Lecture 6 - Conformity
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Define conformity.
A change in our behaviour or beliefs in order to accord to others.
*an umbrella term for compliance and obedience
Define compliance.
Publicly acting in accord, but privately disagreeing.
Define obedience.
Acting in accord due to being given a direct order.
Explain a study about how norms are formed?
Muzafer Sherif (1930s)
Sherif used an autokinetic phenomenon to observe how social norms emerge.
An autokinetic phenomenon is when you shine a laser in a dark room and the dot looks like it’s moving but its not.
Sherif found that in the first day, person 1 thought the dot moved 8 inches. Whereas, person 2 and 3 thought the dot moved much less. The scores of each person was visible to each participant and so, on the second day, all the scores started to conform to something similar, even though the dot still had not moved.
Therefore, just by being able to compare other’s answers, a norm of how much people saw the dot ‘move’ was formed.
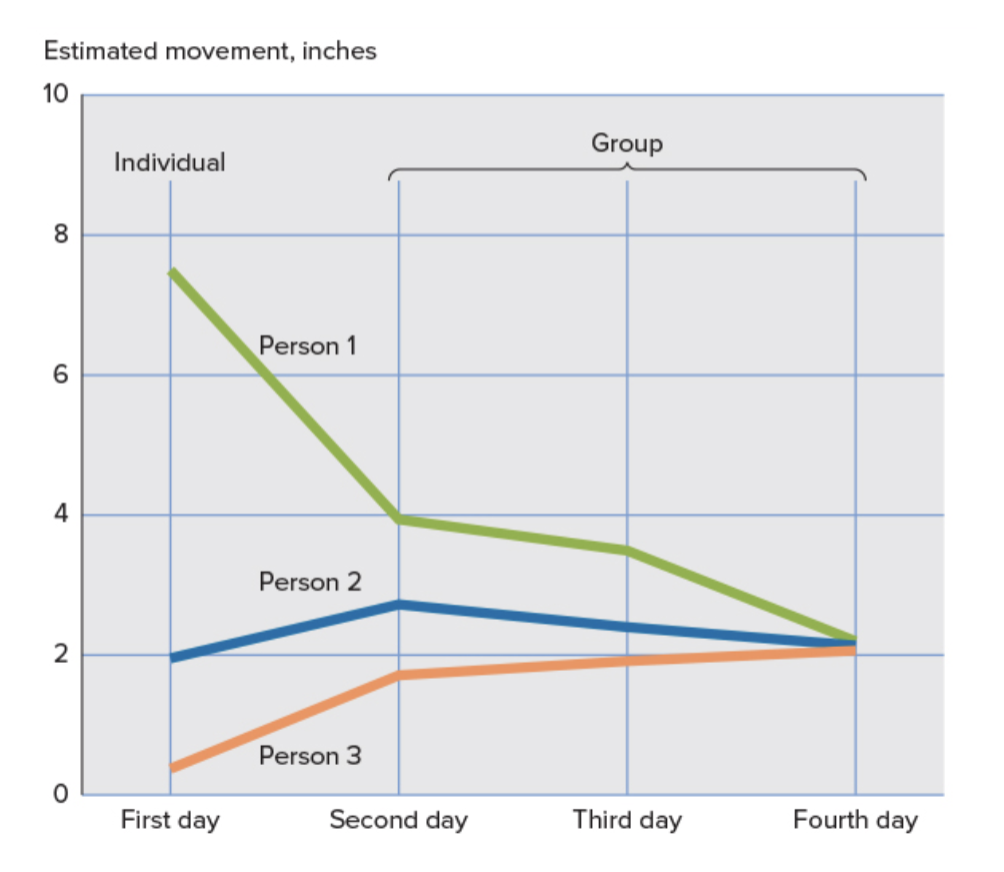
What did Sherif’s experiment show about how social norms can emerge?
It highlighted the influence of others and how quickly comparison can cause social norms to form.
Explain a study about group influence?
Solomon Asch (1955)
A group of people were asked to say which lines they thought were closest to the standard line. Amongst the group were confederates who purposefully picked the wrong line.
