PHA 329 - Endocrine System (Part 1)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
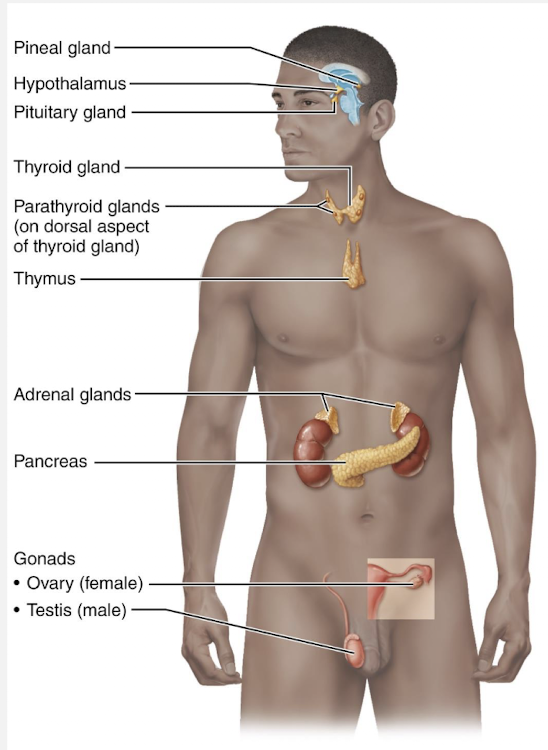
Endocrine system
A system of ductless glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream to regulate target tissues
Hormone
Chemical messenger released into the blood that binds receptors on target tissues to produce a physiological response
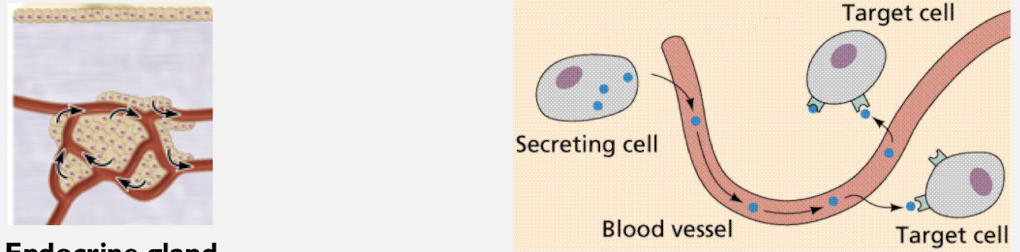
Endocrine gland
Group of epithelial-derived cells that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream
Target tissue
Tissue that contains specific receptors for a hormone and responds when the hormone binds
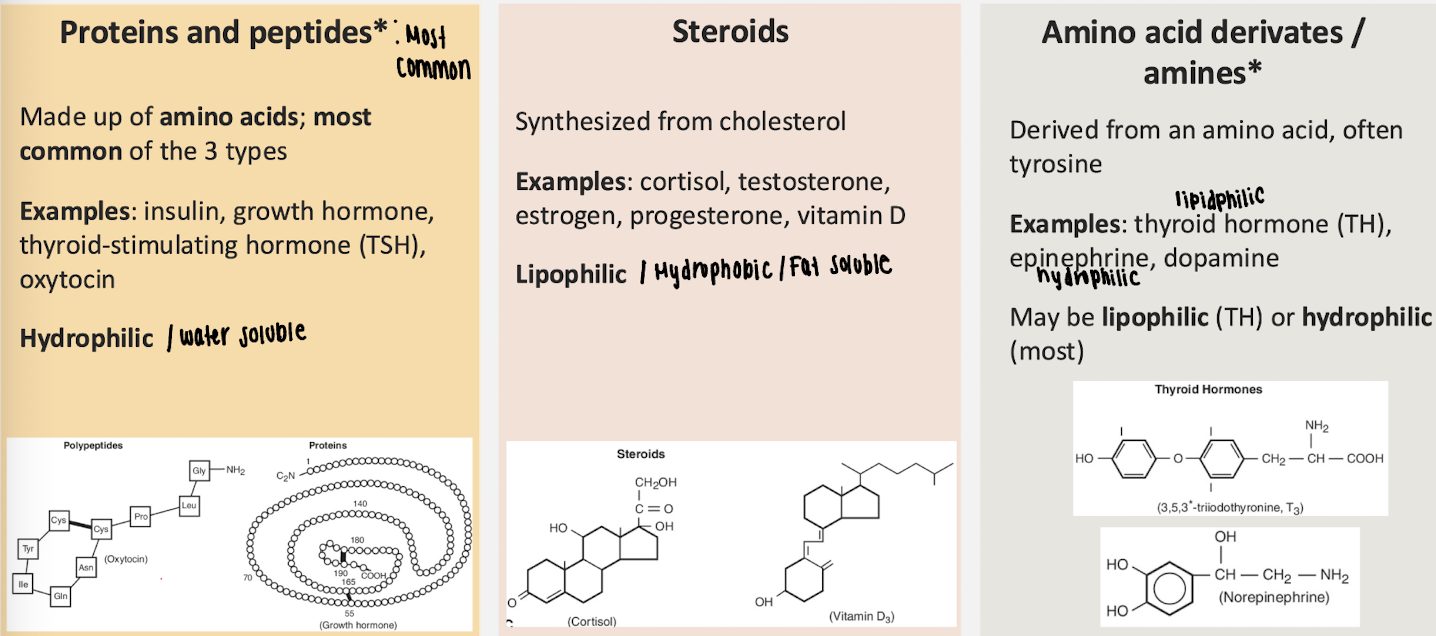
Chemical classes of hormones
Peptide/protein hormones, steroid hormones, and amino acid–derived hormones
Peptide/protein hormones
Hormones made of amino acids; hydrophilic; stored in vesicles and released by exocytosis
Examples of peptide hormones
Insulin, growth hormone, TSH, oxytocin
Steroid hormones
Hormones synthesized from cholesterol; lipophilic; synthesized on demand and diffuse across membranes
Examples of steroid hormones
Cortisol, aldosterone, testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, vitamin D
Amino acid–derived hormones
Hormones derived from amino acids (usually tyrosine); can be hydrophilic or lipophilic
Examples of amino acid–derived hormones
Epinephrine, dopamine, thyroid hormone
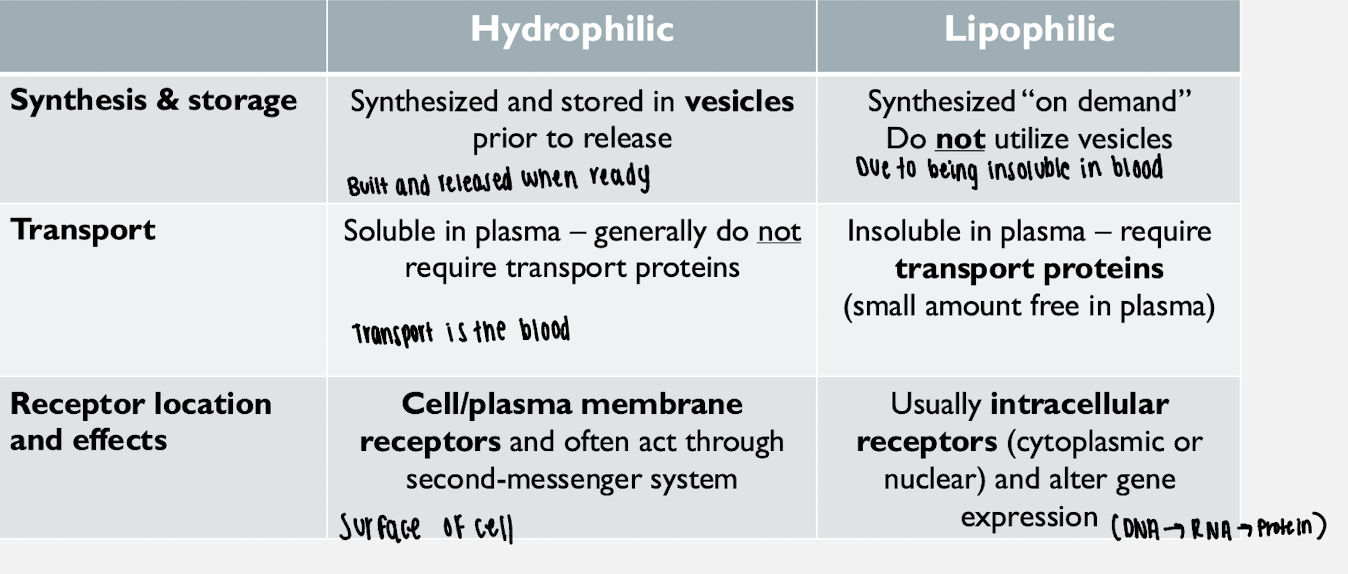
Hydrophilic hormones
Hormones that are water-soluble, circulate freely in plasma, and bind cell membrane receptors
Lipophilic hormones
Hormones that are lipid-soluble, require carrier proteins in blood, and bind intracellular receptors
Protein hormone synthesis
Preprohormone → prohormone → active hormone with storage in secretory vesicles
Steroid hormone synthesis
Synthesized from cholesterol with pregnenolone as the rate-limiting step
On-demand synthesis
Hormone synthesis that occurs as needed rather than being stored, typical of steroid hormones
Hormone release via exocytosis
Method used by peptide and protein hormones to enter the bloodstream
Diffusion across membrane
Method used by lipophilic hormones to leave endocrine cells
