques in Diagnosis
ELISA: Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Direct, indirect, and sandwich
fastest way to detect the presence of suspected pathogen in biological samples
Western blot:
Combines separation and detection with specific antibodies
Detection of different isoforms of target protein
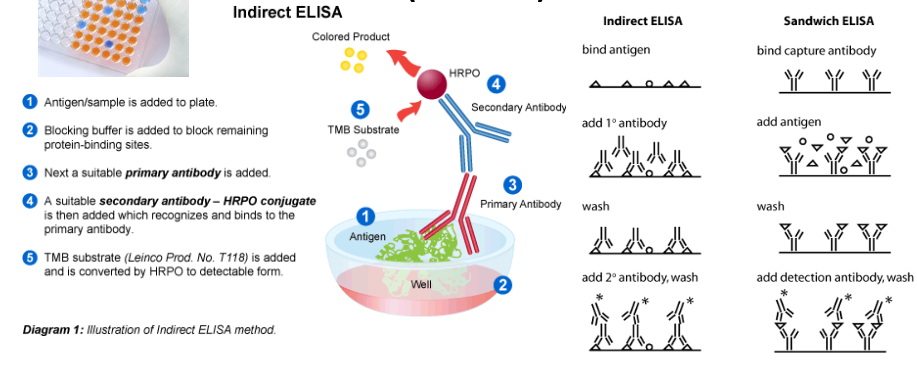
What is ELISA used to detect? Describe Indirect and Sandwich Elisa
used to detect and quantitate a protein content in clinical samples:
Blood proteins (troponin and C-reactive protein (CRP)
Cerebrospinal fluid proteins.
Can be used for screening a large number of samples for the presence of infection agents or Abs
What is western blot a combination of? What are the steps?
Protein separation by size using SDS PAGE and Detection of specific protein(s) using antibodies.
