Lecture 5: Enzyme Regulation Part 2
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
PRPP Synthetase (PRS) (Hint: 3)
Enzyme that catalyzes the first step in the synthesis of PRPP
Important for purine (adenine, guanine) production
Uses ATP; Ribose-5-phosphate -> PRPP
Isoenzymes (Hint: 4)
AKA isozymes
Enzymes that are encoded by different genes
Catalyze the same reaction by may display different regulatory properties
May be expressed in a tissue-specific or developmentally specific pattern
H Isozyme
Heart isozyme
M Isozyme
Muscle isozyme
Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) (Hint: 2)
Important enzyme for lactic acid fermentation
4 subunits
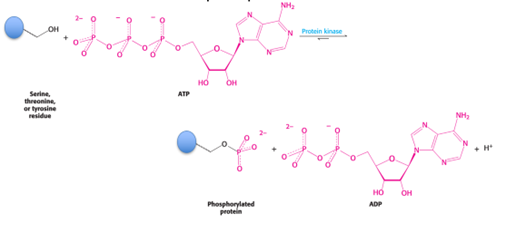
Protein Kinases (Hint: 3)
Modify proteins by attaching a phosphate to a serine, threonine, or tyrosine residue
ATP serves as the phosphate donor
OH groups can be modified through phosphates
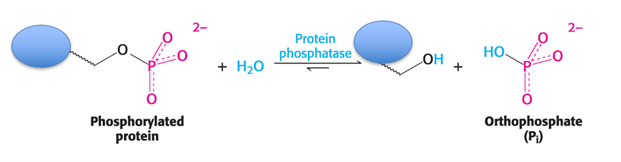
Protein Phosphatases (Hint: 3)
Remove phosphates added by kinases
Hydrolysis reaction
Important because over phosphorylation can lead to diseases like cancer
Phosphorylation
A highly effective means of regulating the activities of target proteins
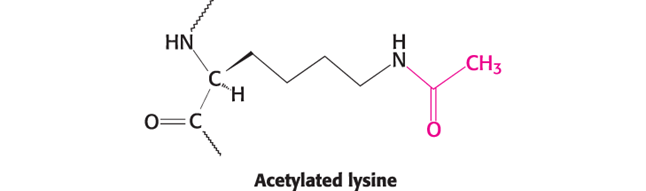
Acetylation (Hint: 3)
Addition of acetyl group
Lysine in proteins can be acetylated
Remove (+) charge
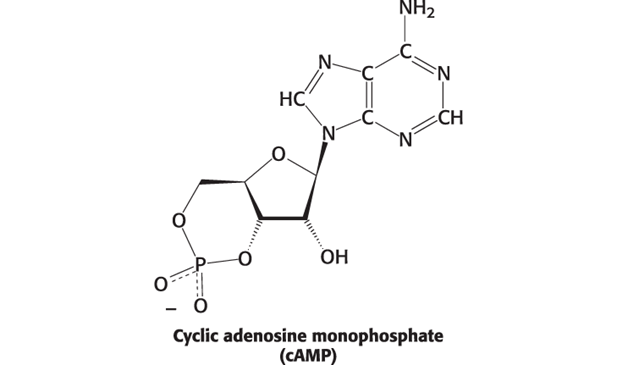
cAMP (Hint: 3)
Signal molecule
Only made in certain circumstances
2nd messenger
Cushing’s Syndrome (Hint: 4)
Collection of diseases resulting from excess secretion of the hormone cortisol by the adrenal cortex