Asch did this because he wanted to know how group’s would influence people’s answers.
63% of the people in the group did not conform to what the confederates were saying, but the rest did conform.
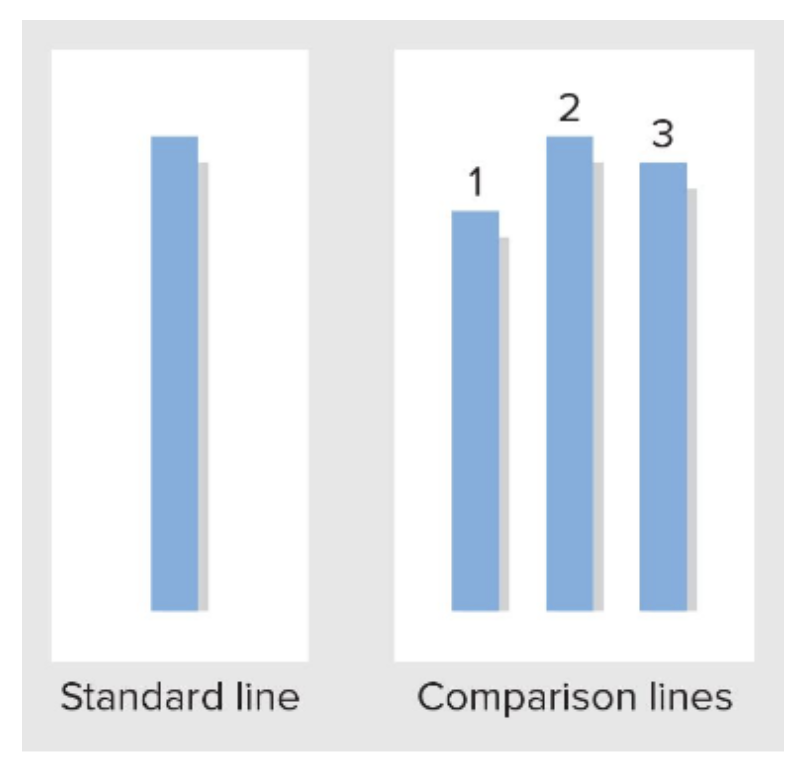
What did Asch’s experiment indicate about group influence?
It showed that we comply (doing it even though we don’t really believe in it) to ‘social norms’ set by the group in order to fit in and also because we start to doubt our own judgements.
How does complying affect our beliefs?
The more we comply, the more we may start to believe what we are doing.
Explain a study about obedience.
Stanley Milgrim
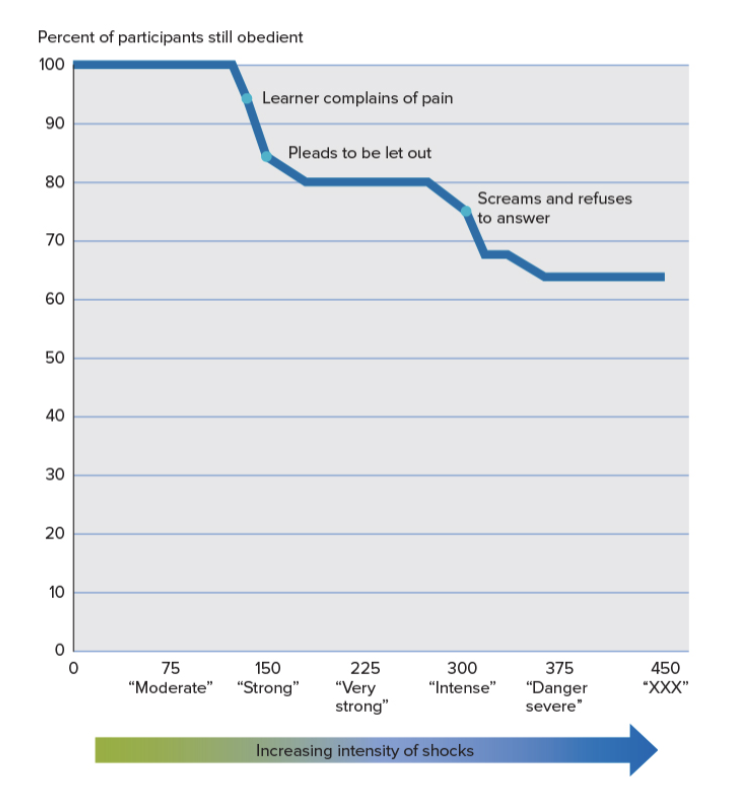
Participants had to give out electric shocks to other participants as punishment for errors. Milgrim tested how obedient participants would be when administering the electric shocks that got progressively more intense and dangerous (participants could see the person’s reaction to the shocks—which got more and more intense).
