bis2a final exam review
1/234
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
235 Terms
which atoms would you consider more electronegative than carbon out of the following? mark all that apply: F O N H
F O N
which of these bonds would you consider a polar covalent bond? mark all that apply:
(a) C-O
(b) C-H
(c) C-C
(d) H-N
(e) H-O
ade
which part of the following statement is incorrect: water molecules repel non-polar substances. (mark all that apply)
(a) repel needs to be replaced with "do not attract"
(b) non-polar needs to be replaced with "polar"
(c) away needs to be replaced with "towards"
(d) the corrected statement should read: non-polar compounds such as lipids attract each other and repel polar molecules like water.
(e) the corrected statement should read: water molecules do not interact with non-polar compounds, which become oriented away from water.
(f) the corrected statement should read: water molecules attract polar and non-polar compounds, but the non-polar compounds are 'sticky' so they stick together.
ae
pair the macromolecule with its building block: starch
carbohydrate
pair the macromolecule with its building block: protein
amino acid
pair the macromolecule with its building block: nucleic acid
nucleotide
pair the macromolecule with its building block: triglyceride
lipid
polar covalent bond
a type of covalent bond where electrons are shared unequally
electronegativity
the tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards itself
hydrogen bond
bond that forms between an electronegative atom and a hydrogen atom with a positive dipole
type of covalent bond where electrons are shared equally
nonpolar covalent
carbohydrate
macromolecule that can exist as linear or cyclized, where it has a 1:2:1 ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
lipid
macromolecule that can exist as linear oc cyclized, where it has a polar "head" group and a majority non-polar "tail" group
ionic bond
a bond that exists between two full, opposite charges
protein
a macromolecule that exists with a backbone where the functional groups are the amine and the carboxylic acid
nucleic acid
a macromolecule that contains a sugar a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base
in thermodynamics, a living organism is an example of a
(a) open system
(b) closed system
(c) isolated system
(d) system equilibrium
a
a chemical reaction occurs in a test tube in lab. during the reaction, "reactants" gradually become "products" until equilibrium is reached. At equilibrium:
(a) delta G = 0
(b) no more reactions occur: no molecules of reactant become product, and no molecules of product become reactant
(c) some molecules of reactant become product, and some molecules of product become reactant
(d) both a and c are true
d
in the reaction 2H2 + O2 --> 2H2O, what is being oxidized?
(a) H2O
(b) H2
(c) O2
(d) there is no redox in this reaction
b
in living things, the two major components of G, "potential energy", are:
(a) concentration and dilution
(b) gibbs free energy and work
(c) pressure and volume
(d) concentration and molecular structure
d
a glucose molecule has a bond between O and C. this is a:
(a) hydrogen bond
(b) non-polar covalent
(c) ionic bond
(d) polar covalent
d
deltaG' refers to the change in Gibbs free energy under (biological) standard conditions. these standard conditions include:
(a) pH=0
(b) all chemical components (reactants and products) are constantly at 1 Molar
(c) temperature = 25 F
(d) reaction is at equilibrium
b
H2O is a liquid at room temperature while CO2 is a gas. why is this?
(a) water has a higher molecular weight than CO2
(b) the polar covalent bond in CO2 cause the molecules to repel each other
(c) water molecules are attracted to each other, CO2 molecules are not
(d) water has a lower molecular weight than CO2
c
the ingredients listed below will give you 2 ml of 1/2 molar sodium chloride after mixing. which will release the greatest amount of energy (=has the largest negative deltaG) when doing so?
(a) mixing dry NaCl (enough to make a 1mL, 1 molar NaCl solution), plus 2mL water
(b) mixing enough sodium metal and Cl2 gas to produce the amount of sodium chloride salt described above, with 2mL water
(c) mixing two 1mL tubes of 1/2 molar NaCl
(d) mixing 1mL of 1 molar NaCl, plus 1mL of water
b
what is the difference between the transition state energy and the activation energy of a particular reaction?
(a) activation energy is the amount of energy in the structure of the transition state
(b) changes in delta Gact cause changes in delta Grx, but changes in transition state energy do not
(c) the transition state energy is a constant, activation energy is not
(d) nothing. transition state energy and activation energy are two terms for the same thing
a
sort the following items in the order in which they occurred:
1 eukaryotes evolve
2 oceans present on earth
3 collision of the earth with the planetoid theia
4 photosynthesis evolves
5 cyanobacteria evolve a pathway to oxidize water
32451
OIL RIG
oxidation is loss, reduction is gain
in the redox tower, more negative E values means
more likely to donate electrons
in the redox tower, more positive E values means
more likely to accept electrons
in the redox tower, compounds on the right side of the slash are:
the reduced form
in the redox tower, compounds on the left side of the slash are:
the oxidized form
oxidation
loss of electrons
reduction
gain of electrons
compound that becomes reduced acts as the
oxidizing agent
compound that becomes oxidized acts as the
reducing agent
the measure of a compound's likeliness to gain or lose an electron is its ________ (E value).
reduction potential
NAD+ is in the ______ state.
oxidized
NADH is in the ______ state.
reduced
which of the following phosphate containing molecules is the strongest phosphate donor?