One cause is now known to a mutation that causes protein kinase A to be constitutive active (always on)
Mutation causes the catalytic (C) subunit to no longer bind the regulatory (R) subunit so that the enzyme is active even when cAMP is absent
Causes unregulated secretion of cortisol, which has various physiological effects, including suppression of the immune system and inhibition of bone growth
Cortisol (Hint: 2)
Stress hormone
Suppresses immune system
Phosphoproteomics
The study of the phosphoproteome
Phosphoproteome
All proteins that are modified by phosphorylation
Zymogens
Inactive precursors
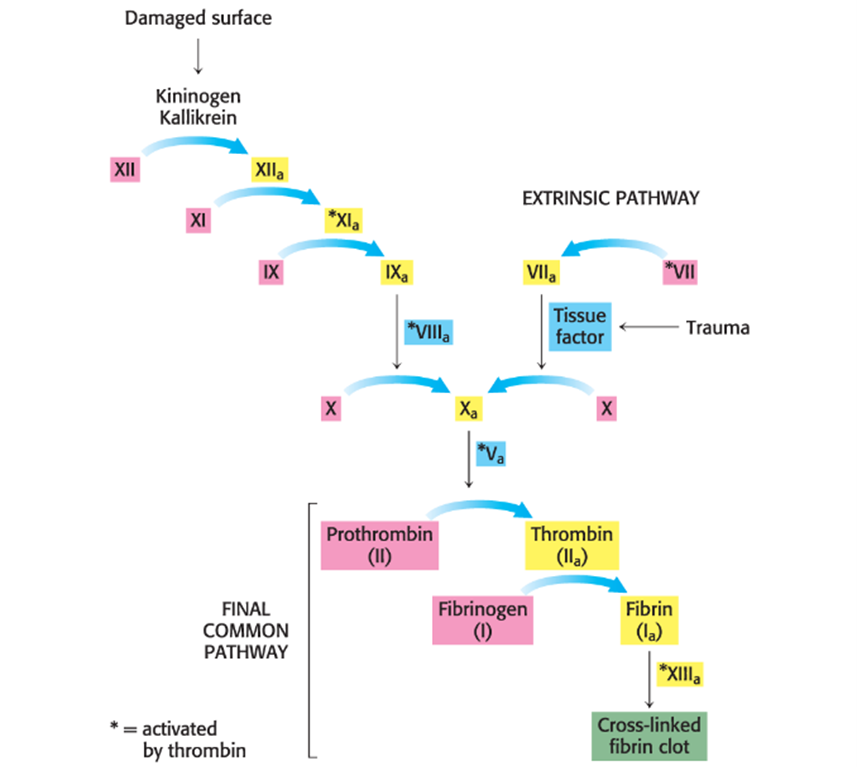
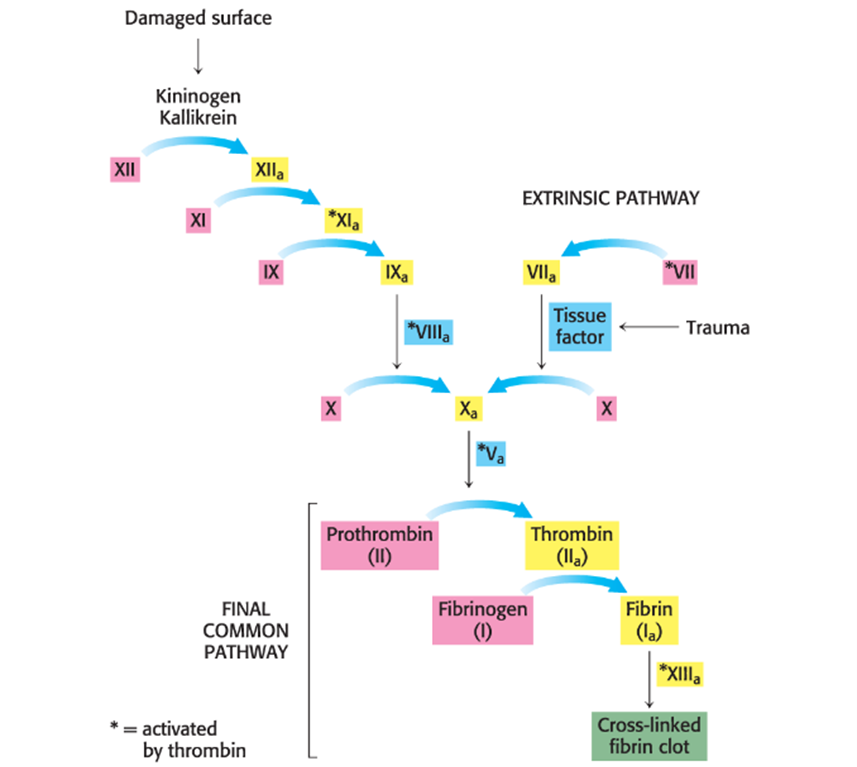
Hemophilia A (Hint: 4)
AKA the royal disease
Sex-linked recessive disorder (only affects men) caused by inactive or missing factor VIII of the pathway
Factor VIII is not protease, but should cause activation of factor X, the final protease in the pathway
Treated with recombinant factor VIII
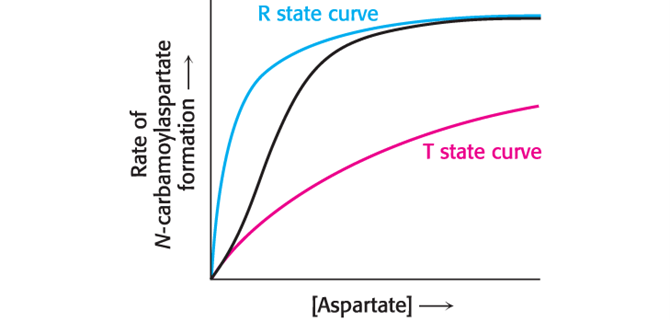
Describe the Basis for Sigmoidal Curve for Allosteric Enzymes (Hint; 3)
Imagine an allosteric enzyme as a mixture of two Michaelis-Menten enzymes
One with a high value of Km that corresponds to the T state (Inhibited; V-max lowered)
Another with a low value of Km that corresponds to the R state
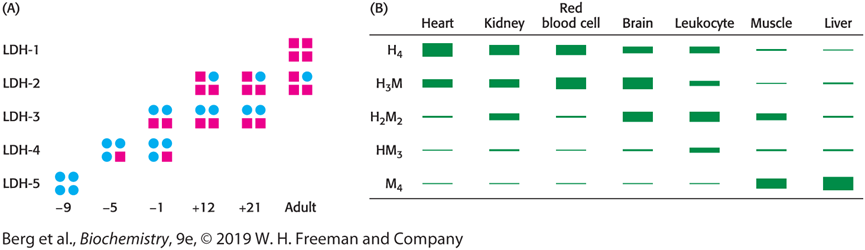
Describe an example of how the appearance of certain isozymes in the blood is a sign of tissue damage
