A&P respiratory system (portage learning)
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
Is pulmonary fibrosis obstructive or restrictive?
Restrictive
Why is pulmonary ventilation measured?
to assess pulmonary function, to assess severity of pulmonary disease, and to monitor improvement or deterioration of a disease process
Alveolar Ventilation Rate Formula (AVR)
Tidal Volume x Ventilation Rate (BPM)
differentiate between a normal pediatric tidal volume and an adult normal tidal volume
350ml vs 500ml
Is pulmonary edema a restrictive or obstructive lung disease?
restrictive
What discerns a restrictive vs obstructive lung disease?
Restrictive: difficulty taking air in due to a reduction in lung volume. Obstructive: Difficulty exhaling due to a reduction in airflow
Is sarcoidosis restrictive or obstructive?
Restrictive
Is emphysema restrictive or obstructive?
obstructive
Is emphysema restrictive or obstructive?
obstructive
Is Asthma restrictive or obstructive?
obstructive
Is Black Lung restrictive or obstructive?
obstructive
What is the oxygen carrying capacity of a red blood cell?
Greater than one billion molecules
Describe a hemoglobin molecule
four polypeptide chains each containing an iron group called a Heme. It is the heme which binds with the oxygen molecule.
What shape is the diaphragm at rest?
Dome-shaped
How much water does the average human lose per day in a relative humidity of 50%?
350ml
Features of an effective gas exchange region
moist, thin, and large in relation to body size
Function of the Type II cell besides production of Surfactant
divide to produce type I cells if Type I cell is damaged
What direction do the cilia in the trachea and bronchi move?
upward, to carry mucus, dust, and aspirated food toward the throat
Adam’s apple
layman’s term for the thyroid cartilage
anatomical orientation of the laryngopharynx
superior and posterior to the larynx
anatomical orientation of the oropharynx
posterior to the mouth and anterior to the epiglottis
eustachian tubes
pathways between the nasopharynx and the middle ear
function of the nasal conche
increases the surface area of the nasal cavity to increase the air’s exposure to blood flow to warm the air
the state of air when it reaches the lungs
at body temperature / warm, humidified, and free of debris
Anatomy of the Respiratory Portion
Respiratory Bronchioles, Alveolar ducts, Alveolar Sacs, Alveoli
Anatomy of the Filtration Portion
nostrils (hairs, cilia, mucus) and trachea and bronchi (cilia and goblet cells)
anatomy of the conduction portion
nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, paired main bronchi, and bronchioles
vocalizations, smell, and the regulation of pH
other functions of the respiratory system
diseased state of the pleurae
when air or excessive fluids is found between the visceral pleura and the parietal pleura (AKA the pleural space / cavity)
inhalation
the active process in respiration
exhalation
the passive process in respiration
760 mmHg
1 atm =
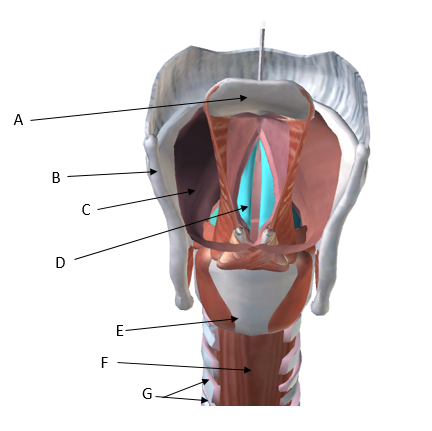
A Epiglottis, B Thyroid Cartilage, C Larynx, D Vocal Folds, E Cricoid Cartilage, F Trachea, G Cartilaginous rings of trachea
Label the following
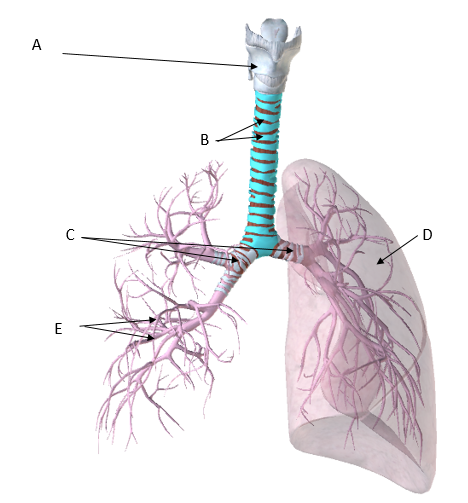
A Larynx, B Cartilaginous rings of the trachea, C Bronchi, D Left Lung, E Bronchioles
Label the following
Minute Volume Formula
tidal volume (norm = 500ml) x respiratory rate
Functional Residual Capacity Formula
Residual Volume + Expiratory Reserve Volume
Inspiratory Capacity Formula
Tidal Volume + Inspiratory Reserve Volume or Vital Capacity - Expiratory Reserve Volume
Total Lung Capacity Formula
Vital Capacity + Residual Volume
Vital Capacity (VC) Formula
Expiratory Reserve Volume + Tidal Volume + Inspiratory Reserve Volume
residual volume (RV)
amount of air remaining in lung that cannot be exhaled, typically about 1300ml
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)
maximum amount of air able to be exhaled beyond normal exhalation, typically around 1200ml of air
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
maximum amount of air able to be inhaled beyond normal inhalation. This is typically around 3000ml
exhalation
the rib cage lowers and the diaphragm rises, thoracic pressure increases, and air moves out of the lungs
inhalation
the rib cage lifts superiorly and anteriorly to open and expand the lungs
ventilation
occurs when lungs move air into the respiratory tract (inhalation) and out of the respiratory tract (exhalation)
internal respiration
gas exchange between blood and tissue