(a) AMP
(b) glucose 6-P
(c) ADP
(d) PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate), the last molecule in glycolysis before pyruvate
(e) ATP
d
fermentation occurs when:
(a) the cell needs more NAD+ to perform glycolysis, and no external electron acceptor is available
(b) the cell needs to get as much energy as possible from glucose, burning it to completion (CO2)
(c) the cell has an external electron acceptor it can use
(d) the cell has too much NAD+
(e) glucose is not available
a
glucose is processed via glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and the citric acid cycle. what is left of the original glucose molecule when this processing is complete?
(a) water and CO2, plus energy stored in many (30+) ATPs
(b) 2 pyruvates and some energy stored as ATP
(c) CO2, some energy (stored as ATP), and some high energy electrons (stored as NADH and FADH2)
(d) Acetyl CoA, CO2, and 2 ATPs
(e) 2 Oxaloacetates, a few ATPS built by substrate-level phosphorylation, and 6CO2
c
the first few steps of glycolysis are referred to as the 'investment' phase. why is that?
(a) because you lose some ATP, turning them into ADP, in these steps
(b) because they have a negative deltaG
(c) because NAD+ is made
(d) because they generate ATP from ADP + Pi
(e) because they have a positive deltaG
a
in the reaction C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 +6H2O + energy, the reactant C6H12O6 enters your body through
food
in the reaction C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 +6H2O + energy, the reactant 6O2 enters your body through
breathing
in the reaction C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 +6H2O + energy, the product 6CO2 leaves your body through
breathing
what happens to ATP when you "use" it?
(a) ATP is converted into energy and used up by the cell.
(b) ATP is converted to ADP which can be recycled back into ATP
(c) ATP is converted into a waste product that the cell excretes
(d) ATP is broken down into its individual parts and would need to be re-made through metabolism to be used again.
b
Oxidation of glucose means (mark all):
(a) combining glucose with oxygen through metabolism
(b) loss of electrons from glucose
(c) oxidation of glucose
(d) combining oxygen with sugar to make energy
bc
In the reaction C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 +6H2O + energy, the reactant 6CO2 enters the plant
from the atmosphere
In the reaction C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 +6H2O + energy, the reactant energy enters the plant through
the sunlight
In the reaction C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 +6H2O + energy, the product C6H12O6 is metabolized by the plant in its
mitochondria
In the reaction C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 +6H2O + energy, the product C6H12O6 is created through reduction of
CO2
In the reaction C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 +6H2O + energy, the product 6O2 is considered a waste product of
oxygenic photosynthesis
Oxidative phosphorylation is a metabolic pathway that (oxidizes or reduces) an energy-rich source to produce ATP from ADP
oxidizes
In oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are transferred from electron (donors or acceptors) to compounds with a (weaker or stronger) reduction potential.
donors, stronger
In oxidative phosphorylation, as electrons move through an electron transport chain, ETC, the energy in the electron is used to pump ------ across a membrane.
protons
In oxidative phosphorylation, the pumping of these molecules against their concentration gradient is a form of ------ transport. The movement of these molecules back into the cell (down their concentration gradient) releases energy which the cell couples to the formation of ------.
active, ATP
In photosynthesis, energy in ------ is absorbed by an electron in a photocenter.
light
In photosynthesis, the ETC creates ------- which is used by the cell to power the formation of ATP.
proton motive force
In (cyclic or non-cylic) photosynthesis the electron returns to the photocenter.
cyclic
In (cyclic or non-cyclic) photosynthesis the electron reduces NADP+ to form -------.
non-cylic, NADPH
Autotrophs can (choose all that apply):
(a) Capture high energy electrons from organic sources
(b) Capture high energy electrons from inorganic sources
(c) Fix carbon from CO2
(d) None of the options apply
abc
What is the external source of electrons used to build NADPH from NADP in green sulfur bacteria?
(a) Green sulfur bacteria only do cyclic photosynthesis- they make ATP but not NADPH
(b) Glucose
(c) Water
(d) Reduced sulfur compounds, like H2S
(e) Green sulfur
d
What's the difference between a photosystem (ie, PSI) and a photoreaction center (ie, P700)?