Heart Attack Patient: Look for isozymes found in heart muscles but not in other tissues
Describe Isozymes of Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) (Hint: 3)
LDH has two different isozymes
Can be combination of both H and M
Every cell has different LDH requirements
Describe How Covalent Modification is a Means of Regulating Enzyme Activity (Hint: 3)
Enzymes can be modified by the covalent attachment of a molecule
Phosphorylation and acetylation are common modifications
Most covalent modifications are reversible
List the 3 key features of regulation by phosphorylation
The addition of the phosphoryl group alters electrostatic interactions (charge interactions; changes how amino acids nearby can react)
A phosphoryl group can form hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds
Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation can occur rapidly (most important point; cells can respond quickly; so fast they help mediate quick reactions)
How does cyclic AMP activate Protein Kinase A? (Hint: 4)
By altering the quaternary structure
cAMP stimulates protein kinase A (PKA) by binding to PKA’s regulatory (R) subunits, causing their dissociation from the catalytic subunits
The free catalytic (C) subunits are in the active form and can go phosphorylate transcription factors
Example: Epinephrine
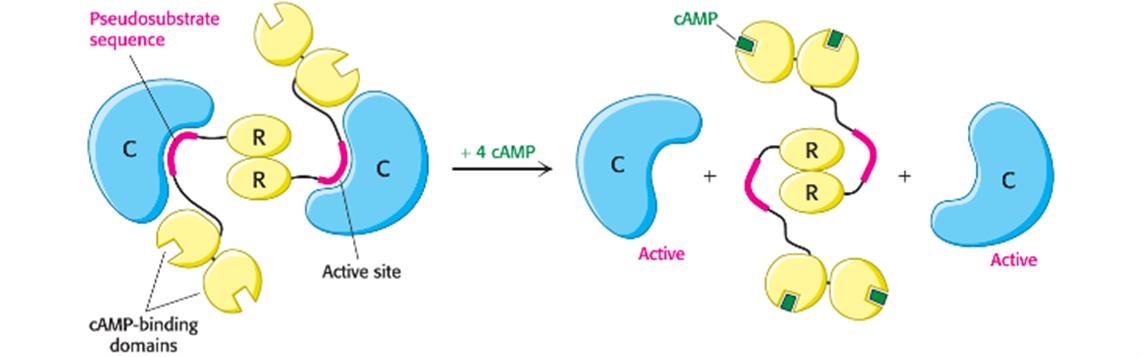
Describe Epinephrine (Hint: 2)
Epinephrine (adrenaline; 1st messenger) induces the “fight-or-flight” response in muscles
In muscle cells exposed to epinephrine, cAMP is synthesized
