2.11 - Eicosanoids
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Eicosanoids are derived from
membrane lipids
The precursor fatty acids for eicosanoids contain how many carbons
20
Most abundant eicosanoid precurser in humans
Arachadonic Acid (AA)
How is Arachadonic Acid stored?
as part of cell membrane phospholipids
How is Arachadonic Acid released
released from phospholipids by hydrolysis mediated phospholipases (notably PLA2)
What initiates the release of arachadonic acid from phospholipids mediated by Phospholipases
initiated by Ca2+ dependent translocation of PLA2 from cyrosol membrane

Metabolites of Arachadonic Acid include:
Prostandlandins (PG)
Leukotrienes (LT)
Thromboxanes (TXA)
all are autocoids
How are eicosanoids stored
Eicosanoids are NOT stored. They are produced as needed when physical, chemical and/or hormonalstimuli activate phospholipases
Biosynthesis of eicosanoids is limited by availability of
Arachadonic Acid
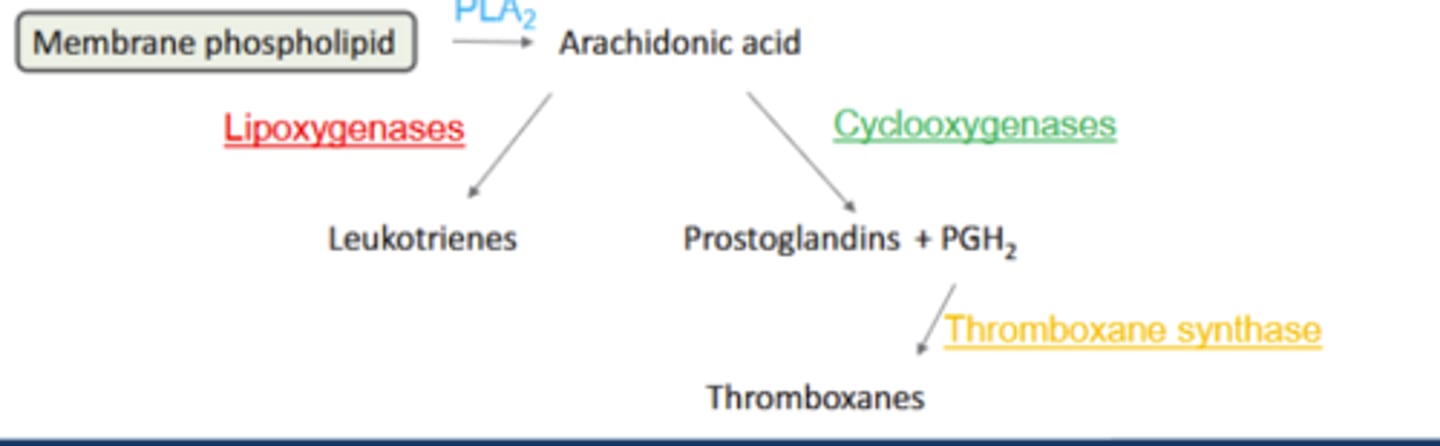
How are Leukotrienes (LTA,B,C,D, or E) synthesized from AA
Lipoxygenases (LOX): Convert AA to leukotrienes (LTA, B, C, D or E)
LT: potent inflammatory + bronchoconstrictors: asthma, anaphylaxis
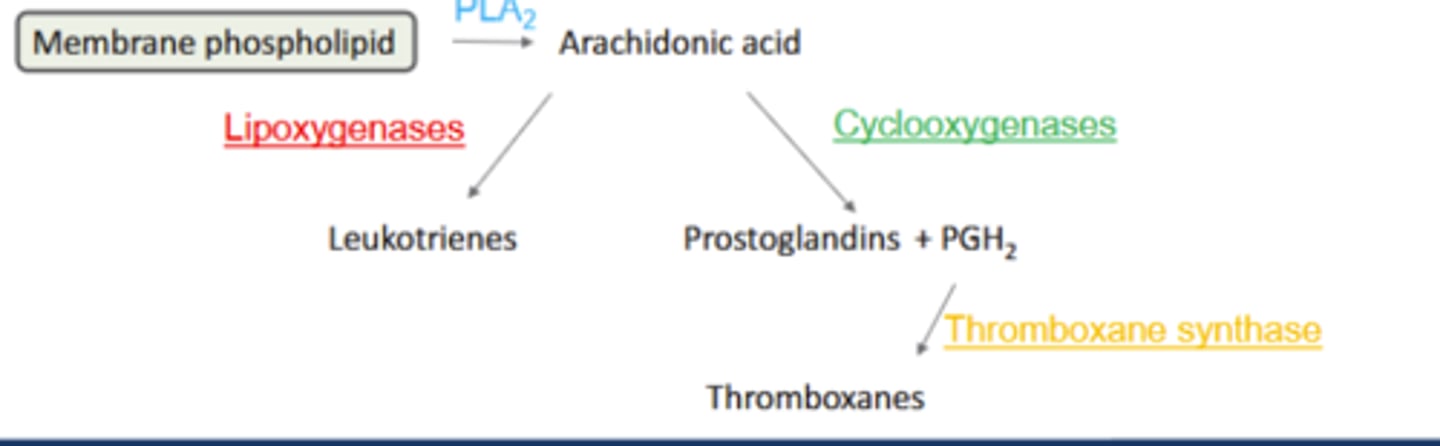
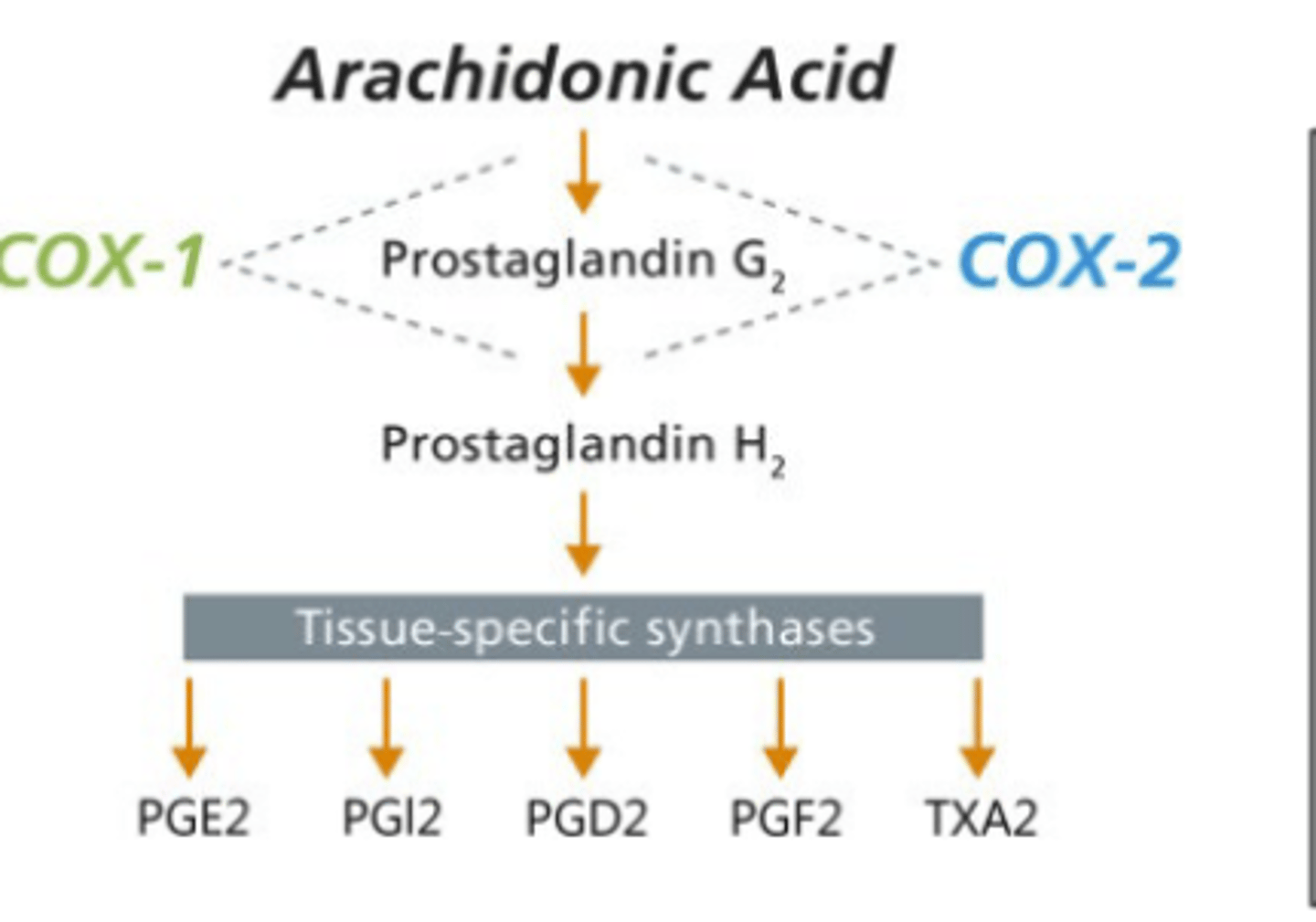
How are prostaglandins synthesized from AA?
Cyclooxygenases (COX): Convert AA to prostaglandins (PGD, E, F, G, H or I)
Diverse functions: fever, sleep, pain; ↑inflammation
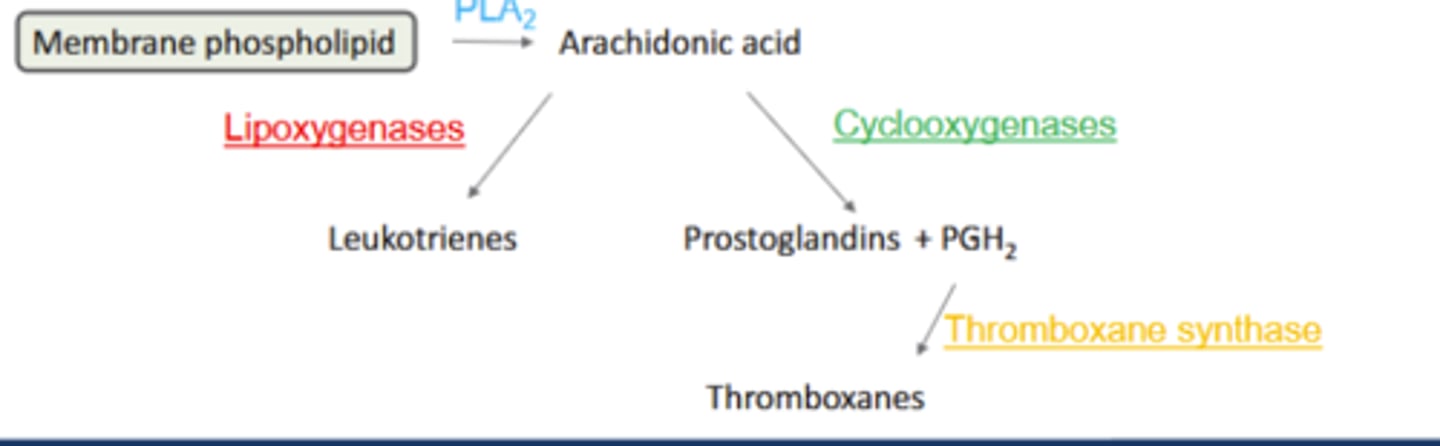
How are Thromboxanes synthesized from AA
Thromboxane synthase: PGH2 converted to thromboxanes (TxA)
TxA: smooth muscle cell mitogen and potent platelet aggregator
rostaglandin synthesis is accomplished in a _________________ by a complex of microsomal enzymes.
stepwise oxidation
What serves are a major intermediate for the stepwise oxidation for prostaglandin synthesis?