(a) They are two terms for the same thing
(b) A photoreaction center contains many pigments (including chlorophylls) that can collect photons, while a photosystem (embedded in the reaction center) contains one or more "special" chlorophylls that can actually do photochemistry
(c) A photoreaction center contains many different pigments and proteins, but only a subset of these pigments (called the photosystem) can actually perform photochemistry- donating electrons to an ETC.
(d) One term (photoreaction center) is used for photosynthetic prokaryotes, the other (photosystem) is used for photosynthetic eukaryotes
b
The leaves of green plants are green because:
(a) When energy cannot be transferred to the ETC from excited chlorophyll, the electron will relax to a lower-energy orbital, emitting a green photon.
(b) The pigments in the leaves of green plants absorbs green light most strongly, of all visible light photons
(c) The pigments in the leaves of green plants do not absorb green light as strongly as they absorb other visible light photos.
(d) The sun emits most of its radiation as photons that are green
c
In the absorbance spectrum shown below is from an extract of leaves of a plant that produces two pigments chlorophyl A and chlorophyl B. You're buying LED lamps to grow this plant indoors, and each lamp only emits photons at one wavelength. If we assume all lamps emit the same number of photos per second, which bulb/wavelength would be the worst choice to support the growth of this plant?
(a) 480nm
(b) 550nm
(c) 640nm
(d) 420nm
b
Per molecule, which of the following organic compounds would provide the most ATP when completely catabolized (to CO2) via aerobic respiration?
(a) Phosphoenolpyruvate ("PEP", the compound right before Pyruvate in glycolysis)
(b) Stearic acid (a fatty acid, see structure below, fatty acid processing is described in lecture 8 slide four)
(c) Glucose
(d) Pyruvate
b
Ferredoxinox/red is an electron carrier in the ETC that runs from PSI* to NADP, forming NADPH. Would you expect to find this carrier in the ETC required for respiration of NADH, running from NADH to O2, forming water?
(a) No, because Fdred is a weak reducing agent, weaker than NADH
(b) Yes, because Fdox is a strong oxidizing agent- stronger that NAD+