Hormone transport
Movement of hormones through the bloodstream to target tissues
Carrier proteins
Plasma proteins that bind lipophilic hormones for transport in blood
Free hormone
Fraction of hormone not bound to carrier protein and biologically active
Cell membrane receptor
Receptor located on the plasma membrane used by hydrophilic hormones
Second messenger system
Intracellular signaling pathway activated by hydrophilic hormones after receptor binding
Intracellular receptor
Cytoplasmic or nuclear receptor used by lipophilic hormones
Gene transcription alteration
Process by which lipophilic hormone–receptor complexes change gene expression
Humoral stimulus
Hormone release triggered by changes in blood levels of ions or nutrients
Neural stimulus
Hormone release triggered by nervous system input
Hormonal stimulus
Hormone release triggered by another hormone (tropic hormone)
Negative feedback loop
Regulatory mechanism where the final hormone inhibits earlier hormone release to maintain homeostasis
Positive feedback loop
Regulatory mechanism where hormones amplify each other to produce a specific event
Homeostasis
Maintenance of a stable internal environment
Example of negative feedback
Thyroid hormone inhibiting TSH release
Example of positive feedback
Estrogen increasing LH and FSH during ovulation
Permissiveness
One hormone must be present for another hormone to exert its full effect
Example of permissiveness
Thyroid hormone required for normal reproductive development
Synergism
Two hormones produce the same effect and their combined effect is greater than additive
Example of synergism
Glucagon and epinephrine increasing blood glucose together
Antagonism
Two hormones have opposite physiological effects
Example of antagonism
Insulin lowers blood glucose while glucagon raises blood glucose
Up-regulation
Increase in number of receptors to enhance hormone signaling
Down-regulation
Decrease in number of receptors to reduce hormone signaling
Receptor desensitization
Decreased receptor responsiveness due to prolonged hormone exposure
Example of desensitization
Insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes