Properties of period 3 elements and their oxides (3.2.4)
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
How do Mg and Na react with water?
Sodium
2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
Na reacts vigorously with water, melting into a ball and fizzing. Na floats on water
Magnesium
Mg reacts slowly with water:
Mg(s) + H2O(l) → Mg(OH)2(aq) + H2(g)
Mg(OH)2 is sparingly soluble and is a weak alkaline
Mg reacts much faster with steam:
Mg(s) + H2O(g) → MgO(s) + H2(g)
What are the ionic oxides that are formed by sodium and magnesium?
Sodium - Na2O
Magnesium - MgO
How do the ionic oxides react with water?
Na2O(s) + H2O(l) → 2NaOH(l)
MgO(s) + H2O(l) → Mg(OH)2(aq)
These form alkaline solutions with pH of 10-14
What are the simple molecular oxides that are formed from sulfur and phosphorus?
Phosphorus - P4O10
Sulfur - SO2 , SO3
SO3 requires a catalyst and high temperature to be formed
How do simple molecular oxides react with water?
P4O10(s) + 6H2O(l) → 4H3PO4(aq) - phosphoric (V) acid
SO2(g) + H2O(l) → H2SO3(aq) - sulfurous acid
SO3(l) + H2O → H2SO4(aq) - sulfuric (VI) acid
They form acidic solutions with a pH of 0-2
What are the oxides formed by silicon and aluminium?
Silicon - SiO2 - insoluble in water. It’s an acid as it reacts with a base. Macromolecular structure
Aluminium - Al2O3 - It’s both covalent and ionic and it’s insoluble in water. It’s amphoteric as it reacts with both bases and acids to form salts.
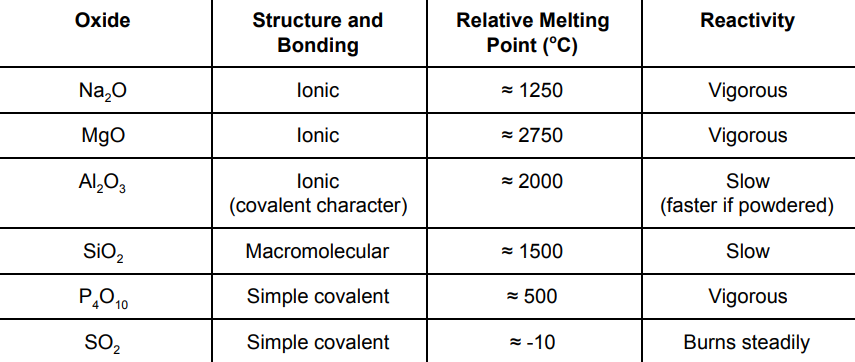
What are the melting points and reactivities of the oxides?
How do the basic oxides react with acids?
Na2O(s) + H2SO4(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + H2O(l)
MgO(s) + 2HCl(aq) →MgCl2(aq) +H2O(l)
Base + acid → salt + water
How do acidic oxides react with bases?
SiO2(s) + 2NaOH(aq) → Na2SiO3(aq) + H2O(l)
P4O10(s) + 12NaOH(aq) → 4Na3PO4(aq) + 6H2O(l)
SO2(g) + 2NaOH(aq) →Na2SO3(aq) + H2O(l)
SO3(l) + 2NaOH(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + H2O(l)
How do amphoteric oxides react?
Acting as an acid - Al2O3(s) + 2NaOH(aq) + 3H2O(l) → 2NaAl(OH)4(aq)
Acting as a base - Al2O3(s) + 3H2SO4(aq) → Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3H2O(l)
How do you test for the oxides?

Thus by adding universal indicator the trend can be seen with the ionic oxides turning into a purple/blue solution and the simple molecular oxides having a orange/red solution