(c) No, because Fdred is a strong reducing agent, stronger than NADH
(d) Yes, because Fdox is a strong reducing agent, stronger than NADH
c
In carbon fixation, CO2 is reduced and incorporated into a larger carbon skeleton, which could then be converted to other storage forms of carbon and energy. The reverse citric acid cycle produces ____ and the Calvin cycle produces ______
(a) sugars, fats
(b) fats, sugars
(c) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P), acetyl coA
(d) acetyl coA, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P)
d
In order to occur spontaneously (and therefor provide energy that can be captured to do work) a redox reaction must have
(a) A negative ∆E, which is a positive ∆G
(b) A positive ∆E, which is a positive ∆G
(c) A negative ∆E, which is a positive ∆G
(d) A positive ∆E which is a negative ∆G
d
Which of the following processes are shared by both respiration and the light reactions of photosynthesis? Check all that apply.
(a) Pyruvate oxidation
(b) None are shared by both respiration and the light reactions of photosynthesis
(c) ATP synthase
(d) An electron transport chain
cd
primary structure of protein
sequence of amino acids
secondary structure of protein
hydrogen bonds are formed through the backbone atoms
tertiary structure of protein
hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, covalent bonds, are formed between the R-groups
quaternary structure of protein
multiple proteins in the tertiary structure come together to form a larger functioning enzyme
condensation reaction
a reaction that results in the formation of water as an end product
hydrolysis
a reaction that requires water as a reactant
amine
a functional group on an amino acid that is polar, basic, part of the amino acid backbone, and can become positively charged
carboxylic acid
a functional group on an amino acid that is polar, acidic, part of the amino acid backbone, and can become negatively charged
N-terminus
denotes the beginning of a protein chain (first amino acid in the chain)
C-terminus
denotes the end of a protein chain (the last amino acid in the chain)
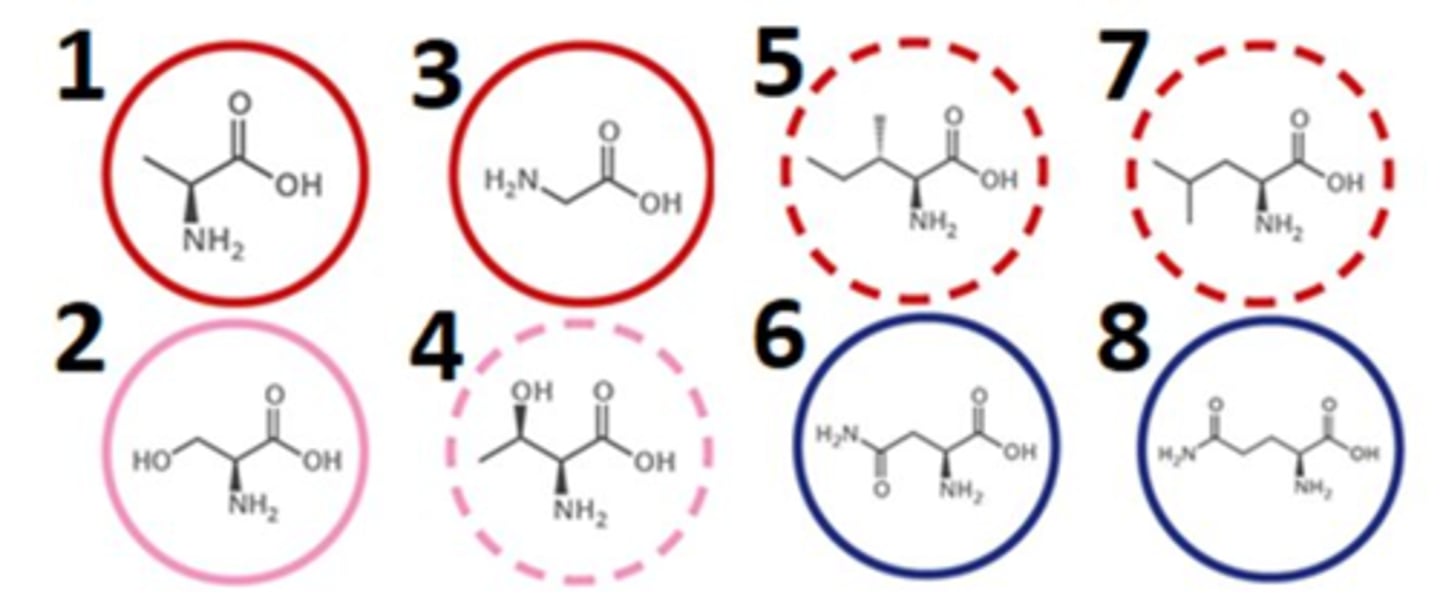
which of the following amino acids contain polar R groups?
2468
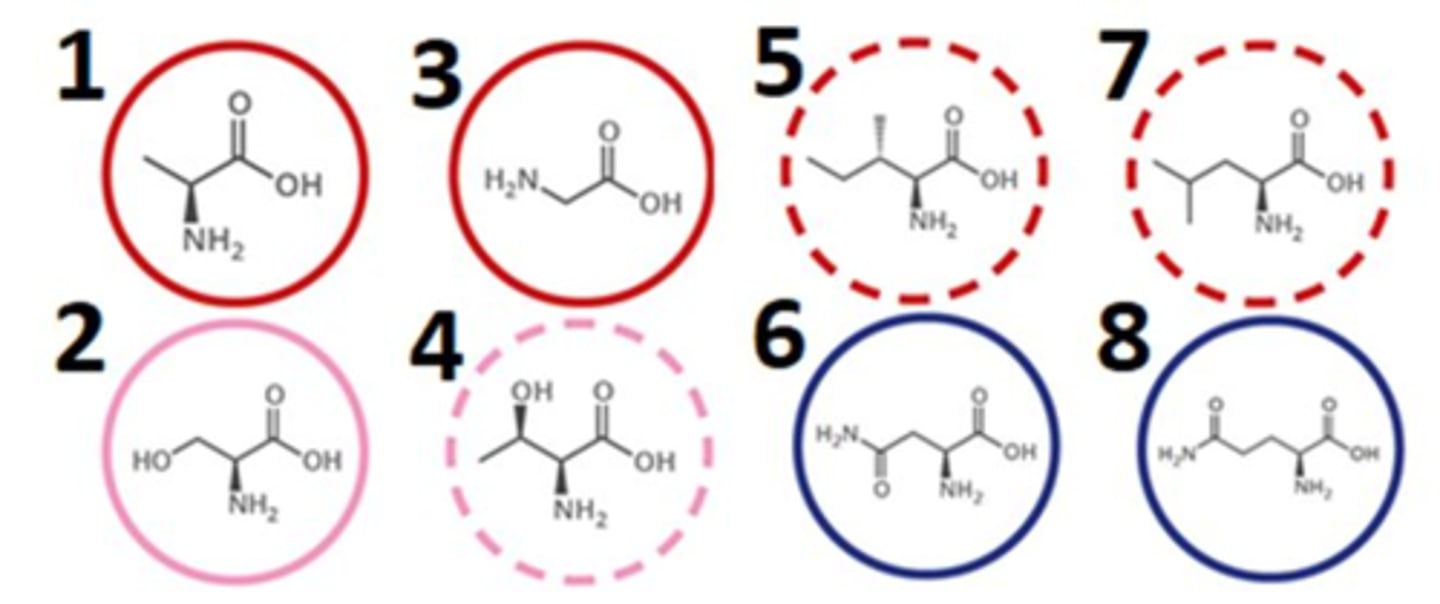
which of the following amino acids contain non-polar R groups?
