chapter 9 : enthalpy
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
what is enthalpy and its unit
the measure of heat energy in a chemical system (H)
what is a chemical system
the atoms, molecules or ions making up the chemicals
how is enthalpy measured
since you can’t directly measured it the enthalpy change is measured from the reactants and products
equation for enthalpy change\Delta H
H(products) - H(reactants) = \Delta H
what are exothermic reactions
reactions that give out heat energy from the system to the surroundings
temperature increase
what are endothermic reactions
reactions that absorb heat energy from the surroundings into the system
temperature decrease
when is enthalpy change positive and negative
positive endothermic
negative exothermic
what is activation energy
the minimum energy input required to break bonds for a chemical reaction to occur
draw energy profile diagrams for an endothermic and exothermic reaction
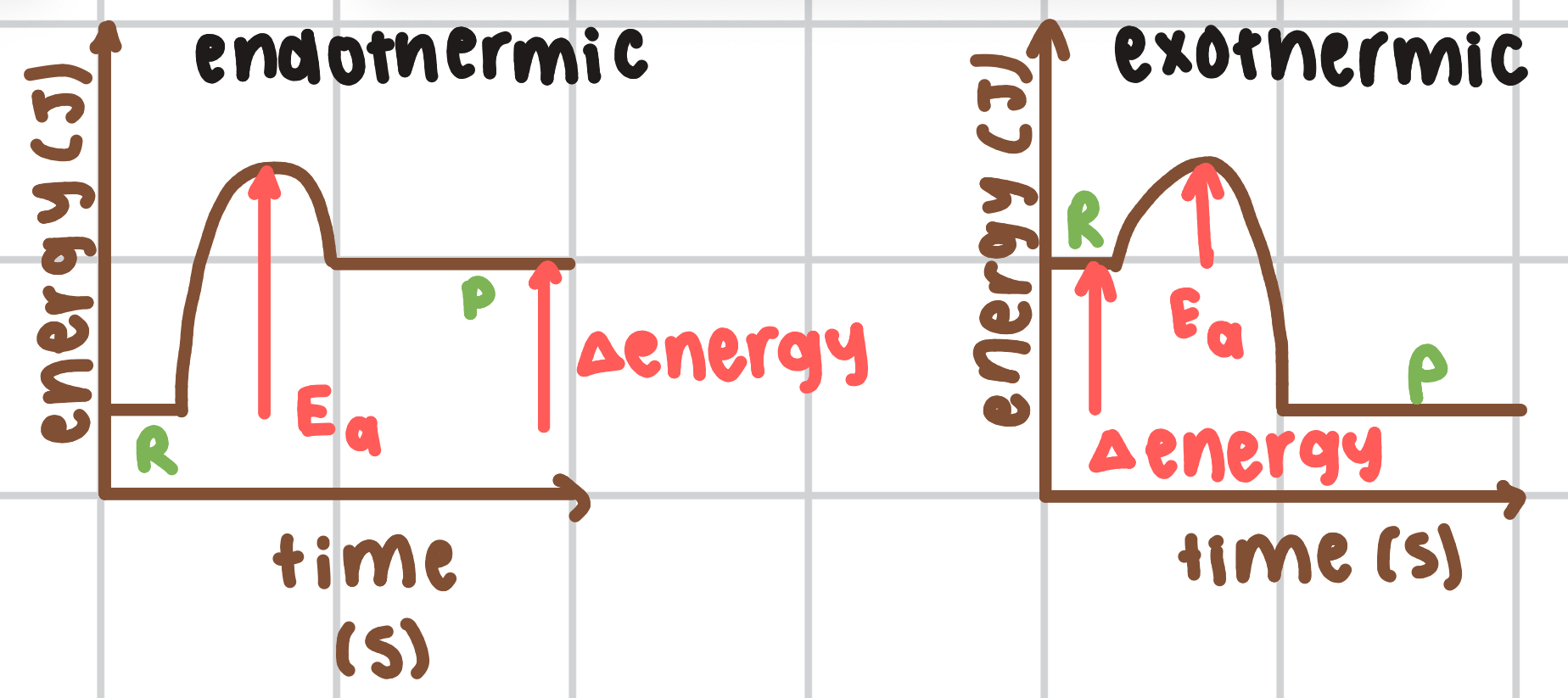
when will a reaction occur
if reactant particles collide in the correct orientation with sufficient activation energy
what are the standard conditions
10 kPa
25 C / 298 K
1 mol dm-3
substances in state under standard conditions
what is the enthalpy change of a reaction
the enthalpy change that accompanies a reaction in the molar quantities shown in a chemical equation under standard conditions with all reactants and products in their standard states
what is the enthalpy change of neutralisation
enthalpy change that takes place in the reaction of an acid by a base to form 1 mol of H20 (l)
what is the enthalpy change of formation
enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states
what is the enthalpy change of combustion
the enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is completely combusted or reacts in excess oxygen
what is calorimetry
the quantitative study method of energy in a chemical reaction
what 3 figures do you need to calculate energy change
mass
specific heat capacity
temperature change
how do you measure mass and temperature to find energy change
mass of surroundings (that are changing temperature) by weighing (g)
temperature change of surroundings by a thermometer
what is the formula for energy change (Q)
Q = mass (of surroundings) x SHC x change in temperature
what is specific heat capacity
energy to raise temperature of 1g of a substance by 1K
describe a way to measure energy change (7)
measure volume of water in a beaker
record initial temperature of water
weigh mass of methanol in spirit burner
light burner and place under beaker to heat while stirring water with thermometer
record maximum temperature of water after 3 mins
reweigh methanol and find change in mass
use formula to find energy change
4 reasons why less energy is transferred in a energy change experiment than supposed to
heat loss to surroundings other than water
incomplete combustion of methanol
evaporation of methanol from the wick
non-standard conditions (textbook values are standard)
2 ways to minimise errors in an energy change experiment
input of oxygen gas to avoid incomplete combustion
drought screens to minimise heat loss
how to determine an enthalpy change of reaction
using a polystyrene cup as it’s an insulator
what is the surroundings in a enthalpy change of reaction experiment
the aqueous solution itself
what is average bond enthalpy
energy required to break one mole of a specified type of bond in a gaseous molecule
why are bond enthalpies always positive
bond enthalpy is the energy to break bonds
therefore energy is taken into the system
therefore bond enthalpies are endothermic
so they always have a positive enthalpy value
what is used to calculate average bond enthalpy
actual bond enthalpy in different chemical environments
what determines whether a reaction is endothermic or exothermic
the difference in energy required for breaking bonds and the energy released when a bond is broken
what are 2 limitations of bond enthalpies
the actual bond enthalpies will be slightly different compared to the average bond enthalpies that are used
calculations using average bond enthalpies must be with gaseous molecules so they aren’t standard
what is hess’ law
if a reaction can take place by two routs and the starting and ending conditions are the same the total enthalpy change is the same for each route
what is the formula for enthalpy change of formation and combustion
formation: products - reactants
combustion: reactants - products