PGH2
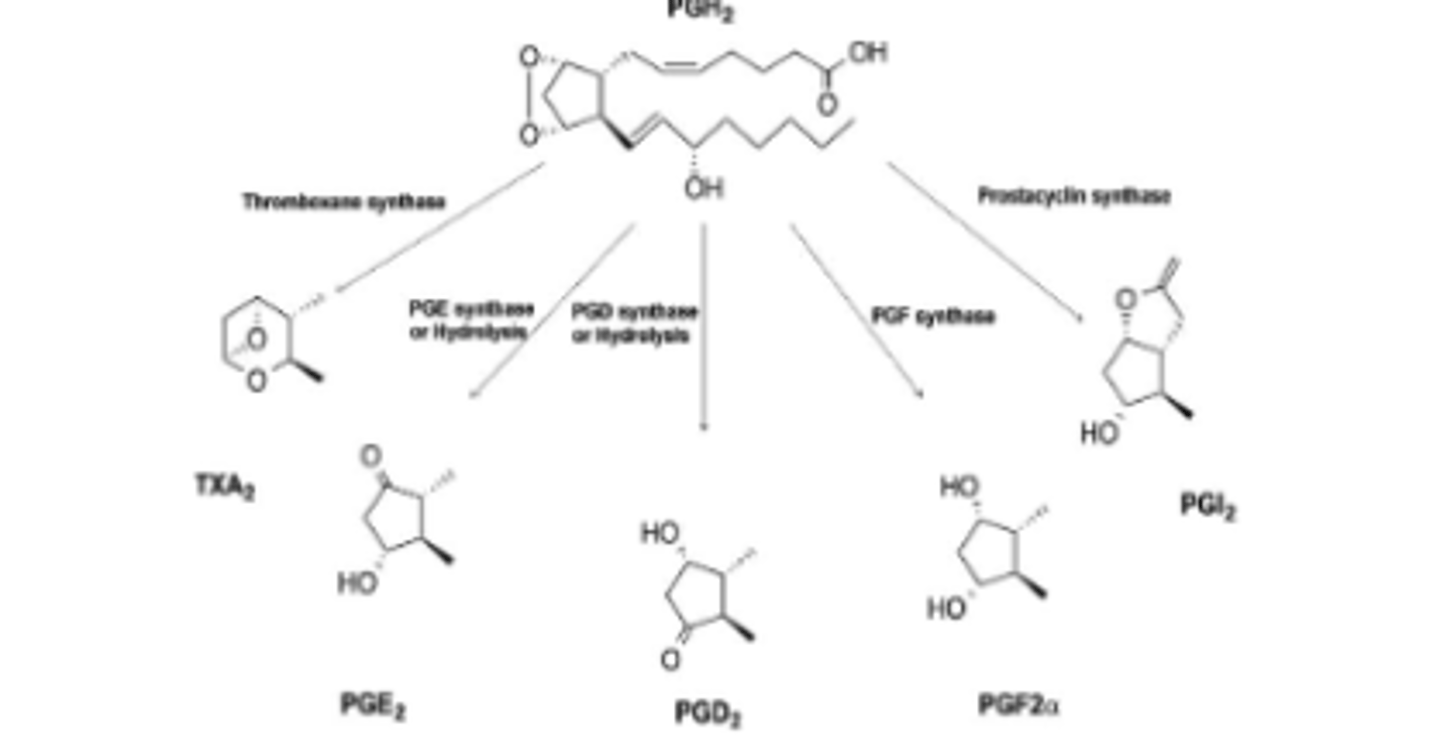
Prostaglandins with subscript 2 are derived from___ and are major series in mammals
AA
Which enxyme involved in Prostaglandin synthesis is "Expressed constitutively in most cells; main source of PG"
Cyclooxygenase 1 (COX-1)
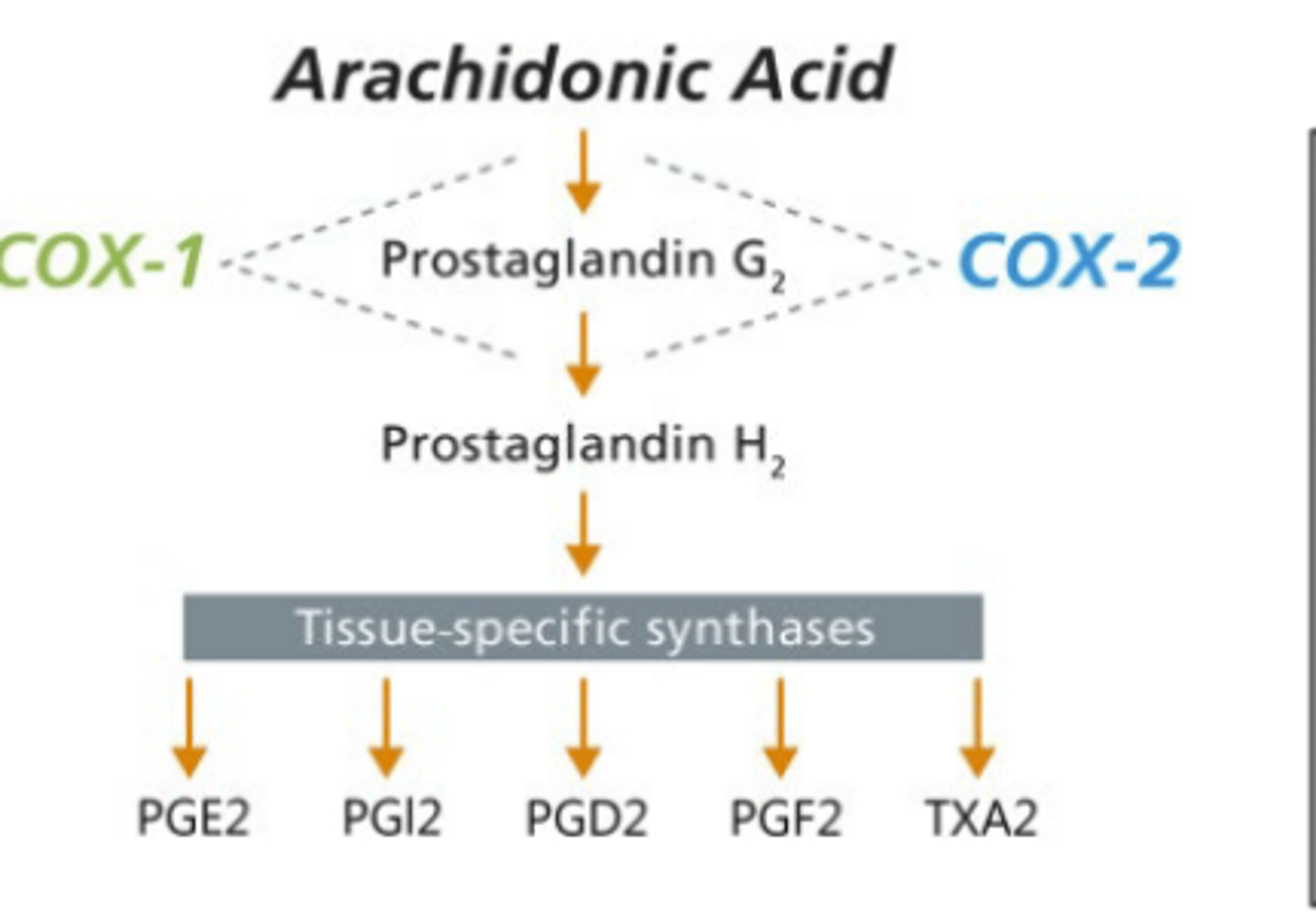
Which enzyme involved in prostaglandin synthesis is "ctivated by cytokines, stress; produces PG in cancer, inflammation"
Cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2)
How do COX inhibitors (NSAIDs) affect prostaglandin production
decrease PG production (aspirin, ibuprofin, naproxen)
How do COX-2 Inhibitors (Celecoxib) work and what is the result?