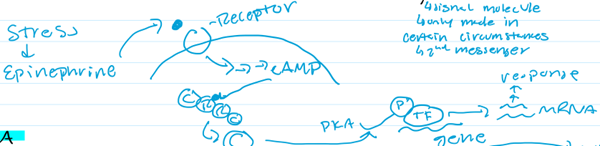
Describe how Exercise Modifies the Phosphorylation of Many Proteins (Hint: 3)
Recent research has shown that exercise results in the phosphorylation of nearly 600 different proteins
The kinases that catalyze these reactions include protein kinase A and AMP-activated kinase (AMPK)
These modifications affect many biological functions, including an increase in the ability to process fuels aerobically
Proteolytic cleavage plays a key role in what 2 examples of biochemical processes?
Activation of digestive enzyme
Blood clotting
Describe Chymotrypsinogen (Hint: 4)
Activated by specific cleavage of a single peptide bonds
The digestive enzyme chymotrypsin is synthesized as an inactive precursor called chymotrypsinogen
Multiple cleavages yields the mature enzyme, α-chymotrypsin
Digestive enzymes are dangerous if their activation is not controlled
Describe an example of a cascade of protease-activated zymogens that facilitates blood-clotting
Hemophilia is a defect in an early step in clotting
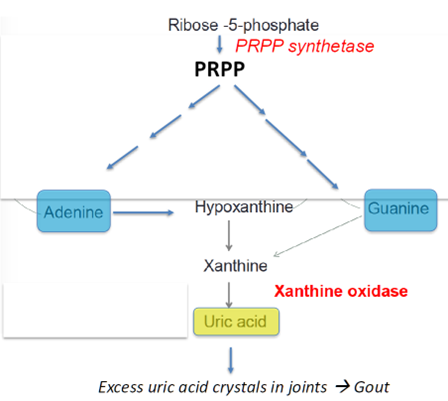
Why is Feedback Inhibition Important? PRPP Synthetase-Induced Gout (Hint: 4)
One of the causes of gout is a mutation in PRPP synthetase (PRS); Can’t bind purines (inhibitors); Defective feedback inhibition
Urate/uric acid is a final product of purine degradation
Gout is a joint disease in which excess urate crystals form in the fluid and lining of the joints; Overproduction of nucleotides
Painful inflammation results when immune cells engulf the crystals