1357
what is the H2N section called?
amine group
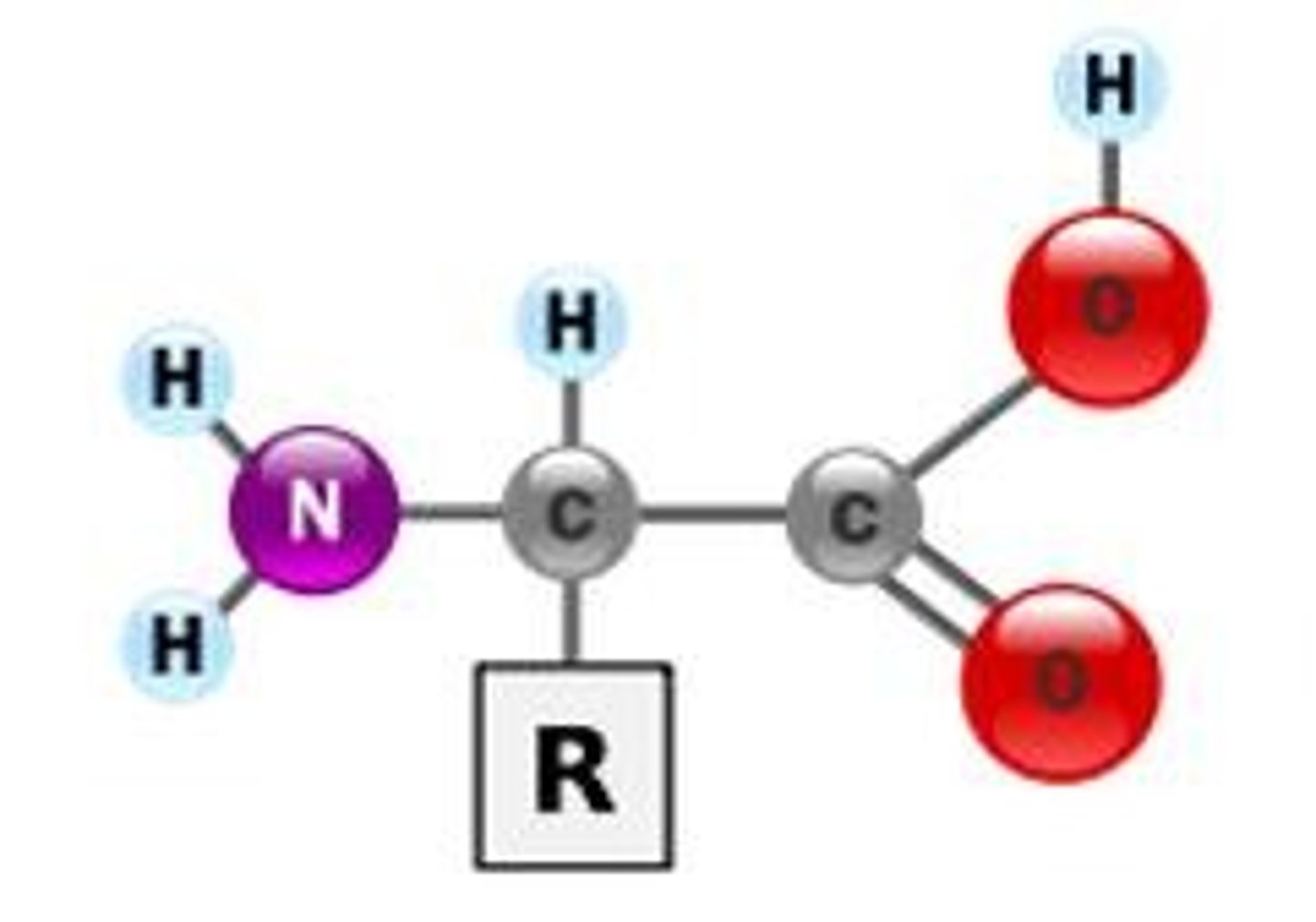
what is the COOH section called?