Selective inhibition of COX-2
reduce induced inflammation and pain
How do PLA2 inhibitors (annexins, glucocorticoids) work?
decrease AA release therby decreasing synthesis of all eicosanoids
Prostaglandin release from the synthesizing cell is accomplished by the
prostaglandin transporter (PGT)
PGs are highly lipophilic, and may cross cells through __________ (but this is insufficient by itself)
Passive diffusion
Prostaglandin release mediated by
ATP-dependent multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4) specific transporter
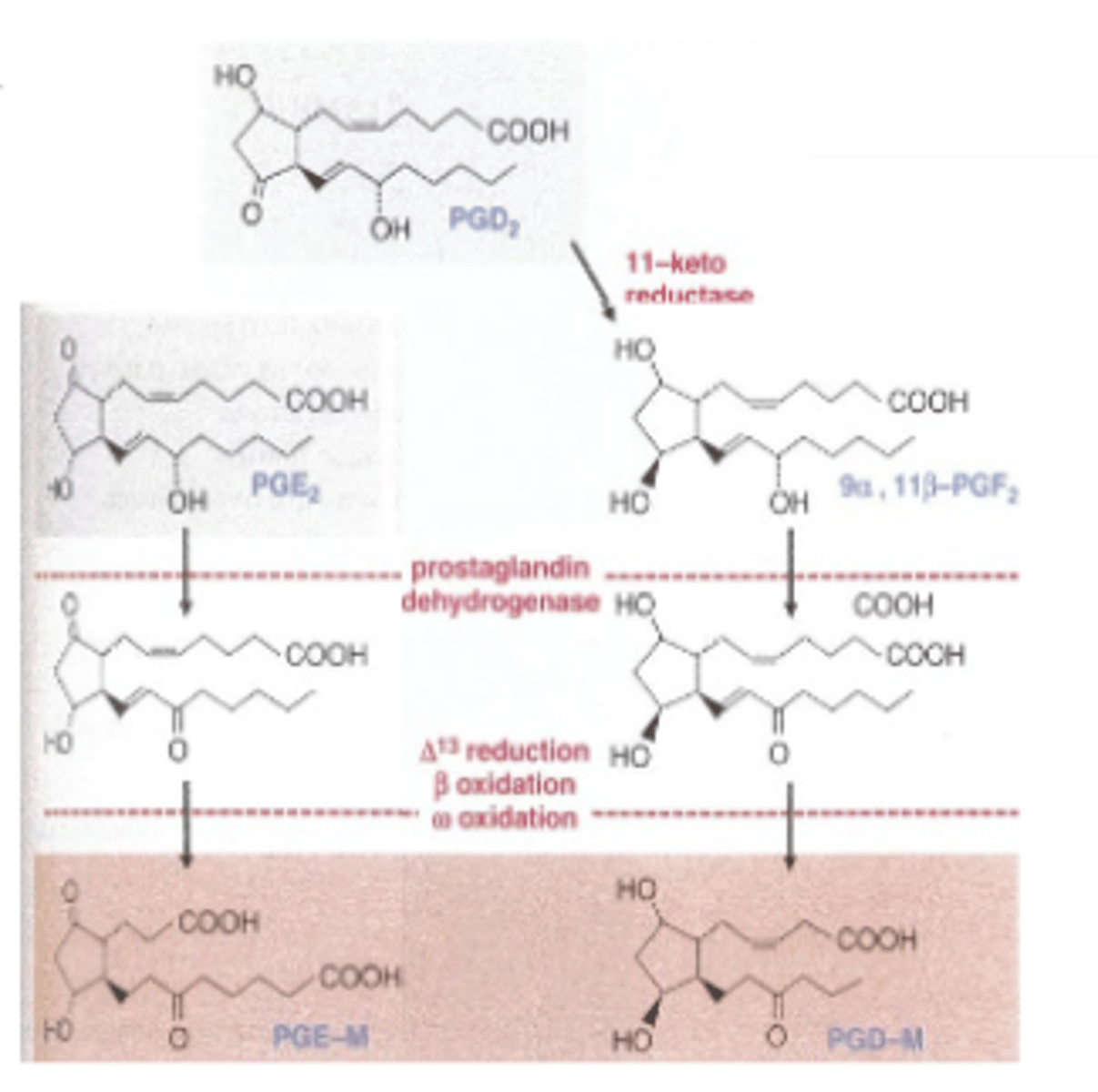
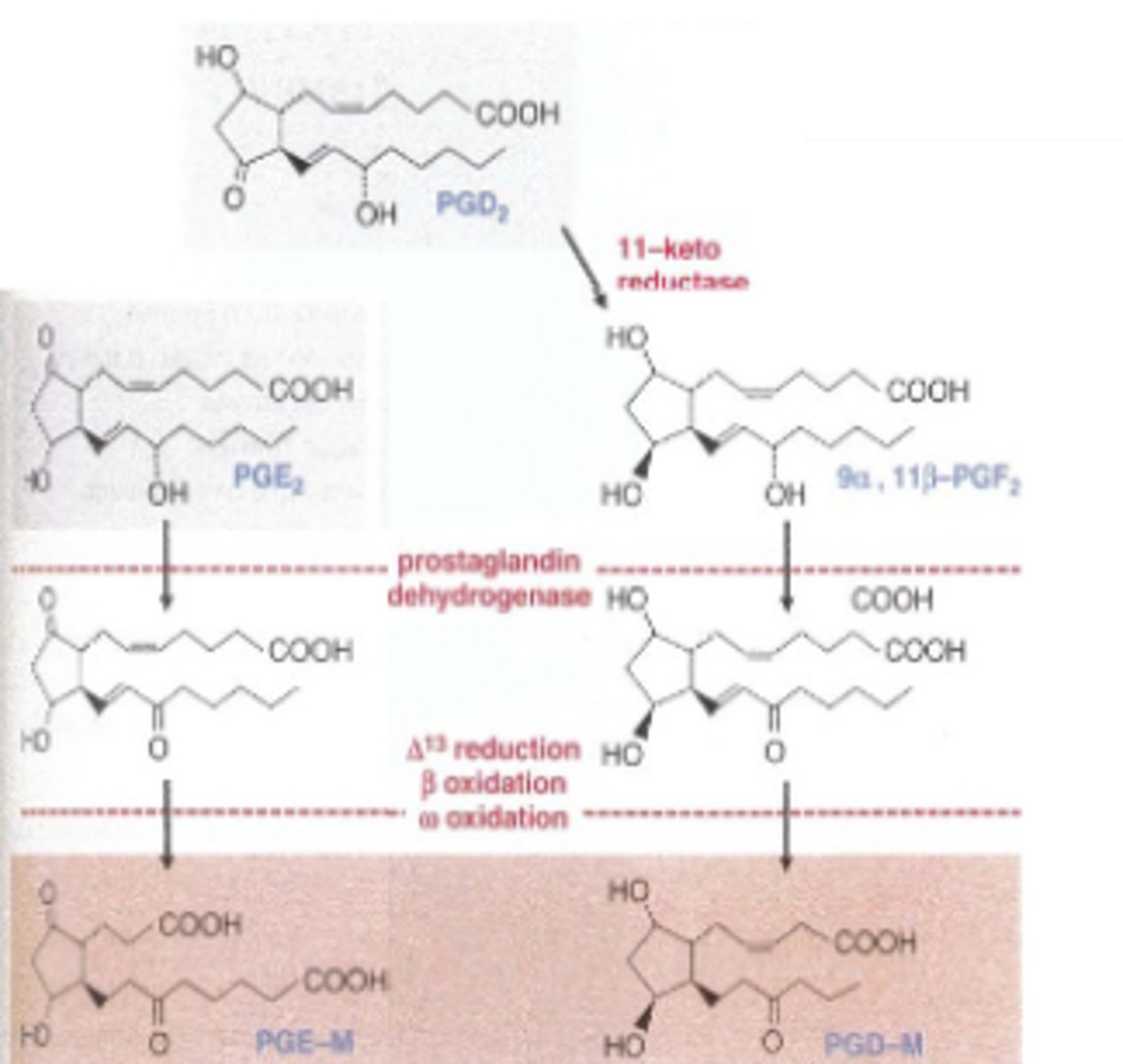
Metabolism of Eicosinoids Steps:
Most (95%) of eicosanoids are rapidly catabolized
1) Rapid initial step by PG-specific enzyme (PGE 2:prostaglandin dehydrogenase)
PGs lose most of their biological activity after action
2)Second step in which metabolites are oxidized throughmultiple enzyme
What effect would a cox-2 inhibitor have onfever? What is the mechanism?
It would decrease fever by decreasing prostaglandin production, thereby lowering PGE2 release