Most participants (63%) fully complied with the experimenter’s demands even when they did not want to continue and when they saw the person being tortured.
What did Milgrim’s experiment show about obedience?
It showed how strong our sense of obedience can be.
For example, Milgrim’s study was conducted at Stanford university which is a world-renowned university. Therefore, participants deemed the experiment and experimenters as credible, resulting in them to ‘blindly’ follow the instructions in spite of being uncomfortable with the tasks.
What creates obedience?
The victims distance from the participant
The closeness and legitimacy of authority
Institutional authority
liberating effects of group influence
Why does the victims distance create obedience?
It is due to the depersonalisation effect.
For example, when participants could not see the people they were shocking, more complied because it wasn’t as personal. However, when they could see/touch who they were shocking, it became much more personal, resulting in less complying.
Why does the closeness and legitimacy of authority create obedience?
The closer the authority figures are, the more pressured people feel to listen and keep going. Contrastingly, when Milgrim gave instructions over the phone, obedience decreased and some lied about complying.
The authority figure must also seem legit to the participants which instills trust and influences the participant to be more obedient.
Why does institutional authority create obedience?
When an authority figure is legitimised by a formal organisation the commands were also legitimised.
Therefore, making people more obedient to what they were told to do.
Why does being in a group create obedience?
This is because it takes the responsibility off on the person, making them more obedient to whatever tasks they are told to do.
What is a real-life example of norm formation?
When we start to appreciate a certain food only after hearing that others love it.
What is a real-life example of conformity?
When you laugh at a joke that you don’t find funny just because others are laughing.
What is a real-life example of obedience?
When soldiers follow questionable orders just because they were told to do so.
What are the major themes learned from the 3 studies mentioned?
Behaviour and attitude
when you have a very strong attitude you are less ‘malleable’ and less likely to conform
Power and situation
when you are in a specific situation, you may easily conform because there are external pressures pushing you to do so
Shifting responsibility
when you are able to shift responsibility away from yourself it can help reduce any dissonance for acting in a way that’s different than how you would typically act. Therefore, making you more obedient or compliant.
What factors predict conformity?
group size
unanimity
cohesion
status
public response
no prior commitment
Explain a study that illustrates how group size affects conformity.
A researcher got people in the streets to look up at the sky. When 1 or 2 people were tasked to look up, not many people looked up. However, when 3 people were tasked to look up there was a greater a influence.
Lastly, when 5 people were tasked to look up, 90% of people also looked up (after 5 people the influence remains about the same—it plateaus).
Therefore, suggesting that group size does affect the number of people who conform—5 people being the minimum group size to significantly influence people.