carboxylic acid
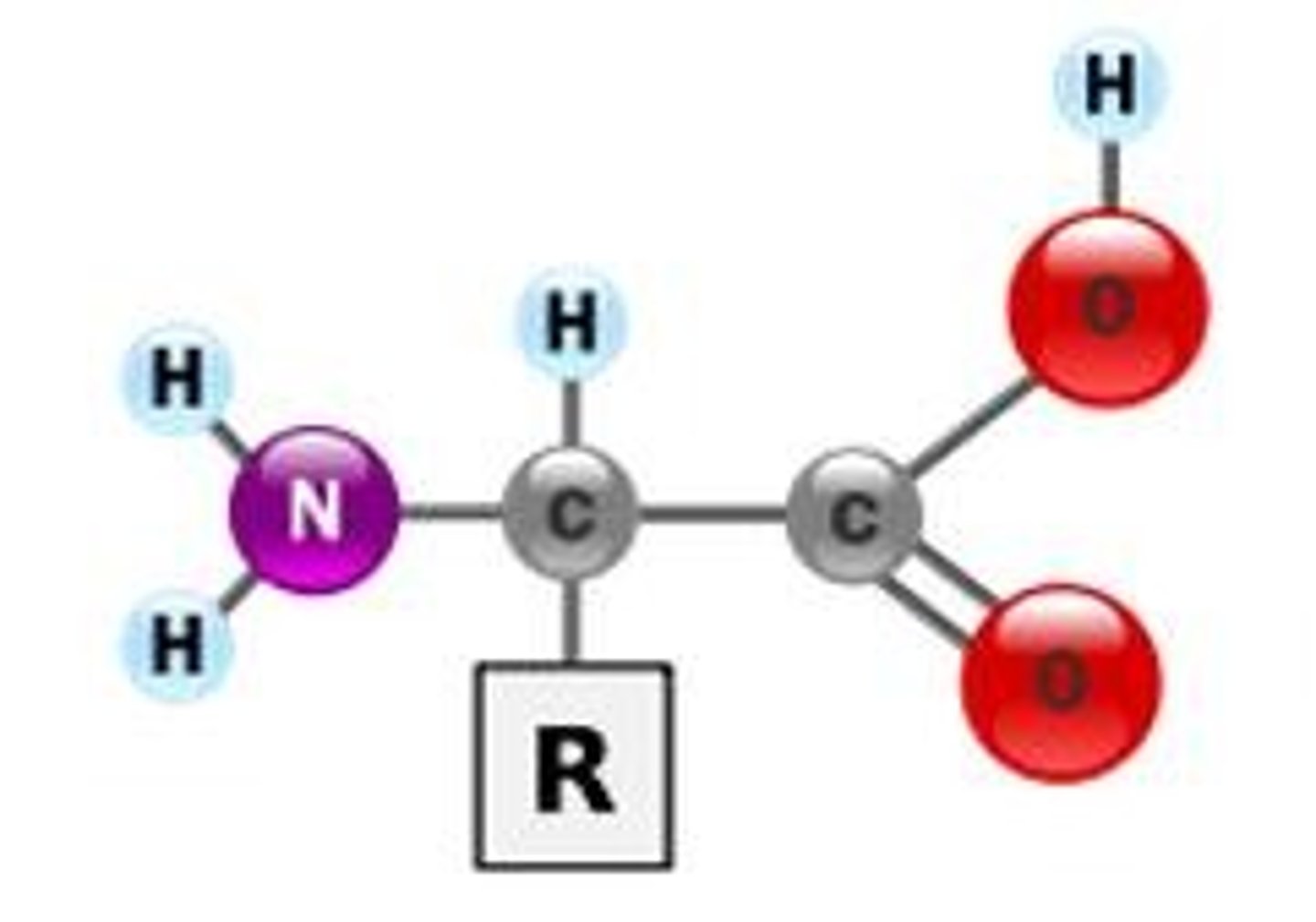