Release of eicosanoids activate ______________ locally near the producing cell
membrane receptors
-Receptors widely distributed throughout brain and body
-PG effects vary greatly due to diverse family of distinct receptors
Eicosanoid membrane receptors are all:
All metabotropic receptors: members of 7TM GPCR superfamily
Receptors (mostly) share high homology; ancient origin
Diversity suggests biological importance
DP 1 and 2
Binds PGD2 .
DP1: Gs-linked; DP 2: Gi-linked!
DP2 receptor linked to airway inflam.; also called CRTH2
EP 1,2,3 and, 4
Binds PGE2. Linked to big variety of G proteins;
FP
Binds PGF2α. Excitatory: Gq-linked
IP
Binds PGI 2. Excitatory: Gs-linked
May now have a second receptor (IP2); also binds PGI
TP alpha and beta
Binds TxA2. Gq,s,i,12/13,+16 linked (!) Mediates clotting.
ctivates RhoGEF pathway; promotes growth and repair
BLT1:
Binds LTB 4. Inhibitory: Gi-linked
BLT 2
Binds LTB 4. Excitatory: Gq-linked
CysLT1
Binds LTD4 Excitatory: Gq-linke
CycLT2
Binds LTC4/LTD4 Excitatory: Gq-linked
Three phylogenic clusters among PGs are all___ linked
Gs
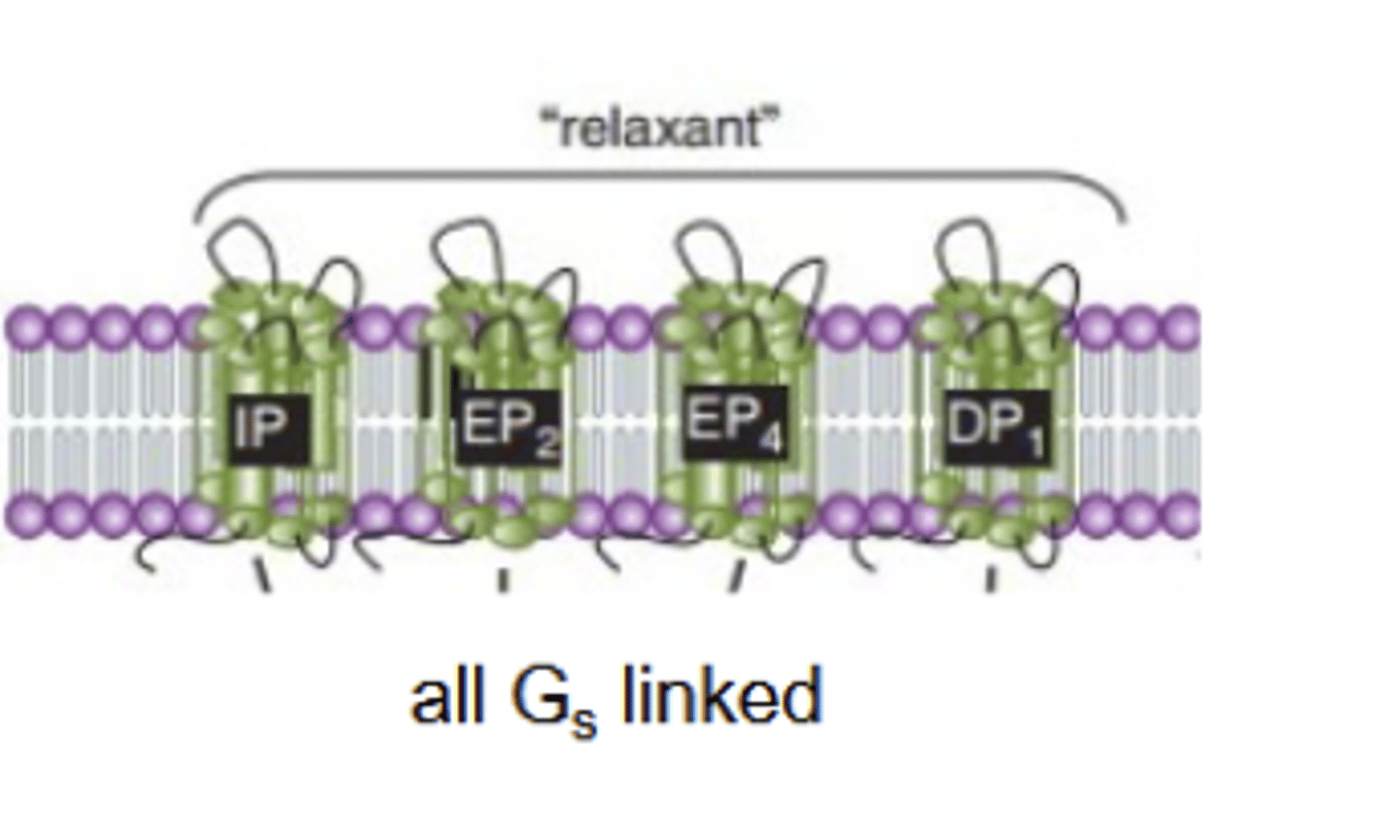