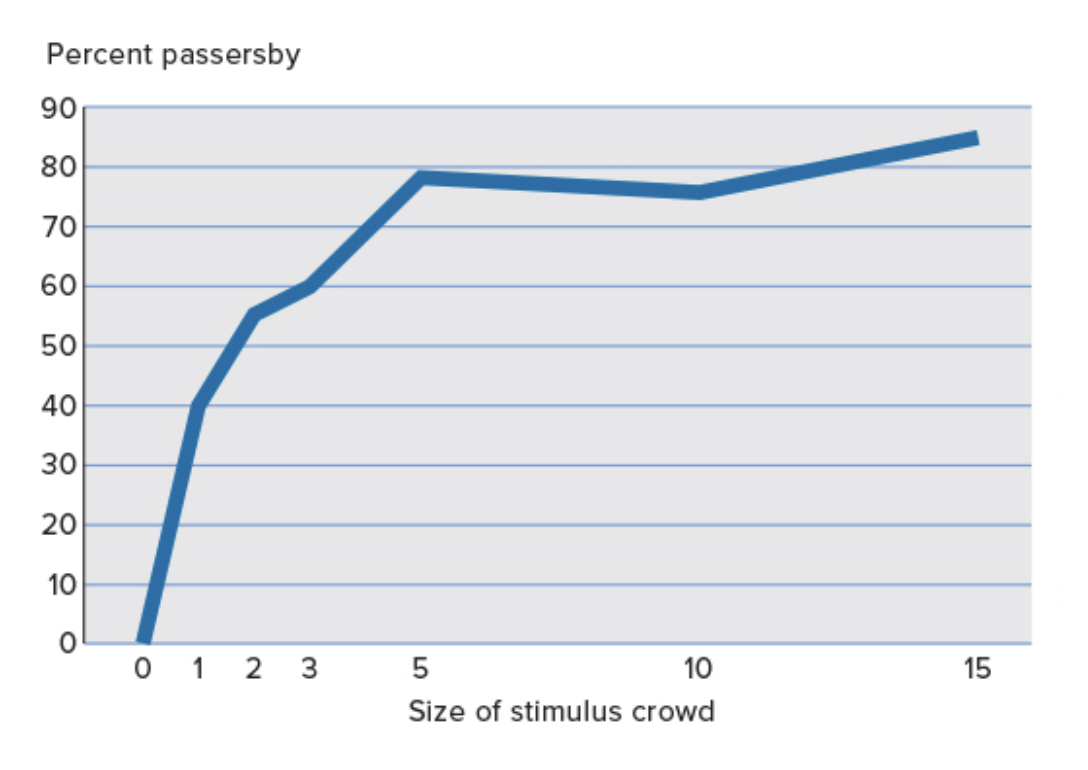
How does group configuration affect conformity?
ie. group of 5 is split into a couple and a group of 3 friends,
The couple will be seen as a unit, so one person. Therefore, the group will be considered as 4 people and the effect won’t be as impactful if there were just 5 people.
Hence, the groups configuration can create an entirely new effect on people, in spite of the overall group still consisting of 5 people.
How does unanimity affect conformity?
If the choice is unanimous then everyone usually conforms.
If at least one person disagrees then the likelihood of conforming drops by 25%.
Why does 1 person disagreeing affect conformity that much?
This is because that disagreeing person ‘pops’ the pressure of the group influence and gives people the opportunity to come out of it and start thinking for themselves.
How does cohesion affect conformity?
The more tight-knit you are with the group, the more likely you will conform.
How does status affect conformity?
The higher someone’s status is in something related to what we are doing, the more likely we will conform to that person’s views.
How do public responses affect conformity?
If there is a big implication of not conforming, people will likely conform. And vice versa.
How does having no prior commitments affect conformity?
The more committed one is to their belief, the less likely they are to conform.
Define normative influence.
When we conform to avoid rejection, stay in people’s good graces or gain their approval.
What can normative influence lead to? Why?
Public compliance—when you look like you agree on the outside, but on the inside you don’t.
This is because, in an effort to avoid rejection, we try to look like we agree even though we do not.
Define informational influence.
When you conform to others’ points of view, in order to be right in ambiguous situations.
What do informational influences lead to? Why?
Private acceptance.
ie. when others sound confident about their answers we conform and agree with them in order to be right. This eventually leads to private acceptance.
When is personality a better predictor of our behaviour?
Our personality is a better predictor of behaviour when our social influences are weak.
Who conforms?
gender (women more likely conform to men)
social roles (police officer asks you to do something you’ll likely to conform)
Define reactance.
When we do the opposite of what other’s want us to do due to the motive to protect or restore one’s sense of freedom when we feel it is being compromised.
Define asserting uniqueness.
The preference to be moderately unique.
*to still be distinct but not entirely fit in