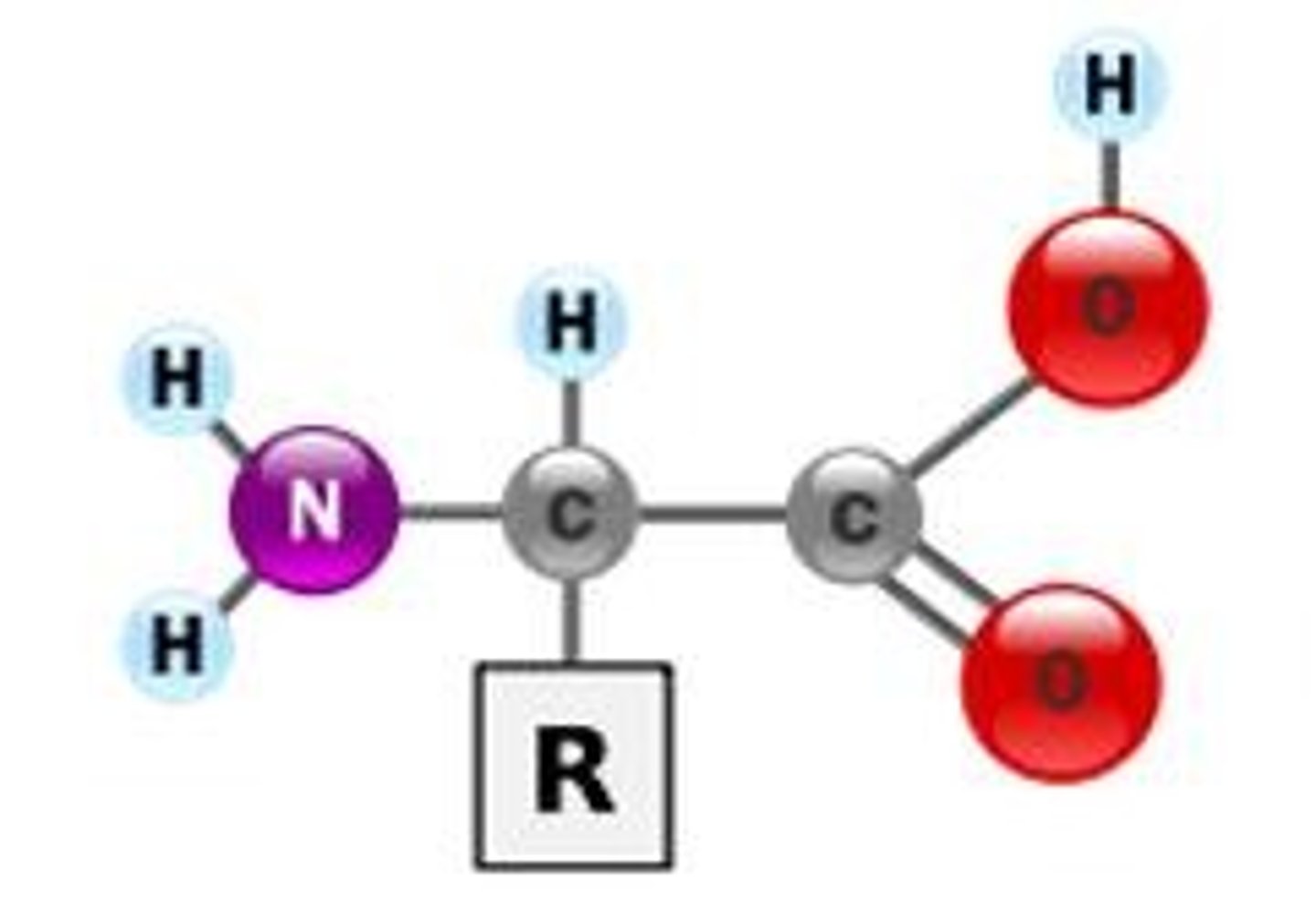
what is the R section called?