DP2 genetically distinct; more closely related to ______receptor family.
fMLP
CNS effects of PG receptors are primarily mediated by:
PGD2,PGE2,PGI2
DP receptor: primarly ligand, key function, CNS function
primary ligand: PGD2
Key function: allergic athsma
CNS: PGD2 increases sleep (receptor uncertain)
DP2/CHRT2 receptor: primary ligand and key finction
Primary ligand: PGD2
Key function: airway inflammation
EP1 receptor: key ligand, key function, and CNS function:
Primary ligand: PGE2
Key function: vasoconstriction, GIT smooth muscle contraction
CNS: sensitize noiciceptoer threshold, increased hyperalgesia and pain
EP2 Receptor: primary ligand and key function
Primary ligand: PGE2
Key function: bronchodilation, vasodilation, GIT smooth muscle relaxation
EP3 I-VI,e,f receptor: primary ligand, key functions, and CNS functions
Key ligand: PGE2
Key function: cardiovascular protection, GIT smooth muscle contraction, pltalet aggregation, decreased gastric acid, increased autonomic neurotransmitters
CNS: increased fever and body temp
EP4 Receptor: Primary ligand and key functions
Primary Ligand: PGE2
Key function: immune responses in skin, activates T-cells
CNS: sensitixe noiciceptor threshold, increased hyperalgeisia and pain
FP A+B Recetor: primary ligand and key functions
Primary ligand: PGF 2 alpha
Key function: bronchoconstriction, uterine contraction
IP receptor: primary ligand, key function, CNS functions
Primary Ligand: PGI2
Key functions: vasodilation, inhibit platlet aggregation, bronchodilation
CNS: sensitize noiciceptor threshold, increased hyperalgesia and pain
Prostaglandins (esp. PGE2 and PGI 2) generally promote
acute inflammation (although exceptions exist).
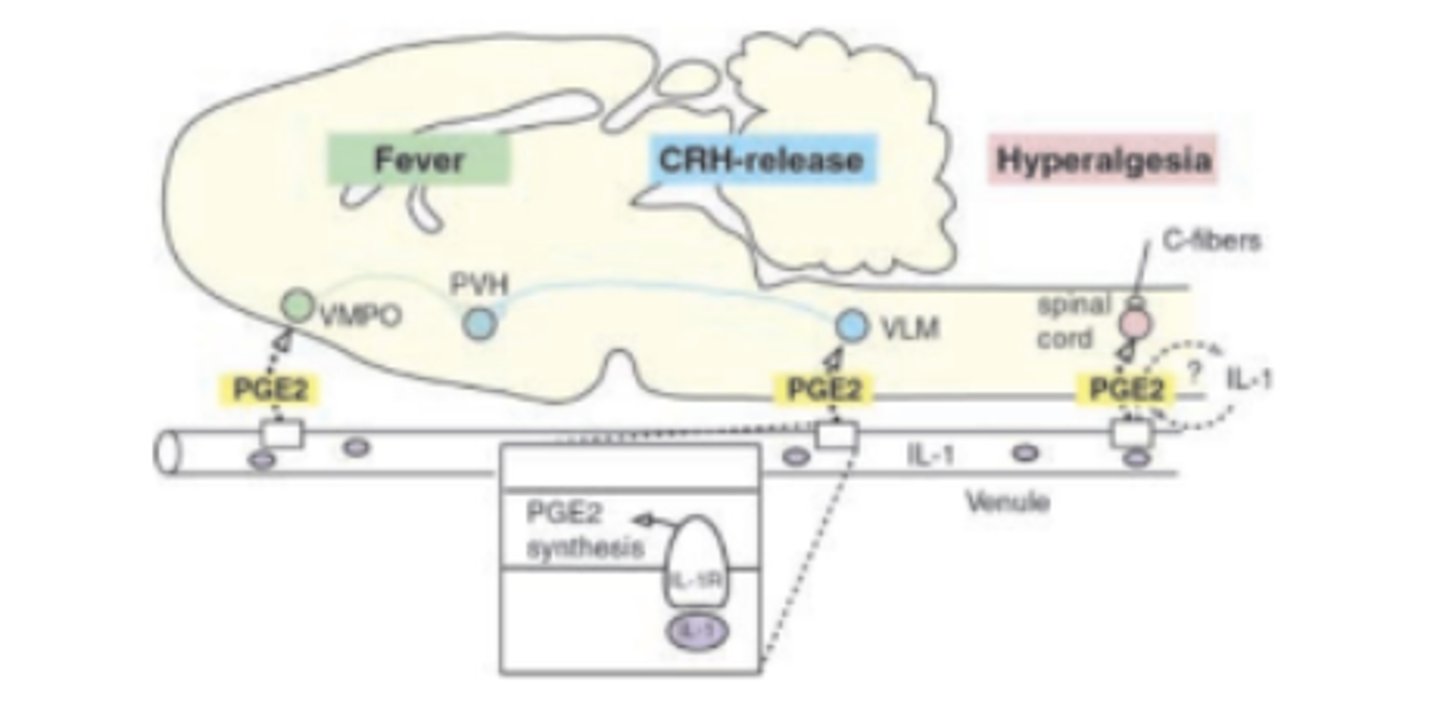
PGE2 a major promotor of:
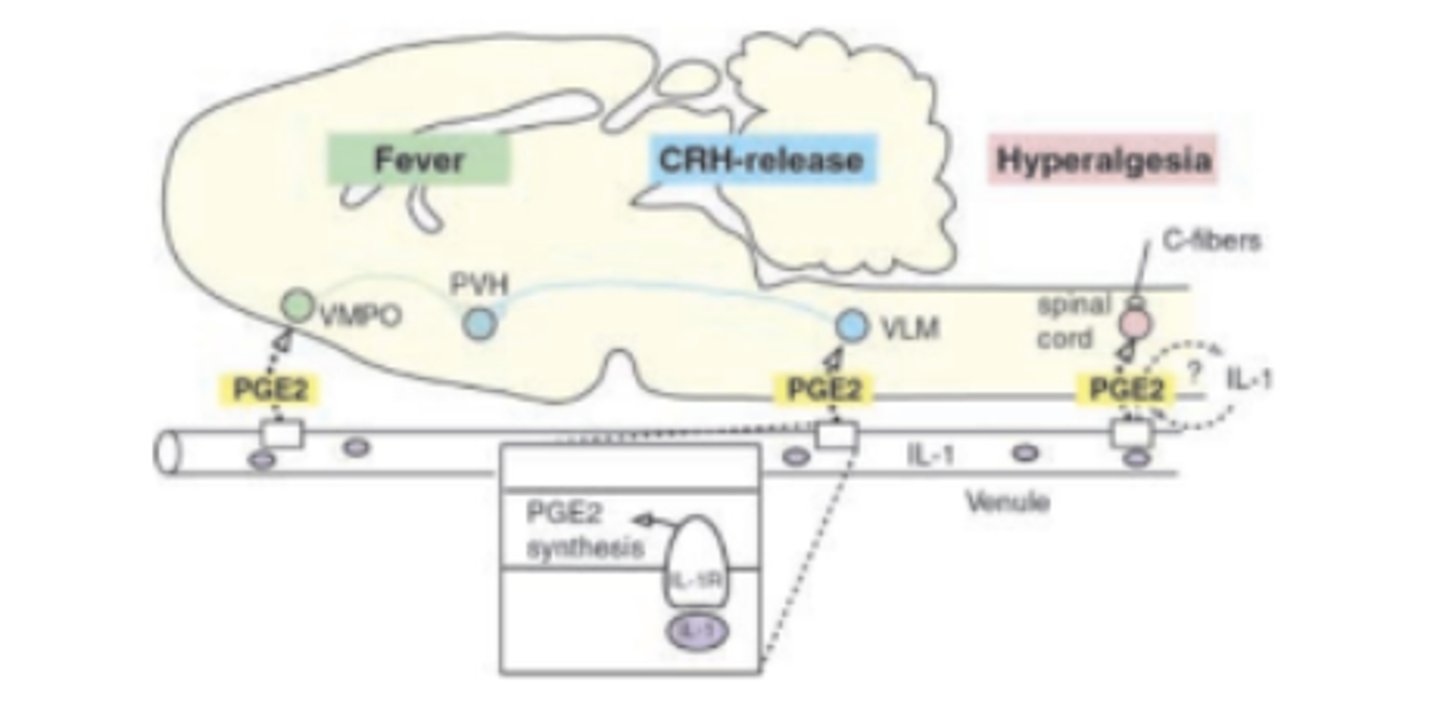
fever. Hypothalamus releases PGE 2 acts on neuronal EP 3 to ↑body temp
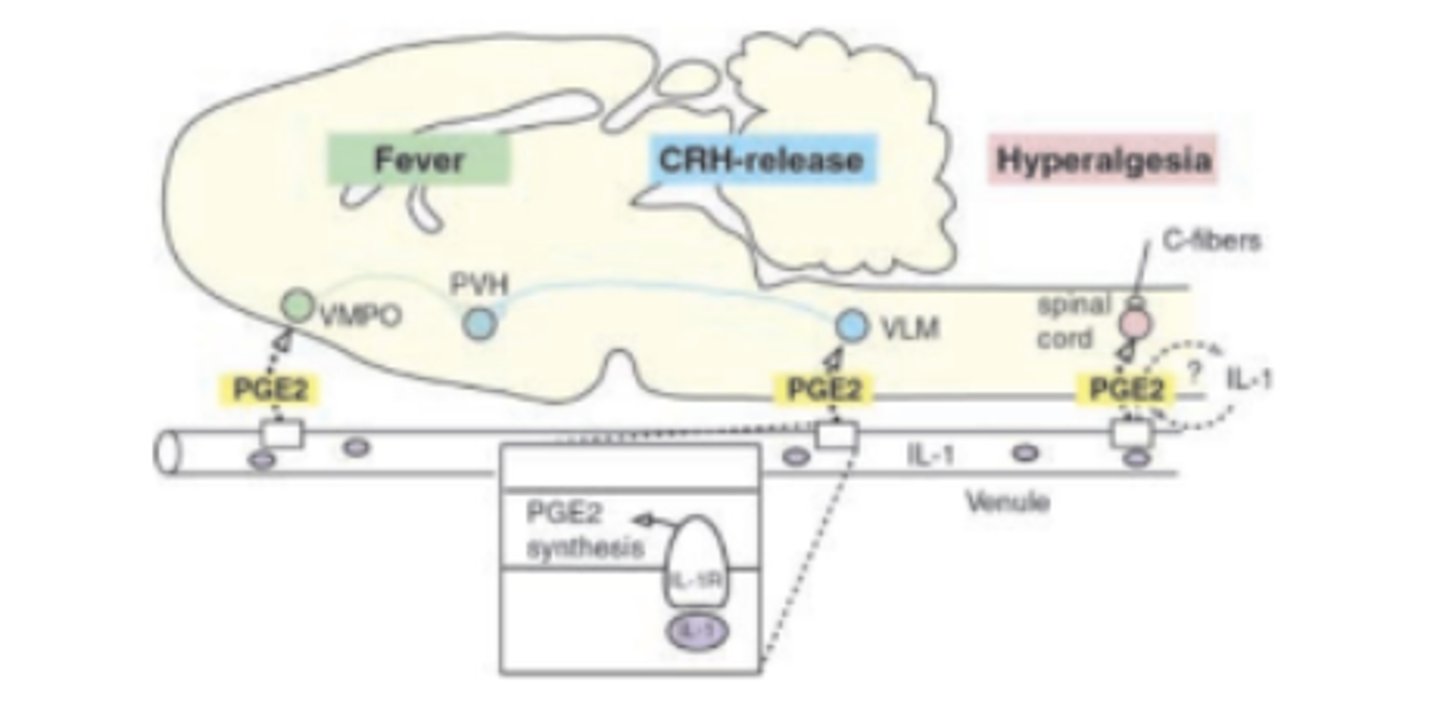
PGD2 promotes:
sleep. Increases adenosine in basal forebrain that, in turn, promotes sleep
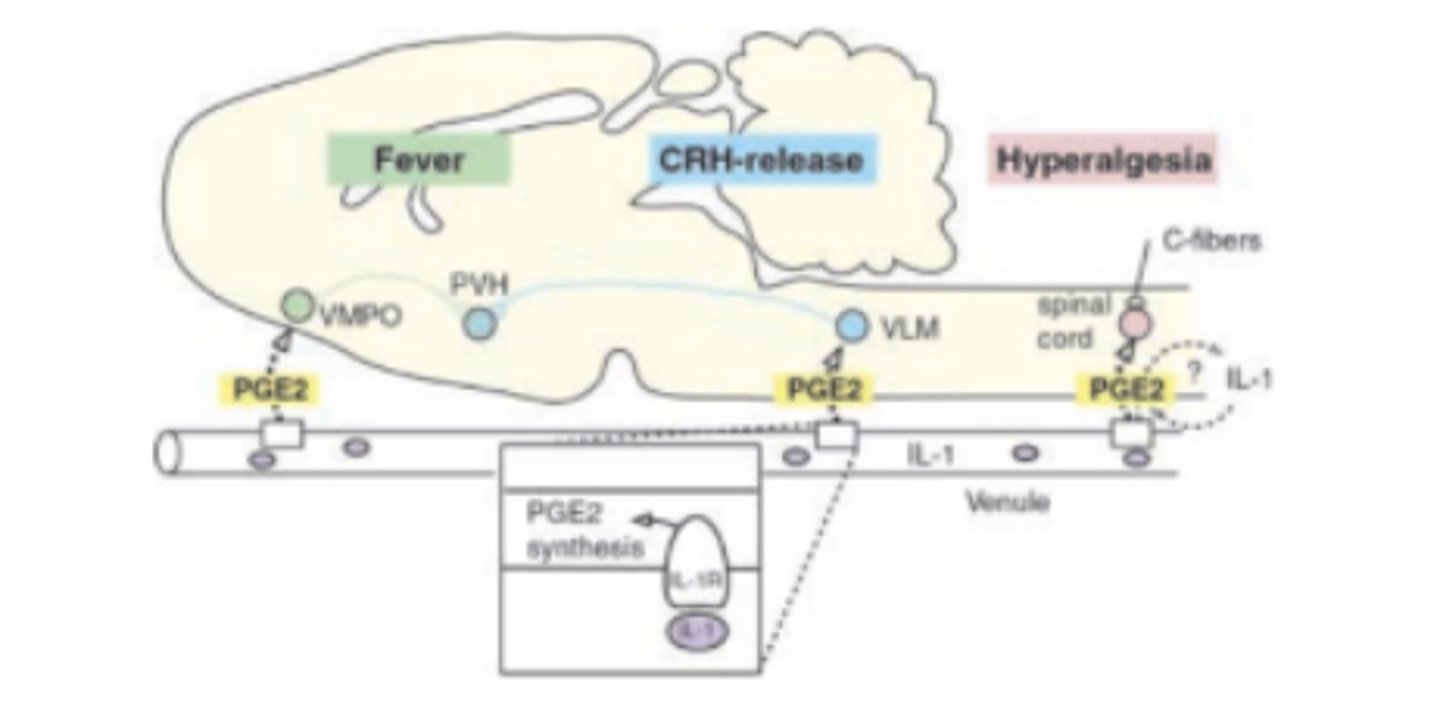
PGE2 and PGI 2 increase excitability in spinal and brain pain path pathways resulting in:
Amplifies perception of pain; also ↑hyperalgesia and ↑allodynia