external respiration
gas exchange with air in alveoli
pseudostratified
cells that appear to be in layers
cilia
hair-like projections found on the cells of the respiratory epithelium
histology
the study of cellular anatomy or a tissue or organ that can be viewed through a microscope
concentration gradient
the direction of gas flow from higher to lower concentrations
respiratory bronchioles
the transitional zone in the respiratory system concerned with both air conduction and gas exchange
terminal bronchioles
the smallest conducting bronchioles
respiratory epithelium
lines the entire bronchial tree
bronchi
marks the transition from single conduction pathway of upper airways to the large surface area required for gas exchange
bronchioles
smaller passages within the bronchial tree
main bronchi
the primary division of the trachea into left and right parts
esophagus
tube which food and water passes down to enter stomach, lies posterior to the larynx and trachea
epiglottis
a flap of skin that moves inferiorly to cover the trachea to prevent food or liquid form entering the lungs
pneumonia
infection of the lungs
expectorated
spit up
vocal folds
Flexible bands of connective tissue that vibrate to produce sound when air is expelled past them through the glottis from the larynx
hard palate and soft palate
what separates the nasal cavities from the mouth
vestibule
the most external portion of the nasal cavity just inside the nostrils, lined with stratified squamous epithelium. Short hairs are found here that act as a screening device
nasal cavities (or fossae)
composed of bone and cartilage, divided by septum
respiration
the exchange of gasses
pleural space / cavity
the space that is formed between the visceral and parietal pleurae
parietal pleura
membrane that covers the surfaces surrounding the lungs: the rib cage, diaphragm, and mediastinum
visceral pleura
membrane that directly covers the lungs
pleurae
membranes that cover the surface of the lung and the cavity surrounding the lungs
What are the three main functions of the respiratory system? (Anatomical organization)
Air conduction, air filtration, and respiration
What are the 3 parts of the pharynx?
Nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx
Do the cartilaginous rings of the trachea meet on the posterior side?
False
The larynx rises and epiglottis moves inferiorly to cover the trachea.
What important steps happen during the swallowing process to prevent aspiration?
Why does the soft palate elevate?
To prevent food or liquid from entering nasal passages.
glottis
An opening in the larynx where the vocal cords are located.
aspiration
When food or liquid enters the trachea
right lung lobes
superior, middle, inferior
Functions of pleura
Facilitate movement of lungs with body wall, enclose the lungs.
Major histology type in respiratory system?
Ciliated pseudo-stratified columnar epithelium
basement membrane
"Floor" of the epithelial tissue
goblet cells
Wine-glass shaped mucus producing cells
columnar cells
taller than they are wide
alveolar macrophages
Most abundant cell found within alveoli
left lung lobes
superior and inferior
Surfactant
A lipoprotein that covers the luminal surface and keeps alveoli from sticking together during exhalation
type 1 alveolar cells
Thin, simple squamous epithelium in junction with capillaries, 95% of alveolar epithelium
type 2 alveolar cells
secrete pulmonary surfactant to keep alveoli open, 5% of alveolar epithelium
negative pressure
Pressure inside this space is less than that of the atmosphere, allowing air to naturally flow into the lungs.
Is exhalation an active or passive process?
passive process
hemoglobin
Combines with oxygen entering the blood to carry the oxygen in the blood system
Diaphragm
Muscle responsible for providing movement for respiration
pulmonary alveoli
where gas exchange occurs by diffusion
bicarbonate ions
carbonic anhydrase + carbon dioxide + water, 90% of carbon dioxide is carried this way
Boyle's Law
Gas pressure is inversely proportional to volume. Smaller volume = higher pressure
Charles' Law
Volume of a given quantity of gas is directly proportional to its temperature, higher temperature = higher gas volume
Dalton's Law
The total pressure of a mixture of gases is the sum of the individual pressures
Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)
Amount of air that can be forcefully exhaled after a normal tidal volume exhalation
Tidal Volume (TV)
amount of air inhaled or exhaled with each breath under resting conditions, typically around 500ml