variable group
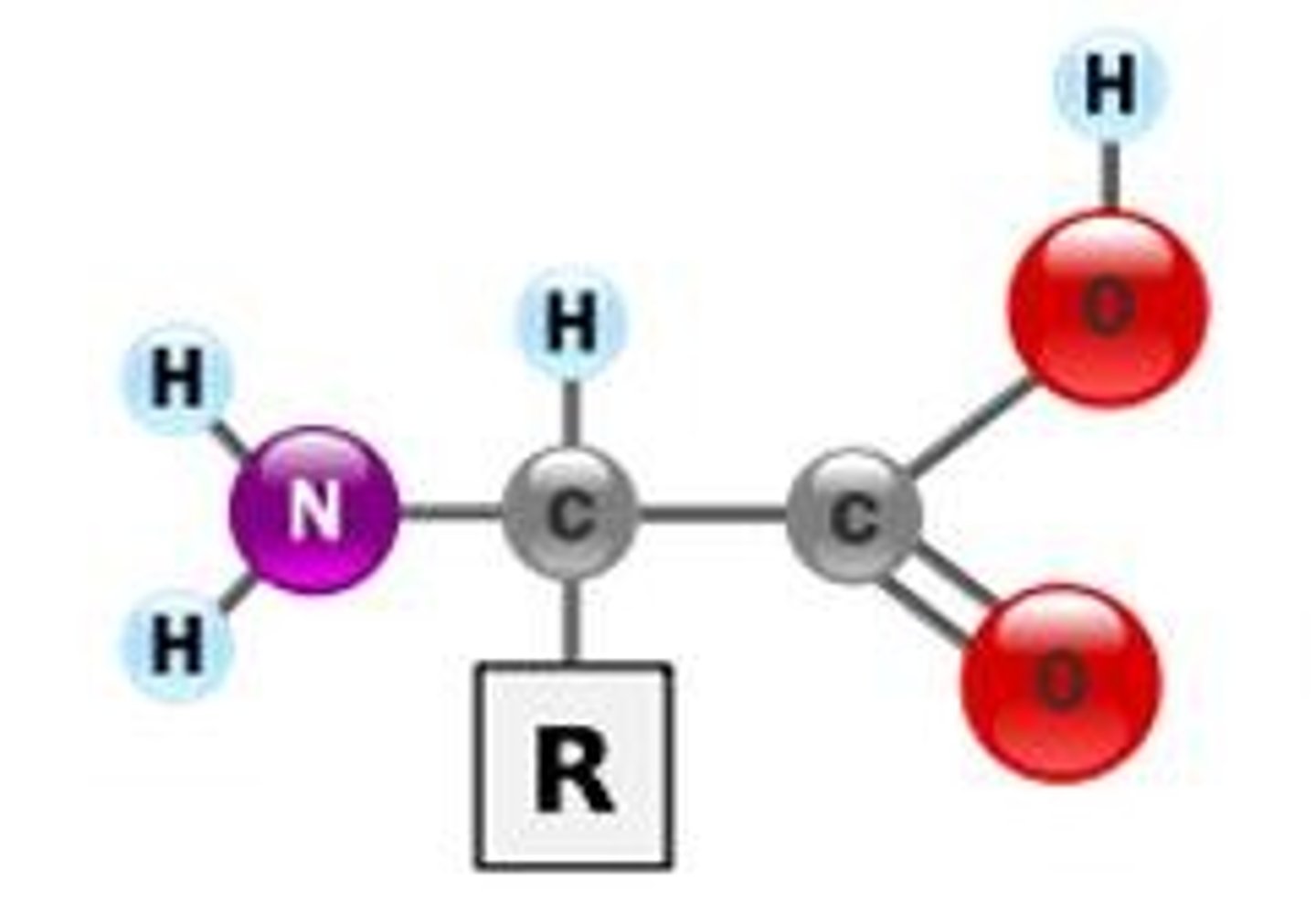
what is the center carbon section called?
alpha carbon
a protein's primary structure is maintained by
covalent bonds
protein cofactors are
required for the function of their protein
a small inhibitory molecule binds to the regulatory site on an enzyme, resulting in a change of the protein's shape. this makes the active site inaccessible to substrate.
this change in shape is probably due to
a rearrangement of the tertiary or quaternary structure, that extends from the regulatory site to the active site
in which compartment of the mitochondria does glycolysis occur?
glycolysis doesn't occur in the mitochondrion
which of the following compartments would be expected to be most acidic when O2 is available?
(a) the outer membrane
(b) the inner membrane
(c) the intermembrane space
(d) the matrix
(e) the entire mitochondrion should be at the same pH
c
in which compartment of the chloroplast does water-splitting occur?
the lumen of the thylakoids
which compartment of the chloroplast is the most acidic when light is available?
the lumen of the thylakoids
a heme cofactor carrying an Fe atom is part of a cytochrome protein involved in electron transfer. two closely related species have different versions of this protein.
one version (A) carries the cytochrome in an active site that has a neutral charge. the other (B) has the cytochrome in an active site that has a net charge of -2.
what would you predict would be the effect, if any, on the ability of the oxidized cytochrome to ACCEPT electrons from other molecules?
the reduction potential of B would be lower (more negative), and it would be a weaker electron acceptor
which of the following parts of metabolism occur in and require the membrane? choose all that apply:
(a) electron transport
(b) light reaction of photosynthesis
(c) pmf formation
(d) atp synthesis
abcd
the cell membrane is considered ------- because it only allows certain compounds to travel through freely
semipermeable
the random movement of molecules down their concentration gradient is called
diffusion
moving down a concentration gradient means moving from a (lower or higher) to a (lower or higher) concentration.
higher, lower
some compounds need to travel into the cell through a membrane protein, this is an example of --------
facilitated diffusion
when compounds are pumped against their concentration gradient they are being moved from (lower or higher) to (lower or higher)
lower, higher