_____ are potently pro-inflammatory and bronchoconstrictors: asthma, anaphylaxis
Leukotrienes
____ have diverse physiological functions, but also promote fever, sleep, inflammation and pain- PGD2, PGE2 and PGI 2 of importance in CNS, pain and inflammation
Prostaglandins
_____ are smooth muscle cell mitogens and potent platelet aggregator, and promote repair
Thromboxanes
Aspirin
WHO essential medicine
nonselective NSAID; permanently inhibits COX-1 and COX-2. Anti-inflammatory; weak analgesic
Increases clotting time (blocks TxA synthesis indirectly)
Salicylic acid (methylsalicylate):
Non selective NSAID; absorbed through skin. Inhibits COX-1 and COX-2.
Suppresses expression of COX-1 and COX-2. Anti-inflammatory; weak analgesic.
WHO essential medicine
Ibuprofin, Naproxen:
-WHO essential medicine
reversible NSAID. Anti-inflammatory, weak analgesic, antipyretic.
Acetominophen
WHO essential medicine
Reversible "NSAID." Modest analgesic, antipyretic. No efficacy against inflammation.
Celecoxib
NSAID; selective COX-2 inhibitor. Analgesic; significant anti-inflammatory; used totreat rheumatoid arthritis. #20 on the list of Top 100 drugs.