Vet nursing surgical instruments
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms

Dressing Thumb Forceps
To grasp inanimate objects such as dressings
Should not be used on live tissue as it may cause tissue trauma
Has serrations or grooves rather than teeth

Brown-Adson (or Adson-Brown)Thumb Forceps
Minimal tissue trauma
Two rows of fine intermeshing
teeth
Holds tissue securely
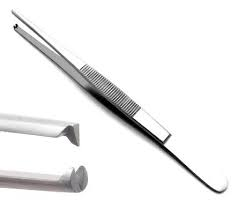
Rat-Tooth Thumb Forceps
Sharp teeth cause more tissue trauma
Holds tissue securely
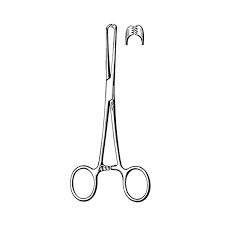
Allis Tissue Forceps
Used to hold tissues in place and crush it
Self-retaining, secure grip
Jaws/teeth look like folded hands/finger
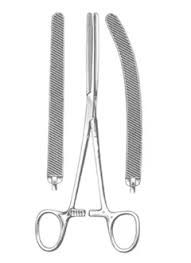
Doyen Intestinal Forceps
Used to hold intestine and
block flow of material through
it during surgery
Self-retaining
Smooth surface grasps tissue
very gently
Dont have

Towel Clamp Forceps
Used to secure drapes to patient’s skin
Pierce the skin, but rarely cause bleeding
Sharp points; watch your fingers!
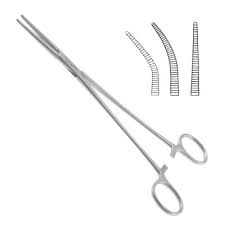
Mosquito forceps
• Used for small vessels
• May be straight or curved
•Transverse grooves
NOTE: Similar to Crile forceps
(next slide), but smaller and
more delicate looking.
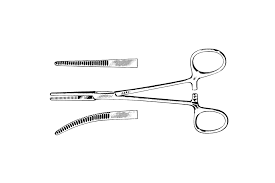
Kelly Forceps
To clamp intermediate size vessels
grooves distal only(not along entire jaws)
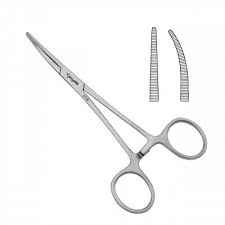
Crile Forceps
to clamp intermediate size vessels
grooves along entirety of the jaws

Rochester Carmalt
Grooves run lengthwise/
longitudinally
Transverse grooves at
the tip only
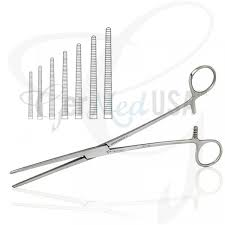
Rochester Pean
- Grooves are transverse
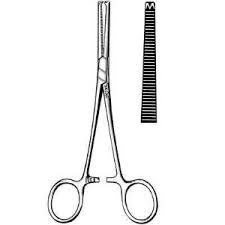
Rochester Oschner Forceps
Clamp large vessels
Similar to Rochester Pean but tip similar to rat tooth thumb forceps
Transverse grooves
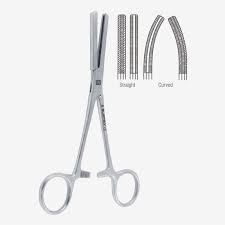
Ferguson Angiotribe
For very large vessels and tissues
Has one large longitudinal
groove with many small
transverse grooves

OB Forceps
Place over head of fetus to retrieve from uterus/vagina
Must avoid placing pressure on eyes
Shallow serrations grip gently, do not crush
Jaws are curved

Alligator Forceps
Used for retrieval of foreign objects
Reaches difficult-to-reach locations

Sponge Forceps
Grasp sponges & insert into body cavities to absorb fluids
Be sure not to leave sponges behind!
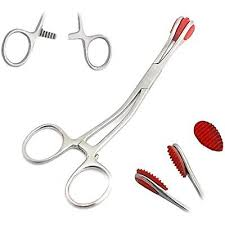
Tongue Forceps
Grasp tongue to:
Intubate animal
Examine larynx/pharynx
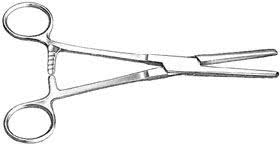
Tube Occluding Forceps
Occlusion – Blockage
Used to clamp rubber tubing without damaging it
Note the smooth surface; you must look at this in
order to identify this instrument!(no ridges or grooves)

Mouth Gag
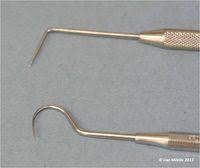
Dental Explorers
Used to explore tooth surface for tartar and defects (decay, fracture, etc.)
Not to be used for scaling
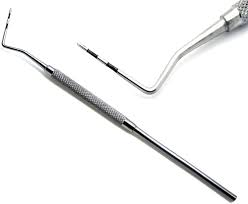
Periodontal Probe
Used to measure the depth of periodontal pockets by
gently “walking” probe around circumference of tooth
2 mm depth is normal
Often has a Shepherd hook explorer at the opposite end
There are different mm calibrations
on different types of probes
Peri – Around
-odontal – Refers to the tooth
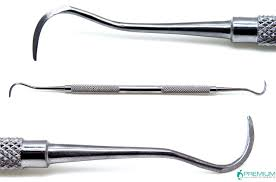
Scaler
Scale – Remove tartar from teeth
Used for supragingival (supra = above, gingival
= gumline) scaling, scaling the crowns of the teeth
Have sharp edges on both sides, which taper to a
pointed tip
Should not be used below the gumline, as the
pointed tip may damage the tissues

Curettes
Used for subgingival (sub = under,
gingival = gumline) scaling
Have a rounded tip, to avoid damaging
the subgingival tissues

Mayo scissors
blunt-blunt

metzenbaum scissors
sharp-blunt
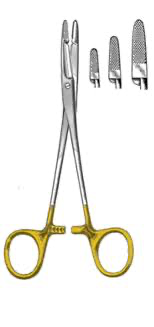
olsen-hager needle holders
scissor needle holder combo
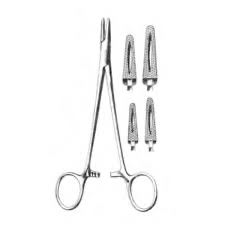
mayo Hager needle holders
periosteal elevators
used to remove periosteal from bone